Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
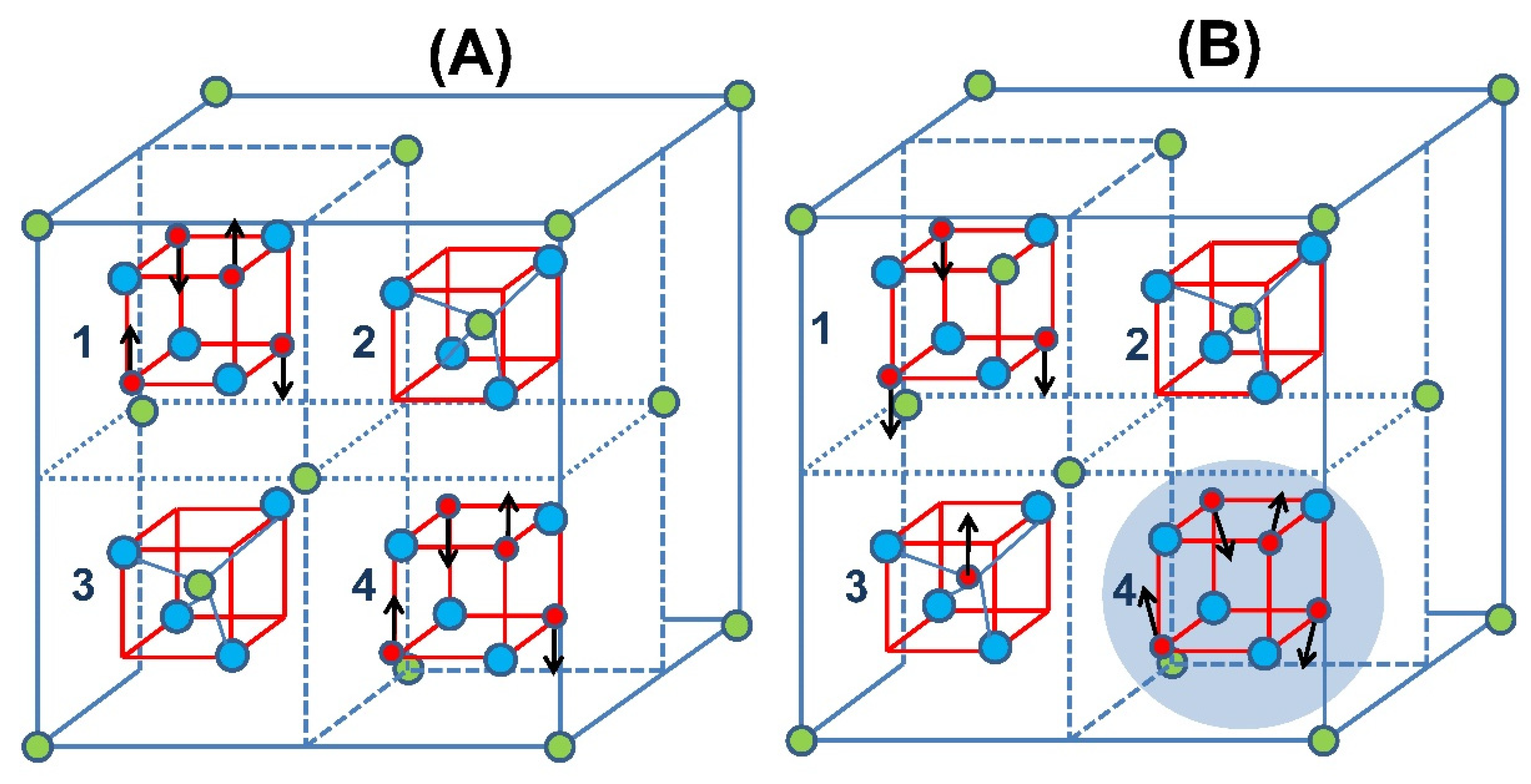
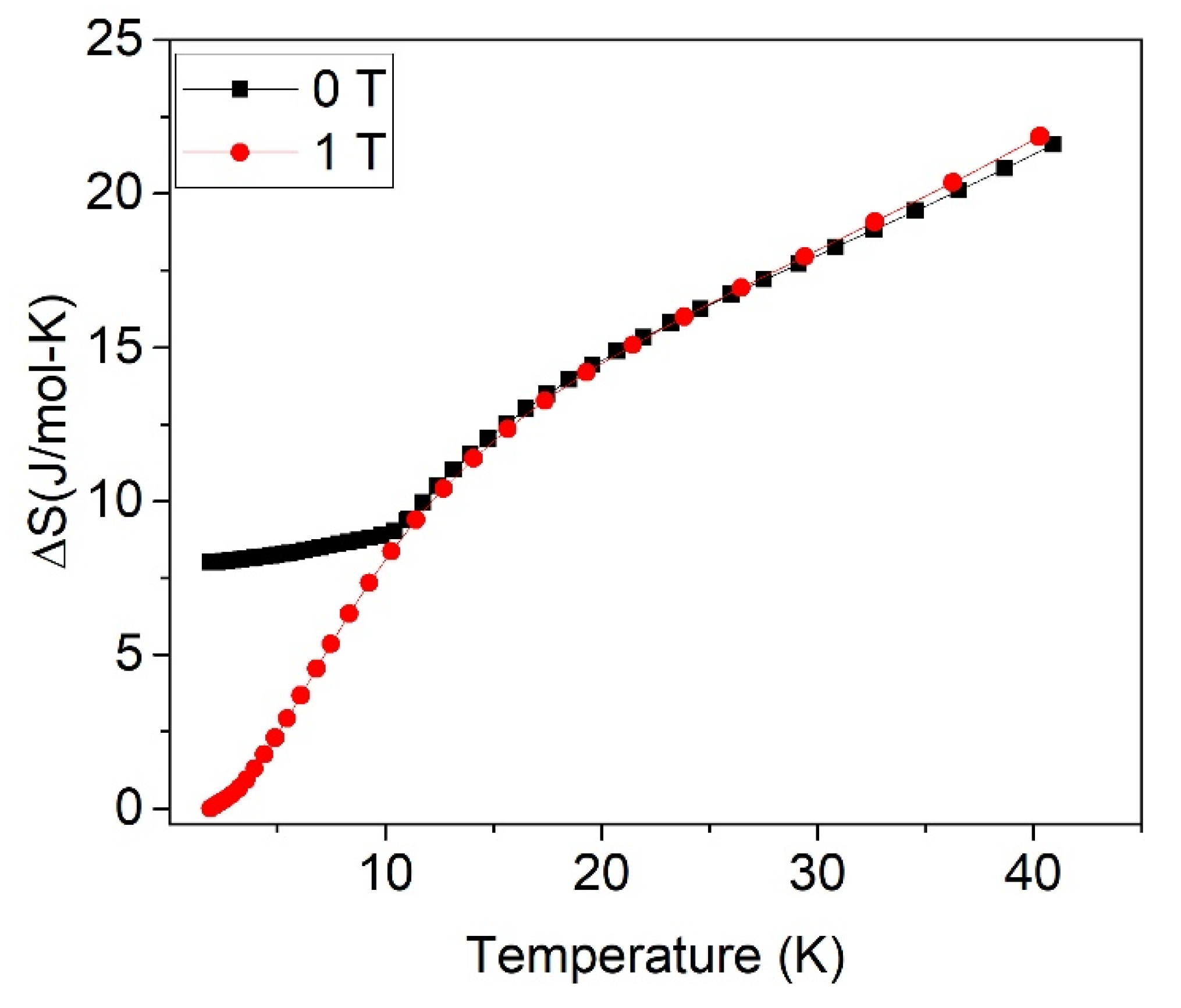
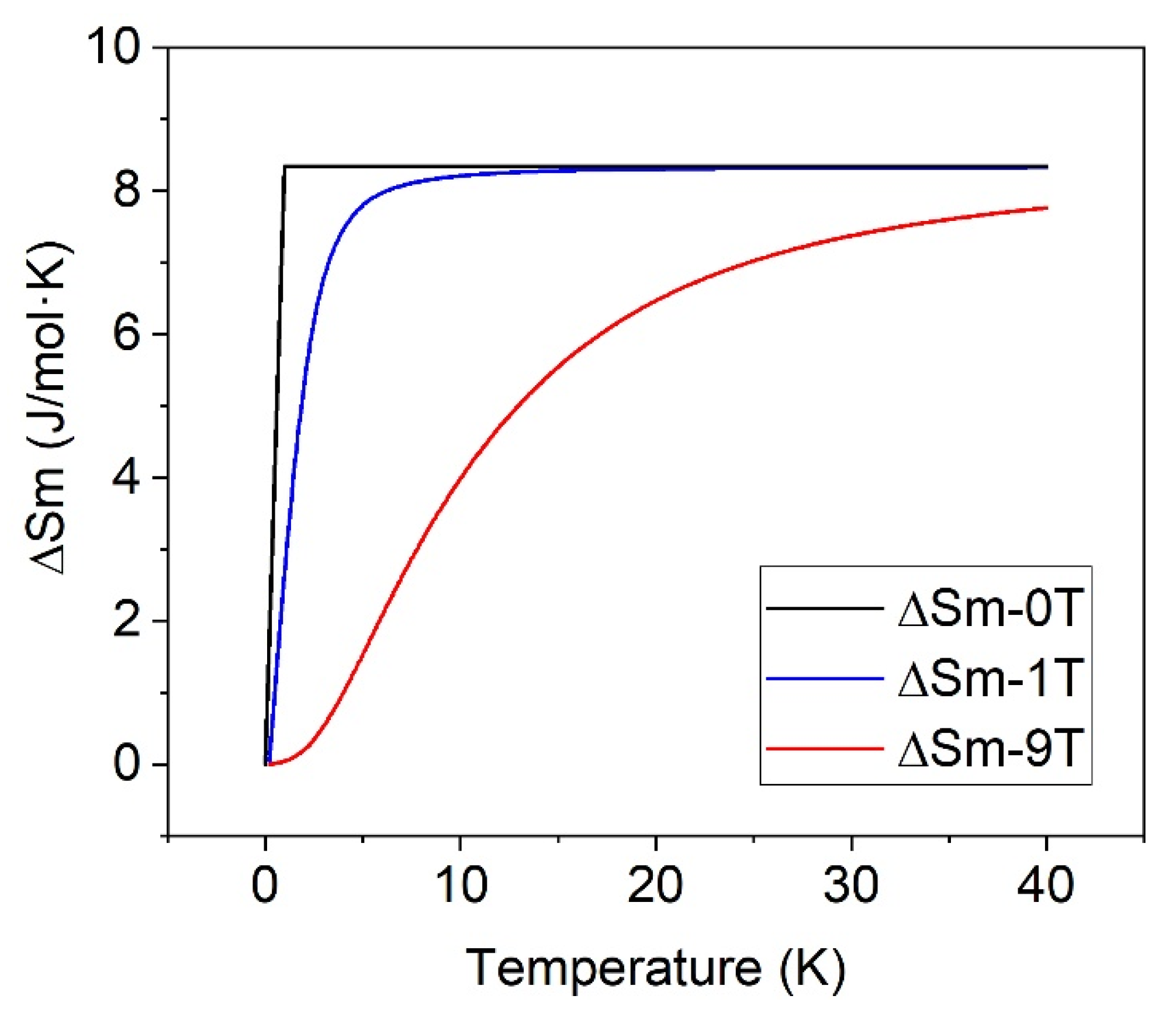
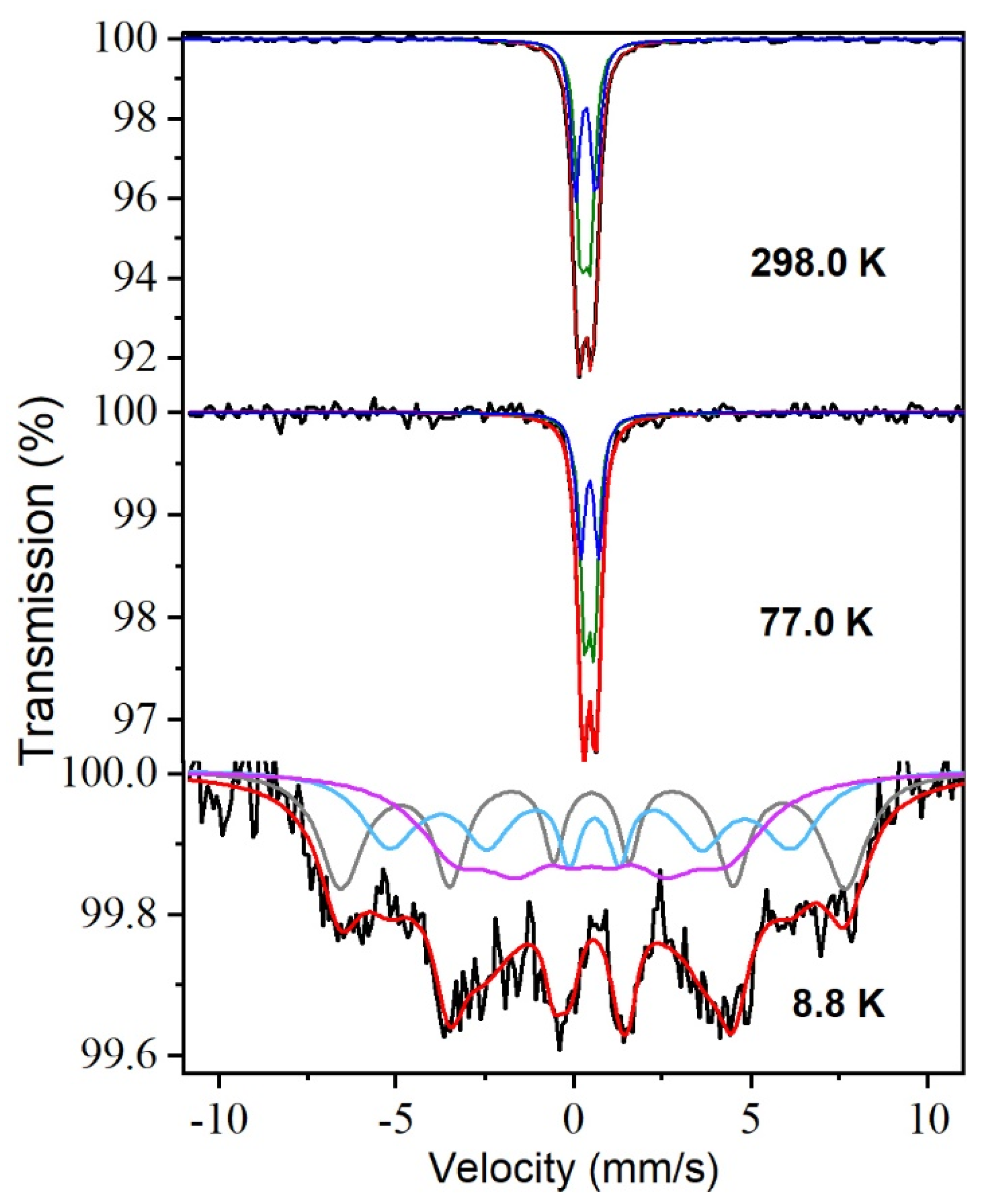
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolcet, P.; Kirchberg, K.; Antonello, A.; Suchomski, C.; Marschall, R.; Diodati, S.; Munoz-Espi, R.; Landfester, K.; Gross, S. Exploring wet chemistry approaches to ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles with different inversion degrees: A comparative study. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, M.; Alman, V.; Arras, R. Nanostructured ZnFe2O4: An Exotic Energy Material. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, R.; Arackal, S.; Kahmei, R.D.R.; Bhat, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Shivashankar, S.A. Crystallographic inversion-mediated superparamagnetic relaxation in Zn-ferrite nanocrystals. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.A.; de la Presa, P.; Llorente, I.; Alonso, J.M.; Garcia-Escorial, A.; Marin, P.; Hernando, A.; Jimenez, J.A. Magnetic Phase Diagram of Nanostructured Zinc Ferrite as a Function of Inversion Degree delta. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 17472–17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafet, Y.; Kittel, C. Antiferromagnetic Arrangements in Ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1952, 87, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.M.; Corliss, L.M. An Antiferromagnetic Transition In Zinc Ferrite. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Campbell, S.J.; Ehrhardt, H.; Feyerherm, R. The magnetic behaviour of nanostructured zinc ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5057–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, H.; Campbell, S.J.; Hofmann, M. Magnetism of the nanostructured spinel zinc ferrite. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usa, T.; Kamazawa, K.; Sekiya, H.; Nakamura, S.; Tsunoda, Y.; Kohn, K.; Tanaka, M. Magnetic Properties of ZnFe2O4 as a 3-D Geometrical Spin Frustration System. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 73, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiessl, W.; Potzel, W.; Karzel, H.; Steiner, M.; Kalvius, G.M.; Martin, A.; Krause, M.K.; Halevy, I.; Gal, J.; Schäfer, W.; et al. Magnetic properties of the ZnFe2O4 spinel. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 9143–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneill, H.S. Temperature-Dependence Of The Cation Distribution In Zinc Ferrite (ZnFe2O4) From Powder Xrd Structural Refinements. Eur. J. Mineral. 1992, 4, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.S.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.B.; Zhou, Q.G.; Zhou, X.Z.; Kunkel, H.P.; Williams, G. Site preference of Fe in nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 268, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.Á.; de la Presa, P.; Puente-Orench, I.; Llorente, I.; Morales, I.; García-Escorial, A.; Hernando, A.; Jiménez, J.A. Coexistence of antiferro- and ferrimagnetism in the spinel ZnFe2O4 with an inversion degree delta lower than 0.3. Ceram. Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, N.W. On the specific-heat of compounds with spinel structure—II Zinc ferrite, a paramagnetic compound with magnetic ion occupying octahedral site. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A-Math. Phys. Sci. 1974, 338, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.C.; Hamdeh, H.