Modeling of Biological Activity of PEO-Coated Titanium Implants with Conjugates of Cyclic RGD Peptide with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
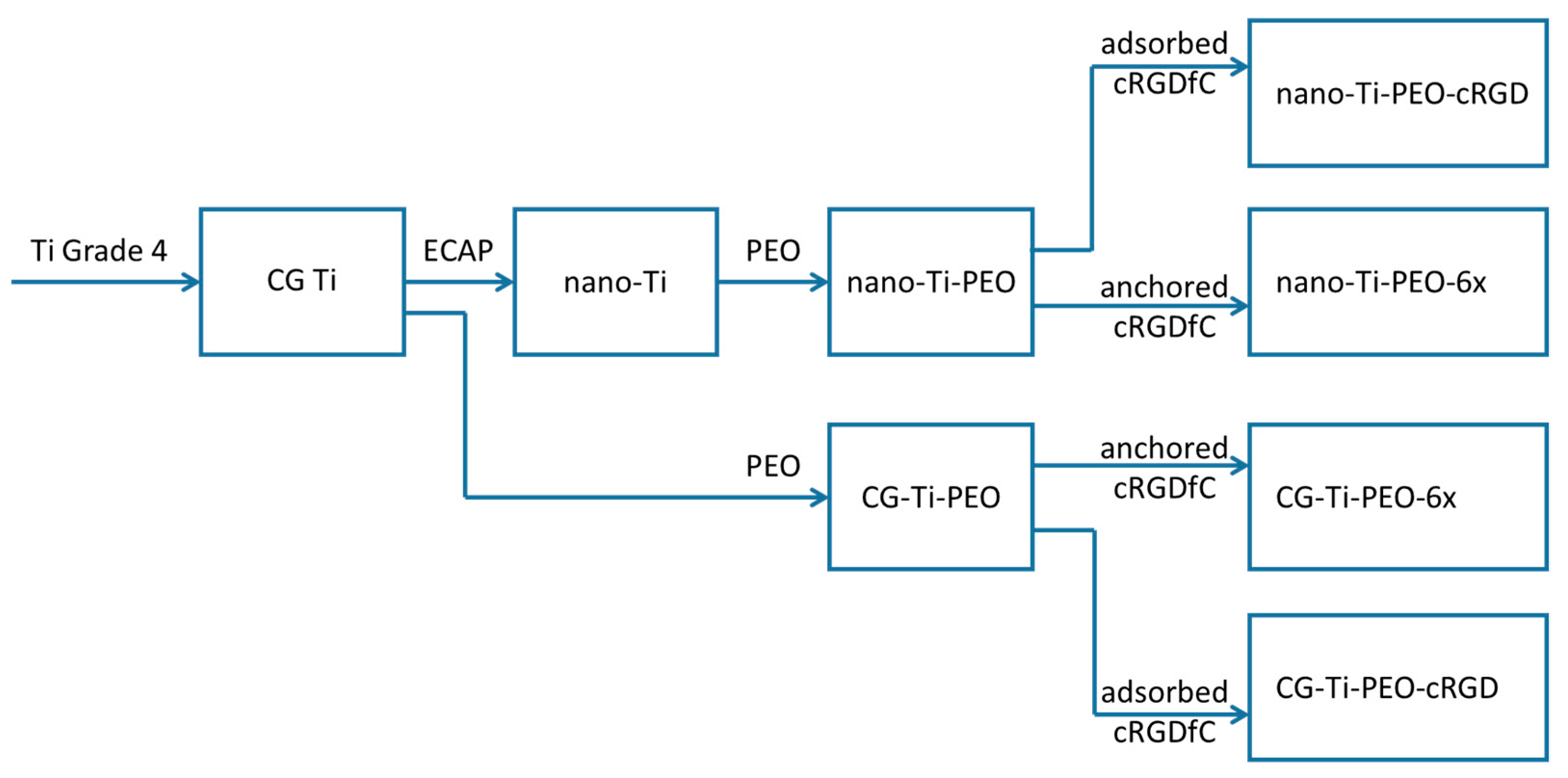
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Preparation of Titanium Samples and PEO Coating
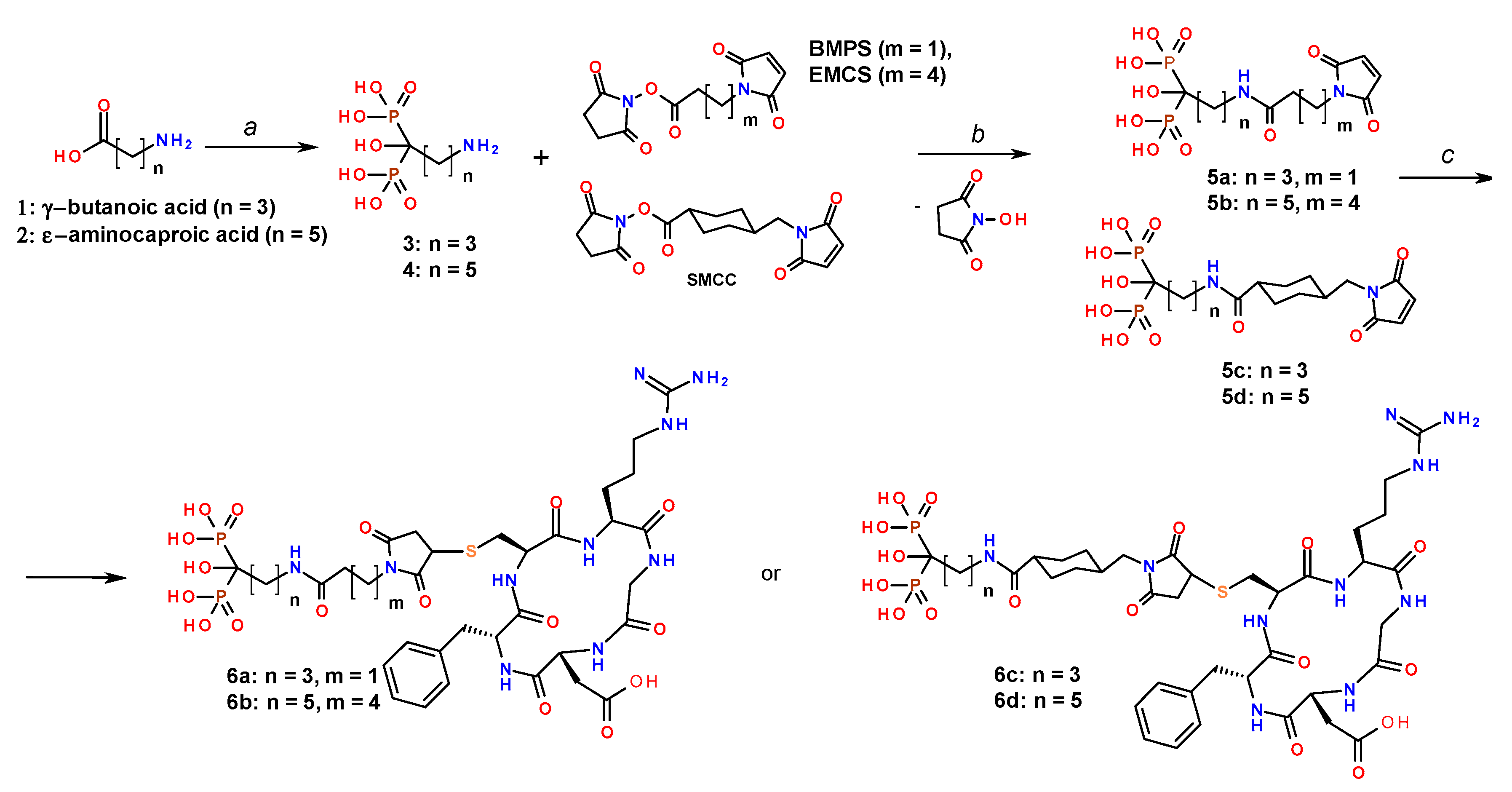
2.3. Synthesis of Conjugates of cRGD with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates
2.4. Surface Characterization
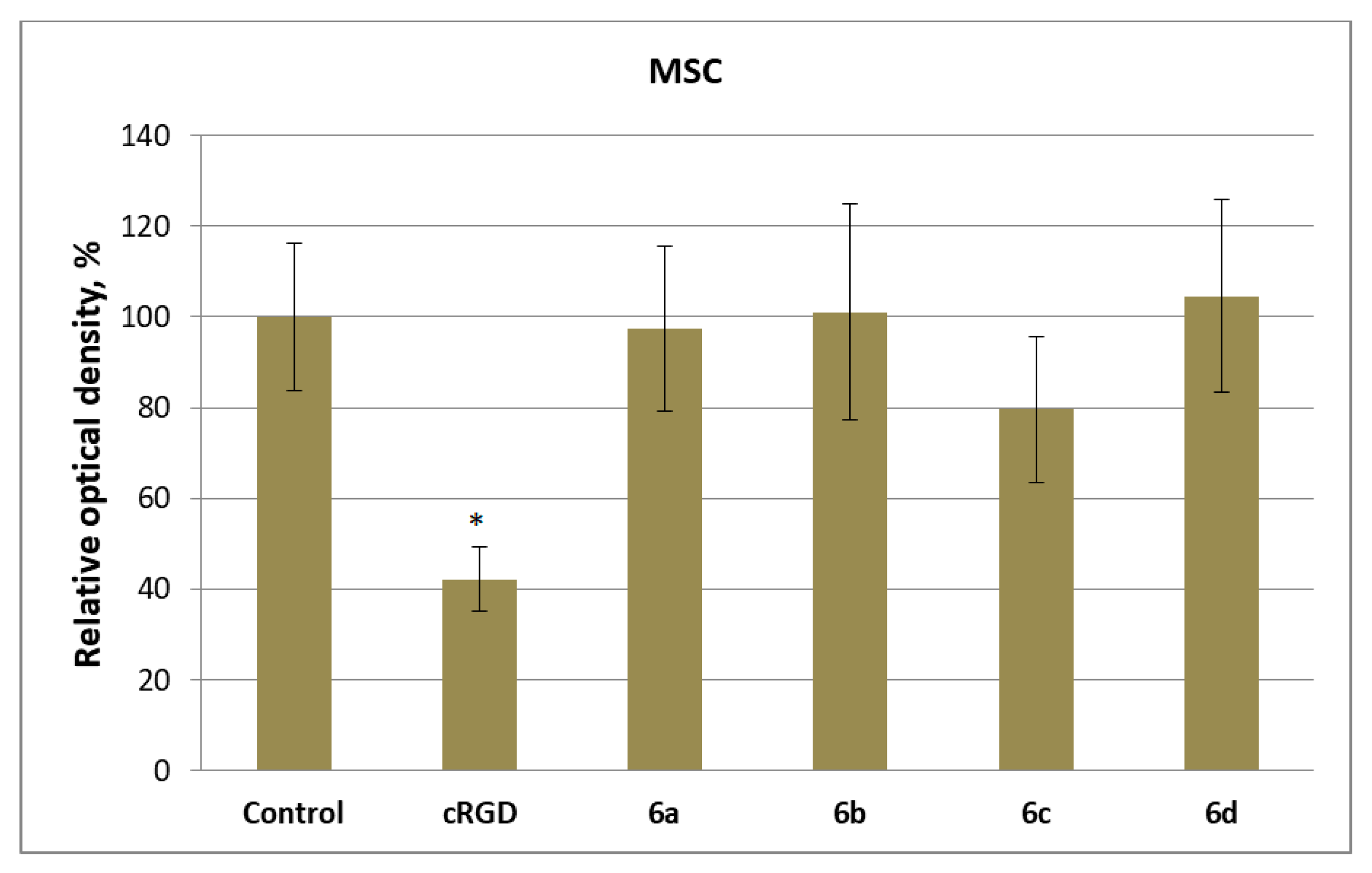
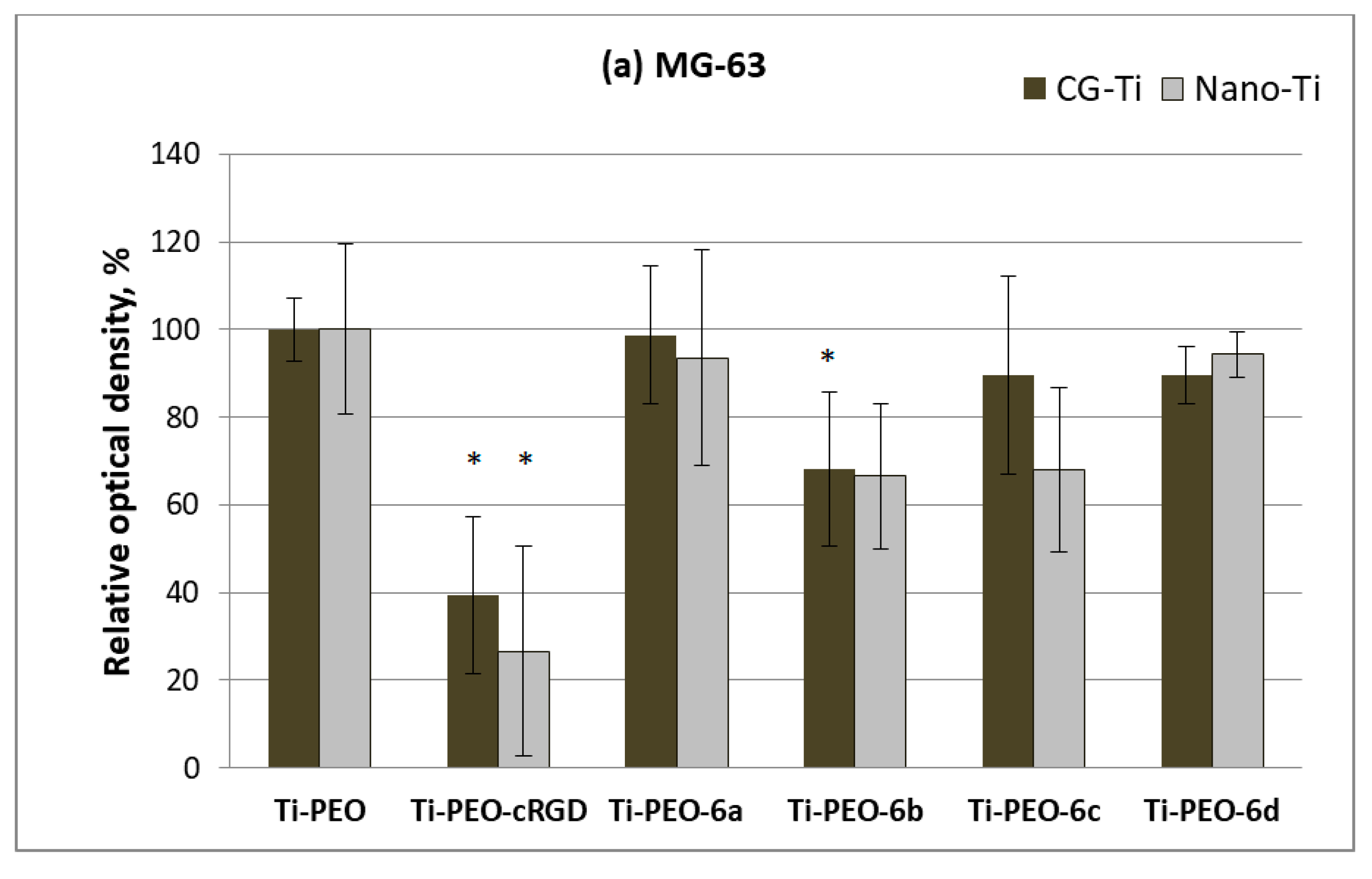
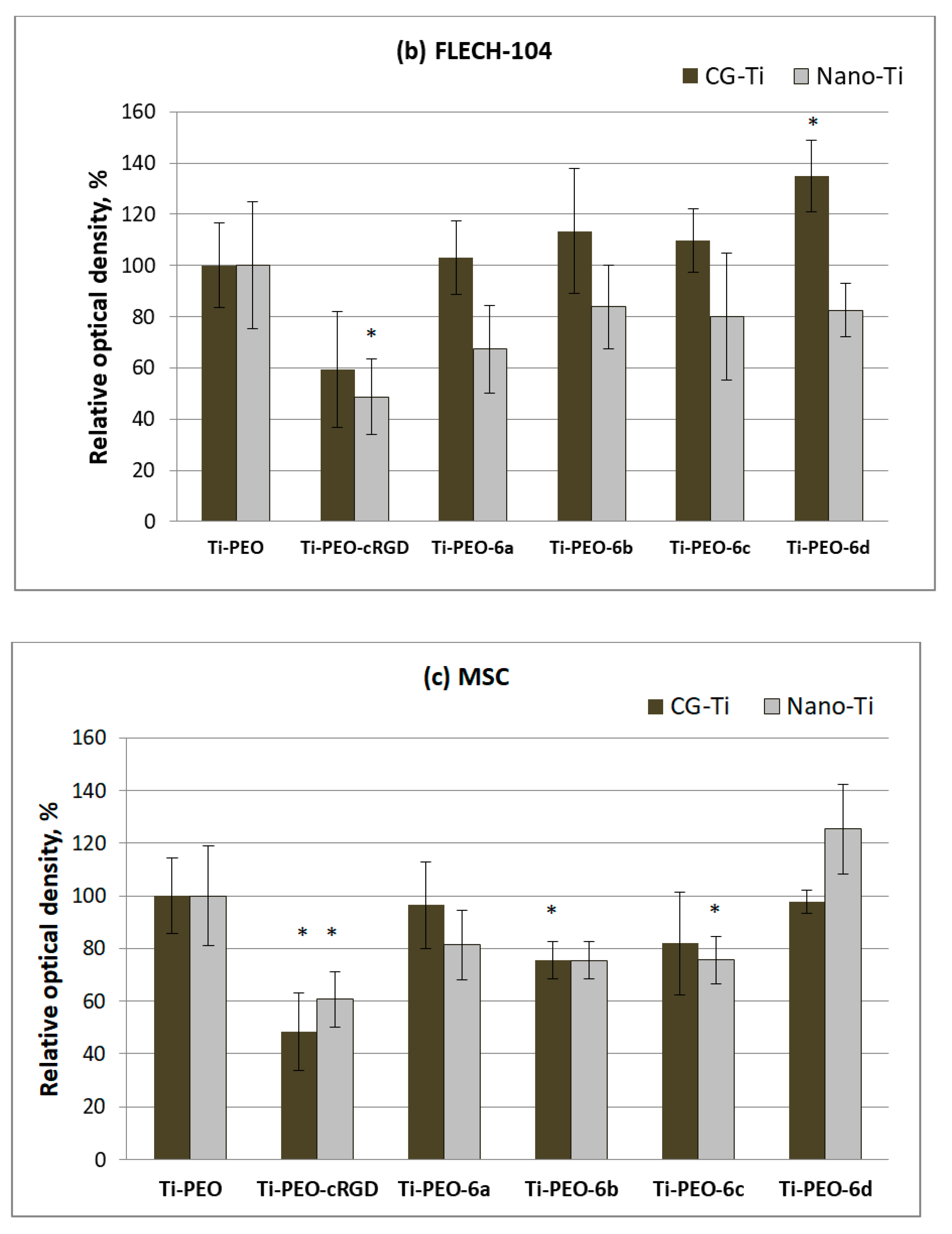
2.5. Response of Human Cells to Conjugates of c(RGDfC) with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates and Ti-PEO Coating
3. Results and Discussions
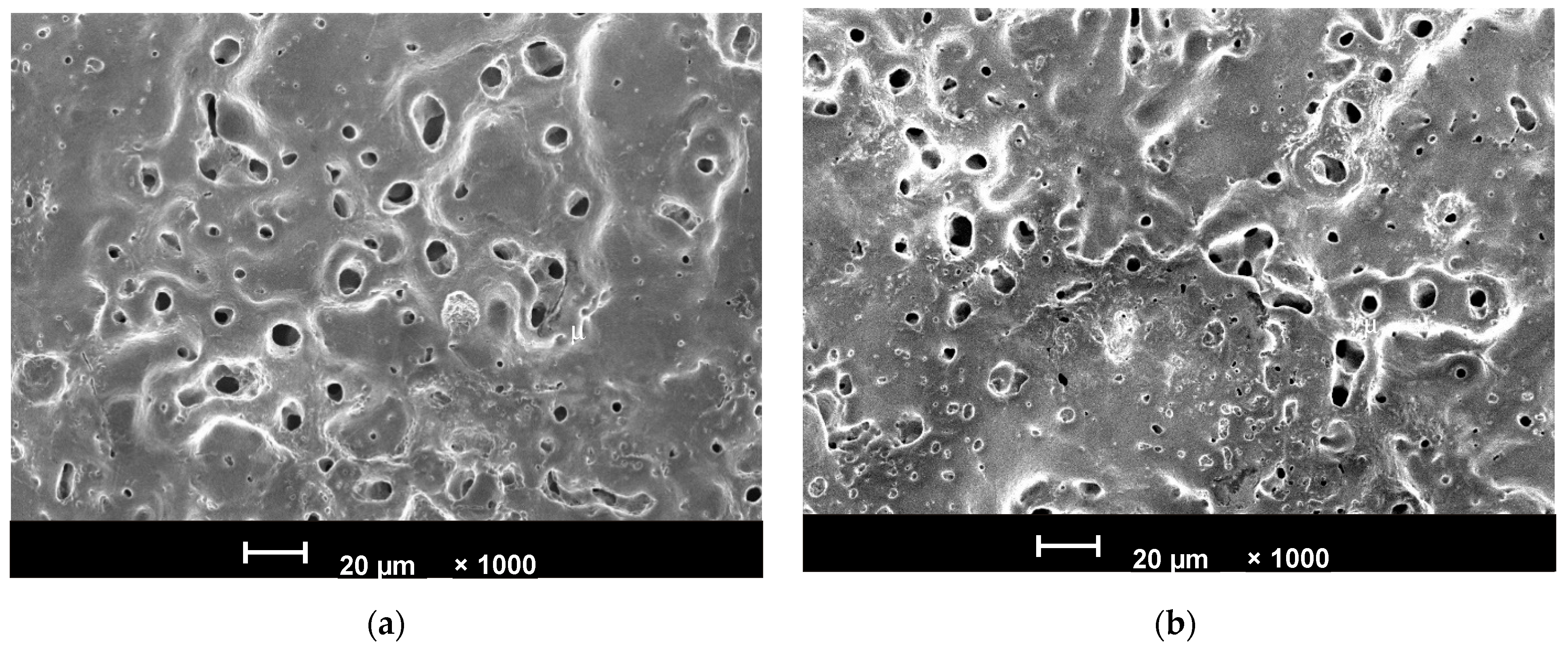
3.1. Surface Properties of the PEO-Coated Ti Disks as Substrates for the cRGDfC Assessment
3.2. Synthesis and Biological Properties of the cRGDfC Organic Coatings
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Sabirov, I.; Zemtsova, E.G.; Parfenov, E.V.; Dluhoš, L.; Lowe, T.C. Nanostructured commercially pure titanium for development of miniaturized biomedical implants. In Titanium in Medical and Dental Applications; Froes, F.H., Qian, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 393–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.R.; Grinstaff, M.W. Biocompatible and bioactive surface modifications for prolonged in vivo efficacy. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliofkhazraei, M.; Macdonald, D.D.; Matykina, E.; Parfenov, E.V.; Egorkin, V.S.; Curran, J.A.; Troughton, S.C.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Gnedenkov, S.V.; Lampke, T.; et al. Review of plasma electrolytic oxidation of titanium substrates: Mechanism, properties, applications and limitations. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 5, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, C.D.; Petrie, T.A.; Burns, K.L.; Schwartz, Z.; García, A.J. Biomolecular surface coating to enhance orthopaedic tissue healing and integration. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3228–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E. RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996, 12, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Mark, K.; Park, J.; Bauer, S.; Schmuki, P. Nanoscale engineering of biomimetic surfaces: Cues from the extracellular matrix. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; D’Amico, G.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M.; Reynolds, L.E. Integrins: The keys to unlocking angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, D.M.; Moodie, G.D.; Dimond, P.M.; Giorani, C.W.D.; Ehrlich, M.G.; Valentini, R.F. RGD-coated titanium implants stimulate increased bone formation in vivo. