Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Produced Using Sol-Gel Method for Treatment of Heavy Metals in Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization Techniques
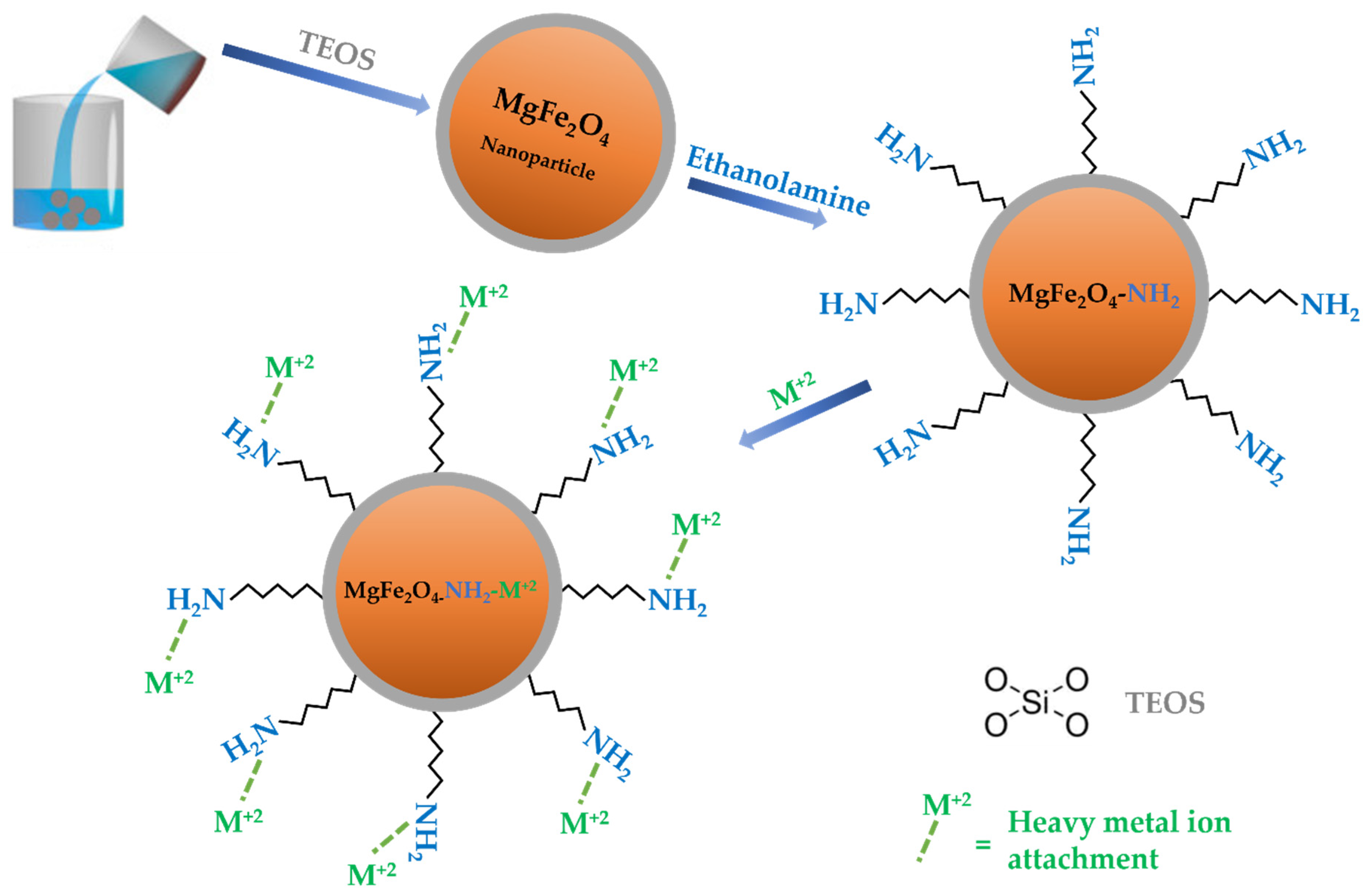
2.3. Amine Functionalization of Ferrite Nanoparticles
2.4. Adsorption of Heavy Metals
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metal Ion Adsorption Mechanism
3.2. FTIR and TGA Analysis of Amine-Functionalized Adsorbent
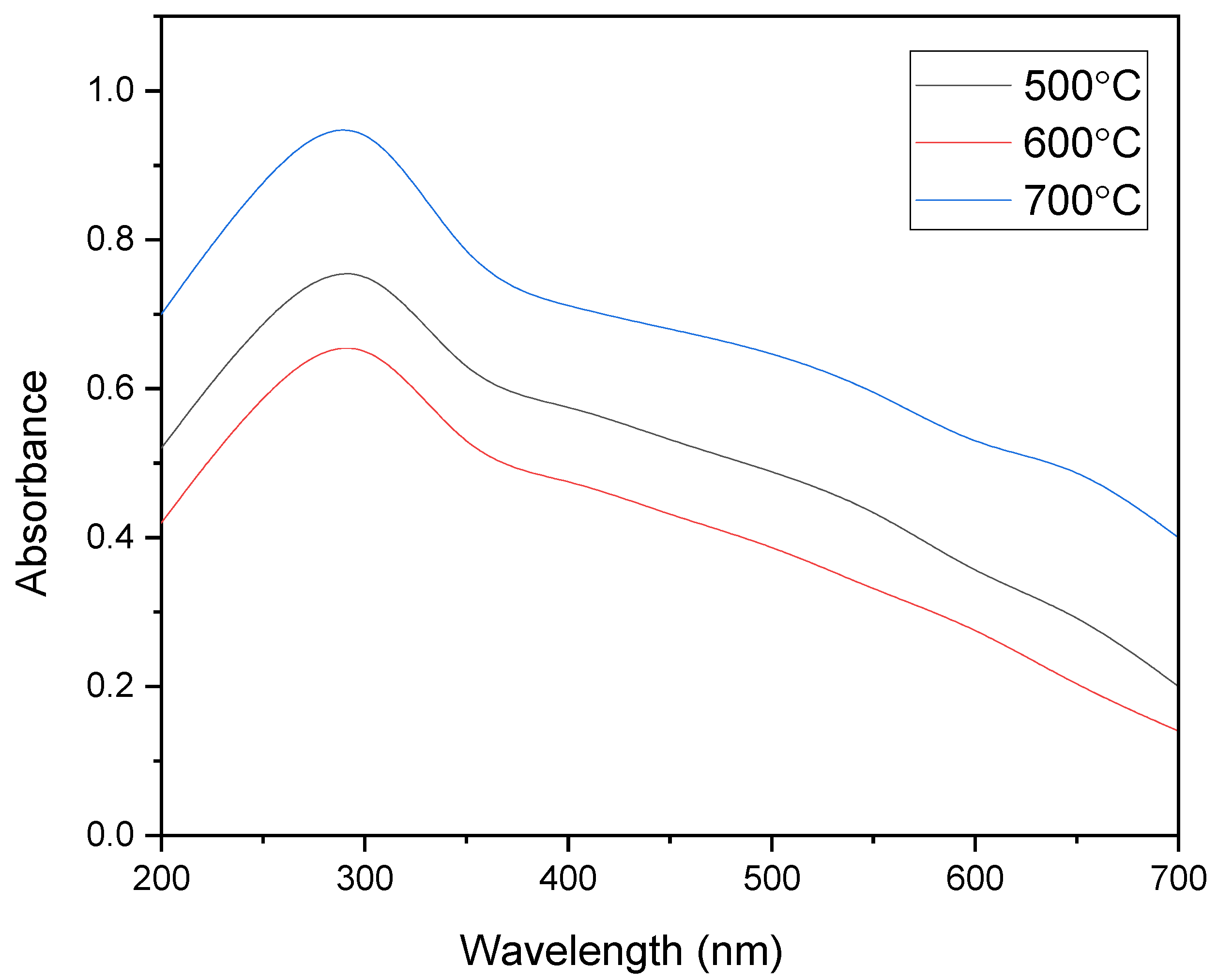
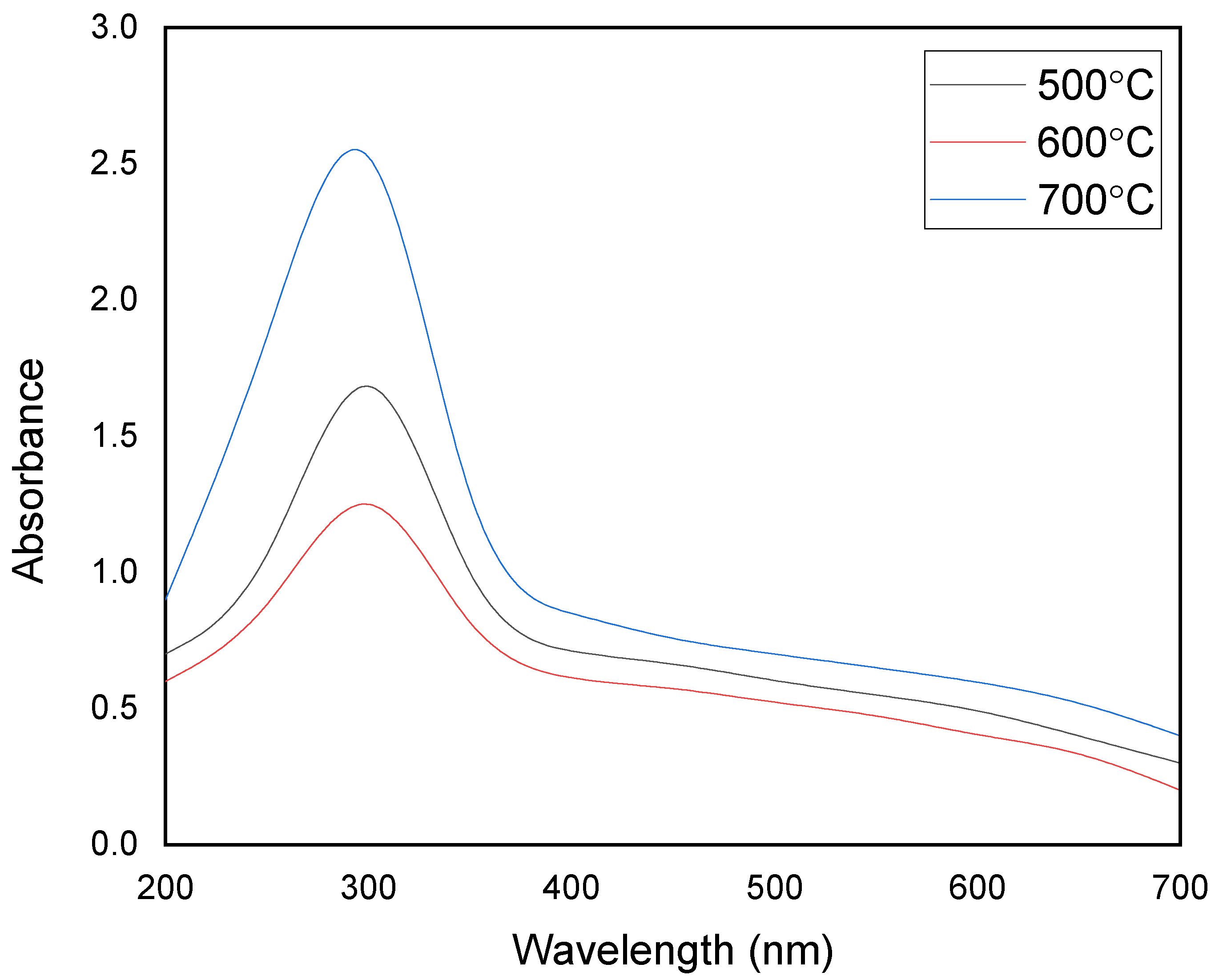
3.3. UV-Visible Analysis
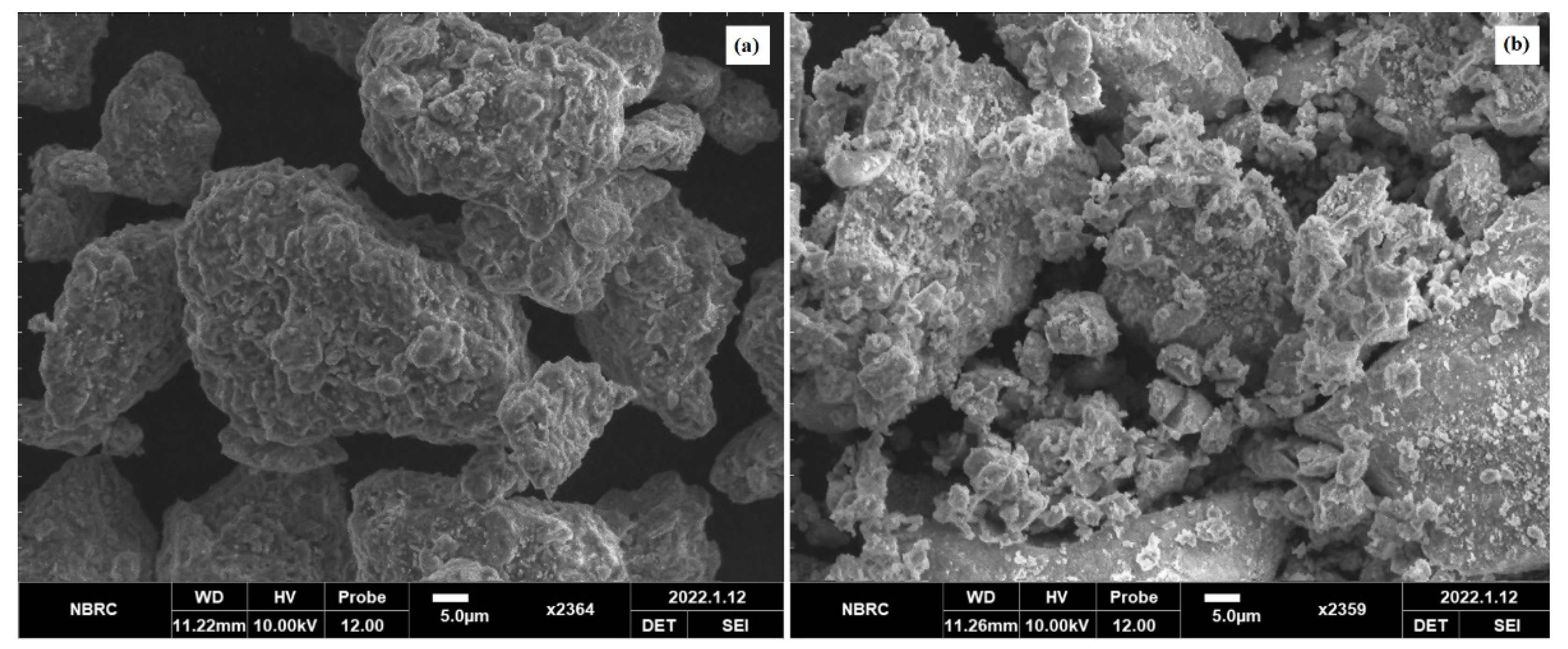
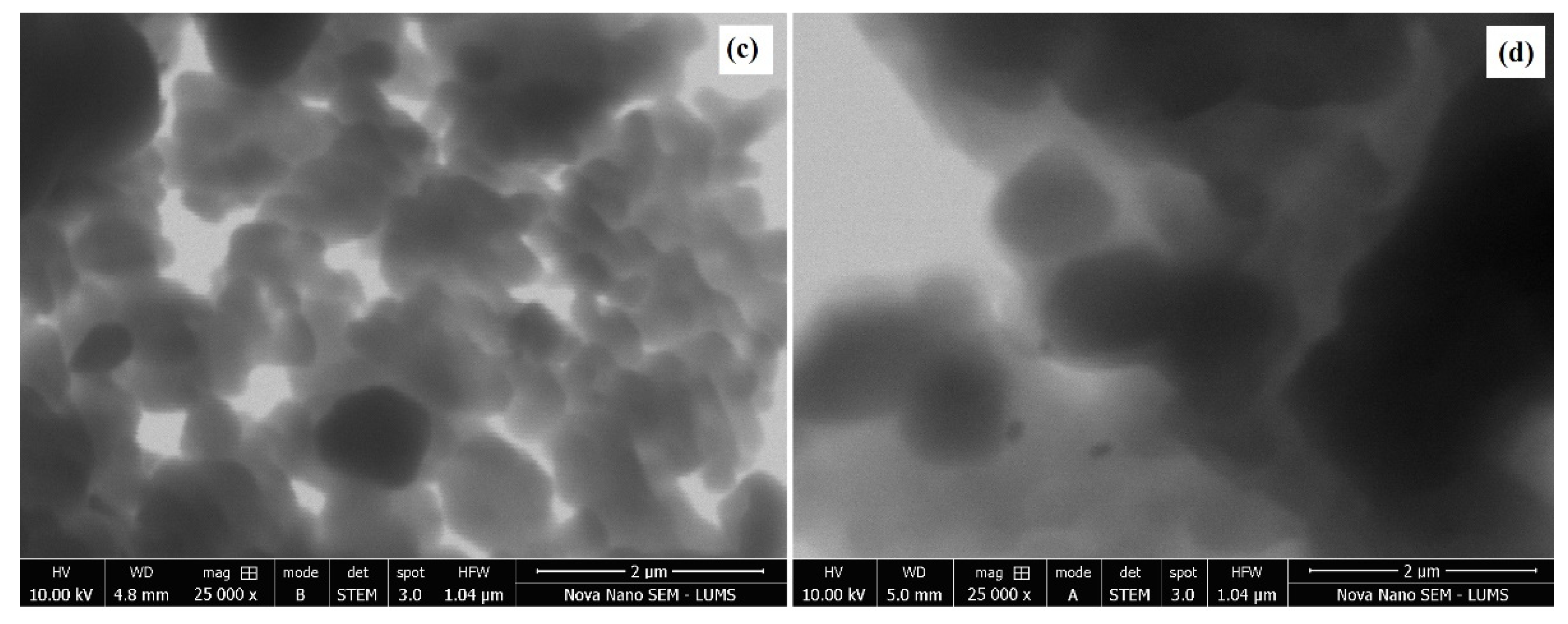
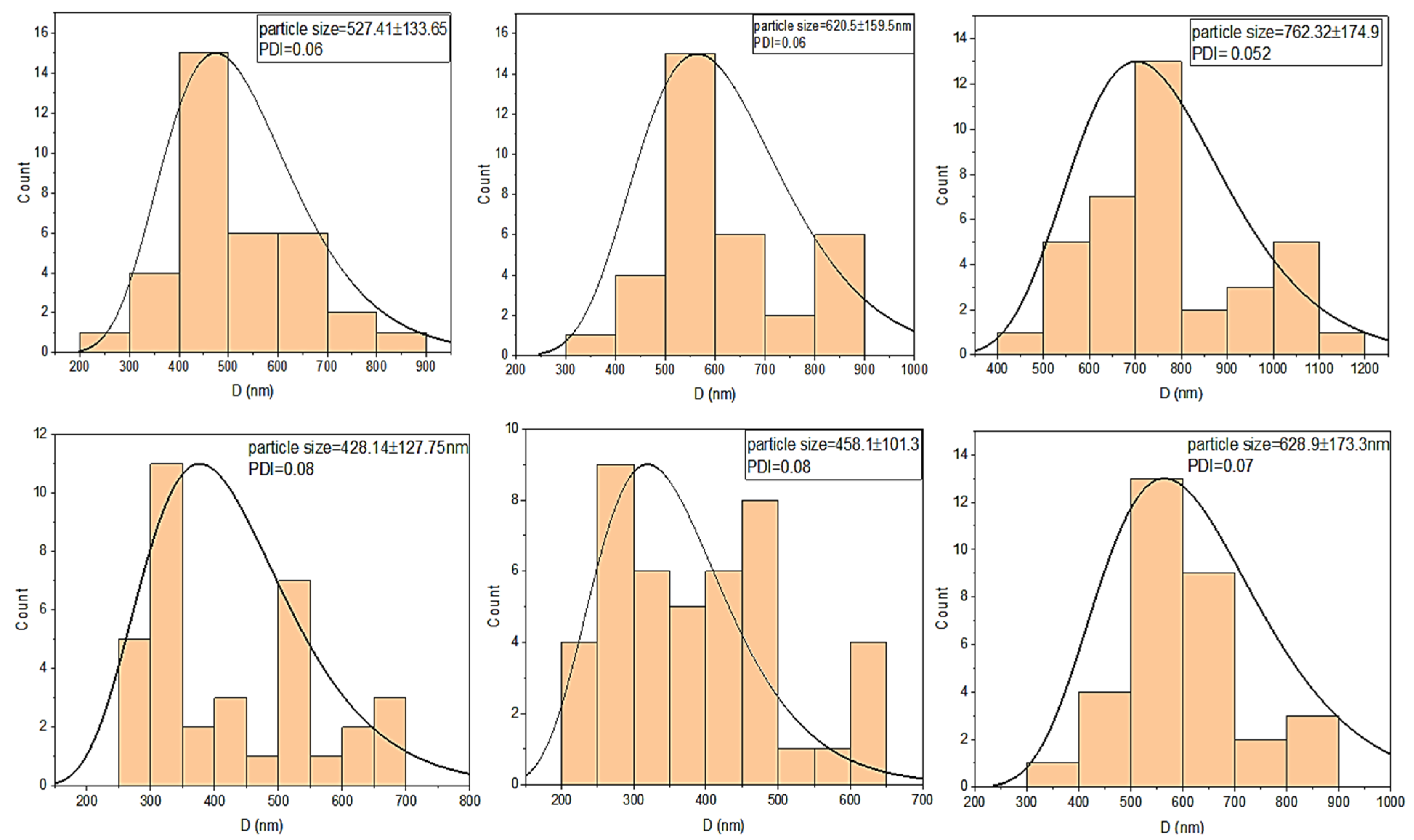
4. Morphology and Size Distribution
4.1. Adsorption Kinetics
4.2. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics
4.3. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics
4.4. Pseudo Models for Adsorption of Cu2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
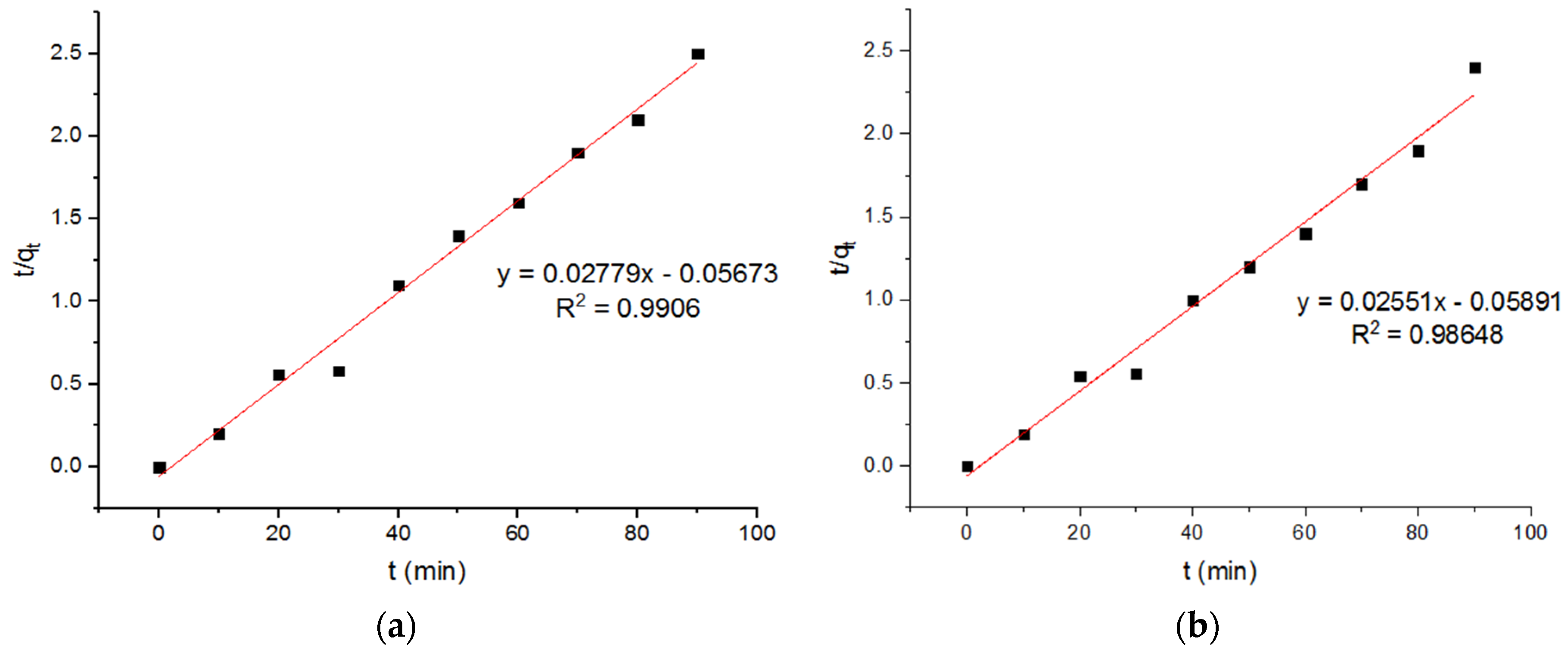
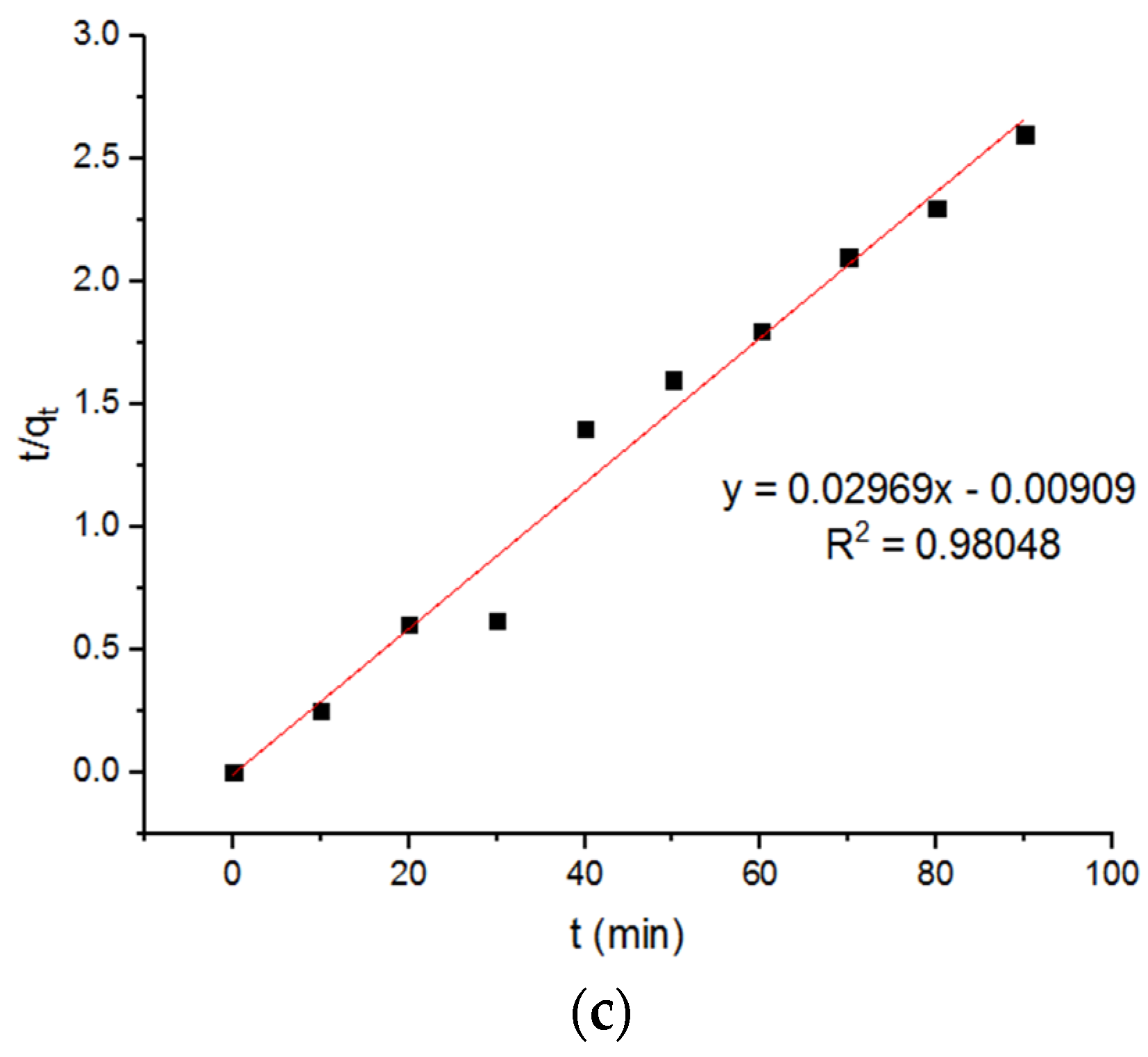
4.5. Pseudo Models for Adsorption of Pb2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
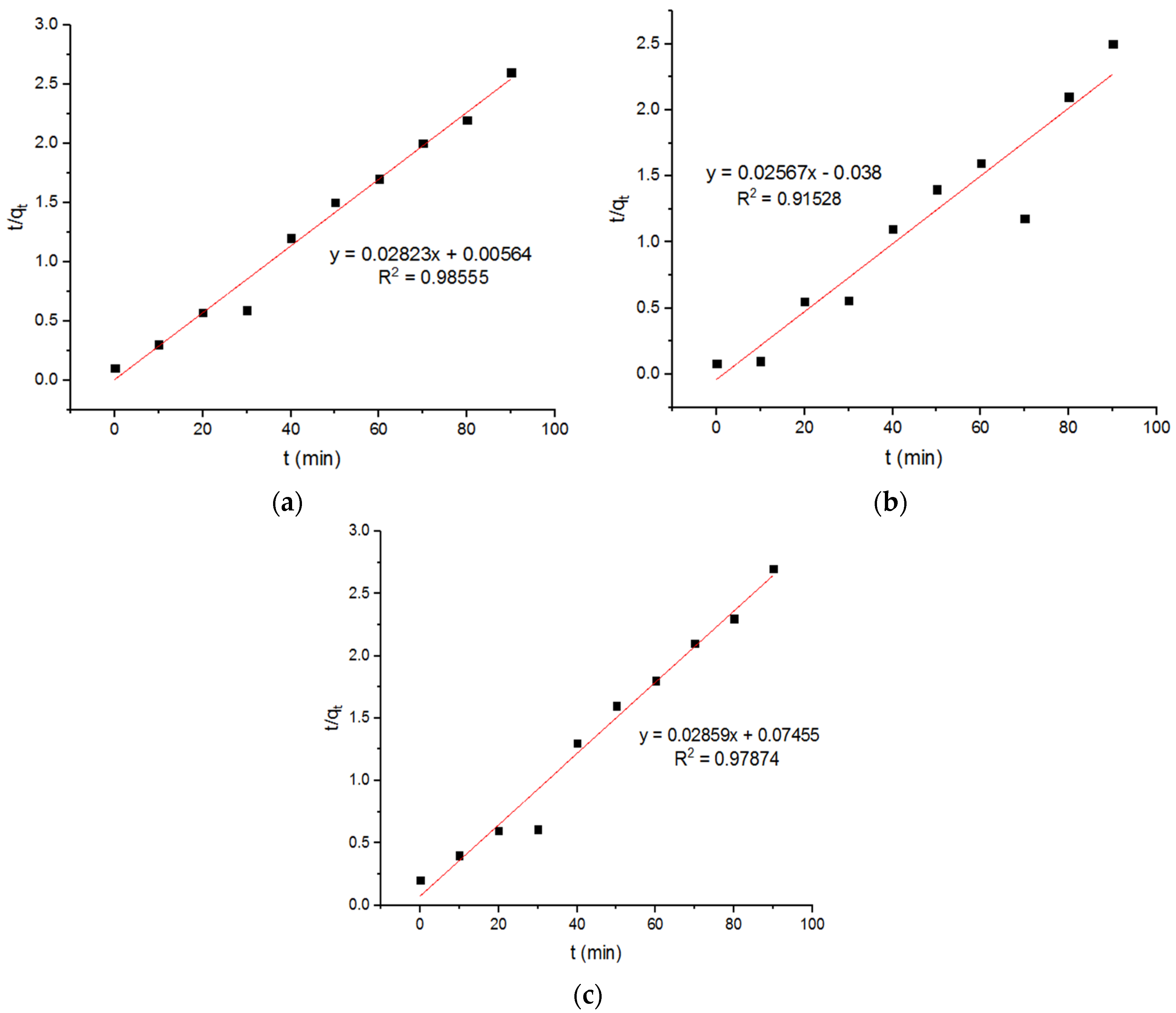
4.6. Pseudo Models for Adsorption of Zn2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
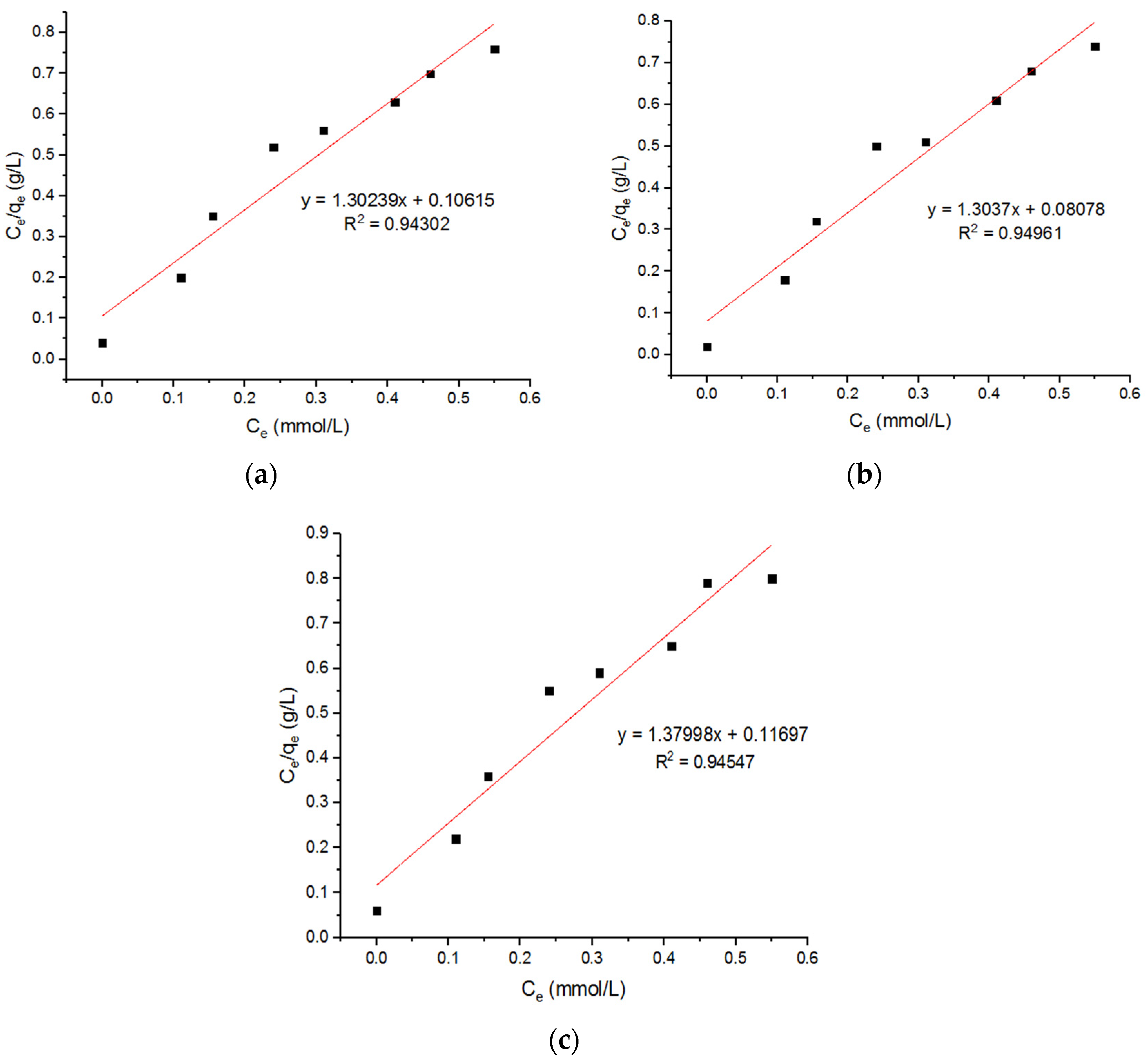
5. Adsorption Isotherms
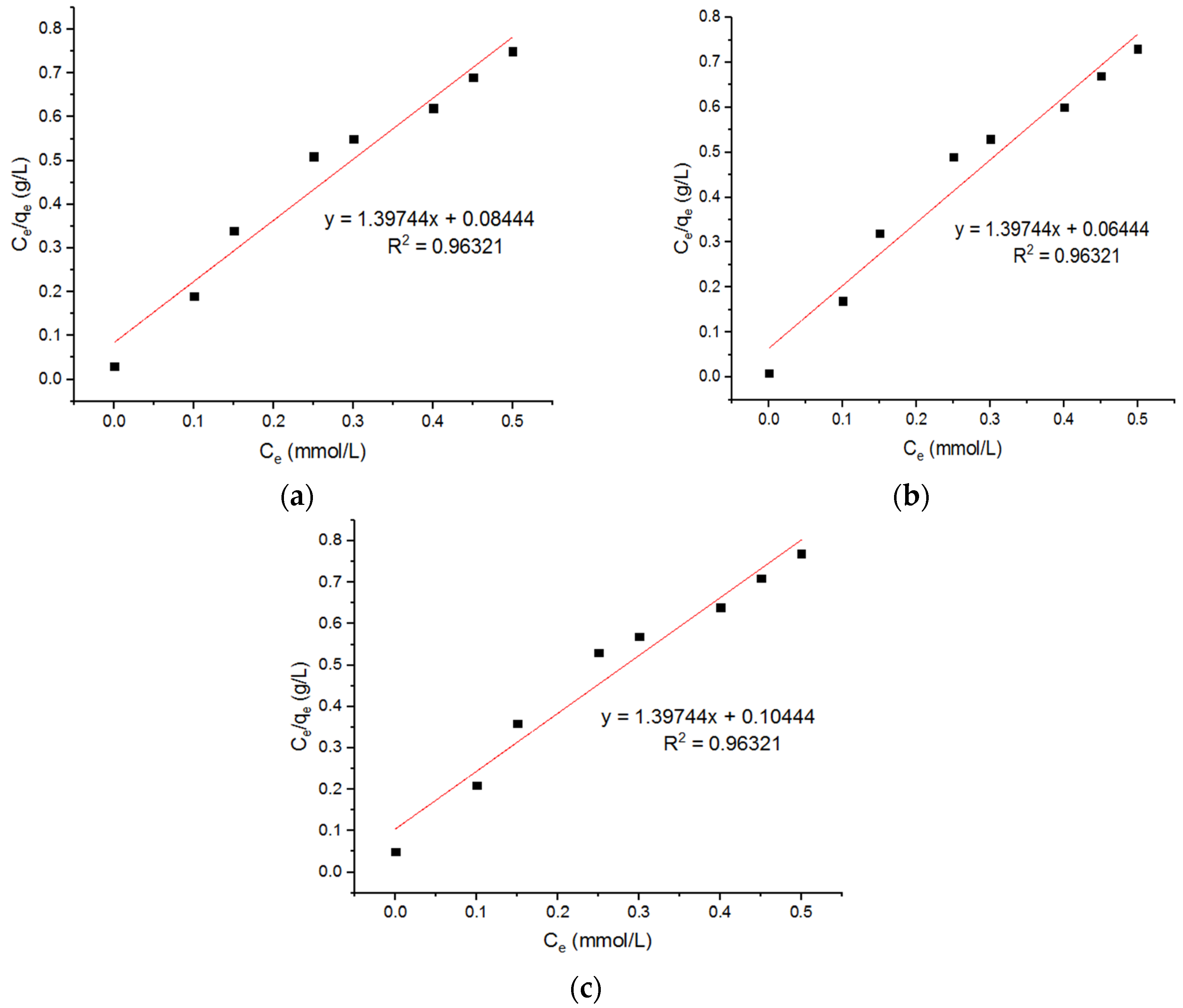
5.1. Langmuir Model
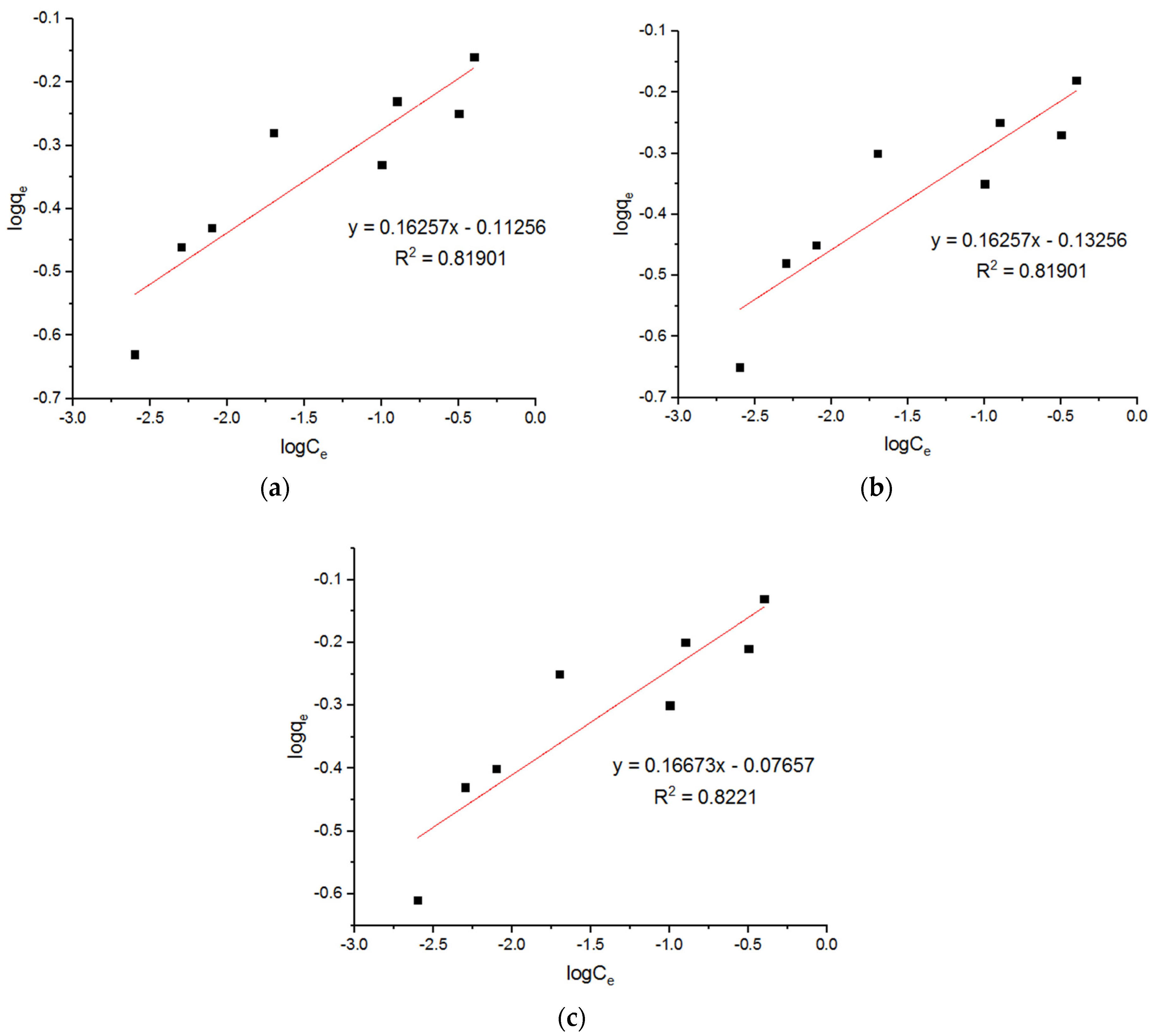
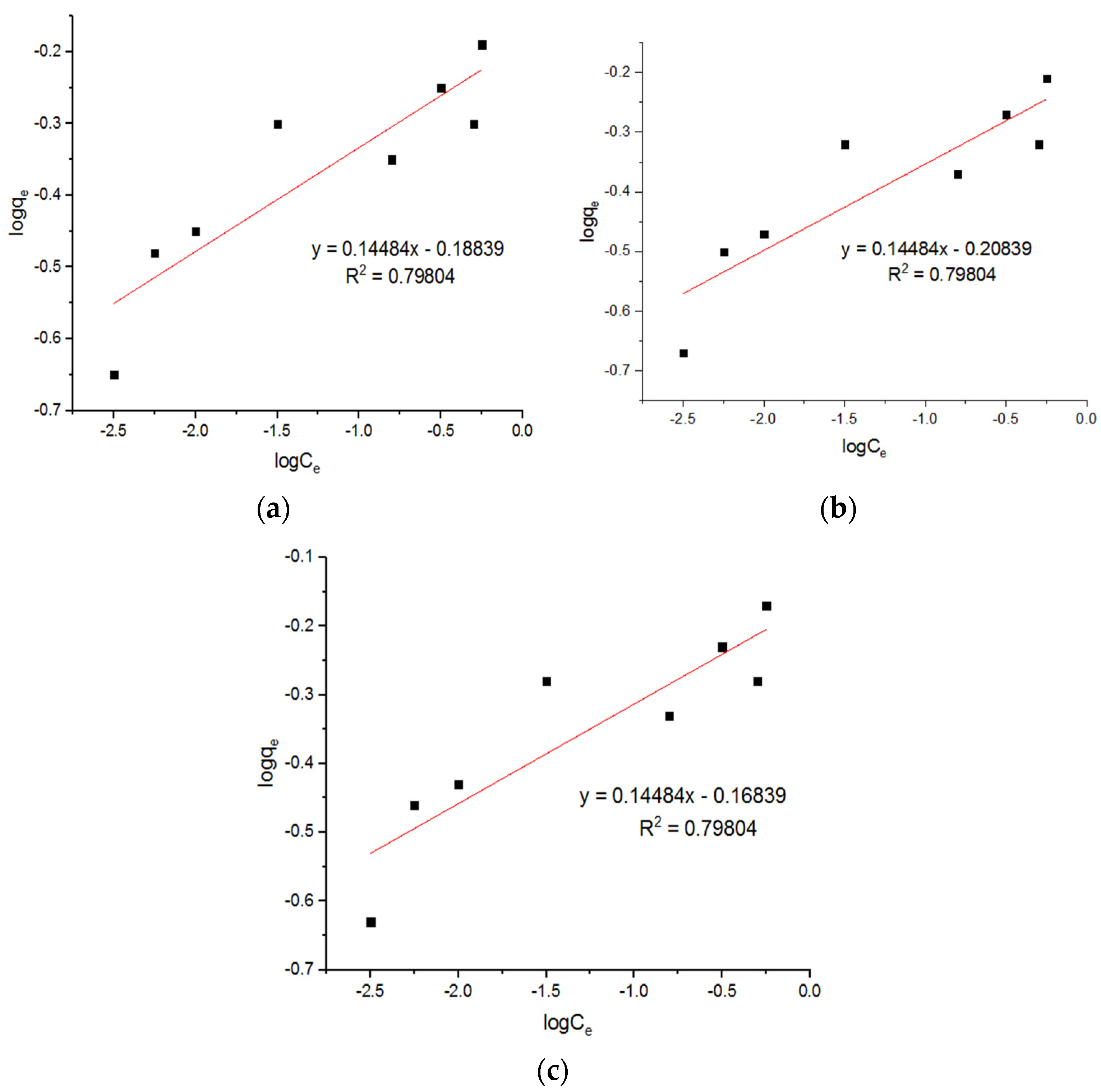
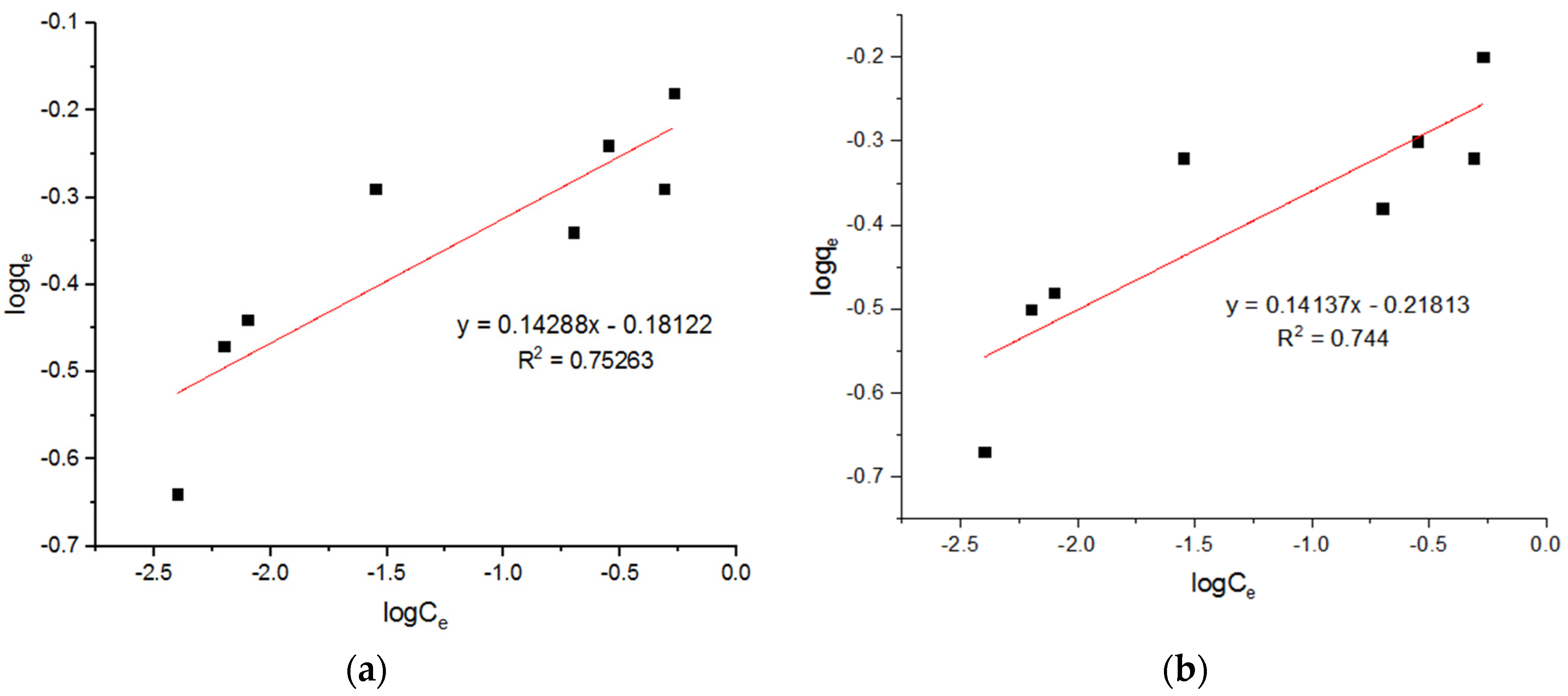
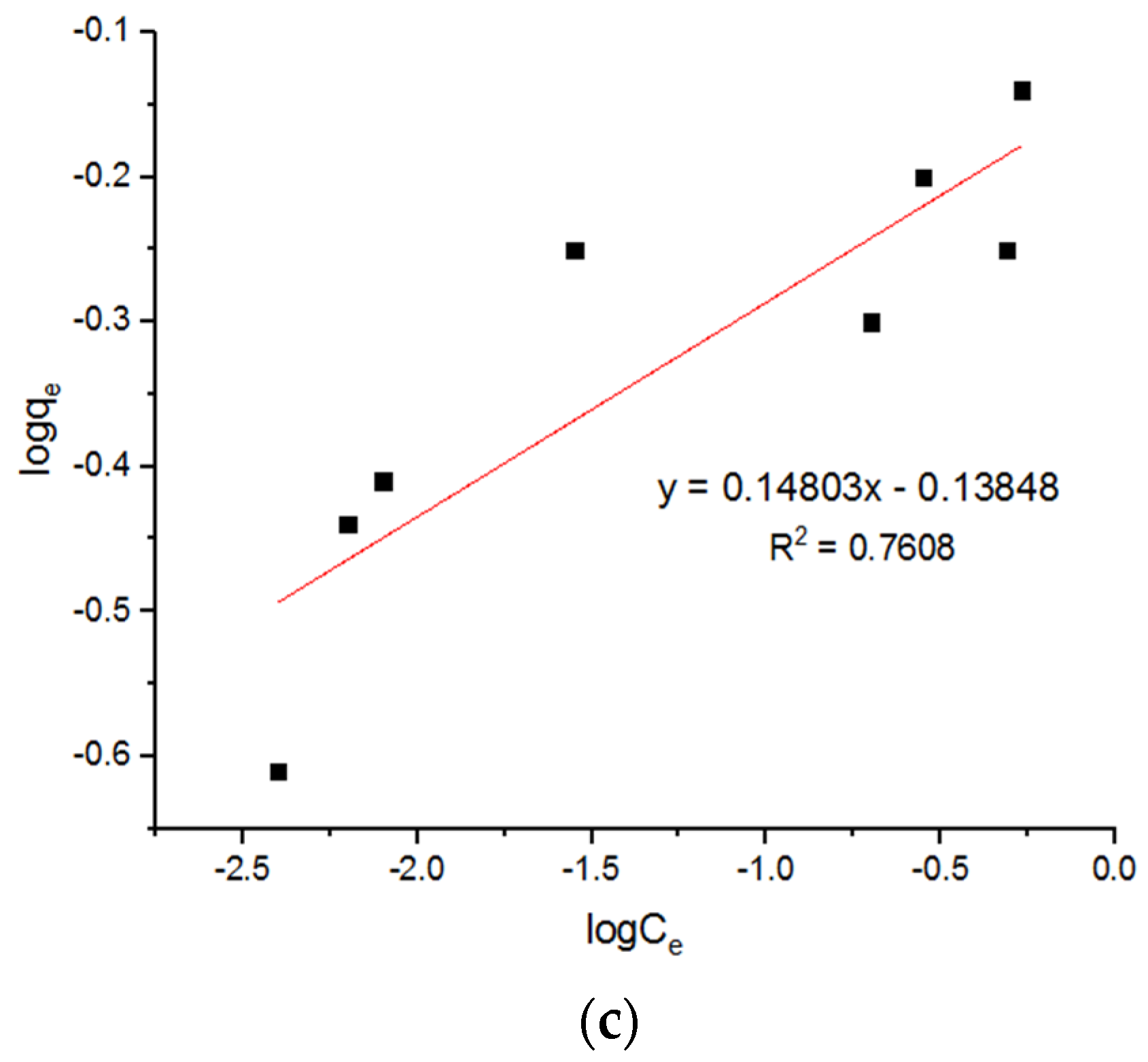
5.2. Freundlich Model
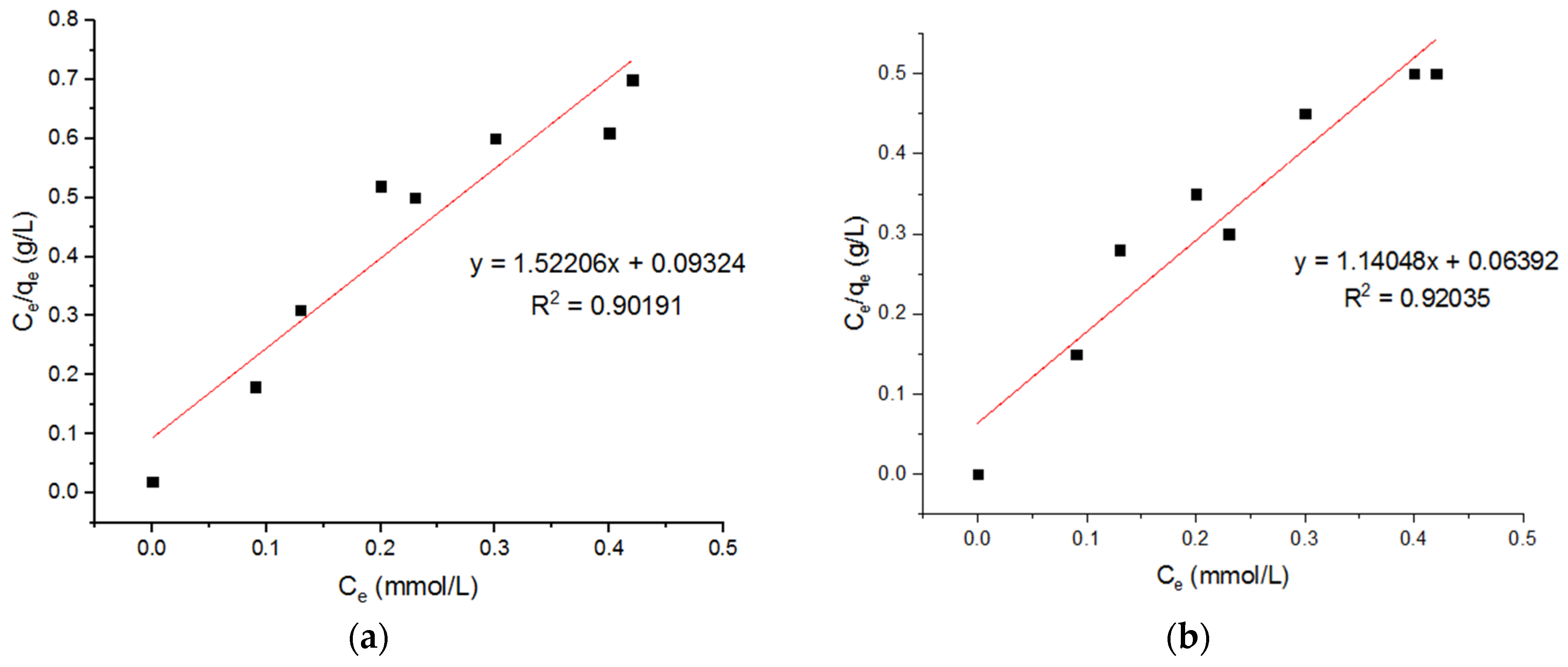
5.3. Isotherm Models for Cu2+ Adsorption onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
5.4. Isotherm Models for Pb2+ Adsorption onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
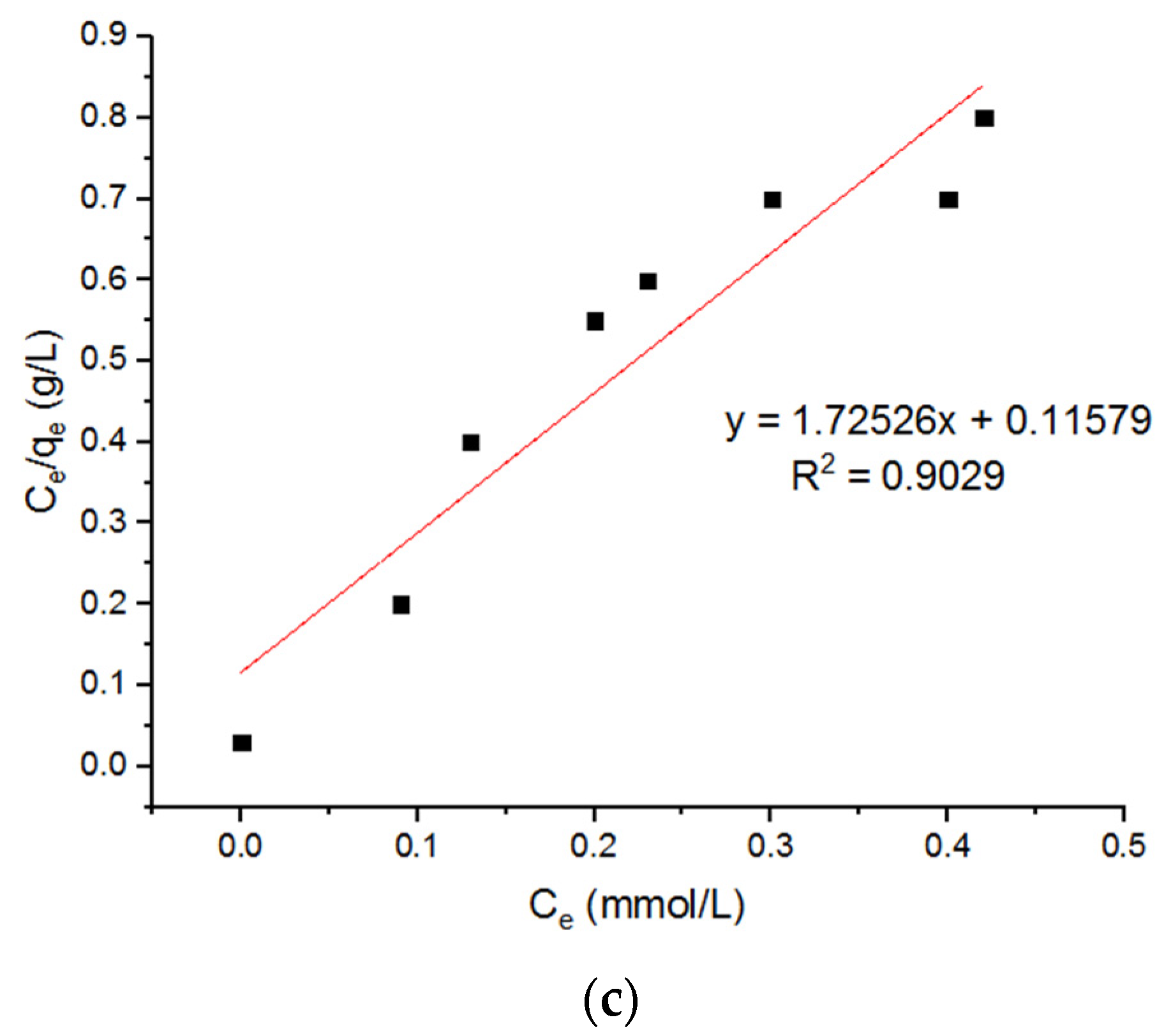
5.5. Isotherm Models for Zn2+ Adsorption onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles
| Adsorbent | qm (mg/g) | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb2+ | Cu2+ | ||
