Aqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Different Iron Ferrites: From 3D to 2D
Abstract
1. Introduction
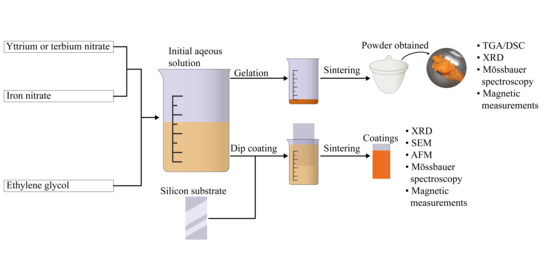
2. Materials and Methods
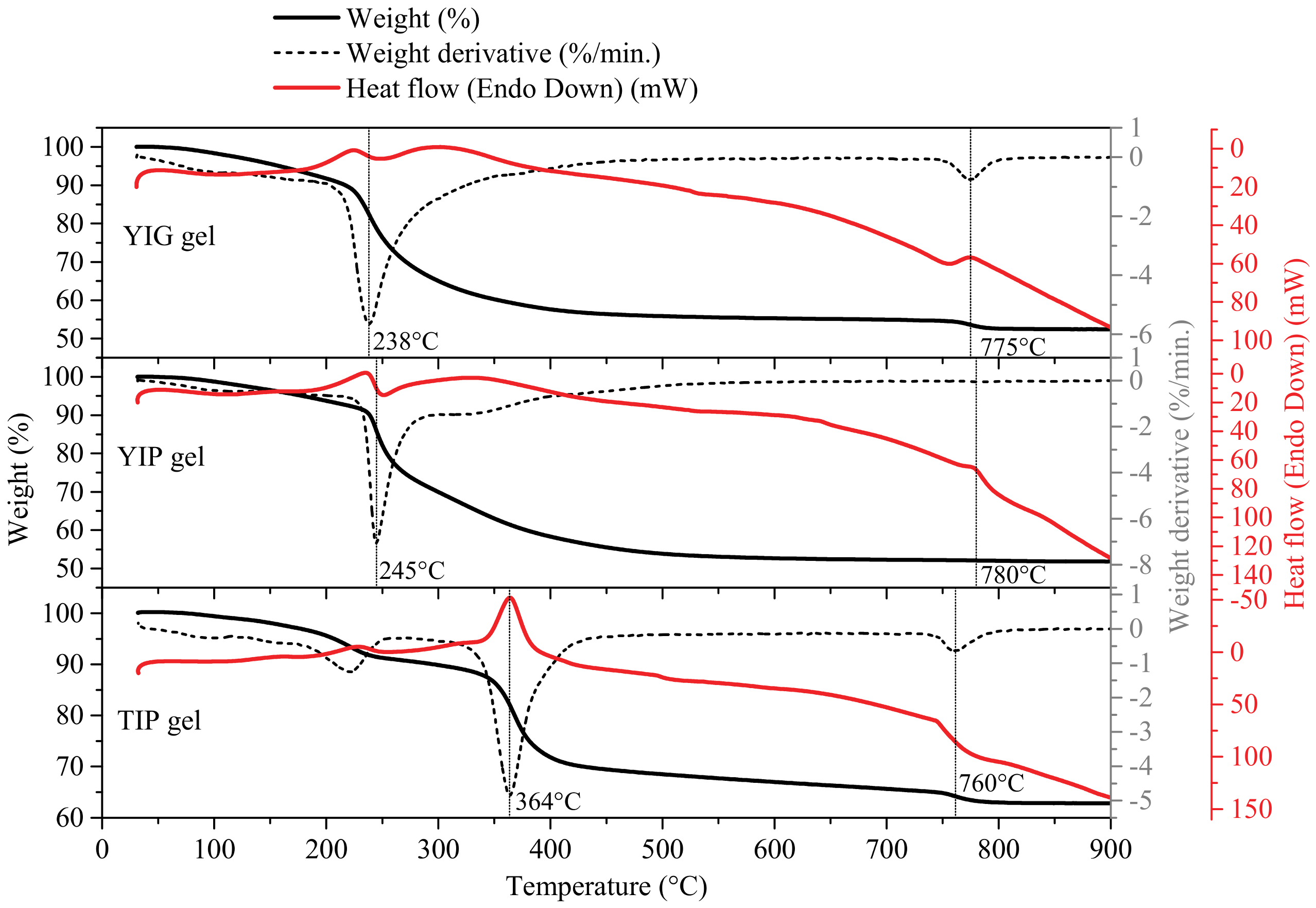
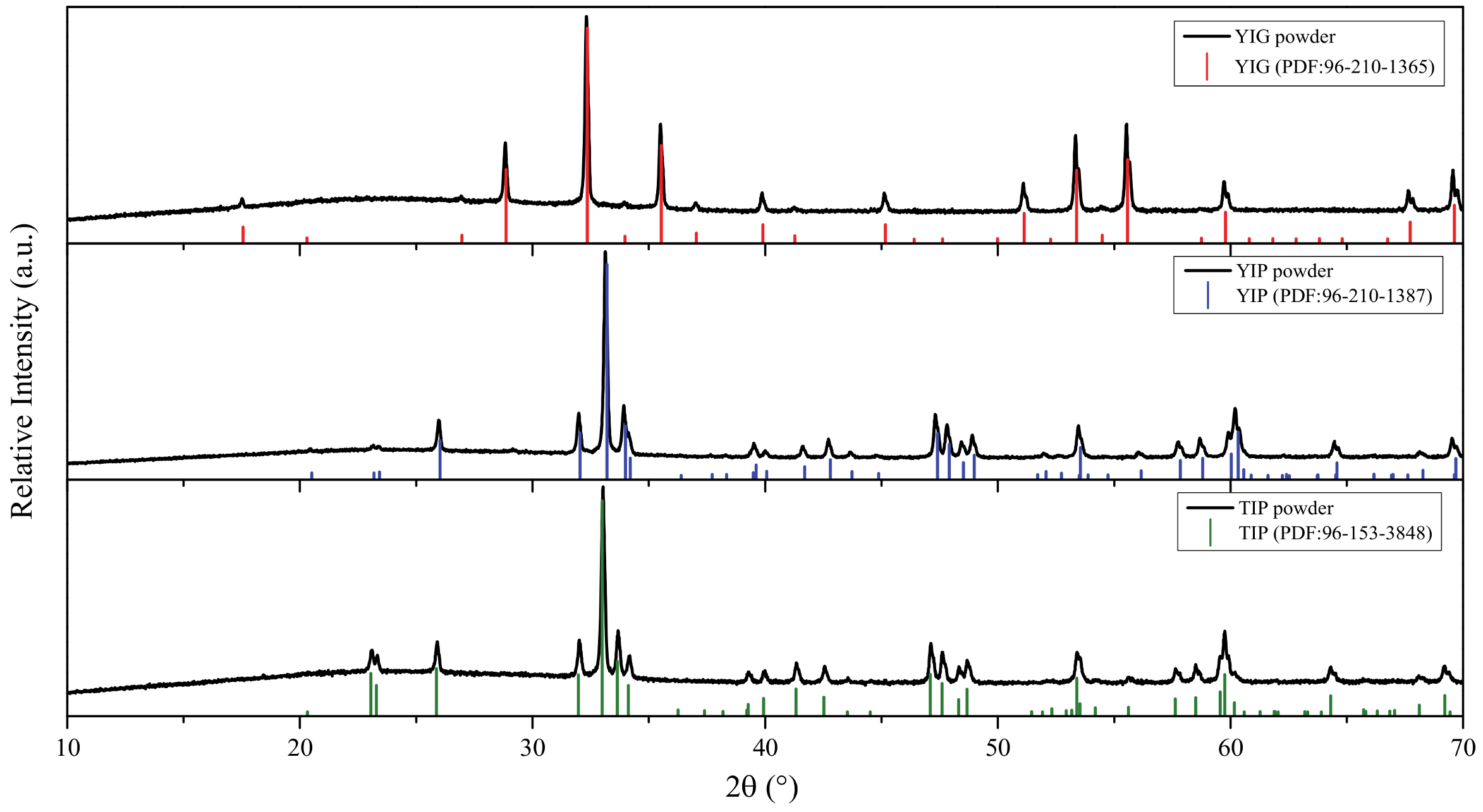
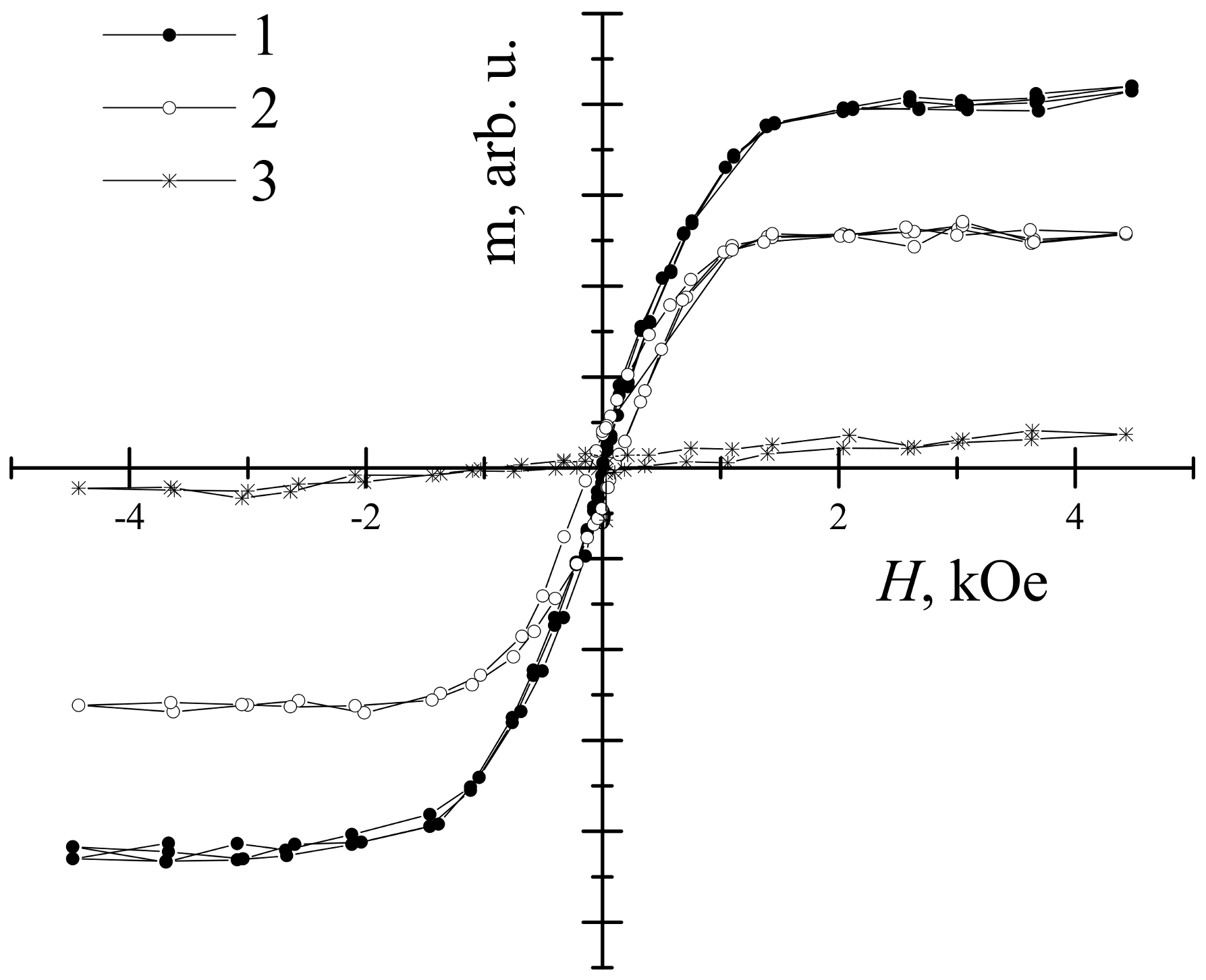
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, X.; Chueh, C.-C.; Yip, H.-L.; Zhu, Z.; Jen, A.K.Y. Highly Efficient All-Inorganic Perovskite Solar Cells with Suppressed Non-Radiative Recombination by a Lewis base. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhm, H.; Leonhard, T.; Schulz, A.D.; Wagner, S.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Colsmann, A. Ferroelectric Properties of Perovskite Thin Films and Their Implications for Solar Energy Conversion. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onbasli, M.C.; Beran, L.; Zahradnik, M.; Kucera, M.; Antos, R.; Mistrik, J.; Dionne, G.F.; Veis, M.; Ross, C.A. Optical and magneto-optical behavior of Cerium Yttrium Iron Garnet thin films at wavelengths of 200–1770 nm. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishin, A.; Khartsev, S. All-Garnet Magneto-Optical Photonic Crystals. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 32, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednorz, J.G.; Müller, K.A. Perovskite-Type Oxides-the New Approach to High-Tc Superconductivity. Nobel Lecture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1988, 27, 735–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auciello, O.; Paz de Araujo, C.A.; Celinska, J. Review of the Science and Technology for Low- and High-Density Nonvolatile Ferroelectric Memories. In Emerging Non-Volatile Memories; Hong, S., Auciello, O., Wouters, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781489975379. [Google Scholar]