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 2323–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, P.; Witkowska, J.; Rodziewicz-Motowidło, S.; Lach, S. Proteins, peptides and peptidomimetics as active agents in implant surface functionalization. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 276, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, A.; Akbaba, S.; Buchholz, J.; Türkkan, S.; Tezcaner, A.; Woche, S.K.; Guggenberger, G.; Kirschning, A.; Dräger, G. RGD-Modified Titanium as an Improved Osteoinductive Biomaterial for Use in Dental and Orthopedic Implants. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmengaard, B.; Bechtold, J.E.; Søballe, K. In vivo study of the effect of RGD treatment on bone ongrowth on press-fit titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammelt, S.; Illert, T.; Bierbaum, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Zwipp, H.; Schneiders, W. Coating of titanium implants with collagen, RGD peptide and chondroitin sulfate. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5561–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuvelot, J.; Portet, D.; Lecollinet, G.; Moreau, M.F.; Baslé, M.F.; Chappard, D.; Libouban, H. In vitro kinetic study of growth and mineralization of osteoblast-like cells (Saos-2) on titanium surface coated with a RGD functionalized bisphosphonate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, T.A.; Ho, J.E.; De Ranieri, A.; Virdi, A.S.; Sumner, D.R.; Healy, K.E. Peri-implant bone formation and implant integration strength of peptide-modified p(AAM-co-EG/AAC) interpenetrating polymer network-coated titanium implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 80, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.E.; Barber, T.A.; Virdi, A.S.; Sumner, D.R.; Healy, K.E. The effect of enzymatically degradable IPN coatings on peri-implant bone formation and implant fixation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2007, 81, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Martínez-de-Tejada, G.; Gomes, P.A.C.; Martins, M.C.L.; Costa, F. Antimicrobial Peptides in the Battle against Orthopedic Implant-Related Infections: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, H.; Kong, X.; Zhang, S.M.; Lee, I.S. Immobilizing osteogenic growth peptide with and without fibronectin on a titanium surface: Effects of loading methods on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kong, X.; Zhang, S.-M.; Lee, I.