Influence of Low Sintering Temperature on BaCe0.2Zr0.6Y0.2O3−δ IT-SOFC Perovskite Electrolyte Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results
3.1. XRD Analysis
3.2. Density Measurements
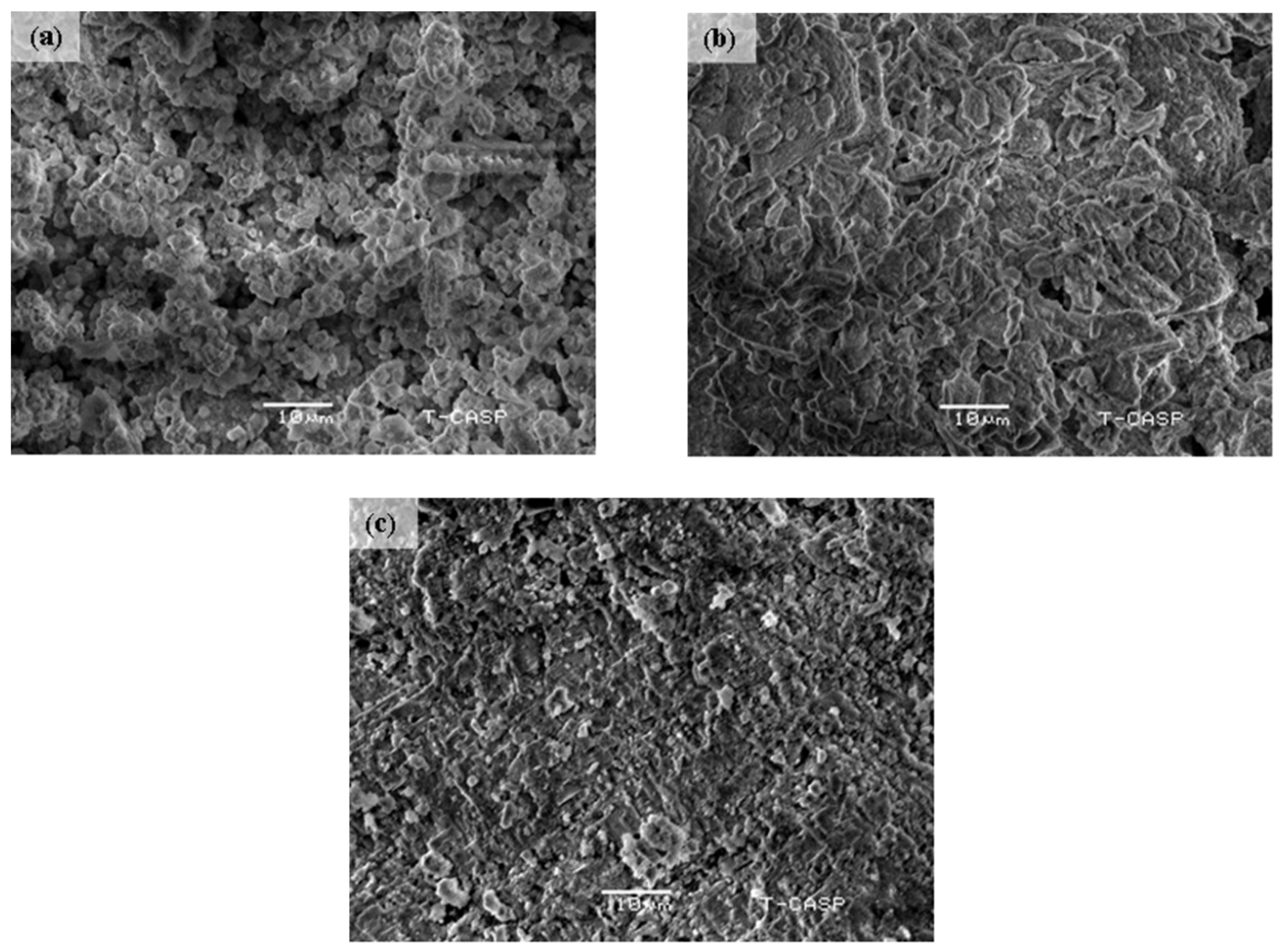
3.3. Surface Morphology
3.4. Thermal Stability Analysis
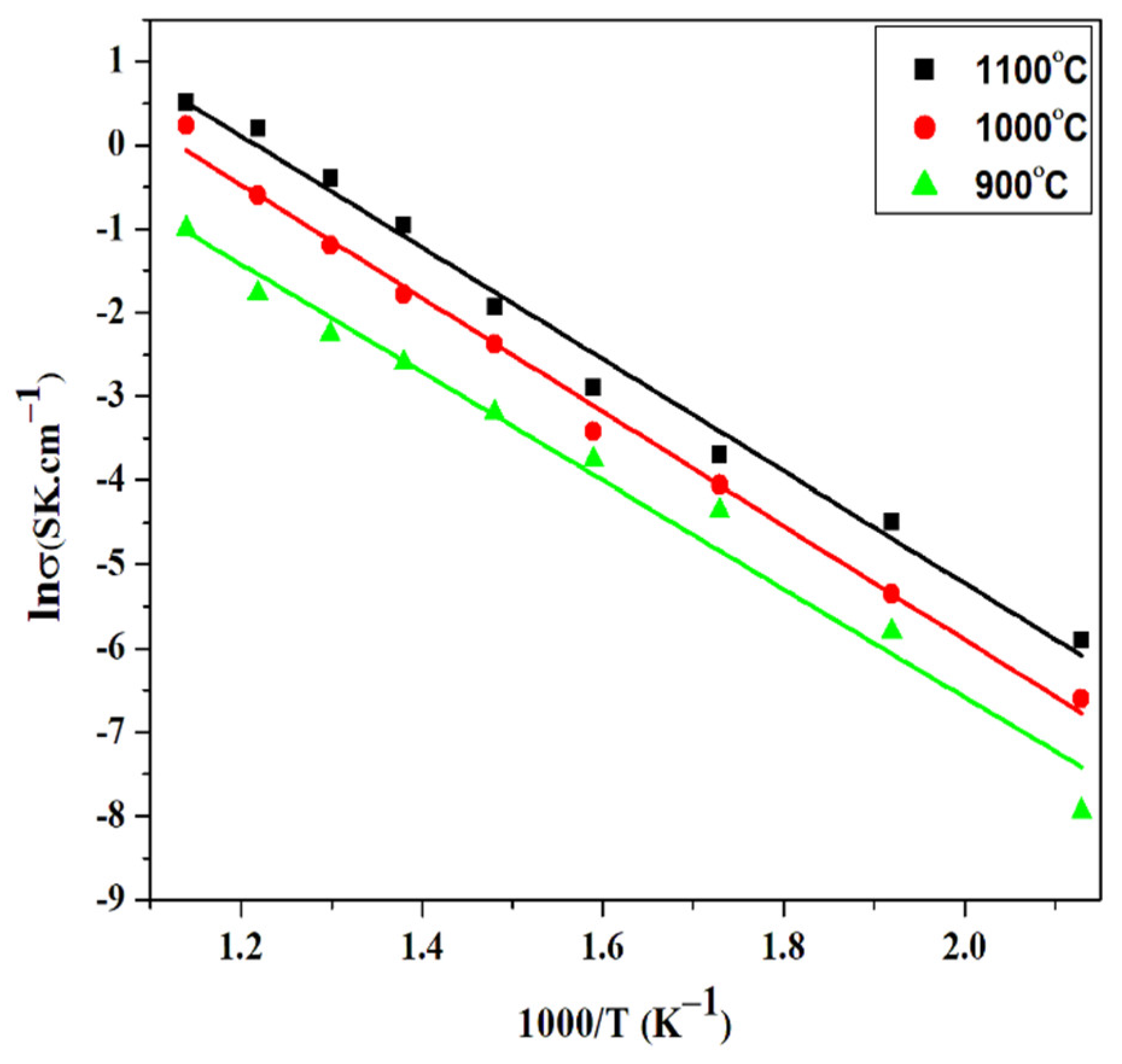
3.5. Conductivity
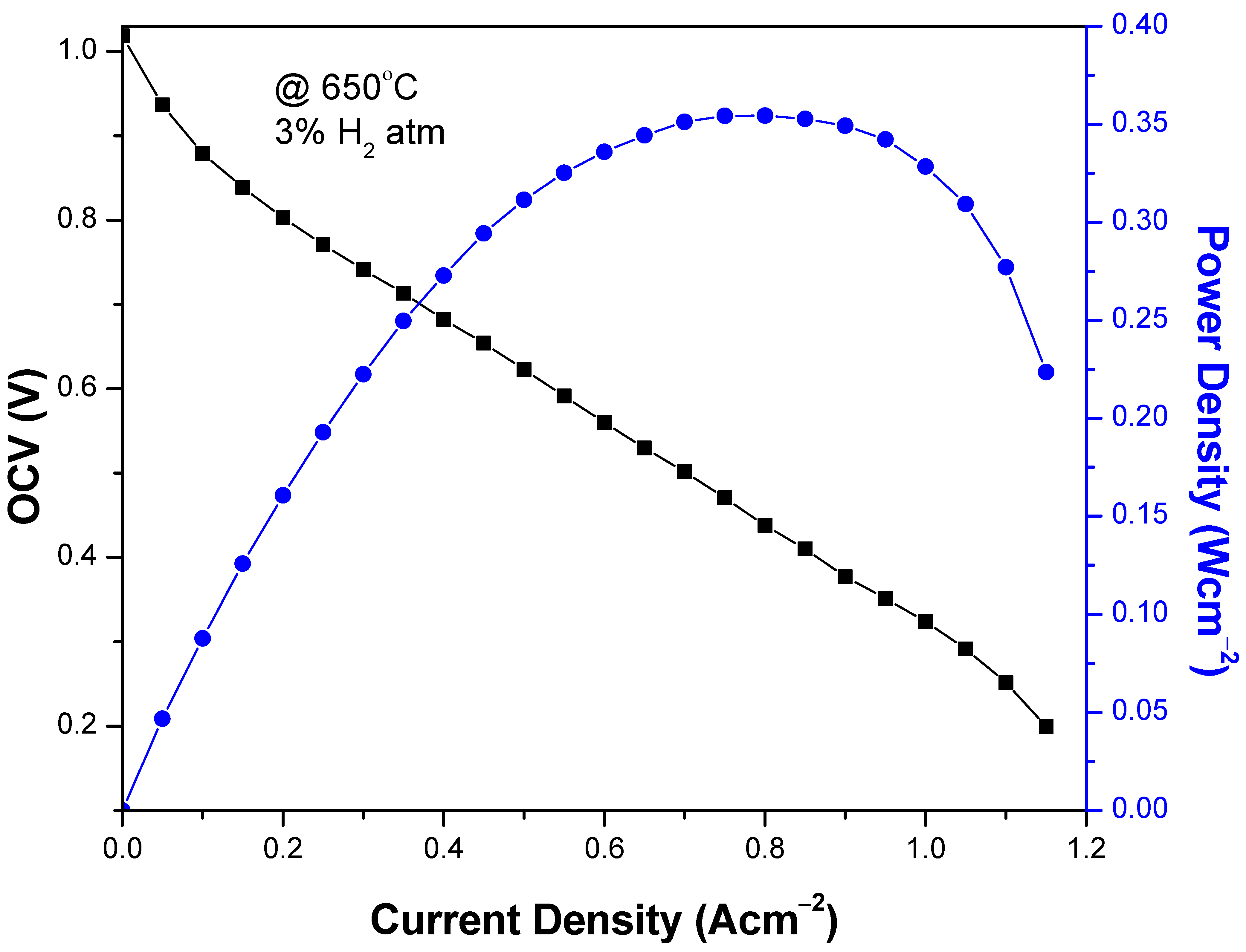
3.6. Cell Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersson, M.; Paradis, H.; Yuan, J.; Sundén, B. Review of catalyst materials and catalytic steam reforming reactions in SOFC anodes. Int. J. Energy Res. 2011, 35, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.M.; Hossain, S.; Azad, A.T.; Petra PM, I.; Begum, F.; Eriksson, S.G.; Azad, A.K. Nanomaterials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stambouli, A.; Traversa, E. Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs): A review of an environmentally clean and efficient source of energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, R.; Ahmad, M.A.; Iqbal, J.; Akram, N.; Gao, Z.; Javed, S.; Zhu, B. Ce0.8(SmZr)0.2O2-Carbonate Nanocomposite Electrolyte for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell. Int. J. Energy Res. 2014, 38, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenahmad, N.; Afif, A.; Petra, P.I.; Rahman, S.M.; Eriksson, S.G.; Azad, A.K. Proton-Conducting Electrolytes for Direct Methanol and Direct Urea Fuel Cells—A State-of-the-Art Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroze, S.; Karim, A.; Cheok, Q.; Eriksson, S.; Azad, A.K. Latest development of double perovskite electrode materials for solid oxide fuel cells: A review. Front. Energy 2019, 13, 770–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Idrees, R.; Siraj, K.; Shakir, I.; Rafique, M.; Ain, Q.U.; Raza, R. Electrochemical evaluation of mixed ionic electronic perovskite cathode LaNi1−xCoxO3−δ for IT-SOFC synthesized by high temperature decomposition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 46, 10448–10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, F.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z. Development of solid oxide fuel cell materials for intermediate-to-low temperature operation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Fu, X.-Z.; Luo, J.