Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy Prepared by Integration of Gel-Casting and Microwave Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Raw Powder and Reagent
2.2. Experimental Process
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
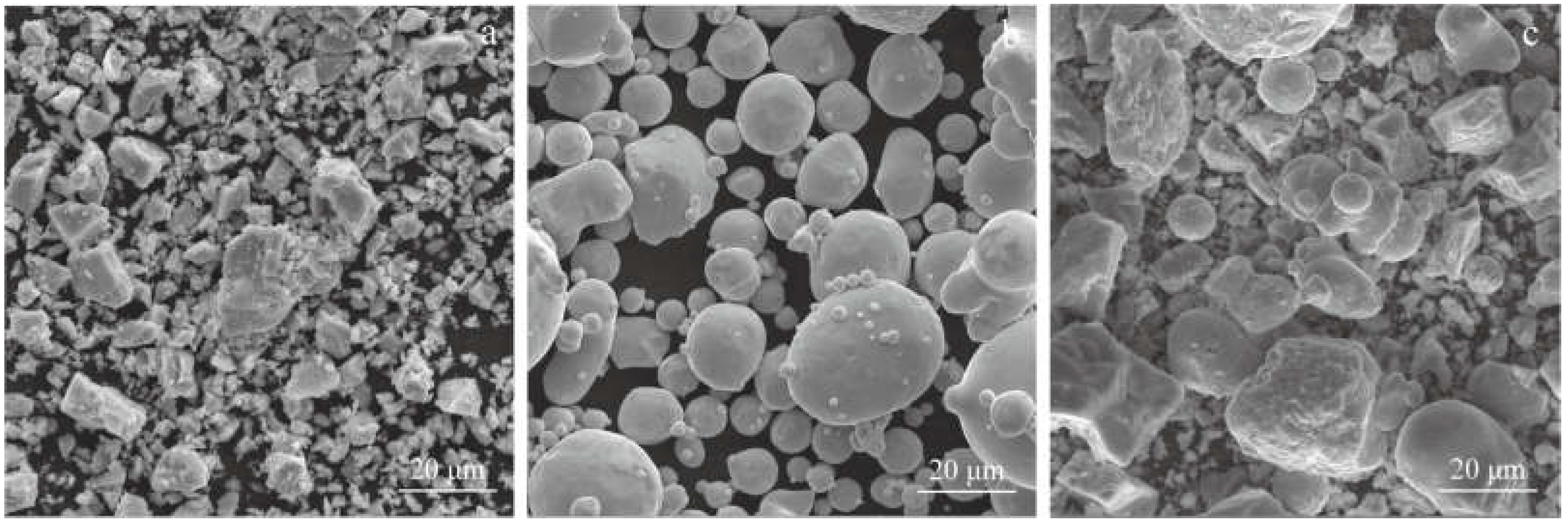
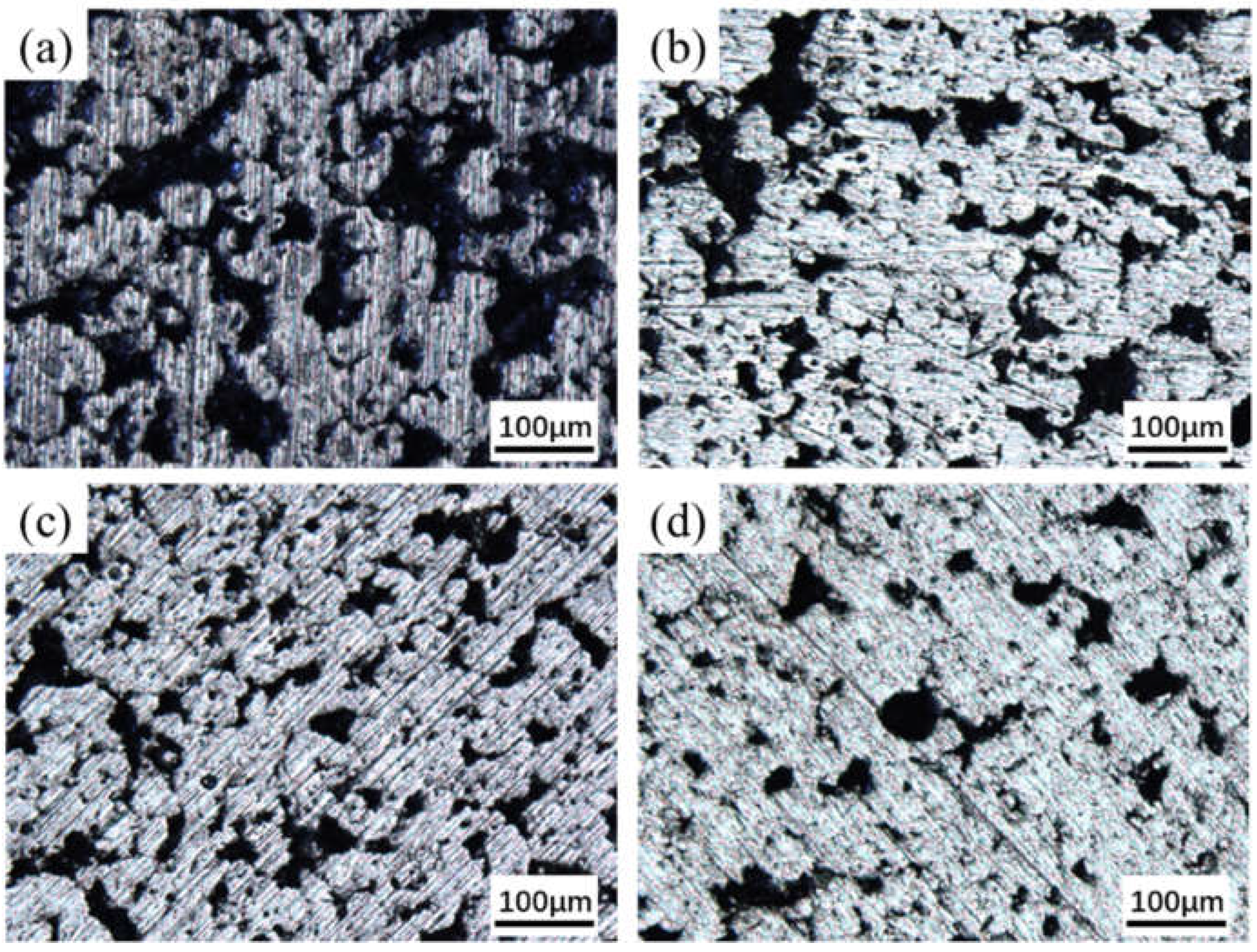
