Effects of Substrate Roughness on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- (b)
- How does substrate roughness affect coating microstructure?
- (c)
- Although the mechanism for the reduction of the fatigue properties of oxide layers has been reported, whether or not this mechanism is still valid when the substrate roughness changes needs to be verified.
2. Experimental
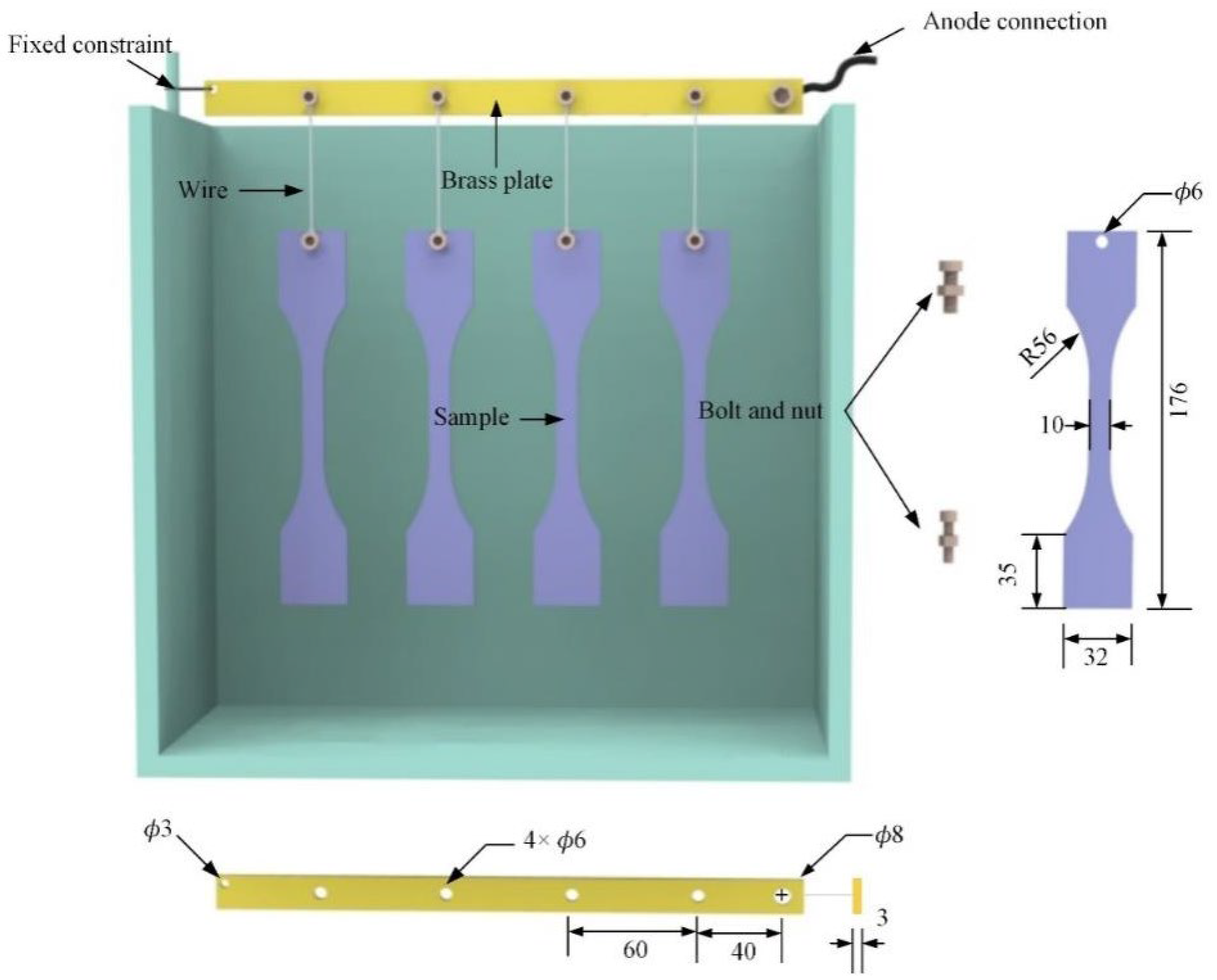
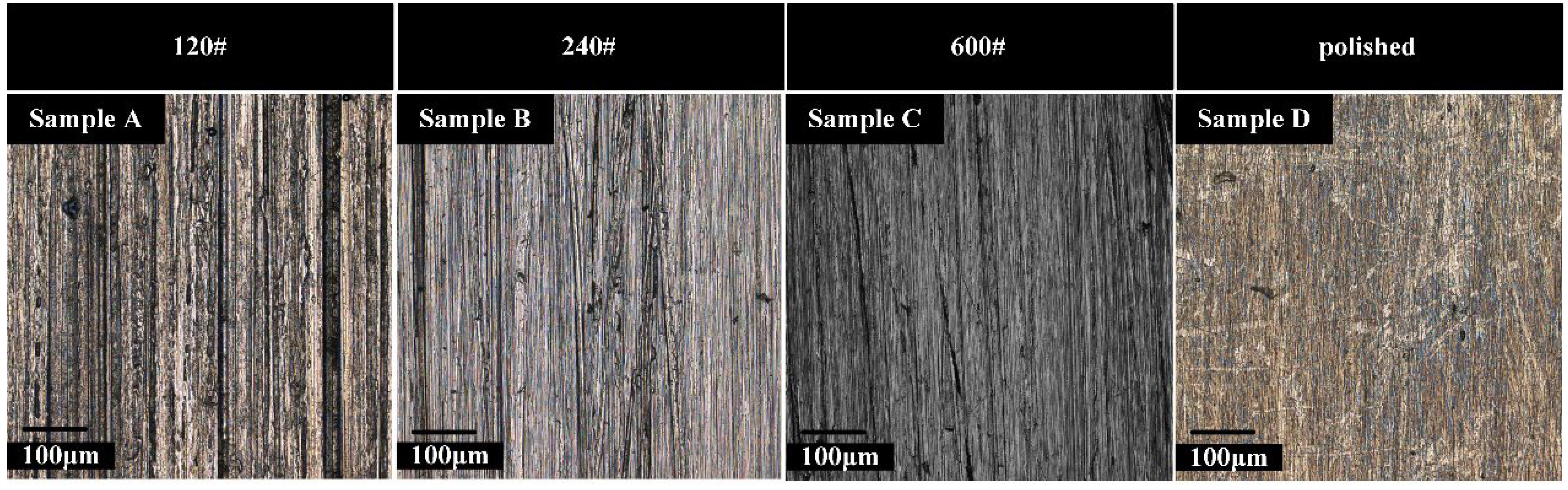
2.1. Preparation of Substrate Samples
2.2. Preparation of Coating on Ti-6Al-4V by PEO Treatment
2.3. Microstructure of Coatings
2.4. Phase Composition of Coatings
2.5. Residual Stresses of Coatings
2.6. Fatigue Properties of Coatings
3. Results and Discussion
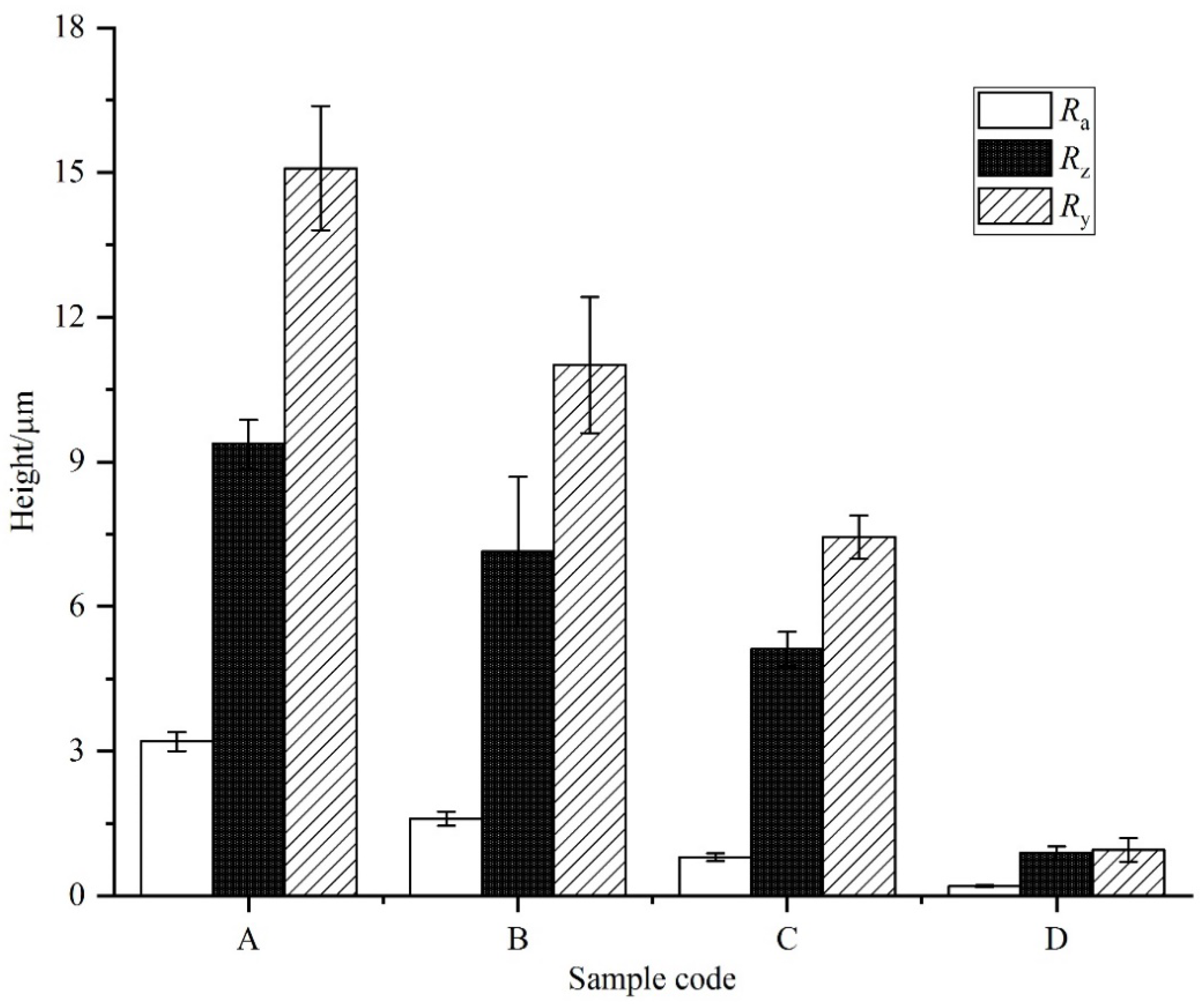
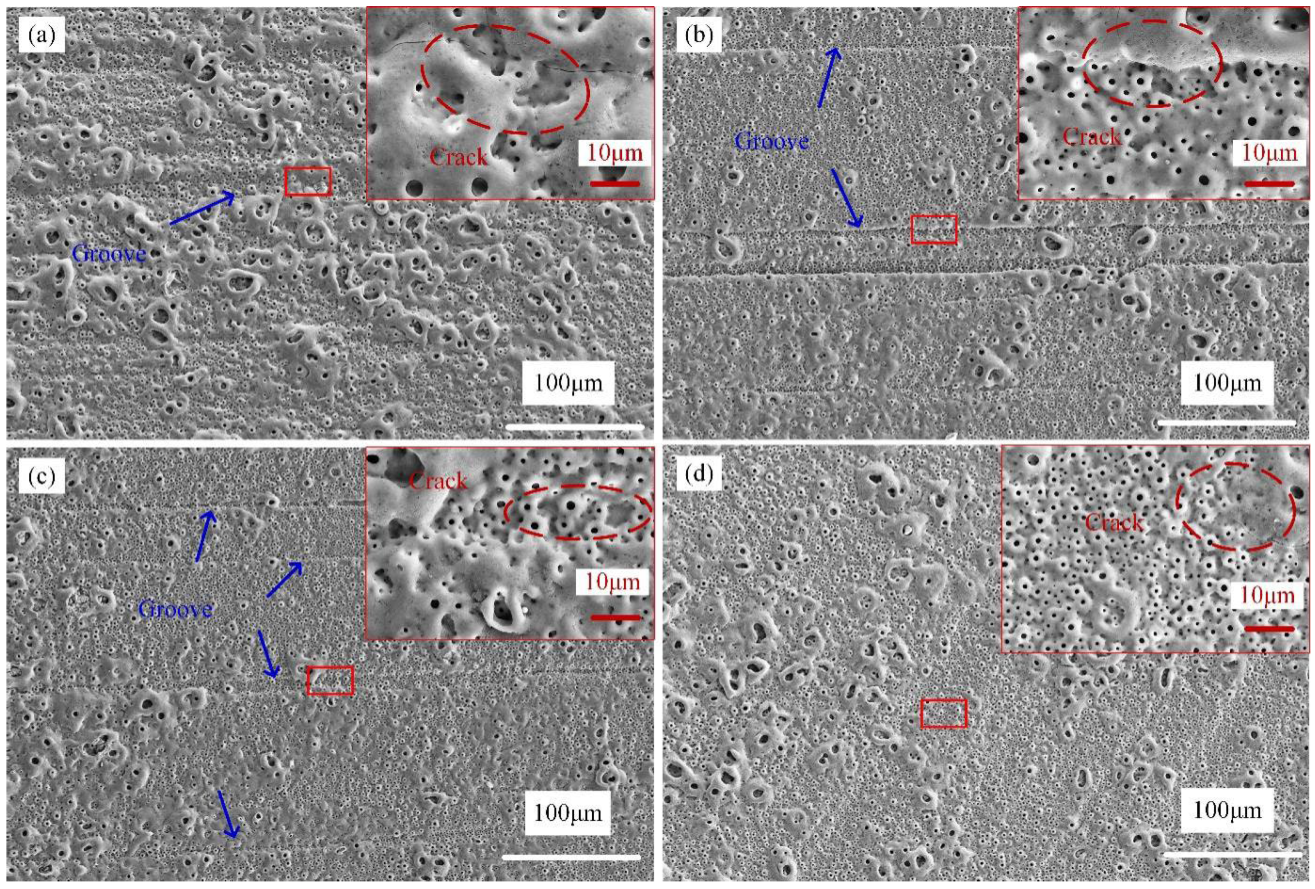
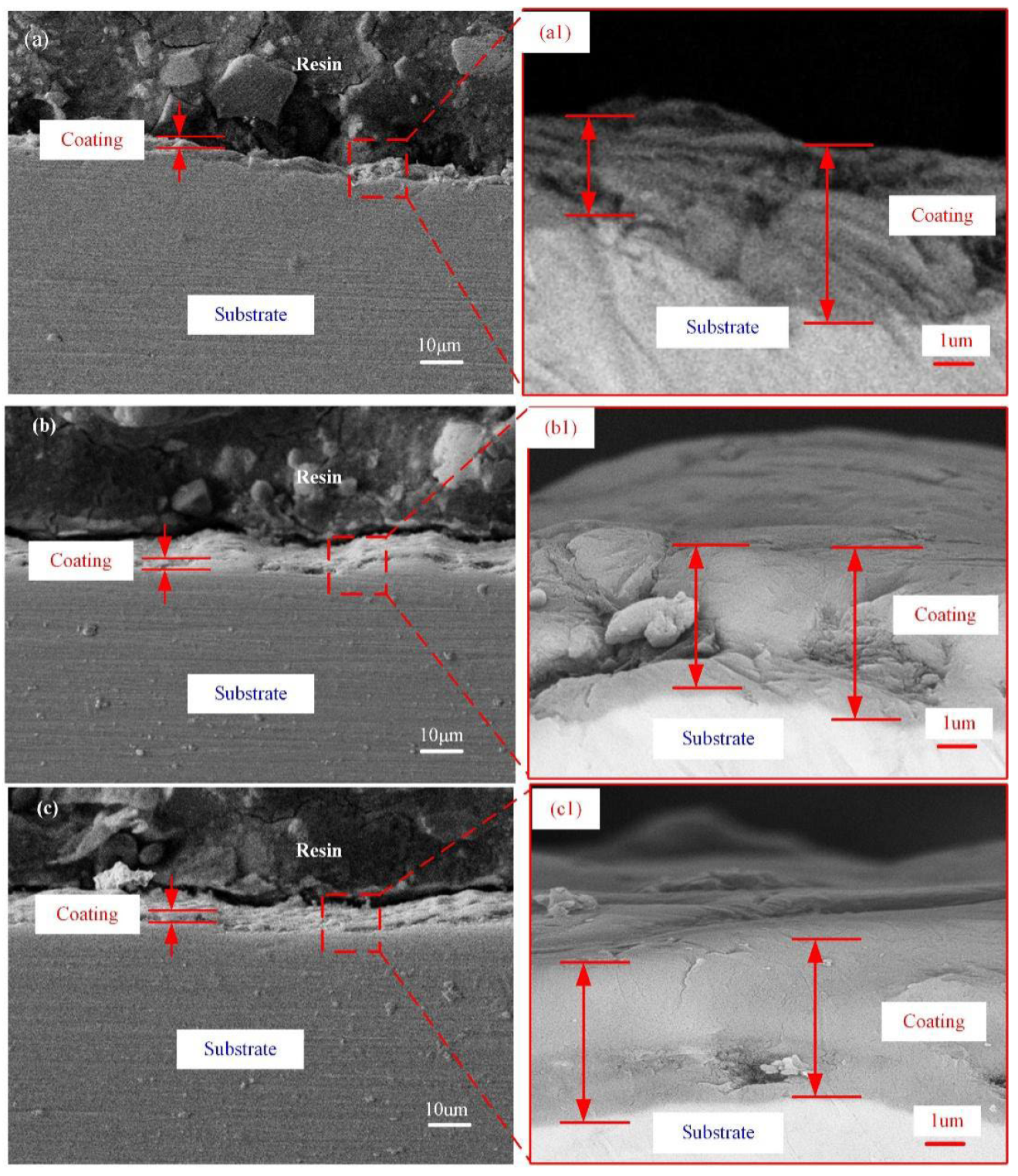
3.1. Microstructure of PEO Coatings
3.2. Residual Stress on the Surface of the Substrate and PEO Coating
3.3. Phase Compositions of PEO Coating Samples
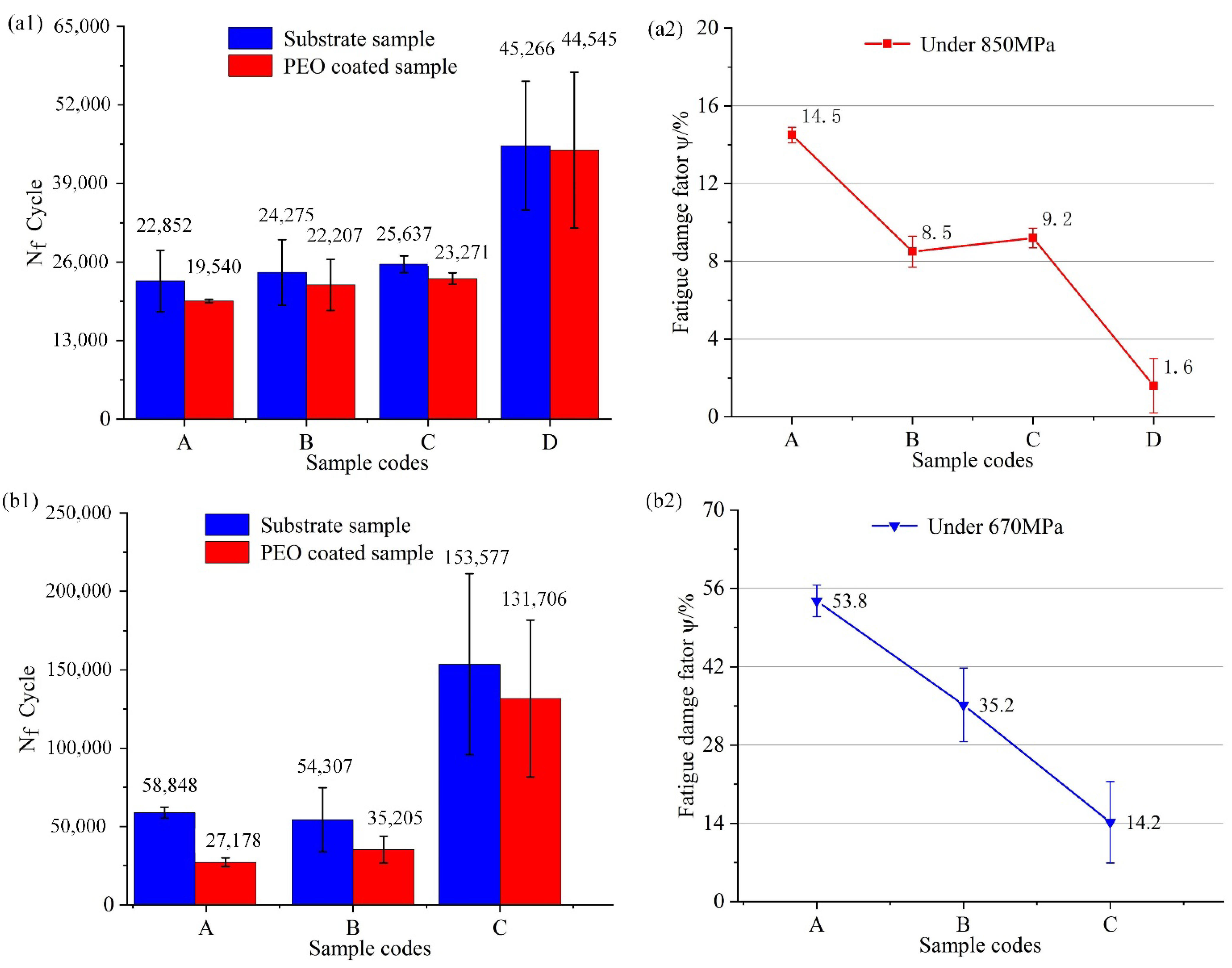
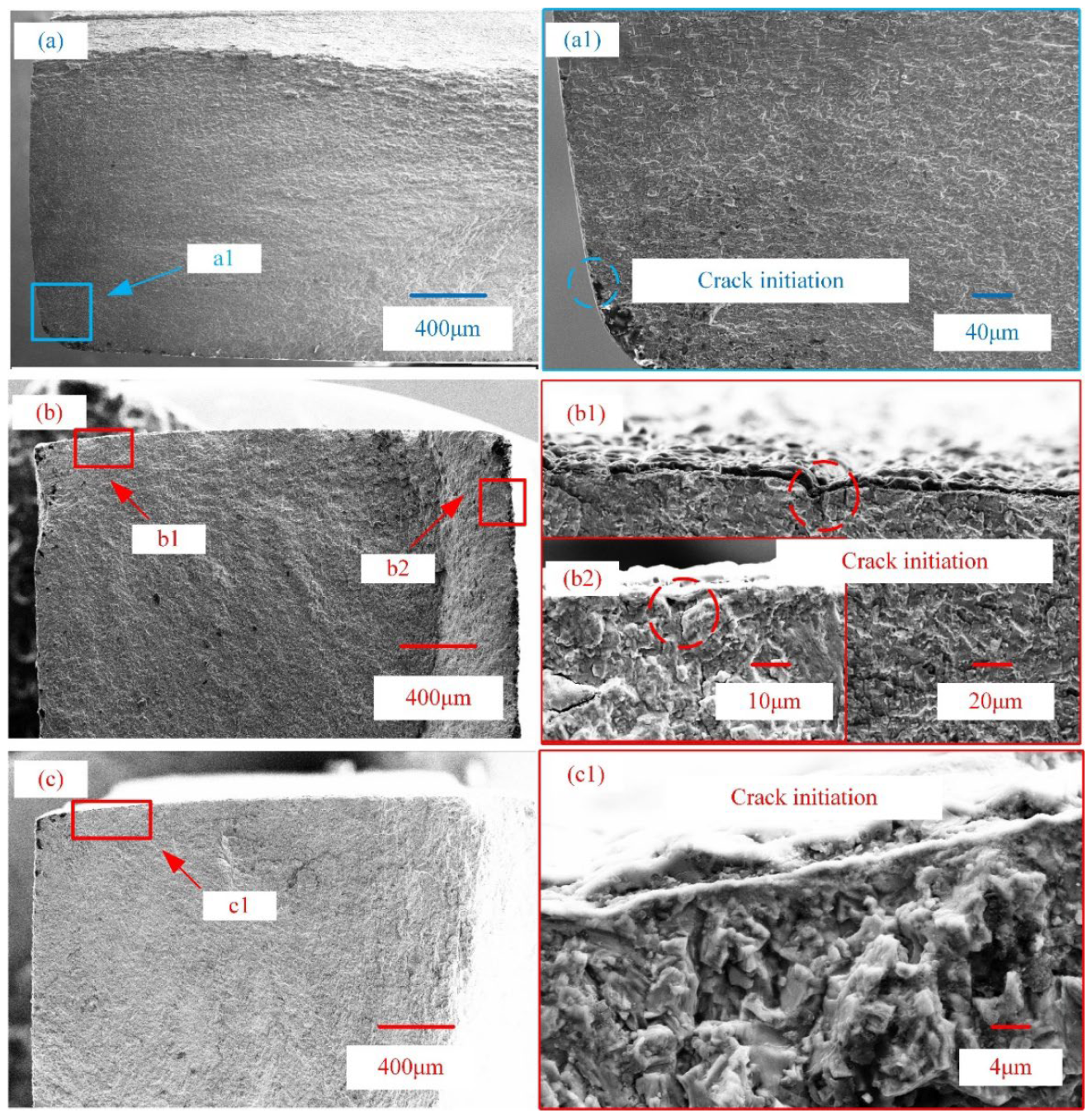
3.4. Fatigue Performance of Substrate and PEO Coatings
