Oxidation-Induced and Hydrothermal-Assisted Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 for Adsorption of Acid Orange 7
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Starting Materials
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Evaluation of Adsorption Capacity
3. Results and Discussion
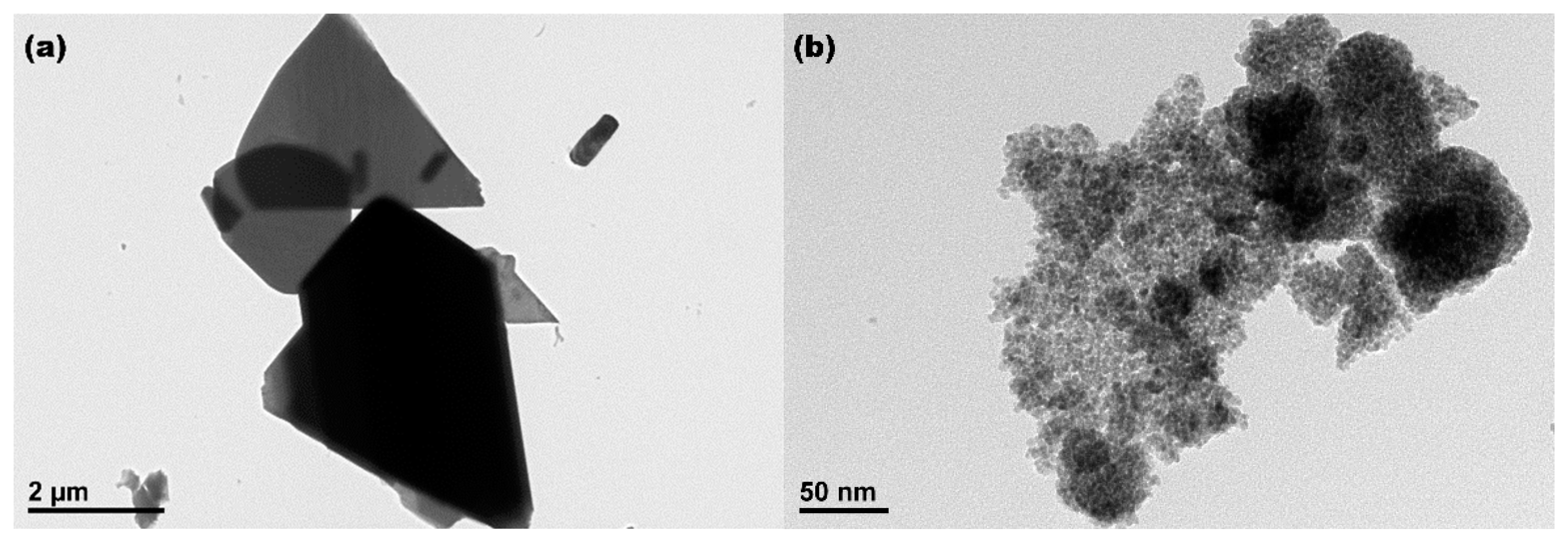
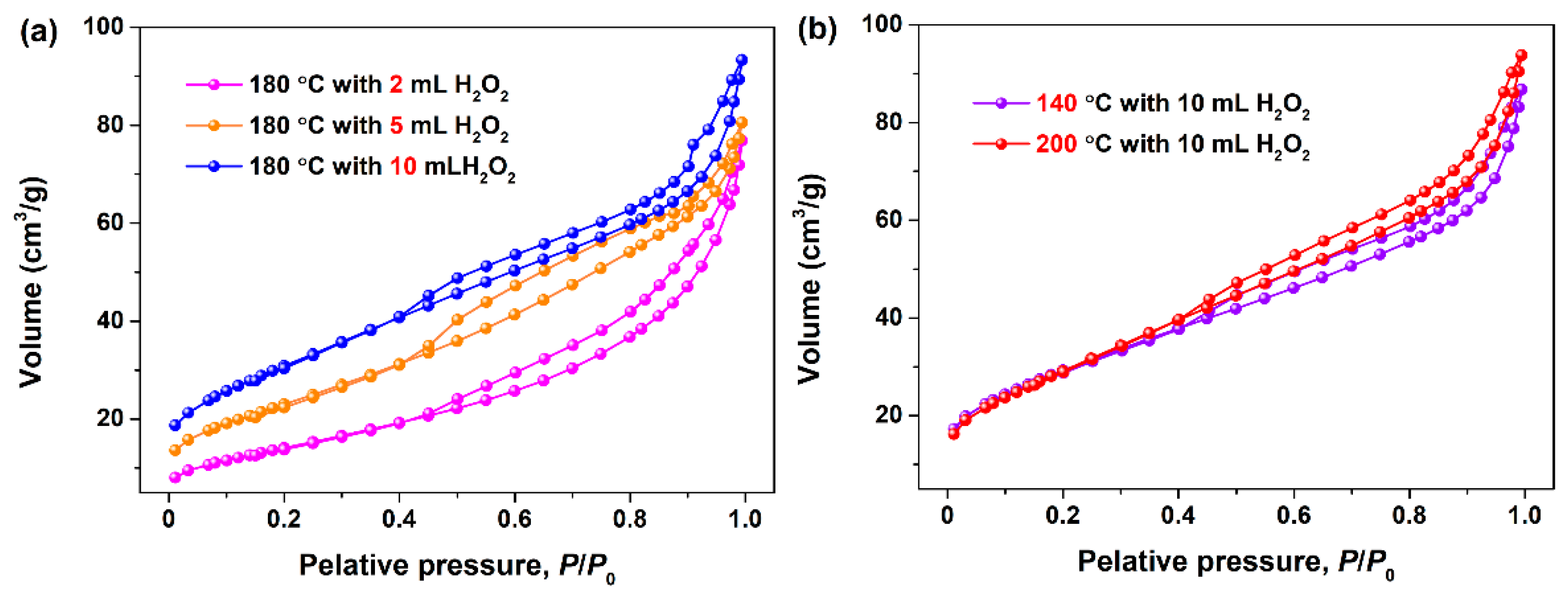
3.1. Characterization of Mesoporous CeO2
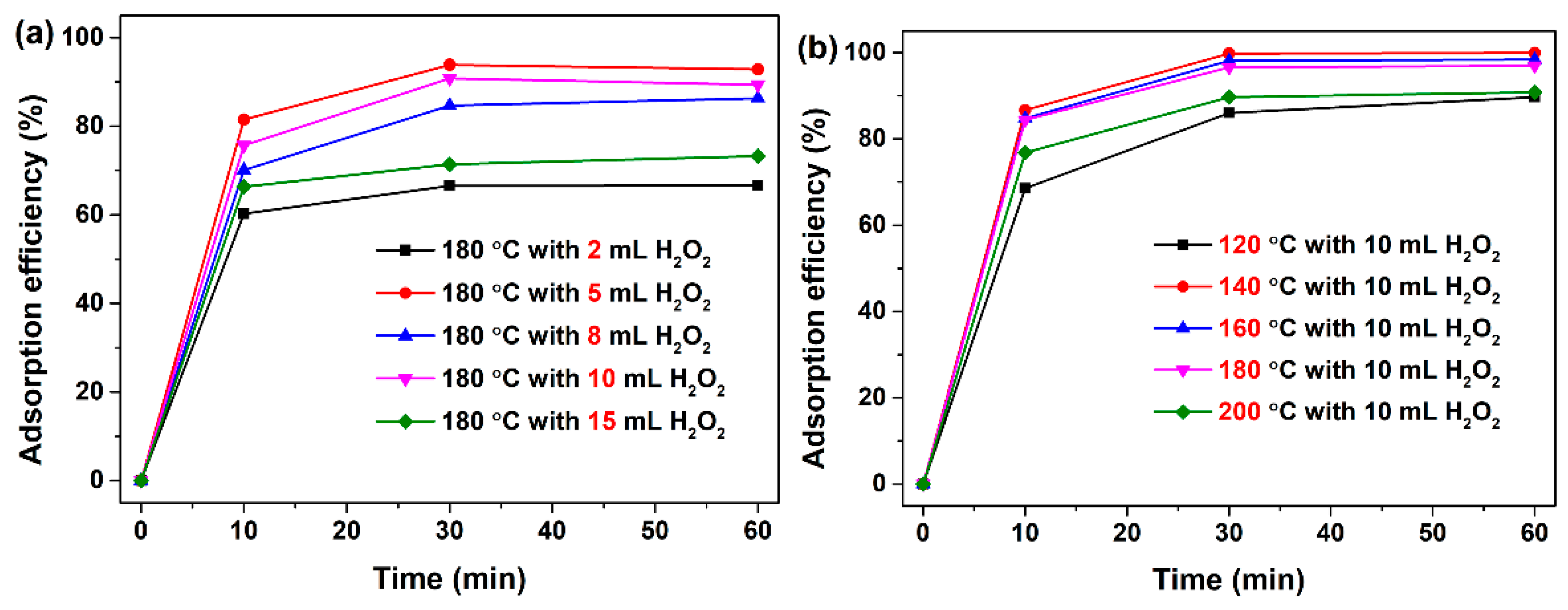
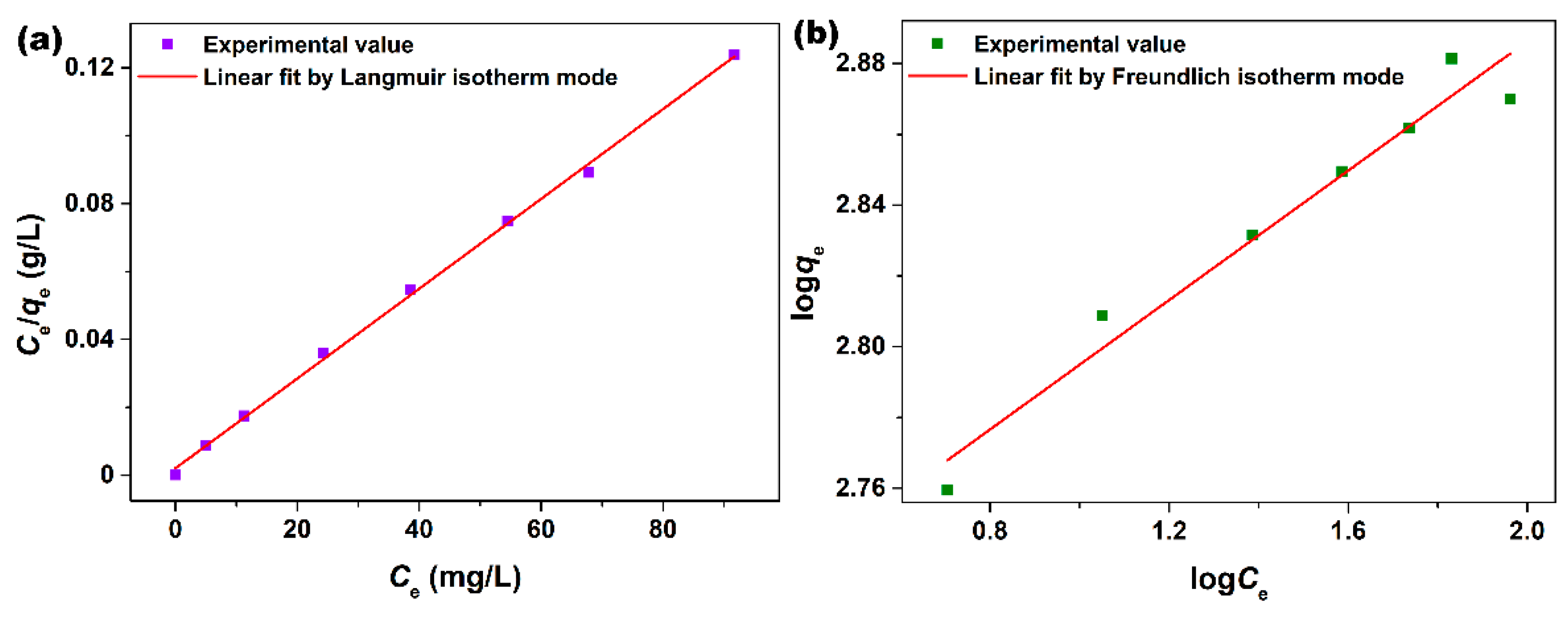
3.2. Adsorption Characteristics
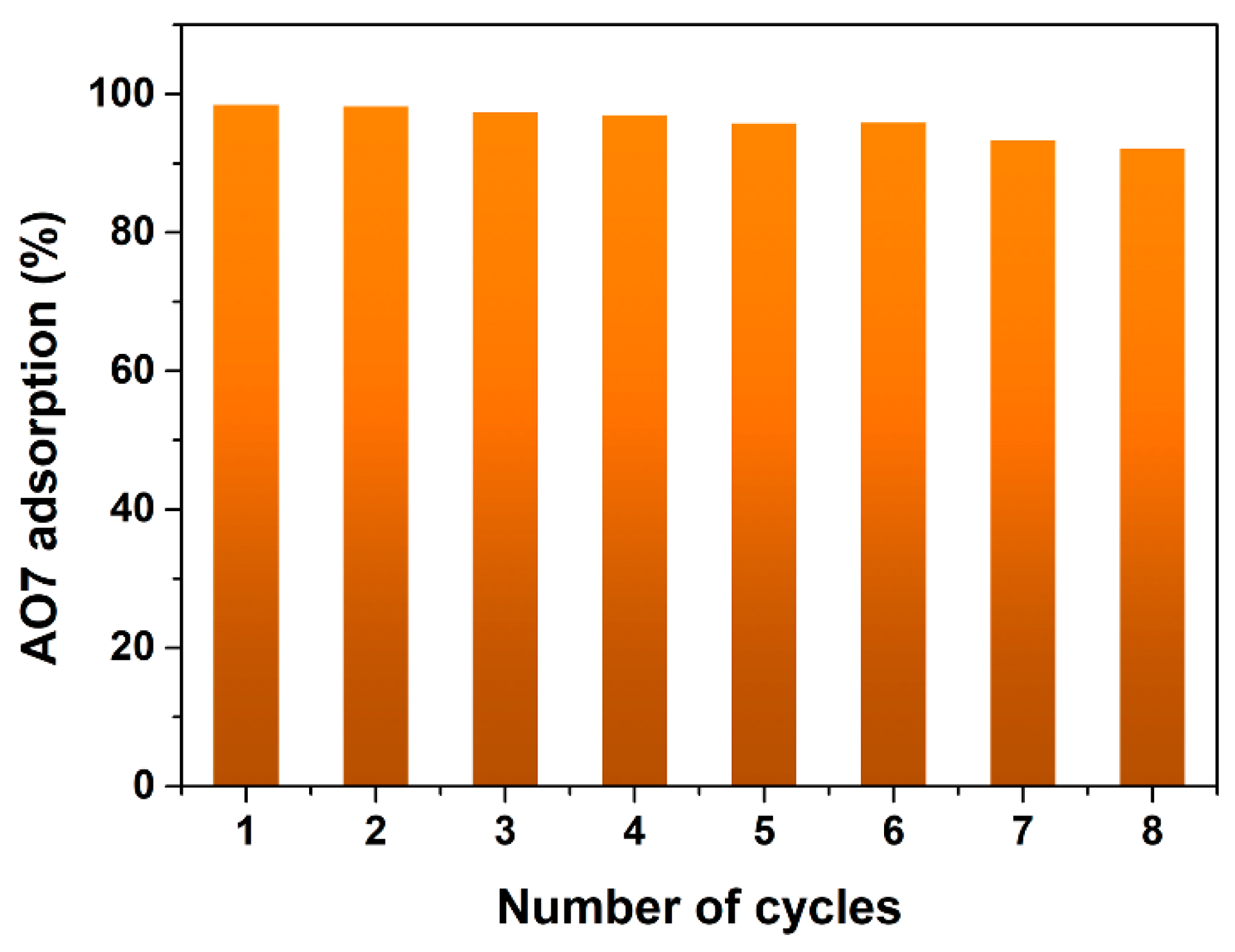
3.3. Desorption and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waheed, A.; Baig, N.; Ullah, N.; Falath, W. Removal of hazardous dyes, toxic metal ions and organic pollutants from wastewater by using porous hyper-cross-linked polymeric materials: A review of recent advances. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, H.S.; Reife, A. Dyes, Environmental Chemistry. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulescu, M.; Rotaru, A.; Moanţă, A.; Iacobescu, G.; Pălărie, I.; Cioateră, N.; Popescu, M.; Criveanu, M.C.; Morîntale, E.; Bojan, M.; et al. Azorubine: Physical, thermal and bioactive properties of the widely employed food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic red azo dye material. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 143, 3945–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, W.G. Metabolism of AZO Dyes: Implication for Detoxication and Activation. Drug Metab. Rev. 1991, 23, 253–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, P.; Ma, W. LiBH4 for hydrogen storage: New perspectives. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Padermpole, K.; Hisanaga, T. Photocatalytic degradation of commercial azo dyes. Water Res. 2000, 34, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Li, H.; Shaw, L. New insights into the solid-state hydrogen storage of nanostructured LiBH4-MgH2 system. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yang, W.; Huo, K.; Shaw, L. Thermodynamics and kinetics tuning of LiBH4 for hydrogen storage. Prog. Chem. 2021, 33, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, C.; Gupta, R.; Bedadeep, D.; Narayanasamy, S. Surface treated acid-activated carbon for adsorption of anionic azo dyes from single and binary adsorptive systems: A detail insight. