Development of Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Starting Powder
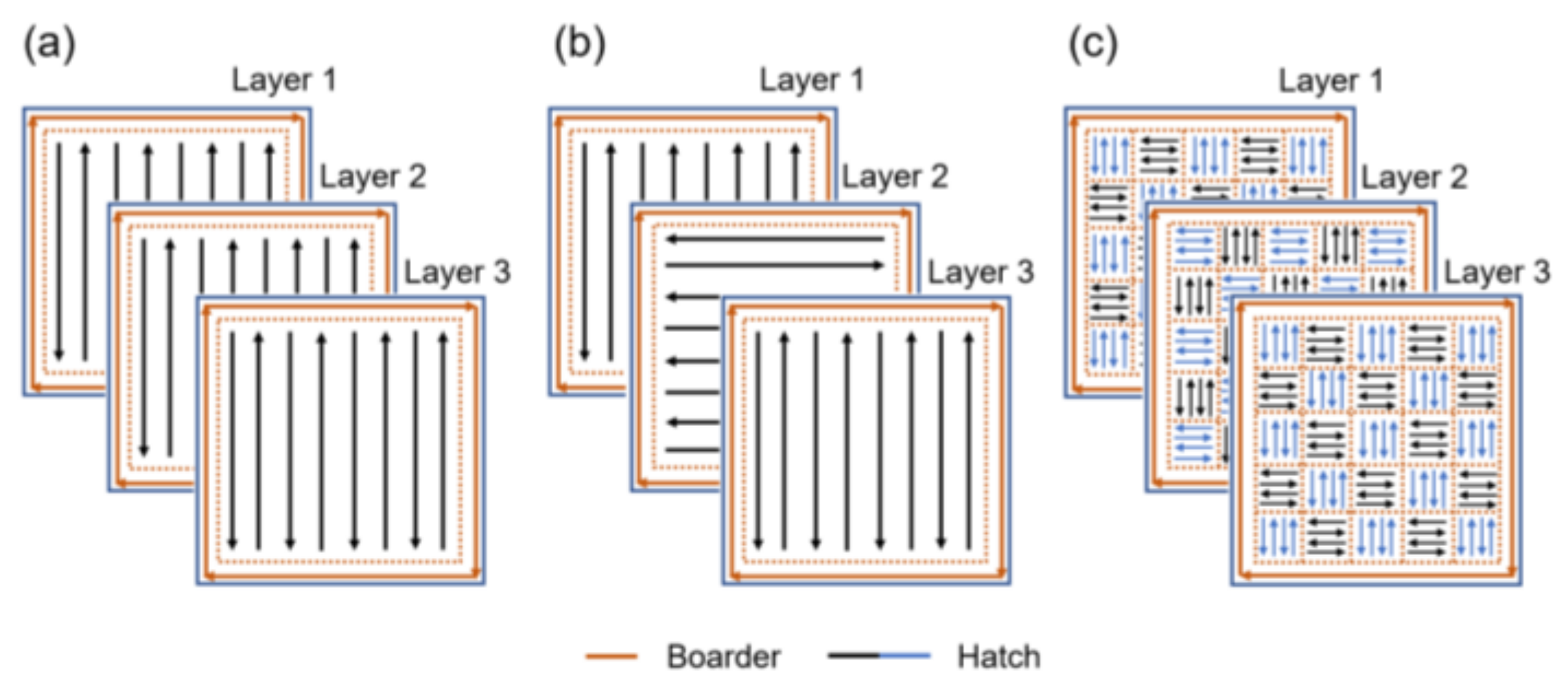
2.2. LPBF Process Set Up for Microfabrication
2.3. Attaining Process Parameters
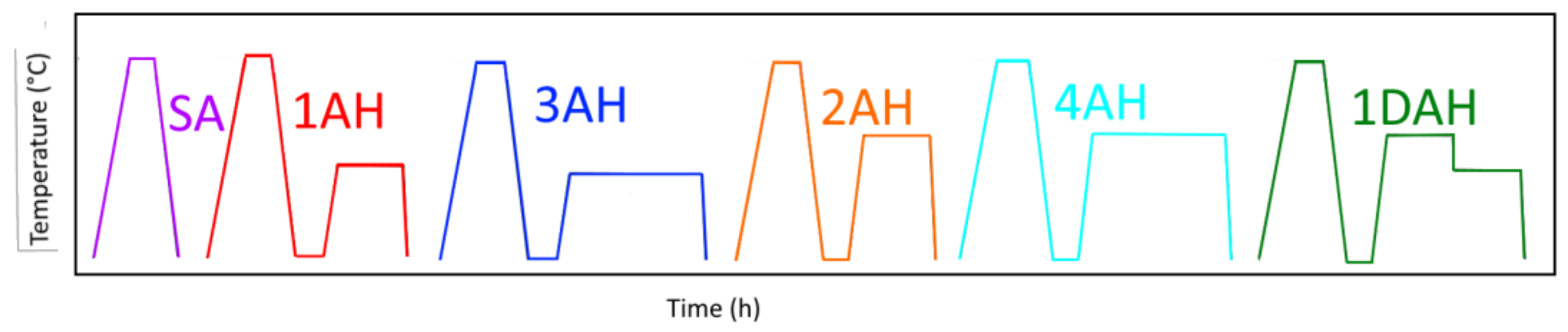
2.4. Heat Treatment Cycles
2.5. Characterization of LPBF Products
2.5.1. Density Measurement
2.5.2. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.5.3. Microstructural Analysis
