Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Theoretical Background
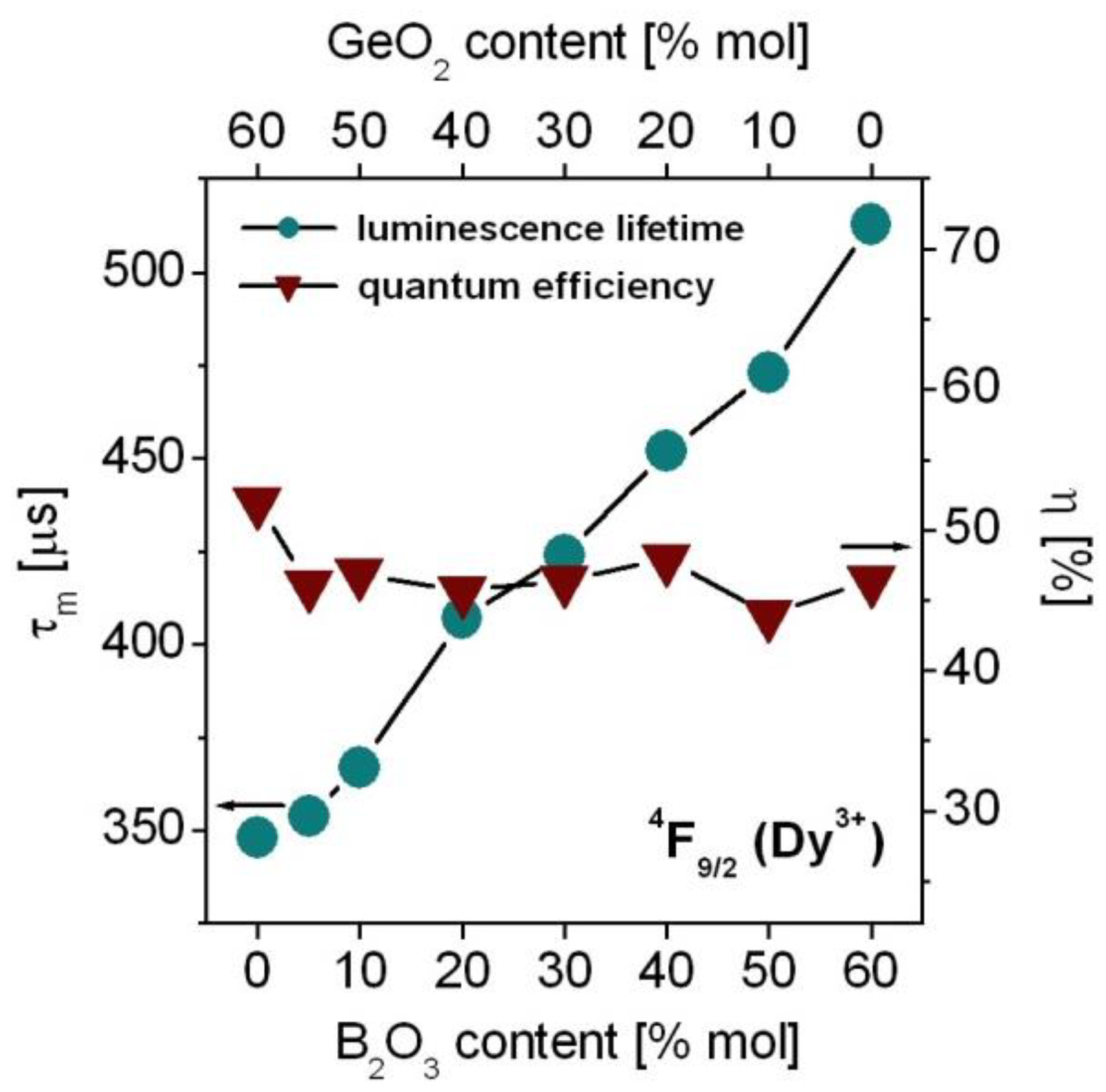
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Judd, B.R. Optical absorption intensities of rare-earth ions. Phys. Rev. 1962, 127, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofelt, G.S. Intensities of crystal spectra of rare-earth ions. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlen, M.P.; Brik, M.G.; Krämer, K.W. 50th anniversary of the Judd–Ofelt theory: An experimentalist’s view of the formalism and its application. J. Lumin. 2013, 136, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, D. Judd–Ofelt analysis and energy transfer processes of Er3+ and Nd3+ doped fluoroaluminate glasses with low phosphate content. Opt. Mater. 2014, 38, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, E.A.; Konstantinidis, M.; De Souza, I.; Daly, M.G.; Martín, I.R.; Lavín, V.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, U.R. Judd-Ofelt parameters of RE3+-doped fluorotellurite glass (RE3+ = Pr3+, Nd3+, Sm3+, Tb3+, Dy3+, Ho3+, Er3+, and Tm3+). J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 845, 156028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, X.; Tan, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, S.; Yue, Y. Spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped oxyfluoro-germanate glass ceramics: A Judd-Ofelt theory analysis. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 574, 121167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, M.-H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, D.-L.; Zhang, P.; Wong, W.-H. Judd-Ofelt spectroscopic properties of Er3+-doped NaLa(WO4)2 polycrystalline powder. Spectrochim. Acta A 2021, 249, 119335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.; Lei, W.; Luo, Z.; Lu, A. Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped SiO2-Al2O3-CaO-CaF2 glass: Structure, J-O analysis and fluorescent properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 264, 114919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Margaryan, A.; Margaryan, A.; Shi, F.G. Judd–Ofelt analysis of spectroscopic properties of Nd3+-doped novel fluorophosphate glass. J. Lumin. 2005, 114, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.N.H.; Rao, J.L.; Prasad, K.R.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Fluorescence and Judd–Ofelt analysis of Nd3+ doped P2O5–Na2O–K2O glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.N.; Reddy, C.A.; Sailaja, S.; Seo, H.J.; Reddy, B.S. Judd–Ofelt theory: Optical absorption and NIR emission spectral studies of Nd3+:CdO–Bi2O3–B2O3 glasses for laser applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanthima, N.; Kaewkhao, J.; Tariwong, Y.; Sangwaranatee, N.; Sangwaranatee, N.W. Luminescence study and Judd-Ofelt analysis of CaO-BaO-P2O5 glasses doped with Nd3+ ions. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.; Srisittipokakun, N.; Rooh, G.; Khattak, S.A.; Singkiburin, N.; Kim, H.J.; Sangwaranatee, N.; Kaewkhao, J. Investigation of Li2O–Gd2O3–MO–B2O3–Nd2O3 (MO=Ba/Bi) glasses for laser applications by Judd–Ofelt (J–O) theory. J. Lumin. 2019, 215, 116639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahraz, Z.A.S.; Sazali, E.S.; Sahar, M.R.; Amran, N.U.; Yaacob, S.N.S.; Aziz, S.M.; Mawlud, S.Q.; Noor, F.M.; Harun, A.N. Spectroscopic investigations of near-infrared emission from Nd3+-doped zinc-phosphate glasses: Judd-Ofelt evaluation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 509, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.U.; Hashim, S.; Goshal, S.K. Optical traits of neodymium-doped new types of borate glasses: Judd-Ofelt analysis. Optik 2019, 199, 163515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, K.; Aseev, V.; Ivanov, S.; Ignatiev, A.; Nikonorov, N. Optical, spectroscopic properties and Judd–Ofelt analysis of Nd3+-doped photo-thermo-refractive glass. J. Lumin. 2019, 213, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Liang, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, T.; Ning, T.; Lu, A. Thermal and fluorescence properties of Nd2O3-doped Gd2O3-Ga2O3-GeO2 glass based on the Judd-Ofelt theory. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 594, 121810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Ohyagi, T.; Soga, N.; Hanada, T. Compositional dependence of Judd-Ofelt parameters of Er3+ ions in alkali-metal borate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 3305–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jlassi, I.; Elhouichet, H.; Ferid, M.; Barthou, C. Judd–Ofelt analysis and improvement of thermal and optical properties of tellurite glasses by adding P2O5. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, A.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Sahar, M.R.; Dousti, M.R.; Amjad, R.J.; Nawaz, F. Enhanced spectroscopic properties and Judd-Ofelt parameters of Er-doped tellurite glass: Effect of gold nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, R.J.; Dousti, M.R.; Sahar, M.R. Spectroscopic investigation and Judd-Ofelt analysis of silver nanoparticles embedded Er3+-doped tellurite glass. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2015, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, M.S.; Marzouk, S.Y. Judd-Ofelt analysis of spectroscopic properties of Er3+ doped TeO2-BaO-ZnO glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.N.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Azlan, M.N. Optical properties of titania nanoparticles embedded Er3+-doped tellurite glass: Judd-Ofelt analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 724, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, S.Y.; Sahar, M.R.; Ghoshal, S.K. Spectroscopic attributes of Er3+ ions in antimony phosphate glass incorporated with Ag nanoparticles: Judd-Ofelt analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachheb, R.; Herrmann, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Reiter, J.; Körner, J.; Hein, J.; Rüssel, C.; Maâlej, R.; Damak, K. Judd–Ofelt analysis and experimental spectroscopic study of erbium doped phosphate glasses. J. Lumin. 2018, 201, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodin, N.L.A.; Sahar, M.R. Erbium doped sodium magnesium boro-tellurite glass: Stability and Judd-Ofelt analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyappan, M.; Arunkumar, S.; Marimuthu, K. Judd-Ofelt analysis and NIR luminescence investigations on Er3+ ions doped B2O3–Bi2O3–Li2O–K2O glasses for photonic applications. Phys. B 2019, 572, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Aditya, S.; Ghosh, S. Optimization of rare earth (Er3+) doping level in lead zinc phosphate glass through Judd-Ofelt analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 246, 122802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanane, H.; Velazquez, M.; Denux, D.; Duclere, J.-R.; Cornette, J.; Kermaoui, A.; Kellou, H.; Lahaye, M.; Buffiere, S. Judd-Ofelt analysis and crystal field calculations of Er3+ ions in new oxyfluorogermanotellurite glasses and glass-ceramics. Opt. Mater. 2020, 100, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezid, M.; Goumeidane, F.; Abidi, A.; Poulain, M.; Legouera, M.; Prasad, P.S.; Środa, M.; Rao, P.V. Judd-Ofelt analysis and luminescence studies of Er3+ doped halogeno-antimonate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2021, 120, 111422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasimhadri, M.; Cho, E.-J.; Jang, K.-W.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.I. Spectroscopic properties and Judd–Ofelt analysis of Sm3+ doped lead–germanate–tellurite glasses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 175101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Shukla, R.; Sanghi, S.; Agarwal, A.; Pal, I. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped lead bismosilicate glasses using Judd–Ofelt theory. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 117, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, S.; Herrmann, A.; Rüssel, C. Judd–Ofelt analysis of Sm3+-doped lanthanum-aluminosilicate glasses. J. Lumin. 2015, 157, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawlud, S.Q.; Ameen, M.M.; Sahar, M.R.; Mahraz, Z.A.S.; Ahmed, K.F. Spectroscopic properties of Sm3+ doped sodium-tellurite glasses: Judd-Ofelt analysis. Opt. Mater. 