| Magnetic porous ferrospinel MnFe2O4 | 69 | 37 | [27] |
| EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 | 12.5 | 44 | [34] |
| Fe3O4@2,3-diaminophenol and formaldehyde nanorods | 83 | - | [35] |
| Chitosan-coated bentonite beads | - | 12 | [36] |
| Fe3O4-NH2 nanoparticles | 40 | - | [6] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 nanoparticles | 76 | - | [37] |
| Mg0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4 | 57.7 | - | [24] |
| Fe3O4/montmorillonite | 263.15 | 70.92 | [31] |
| PMMA-gft-Alg/Fe3O4 | 62.5 | 35.71 | [32] |
| Co0.6Fe2.4O4 | 44.58 to 70.22 | - | [29] |
| NMag–CS | 114.9 | 123.4 | [33] |
| Fe3O4 | 47.62 to 166.67 | 19.61 to 37.04 | [30] |
| MgFe2O4-NH2 nanoparticles | 145.04 | 55.7 | Present work |
6. Removal Efficiency
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. CHAPTER 1 Contamination of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Media: Transport, Toxicity and Technologies for Remediation. In Heavy Metals in Water: Presence, Removal and Safety; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Jun, B.-M.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, C.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of heavy metals from water sources in the developing world using low-cost materials: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, J.; Uhlik, O.; Viktorova, J.; Macek, T. Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals: A Promising Tool for Clean-Up of Polluted Environment? Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tandy, S.; Bossart, K.; Mueller, R.; Ritschel, J.; Hauser, L.; Schulin, R.; Nowack, B. Extraction of Heavy Metals from Soils Using Biodegradable Chelating Agents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Chen, M.; Hao, Y. High efficient removal of Pb (II) by amino-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nano-particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanets, A.; Srivastava, V.; Roshchina, M.Y.; Sillanpää, M.; Prozorovich, V.; Pankov, V. Magnesium ferrite nanoparticles as a magnetic sorbent for the removal of