Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of BN-CNOs
2.3. Synthesis of HA-DMPE
2.4. Non-Covalent Functionalisation of BN-CNOs with HA-DMPE
2.5. UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3. Results
3.1. UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
3.2. Dynamic Light Scattering and Zeta Potential
3.3. Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4. UV-Vis Absorption and DLS of BN-CNO/HA-DMPE Washed Sample
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ugarte, D. Curling and Closure of Graphitic Networks under Electron-Beam Irradiation. Nature 1992, 359, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowska, D.M.; Czyrko, J.; Brzezinski, K.; Echegoyen, L.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Carbon Nano-Onion Composites: Physicochemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2017, 25, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, M.; Giordani, S. Supramolecular Chemistry of Carbon Nano-Onions. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9352–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugarte, D. Onion-Like Graphitic Particles. In Carbon Nanotubes; Endo, M., Iijima, S., Dresselhaus, M.S., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordkovich, V.Z.; Takeuchi, Y. Multishell Fullerenes by Laser Vaporization of Composite Carbon–Metal Targets. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 355, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhailiv, O.; Lapinski, A.; Molina-Ontoria, A.; Regulska, E.; Echegoyen, L.; Dubis, A.T.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E. Influence of the Synthetic Conditions on the Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Carbon Nano-Onions. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrzejewski, M.; Rummeli, M.H.; Gemming, T.; Lange, H.; Huczko, A. Catalyst-Free Synthesis of Onion-like Carbon Nanoparticles. New Carbon Mater. 2010, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohouli, E.; Shahdost-Fard, F.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Ahmadi, F. Introducing a Novel Nanocomposite Consisting of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions and Gold Nanoparticles for the Electrochemical Sensor to Measure Acetaminophen. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 871, 114309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goclon, J. Manipulation of Structural and Electronic Properties of B-Doped Carbon Nano–Onions Based on DFT Modelling. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 532, 147267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, L.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, H.; Ran, S.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; et al. Nitrogen-Rich Soybean Protein Isolate Derived “Self-Doping” Carbon Nano-Onions for Luminescence Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 595, 153492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohouli, E.; Ghalkhani, M.; Zargar, T.; Joseph, Y.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Ahmadi, F.; Plonska-Brzezinska, M.E.; Ehrlich, H. A New Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Gold/Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for the Detection of Staphylococcus Aureus. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 403, 139633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohouli, E.; Adib, K.; Maddah, B.; Najafi, M. Manganese Dioxide/Cobalt Tungstate/ Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions Nanocomposite as New Supercapacitor Electrode. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amora, M.; Camisasca, A.; Arenal, R.; Giordani, S. In Vitro and In Vivo Biocompatibility of Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camisasca, A.; Sacco, A.; Brescia, R.; Giordani, S. Boron/Nitrogen Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onion Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5763–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’ Amora, M.; Rodio, M.; Bartelmess, J.; Sancataldo, G.; Brescia, R.; Cella Zanacchi, F.; Diaspro, A.; Giordani, S. Biocompatibility and Biodistribution of Functionalized Carbon Nano-Onions (f-CNOs) in a Vertebrate Model. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, H.; Bartkowski, M.; Giordani, S. Biocompatible Dispersants for Carbon Nanomaterials. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuaznabar-Gardona, J.C.; Fragoso, A. Determination of the Hansen Solubility Parameters of Carbon Nano-Onions and Prediction of Their Dispersibility in Organic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelmess, J.; Giordani, S. Carbon Nano-Onions (Multi-Layer Fullerenes): Chemistry and Applications. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 1980–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, J.P.; Fragoso, A. Preparation of Stable Aqueous Dispersions of Carbon Nano-Onions via Supramolecular Crown Ether-Ammonium Interactions with Aminated Biocompatible Polymers. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, M.S.; Poon, R.; Syed, A.M.; Milne, J.; Zhitomirsky, I. New Developments in Non-Covalent Surface Modification, Dispersion and Electrophoretic Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2018, 130, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Biopharmaceutical Delivery and Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery System. J. Control. Release 2018, 278, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passi, A.; Vigetti, D. Hyaluronan as Tunable Drug Delivery System. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 146, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpicco, S.; Bartkowski, M.; Barge, A.; Zonari, D.; Serpe, L.; Milla, P.; Dosio, F.; Stella, B.; Giordani, S. Effects of the Molecular Weight of Hyaluronic Acid in a Carbon Nanotube Drug Delivery Conjugate. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 578008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, E.; Greco, A.; Riva, F.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Genta, I. CD44-Targeted Carriers: The Role of Molecular Weight of Hyaluronic Acid in the Uptake of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopf-Marques, H.; Pravda, M.; Wolfova, L.; Velebny, V.; Schaaf, P.; Vrana, N.E.; Lavalle, P. Hyaluronic Acid and Its Derivatives in Coating and Delivery Systems: Applications in Tissue Engineering, Regenerative Medicine and Immunomodulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 2841–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Amora, M.; Camisasca, A.; Boarino, A.; Arpicco, S.; Giordani, S. Supramolecular Functionalization of Carbon Nano-Onions with Hyaluronic Acid-Phospholipid Conjugates for Selective Targeting of Cancer Cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujigaya, T.; Nakashima, N. Non-Covalent Polymer Wrapping of Carbon Nanotubes and the Role of Wrapped Polymers as Functional Dispersants. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 024802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, S.; Asok, A.K.; Mundayoor, S.; Jisha, M.S. Surfactants: Chemistry, Toxicity and Remediation. In Pollutant Diseases, Remediation and Recycling; Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World; Lichtfouse, E., Schwarzbauer, J., Robert, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 277–320. ISBN 978-3-319-02387-8. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, L.; Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Engineered Nanoparticles Interacting with Cells: Size Matters. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Sonkar, S.K.; Saxena, M.; Sarkar, S. Carbon Nano-Onions for Imaging the Life Cycle of Drosophila Melanogaster. Small 2011, 7, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


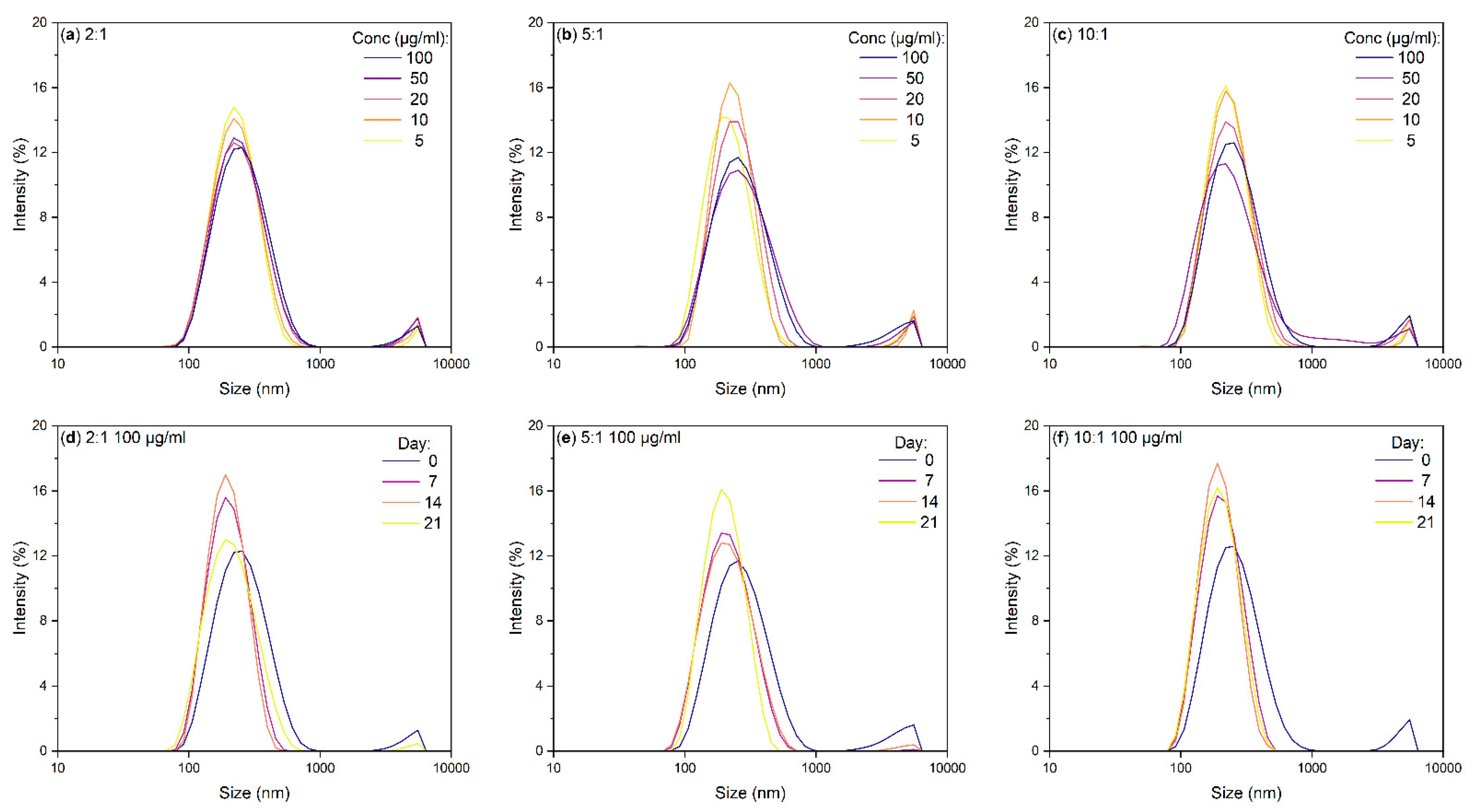


| Day | 2:1 (µg/mL) | 5:1 (µg/mL) | 10:1 (µg/mL) | 2:1 (µg/mL) | 5:1 (µg/mL) | 10:1 (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| 1 | 99 | 97 | 99 | 49 | 46 | 48 |
| 7 | 81 | 73 | 79 | 42 | 43 | 43 |
| 21 | 74 | 60 | 70 | 40 | 36 | 38 |
| 98 | 65 | 54 | 67 | 37 | 35 | 36 |
| 130 | 61 | 47 | 66 | 34 | 35 | 33 |
| 155 | 55 | 42 | 58 | 31 | 31 | 29 |
| 183 | 47 | 38 | 49 | 28 | 26 | 26 |
| (µg/mL) | 2:1 (nm) | 5:1 (nm) | 10:1 (nm) | 2:1 ZP (mV) | 5:1 ZP (mV) | 10:1 ZP (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 270 | 286 | 268 | −28.2 ± 4.6 | −32.4 ± 4.7 | −30.1 ± 4.8 |
| 50 | 260 | 296 | 250 | - | - | - |
| 20 | 256 | 258 | 250 | - | - | - |
| 10 | 248 | 241 | 231 | - | - | - |
| 5 | 237 | 226 | 234 | - | - | - |
| Day | 2:1 (nm) | 5:1 (nm) | 10:1 (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 270 | 286 | 268 |
| 7 | 210 | 227 | 214 |
| 14 | 204 | 209 | 203 |
| 21 | 225 | 229 | 206 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohan, H.; Bincoletto, V.; Arpicco, S.; Giordani, S. Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems. Materials 2022, 15, 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15175987
Mohan H, Bincoletto V, Arpicco S, Giordani S. Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems. Materials. 2022; 15(17):5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15175987
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohan, Hugh, Valeria Bincoletto, Silvia Arpicco, and Silvia Giordani. 2022. "Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems" Materials 15, no. 17: 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15175987
APA StyleMohan, H., Bincoletto, V., Arpicco, S., & Giordani, S. (2022). Supramolecular Functionalisation of B/N Co-Doped Carbon Nano-Onions for Novel Nanocarrier Systems. Materials, 15(17), 5987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15175987








