Microstructure and Thermal Analysis of Metastable Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloy CoCrFeMo0.85Ni
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Phase Evolution in CoCrFeMo0.85Ni High-Entropy Alloy
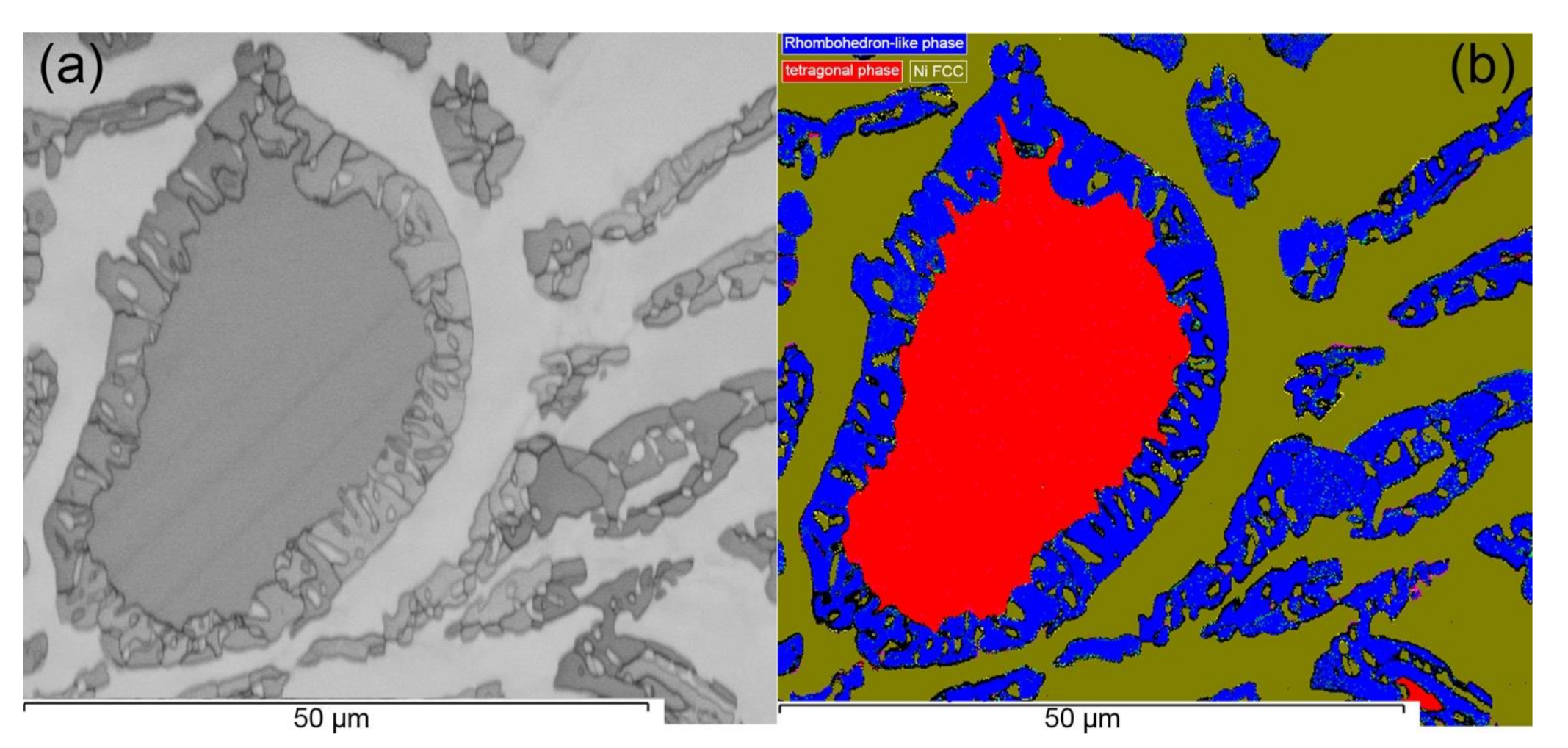
4.2. The Coexistence of σ and µ Phases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tucker, R.C. Thermal spray coatings. In ASM Handbook, Volume 5: Surface Engineering; Cotell, C.M., Sprague, J.A., Smidt, F.A.J., Eds.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.H.; Sergeev, D.; Kobertz, D.; D’Souza, N.; Feng, S.; Müller, M.; Dong, H.B. Vaporization of Ni, Al and Cr in Ni-base alloys and its influence on surface defect formation during manufacturing of single-crystal components. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, N.; Welton, D.; West, G.D.; Edmonds, I.M.; Wang, H. On the roles of oxidation and vaporization in surface micro-structural instability during solution heat treatment of Ni-base superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5968–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, D.; D’Souza, N.; Kelleher, J.; Gardner, S.; Dong, Z.H.; West, G.D.; Dong, H. Discontinuous precipitation in Ni-base superalloys during solution heat treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4298–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.P.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R.O. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.-T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Shiu, M.-H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multiprincipal component CoCrFeNiMox alloys. Mater. Charact. 