Mn2+, Co2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 9097–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G. Extraction procedures for the determination of heavy metals in contaminated soil and sediment. Talanta 1998, 46, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xu, K. Chapter 8—Physicochemical technologies for HRPs and risk control. In High-Risk Pollutants in Wastewater; Ren, H., Zhang, X., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 169–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, R. Simultaneous fluorescence response and adsorption of functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles to Cd2+, Zn2+ and Cu2+. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 459, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pastora, J.; Bringas, E.; Ortiz, I. Recent progress and future challenges on the use of high performance magnetic nano-adsorbents in environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, A.; Priyadharsini, P.; Chandrasekaran, G. Sol–gel route of synthesis of nanoparticles of MgFe2O4 and XRD, FTIR and VSM study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2774–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.; El-Shaarawy, M.; Shash, N.; Maklad, M.; Afifi, F. Controlling the composition, microstructure, electrical and magnetic properties of LiFe5O8 powders synthesized by sol gel auto-combustion method using urea as a fuel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Li, X.; Xing, M.; Fang, W.; Wu, D. Removal of phosphate from water by amine-functionalized copper ferrite chelated with La (III). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonkumwong, J.; Ananta, S.; Srisombat, L. Effective removal of lead (II) from wastewater by amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47382–47393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Gaur, R.; Yadav, M.; Goswami, A.; Zbořil, R.; Gawande, M.B. An efficient copper-based magnetic nanocatalyst for the fixation of carbon dioxide at atmospheric pressure. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaz, F.; Dubey, H.K.; Kumari, C.; Lahiri, P. Structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 nanopowder synthesized via co-precipitation route. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliyan, N.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Akbari, S. The effect of post-calcination on cation distributions and magnetic properties of the coprecipitated MgFe2O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Puerto, M.C.; Warudkar, S.; Buehler, J.; Biswal, S.L. Recyclable amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for efficient demulsification of crude oil-in-water emulsions. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oddo, E.; Pesce, R.M.; Derudi, M.; Magagnin, L. Amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for CO2 capture. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2021, 12, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, T.R.; Prelot, B. Adsorption processes for the removal of contaminants from wastewater: The perspective role of nanomaterials and nanotechnology. In Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 161–222. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.H.; Dong, J.; Liu, Z.L.; Liu, Y.P.; Wu, D.Y. Degradation of Dyes by H2O2 with Activated Charcoal Supported MgFe2O4 under Microwave Irradiation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1004–1005, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.V.; Quang, D.V.; Nguyen Thi, H.P.; Truong, T.N.; La, D.D. Effective Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Media by a New Design of Cu–Mg Binary Ferrite. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7298–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Sultan, N.; Ali, M.; Naz, M.Y.; AbdEl-Salam, N.M.; Ibrahim, K.A. Thermochemical conversion of waste glass and mollusk shells into an absorbent material for separation of direct blue 15 azo dye from industrial wastewater. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18114–18122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Ying, D.