- Gilleo, M.A. Ferromagnetic insulators: Garnets. In Handbook of Ferromagnetic Materials; Wohlfarth, E.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 1–53. ISBN 9780444853127. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Gorrín, A.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, U.; Venkatramu, V.; Monteseguro, V.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.; Martin, I.; Lavín, V. Lanthanide-Doped Y3Ga5O12 Garnets for Nanoheating and Nanothermometry in the First Biological Window. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subkhangulov, R.R.; Mikhaylovskiy, R.V.; Zvezdin, A.K.; Kruglyak, V.V.; Rasing, T.; Kimel, A.V. Terahertz Modulation of the Faraday Rotation by Laser Pulses via the Optical Kerr Effect. Nat. Photon. 2016, 10, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Ou, X.; Huang, B.; Almutlaq, J.; Zhumekenov, A.A.; Guan, X.; Han, S.; Liang, L.; Yi, Z.; et al. All-Inorganic Perovskite Nanocrystal Scintillators. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 561, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, D.; Cheng, H.-C.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yin, A.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wu, H.; He, Q.; et al. Wafer-scale Growth of Large Arrays of Perovskite Microplate Crystals for Functional Electronics and Optoelectronics. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, S.A.; Boix, P.P.; Yantara, N.; Natalia, Y.; Sum, T.C.; Mathews, N.; Mhaisalkar, S.G. Perovskite Materials for Light-Emitting Diodes and Lasers. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6804–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kwon, J.; Hwang, E.; Ra, C.-H.; Yoo, W.J.; Ahn, J.-H.; Park, J.H.; Cho, J.H. High-Performance Perovskite-Graphene Hybrid Photodetector. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Wu, J.; Xiao, D.; Zhu, J. Recent Development in Lead-Free Perovskite Piezoelectric Bulk Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 98, 552–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frukacz, Z.; Pawlak, D.A. Garnets, Growth of. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Buschow, K.H.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S., Veyssière, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 3455–3463. ISBN 9780080431529. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, C.; Wang, F.F. Perovskites and Garnets. In Perovskites and Garnets; Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1976; pp. 525–607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Soh, K.C.K.; Wu, P. Formability of ABO3 Perovskites. J. Alloy Compd. 2004, 372, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.Y.; Onishi, N.; Berger, R.F. Tolerance Factors Revisited: Geometrically Designing the Ideal Environment for Perovskite Dopants. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 23293–23298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Takagi, S.; Deledda, S.; Hauback, B.C.; Orimo, S.