-S. Characterization and in vitro biological evaluation of mineral/osteogenic growth peptide nanocomposites synthesized biomimetically on titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 334, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Moruno, C.; Fraioli, R.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Kapp, T.G.; Kessler, H. αvβ3- or α5β1-Integrin-Selective Peptidomimetics for Surface Coating. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 7048–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, H. Conformation and Biological Activity of Cyclic Peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1982, 21, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubner, R.; Gratias, R.; Diefenbach, B.; Goodman, S.L.; Jonczyk, A.; Kessler, H. Structural and Functional Aspects of RGD-Containing Cyclic Pentapeptides as Highly Potent and Selective Integrin αVβ3 Antagonists. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 7461–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, T.G.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Maltsev, O.V.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Zarka, R.; Reuning, U.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Mas-Moruno, C.; et al. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Activity and Selectivity Profile of Ligands for RGD-binding Integrins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, S.; Pallu, S.; Bareille, R.; Jonczyk, A.; Meyer, J.; Dard, M.; Amédée, J. Function of linear and cyclic RGD-containing peptides in osteoprogenitor cells adhesion process. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxin, Á.; Zheng, G. Flexible or fixed: A comparative review of linear and cyclic cancer-targeting peptides. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1601–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanowich-Knipp, S.J.; Chakrabarti, S.; Williams, T.D.; Dillman, R.K.; Siahaan, T.J. Solution stability of linear vs. cyclic RGD peptides. J. Pept. Res. Off. J. Am. Pept. Soc. 1999, 53, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jois, S.D.; Tambunan, U.S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Siahaan, T.J. Solution structure of a cyclic RGD peptide that inhibits platelet aggregation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1996, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzzas, L.; Zanardi, F.; Battistini, L.; Burreddu, P.; Carta, P.; Rassu, G.; Curti, C.; Casiraghi, G. Targeting αvβ3 Integrin: Design and Applications of Mono- and Multifunctional RGD-Based Peptides and Semipeptides. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1255–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Kantlehner, M.; Schaffner, P.; Finsinger, D.; Meyer, J.; Jonczyk, A.; Diefenbach, B.; Nies, B.; Hölzemann, G.; Goodman, S.L.; Kessler, H. Surface coating with cyclic RGD peptides stimulates osteoblast adhesion and proliferation as well as bone formation. ChemBioChem 2000, 1, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Cervelló, L.; Martin-Gómez, H.; Mandakhbayar, N.; Jo, Y.-W.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Kim, H.-W.; Ginebra, M.-P.; Lee, J.-H.; Mas-Moruno, C. Mimicking Bone Extracellular Matrix: From BMP-2-Derived Sequences to Osteogenic-Multifunctional Coatings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 2022, 2201339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auernheimer, J.; Zukowski, D.; Dahmen, C.; Kantlehner, M.; Enderle, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Kessler, H. Titanium Implant Materials with Improved Biocompatibility through Coating with Phosphonate-Anchored Cyclic RGD Peptides. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Moruno, C.; Dorfner, P.M.; Manzenrieder, F.; Neubauer, S.; Reuning, U.; Burgkart, R.; Kessler, H. Behavior of primary human osteoblasts on trimmed and sandblasted Ti6Al4V surfaces functionalized with integrin αvβ3-selective cyclic RGD peptides. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101A, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel, M.; Meier, R.; Braun, K.; Wiessler, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. On-resin Diels-Alder reaction with inverse electron demand: An efficient ligation method for complex peptides with a varying spacer to optimize cell adhesion. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 4809–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz-Diez, C.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Neubauer, S.; Kessler, H.; Gil, F.J.; Pegueroles, M.; Manero, J.M.; Guillem-Marti, J. Tuning Mesenchymal Stem Cell Response onto Titanium–Niobium–Hafnium Alloy by Recombinant Fibronectin Fragments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, M.; Böge, C.; Janissen, R.; Rohrbeck, D.; Hülsen, T.; Lensing-Höhn, S.; Krauspe, R.; Herten, M. Osteoblastic potency of bone marrow cells cultivated on functionalized biometals with cyclic RGD-peptide. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101A, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auernheimer, J.; Kessler, H. Benzylprotected aromatic phosphonic acids for anchoring peptides on titanium. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmengaard, B.; Bechtold, J.E.; Søballe, K. In vivo effects of RGD-coated titanium implants inserted in two bone-gap models. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2005, 75A, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, S.; Born, R.; Scharnweber, D.; Worch, H.; Sewing, A.; Dard, M. Biomimetic coatings functionalized with adhesion peptides for dental implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dard, M.; Sewing, A.; Meyer, J.; Verrier, S.; Roessler, S.; Scharnweber, D. Tools for tissue engineering of mineralized oral structures. Clin. Oral Investig. 2000, 4, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joner, M.; Cheng, Q.; Schönhofer-Merl, S.; Lopez, M.; Neubauer, S.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Laufer, B.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Kessler, H.; Virmani, R. Polymer-free immobilization of a cyclic RGD peptide on a nitinol stent promotes integrin-dependent endothelial coverage of strut surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2012, 100B, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tátrai, P.; Sági, B.; Szigeti, A.; Szabó, I.; Bösze, S.; Kristóf, Z.; Markó, K.; Szakács, G.; Urbán, I.; Mezö, G.; et al. A novel cyclic RGD-containing peptide polymer improves serum-free adhesion of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to bone implant surfaces. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Yuan, L.; Xu, X.; Ma, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, X.; Ma, J. Biocompatible Nanotube-Strontium/polydopamine-arginine-glycine-aspartic acid coating on Ti6Al4V enhances osteogenic properties for biomedical applications. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Tao, B.; He, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Shen, X.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Y.; Mu, C.; Liu, P.; et al. Biocompatible MoS2/PDA-RGD coating on titanium implant with antibacterial property via intrinsic ROS-independent oxidative stress and NIR irradiation. Biomaterials 2019, 217, 119290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wängler, C.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O.; Schäfer, M.; Schirrmacher, R.; Bartenstein, P.; Eisenhut, M.; Wängler, B. Multimerization of cRGD peptides by click chemistry: Synthetic strategies, chemical limitations, and influence on biological properties. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prante, O.; Einsiedel, J.; Haubner, R.; Gmeiner, P.; Wester, H.-J.; Kuwert, T.; Maschauer, S. 3,4,6-Tri-O-acetyl-2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoroglucopyranosyl Phenylthiosulfonate: A Thiol-Reactive Agent for the Chemoselective 18F-Glycosylation of Peptides. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekaran, A.; García, A.J. Extracellular matrix-mimetic adhesive biomaterials for bone repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96A, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavalikar, P.; Robinson, A.; Lan, Z.; Jenkins, D.; Chwatko, M.; Salhadar, K.; Jose, A.; Kar, R.; Shoga, E.; Kannapiran, A.; et al. Review of Integrin-Targeting Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 2020, e2000795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfenov, E.V.; Parfenova, L.V.; Dyakonov, G.S.; Danilko, K.V.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Lukina, E.S.; Valiev, R.Z. Surface functionalization via PEO coating and RGD peptide for nanostructured titanium implants and their in vitro assessment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 357, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenova, L.V.; Lukina, E.S.; Galimshina, Z.R.; Gil’fanova, G.U.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Danilko, K.V.; Dyakonov, G.S.; Parfenov, E.V. Biocompatible Organic Coatings Based on Bisphosphonic Acid RGD-Derivatives for PEO-Modified Titanium Implants. Molecules 2020, 25, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenov, E.; Parfenova, L.; Mukaeva, V.; Farrakhov, R.; Stotskiy, A.; Raab, A.; Danilko, K.; Rameshbabu, N.; Valiev, R. Biofunctionalization of PEO coatings on titanium implants with inorganic and organic substances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 404, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portet, D.; Denizot, B.; Rump, E.; Lejeune, J.-J.; Jallet, P. Nonpolymeric Coatings of Iron Oxide Colloids for Biological Use as Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 238, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecollinet, G.; Delorme, N.; Edely, M.; Gibaud, A.; Bardeau, J.F.; Hindré, F.; Boury, F.; Portet, D. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Bisphosphonates: Influence of Side Chain Steric Hindrance. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7828–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyakonov, G.S.; Zemtsova, E.; Mironov, S.; Semenova, I.P.; Valiev, R.Z.; Semiatin, S.L. An EBSD investigation of ultrafine-grain titanium for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 648, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.; Buchardt, O. Facile Synthesis of Reagents Containing a Terminal Maleimido Ligand Linked to an Active Ester. Synthesis 1991, 1991, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ede, N.J.; Tregear, G.W.; Haralambidis, J. Routine Preparation of Thiol Oligonucleotides: Application to the Synthesis of Oligonucleotide-Peptide Hybrids. Bioconjug. Chem. 1994, 5, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfenova, L.V.; Galimshina, Z.R.; Gil’fanova, G.U.; Alibaeva, E.I.; Danilko, K.V.; Pashkova, T.M.; Kartashova, O.L.