Hollow Silica Microparticles Based on Amphiphilic Polyphosphazenes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
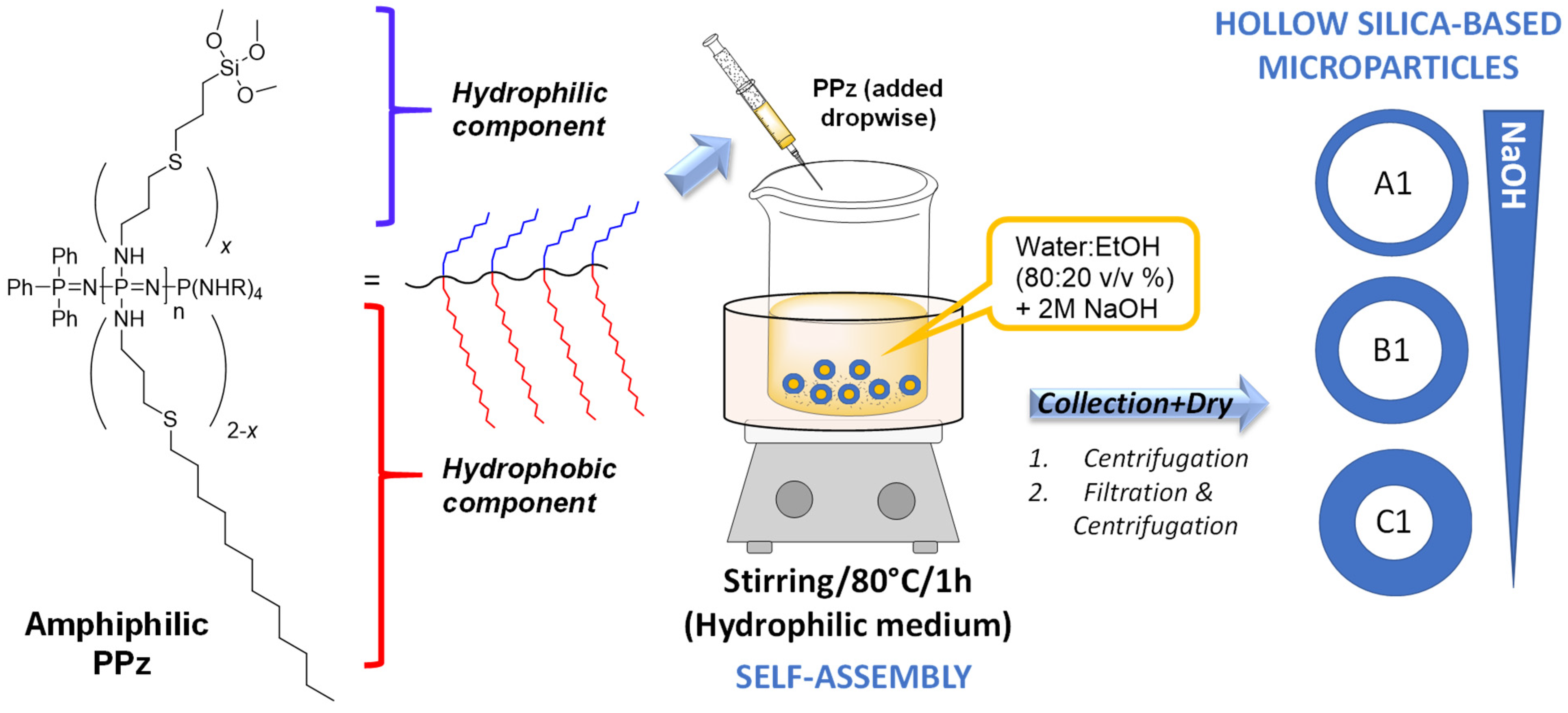
3.1. Synthesis of Silane-Derived Amphiphilic Polymer
3.2. Preparation of Silica Microparticles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, Y.; Na, X.; Wu, J.; Ma, G. The Horizon of the Emulsion Particulate Strategy: Engineering Hollow Particles for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.; Tüysüz, H.; Duyckaerts, N.; Knossalla, J.; Wang, G.-H.; Schüth, F. Hollow Nano- and Microstructures as Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14056–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, S.; He, S.; Shen, F.; Han, X.; Yin, Y.; Gao, C. Scalable synthesis of sub-100 nm hollow carbon nanospheres for energy storage applications. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Gao, T.; Hu, T.; Zhou, G. Synthesis and Electrochemical Energy Storage Applications of Micro/Nanostructured Spherical Materials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; Qi, L.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X. Applications of hollow nanomaterials in environmental remediation and monitoring: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilevskaya, V.V.; Govorun, E.N. Hollow and Vesicle Particles from Macromolecules with Amphiphilic Monomer Units. Polym. Rev. 2019, 59, 625–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.I.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10983–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, H.R. The expanding field of polyphosphazene high polymers. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, S.; Teasdale, I. Preparation of polyphosphazenes: A tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5200–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, Y.; Huang, X.; Xu, Z. Synthesis of Polyphosphazene Derivatives via Thiol-ene Click Reactions in an Aqueous Medium. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2015, 216, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poscher, V.; Teasdale, I.; Salinas, Y. Surfactant-Free Synthesis of Cyclomatrix and Linear Organosilica Phosphazene-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.D.; Li, G.L.