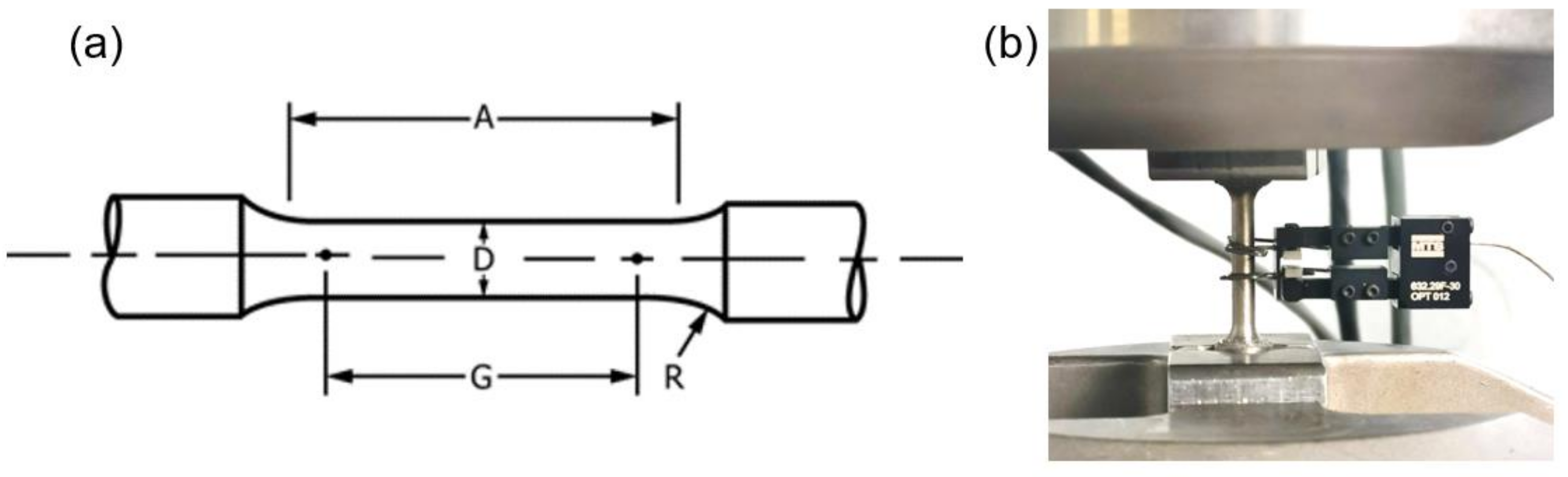
2.5.4. Mechanical Tests
3. Results and Discussion
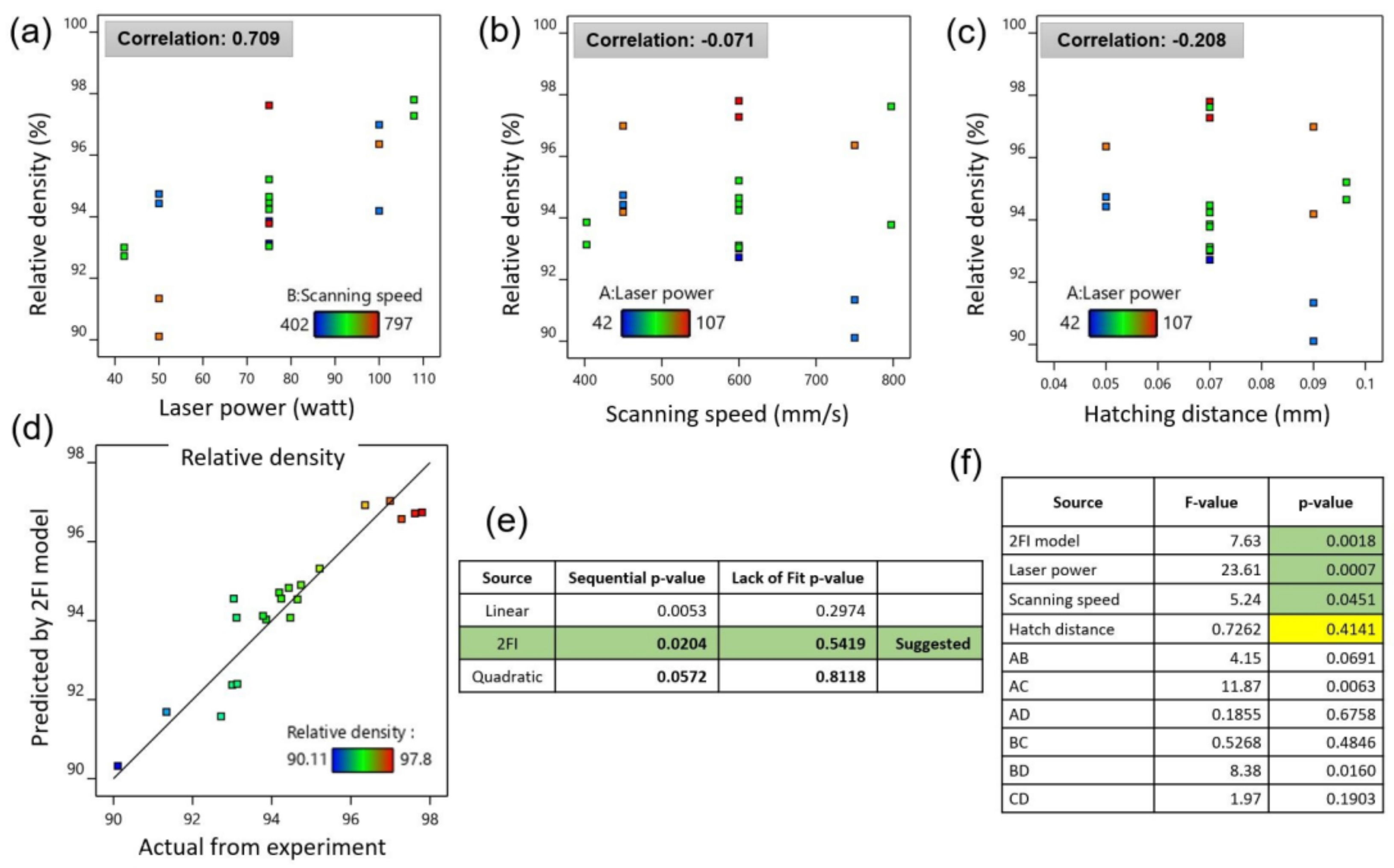
3.1. Optimization of LPBF Process Parameters for Inc718
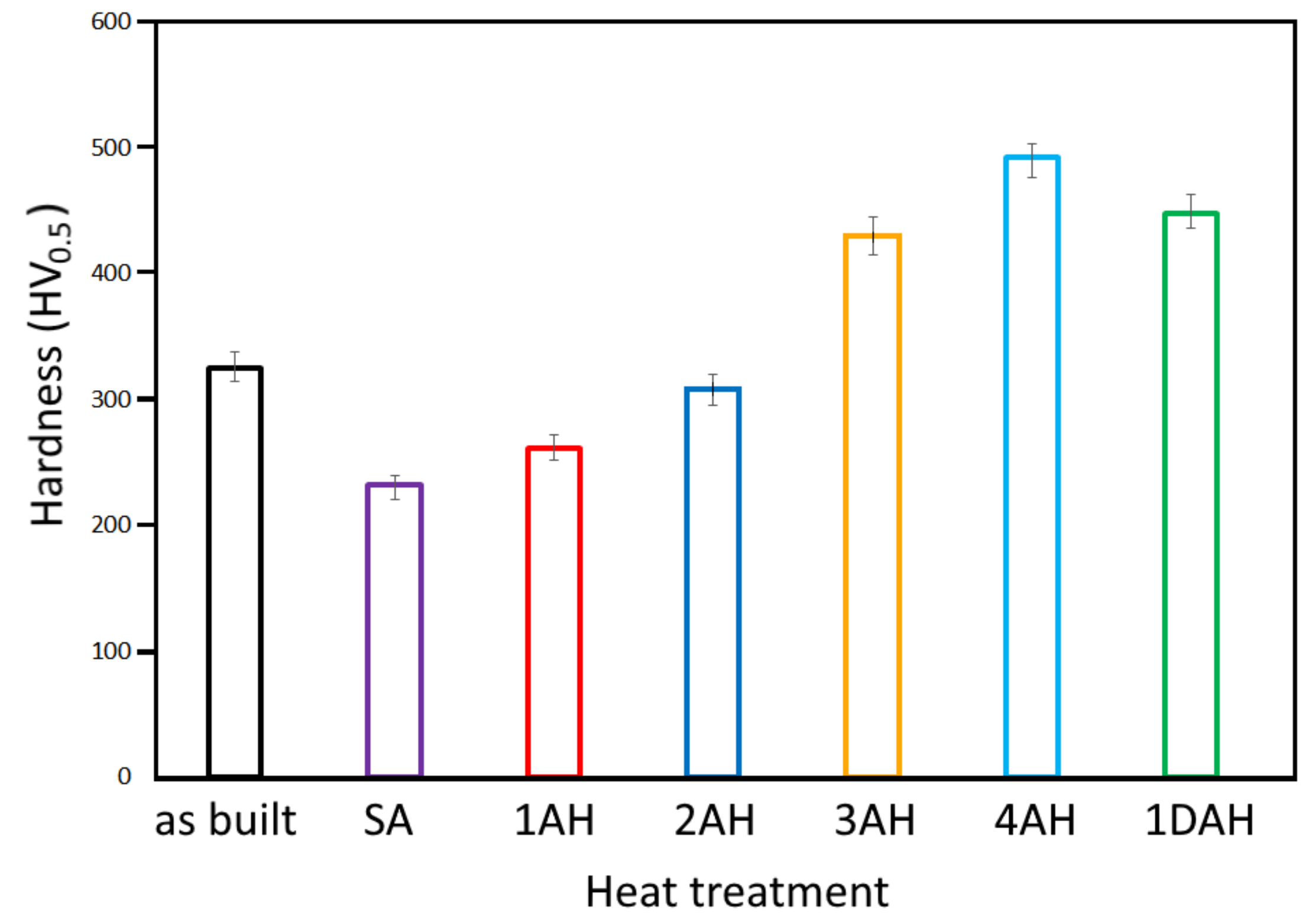
3.2. Microhardness
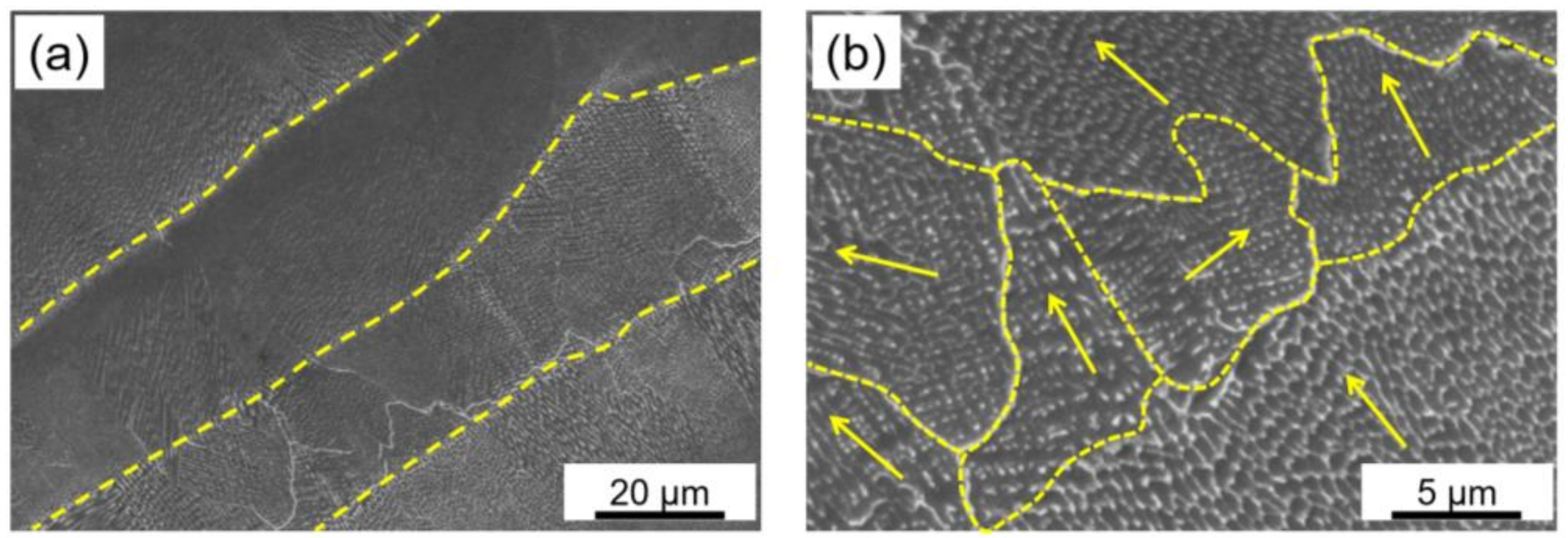
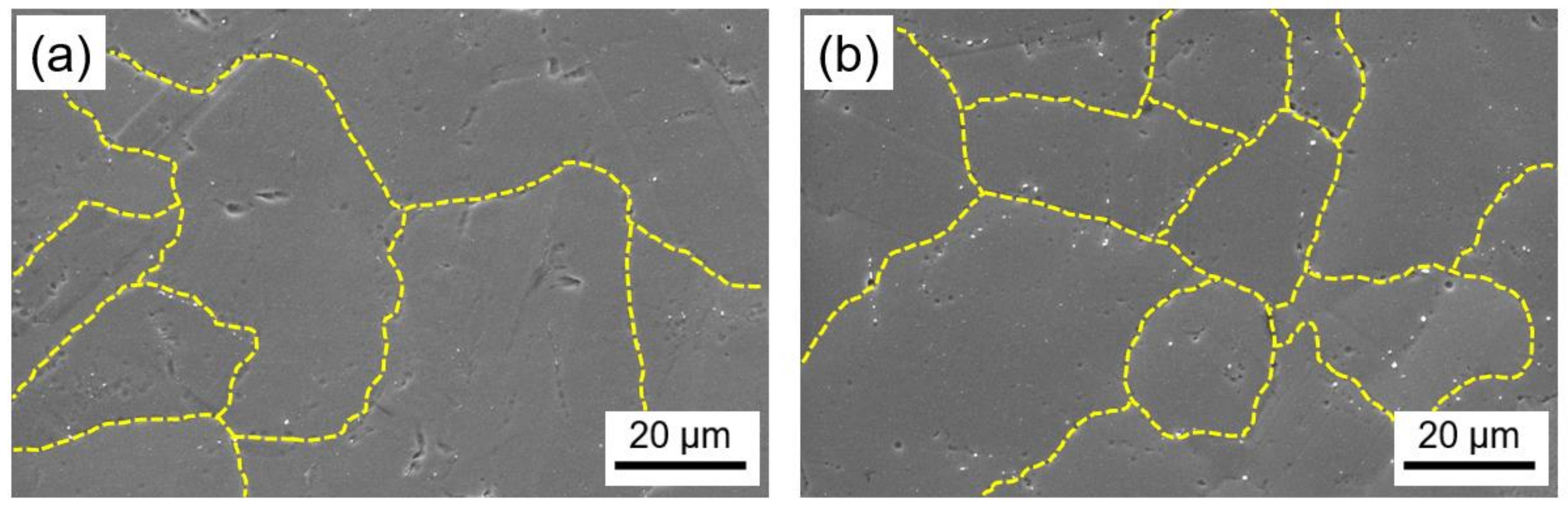
3.3. Microstructure
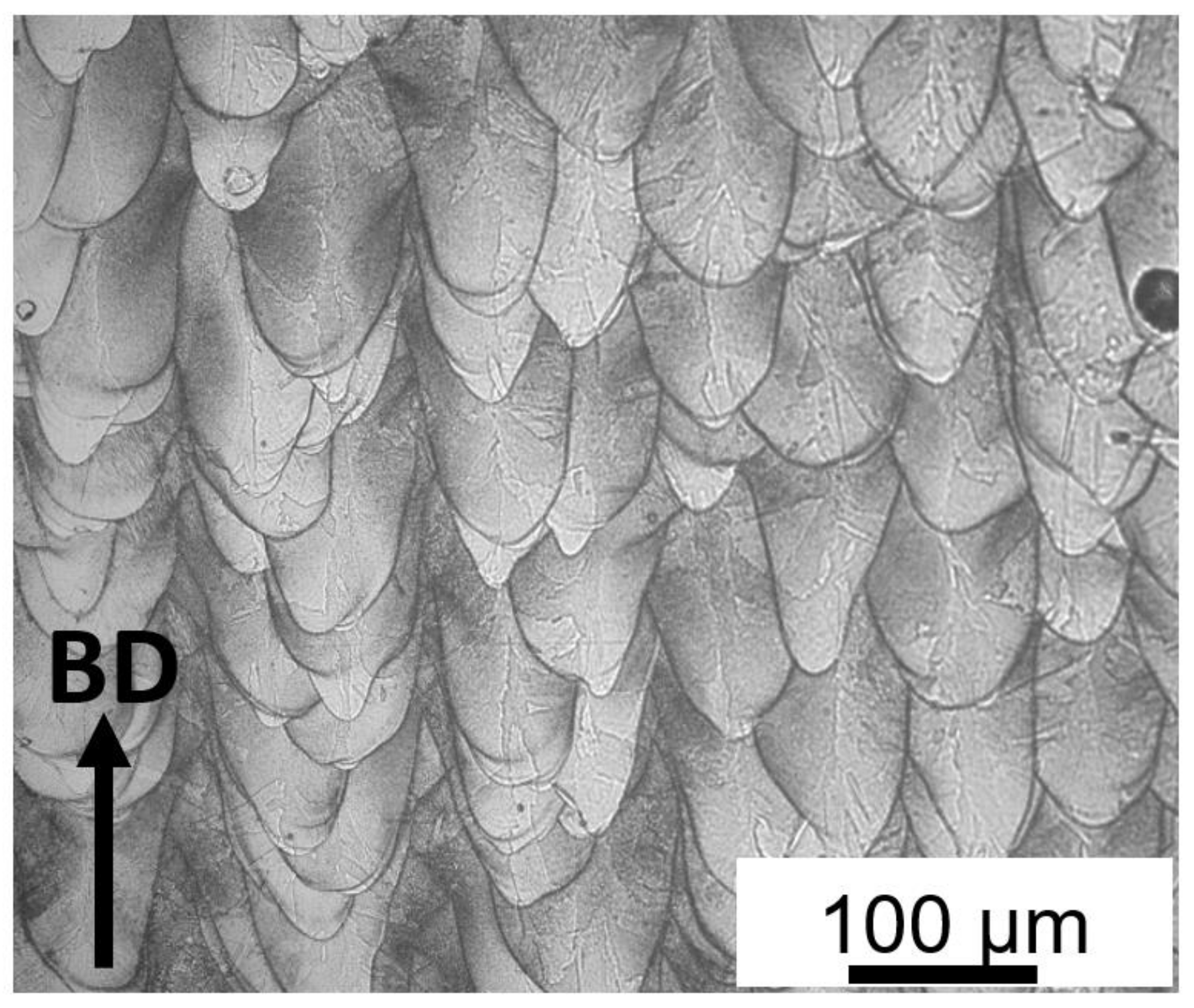
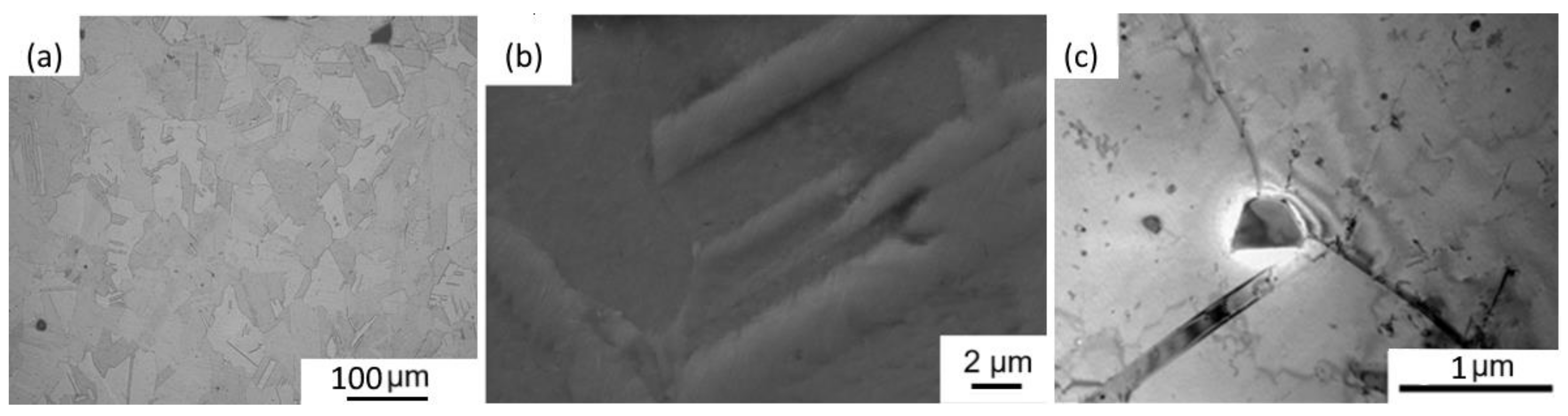