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Yao, Y.D.; Willey, R.J.; Oliver, S.A. Low-temperature calorimetric properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 10122–10126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrum, E.F.; Grimes, D.M. Low temperature heat capacity and thermodynamic properties of zinc ferrite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1957, 3, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Shi, Q.; Schliesser, J.; Woodfield, B.F.; Nan, Z.D. Magnetic and Thermodynamic Properties of Nanosized Zn Ferrite with Normal Spinal Structure Synthesized Using a Facile Method. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 10463–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamazawa, K.; Tsunoda, Y.; Kadowaki, H.; Kohn, K. Magnetic neutron scattering measurements on a single crystal of frustrated ZnFe2O4. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 024412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashley, J.C.; Stevens, R.; Crawford, M.K.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Woodfield, B.F.; Qiu, Y.; Lynn, J.W.; Goddard, P.A.; Fisher, R.A. Specific heat and magnetic susceptibility of the spinels GeNi(2)O(4) and GeCo(2)O(4). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, L.A.; Wills, A.S.; Bramwell, S.T.; Dahlberg, M.; Schiffer, P. Zero-point entropy of the spinel spin glasses CuGa2O4 and CuAl2O4. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 145, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Wynn, P.; Morup, S.; Okada, T.; Berry, F.J. Magnetic structure evolution bn mechanically milled nanostructured ZnFe2O4 particles. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 12, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, D.S.; Juang, R.S. An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 129, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.N.; Narayanasamy, A.; Ponpandian, N.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Guerault, H.; Greneche, J.M. Magnetic properties of nanostructured ferrimagnetic zinc ferrite. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2000, 12, 7795–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.W.; Zeng, Q.S.; Goya, G.F.; Torres, T.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, H.P.; Ge, M.Y.; Zeng, Y.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, J.Z. ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals: Synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12274–12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Nassif, V.; Puente Orench, I. Evolution of the Magnetic Properties with Annealing Temperature of Spinel Zinc Ferrite Disordered by Ball Milling; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Puente Orench, I. Effect of Microstructural Features and Defects Introduced by Mechanical Milling and Thermal Treatments on the Magnetic Order of Spinel Zinc; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Puente Orench, I. Effect of Inversion Degree on the Magnetic Properties of Spinel Zinc Ferrite; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Villars, P.; Cenzual, K. Pearson’s Crystal Data: Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds; ASM International®: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, E.; Schafer, W.; Will, G. R values in analysis of powder diffraction data using Rietveld refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.A.; de la Presa, P.; Llorente, I.; García-Escorial, A.; Hernando, A.; Jiménez, J.A. Effect of preparation methods on magnetic properties of stoichiometric zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 849, 156353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, R.E.; De Grave, E. Mössbauer Effect Studies of Oxidic Spinels. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 59–182. [Google Scholar]
- Goya, G.F.; Leite, E.R. Ferrimagnetism and spin canting of Zn57Fe2O4nanoparticles embedded in ZnO matrix. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, D.G. Analytical Methods for Mössbauer Spectral Analysis of Complex Materials. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Magnetism and Materials Science; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, M.; Tjon, J.A. Mossbauer Spectra in a Fluctuating Environment. Phys. Rev. 1968, 165, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
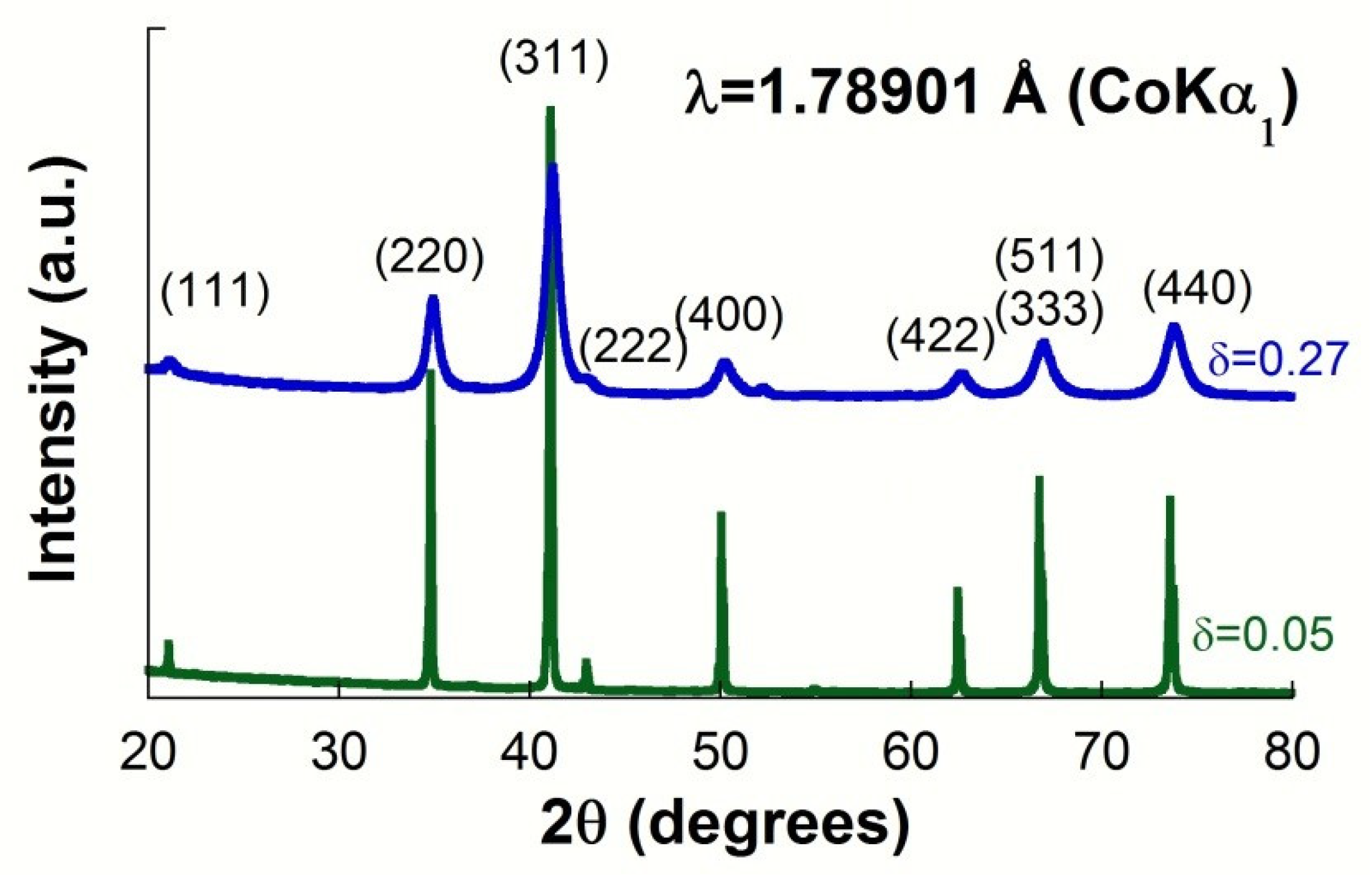



| Sample | Source | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Inversion Degree(δ) | O-Position (x = y = z) | Crystal Size (nm) | μ-Deformation (ε) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZFO-0.05 | XRD | 8.4489(5) | 0.05(1) | 0.2416(9) | >150 | - |
| NPD | 8.4498(5) | 0.05(1) | 0.2397(3) | >150 | - | |
| ZFO-0.27 | XRD | 8.4322(5) | 0.28(2) | 0.2424(5) | 15(1) | 0.0020(2) |
| NPD | 8.4373(5) | 0.20(2) | 0.2414(3) | 14(1) | 0.0019(2) |
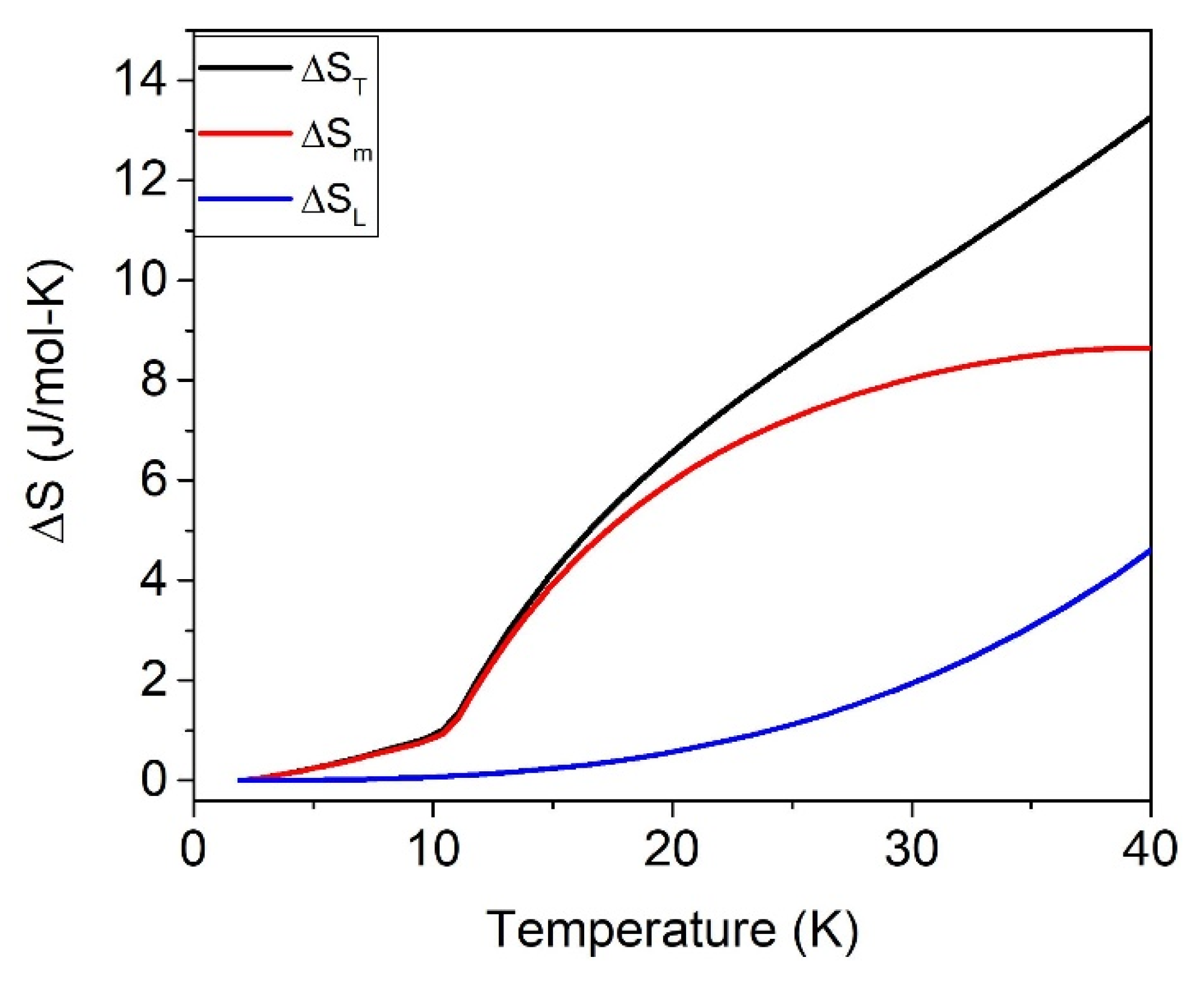
| H (T) | 40 K | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔST | ΔSm | ΔSL | |
| 0 | 13.2 (1) | 8.7 (1) | 4.6 (1) |
| 1–5 | 21.7 (1) | 17.1 (1) | 4.6 (1) |
| 9 | 18.9 (1) | 14.2 (1) | 4.7 (1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cobos, M.A.; Hernando, A.; Marco, J.F.; Puente-Orench, I.; Jiménez, J.A.; Llorente, I.; García-Escorial, A.; de la Presa, P. Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials 2022, 15, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
Cobos MA, Hernando A, Marco JF, Puente-Orench I, Jiménez JA, Llorente I, García-Escorial A, de la Presa P. Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
Chicago/Turabian StyleCobos, Miguel Angel, Antonio Hernando, José Francisco Marco, Inés Puente-Orench, José Antonio Jiménez, Irene Llorente, Asunción García-Escorial, and Patricia de la Presa. 2022. "Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4" Materials 15, no. 3: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
APA StyleCobos, M. A., Hernando, A., Marco, J. F., Puente-Orench, I., Jiménez, J. A., Llorente, I., García-Escorial, A., & de la Presa, P. (2022). Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials, 15(3), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198