2017, 69, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina; Naveen; Sheetal; Kumar, V.; Dahiya, S.; Deopa, N.; Punia, R.; Rao, A.S. Judd-Ofelt itemization and influence of energy transfer on Sm3+ ions activated B2O3–ZnF2–SrO–SiO2 glasses for orange-red emitting devices. J. Lumin. 2021, 229, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Doualan, J.-L.; Nazabal, V.; Camy, P.; Adam, J.-L. Spectroscopic study and Judd–Ofelt analysis of Pr3+-doped Zr–Ba–La–Al glasses in visible spectral range. J. Opt. Soc. Amer. B 2013, 30, 2032–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.V.V.; Gopal, K.R.; Reddy, R.R.; Reddy, G.V.L.; Hussain, N.S.; Jamalaiah, B.C. Application of modified Judd–Ofelt theory and the evaluation of radiative properties of Pr3+-doped lead telluroborate glasses for laser applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 364, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bi, Z.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Z. Luminescence and Judd–Ofelt analysis of the Pr3+ doped fluorotellurite glass. J. Lumin. 2015, 160, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flizikowski, G.A.S.; Zanuto, V.S.; Nunes, L.A.O.; Baesso, M.L.; Malacarne, L.C.; Astrath, N.G.C. Standard and modified Judd-Ofelt theories in Pr3+-doped calcium aluminosilicate glasses: A comparative analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 780, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Khan, I.; Rooh, G.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Islam, M.A.; Chanthima, N.; Kothan, S.; Ullah, I.; Ahad, A.; Kaewkhao, J. Judd-Ofelt and luminescence properties of Pr3+ doped ZnO-Gd2O3/GdF3-BaO-P2O5 glasses for visible and NIR applications. J. Lumin. 2022, 247, 118884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, L.R.; Rao, T.S.; Janardhanam, K.; Rao, A.S.; Subramanyam, Y. Judd-Ofelt parametrization and radiative transitions analysis of Tm3+ doped alkali chloroborophosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 1999, 12, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, A.; Florez, M.; Messaddeq, Y.; Aegerter, M.A.; Porcher, P. Application of standard and modified Judd-Ofelt theories to thulium doped fluoroindate glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1999, 247, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, K.; Yazawa, T.; Shojiya, M.; Kawamoto, Y. Judd-Ofelt analysis and luminescence property of Tm3+ in Ga2S3-GeS2-La2S3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 274, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S. Judd–Ofelt and laser parameterization of Tm3+-doped barium gallo-germanate glass fabricated with efficient dehydration methods. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojiya, M.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kadono, K. Judd–Ofelt parameters and multiphonon relaxation of Ho3+ ions in ZnCl2-based glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 4944–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H.; Yang, D.; Huang, L. Judd–Ofelt analysis, frequency upconversion, and infrared photoluminescence of Ho3+-doped and Ho3+/Yb3+-codoped lead bismuth gallate oxide glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 103105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; Sontakke, A.D.; Sen, R.; Kalyandurg, A. Efficient ~2.0 μm emission from Ho3+ doped tellurite glass sensitized by Yb3+ ions: Judd-Ofelt analysis and energy transfer mechanism. Opt. Mater. Exp. 2011, 1, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Rai, V.K. Ho3+-Yb3+ codoped tellurite based glasses in visible lasers and optical devices: Judd-Ofelt analysis and frequency upconversion. Solid State Sci. 2017, 66, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarni, A.S.; Hussin, R.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Alamri, S.N.; Yamusa, Y.A.; Jupri, S.A. Intense red and green luminescence from holmium activated zincsulfo-boro-phosphate glass: Judd-Ofelt evaluation. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 808, 151706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Mohanty, D.K.; Rai, V.K.; Singh, K. Luminescence and Judd-Ofelt study of Ho3+/Ho3+-Yb3+ doped/ codoped lead tellurite glasses for multifunctional applications. J. Lumin. 2021, 239, 118319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, O.; Reddy, C.M.; Reddy, B.S.; Raju, B.D.P. Judd–Ofelt analysis and spectral properties of Dy3+ ions doped niobium containing tellurium calcium zinc borate glasses. Opt. Commun. 2014, 312, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maaref, A.A.; Shaaban, K.H.S.; Abdelawwad, M.; Saddeek, Y.B. Optical characterizations and Judd-Ofelt analysis of Dy3+ doped borosilicate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2017, 72, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, V.P.; Quang, V.X.; Do, P.V.; Thanh, L.D.; Ca, N.X.; Hoa, V.X.; van Tuat, L.; Thi, L.A.; Nogami, M. An in-depth study of the Judd-Ofelt analysis, spectroscopic properties and energy transfer of Dy3+ in alumino-lithium-telluroborate glasses. J. Lumin. 2019, 210, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, H.; Deopa, N.; Kaur, S.; Prasad, A.; Sreenivasulu, M.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Rao, A.S. Judd-Ofelt parametrization and radiative analysis of Dy3+ ions doped Sodium Bismuth Strontium Phosphate glasses. J. Lumin. 2019, 215, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoja, A.; Hashim, S.; Ghoshal, S.K. Judd−Ofelt calculations for spectroscopic characteristics of Dy3+-activated strontium magnesium borate glass. Optik 2020, 218, 165001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonam; Shivani; Anu; Kumar, A.; Sahu, M.K.; Rani, P.R.; Deopa, N.; Punia, R.; Rao, A.S. Judd-Ofelt Parameterization and Luminescence Characterization of Dy3+ Doped Oxyfluoride Lithium Zinc Borosilicate Glasses for Lasers and w-LEDs. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2020, 544, 120187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, G.; Wagh, A.; Lira, A.; Kityk, I.V.; Lee, D.-E.; Yoon, J.; Park, T. Dy3+: B2O3–Al2O3–ZnO–Bi2O3–BaO–M2O (M = Li; Na; and K) glasses: Judd–Ofelt analysis and photoluminescence investigation for WLED applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 2481–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasha, A.; Marzouk, S.Y. Linear and nonlinear optical properties and luminescence of Dy+3-doped aluminoborate glasses: Judd–Ofelt investigation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 20431–20444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divina, R.; Teresa, P.E.; Marimuthu, K. Dy3+ ion as optical probe to study the luminescence behavior of Alkali lead bismuth borate glasses for w-LED application. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 883, 160845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamuda, S.K.; Syed, F.; Devi, C.B.A.; Swapna, K.; Prasad, M.V.V.K.S.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S. Spectral characterization of Dy3+ ions doped phosphate glasses for yellow laser applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 555, 120538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhi; Ankita; Anu; Rao, A. S. Spectroscopic characterizations of Dy3+ ions doped phosphate glasses for epoxy-free white LED applications. Opt. Mater. 2022, 132, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrappa, V.; Basavapoornima, C.; Kesavulu, C.R.; Babu, A.M.; Depuru, S.R.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectral studies of Dy3+:zincphosphate glasses for white light source emission applications: A comparative study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 583, 121466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu; Deopa, N.; Rao, A.S. Structural and luminescence characteristics of thermally stable Dy3+ doped oxyfluoride strontium zinc borosilicate glasses for photonic device applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 154, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojha, M.K.K.; Vijayakumar, M.; Matheswaran, P.; Yousef, E.S.; Marimuthu, K. Modifier’s influence on spectral properties of dysprosium ions doped lead boro-telluro-phosphate glasses for white light applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 156, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, N.; Neelima, G.; Nallabala, N.K.R.; Kummara, V.K.; Ravanamma, R.; Reddy, V.J.; Prasanth, M.; Suresh, K.; Babu, P.; Venkatramu, V. Role of excitation wavelength and dopant concentration on white light tunability of dysprosium doped titania-fluorophosphate glasses. Opt. Mater. 