3.3.1. Micro-LPBF As-Built Inc718
3.3.2. Solution Annealing of Inc718 Produced by LPBF
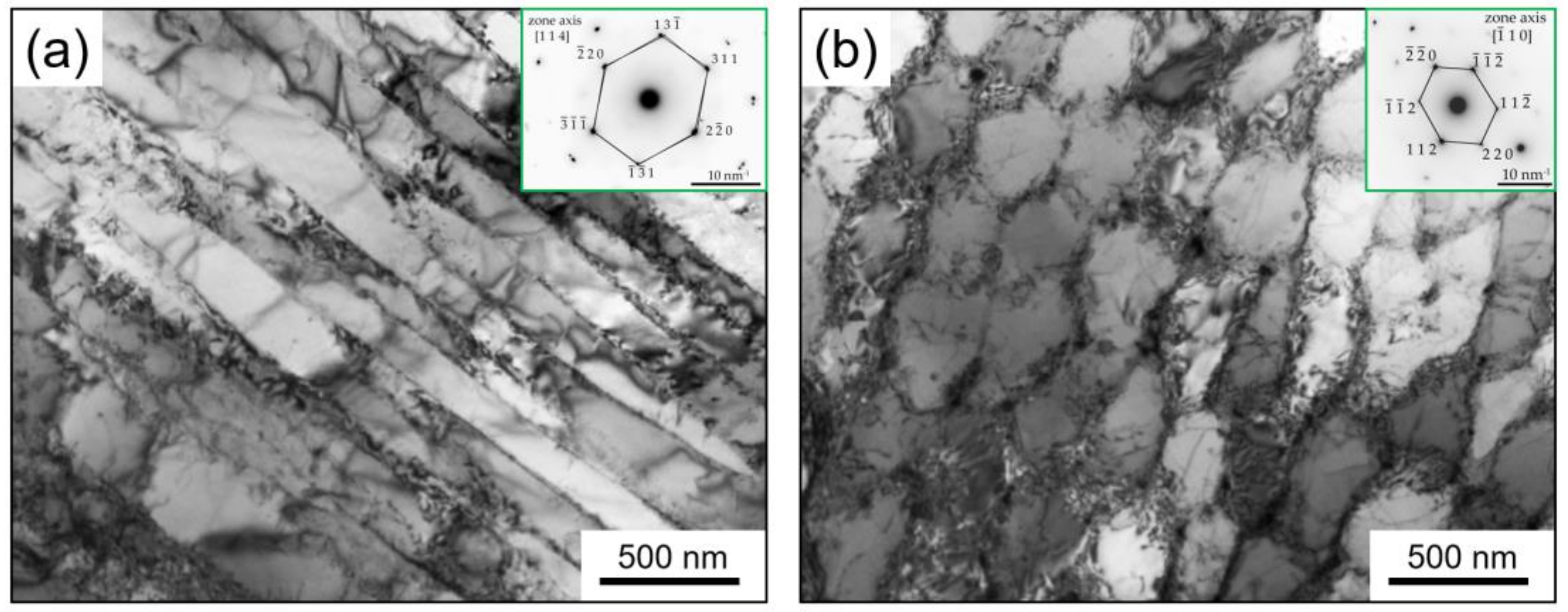
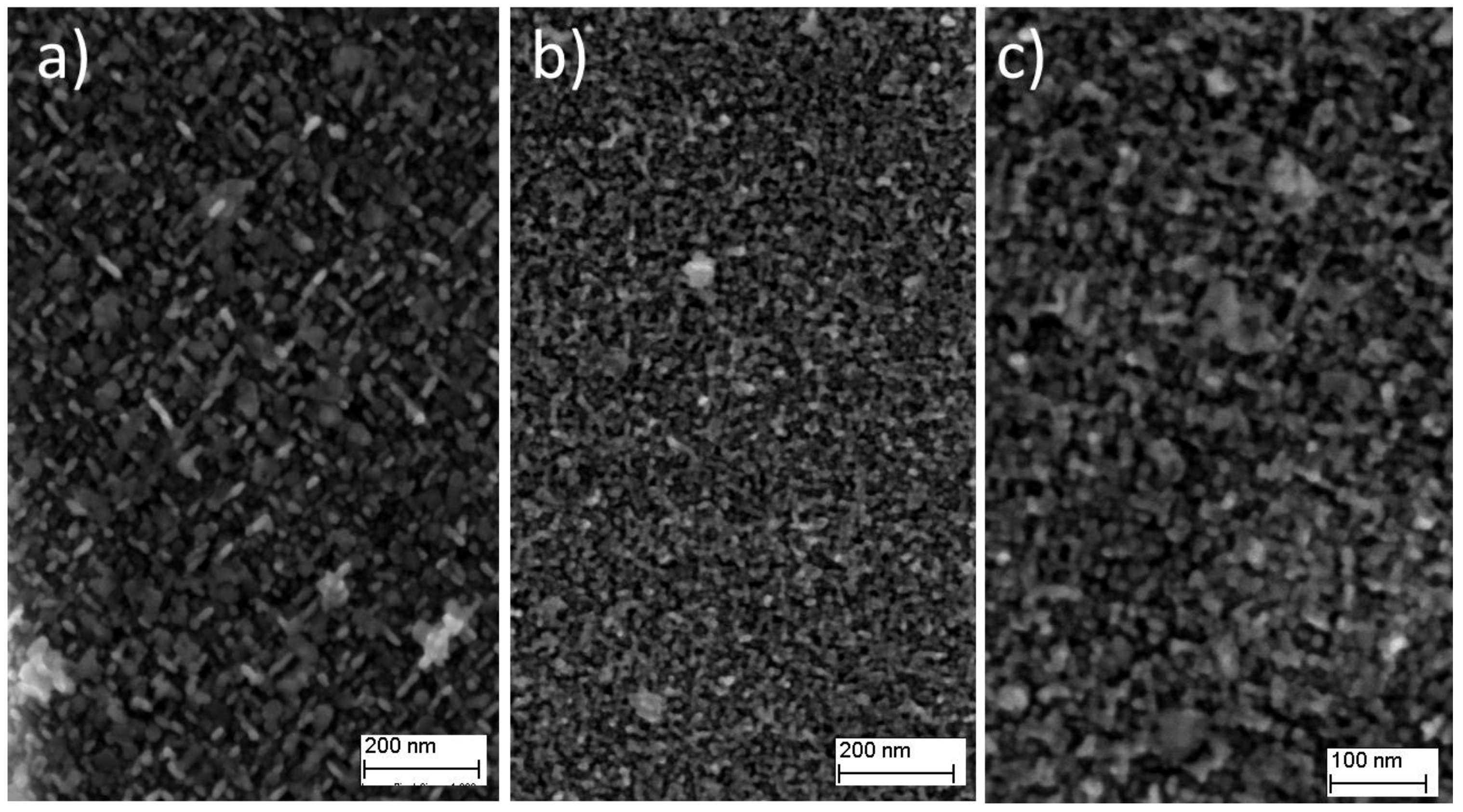
3.3.3. Ageing Hardening of Inc718 Produced by LPBF
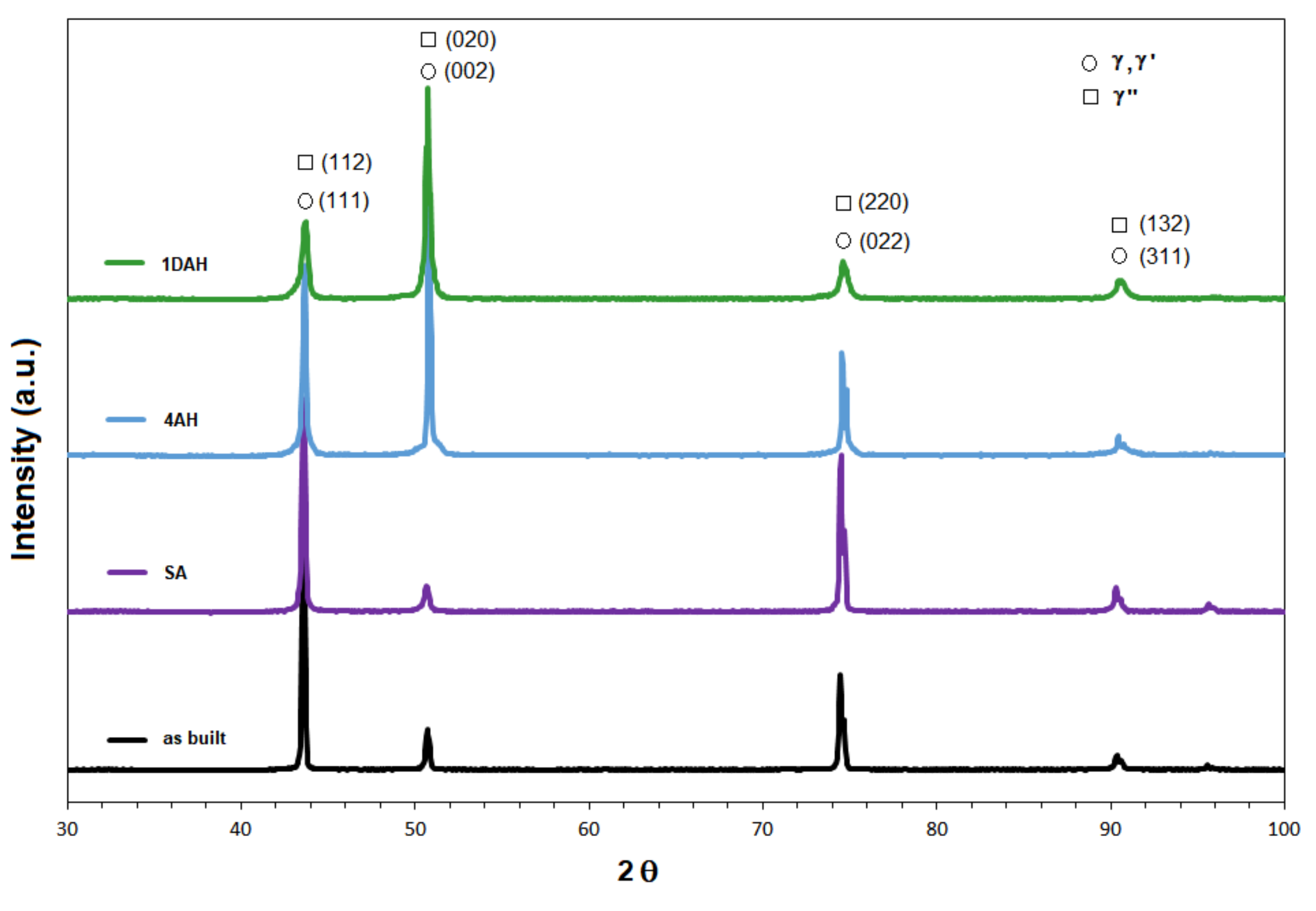
3.4. X-Ray Diffraction
3.5. Mechanical Tests
3.5.1. Uniaxial Tensile Test
3.5.2. Fractography
4. Conclusions
- The outputs of DOE were used to plot process maps. Maximum relative density (99.9%) and relatively minimum surface roughness (<10 µm) were obtained using 95 W of laser powder, 750 mm/s of scanning speed, and hatch distance of 0.08 mm;
- The as-built microstructure features distinctive columnar and equiaxed cellular substructures with an average size of 200 nm which is finer than reported values in the literature. This was attributed to the small melt pool induced by the micro-LPBF process and the consequently high recrystallization rate which led to fine microstructure;
- Precipitation of very fine spherical γ′ phase and long disc-shaped γ″ phase was detected in Inc718 samples subjected to solution annealing and subsequent age hardening. The FESEM and TEM analysis revealed that double age hardening resulted in smaller precipitates (<10 nm) compared with a single-step age hardening;
- Age hardening heat treatment significantly increased the yield stress (28% after single age hardening) and ultimate tensile strength (39% after single age hardening) due to the formation and even distribution of the strengthening γ′ and γ″ phases;
- Single age hardening (720 °C for 8 h) induced the precipitation of a higher amount of γ′ precipitates and higher values of mechanical strength than double age hardening (720 °C and 620 °C for 4 h).