2012, 70, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shun, T.-T.; Chang, L.-Y.; Shiu, M.-H. Age-hardening of the CoCrFeNiMo0.85 high-entropy alloy. Mater. Charact. 2013, 81, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanicchia, F.; Csaki, I.; Geambazu, L.E.; Begg, H.; Paul, S. Effect of microstructural modifications on the corrosion resistance of CoCrFeMo0.85Ni compositionally complex alloy coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Yang, Y.; Bei, H.; George, E.P. Relative effects of enthalpy and entropy on the phase stability of equiatomic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, L.; Bernstein, H. Computer Calculation of Phase Diagrams with Special Reference to Refractory Metals; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S.; Cao, W. Computational thermodynamics aided high-entropy alloy design. JOM 2012, 64, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.B.; Hunt, J.D. A numerical model for a heat flux DSC: Determining heat transfer coefficients within a DSC. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 413–414, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.P. The Co-Cr-Mo (Cobalt-Chromium-Molybdenum) system. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2005, 26, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Cr-Fe-Mo (chromium-iron-molybdenum). J. Phase Equilibria 2003, 24, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, U.; Gein, S.; Stryzhyboroda, O.; Eshed, E.; Osovski, S. The BCC-FCC phase transformation pathways and crystal orientation relationships in dual phase materials from Al-(Co)-Cr-Fe-Ni alloys. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhao, J.