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Isloor, A.M.; Todeti, S.R.; Ibrahim, G.P.S.; Inamuddin, I.A.F.; Asiri, A.M. Improved separation of dyes and proteins using membranes made of polyphenylsulfone/cellulose acetate or acetate phthalate. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, T.; Mei, M.; Chen, S.; Li, J. Peroxydisulfate activation by digestate-derived biochar for azo dye degradation: Mechanism and performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderete, B.L.; Silva, J.D.; Godoi, R.; Silva, F.; Picada, J.N. Evaluation of toxicity and mutagenicity of a synthetic effluent containing azo dye after Advanced Oxidation Process treatment. Chemosphere 2020, 263, 128291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; An, X.; Li, H.; Lai, F.; Yuan, E.; Xia, X.; Zhang, Q. Detoxification of azo dye Direct Black G by thermophilic Anoxybacillus sp. PDR2 and its application potential in bioremediation. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-L.; Qin, J.-H.; Ji, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, R.; Li, B.-J.; Zang, S.-Q.; Hou, H.-W.; Batten, S.R. Anionic porous metal-organic framework with novel 5-connected vbk topology for rapid adsorption of dyes and tunable white light emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lu, Y.; Li, L.; Shaw, L. High Reversible Capacity Hydrogen Storage Through Nano-LiBH4 + Nano-MgH2 System. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 20, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-H.; Manivel, A.; Lee, G.-J.; Wu, J.J. Synthesis of mesoporous Bi2O3/CeO2 microsphere for photocatalytic degradation of Orange II dye. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 4174–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.F.; Deng, Z.P.; Gao, S. Facile tree leaf-templated synthesis of mesoporous CeO2 nanosheets for enhanced sensing detection of p-xylene vapors. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. Ordered mesoporous Ag/CeO2 nanocrystalline via silica-templated solution combustion for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Colloid. Surface. A 2020, 604, 125301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farvardin, N.; Jahani, S.; Kazemipour, M.; Foroughi, M.M. The synthesis and characterization of 3D mesoporous CeO2 hollow spheres as a modifier for the simultaneous determination of amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide and valsartan. