Crystal Growth, Thermal and Spectral Properties of Er: LGGG Crystal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Crystal Growth
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crystal Growth
3.2. Structural Properties
3.3. Effective Segregation Coefficient
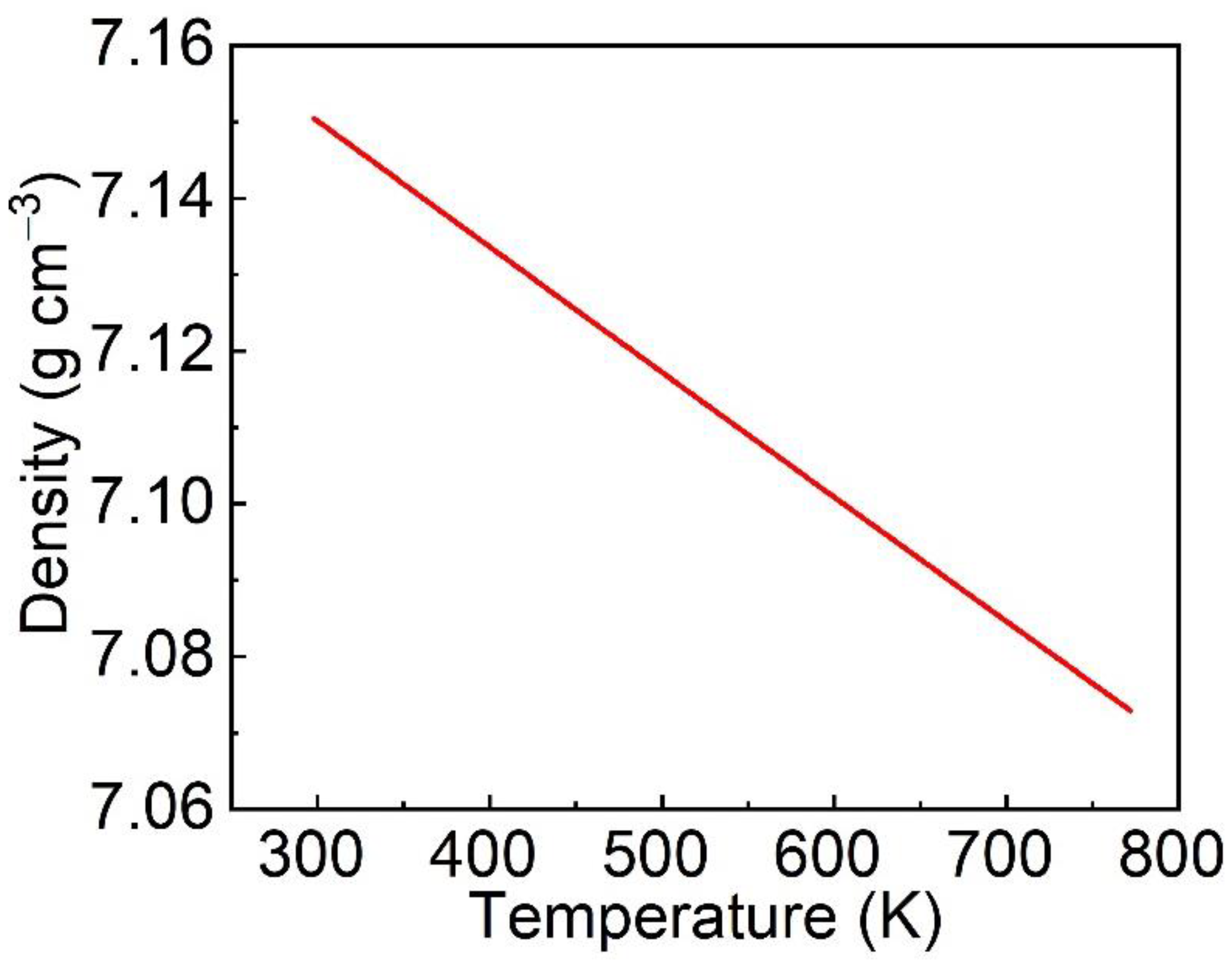
3.4. Crystal Density
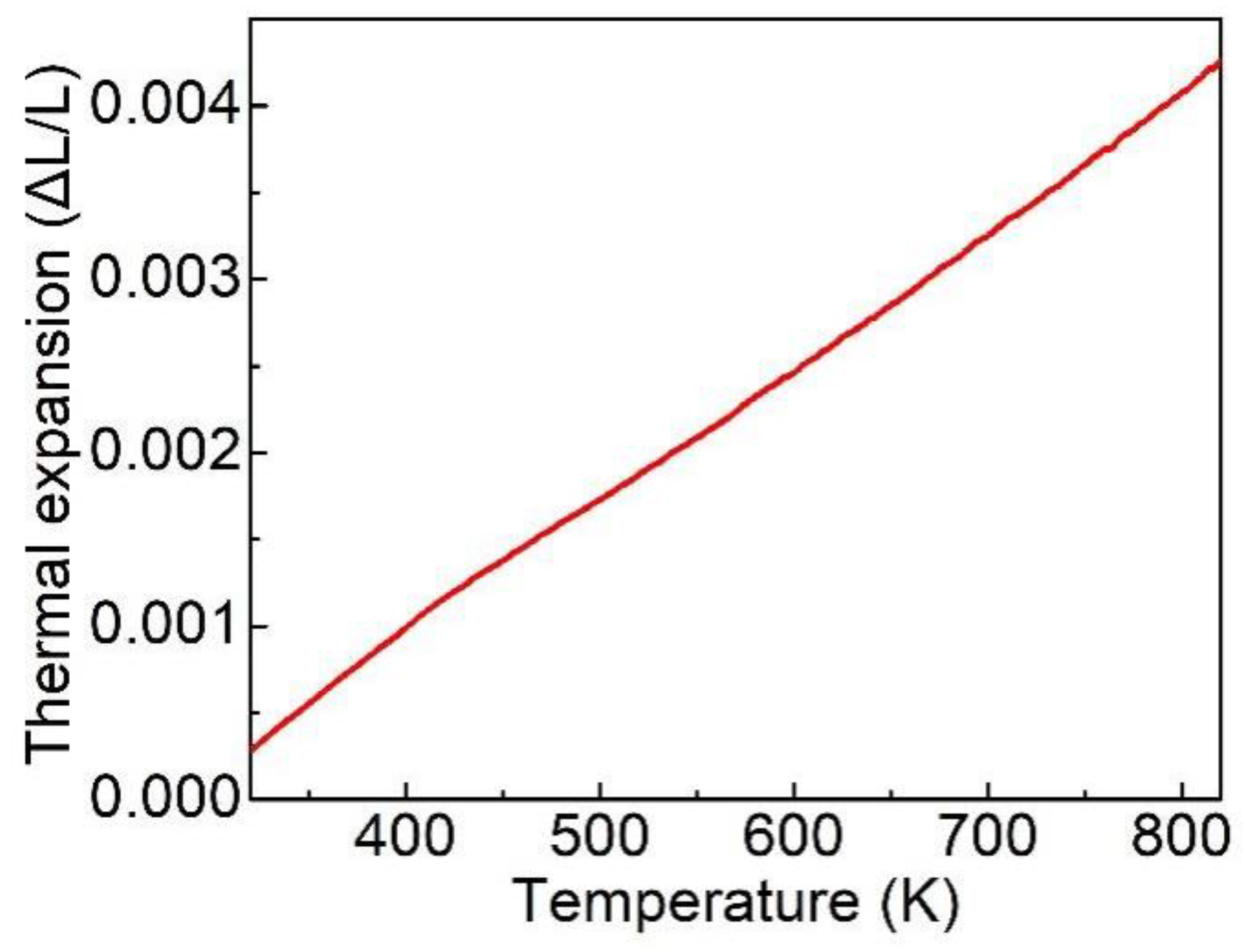
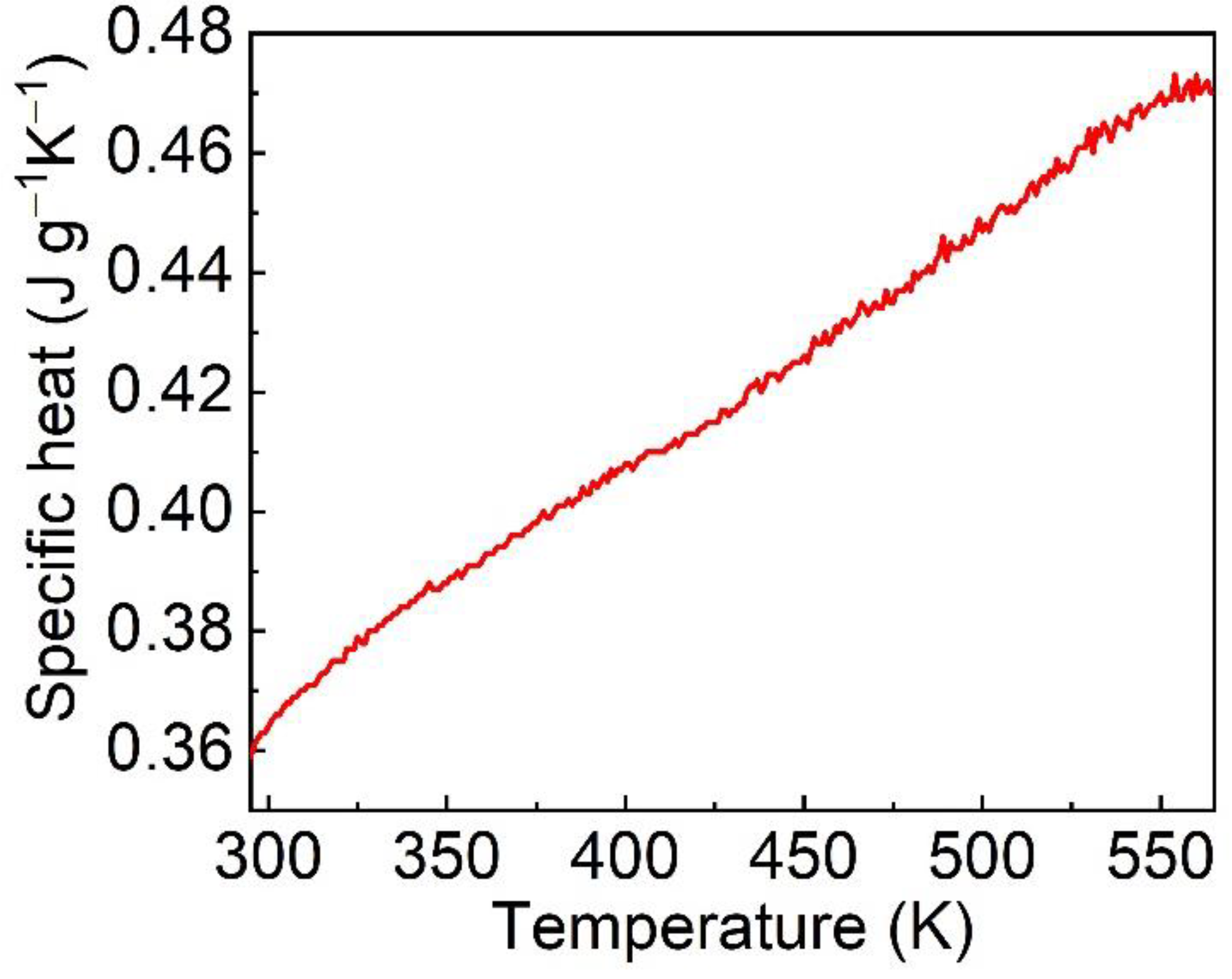
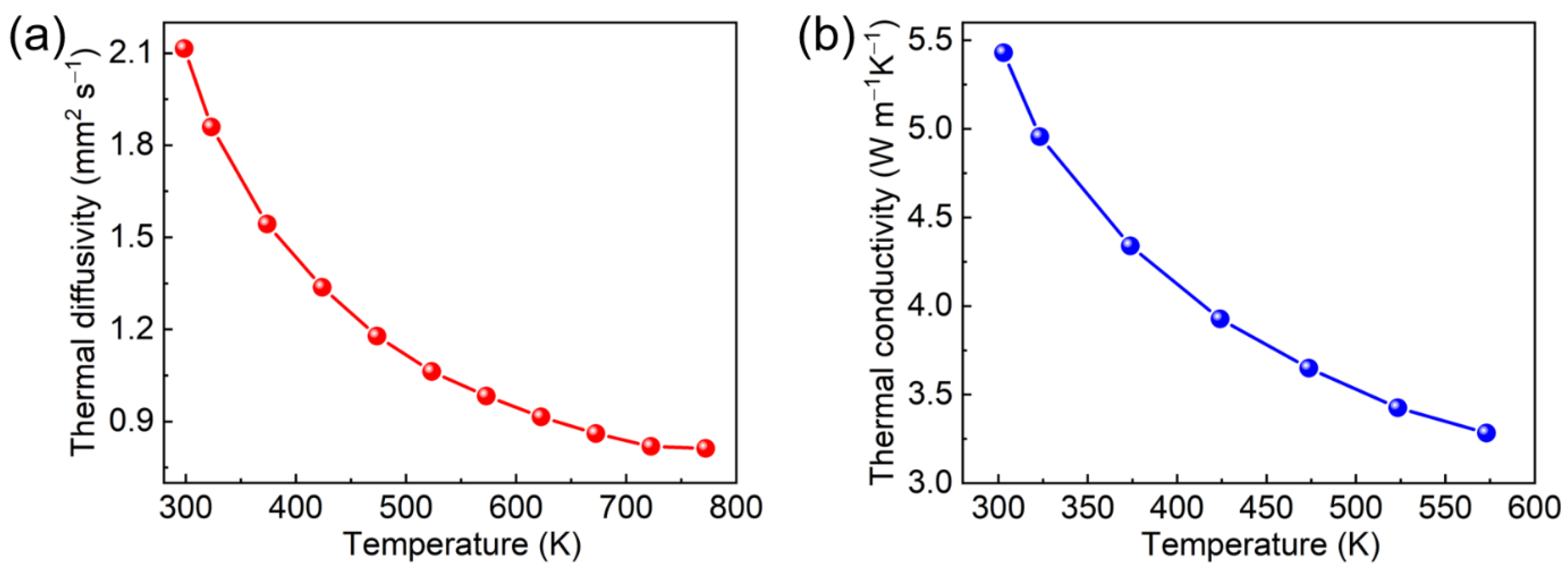
3.5. Thermal Properties
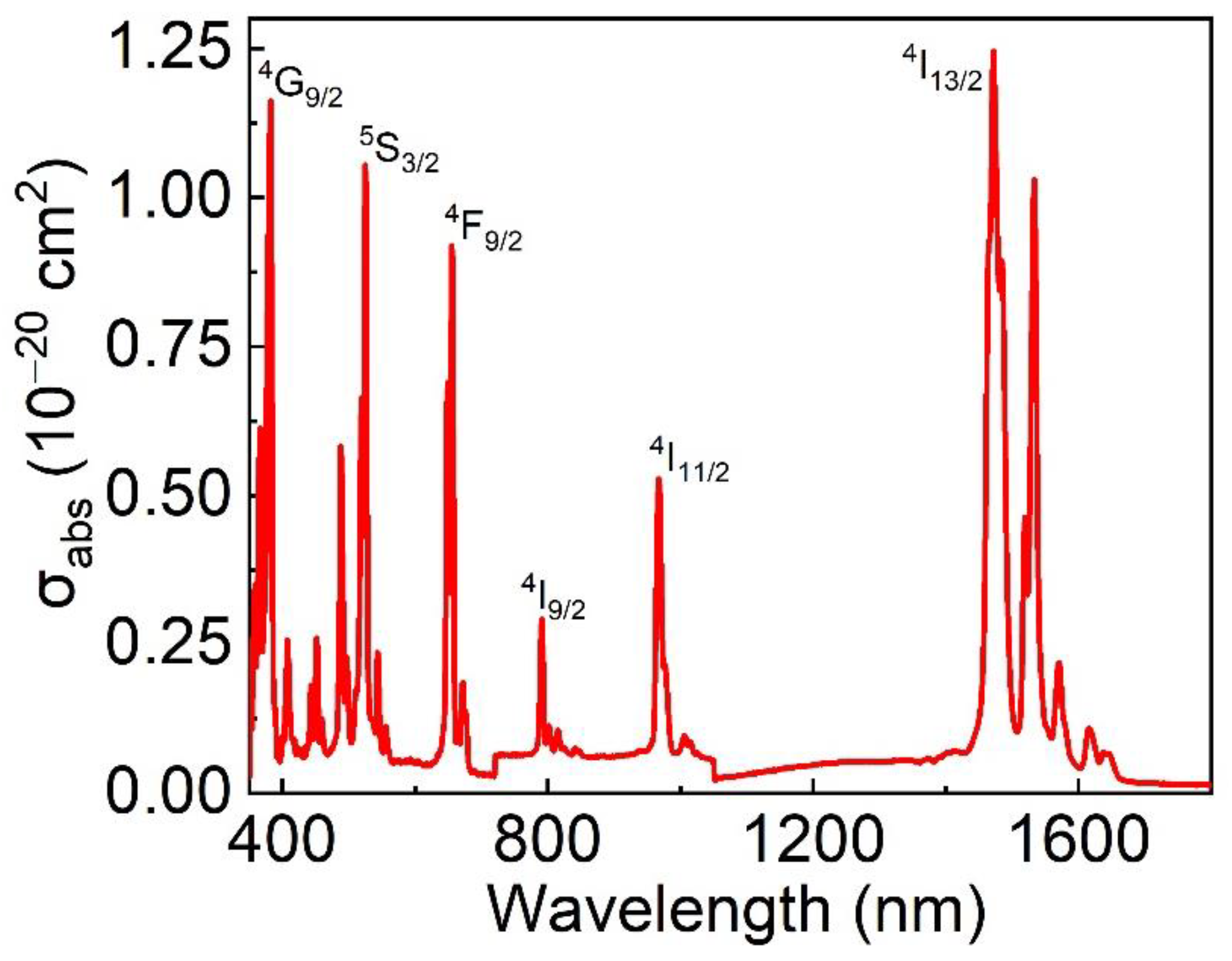
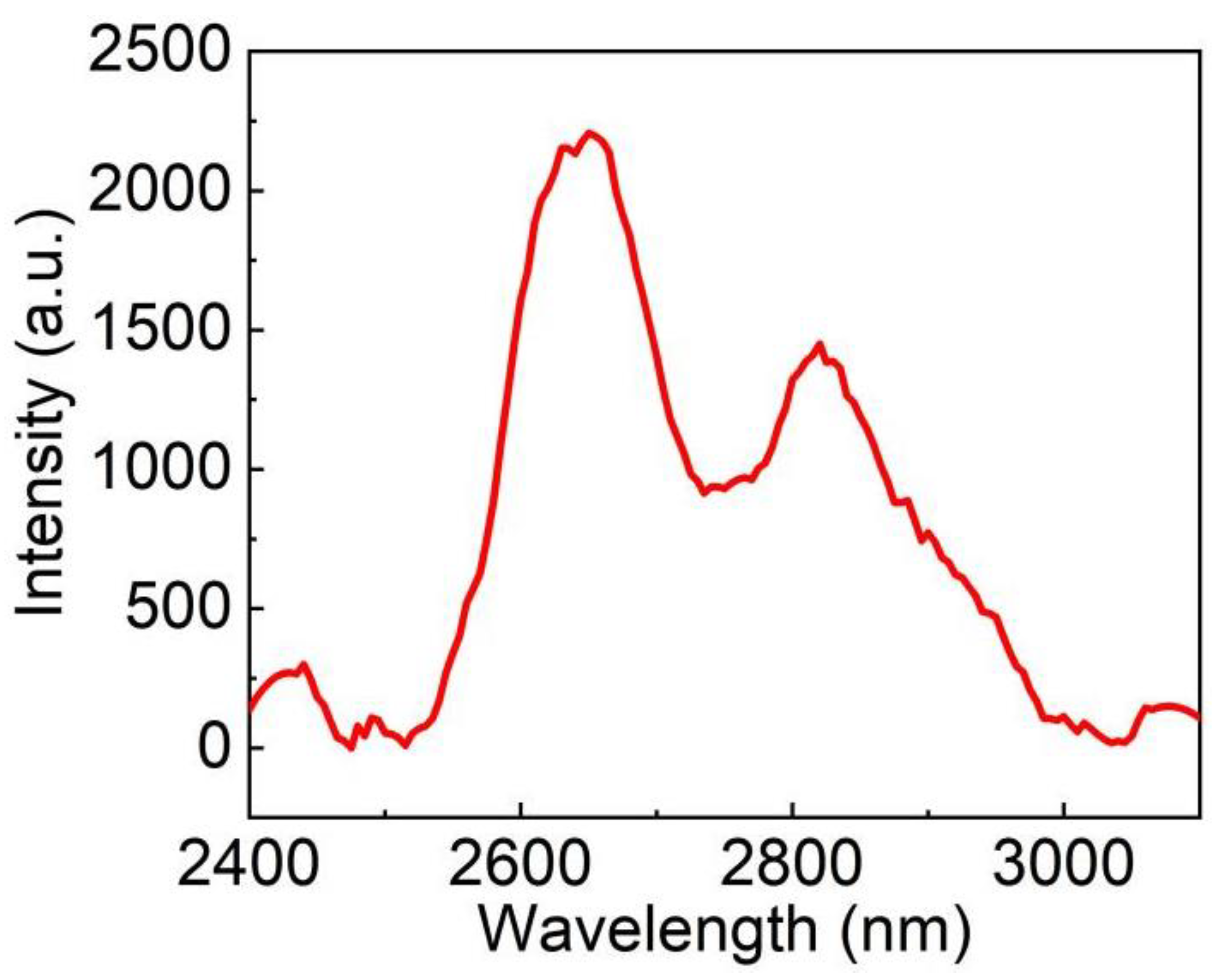
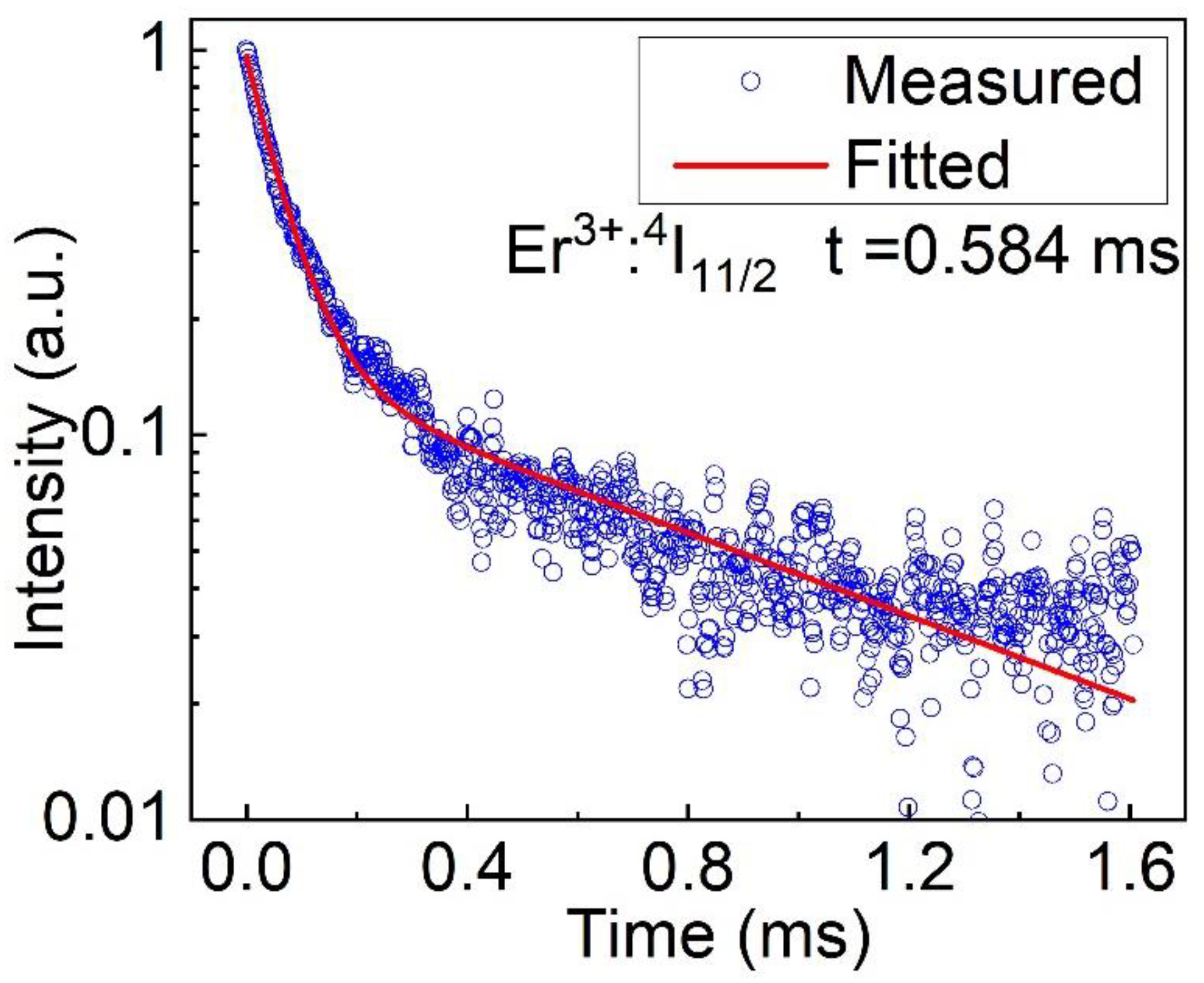
3.6. Spectral Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skorczakowski, M.; Swiderski, J.; Pichola, W.; Nyga, P.; Zajac, A.; Maciejewska, M.; Galecki, L.; Kasprzak, J.; Gross, S.; Heinrich, A.; et al. Mid-infrared Q-switched Er:YAG laser for medical applications. Laser Phys. Lett. 2010, 7, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, A.; Skorczakowski, M.; Swiderski, J.; Nyga, P. Electrooptically