-L.; Chuang, K.T.; Sanger, A.R. Evaluation of molybdenum carbide as anode catalyst for proton-conducting hydrogen and ethane solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 15, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B. Solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) technical challenges and solutions from nano-aspects. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 33, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, L. A review of zirconia-based solid electrolytes. Ionics 2016, 22, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Chan, S.; Jiang, S.; Khor, K. Low-temperature SOFC with thin film GDC electrolyte prepared in situ by solid-state reaction. Solid State Ion. 2004, 170, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, M.S.; Nawaz, H.; Tahir, M.B.; Nabi, G.; Khalid, N. Material and method selection for efficient solid oxide fuel cell anode: Recent advancements and reviews. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 2423–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Rafique, M.; Usman, M.; Ain, Q.U.; Ghaffar, A. Evaluation of densification effects on the properties of 8 mol% yttria stabilized zirconia electrolyte synthesized by cost effective coprecipitation route. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, P.; Tadé, M.O.; Shao, Z. Statistical method-based calibration and validation of a solid oxide fuel cell model. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 2478–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; He, C.; Zhu, B. Role of carbonate phase in ceria-carbonate composite for low temperature solid oxide fuel cells: A review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2017, 41, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Abdalla, A.M.; Jamain, S.N.B.; Zaini, J.; Azad, A. A review on proton conducting electrolytes for clean energy and intermediate temperature-solid oxide fuel cells. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Khalid, M.; Rafique, M.; Ahmad, N.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Sadiq, M.; Ahsan, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Ashfaq, A. Evaluation of BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.2−xNixO3−δ perovskite cathode using nickel as a sintering aid for IT-SOFC. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Ali, A.; Tiwari, P.; Zhu, B.; Rafique, A.; Ali, A.; Ullah, M.K.; Usman, A. A Brief Description of High Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cell’s Operation, Materials, Design, Fabrication Technologies and Performance. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.L.R.M.; Samat, A.A.; Jais, A.A.; Somalu, M.R.; Muchtar, A.; Baharuddin, N.A.; Isahak, W.N.R.W. Review on zirconate-cerate-based electrolytes for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cell. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 6605–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Zha, S.; Liu, M.; Hatano, M.; Uchiyama, M. Ba(Zr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2)O3–δ as an Electrolyte for Low-Temperature Solid-Oxide Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 3318–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sumi, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nomura, K.; Fujishiro, Y. Effect of Ni Diffusion into BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3−δ Electrolyte During High Temperature Co-Sintering in Anode-Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 3134–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Shen, S. The microstructure effect on ion conduction in composite electrolyte. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 4229–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Leung, M.; Leung, D.Y. Technological development of hydrogen production by solid oxide electrolyzer cell (SOEC). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 2337–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.Y.; Seo, K.D.; Park, J.-Y.; Lim, H.-T. Durability tests of BCY-BZY electrolyte fuel cells under severe operating conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyagaeva, J.; Medvedev, D.; Pikalova, E.; Plaksin, S.; Brouzgou, A.; Demin, A.; Tsiakaras, P. A Detailed Analysis of Thermal and Chemical Compatibility of Cathode Materials Suitable for BaCe0.8Y0.2O3−δ and BaZr0.8Y0.2O3−δ Proton Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Sullivan, N.P.; Ricote, S. Double perovskite Ba2FeMoO6−δ as fuel electrode for protonic-ceramic membranes. Solid State Ion. 2017, 306, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naceur, H.; Megriche, A.; El Maaoui, M. Effect of sintering temperature on microstructure and electrical properties of Sr1−x(Na0.5Bi0.5)xBi2Nb2O9 solid solutions. J. Adv. Ceram. 