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Huo, P. g-C3N4 quantum dots-modified mesoporous CeO2 composite photocatalyst for enhanced CO2 photoreduction. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 20495–20512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Jing, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Han, Z.; Jiang, X.; Dai, H. Intermetallic compound PtMny-derived Pt-MnOx supported on mesoporous CeO2: Highly efficient catalysts for the combustion of toluene. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2020, 595, 117509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Luo, J. Mesoporous CeO2-C hybrid spheres as efficient support for platinum nanoparticles towards methanol electrocatalytic oxidation. J. Rare Earth. 2021, 39, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; She, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Xia, D.; Cheng, Z.; et al. A novel Z-scheme CeO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction photocatalyst for degradation of Bisphenol A and hydrogen evolution and insight of the photocatalysis mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 85, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. One Step Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous MnOx/CeO2 Nanocomposite Oxides with Enhanced Low Temperature Catalytic Activity for CO and Hydrocarbon Oxidation. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tseng, C.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Lee, C.A.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Song, L.; Li, X.; He, J.H.; Sakthivel, R.; et al. Template-free synthesis of mesoporous Ce3NbO7/CeO2 hollow nanospheres for label-free electrochemical immunosensing of leptin. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2021, 341, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikanova, K.; Redina, E.; Kapustin, G.; Nissenbaum, V.; Mishin, I.; Kostyukhin, E.; Kustov, L. Template-free one-step synthesis of micro-mesoporous CeO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides with a high surface area for selective hydrogenation. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13980–13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, R. Template-free synthesis of mesoporous CeO2 powders by integrating bottom-up and top-down routes for acid orange 7 adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44828–44834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Hosokawa, S.; Imamura, S.; Inoue, M. Pore-Structure-Controlled Coagulates of CeO2 Nanoparticles for Supporting Ru Catalysts in Liquid Phase Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 2007, 115, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, Q.; Zuo, P.; Fan, H.; Qu, S.; Shen, W. Hollow Structure and Electron Promotion Effect of Mesoporous Pd/CeO2 Catalyst for Enhanced Catalytic Hydrogenation. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Jia, X. Adsorption mechanism and kinetics of azo dye chemicals on oxide nanotubes: A case study using porous CeO2 nanotubes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y. Template-free hydrothermal synthesis and CO oxidation properties of flower-like CeO2 nanostructures. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 59, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.C.; Peffer, L.A.A.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Pore size determination in modified micro- and mesoporous materials. Pitfalls and limitations in gas adsorption data analysis. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2003, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Bao, H.; He, B.; Wang, F.; Si, D.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wei, S.; Huang, W. Interfacial and surface structures of CeO2–TiO2 mixed oxides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 19078–19085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Chen, F.; Shen, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J. Enhanced catalytic degradation of AO7 in the CeO2-H2O2 system with Fe3+ doping. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2010, 101, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M. Study of adsorption and degradation of acid orange 7 on the surface of CeO2 under visible light irradiation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2009, 85, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Jacques, P.; Kalt, A. Investigation of the interaction between a sulfonated azo dye (AO7) and a TiO2 surface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 307, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of gases on glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; El-Barghouthi, M.I.; Issa, A.A.; Khraisheh, M.A.; Walker, G.M. Sorption