Effect of Accelerators on the Workability, Strength, and Microstructure of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixture Proportions
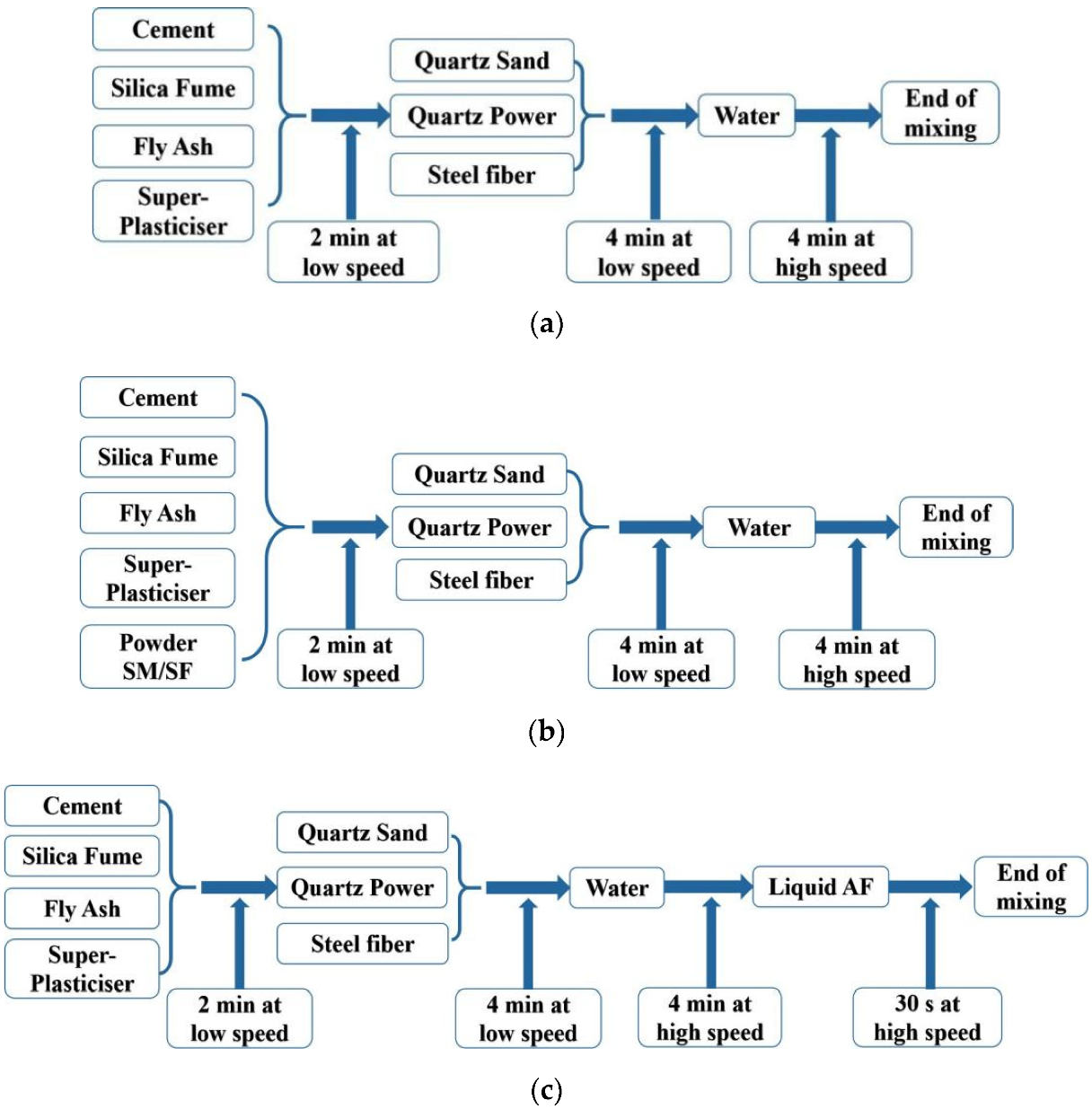
2.3. Specimen Fabrication
2.4. Testing Methods
2.4.1. Setting Time
2.4.2. Fluidity
2.4.3. Mechanical Properties
2.4.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.4.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
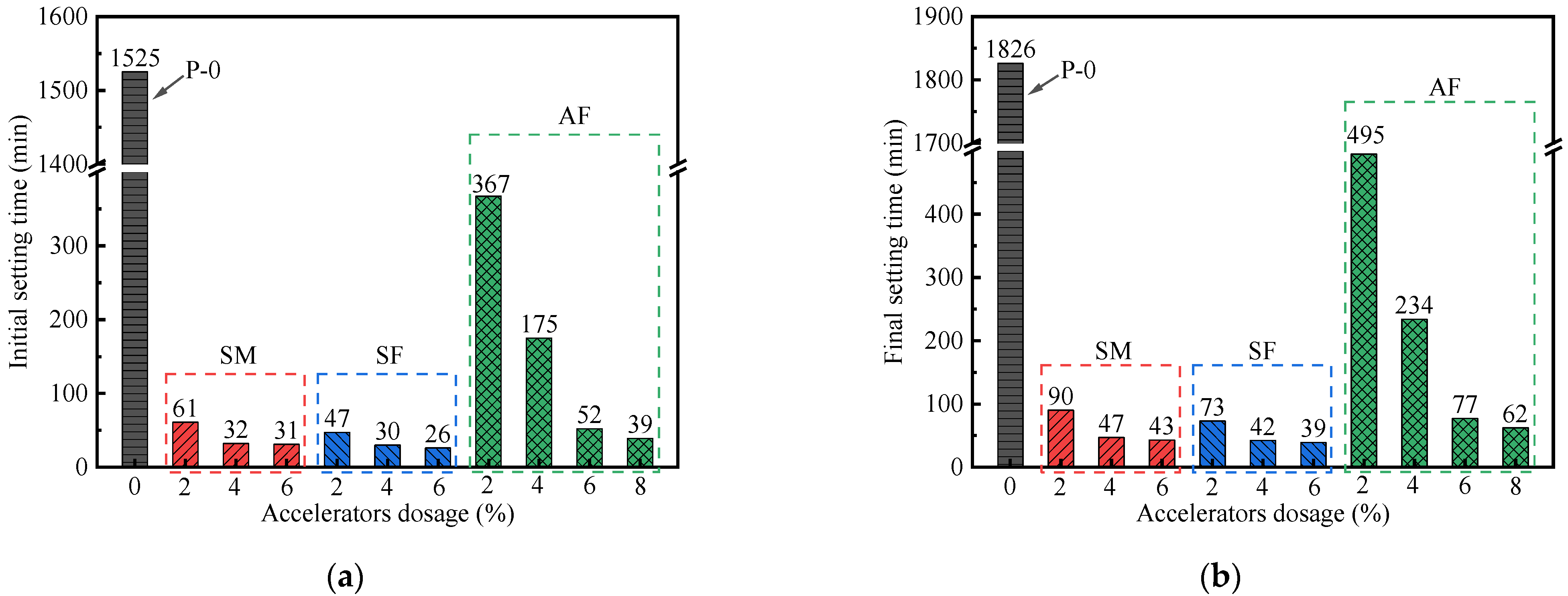
3.1. Setting Time
3.2. Fluidity
3.3. Compressive Strength
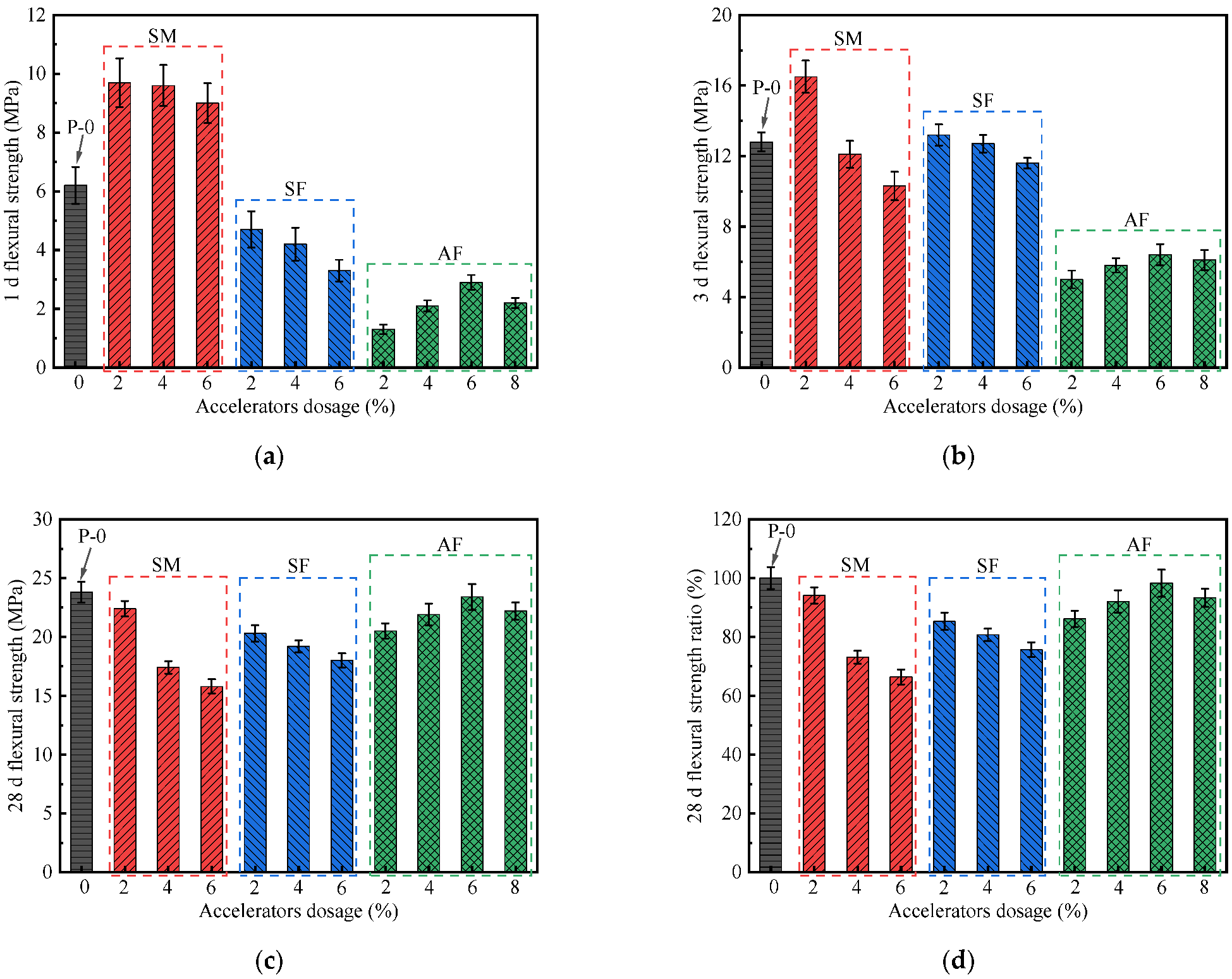
3.4. Flexural Strength
3.5. XRD Pattern
3.6. SEM Examination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richard, P.; Cheyrezy, M. Composition of reactive powder concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Wang, D.; Huang, Z.; Fang, Z. A review on ultra high performance concrete: Part I. Raw materials and mixture design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, C.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Z.; Fang, Z. A review on ultra high performance concrete: Part II. hydration, microstructure and properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaysi, M.; El-Tawil, S.; Liu, Z.; Hansen, W. Effects of silica powder and cement type on durability of ultra high performance concrete (UHPC). Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 66, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davood, M.; Mojtaba, R.N.; Seyed, A.H. Determination of optimized mix design and curing conditions of reactive powder concrete (RPC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 754–767. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaber, M.A.; Hakeem, I.Y. UHPC Evolution, development, and utilization in construction: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1058–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Shao, T.; Fang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Hu, Z. Shear-friction behavior of grooved construction joints between a precast UHPC girder and a cast-in-place concrete slab. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.G.; Wang, Y.C.; Chiu, C.T. A preliminary study of reactive powder concrete as a new repair material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.H.; Walsh, K.K.; Sargand, S.M.; Steinberg, E.P. Interfacial properties of ultra-high-performance concrete and high-strength concrete bridge connections. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04015208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Osta, M.A.; Isa, M.N.; Baluch, M.H.; Rahman, M.K. Flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beams strengthened with ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, C.; He, W. Comparative Study on flexural properties of ultra-high performance concrete with supplementary cementitious materials under different curing regimes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazıcı, H.; Yardımcı, M.Y.; Aydın, S.; Karabulut, A.S. Mechanical properties of reactive powder concrete containing mineral admixtures under different curing regimes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Lu, L.; He, Y.; Rao, M.; Fu, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, S. Experimental investigation on the autogenous shrinkage of steam cured ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, X.; Li, L. Test and simulation of cement hydration degree for shotcrete with alkaline and alkali-free accelerators. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 112, 103684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lim, D.S.; Chun, B.S.; Ryou, J.S. Characterization of a sodium aluminate(NaAlO2)-based accelerator made via a tablet processing method. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2013, 14, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Wang, K.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y. Influence of sodium aluminate on cement hydration and concrete properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renan, P.S.; Sergio, H.P.C.; Ignacio, S.; Antonio, D.F.; Jorge, P. Early age hydration of cement pastes with alkaline and alkali-free accelerators for sprayed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 386–398. [Google Scholar]
- Renan, P.S.; Sergio, H.P.C.; Miguel, C.; Antonio, D.F. Influence of spraying on the early hydration of accelerated cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 88, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B.; Luo, Z.; Wang, D.; Shen, C.; Xia, M. Influence of alkaline and alkali-free accelerators on strength, hydration and microstructure characteristics of ultra-high performance concrete. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 3283–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renan, P.S.; Sergio, H.P.C.; Renata, M.; Antonio, D.F. Relation between chemical processes and mechanical properties of sprayed cementitious matrices with accelerators. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 79, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T50080-2016; Standard for Test Method of Performance on Ordinary Fresh Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Yang, R.; He, T. Influence of liquid accelerators combined with mineral admixtures on early hydration of cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, T. The accelerating mechanism of alkali free liquid accelerator based on fluoroaluminate for shotcrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; LIU, H.; LU, Z.; Wang, D. The influence of silanes on hydration and strength development of cementitious systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.P.; Hwang, U.J.; Lee, S.J. Enhanced long-term strength and durability of shotcrete with high-strength C12A7 mineral-based accelerator. Cem Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.G.; Sung, S.K.; Park, C.G.; Won, J.P. Influence of a C12A7 mineral-based accelerator on the strength and durability of shotcrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, N.; Berube, M.A.; Fournier, B.; Bissonnette, B.; Durand, B. Effects of alkali addition on the mechanical properties and durability of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Holzer, L.; Pakusch, J.; Becker, S.; Figi, R.; Gauckler, L. Interaction of polycarboxylate-based superplasticizers with cements with different C3A amounts. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iljinai, A.; Baltakysl, K.; Bankauskaite, A.; Eisinas, A.; Kitrys, S. The stability of formed CaF2 and its influence on the thermal behavior of C-S-H in CaO-Silica gel waste-H2O system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 127, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, I.L.; Thorstensen, R.T. The influence of steel fibers on compressive and tensile strength of ultra high performance concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, S.; Kumar, A. Flexural and tensile strength of ultra-high-performance concrete with ZnPh-treated steel fibers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 06020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Han, F. Effect of steel fiber on flexural toughness and fracture mechanics behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete with coarse aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | K2O | Na2O | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 21.00 | 2.90 | 65.40 | 5.50 | 3.30 | - | - | 2.00 |
| SF | 94.20 | 0.57 | 0.64 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.87 | 0.16 | - |
| FA | 49.20 | 1.30 | 3.13 | 27.80 | 0.85 | - | - | 1.21 |