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akca, E.; Gürsel, A. A Review on Superalloys and IN718 Nickel-Based INCONEL Superalloy. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Popovich, V.A. A review of mechanical properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, Z. Creep property of Inconel 718 superalloy produced by selective laser melting compared to forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 794, 139947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kumar, R.; Anurag; Panda, A.; Das, R.K. A brief review on machining of inconel 718. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 18664–18673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, J.; Partanen, J.; Tuomi, J.; Walter, M. Rapid manufacturing in the spare parts supply chain: Alternative approaches to capacity deployment. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2010, 21, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, C.; Wang, P.; Meng, W.; Li, C. The Mechanism of In-Situ Laser Polishing and Its Effect on the Surface Quality of Nickel-Based Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2022, 12, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Chou, K. Review on powder-bed laser additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 parts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 231, 1890–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriondo, A.; Esperon-Miguez, M.; Perinpanayagam, S. The present and future of additive manufacturing in the aerospace sector: A review of important aspects. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2015, 229, 2132–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Smurov, I. Selective laser melting technology: From the single laser melted track stability to 3D parts of complex shape. Phys. Procedia 2010, 5, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, C.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Dong, Z.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, D.Q.; Loh, L.E.; Sing, S.L. Review of selective laser melting: Materials and applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2015, 2, 041101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Gu, D. Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 superalloy parts: Densification, microstructure and properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 585, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebus, E.; Gruber, K.; Kuźnicka, B.; Kurzac, J.; Kurzynowski, T. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 processed by selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Jing, G.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, X. Heat treatment of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 750, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, J.; Sun, S.; Feng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, M. Microstructural evolution and phase transformation of Inconel 718 alloys fabricated by selective laser melting under different heat treatment. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 39, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guan, K.; Gao, M.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X. The microstructure and mechanical properties of deposited-IN718 by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 513, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, B.; Hu, Z.; Song, X.; Zhai, W.; Wei, J. Development of Micro Selective Laser Melting: The State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Engineering 2019, 5, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Brockett, A.; Ma, Y.; Razali, A.; Zhao, J.; Harrison, C.; Pan, W.; Dai, X.; Loziak, D. Micro-manufacturing: Research, technology outcomes and development issues. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 47, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khademzadeh, S. Precision Additive Manufacturing of NiTi shape memory parts using Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 7, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, J. Design of Experiments for Engineers and Scientists; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.A.; Kumar, M.; Srinivas, M.; Sarma, D.S. Effect of standard heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of hot isostatically pressed superalloy inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 355, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, W. Study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser rapid forming Inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Khademzadeh, S.; Carmignato, S.; Parvin, N.; Zanini, F.; Bariani, P.F. Micro porosity analysis in additive manufactured NiTi parts using micro computed tomography and electron microscopy. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucho, W.M.; Cuvillier, P.; Sjolyst-Kverneland, A.; Hansen, V. Microstructure and hardness studies of Inconel 718 manufactured by selective laser melting before and after solution heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 689, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, C.H.; Cao, G.H.; Russell, A.M.; Zhou, Z.J.; Li, C.P.; Chen, G.F. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure evolution of Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Sun, Q.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, X. Understanding the effect of scanning strategies on the microstructure and crystallographic texture of Ti-6Al-4V alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 299, 117366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.P.; Shin, G.H.; Yang, S.; Yang, D.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Brochu, M.; Yu, J.H. Densification and microstructural investigation of Inconel 718 parts fabricated by selective laser melting. Powder Technol. 2017, 310, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Niu, W.; Cao, X.; Liu, Z. Effect of standard heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting manufactured Inconel 718 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 644, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Pande, C.S.; Imam, M.A.; Rath, B.B. Formation of annealing twins in f.c.c. crystals. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.S.B.; Yin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liang, J.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. De Effects of the γ’’-Ni3Nb phase on mechanical properties of Inconel 718 superalloys with different heat treatments. Materials 2020, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, D.; Cui, G. Enhancing mechanical properties of the spark plasma sintered inconel 718 alloy by controlling the nano-scale precipitations. Materials 2019, 12, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, D.; Peng, R.L.; Brodin, H.; Moverare, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 produced by selective laser melting: Sample orientation dependence and effects of post heat treatments. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 713, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, V.A.; Borisov, E.V.; Popovich, A.A.; Sufiiarov, V.S.; Masaylo, D.V.; Alzina, L. Impact of heat treatment on mechanical behaviour of Inconel 718 processed with tailored microstructure by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruth, J.-P.; Deckers, J.; Yasa, E.; Wauthlé, R. Assessing and comparing influencing factors of residual stresses in selective laser melting using a novel analysis method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2012, 226, 980–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
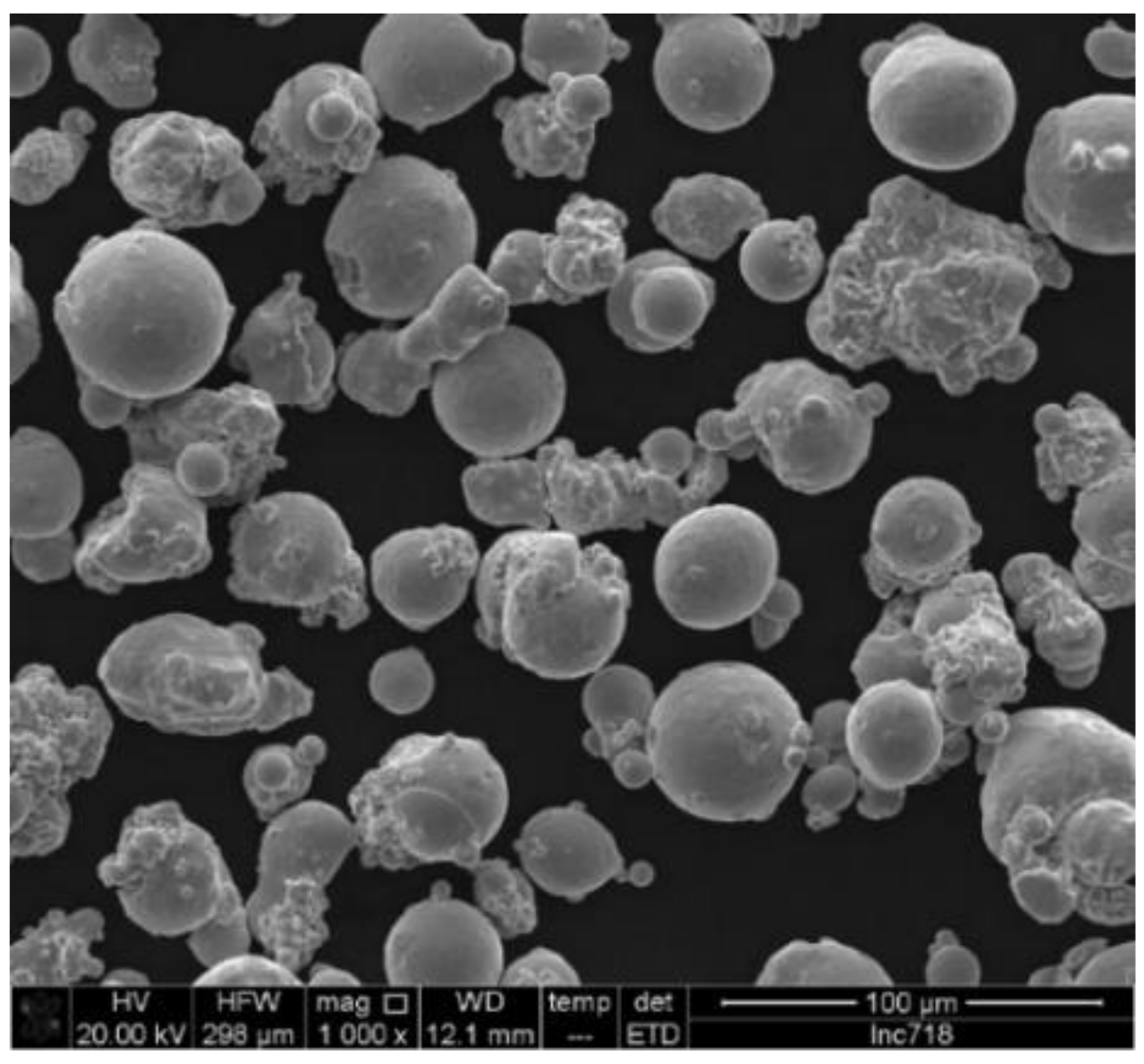






| El | Ni | Cr | Fe | Nb | Mo | Ti | Al | Co | Si | Mn | Cu | C | P | N | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | 53.70 | 17.93 | 18.17 | 5.20 | 2.96 | 0.95 | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.009 | 0.004 | 0.0025 |
| Parameter | Numeric Factors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | −α | Low | Central | High | +α | |
| Laser Power | W | 42 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 108 |
| Scanning speed | mm/s | 400 | 450 | 600 | 750 | 800 |
| Hatch distance | mm | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| Categorical factor | ||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | |||||
| Scanning strategy | Bidirectional | Alternating Bidirectional | ||||
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wrought Inc718 [20] | SA: 980 °C (1 h), AC | DAH: 720 °C (8 h), FC at 55 °C/h to 620 °C (8 h), AC | |
| Casting Inc718 [21] | H: 1080 °C (1.5 h), AC | SA: 980 °C (1 h), AC | DAH: 720 °C (8 h), FC at 55 °C/h to 620 °C (8 h), AC |
| Solution Annealing | Cooling 1 | Ageing 1 | Ageing 2 | Cooling 2 | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | -- | -- | -- | SA |
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | 620 °C, 4 h | -- | WQ | 1AH |
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | 620 °C, 8 h | -- | WQ | 2AH |
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | 720 °C, 4 h | -- | WQ | 3AH |
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | 720 °C, 8 h | -- | WQ | 4AH |
| 1080 °C, 1.5 h | AC | 720 °C, 4 h | 620 °C, 4 h | WQ | 1DAH |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khademzadeh, S.; Gennari, C.; Zanovello, A.; Franceschi, M.; Campagnolo, A.; Brunelli, K. Development of Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718. Materials 2022, 15, 5231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155231
Khademzadeh S, Gennari C, Zanovello A, Franceschi M, Campagnolo A, Brunelli K. Development of Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718. Materials. 2022; 15(15):5231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155231
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhademzadeh, Saeed, Claudio Gennari, Andrea Zanovello, Mattia Franceschi, Alberto Campagnolo, and Katya Brunelli. 2022. "Development of Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718" Materials 15, no. 15: 5231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155231
APA StyleKhademzadeh, S., Gennari, C., Zanovello, A., Franceschi, M., Campagnolo, A., & Brunelli, K. (2022). Development of Micro Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718. Materials, 15(15), 5231. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155231