-I. Extending the Applicability of the Goldschmidt Tolerance Factor to Arbitrary Ionic Compounds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, C.J.; Sutton, C.; Goldsmith, B.R.; Ouyang, R.; Musgrave, C.B.; Ghiringhelli, L.M.; Scheffler, M. New Tolerance Factor to Predict the Stability of Perovskite Oxides and Halides. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav0693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudiar, T.; Payet-Gervy, B.; Blanc-Mignon, M.-F.; Rousseau, J.-J.; Le Berre, M.; Joisten, H. Magneto-Optical Properties of Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) Thin Films Elaborated by Radio Frequency Sputtering. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 284, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, L.; Ge, L.; Yuan, H.; Feng, S. The Multiferroic Perovskite YFeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 062903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-González, O.; Jesús, F.S.-D.; Cortés-Escobedo, C.; Bolarín-Miró, A. Crystal Structure and Multiferroic Behavior of Perovskite YFeO3. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15298–15303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, G.; Xian, T.; Jiang, J. Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Properties of Terbium Orthoferrite Nanopowder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhin, S.; Mostovoy, M.; Jensen, N.P.; Le, D.; Prokes, K.; De Paula, V.G.; Bordallo, H.N.; Maljuk, A.; Landsgesell, S.; Ryll, H.; et al. Solitonic Lattice and Yukawa Forces in the Rare-Earth Orthoferrite TbFeO3. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.; Gorodetsky, G.; Hornreich, R. Magnetization Studies of TbFeO3. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1976, 3, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opuchovic, O.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiva, A. Sol–Gel Derived Tb3Fe5O12 and Y3Fe5O12 Garnets: Synthesis, Phase Purity, Micro-Structure and Improved Design of Morphology. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 647, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opuchovic, O.; Culunlu, S.; Morkan, A.U.; Morkan, I.A.; Niznansky, D.; Garskaite, E.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiva, A. Structural, Morphological, and Magnetic Characterization of Bulk and Thin Films Y 3 Al 5– x Fe x O 12 (YAIG): From the Perspective of Aqueous Sol–Gel Processing. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garskaite, E.; Gibson, K.; Leleckaite, A.; Glaser, J.; Nižňanský, D.; Kareiva, A.; Meyer, H.-J. On the Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Containing Garnets (Y3Fe5O12, YIG and Fe3Al5O12, IAG). Chem. Phys. 2006, 323, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharescu, M.; Predoana, L.; Pandele-Cusu, J. Thermal Analysis on Gels, Glasses, and Powders. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 1st ed.; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1833–1867. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Nano-sized Yttria via a Sol-Gel Process Based on Hydrated Yttrium Nitrate and Ethylene Glycol and Its Catalytic Performance for Thermal Decomposition of NH4ClO4. J. Rare Earths 2006, 24, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, H. Direct Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoporous Fe3O4 Through Pyrolysis of Ferric Nitrate-Ethylene Glycol Gel. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Shen, H.; Leleckaite, A.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiva, A. Low-Temperature Synthesis and Characterization of Yttrium–Gallium Garnet Y3Ga5O12 (YGG). Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minqiang, W.; Xiangying, Z.; Xiaoyong, W.; Liangying, Z.; Xi, Y. Preparation and Annealing Process of Y3Fe5O12by Sol-Gel Method. Ferroelectronics 2001, 264, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, J.; Aegerter, M.A. Dip Coating Technique. Sol-Gel Technologies for Glass Producers and Users; Aegerter, M.A., Mennig, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-387-88953-5. [Google Scholar]

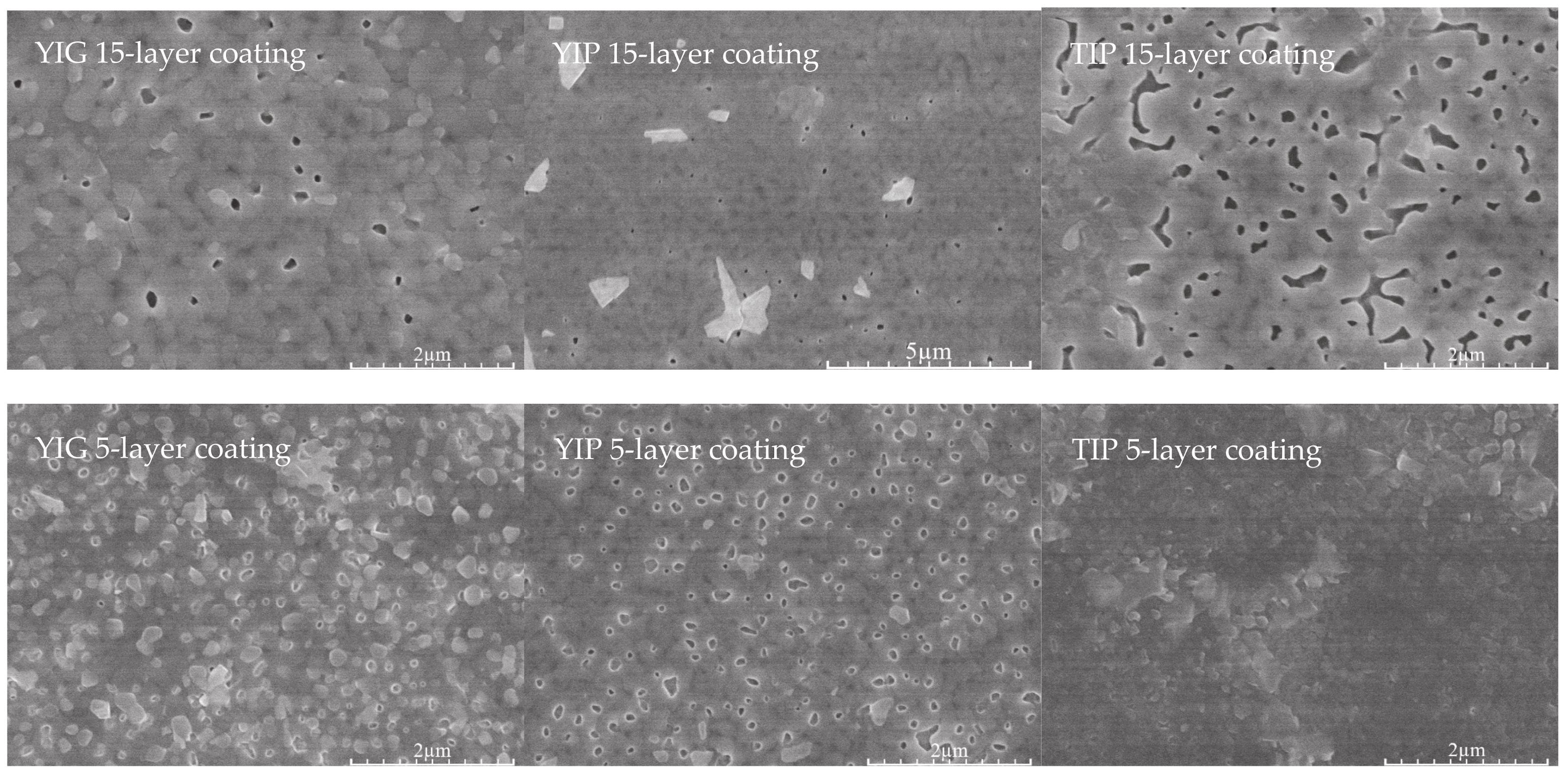
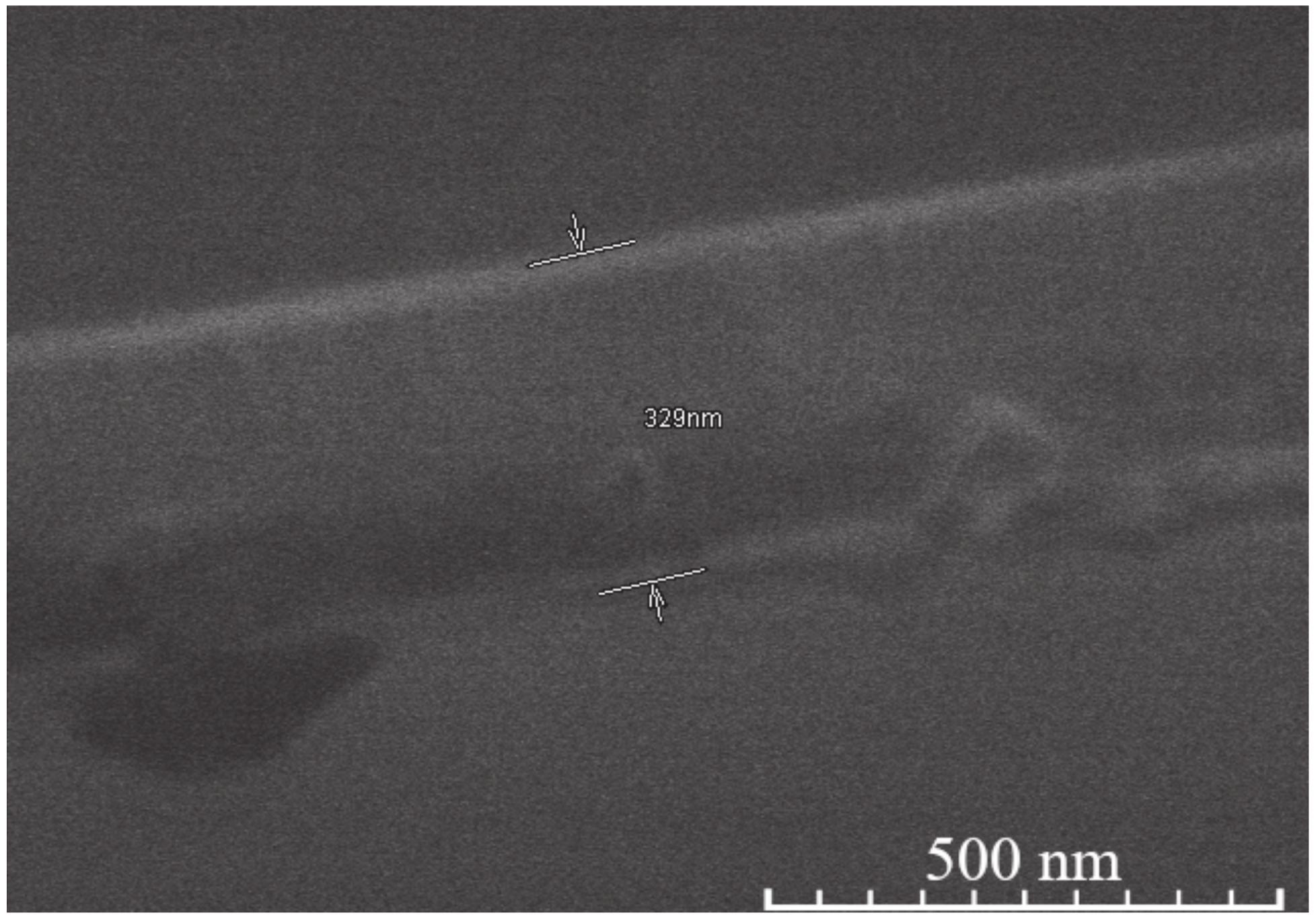
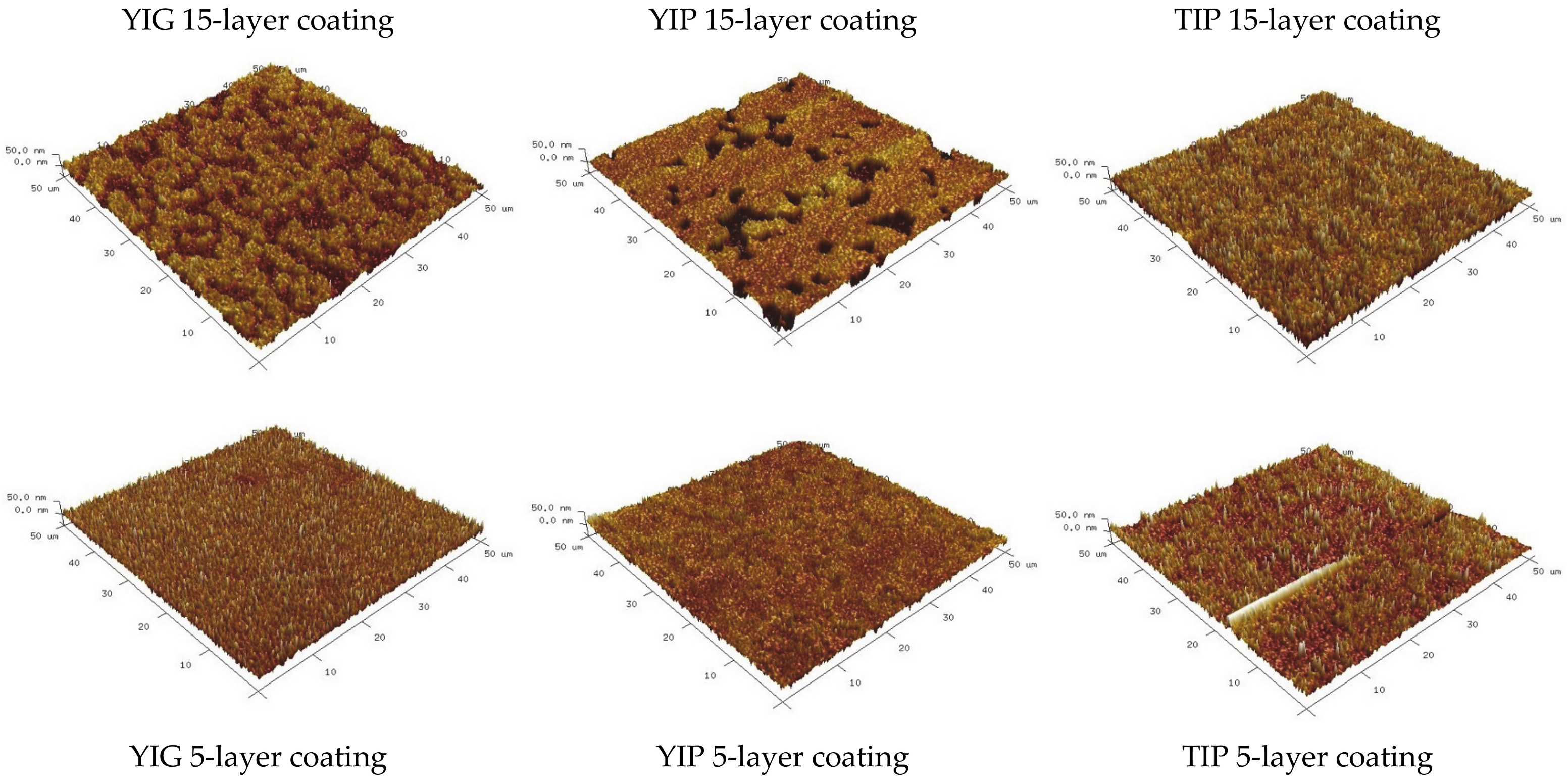

| Sample | Thickness Range, Nm | Average Thickness, Nm | Thickness Median, Nm | Short Analysis * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15-layer | YIG | 380–472 | 424 | 416 | Mostly even surface. No noticeable pores or cavities. Difficult to measure since separation line between coating and Si not clearly visible. |
| YIP | 485–559 | 511 | 506 | Moderately uneven surface. Few pores, some cavities visible. | |
| TIP | 358–414 | 386 | 385 | Mostly even surface, however either cavities or pores clearly visible. | |