2014, 3, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meng, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, H.; Zou, M.; Duffy, J.; Tong, J.; Brinkman, K.S. A High-Performance Reversible Protonic Ceramic Electrochemical Cell Based on a Novel Sm-Doped BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3−δ Electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2019, 439, 227093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhou, M.; Cao, D.; Liu, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Huang, J.; Shao, J.; Liu, J. Multiple Effects of Iron and Nickel Additives on the Properties of Proton Conducting Yttrium-Doped Barium Cerate-Zirconate Electrolytes for High-Performance Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50433–50445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-R.; Tseng, C.-J.; Jang, S.-C.; Lin, J.-C.; Wang, K.-W.; Chang, J.-K.; Chen, T.-C.; Lee, S.-W. Fabrication of anode-supported thin BCZY electrolyte protonic fuel cells using NiO sintering aid. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 23784–23792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, Z.U.D.; Hanif, M.B.; Gao, J.T.; Li, C.J.; Li, C.X. Sintering Behavior of BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3−δ Electrolyte at 1150 °C with the Utilization of Cuo and Bi2O3 as Sintering Aids and Its Electrical Performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 7403–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.; Irshad, M.; Fu, P.F.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Javed, F. The effect of calcination temperature on the properties of Ni-SDC cermet anode. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konwar, D.; Nguyen NT, Q.; Yoon, H.H. Evaluation of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3−δ Electrolyte Prepared by Carbonate Precipitation for a Mixed Ion-Conducting Sofc. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11651–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Mao, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z. Composite Electrolyte Based on Nanostructured Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9 (Sdc) for Low-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2009, 33, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and thermal expansion of barium titanate-based ceramics. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 419, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabacı, A.; Öksüzömer, F. Preparation and characterization of 10 mol% Gd doped CeO2 (GDC) electrolyte for SOFC applications. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6509–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.; Hoque, S.M.; Choudhury, S. Effects of Sintering Temperature on Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of NiFe2O4 Prepared from Nano Size Powder of Nio and Fe2O3. J. Bangladesh Acad. Sci. 2010, 34, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Irshad, M.; Ain, Q.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Tabish, A.N.; Rafique, M.; Idrees, R.; Khan, F.; Majeed, S.; Ahsan, M. Evaluation of BaZr0.8X0.2 (X = Y, Gd, Sm) proton conducting electrolytes sintered at low temperature for IT-SOFC synthesized by cost effective combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Siraj, K.; Raza, R.; Javed, F.; Ahsan, M.; Shakir, I.; Rafique, M.S. High performance of SDC and GDC core shell type composite electrolytes using methane as a fuel for low temperature SOFC. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 025202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourashiya, M.G.; Patil, J.Y.; Pawar, S.H.; Jadhav, L.D. Studies on Structural, Morphological and Electrical Properties of Ce1−x GdxO2−(x/2). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 109, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, E.; Bi, L.; Tanaka, H.; Pergolesi, D.; Traversa, E. Chemically Stable Pr and Y Co-Doped Barium Zirconate Electrolytes with High Proton Conductivity for Intermediate-Temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affandi, N.S.M.; Osman, N.; Hassan, O.H. Ac Conductivity of BaCe0.54Zr0.36 Y0.1 O3−δ Electrolyte in Dry and Wet Nitrogen Atmospheres. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2031, 020018. [Google Scholar]