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J. Comparative and competitive adsorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) using tetraethylenepentamine modified chitosan/CoFe2O4 particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Li, N.; Feng, J.; Luan, T.; Wen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cu (II) from aqueous solution on magnetic porous ferrospinel MnFe2O4. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Wei, W.; Shuo, L.; Song, M.H.; Yun, Y.S. Fabrication of Stable and Regenerable Amine Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Potential Material for Pt(IV) Recovery from Acidic Solutions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18650–18659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Tang, R.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Zeng, S.; Sun, D. Effective removal of Pb(II) using magnetic Co0.6Fe2.4O4 micro-particles as the adsorbent: Synthesis and study on the kinetic and thermodynamic behaviors for its adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamez, C.; Hernandez, R.; Parsons, J.G. Removal of Cu (II) and Pb (II) from aqueous solution using engineered iron oxide nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalantari, K.; Ahmad, M.B.; Fard Masoumi, H.R.; Shameli, K.; Basri, M.; Khandanlou, R. Rapid and high capacity adsorption of heavy metals by Fe3O4/montmorillonite nanocomposite using response surface methodology: Preparation, characterization, optimization, equilibrium isotherms, and adsorption kinetics study. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 49, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, A.; Ahmad, R.; Hasan, I. Poly (methyl methacrylate)-grafted alginate/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Synthesis and its application for the removal of heavy metal ions. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 19820–19833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.R.; El-Sherif, I.Y.; Tawfik, M.E.; El-Wakeel, S.T.; El-Shahat, M.F. Preparation and adsorption properties of nano magnetite chitosan films for heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 80, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Abbood, H.A.; He, F.; Peng, H.; Huang, K. Magnetic EDTA-modified chitosan/SiO2/Fe3O4 adsorbent: Preparation, characterization, and application in heavy metal adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Yoon, M. Core–shell ferromagnetic nanorod based on amine polymer composite (Fe3O4@ DAPF) for fast removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solutions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25362–25372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, N.; Zhang, D. Poly (N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) modification of activated carbon for copper ions removal. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@ SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




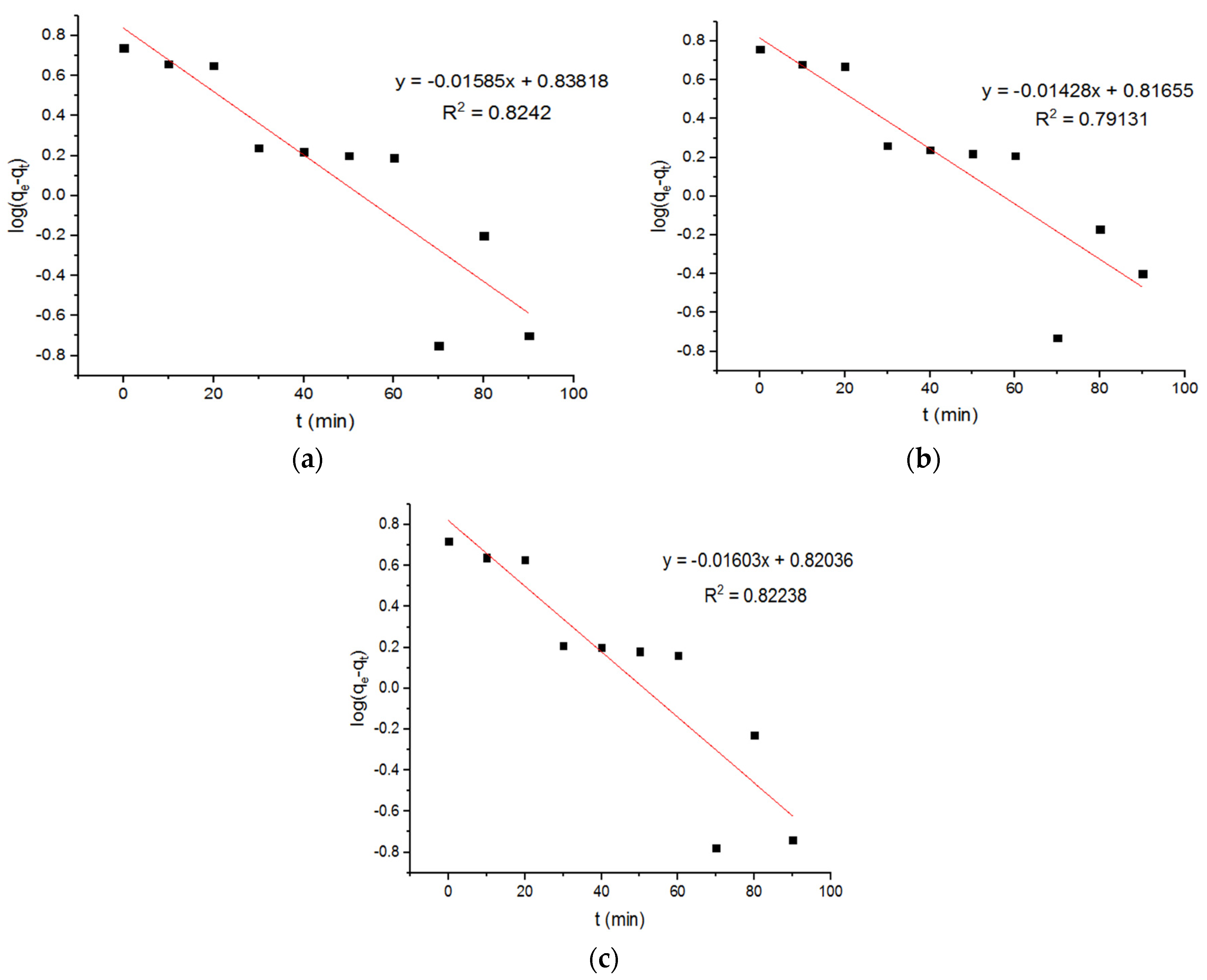
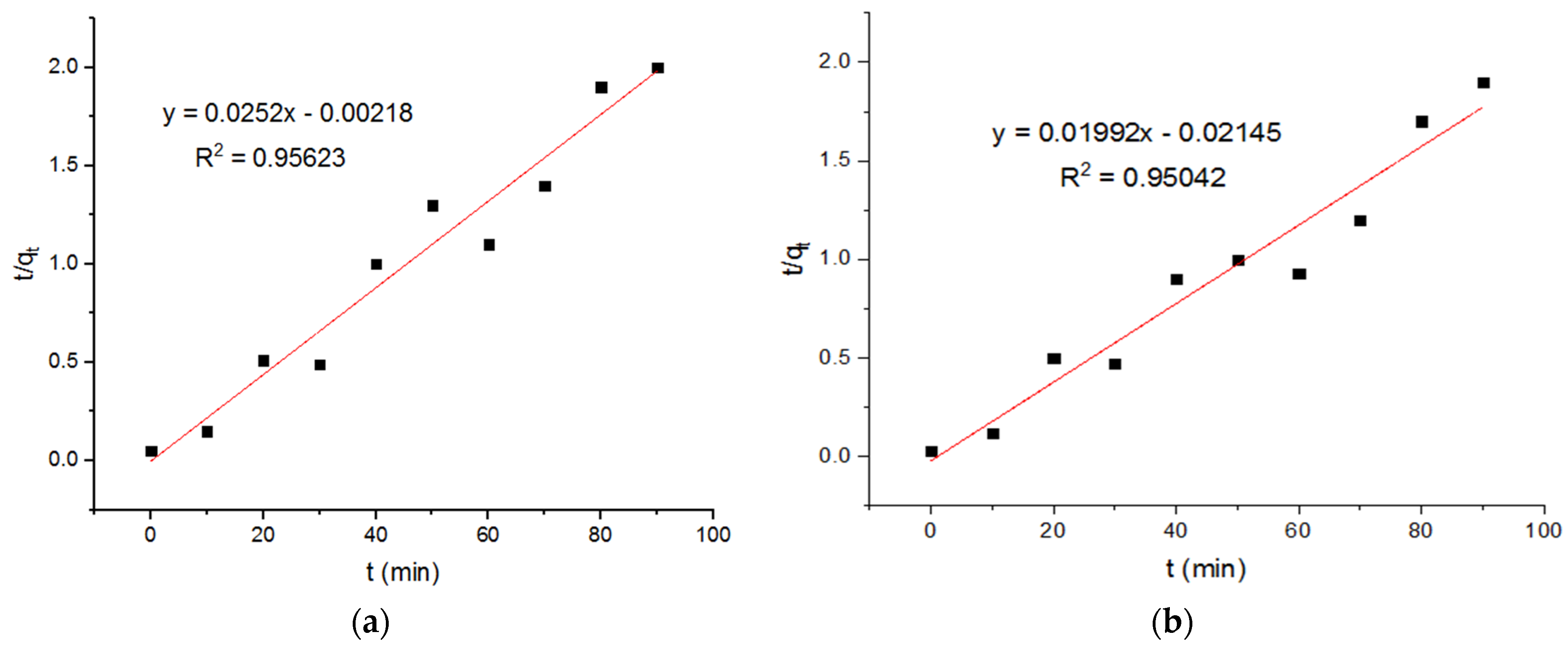

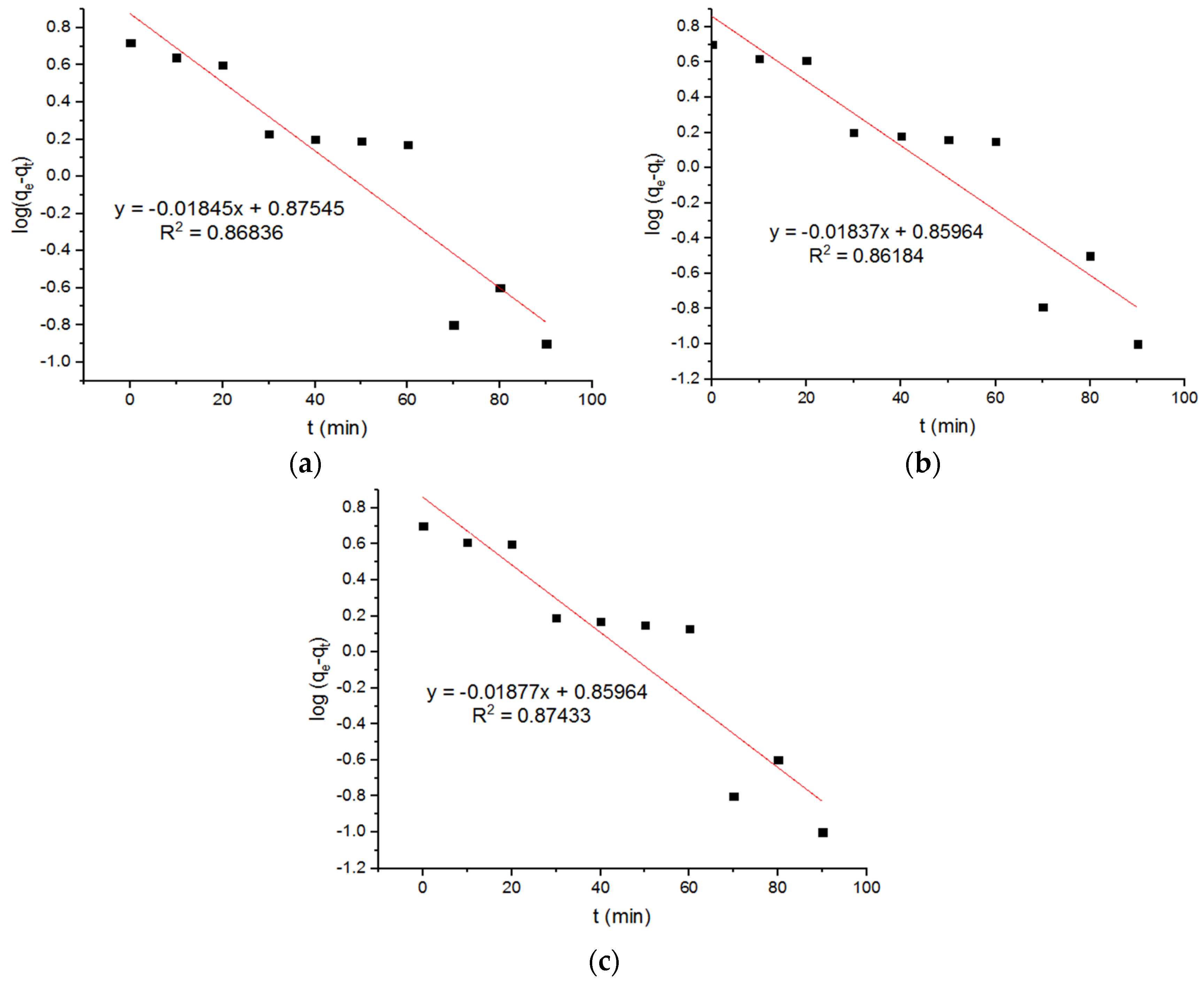


| Adsorption of Cu+2 onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (First-Order Model) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.036 | 6.89 | 0.8242 | 0.032 | 6.55 | 0.79131 | 0.037 | 6.61 | 0.82238 |
| Adsorption of Cu+2 onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (Second-Order Model) | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| −0.291 | 39.68 | 0.95623 | −0.018 | 50.20 | 0.95042 | −0.136 | 39.38 | 0.96127 |
| Adsorption of Pb2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (Pseudo-First-Order Model) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.042 | 7.24 | 0.86184 | 0.0425 | 7.50 | 0.86836 | 0.043 | 7.23 | 0.87433 |
| Adsorption of Pb2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (Pseudo-Second-Order Model) | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| −0.0136 | 35.98 | 0.9906 | −0.011 | 39.2 | 0.98648 | −0.096 | 33.68 | 0.98048 |
| Adsorption of Zn+2 onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (Pseudo-Firstst-Order Model) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k1 (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.039 | 7.106 | 0.83718 | 0.037 | 7 | 0.83735 | 0.0395 | 6.79 | 0.83718 |