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Substrate roughness influences the formation of PEO coatings. Although the growth rate of the rough sample was higher than that of the smooth sample, the defects of the coating become more serious.
- (2)
- Substrate roughness has a small effect on the phase compositions and properties of residual stresses of oxide layers. Although the initial roughness of substrate samples is different, the final roughness of coated samples is more similar.
- (3)
- The fatigue life of the coated Ti-6Al-4V alloy can be improved by reducing the substrate roughness. The fatigue damage of PEO coatings decreases with the surface roughness of substrates decreasing under low cyclic stress, because of the synergistic effect of coating surface defects and coating/substrate interface roughness.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Fan, G. Effects of tool coating materials and coating thickness on cutting temperature distribution with coated tools. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.F.; de Carvalho, S.R.; Silva, S.M.M.D.L.E.; Ferreira, J.R. Thermal analysis in coated cutting tools. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorkyan, E.; Rucki, M.; Panchenko, S.; Sofronov, D.; Chałko, L.; Mazur, T. Effect of SiC Addition to Al2O3 Ceramics Used in Cutting Tools. Materials 2020, 13, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka, A.; Kwatera, A.; Woźnicki, A.; Zasadziński, J. Cemented carbide cutting tools life with nanocrystalline Al2O3 layer deposited by MOCVD. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2016, 16, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonyuk, B.; Apachitei, I.; Duszczyk, J. The effect of oxide coatings on fatigue properties of 7475-T6 aluminium alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2007, 201, 8688–8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, T.; Jiang, B.; Guo, L. Growth, microstructure and mechanical properties of microarc oxidation coatings on titanium alloy in phosphate-containing solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 233, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, N.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Enhanced fatigue performance of modified plasma electrolytic oxidation coated Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Effect of residual stress and gradient nanostructure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 489, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, L.; Duarte, L.T.; da Silva, P.S.C.P.; Bolfarini, C. Fatigue behavior of modified surface of Ti–6Al–7Nb and CP-Ti by micro-arc oxidation. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Shin, K.R.; Hwang, D.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, D.H. Effect of surface roughness on leakage current and corrosion resistance of oxide layer on AZ91 Mg alloy prepared by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6667–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Petrova, R.S.; Gashinski, J.P.; Yang, Z. The effect of surface roughness on PEO-treated Ti-6Al-4V alloy and corrosion resistance. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2017, 325, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanjun, H.; Zhen, C.; Xingguang, L.; Xingguo, F.; Yugang, Z.; Kaifeng, Z.; Hui, Z. Effects of substrate roughness on the vacuum tribological properties of duplex PEO/bonded-MoS2 coatings on Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, H.; He, M.; Wangyang, P.; Gu, L. Effect of micro-groove on microstructure and performance of MAO ceramic coating fabricated on the surface of aluminum alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 777, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashrah, N.; Kamil, M.; Yoon, D.; Kim, Y.; Ko, Y. Formation mechanism of oxide layer on AZ31 Mg alloy subjected to micro-arc oxidation considering surface roughness. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 497, 143772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.B.; Yuan, L.X.; Li, C.Y.; He, D.; Jia, D.W.; Zhang, Y.M. The effect of surface roughness of the substrate on fatigue life of coated aluminum alloy by micro-arc oxidation. J. Alloy Compd. 2018, 765, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Guo, L.; Ouyang, J.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, D. Effect of microarc oxidation coating on fatigue performance of Ti–Al–Zr alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8616–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfi, M.; Bontempi, E.; Roberti, R.; Depero, L. X-ray diffraction Debye Ring Analysis for STress measurement (DRAST): A new method to evaluate residual stresses. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härting, M.; Fritsch, G. Determination of the residual stress state in a natural titanium oxide layer. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dai, W.; Duan, F.; Zhang, Y.; He, D. Fatigue Life Estimation of Medium-Carbon Steel with Different Surface Roughness. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, W.; Deng, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, T. Growth regularity of ceramic coatings formed by microarc oxidation on Al–Cu–Mg alloy. Thin Solid Films 2000, 372, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.B.; Liang, J.; Blawert, C.; Störmer, M.; Dietzel, W. Effect of current density on the microstructure and corrosion behaviour of plasma electrolytic oxidation treated AM50 magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Jing, X. Effect of current density on the structure, composition and corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on Mg–Li alloy. J. Alloy Compd. 2012, 541, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Li, D.; Guo, C.; Jiang, G.; Shen, D.; Yu, S.; Nash, P. Micro-structures and growth mechanisms of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on aluminium at different current densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 321, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Yi, D. Theoretical study of mechanical and thermodynamic properties of titanium oxides Ti x O y. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 213, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apachitei, I.; Lonyuk, B.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.; Zhou, J.; Duszczyk, J. Fatigue response of porous coated titanium biomedical alloys. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xi, Y.; Gao, K.; Yang, H.; Pang, X.; Yang, X.; Volinsky, A.A. Brittle coating effects on fatigue cracks behavior in Ti alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 125, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; He, D.; Jia, D.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Z. Fatigue life of micro-arc oxidation coated AA2024-T3 and AA7075-T6 alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, A.; Apachitei, I.; Riemslag, A.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.; Duszczyk, J. In vitro fatigue behavior of surface oxidized Ti35Zr10Nb biomedical alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Miyashita, Y.; Mutoh, Y.; Koike, T. Effect of anodized layer thickness on fatigue behavior of magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 474, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| PEO Sample | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness (µm) | 3.96 ± 1.09 | 3.65 ± 0.80 | 3.80 ± 0.54 | 3.60 ± 0.50 |
| Td (%) | 44.0% | 24.3% | 18.4% | 7.7% |
| Porosity (%) | 5.97 | 5.20 | 4.43 | 4.96 |
| Mean pore diameter (µm) | 0.907 | 0.850 | 0.865 | 0.808 |
| Roughness (µm) | 1.32 ± 0.13 µm | 1.04 ± 0.10 µm | 1.05 ± 0.10 µm | 1.18 ± 0.12 µm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, W.; Tian, Y. Effects of Substrate Roughness on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 4256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124256
Xi F, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Dai W, Tian Y. Effects of Substrate Roughness on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials. 2022; 15(12):4256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124256
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Fangquan, Yong Huang, Yahui Zhao, Yang Liu, Weibing Dai, and Yanzhong Tian. 2022. "Effects of Substrate Roughness on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy" Materials 15, no. 12: 4256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124256
APA StyleXi, F., Huang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, Y., Dai, W., & Tian, Y. (2022). Effects of Substrate Roughness on Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation-Coated Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials, 15(12), 4256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15124256