2021, 111, 110593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Kuwik, M.; Polak, J.; Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A. Transition Metals (Cr3+) and Lanthanides (Eu3+) in Inorganic Glasses with Extremely Different Glass-Formers B2O3 and GeO2. Materials 2021, 14, 7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Liu, C.; Ruan, J. Ultrafast charge carrier dynamics and photoluminescence of CsPbBr3−xIx quantum dots in boro-germanate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 7228–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, M.; Şentürk, U.; Uslu, D.K.; Burgaz, G.; Şahin, Y.; Gökçe, A.G. Investigation of europium concentration dependence on luminescent properties of borogermanate glasses. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malashkevich, G.E.; Sigaev, V.N.; Golubev, N.V.; Savinkov, V.I.; Sarkisov, P.D.; Khodasevich, I.A.; Dashkevich, V.I.; Mudryi, A.V. Luminescence of borogermanate glasses activated by Er3+ and Yb3+ ions. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2011, 357, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, M.; Kocyiğit, D. Spectroscopic investigations of Dy3+ doped borogermanate glasses for laser and wLED applications. Opt. Mater. 2019, 89, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manasa, P.; Jayasankar, C.K. Spectroscopic assessment of Dy3+ ions in lead fluorosilicate glass as a prospective material for solid state yellow laser. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 212, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, P.R.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Mahamuda, S.; Swapna, K.; Deopa, N.; Rao, A.S. Spectroscopic studies of Dy3+ ions doped barium lead alumino fluoro borate glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 787, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, T.A.; Dantas, N.F.; Goncalves, T.S.; de Camargo, A.S.S.; Pedrochi, F.; Steimacher, A. Dy3+ doped calcium boroaluminate glasses and Blue Led for smart white light generation. J. Lumin. 2019, 207, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kıbrıslı, O.; Ersundu, A.E.; Ersundu, M.C. Dy3+ doped tellurite glasses for solid-state lighting: An investigation through physical, thermal, structural and optical spectroscopy studies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 513, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shasmal, N.; Karmakar, B. White light-emitting Dy3+-doped transparent chloroborosilicate glass: Synthesis and optical properties. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2019, 7, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Rajaramakrishna, R.; Rooh, G.; Chanthima, N.; Kim, H.J.; Saiyasombat, C.; Botta, R.; Nuntawong, N.; Kothan, S.; Kaewkhao, J. Structural and luminescence study of Dy3+ doped phosphate glasses for solid state lighting applications. Opt. Mater. 2020, 109, 110322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.; Srisittipokakun, N.; Rooh, G.; Khattak, S.A.; Kaewkhao, J.; Rani, M.; Kim, H.J. Comparative study of Dy3+ doped borate glasses on the basis of luminescence and lasing properties for white-light generation. Opt. Mater. 2021, 119, 111308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, R.J.; Sales, T.O.; Sattar, A.; Jacinto, C.; Dousti, M.R. Spectral studies of highly Dy3+ doped PbO–ZnO–B2O3–P2O5 glasses. J. Lumin. 2021, 231, 117839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopa, B.; Eraiah, B. Experimental and theoretical approach on the physical, structural and optical properties of ZrO2-Na2O-B2O3 glasses doped with Dy2O3. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2021, 551, 120394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.H.D.; Mahamuda, S.