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Mukaeva, V.R.; Parfenov, E.V.; et al. Hyaluronic acid bisphosphonates as antifouling antimicrobial coatings for PEO-modified titanium implants. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, X.; Wan, P.; Zhu, B.; Chen, W. The anatase phase of nanotopography titania plays an important role on osteoblast cell morphology and proliferation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubakirova, V.; Farrakhov, R.; Sharipov, A.; Polyakova, V.; Parfenova, L.; Parfenov, E. Investigation of biocompatible PEO coating growth on cp-Ti with in situ spectroscopic methods. Materials 2022, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Yu, L. RGD-containing peptides trigger apoptosis in glomerular mesangial cells of adult human kidneys. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, C.D.; Pilling, D.; Henriquez, N.V.; Parsonage, G.; Threifall, K.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Simmons, D.L.; Akbarf, A.N.; Lord, J.M.; Salmon, M. RGD peptides induce apoptosis by direct caspase-3 activation. Nature 1999, 397, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Electrolyte Composition | Positive Pulse | Negative Pulse | Frequency (Hz) | Temperature (°C) | Duration (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | Duty Cycle (%) | Voltage (V) | Duty Cycle (%) | ||||
| 20 g/L Na3PO4·12 H2O | 470 ± 5 | 51 ± 0.1 | 40 ± 1 | 26 ± 0.1 | 300 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 5′ ± 5″ |
| Sample | h (μm) | Rz (μm) | Ra (μm) | Porosity (%) | Average Pore Size (μm) | Anatase Content (%) | Rutile Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG-Ti-PEO | 18.9 ± 1.1 | 15.6 ± 0.54 | 2.6 ± 0.13 | 7.6 ± 1.4 | 1.44 ± 0.17 | 62 ± 2% | 38 ± 2% |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 21.6 ± 1.3 | 17.3 ± 2.54 | 2.5 ± 0.05 | 7.6 ± 1.5 | 0.61 ± 0.11 | 70 ± 2% | 30 ± 2% |
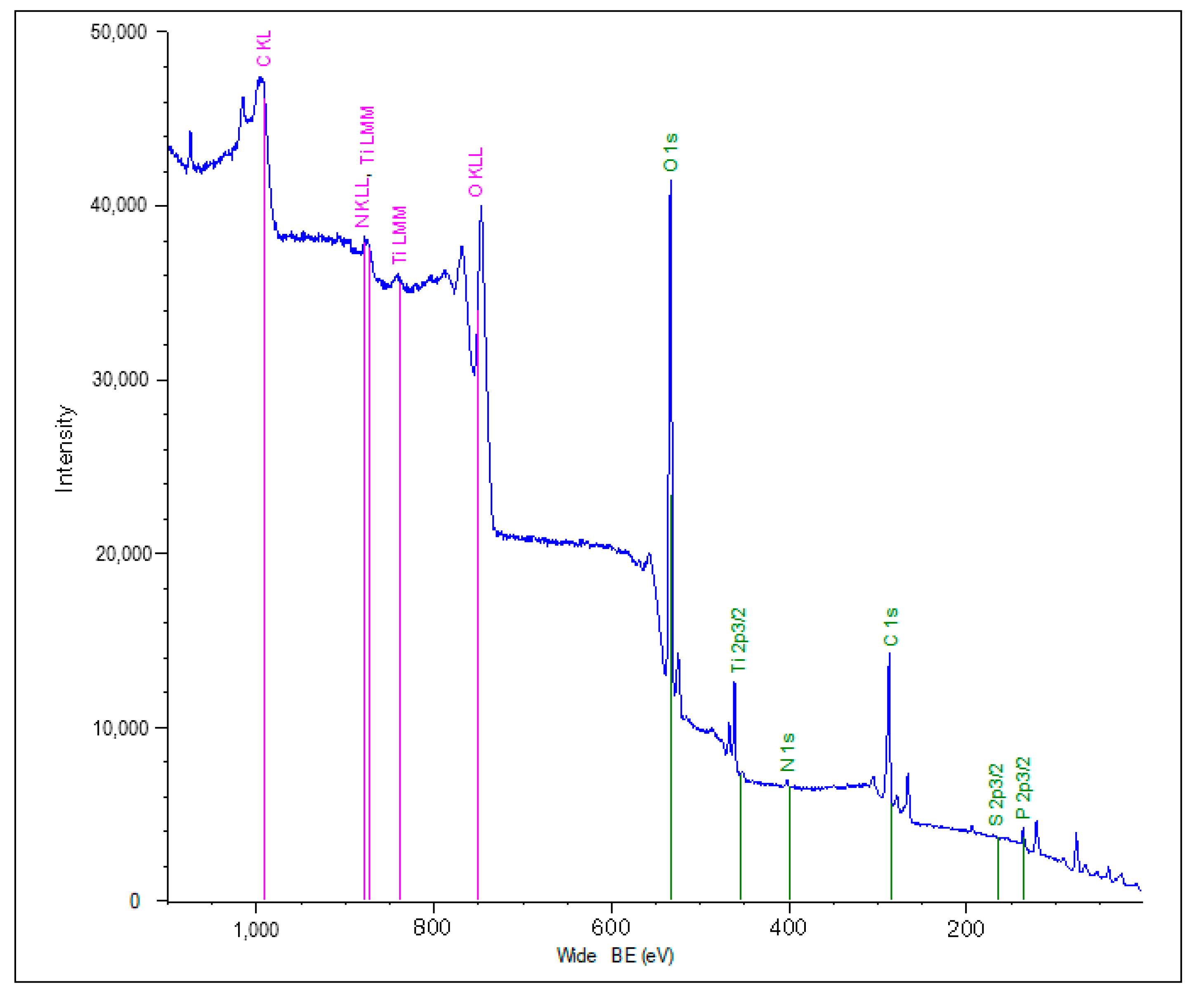
| Sample | Atomic Composition (%) | Atomic Ratio | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Organic Coating | Substrate | Ti2p | O1s | C1s | N1s | P2p | S2s | Ti2p/O1s | Ti2p/C1s | Ti2p/N1s |
| - | CG-Ti-PEO | 11.70 | 60.70 | 20.45 | 0.79 | 2.47 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.57 | 14.81 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 9.78 | 58.38 | 25.36 | 0.95 | 2.45 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 10.29 | |
| c(RGDfC) | CG-Ti-PEO | 5.50 | 67.42 | 22.78 | 0.54 | 1.63 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 10.19 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 4.07 | 76.25 | 17.19 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 10.18 | |