of Zn(II), Pb(II), and Co(II) using natural sorbents: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2645–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro Silva, J.; Sousa, S.; Rodrigues, J.; Antunes, H.; Porter, J.J.; Gonçalves, I.; Ferreira-Dias, S. Adsorption of acid orange 7 dye in aqueous solutions by spent brewery grains. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, Y.; Ashori, A.; Azadeh, E.; Abdulkhani, A. Removal of Acid Orange 7 and Remazol Black 5 reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using a novel biosorbent. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater 2012, 32, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashori, A.; Hamzeh, Y.; Ziapour, A. Application of soybean stalk for the removal of hazardous dyes from aqueous solutions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 54, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Liang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, F. Selective adsorption of organic pigments on inorganically modified mesoporous biochar and its mechanism based on molecular structure. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2020, 573, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorimotlagh, Z.; Darvishi Cheshmeh Soltani, R.; Khataee, A.R.; Shahriyar, S.; Nourmoradi, H. Adsorption of a textile dye in aqueous phase using mesoporous activated carbon prepared from Iranian milk vetch. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E. 2014, 45, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.K.; Bay, H.H.; Neoh, C.H.; Aris, A.; Abdul Majid, Z.; Ibrahim, Z. Application of zeolite-activated carbon macrocomposite for the adsorption of Acid Orange 7: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7243–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aber, S.; Daneshvar, N.; Soroureddin, S.M.; Chabok, A.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K. Study of acid orange 7 removal from aqueous solutions by powdered activated carbon and modeling of experimental results by artificial neural network. Desalination 2007, 211, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C. Modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes assisted foam fractionation for effective removal of acid orange 7 from the dyestuff wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 262, 