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Sailaja, P.; Swapna, K.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Olarinoye, I.O.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Synthesis and characterization of B2O3–Bi2O3–SrO–Al2O3–PbO–Dy2O3 glass system: The role of Bi2O3/Dy2O3 on the optical, structural, and radiation absorption parameters. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 155, 111952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasimhadri, V.M.; Divi Haranath, D. Spectroscopic investigations of Dy3+-doped tungstate–tellurite glasses for solid-state lighting applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2022, 13, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrappa, V.; Basavapoornima, C.; Venkatramu, V.; Depuru, S.R.; Kaewkhao, J.; Pecharapa, W.; Jayasankar, C.K. A critical review and future prospects of Dy3+-doped glasses for white light emission applications. Optik 2022, 266, 169583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, F.; Su, Z. Luminescent properties and structure of Dy3+ doped germanosilicate glass. J. Lumin. 2020, 226, 117378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, M.; Mazumder, N.; Lakshminarayana, G.; Mandal, S.; Kamath, S.D. Energy transfer and luminescence study of Dy3+ doped zincaluminoborosilicate glasses for white light emission. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwik, M.; Górny, A.; Pisarski, W.A.; Pisarska, J. Influence of glass formers and glass modifiers on spectral properties and CIE coordinates of Dy3+ ions in lead-free borate glasses. Spectrochim. Acta A 2022, 268, 120693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasankar, C.K.; Rukmini, E. Spectroscopic investigations of Dy3+ ions in borosulphate glasses. Phys. B 1997, 240, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Shen, L.F.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H. Dy3+-doped germanate glasses for waveguide-typed irradiation light sources. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 646, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Chen, B.J.; Pun, E.Y.B.; Lin, H. Multichannel transition emissions of Dy3+ in fiber-adaptive germanium tellurite glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 123507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.S.; Pavani, K.; Babu, A.M.; Giri, N.K.; Rai, S.B.; Moorthy, L.R. Fluorescence characteristics of Dy3+ ions in calcium fluoroborate glasses. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swapna, K.; Mahamuda, S.; Rao, A.S.; Jayasimhadri, M.; Sasikala, T.; Moorthy, L.R. Visible fluorescence characteristics of Dy3+ doped zinc alumino bismuth borate glasses for optoelectronic devices. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8459–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Saidi, M.S.A.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Arifin, R.; Roslan, M.K.; Muhammad, R.; Shamsuri, W.N.W.; Abdullah, M.; Shaharin, M.S. Spectroscopic properties of Dy3+ doped tellurite glass with Ag/TiO2 nanoparticles inclusion: Judd-Ofelt analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 754, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huy, B.T.; Seo, M.-H.; Lim, J.-M.; Lee, Y.-I.; Thanh, N.T.; Quang, V.X.; Hoai, T.T.; Hong, N.A. Application of the Judd—Ofelt Theory to Dy3+-Doped Fluoroborate/Sulphate Glasses. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2011, 59, 3300–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naick, B.N.; Damodaraiah, S.; Prasad, V.R.; Vijaya Lakshmi, R.P.; Ratnakaram, Y.C. Judd-Ofelt analysis and luminescence studies on Dy3+ -doped different phosphate glasses for white light emitting material applications. Optik 2019, 192, 162980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.U.; Hashim, S.; Ghoshal, S.K. Spectroscopic characteristics of Dy3+ impurities–doped borate-based glasses: Judd–Ofelt calculation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 253, 123386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L. Spectroscopic properties and Judd-Ofelt theory analysis of Dy3+ doped oxyfluoride silicate glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 043110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekri, M.; Hermann, A.; Turki, R.; Rüssel, C.; Maâlej, R.; Damak, K. Experimental and theoretical studies of Dy3+ doped alkaline earth aluminosilicate glasses. J. Lumin. 