| 6a | CG-Ti-PEO | 0.89 | 76.00 | 21.90 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 3.42 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 5.59 | 70.58 | 20.16 | 0.65 | 1.28 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 8.60 | |
| 6b | CG-Ti-PEO | 4.65 | 69.48 | 22.66 | 0.68 | 0.82 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 6.84 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 3.46 | 68.09 | 23.27 | 0.55 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 6.29 | |
| 6c | CG-Ti-PEO | 9.08 | 70.59 | 14.44 | 0.71 | 2.01 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 12.79 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 3.10 | 68.35 | 25.95 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 5.54 | |
| 6d | CG-Ti-PEO | 6.28 | 68.19 | 19.52 | 2.28 | 1.15 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 2.75 |
| Nano-Ti-PEO | 6.39 | 68.66 | 20.26 | 0.65 | 1.32 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.32 | 9.83 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parfenova, L.V.; Galimshina, Z.R.; Gil’fanova, G.U.; Alibaeva, E.I.; Danilko, K.V.; Aubakirova, V.R.; Farrakhov, R.G.; Parfenov, E.V.; Valiev, R.Z. Modeling of Biological Activity of PEO-Coated Titanium Implants with Conjugates of Cyclic RGD Peptide with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates. Materials 2022, 15, 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228120
Parfenova LV, Galimshina ZR, Gil’fanova GU, Alibaeva EI, Danilko KV, Aubakirova VR, Farrakhov RG, Parfenov EV, Valiev RZ. Modeling of Biological Activity of PEO-Coated Titanium Implants with Conjugates of Cyclic RGD Peptide with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates. Materials. 2022; 15(22):8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228120
Chicago/Turabian StyleParfenova, Lyudmila V., Zulfiya R. Galimshina, Guzel U. Gil’fanova, Eliza I. Alibaeva, Ksenia V. Danilko, Veta R. Aubakirova, Ruzil G. Farrakhov, Evgeny V. Parfenov, and Ruslan Z. Valiev. 2022. "Modeling of Biological Activity of PEO-Coated Titanium Implants with Conjugates of Cyclic RGD Peptide with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates" Materials 15, no. 22: 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228120
APA StyleParfenova, L. V., Galimshina, Z. R., Gil’fanova, G. U., Alibaeva, E. I., Danilko, K. V., Aubakirova, V. R., Farrakhov, R. G., Parfenov, E. V., & Valiev, R. Z. (2022). Modeling of Biological Activity of PEO-Coated Titanium Implants with Conjugates of Cyclic RGD Peptide with Amino Acid Bisphosphonates. Materials, 15(22), 8120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15228120