Q-switched mid-infrared Er:YAG laser for medical applications. Opt. Lett. 2004, 12, 5125–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulon, G. Fifty years of advances in solid-state laser materials. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Tao, X.; Dong, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, F.; Jiang, M. Study on crystal growth of large size Nd3+:Gd3Ga5O12 (Nd3+:GGG) by Czochralski method. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 292, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodopyanov, K.L.; Ganikhanov, F.; Maffetone, J.P.; Zwieback, I.; Ruderman, W. ZnGeP2 optical parametric oscillator with 3.8–12.4 µm tunability. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafetinides, A.A.; Papayannis, A.D.; Fabrikesi, E.T.; Rickwood, K.R.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.W.; Miyagi, M.; Croitoru, N.; Harrington, J.; Nubling, R. Lasers, waveguides and fibers for 3.0 μm medical applications. In Proceedings of the Second GR-I International Conference on New Laser Technologies and Applications, Olympia, Greece, 14 July 1998; Volume 3423, pp. 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Huang, H.T.; Ren, X.J.; Wang, J.; Shen, D.Y.; Zhao, Y.G.; Zhou, W.; Liu, P.; Tang, D.Y. Nanosecond Pulse Generation at 2.7 μm From a Passively Q-Switched Er:Y2O3 Ceramic Laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2018, 24, 1600906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, H.; Tokita, S.; Kawanaka, J.; Konishi, D.; Murakami, M.; Yasuhara, R. A passively Q-switched compact Er:Lu2O3 ceramics laser at 2.8 μm with a graphene saturable absorber. Appl. Phys. Express 2019, 12, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolek, C.; Ernst, H.; Will, G.F.; Lubatschowski, H.; Welling, H.; Ertmer, W. High-repetition-rate, high-average-power, diode-pumped 2.94 µm Er:YAG laser. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Tu, C. Single-longitudinal-mode Er:GGG microchip laser operating at 2.7 μm. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3845–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.Y.; Li, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.B.; Zhu, Z.J.; Tu, C.Y. Spectroscopic and laser properties of Er:LuGG crystal at 2.8 μm. Appl. Phys. Express 2019, 12, 052019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.K.; Hu, Q.Q.; Zhang, B.T.; Sun, X.L.; Tian, H.L.; Wang, Y.R.; Yan, B.Z.; Jia, Z.T.; Yang, K.J.; Tao, X.T.; et al. Highly Efficient Continuous-Wave and Passively Q-Switching 2.8 μm Er:YSGG Laser. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2018, 30, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.N.; Zhang, H.; Ma, W.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Su, L.B. Black phosphorus saturable absorber for a diode-pumped passively Q-switched Er:CaF2 mid-infrared laser. Opt. Commun. 2018, 406, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, V.A.; Shcherbakov, I.A. Rare-earth scandium chromium garnets as active media for solid-state lasers. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1988, 24, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, S.A.; Chang, D.B.; Birnbaum, M.; Kokta, M. Upconversion-pumped 2.8–2.9 μm lasing of Er3+ ion in garnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 7227–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.C.; Zhao, G.J.; Xu, X.D. Crystal growth and spectroscopic properties of erbium doped Lu2SiO5. J. Cryst. 2010, 312, 2103–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandle, C.D. Growth of 3’’ diameter Gd3Ga5O12 crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 49, 1855–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.T.; Tao, X.T.; Yu, H.H.; Dong, C.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, Z.P.; Jiang, M.H. Growth and properties of Nd:(LuxGd1-x)3Ga5O12 laser crystal by Czochralski method. Opt. Mater. 