| Length/mm | Equivalent Diameter/mm | Density/(g·cm−3) | Tensile Strength/MPa | Elastic Modulus/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 0.2 | 7.85 | 2000 | 750 |
| Type | Fineness (80 μm Sieve Residue)/% | pH/% | Solid Content/% | Density /(g·cm−3) | Cl- /% | Setting Time/min | 1 d Strength/MPa | 28 d Strength Ratio/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||||||||
| SM | 11.5 | - | - | - | 0.06 | 2.5 | 7.1 | 8.2 | 90 |
| SF | 10.0 | - | - | - | 0.04 | 2.6 | 8.0 | 10.5 | 75 |
| AS | - | 3.8 | 48.5 | 1.47 | 0.06 | 3.2 | 7.0 | 7.6 | 90 |
| NO. | C | SF | FA | QS | QP | Steel Fiber | w/b | PS (wt %) | SM (wt %) | SF (wt %) | AF (wt %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-0 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | - | - |
| SM-2 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 2 | - | - |
| SM-4 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 4 | - | - |
| SM-6 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 6 | - | - |
| SF-2 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | 2 | - |
| SF-4 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | 4 | - |
| SF-6 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | 6 | - |
| AF-2 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | - | 2 |
| AF-4 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | - | 4 |
| AF-6 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | - | 6 |
| AF-8 | 783 | 196 | 78 | 861 | 235 | 158 | 0.18 | 0.5 | - | - | 8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Y.; Luo, B.; Luo, Z.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, D. Effect of Accelerators on the Workability, Strength, and Microstructure of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010159
Su Y, Luo B, Luo Z, Huang H, Li J, Wang D. Effect of Accelerators on the Workability, Strength, and Microstructure of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Materials. 2022; 15(1):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010159
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Yonghua, Biao Luo, Zhengdong Luo, He Huang, Jianbao Li, and Dehui Wang. 2022. "Effect of Accelerators on the Workability, Strength, and Microstructure of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete" Materials 15, no. 1: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010159
APA StyleSu, Y., Luo, B., Luo, Z., Huang, H., Li, J., & Wang, D. (2022). Effect of Accelerators on the Workability, Strength, and Microstructure of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Materials, 15(1), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010159