110260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Ghiasvand, A.R.; Noorimotlagh, Z. Removal of methylene blue and acid orange 7 from aqueous solutions by activated carbon coated with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 55, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Shams, M.; Qasemi, M.; Afsharnia, M. Data on efficient removal of acid orange 7 by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Data Brief 2019, 23, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.; Zhou, J. Novel Fe3O4-poly(methacryloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride) adsorbent for the ultrafast and efficient removal of anionic dyes. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Xie, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N. Selective adsorption of anionic dyes from aqueous solution by nickel (II) oxide. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2019, 68, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, F.; Zeng, X. Synthesis and adsorption application of amine shield-introduced-released porous chitosan hydrogel beads for removal of acid orange 7 from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62778–62787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Generic Name | Chemical Formula | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Cas Number | λmax (nm) | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid orange 7 | C16H11N2NaO4S |  | 350.3 | 633-96-5 | 484 | Orange-red |
| Synthesis Conditions | 180 °C with Desired Amounts of H2O2 | Different Temperaments with 10 mL H2O2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mL | 5 mL | 10 mL | 140 °C | 200 °C | |
| SBET (m2/g) | 52.5 | 84.9 | 112.8 | 107.0 | 109.4 |
| Pore diameter (nm) | 8.95 | 5.81 | 5.09 | 4.98 | 5.28 |
| Pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.1174 | 0.1234 | 0.1436 | 0.1332 | 0.1445 |
| Langmuir Isotherm Model | Freundlich Isotherm Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 |
| 757.6 | 0.6256 | 0.9985 | 10.94 | 505.3 | 0.9512 |
| Authors | Adsorbent Name | Sorption Conditions | SBET (m2/g) | qm (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pedro Silva [40] | Spent brewery grains (SBG) | 30 °C | / | 30.5 |
| Hamzeh [41] | Canola stalks (CS) | 25 °C; pH = 2.5 | / | 25.1 |
| Ashori [42] | Soybean stalk (SS) | 25 °C; pH = 2.0 | / | 17.5 |