- Ricote, S.; Caboche, G.; Estournès, C.; Bonanos, N. Synthesis, Sintering, and Electrical Properties of BaCe0.9−xZrxY0.1 O3−δ. J. Nanomater. 2008, 2008, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, A.K.; Tsur, Y. Sintering Aid (Zno) Effect on Proton Transport in BaCe0.35Zr0.5Y0.15O3−δ and Electrode Phenomena Studied by Distribution Function of Relaxation Times. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Khalid, M.; Rafique, M.; Tabish, A.N.; Shakeel, A.; Siraj, K.; Ghaffar, A.; Raza, R.; Ahsan, M.; Ain, Q.T. Electrochemical Investigations of BaCe0.7−xSmxZr0.2Y0.1O3−δ Sintered at a Low Sintering Temperature as a Perovskite Electrolyte for It-Sofcs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrolyte | BaCe0.4Zr0.4Y0.2O3−δ | BaCe0.5Zr0.35Y0.15O3−δ | BaZr0.4Ce0.4Y0.2O3−δ | BaZr0.1Ce00.7Y0.2O3−δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cathode | PrNi | LSC | BSCF | LSCF |
| Anode | Ni-BCZY | Ni-BCZY | Ni-BCZY | Ni-BCZY |
| Temperature (°C) | 550 | 550 | 600 | 600 |
| Power Density (mW cm−2) | 63 | 300 | 360 | 477 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafique, M.; Safdar, N.; Irshad, M.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, M.; Saleem, M.W.; Abbas, M.M.; Ashour, A.; Soudagar, M.E. Influence of Low Sintering Temperature on BaCe0.2Zr0.6Y0.2O3−δ IT-SOFC Perovskite Electrolyte Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials 2022, 15, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103585
Rafique M, Safdar N, Irshad M, Usman M, Akhtar M, Saleem MW, Abbas MM, Ashour A, Soudagar ME. Influence of Low Sintering Temperature on BaCe0.2Zr0.6Y0.2O3−δ IT-SOFC Perovskite Electrolyte Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials. 2022; 15(10):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103585
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafique, Muhammad, Neelam Safdar, Muneeb Irshad, Muhammad Usman, Maaz Akhtar, Muhammad Wajid Saleem, Muhammad Mujtaba Abbas, Ahmed Ashour, and Manzoore Elahi Soudagar. 2022. "Influence of Low Sintering Temperature on BaCe0.2Zr0.6Y0.2O3−δ IT-SOFC Perovskite Electrolyte Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method" Materials 15, no. 10: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103585
APA StyleRafique, M., Safdar, N., Irshad, M., Usman, M., Akhtar, M., Saleem, M. W., Abbas, M. M., Ashour, A., & Soudagar, M. E. (2022). Influence of Low Sintering Temperature on BaCe0.2Zr0.6Y0.2O3−δ IT-SOFC Perovskite Electrolyte Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. Materials, 15(10), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103585