-C. Determination of the Fe-Cr-Mo phase diagram at intermediate temperatures using dual-anneal diffusion multiples. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2016, 37, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, N.; Dong, H.B.; Ardakani, M.G.; Shollock, B.A. Solidification path in the Ni-base superalloy, IN713LC—Quantitative correlation of last stage solidification. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, N.; Dong, H.B. Solidification path in third-generation Ni-based superalloys, with an emphasis on last stage solidification. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, G.; Dong, H.B.; Green, N.R.; D’Souza, N. Surface segregation during directional solidification of Ni-base superalloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2008, 39, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Wanderka, N.; Kiefer, K.; Siemensmeyer, K.; Banhart, J. Effect of decomposition of the Cr–Fe–Co rich phase of AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy on magnetic properties. Ultramicroscopy 2011, 111, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.G.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.T. Phase separation of metastable CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2017, 126, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Mao, H.H.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Precipitation behavior and its effects on tensile properties of FeCoNiCr high-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2016, 79, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, R.W.; Greer, A.L. Chapter 19—Metastable states of alloys. In Physical Metallurgy, 4th ed.; Cahn, R.W., Haasen, P., Eds.; North-Holland: Oxford, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.H.; Lu, Z.P.; He, J.Y.; Luan, J.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.W.; Liu, C.T. Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater. 2016, 116, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liu, B.; Kabra, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, K.; Lee, P.D.; Liu, Y. Deformation mechanisms of Mo alloyed FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy: In situ neutron diffraction. Acta Mater. 2017, 127, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Haasen, P.; Wagner, R. An atom probe study of the decomposition of Fe-Cr-Co permanent magnet alloys. Acta Metall. 1986, 34, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.K.; Hyde, J.M.; Hetherington, M.G.; Cerezo, A.; Smith, G.D.W.; Elliott, C.M. Spinodal decomposition in Fe-Cr alloys: Experimental study at the atomic level and comparison with computer models—I. Introduction and methodology. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 3385–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, F.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Revealing the selection of σ and μ phases in CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys by CALPHAD. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2018, 39, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, K.; Bi, X.; Wang, J. Precipitation strengthening of ductile Cr15Fe20Co35Ni20Mo10 alloys. Scr. Mater. 