| Adsorption of Zn2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 NPs (Pseudo-Second-Order Model) | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg. min) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.141 | 35.42 | 0.98555 | −0.0173 | 38.95 | 0.91528 | 0.01 | 34.98 | 0.97874 |
| Langmuir Model for Adsorption of Cu2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 |
| 0.657 | 16.324 | 0.9019 | 0.877 | 17.84 | 0.92035 | 0.579 | 14.92 | 0.9029 |
| Freundlich Model for Adsorption of Cu2+ onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 |
| 0.77 | 6.15 | 0.8190 | 0.73 | 6.15 | 0.8190 | 0.84 | 5.9 | 0.8221 |
| Langmuir Model for Adsorption of Pb2+ Ions onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles Pre-Functionalization Thermally Treated at 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C. | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 |
| 0.715 | 16.56 | 0.96321 | 0.7155 | 21.69 | 0.96321 | 0.7156 | 13.38 | 0.96321 |
| Freundlich Model for Adsorption of Pb2+ Ions onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles Pre-Functionalization Thermally Treated at 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C. | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 |
| 0.648 | 6.9 | 0.79804 | 0.61 | 6.90 | 0.7984 | 0.67 | 6.9 | 0.79804 |
| Langmuir Model for Adsorption of Zn2+ Ions onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles Pre-Functionalization Thermally Treated at 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C. | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 | qm (mmol/g) | KL (L/mmol) | R2 |
| 0.768 | 12.27 | 0.94302 | 0.767 | 16.14 | 0.94961 | 0.724 | 11.80 | 0.94547 |
| Freundlich Model for Adsorption of Zn2+ Ions onto MgFe2O4-NH2 Nanoparticles Pre-Functionalization Thermally Treated at 500 °C, 600 °C, and 700 °C. | ||||||||
| 500 °C | 600 °C | 700 °C | ||||||
| KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | N | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 | KF (mmol1(1/n)L1/n/g) | n | R2 |