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T. Hollow polymeric nanostructures—Synthesis, morphology and function. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 127–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Polizos, G. Hollow Silica Particles: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y. Self-templated synthesis of hollow nanostructures. Nano Today 2009, 4, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, W.; Chen, C.; Zheng, N. Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, K.; Kawataki, T.; Okuda, S.; Oshima, S.; Kikuchi, J.-I. Spontaneously formed semipermeable organic–inorganic hybrid vesicles permitting molecular weight selective transmembrane passage. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Rivard, E.; Manners, I. A New High-Yield Synthesis of Cl3PNSiMe3, a Monomeric Precursor for the Controlled Preparation of High Molecular Weight Polyphosphazenes. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfert, S.; Henke, H.; Schoefberger, W.; Brüggemann, O.; Teasdale, I. Chain-End-Functionalized Polyphosphazenes via a One-Pot Phosphine-Mediated Living Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Fu, J. Applications of Self-Assembled Polyphosphazene Nano-Aggregates in Drug Delivery. In Polyphosphazenes in Biomedicine, Engineering, and Pioneering Synthesis; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, J.; Qiu, L. Drug -driven self-assembly of pH-sensitive nano-vesicles with high loading capacity and anti-tumor efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3348–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Armes, S.P. Preparation of Primary Amine-Based Block Copolymer Vesicles by Direct Dissolution in Water and Subsequent Stabilization by Sol−Gel Chemistry. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13710–13716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, S.; Dixit, C.K.; Bist, I.; Jalil, K.A.; Suib, S.L.; Rusling, J.F. Sodium hydroxide catalyzed monodispersed high surface area silica nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 075025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, J.; Chen, Y. Preparation of Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Hollow Particles Based on Gelation of Polymer Vesicles. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 5710–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C.C.; Fischer, K.; Schmidt, M. Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Vesicles Based on A Reactive Block Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14710–14711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


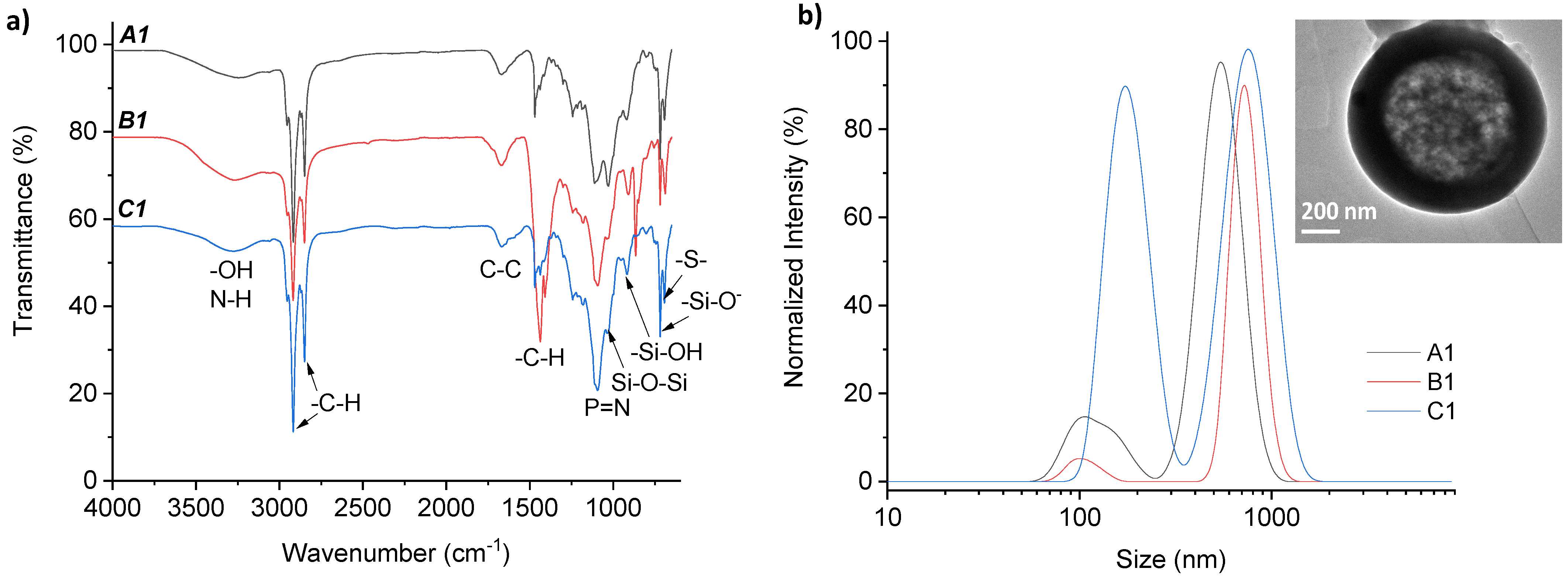

| Hollow Silica Microparticles | PPz Solution (mL) | 2 M NaOH (mL) | PPz Addition Method | Particles Collection Method | Dh-DLS (nm) | DSEM (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.5 | 8 | Dropwise | Centrifugation | 635 ± 139; 152 ± 28 | <90 |
| B1 | 0.5 | 6 | Dropwise | Centrifugation | 653 ± 97; 87 ± 8 | <14.5 |
| C1 | 0.5 | 4 | Dropwise | Centrifugation | 734 ± 158; 158 ± 27 | <4 |
| C2 | 0.5 | 4 | Dropwise | Filtration and centrifugation | - | <4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salinas, Y.; Poscher, V.; Brüggemann, O.; Teasdale, I. Hollow Silica Microparticles Based on Amphiphilic Polyphosphazenes. Materials 2022, 15, 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144763
Salinas Y, Poscher V, Brüggemann O, Teasdale I. Hollow Silica Microparticles Based on Amphiphilic Polyphosphazenes. Materials. 2022; 15(14):4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144763
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalinas, Yolanda, Vanessa Poscher, Oliver Brüggemann, and Ian Teasdale. 2022. "Hollow Silica Microparticles Based on Amphiphilic Polyphosphazenes" Materials 15, no. 14: 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144763
APA StyleSalinas, Y., Poscher, V., Brüggemann, O., & Teasdale, I. (2022). Hollow Silica Microparticles Based on Amphiphilic Polyphosphazenes. Materials, 15(14), 4763. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15144763