2017, 137, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, B.; Mendez-Martin, F.; Völker, B.; George, E.P.; Clemens, H.; Pippan, R.; Hohenwarter, A. Mechanical properties, microstructure and thermal stability of a nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy after severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater. 2015, 96, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.K.; Ponge, D.; Peng, Z.; Inden, G.; Lu, Y.; Breen, A.; Gault, B.; Raabe, D. Phase nucleation through confined spinodal fluctuations at crystal defects evidenced in Fe-Mn alloys. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, A.; Daoud, H.; Völkl, R.; Glatzel, U.; Wanderka, N. Phase separation in equiatomic AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Ultramicroscopy 2013, 132, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; da Silva, A.K.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Gault, B.; Raabe, D. Segregation-driven grain boundary spinodal decomposition as a pathway for phase nucleation in a high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2019, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isheim, D. Metastable phase formation during the decomposition of Fe–20 at.% Mo. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 2873–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.M.; D’Souza, N.; Panwisawas, C.; Papadaki, C.; West, G.D.; Kostka, A.; Kontis, P. Spinodal decomposition versus classical γ’ nucleation in a nickel-base superalloy powder: An in-situ neutron diffraction and atomic-scale analysis. Acta Mater. 2020, 200, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsdottir, S.N.; Geambazu, L.E.; Csaki, I.; Thorhallsson, A.I.; Stefanoiu, R.; Magnus, F.; Cotrut, C. Phase evolution and microstructure analysis of CoCrFeNiMo high-entropy alloy for electro-spark-deposited coatings for geothermal environment. Coatings 