| 0.658 | 6.99 | 0.75263 | 0.605 | 7.07 | 0.744 | 0.727 | 6.75 | 0.7608 |
| Metal Ions | Removal Efficiency at 500 °C (%) | Removal Efficiency at 600 °C (%) | Removal Efficiency at 700 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb2+ | 73 | 58 | 55 |
| Cu2+ | 59 | 58 | 56 |
| Zn2+ | 62 | 58 | 56 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irfan, M.; Zaheer, F.; Hussain, H.; Naz, M.Y.; Shukrullah, S.; Legutko, S.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Alsaiari, M.A.; Ghanim, A.A.J.; Rahman, S.; et al. Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Produced Using Sol-Gel Method for Treatment of Heavy Metals in Wastewater. Materials 2022, 15, 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15114009
Irfan M, Zaheer F, Hussain H, Naz MY, Shukrullah S, Legutko S, Mahnashi MH, Alsaiari MA, Ghanim AAJ, Rahman S, et al. Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Produced Using Sol-Gel Method for Treatment of Heavy Metals in Wastewater. Materials. 2022; 15(11):4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15114009
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrfan, Muhammad, Fareeda Zaheer, Humaira Hussain, Muhammad Yasin Naz, Shazia Shukrullah, Stanislaw Legutko, Mater H. Mahnashi, Mabkhoot A. Alsaiari, Abdulnour Ali Jazem Ghanim, Saifur Rahman, and et al. 2022. "Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Produced Using Sol-Gel Method for Treatment of Heavy Metals in Wastewater" Materials 15, no. 11: 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15114009
APA StyleIrfan, M., Zaheer, F., Hussain, H., Naz, M. Y., Shukrullah, S., Legutko, S., Mahnashi, M. H., Alsaiari, M. A., Ghanim, A. A. J., Rahman, S., Alshorman, O., Alkahtani, F. S., Khan, M. K. A., Kruszelnicka, I., & Ginter-Kramarczyk, D. (2022). Kinetics and Adsorption Isotherms of Amine-Functionalized Magnesium Ferrite Produced Using Sol-Gel Method for Treatment of Heavy Metals in Wastewater. Materials, 15(11), 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15114009