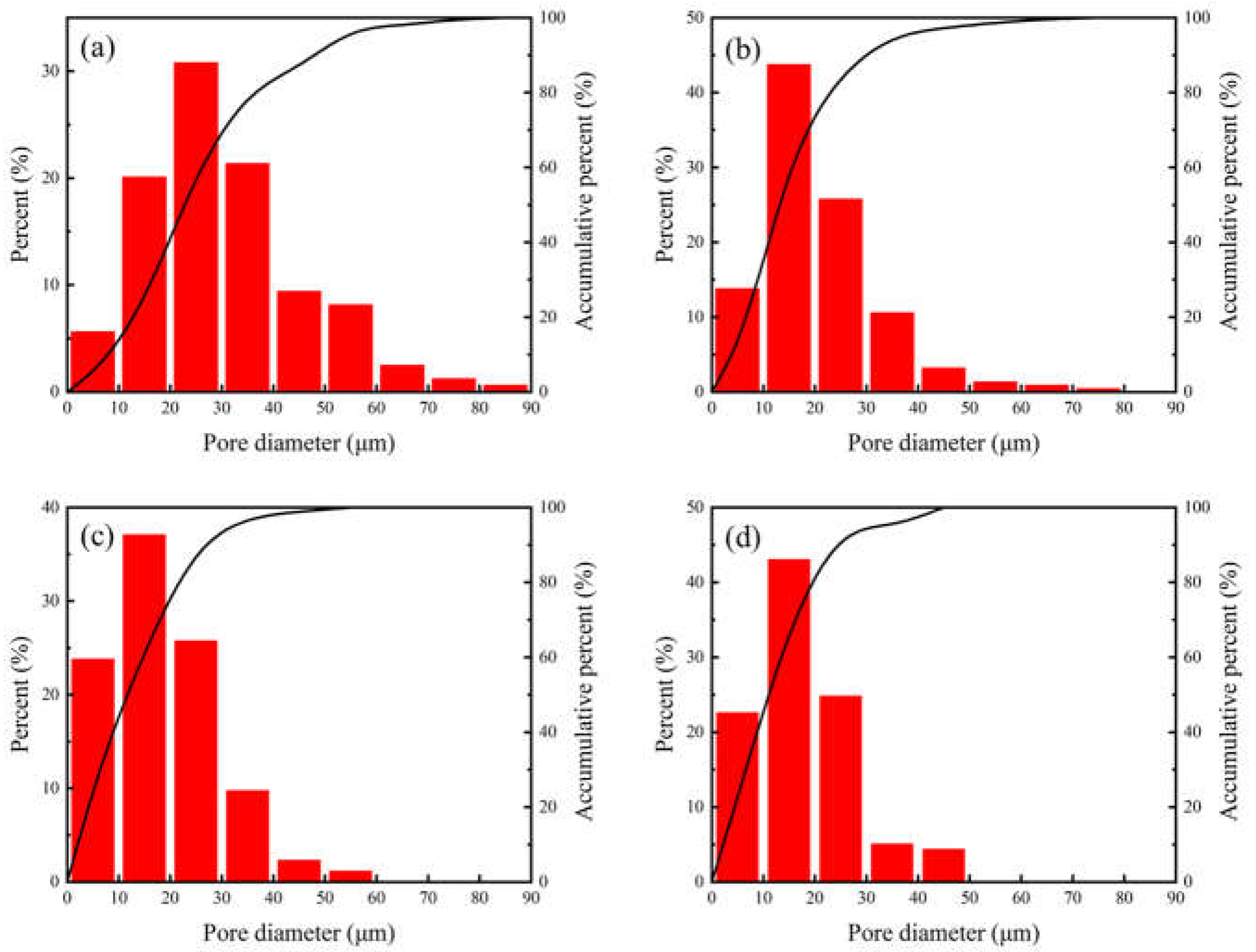
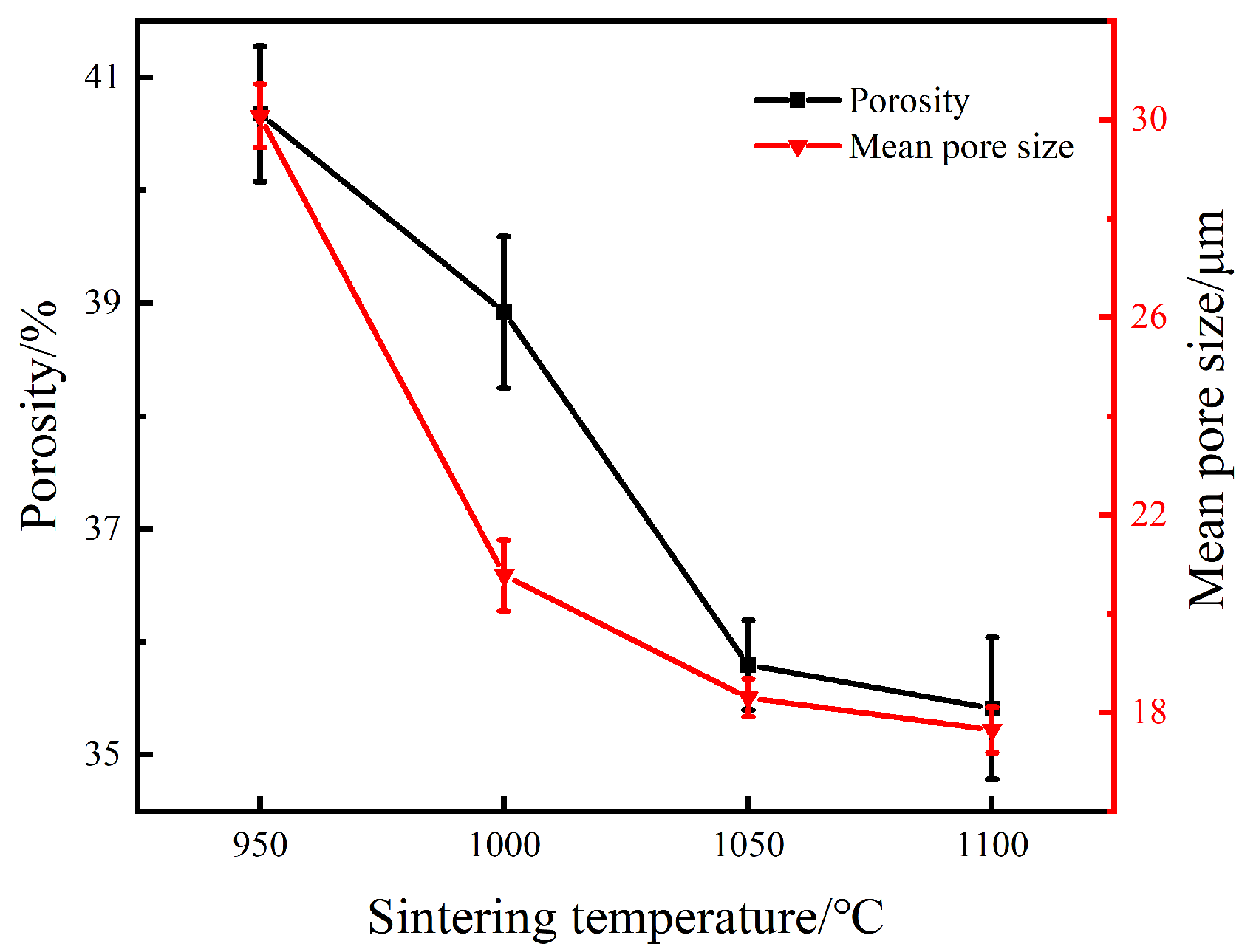
3.1. Pore Structure
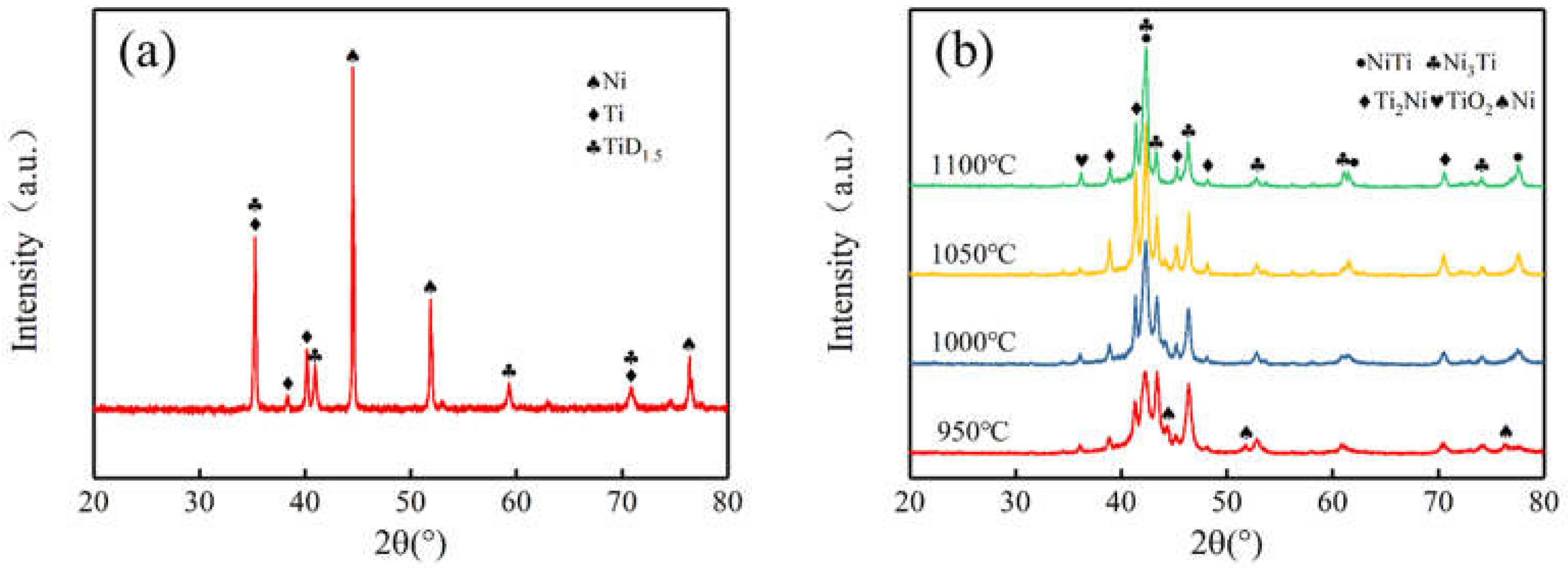
3.2. Phase Composition
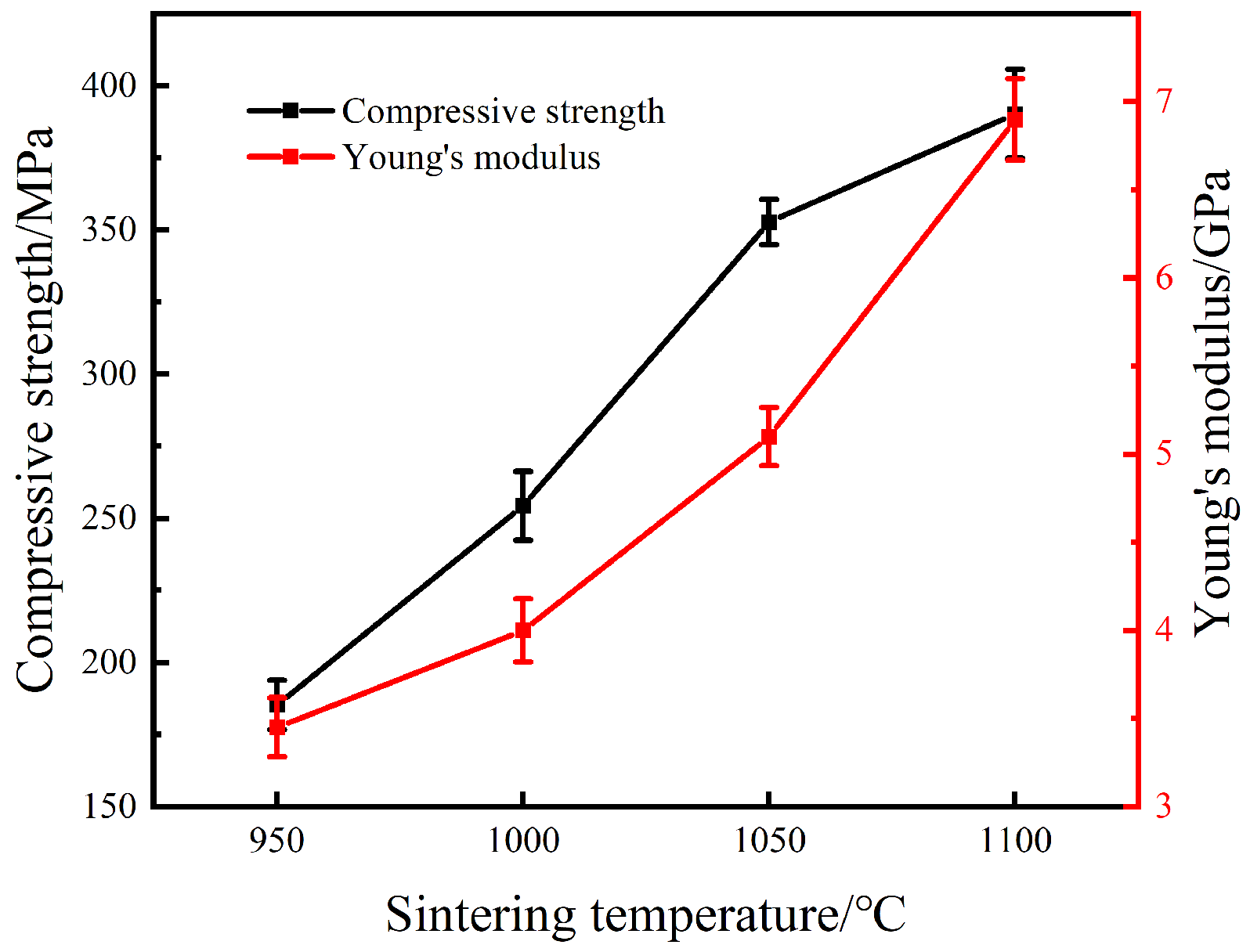
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Fracture
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- With increasing sintering temperature, the atoms diffused sufficiently and the morphology of pores became smooth and regular. Moreover, the porosity and the mean pore diameter of the specimen was correspondingly reduced.