2008, 31, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; You, Z.Y.; Li, J.F.; Zhu, Z.J.; Ma, E.; Tu, C.Y. Spectroscopic investigations of highly doped Er3+: GGG and Er3+/Pr3+ : GGG crystals. J. Phys. D 2009, 42, 215406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupke, W.F.; Shinn, M.D.; Marion, J.E.; Caird, J.A.; Stokowski, S.E. Spectroscopic, optical, and thermomechanical properties of neodymium-doped and chromium-doped gadolinium scandium gallium garnet. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1986, 3, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Sun, Y.X.; Zhang, C.Q.; Tao, X.T. Anisotropic thermal properties of the polar crystal Cs2TeMo3O12. J Solid State Chem. 2012, 195, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.B.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, Y.G.; Wang, Z.P.; Yu, H.H.; Sun, S.Q.; Xia, H.R.; Jiang, M.H. Growth and characterization of Nd:CLNGG crystal. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 3792–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.J.; Zhu, G.X.; Yan, R.S.; Liu, F.Y.; Guo, X.A.; Yin, S.T. Czochralski Growth of Gadolinium Gallium Garnet (GGG) Single Crystals. IEEE J. Quantu. Electron. 2003, 20, 550–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J. Thermal and optical properties of gadolinium gallium garnet. Mater. Res. Bull. 1982, 17, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.W.; Jia, Z.T.; Li, Y.B.; Yuan, D.S.; Dong, C.M.; Tao, X.T. Growth and characterization of Nd:LGGG laser crystal. J. Cryst. 2012, 353, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; You, Z.; Xu, J.; Tu, C. Dual function of Nd3+ in Nd, Er:LuYSGG crystal for LD pumped 3.0 μm mid-infrared laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 18554–18562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| m0 (g) | 1.0935 | 2.4696 | 3.8052 |
| m0 − m1 (g) | 0.1528 | 0.3435 | 0.5324 |
| ρwater (g/cm3) | 0.998 | ||
| ρexp (g/cm3) | 7.1437 | 7.1768 | 7.1331 |
| ρav (g/cm3) | 7.15 ± 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Q.; Liu, L.; Xin, X.; Fu, X.; Jia, Z.; Tao, X. Crystal Growth, Thermal and Spectral Properties of Er: LGGG Crystal. Materials 2022, 15, 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144819
Chi Q, Liu L, Xin X, Fu X, Jia Z, Tao X. Crystal Growth, Thermal and Spectral Properties of Er: LGGG Crystal. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144819
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Qiaoyun, Lei Liu, Xianhui Xin, Xiuwei Fu, Zhitai Jia, and Xutang Tao. 2022. "Crystal Growth, Thermal and Spectral Properties of Er: LGGG Crystal" Materials 15, no. 14: 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144819
APA StyleChi, Q., Liu, L., Xin, X., Fu, X., Jia, Z., & Tao, X. (2022). Crystal Growth, Thermal and Spectral Properties of Er: LGGG Crystal. Materials, 15(14), 4819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144819