| Lin [43] | Iron oxide-loaded biochar (Fe-BC) from sorghum straw | 25 °C; pH = 6.0; 180 rpm | 216.6 | 59.3 |
| Noorimotlagh [44] | Mesoporous activated carbon prepared from Iranian milk vetch | pH = 7.0 | 565 | 99.0 |
| Lim [45] | Zeolite-activated carbon macrocomposite | Room temperature; pH = 7.0 | 84.7 | 0.19 |
| Aber [46] | Powdered activated carbon | 25 °C; pH = 2.8 | / | 440 |
| Jia [47] | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) | pH = 7.0 | ~1800 | 47.7 ± 0.79 |
| Nourmoradi [48] | Activated carbon coated with zinc oxide (AC-ZnO) | 25 °C | / | 66.2 |
| Ghasemi [49] | Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) | 25 °C; pH = 6.0; 200 rpm | 978 | 80.5 |
| Zhou [50] | Fe3O4-poly(methacryloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride) (Fe3O4-pDMC) | pH = 3.0; 150 rpm | 35.7 | 270.3 |
| Huo [51] | Nickel (II) oxide (NiO) | 25 °C; pH = 5.5 | 251.8 | 178.6 |
| Li [52] | Amine shield-introduced-released porous chitosan hydrogel beads (APCB) | 30 °C; 150 rpm | / | 2571.0 (pH = 2.0); 363.6 (pH = 4.0) |
| Xu [27] | Mesoporous CeO2 synthesized based on integrating bottom-up and top-down routes in the previous report | 25 °C; No pH preadjustment; 200 rpm | 166.5 | 510.2 |
| Xu | Mesoporous CeO2 synthesized hydrothermally at 140 °C for 24 h with 10 mL H2O2 in this work | Room temperature; No pH preadjustment; 200 rpm | 107.0 | 757.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Ding, Z. Oxidation-Induced and Hydrothermal-Assisted Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 for Adsorption of Acid Orange 7. Materials 2022, 15, 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155209
Xu Y, Ding Z. Oxidation-Induced and Hydrothermal-Assisted Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 for Adsorption of Acid Orange 7. Materials. 2022; 15(15):5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155209
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yaohui, and Zhao Ding. 2022. "Oxidation-Induced and Hydrothermal-Assisted Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 for Adsorption of Acid Orange 7" Materials 15, no. 15: 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155209
APA StyleXu, Y., & Ding, Z. (2022). Oxidation-Induced and Hydrothermal-Assisted Template-Free Synthesis of Mesoporous CeO2 for Adsorption of Acid Orange 7. Materials, 15(15), 5209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15155209