2019, 212, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, V.M.; Mahamuda, S.; Talewar, R.A.; Swapna, K.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Rao, A.S. Dy3+ ions doped oxy-fluoro boro tellurite glasses for the prospective optoelectronic device applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 762, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisiecki, R. Oxyfluoride germanatetellurite glasses doped with dysprosium—Spectroscopic characteristic and luminescence thermometry qualities. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 597, 121922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarski, W.A.; Pisarska, J.; Żur, L.; Goryczka, T. Structural and optical aspects for Eu3+ and Dy3+ ions in heavy metal glasses based on PbO–Ga2O3–XO2 (X = Te, Ge, Si). Opt. Mater. 2013, 35, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, J.; Pisarski, W.A.; Lisiecki, R.; Ryba-Romanowski, W. Phonon sideband analysis and near-infrared emission in heavy metal oxide glasses. Materials 2021, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linganna, K.; Haritha, P.; Krishnaiah, K.V.; Venkatramu, V.; Jayasankar, C.K. Optical and luminescence properties of Dy3+ ions in K–Sr–Al phosphate glasses for yellow laser applications. Appl. Phys. B 2014, 117, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
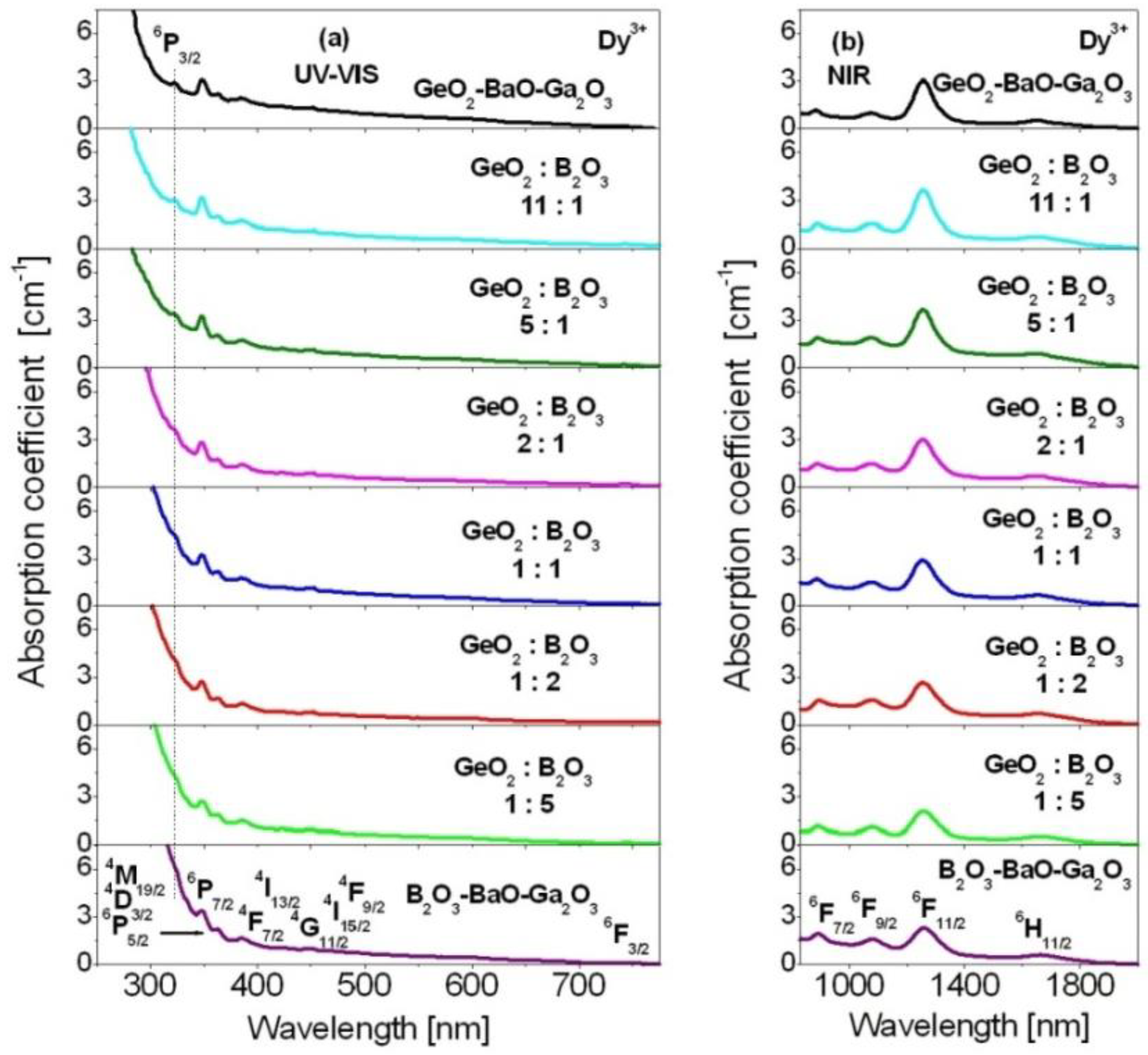

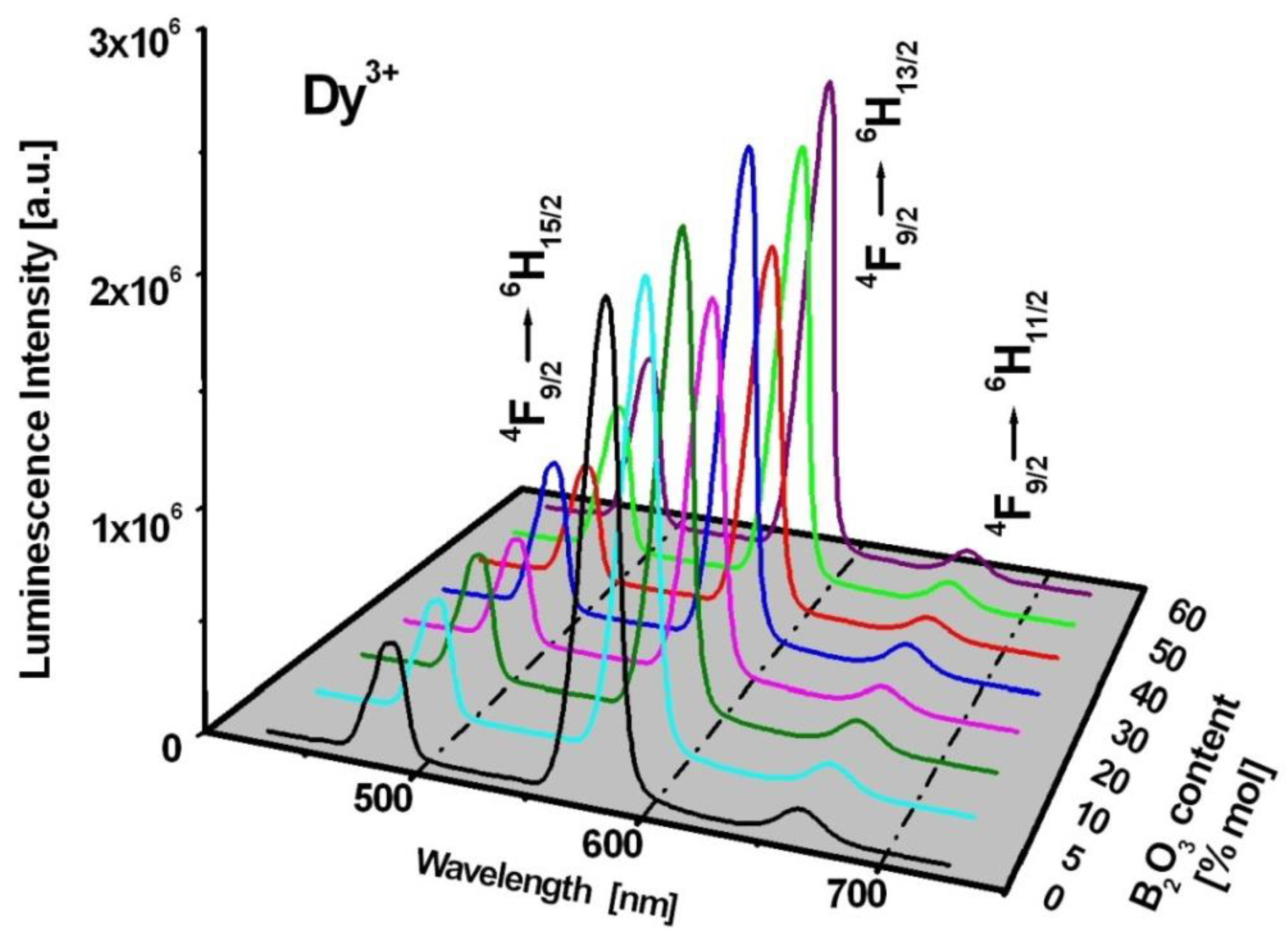



| No | Glass Code | Chemical Composition [mol%] |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | GeO2-BaO-Ga2O3 | 60GeO2-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (2) | GeO2:B2O3 = 11:1 | 55GeO2-5B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (3) | GeO2:B2O3 = 5:1 | 50GeO2-10B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (4) | GeO2:B2O3 = 2:1 | 40GeO2-20B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (5) | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:1 | 30GeO2-30B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (6) | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:2 | 20GeO2-40B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (7) | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:5 | 10GeO2-50B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| (8) | B2O3-BaO-Ga2O3 | 60B2O3-30BaO-9.5Ga2O3-0.5Dy2O3 |
| Parameters | Symbols | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Theoretical oscillator strength | Pcalc | - |
| Measure oscillator strength | Pmeas | - |
| Judd–Ofelt intensity parameters | Ωt (t = 2, 4, 6) | 10−20 cm2 |
| Spectroscopic quality parameter | χ (Ω4/Ω6) | - |
| Radiative transition probability | AJ | s−1 |
| Total radiative transition probability | AT | s−1 |
| Luminescence branching ratio | β | % |
| Radiative lifetime | τrad | µs |
| Measured lifetime | τmeas | µs |
| Quantum efficiency | η | % |
| Peak emission wavelength | λp | nm |
| Emission linewidth | Δλ | nm |
| Full width at half maximum | FWHM | nm |
| Peak stimulated emission cross-section | σem | 10−21 cm2 |
| Levels | Energy [cm−1] | GeO2-BaO-Ga2O3 | GeO2:B2O3 = 11:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 5:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 2:1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | ||
| 6H11/2 6F11/2 6F9/2 6F7/2 6F3/2 4F9/2 4I15/2 4G11/2 4F7/2,4I13/2 4M19/2,4D3/2,6P5/2 6P7/2 | 6040 7960 9300 11,290 13,450 21,200 22,200 23,600 25,900 27,500 28,700 | 1.260 8.220 1.580 1.410 0.090 0.150 0.330 0.075 0.820 0.730 3.070 | 1.109 8.240 1.783 1.391 0.117 0.105 0.360 0.063 0.601 0.932 2.364 | 1.060 8.150 1.500 1.260 0.090 0.080 0.330 0.070 0.750 0.650 3.200 | 0.980 8.161 1.677 1.168 0.092 0.087 0.311 0.069 0.597 0.754 2.648 | 1.190 7.600 1.500 1.580 0.100 0.080 0.310 0.065 0.750 0.720 2.910 | 1.089 7.613 1.748 1.417 0.122 0.107 0.357 0.057 0.573 0.960 2.157 | 1.120 6.980 1.470 1.310 0.100 0.070 0.350 0.090 0.900 0.700 2.770 | 0.987 6.998 1.651 1.298 0.110 0.098 0.322 0.057 0.546 0.871 2.160 |