| 5-layer | YIG | 201–342 | 273 | 280 | Uneven surface, some unusually large or small crystallites on the surface expand thickness range. No hidden cavities visible. |
| YIP | 261–354 | 307 | 316 | Even surface. Few cavities or pores visible. | |
| TIP | 216–256 | 233 | 234 | Even surface, thickness variations due to nature of dip coating. No hidden cavities visible. | |
| Rq, nm | Ra, nm | |
|---|---|---|
| YIG 15-layer sample | 10.7 | 8.7 |
| YIG 5-layer sample | 10.1 | 7.9 |
| YIP 15-layer sample | 12.5 | 8.8 |
| YIP 5-layer sample | 8.56 | 6.5 |
| TIP 15-layer sample | 13.6 | 10.7 |
| TIP 5-layer sample | 10.6 | 7.1 |
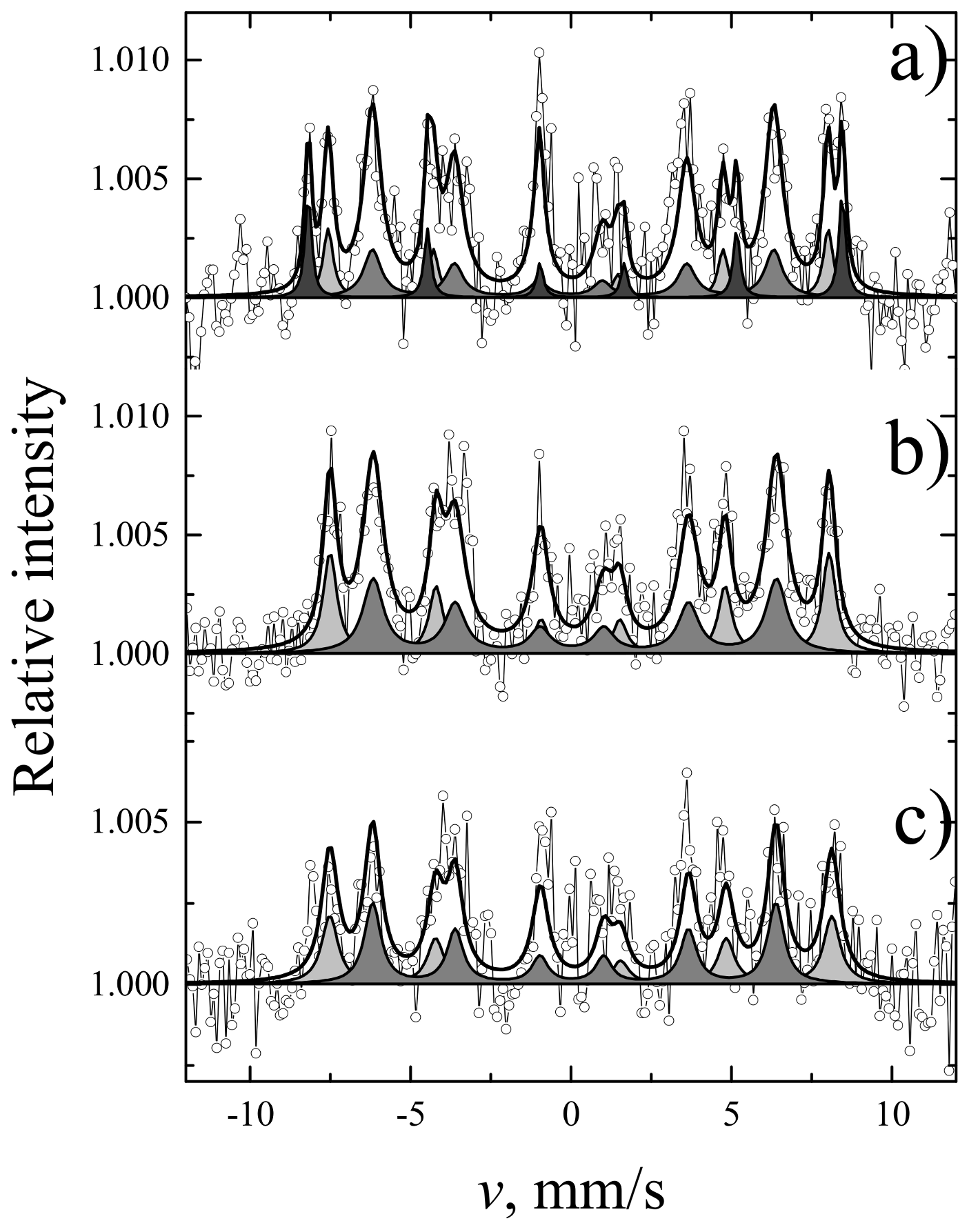
| Sites | S, % | Γ, mm/s | δ, mm/s | 2ε, mm/s | B, T | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YIG | a | 39 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 49.07 ± 0.01 |
| d | 61 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 39.71 ± 0.01 | |
| YIP | - | 100 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 49.78 ± 0.01 |
| TIP | - | 100 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 50.25 ± 0.02 |
| S, % | Γ, mm/s | δ, mm/s | 2ε, mm/s | B, T | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YIG | 26 ± 3 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | 0.00 ± 0.03 | 48.29 ± 0.15 | IG a sites |
| 56 ± 3 | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 38.76 ± 0.13 | IG d sites | |
| 17 ± 3 | 0.25 ± 0.05 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | −0.21 ± 0.02 | 51.58 ± 0.09 | α-Fe2O3 | |
| YIP | 37 ± 2 | 0.51 ± 0.05 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | −0.03 ± 0.03 | 48.20 ± 0.11 | IG a sites |