- (2)
- With increasing sintering temperature, the compressive strength and elastic modulus of the sintered porous NiTi specimen gradually improved.
- (3)
- The sintered porous NiTi alloy was composed of the major NiTi phase with a few Ti2Ni and Ni3Ti second phases, and the relative intensity of the NiTi phase increased with the temperature. It presented a typical brittle fracture.
- (4)
- The pore structure and mechanical properties of samples can be tailored by controlling sintering temperature. A porous NiTi alloy with the porosity of 38.9%, the compressive strength of 254 MPa and the elastic modulus of 4 GPa was obtained at the sintering temperature of 1000 °C for 30 min, which could be in accord with the demand for bone replacement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bansiddhi, A.; Sargeant, T.D.; Stupp, S.I.; Dunand, D.C. Porous NiTi for bone implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Jangra, K.K.; Raj, T. Fabrication of NiTi alloy: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2018, 232, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalovskaya, S.A. Surface, corrosion and biocompatibility aspects of Nitinol as an implant material. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2002, 12, 69–109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Rao, G.B.; Rong, L.J.; Li, Y.Y. The influence of porosity on corrosion characteristics of porous NiTi alloy in simulated body fluid. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Zhang, Y.P.; Eggeler, G.; Zhang, X.P. High porosity and high-strength porous NiTi shape memory alloys with controllable pore characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 470, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Yuan, B.; Zeng, M.Q.; Chung, C.Y.; Zhang, X.P. High porosity and large pore size shape memory alloys fabricated by using pore-forming agent (NH4HCO3) and capsule-free hot isostatic pressing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 192, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, C.; Senthilkumar, V.; Kamala, P.S. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys sintered in the SPS process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2019, 26, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorev, O.V.; Khodorenko, V.N.; Baigonakova, G.A.; Marchenko, E.S.; Yasenchuk, Y.F.; Gunther, V.É.; Anikeev, S.G.; Barashkova, G.A. Metal-glass-ceramic phases on the surface of porous TiNi-based SHS-material for carriers of cells. Russ. Phys. J. 2019, 61, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, V.; Yasenchuk, Y.; Gunther, S.; Marchenko, E.; Yuzhakov, M. Biocompatibility of porous SHS-TiNi. Mater. Sci. Forum. Trans. Tech. Publ. Ltd. 2019, 970, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, A.; Aghajani, H. Fabrication of porous NiTi biomedical alloy by SHS method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghbaei, M.; Mirzaee, O. Microwave versus conventional sintering: A review of fundamentals, advantages and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 494, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, T.; Xu, J.L.; Xiao, Q.F.; Thong, Y.X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Luo, J.M.; Liu, Y. Preparation and characterization of porous NiTi alloys synthesized by microwave sintering using Mg space holder. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 2021, 31, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Wong, C.T. Fabrication and characteristics of porous NiTi shape memory alloy synthesized by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6006–6011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, M.V.; Shishkovsky, I.V.; Morozov, Y.G.; Parkin, I.P. Design of three-dimensional functional articles via layer-by-layer laser sintering of exothermic powder mixtures. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2008, 23, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Krishna, B.V.; Xue, W.; Bose, S. Application of laser engineered net shaping (LENS) to manufacture porous and functionally graded structures for load bearing implants. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andani, M.T.; Saedi, S.; Turabi, A.S.; Karamooz, M.R.; Haberland, C.; Karaca, H.E.; Elahinia, M. Mechanical and shape memory properties of porous Ni50. 1Ti49. 9 alloys manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 68, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Gan, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, C.; Shi, Y. Research status and prospect of additive manufactured nickel-titanium shape memory alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhl, M.; Habijan, T.; Bram, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stöver, D.; Köller, M. Powder metallurgical near-net-shape fabrication of porous NiTi shape memory alloys for use as long-term implants by the combination of the metal injection molding process with the space-Holder technique. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cao, P.; Wen, G.; Edmonds, N.; Li, Y. Using an agar-based binder to produce porous NiTi alloys by metal injection moulding. Intermetallics 2013, 37, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.H.; Hong, H.X.; Wang, D.Z.; Liu, H.J.; Dong, X.J.; Liang, D.D. Porous nickel–titanium alloy prepared by gel-casting. Rare Met. 2014, 33, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.H.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Yingrui, Z.; Chunge, X. Fabrication and properties of porous NiTi alloy by gel-casting with TiH2 powders. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 5118–5125. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Sui, Y.; Guo, Z. Ti6Al4V alloy fabricated by gelcasting based on low-oxygen gel system using hydride-dehydride titanium alloy powders. Powder Technol. 2022, 395, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omatete, O.O.; Janney, M.A.; Strehlow, R.A. Gelcasting: A new ceramic forming process. Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 1991, 70, 1641–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, N.; Qin, X. Fabrication of porous Al2O3 ceramics with submicron-sized pores using a water-based gelcasting method. Materials 2018, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.H.; Shen, T.; Wang, D.Z. Effects of solid loading on pore structure and properties of porous FeAl intermetallics by gel casting. Powder Technol. 2019, 3, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Bao, L.Z.; Liu, A.H.; Jin, X.F.; Luo, J.M.; Zhong, Z.C.; Zheng, Y.F. Effect of pore sizes on the microstructure and properties of the biomedical porous NiTi alloys prepared by microwave sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 645, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Khosrovabadi, P.B.; Lindenhovius, J.H.; Kolster, B.H. TiNi shape memory alloys prepared by normal sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 150, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.Q.; Li, W.J.; Ma, L.L.; Yang, R.H.; Gong, D.Q. Pore characteristics and mechanical behavior of spark plasma sintered porous Zn-Mg alloy for biomedical applications. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2020, 49, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.L.; Yang, X.J.; Fu, D.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Cui, Z.D. Stress–strain behavior of porous NiTi alloys prepared by powders sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 408, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bram, M.; Bitzer, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stover, D. Reproducibility study of NiTi parts made by metal injection molding. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2701–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.H.; Xie, C.G.; Wang, D.Z.; Wan, X. Effect of sintering temperature on properties of porous Ni-Ti alloy prepared by Gel-Casting. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017, 46, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.F.; Li, Q.Y.; He, F.; Huang, Y.; Wan, Y. Mechanical modulation and bioactive surface modification of porous Ti-10Mo alloy for bone implants. Mater. Design. 2012, 42, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Bao, L.Z.; Liu, A.H.; Jin, X.J.; Tong, Y.X.; Luo, J.M.; Zhong, Z.C.; Zheng, Y.F. Microstructure, mechanical properties and superelasticity of biomedical porous NiTi alloy prepared by microwave sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzino, J.D. The Biomedical Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.Y.; Li, Q. Study on effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and compressive property of porous NiTi alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 299, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cao, P.; Edmonds, N. Porous NiTi alloys produced by press-andsinter from Ni/Ti and Ni/TiH2 mixtures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 582, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Duan, B. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy Prepared by Integration of Gel-Casting and Microwave Sintering. Materials 2022, 15, 7331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207331
He Z, Wang Z, Wang D, Liu X, Duan B. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy Prepared by Integration of Gel-Casting and Microwave Sintering. Materials. 2022; 15(20):7331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207331
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zhiqiang, Ze Wang, Dezhi Wang, Xinli Liu, and Bohua Duan. 2022. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy Prepared by Integration of Gel-Casting and Microwave Sintering" Materials 15, no. 20: 7331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207331
APA StyleHe, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Liu, X., & Duan, B. (2022). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Porous NiTi Alloy Prepared by Integration of Gel-Casting and Microwave Sintering. Materials, 15(20), 7331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15207331