| Levels | Energy [cm−1] | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:2 | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:5 | B2O3-BaO-Ga2O3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | Pmeas | Pcalc | ||
| 6H11/2 6F11/2 6F9/2 6F7/2 6F3/2 4F9/2 4I15/2 4G11/2 4F7/2,4I13/2 4M19/2,4D3/2,6P5/2 6P7/2 | 6040 7960 9300 11,290 13,450 21,200 22,200 23,600 25,900 27,500 28,700 | 1.160 6.850 1.650 1.140 0.140 0.130 0.350 0.075 0.750 0.770 2.470 | 1.000 6.871 1.690 1.346 0.115 0.102 0.328 0.056 0.551 0.906 2.160 | 1.170 6.120 1.720 1.860 0.100 0.090 0.360 0.070 0.800 0.870 2.120 | 1.137 6.125 1.867 1.699 0.155 0.130 0.386 0.046 0.549 1.186 1.745 | 1.120 5.600 1.580 1.400 0.100 0.080 0.340 0.065 0.750 0.880 1.970 | 1.004 5.615 1.659 1.481 0.134 0.113 0.339 0.043 0.496 1.029 1.637 | 1.090 5.390 1.740 1.650 0.160 0.100 0.330 0.085 0.810 0.740 2.000 | 1.038 5.397 1.810 1.612 0.146 0.123 0.353 0.046 0.531 1.117 1.800 |
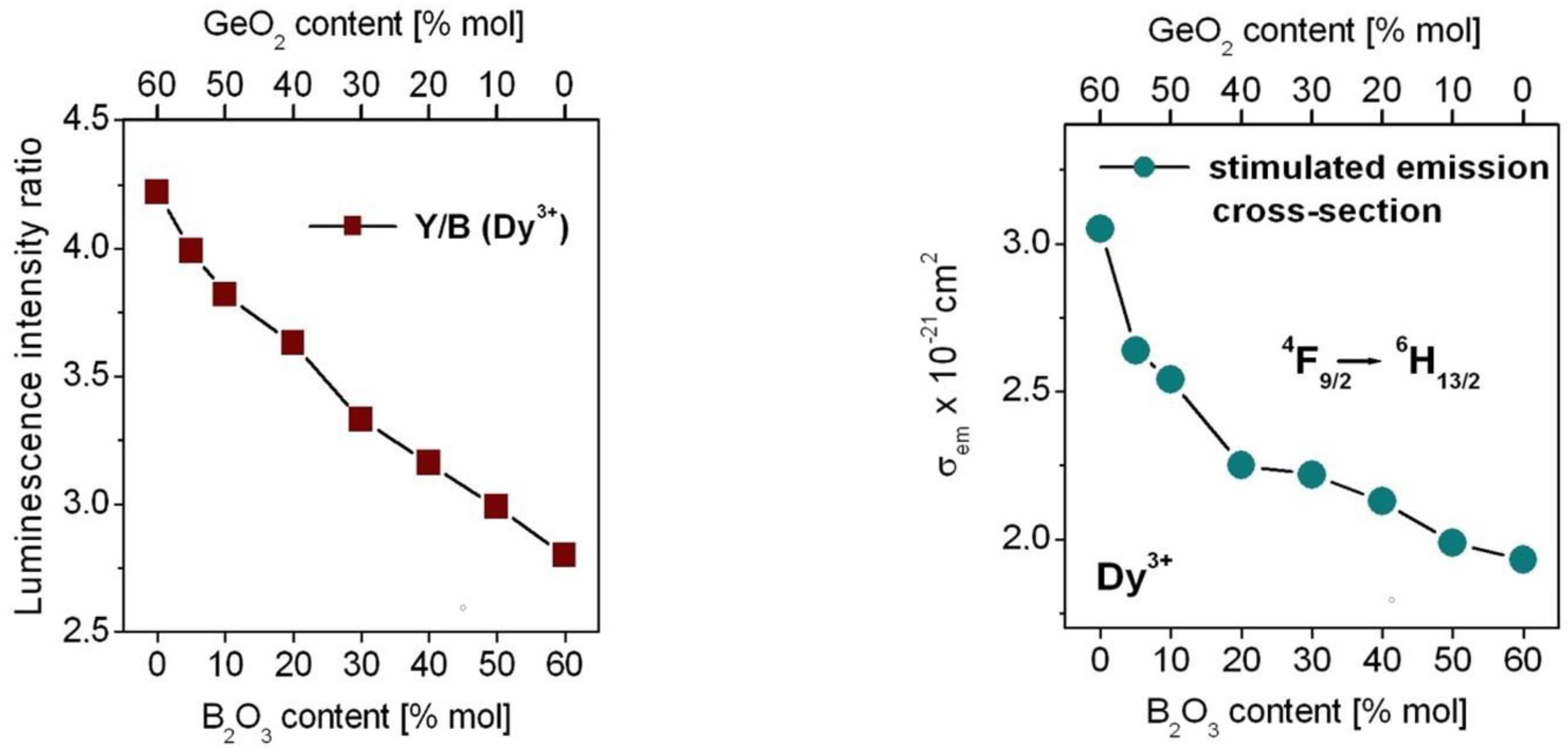
| Glasses | Judd–Ofelt Intensity Parameters Ωt (t = 2, 4, 6) [in 10−20 cm2 Units] | χ (Ω4/Ω6) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ω2 | Ω4 | Ω6 | ||
| GeO2-BaO-Ga2O3 GeO2:B2O3 = 11:1 GeO2:B2O3 = 5:1 GeO2:B2O3 = 2:1 GeO2:B2O3 = 1:1 GeO2:B2O3 = 1:2 GeO2:B2O3 = 1:5 B2O3-BaO-Ga2O3 | 8.73 ± 0.22 8.42 ± 0.17 8.09 ± 0.23 7.52 ± 0.21 7.45 ± 0.19 6.72 ± 0.17 6.27 ± 0.16 5.92 ± 0.13 | 1.44 ± 0.21 1.60 ± 0.15 1.52 ± 0.22 1.35 ± 0.20 1.37 ± 0.18 1.11 ± 0.15 1.06 ± 0.14 1.18 ± 0.12 | 1.33 ± 0.14 1.03 ± 0.10 1.40 ± 0.14 1.29 ± 0.13 1.36 ± 0.12 1.87 ± 0.10 1.65 ± 0.10 1.81 ± 0.08 | 1.08 1.55 1.09 1.05 1.00 0.60 0.64 0.65 |
| Transition | λ [nm] | GeO2-BaO-Ga2O3 | GeO2:B2O3 = 11:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 5:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 2:1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | ||
| 4F9/2 → 6F1/2 6F3/2 6F5/2 6F7/2 6H5/2 6H7/2 6F9/2 6F11/2 6H9/2 6H11/2 6H13/2 6H15/2 | 1373 1275 1156 992 918 836 830 749 746 662 573 480 | >0.1 >0.1 15 6 4 19 11 36 25 125 1088 165 | - - 0.010 0.004 0.003 0.013 0.007 0.024 0.017 0.084 0.728 0.110 | >0.1 >0.1 13 4 3 17 10 32 23 108 976 125 | - - 0.010 0.003 0.002 0.013 0.008 0.024 0.018 0.082 0.745 0.095 | >0.1 >0.1 12 4 3 16 9 30 22 100 932 150 | - - 0.009 0.004 0.003 0.013 0.007 0.023 0.017 0.078 0.729 0.117 | >0.1 >0.1 11 4 3 15 8 26 19 88 818 132 | - - 0.010 0.004 0.003 0.013 0.007 0.023 0.017 0.078 0.728 0.117 |
| Transition | λ [nm] | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:1 | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:2 | GeO2:B2O3 = 1:5 | B2O3-BaO-Ga2O3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | AJ [s−1] | β | ||
| 4F9/2 → 6F1/2 6F3/2 6F5/2 6F7/2 6H5/2 6H7/2 6F9/2 6F11/2 6H9/2 6H11/2 6H13/2 6H15/2 | 1373 1275 1156 992 918 836 830 749 746 662 573 480 | >0.1 >0.1 10 4 3 15 8 25 19 85 792 134 | - - 0.009 0.004 0.003 0.014 0.007 0.023 0.017 0.078 0.723 0.122 | >0.1 >0.1 9 4 3 15 7 23 18 76 743 167 | - - 0.008 0.004 0.003 0.014 0.007 0.022 0.016 0.071 0.698 0.157 | >0.1 >0.1 8 3 2 13 6 20 16 67 656 142 | - - 0.009 0.003 0.002 0.014 0.007 0.021 0.017 0.072 0.703 0.152 | >0.1 >0.1 7 3 2 13 6 19 15 63 625 151 | - - 0.008 0.003 0.002 0.014 0.007 0.021 0.017 0.070 0.691 0.167 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pisarski, W.A. Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses. Materials 2022, 15, 9042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15249042
Pisarski WA. Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses. Materials. 2022; 15(24):9042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15249042
Chicago/Turabian StylePisarski, Wojciech A. 2022. "Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses" Materials 15, no. 24: 9042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15249042
APA StylePisarski, W. A. (2022). Judd–Ofelt Analysis and Emission Properties of Dy3+ Ions in Borogermanate Glasses. Materials, 15(24), 9042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15249042