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Song, X.; Wen, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, X. Effect of Mo and aging temperature on corrosion behavior of (CoCrFeNi)100-xMox high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 812, 152139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Amar, A.; Jiang, C.; Luan, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Le, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; et al. CoCrFeNiMo0.2 high entropy alloy by laser melting deposition: Prospective material for low temperature and corrosion resistant applications. Intermetallics 2020, 119, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenfest, P. Phasenumwandlungen im Ueblichen und Erweiterten Sinn, Classifiziert nach den Entsprechenden Singularitaeten des Thermodynamischen Potentiales; NV Noord-Hollandsche Uitgevers Maatschappij: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1933. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, S.M. Spinodal decomposition. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Buschow, K.H.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S., Veyssière, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 8761–8764. [Google Scholar]
- Debenedetti, P.G. Phase separation by nucleation and by spinodal decomposition: Fundamentals. In Supercritical Fluids: Fundamentals and Applications; Kiran, E., Debenedetti, P.G., Peters, C.J., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 123–166. [Google Scholar]
- Isheim, D.; Hellman, O.C.; Seidman, D.N.; Danoix, F.; Blavette, D. Atomic-scale study of second-phase formation involving large coherency strains in Fe–20 at.% Mo. Scr. Mater. 2000, 42, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Takagishi, S.; Mori, H.; Kozakai, T. The phase decomposition of iron-molybdenum binary alloys by spinodal mechanism. Acta Metall. 1980, 28, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagishi, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Mori, H.; Kozakai, T. Modulated structure in iron-molybdenum alloys. Scr. Metallurgica 1979, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Li, Z.; Ponge, D. Metastability alloy design. MRS Bull. 2019, 44, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
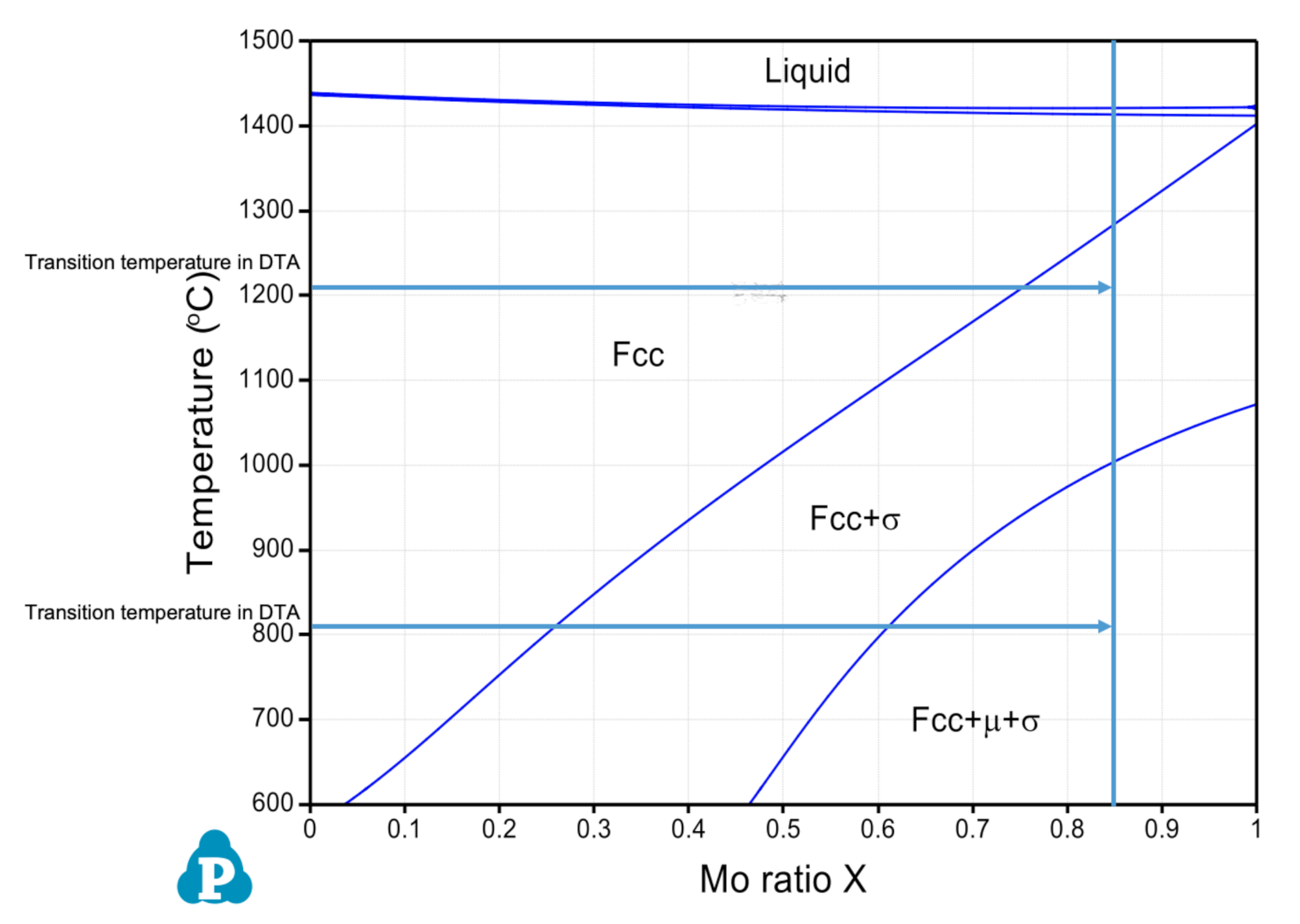
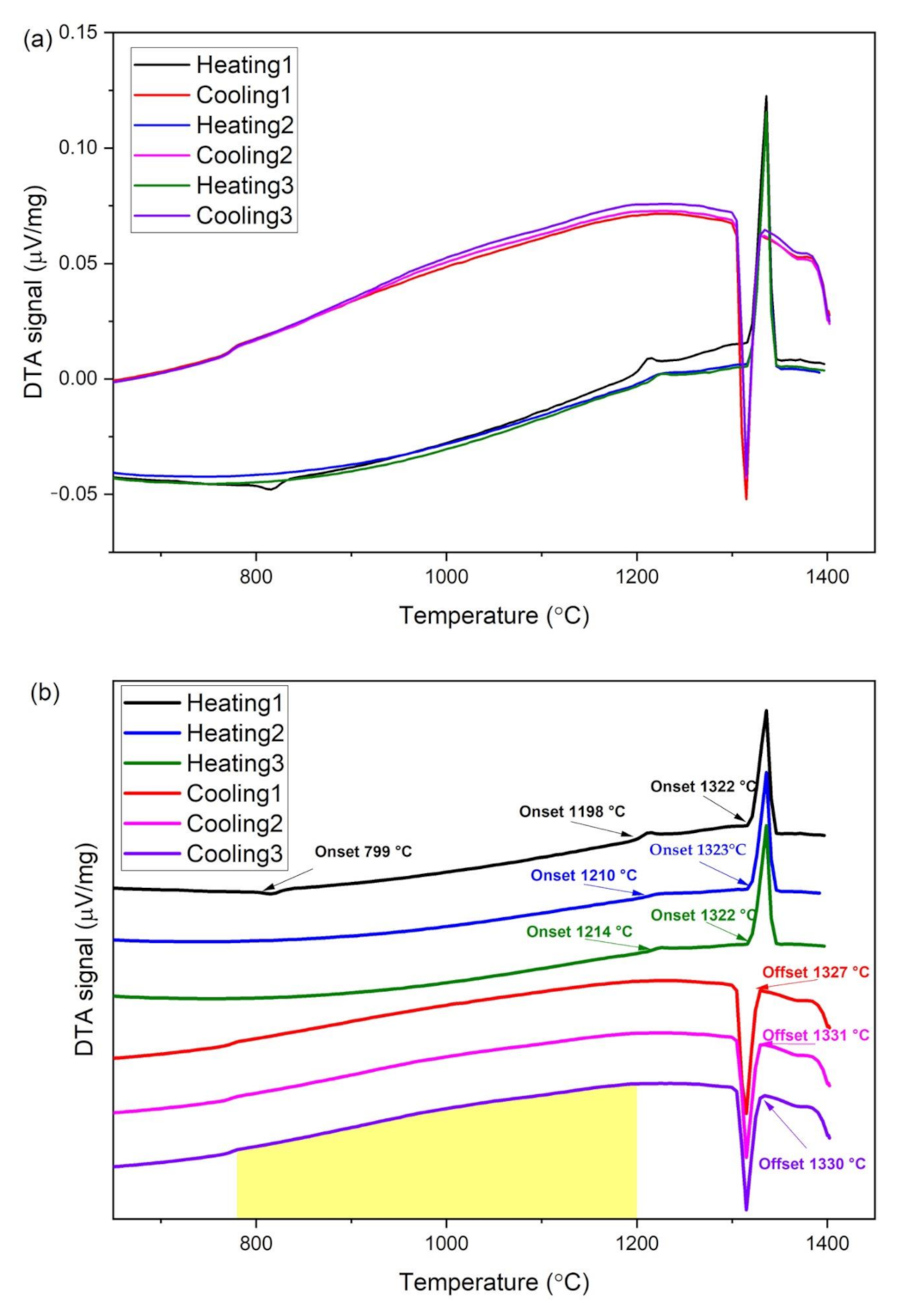
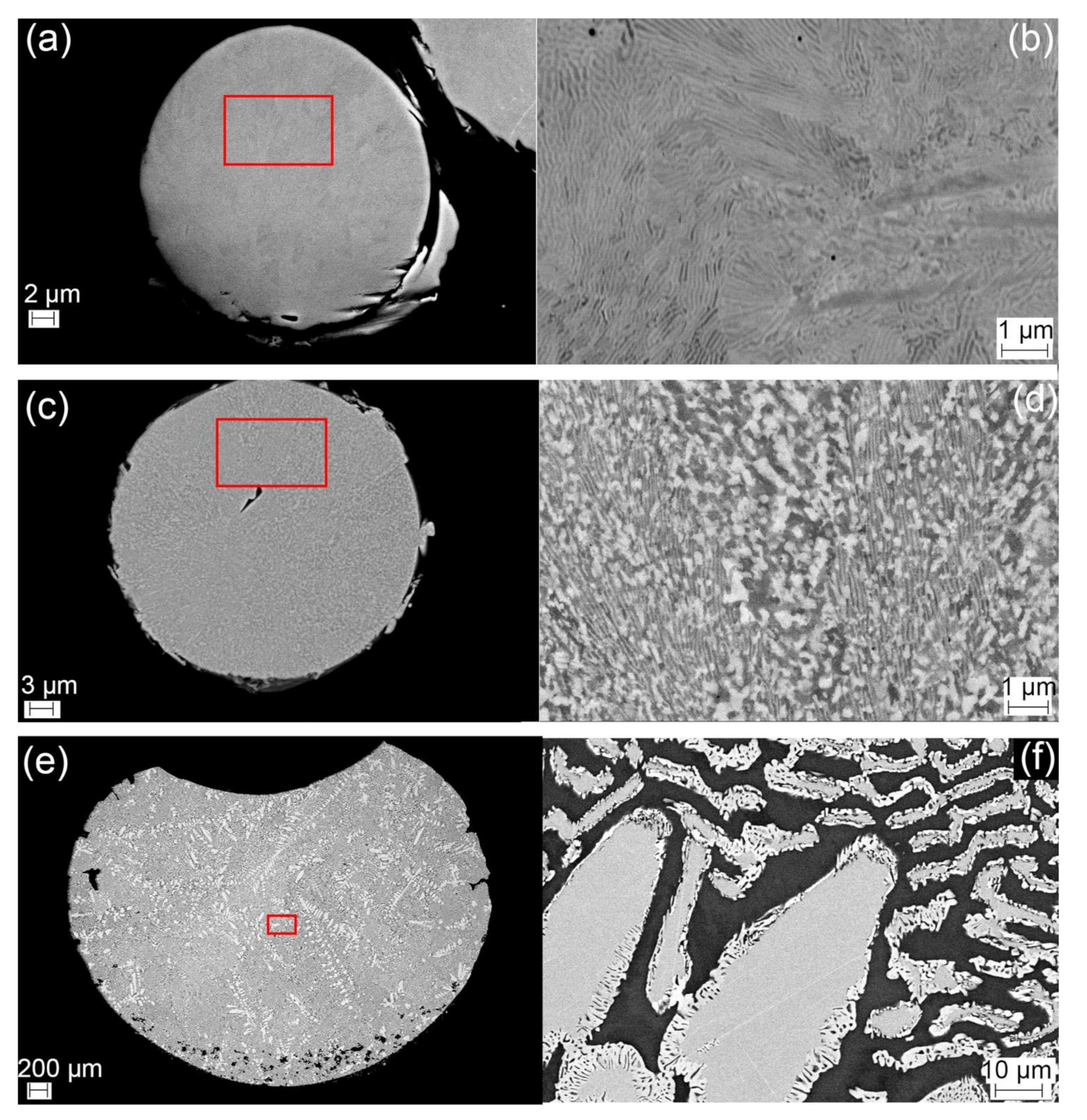
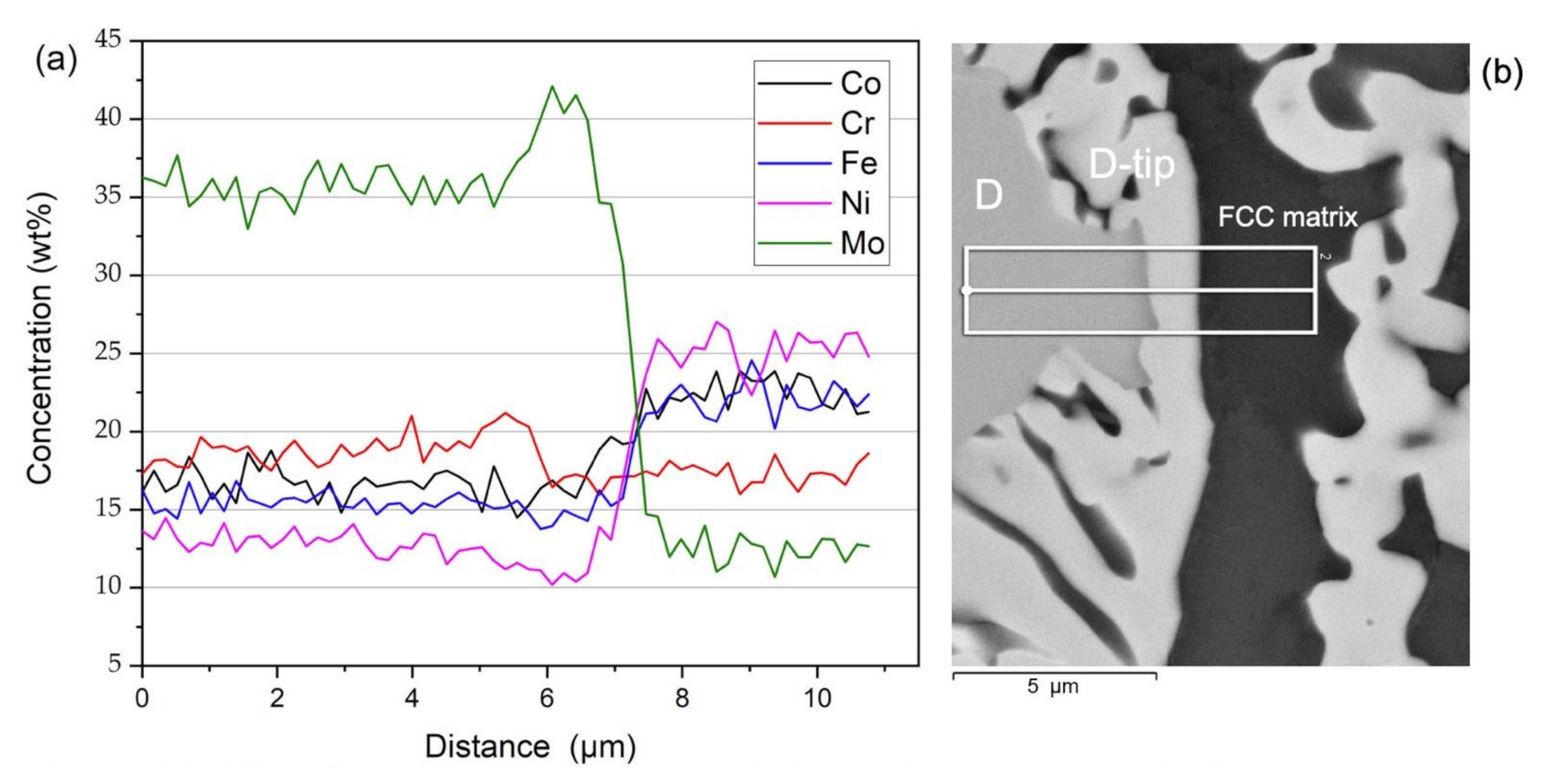

| CoCrFeMo0.85Ni HEA | Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | Max 0.10 | 19.2 ± 0.2 | 16.94 ± 0.2 | 18.19 ± 0.2 | 26.55 ± 0.2 | 19.12 ± 0.2 |
| at% | Max 0.10 | 20.62 ± 0.2 | 20.62 ± 0.2 | 20.62 ± 0.2 | 17.52 ± 0.2 | 20.62 ± 0.2 |
| Measurements Cycles | DTA | DSC with Baseline |
|---|---|---|
| Mass before (mg) | 428.75 | 129.3 |
| Mass after (mg) | 428.76 | 130.1 |
| Measurements Cycles | DTA | DSC with Baseline | Interrupted 900 °C DTA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st heating (°C) | 799 (exo *) 1198 1322 | 803 (exo *) 1197 1319 | 801 (exo *) |
| 1st cooling (°C) | 1327 1321 | 1320 | - |
| 2nd heating (°C) | 1210 1323 | 1221 1318 | - |
| 2nd cooling (°C) | 1331 1323 | 1319 | - |
| 3rd heating (°C) | 1214 1322 | 1233 1318 | - |
| 3rd cooling (°C) | 1330 1323 | 1319 1169 | - |
| Co | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | 19.2 ± 0.2 | 16.9 ± 0.2 | 18.2 ± 0.2 | 26.6 ± 0.2 | 19.1 ± 0.2 |