| 63 ± 2 | 0.77 ± 0.06 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 38.94 ± 0.12 | IG d sites | |
| TIP | 46 ± 5 | 0.62 ± 0.10 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | −0.00 ± 0.06 | 48.49 ± 0.22 | IG a sites |
| 54 ± 5 | 0.61 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 38.95 ± 0.18 | IG d sites |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Januskevicius, J.; Stankeviciute, Z.; Baltrunas, D.; Mažeika, K.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiva, A. Aqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Different Iron Ferrites: From 3D to 2D. Materials 2021, 14, 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061554
Januskevicius J, Stankeviciute Z, Baltrunas D, Mažeika K, Beganskiene A, Kareiva A. Aqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Different Iron Ferrites: From 3D to 2D. Materials. 2021; 14(6):1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061554
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanuskevicius, Justinas, Zivile Stankeviciute, Dalis Baltrunas, Kęstutis Mažeika, Aldona Beganskiene, and Aivaras Kareiva. 2021. "Aqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Different Iron Ferrites: From 3D to 2D" Materials 14, no. 6: 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061554
APA StyleJanuskevicius, J., Stankeviciute, Z., Baltrunas, D., Mažeika, K., Beganskiene, A., & Kareiva, A. (2021). Aqueous Sol-Gel Synthesis of Different Iron Ferrites: From 3D to 2D. Materials, 14(6), 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14061554