| As-received EDX (raw powder) | 19.28 ± 0.24 | 17.10 ± 0.18 | 17.93 ± 0.2 | 27.34 ± 0.3 | 18.35 ± 0.24 |
| DTA FCC matrix | 22.23 ± 0.24 | 16.03 ± 0.17 | 21.09 ± 0.21 | 16.32 ± 0.26 | 24.33 ± 0.26 |
| DTA central dendrite (σ) | 16.42 ± 0.20 | 18.62 ± 0.19 | 15.25 ± 0.20 | 36.72 ± 0.31 | 12.99 ± 0.22 |
| DTA dendrite tip (µ) | 16.13 ± 0.23 | 17.51 ± 0.18 | 13.86 ± 0.19 | 42.49 ± 0.31 | 10.01 ± 0.21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Sergeev, D.; Dodge, M.F.; Fanicchia, F.; Müller, M.; Paul, S.; Dong, H. Microstructure and Thermal Analysis of Metastable Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloy CoCrFeMo0.85Ni. Materials 2021, 14, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051073
Dong Z, Sergeev D, Dodge MF, Fanicchia F, Müller M, Paul S, Dong H. Microstructure and Thermal Analysis of Metastable Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloy CoCrFeMo0.85Ni. Materials. 2021; 14(5):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051073
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zihui, Dmitry Sergeev, Michael F. Dodge, Francesco Fanicchia, Michael Müller, Shiladitya Paul, and Hongbiao Dong. 2021. "Microstructure and Thermal Analysis of Metastable Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloy CoCrFeMo0.85Ni" Materials 14, no. 5: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051073
APA StyleDong, Z., Sergeev, D., Dodge, M. F., Fanicchia, F., Müller, M., Paul, S., & Dong, H. (2021). Microstructure and Thermal Analysis of Metastable Intermetallic Phases in High-Entropy Alloy CoCrFeMo0.85Ni. Materials, 14(5), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14051073








