Permanent Deformation and Rutting Resistance of Demolition Waste Triple Blends in Unbound Pavement Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ardalan, N.; Wilson, D.J.; Larkin, T.J. Analyzing the Application of Different Sources of Recycled Concrete Aggregate for Road Construction. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2020, 2674, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghoolpilehrood, F.; Disfani, M.M.; Arulrajah, A. Geotechnical Characteristics of Aged Biosolids Stabilized with Cement and Lime. Aust. Geomech. J. 2013, 48, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Senate, T. Environment and Communications References Committee: Never Waste a Crisis: The Waste and Recycling Industry in Australia; Parliament House Canberra ACT: Canberra, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arulrajah, A.; Arulrajah, A.; Mohammadinia, A.; Mirzababaei, M.; Horpibulsuk, S. Wheel tracker testing of recycled concrete and tyre aggregates in Australia. Geotech. Res. 2020, 7, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.F.; Chan, F.W.K. Reduced rutting in unbound granular pavement layers through improved grading design. In Institution of Civil Engineers—Transport; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 1996; Volume 117, pp. 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Disfani, M.M.; Arulrajah, A.; Ali, M.M.Y.; Bo, M.W. Fine recycled glass: A sustainable alternative to natural aggregates. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 5, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.Y.; Arulrajah, A.; Disfani, M.M.; Piratheepan, J. Suitability of Using Recycled Glass-Crushed Rock Blends for Pavement Subbase Applications. Geo-Frontiers 2011, 2011, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Debieb, F.; Kenai, S. The use of coarse and fine crushed bricks as aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suddeepong, A.; Sari, N.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijniwat, C.; Arulrajah, A. Interface shear behaviors between recycled concrete aggregate and geogrid for pavement applications. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 21, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.; Orhan, M. Reuse of waste bricks in the production line. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatheesan, T.; Arulrajah, A.; Bo, M.W.; Vuong, B.; Wilson, J.L. Crushed brick blends with crushed rock for pavement systems. In Institution of Civil Engineers—Waste and Resource Management; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2010; Volume 163, pp. 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakugan, N.; Arulrajah, A.; Bo, M.W. Laboratory Testing of Soils, Rocks and Aggregates, 1st ed.; J. Ross Publishing: Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Arulrajah, A.; Ali, M.M.Y.; Piratheepan, J.; Bo, M.W. Geotechnical Properties of Waste Excavation Rock in Pavement Subbase Applications. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, K. Innovative fracture-resistant construction material from C&D waste aggregate, fly ash and recycled plastics. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 31, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Montardo, J.P.; Prietto, P.D.M.; Pasa, G.S. Engineering Behavior of a Sand Reinforced with Plastic Waste. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2002, 128, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, M.; Rachan, R.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Arulrajah, A.; Mirzababaei, M. Effect of wetting–drying cycles on compressive strength and microstructure of recycled asphalt pavement—Fly ash geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppala, A.J.; Hoyos, L.R.; Potturi, A.K. Resilient Moduli Response of Moderately Cement-Treated Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Aggregates. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthagaran, V.; Arulrajah, A.; Bo, M.W. Geotechnical laboratory testing of biosolids. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2010, 4, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Maghoolpilehrood, F.; Disfani, M.M.; Horpibulsuk, S. Spent coffee grounds as a non-structural embankment fill material: Engineering and environmental considerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 72, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberian, M.; Li, J.; Setunge, S. Evaluation of permanent deformation of a new pavement base and subbase containing unbound granular materials, crumb rubber and crushed glass. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Mohammadinia, A.; Maghool, F.; Horpibulsuk, S. Tire derived aggregates as a supplementary material with recycled demolition concrete for pavement applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Maghoolpilehrood, F.; Samingthong, W.; Du, Y.-J.; Shen, S.-L. Evaluation of Interface Shear Strength Properties of Geogrid Reinforced Foamed Recycled Glass Using a Large-Scale Direct Shear Testing Apparatus. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghool, F.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Du, Y.-J. Laboratory Evaluation of Ladle Furnace Slag in Unbound Pavement-Base/Subbase Applications. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04016197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghool, F.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Mohajerani, A. Engineering and Leachate Characteristics of Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag as a Construction Material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghool, F.; Arulrajah, A.; Du, Y.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Chinkulkijniwat, A. Environmental impacts of utilizing waste steel slag aggregatesas recycled road construction materials. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 19, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlashi, S.M.H.; Vaillancourt, M.; Carter, A.; Bilodeau, J.-P. Resilient modulus of pavement unbound granular materials containing recycled glass aggregate. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Piratheepan, J.; Aatheesan, T.; Bo, M.W. Geotechnical Properties of Recycled Crushed Brick in Pavement Applications. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disfani, M.M.; Arulrajah, A.; Haghighi, H.; Mohammadinia, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Flexural beam fatigue strength evaluation of crushed brick as a supplementary material in cement stabilized recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disfani, M.; Arulrajah, A.; Bo, M.W.; Sivakugan, N. Environmental risks of using recycled crushed glass in road applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 20, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Piratheepan, J.; Ali, M.M.Y.; Bo, M.W. Geotechnical Properties of Recycled Concrete Aggregate in Pavement Sub-Base Applications. Geotech. Test. J. 2012, 35, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS. Method for Sampling and Testing Aggregates—Particle Size Distribution by Sieving; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 1996; Australian Standard 1141.11. [Google Scholar]
- AS. Particle Density and Water Absorption of Fine Aggregate; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 2000; Australian Standard 1141.5. [Google Scholar]
- AS. Particle Density and Water Absorption of Coarse Aggregate—Weighing-in-Water Method; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 2000; Australian Standard 1141.6.1. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Methods for Moisture, Ash, and Organic Matter of Peat and Other Organic Soils; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007; ASTM Standard D2974. [Google Scholar]
- AS. Methods for Sampling and Testing Aggregates-Method 15: Flakiness Index; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 1999; Australian standard AS 1141.15. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard Test Method for Resistance to Degradation of Small-Size Coarse Aggregate by Abrasion and Impact in the Los Angeles Machine; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2006; ASTM Standard C131. [Google Scholar]
- AS. Soil Compaction and Density Tests—Determination of the Dry Density/Moisture Content Relation of a Soil Using Modified Compactive Effort; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 2003; Australian Standard 1289.5.2.1. [Google Scholar]
- AS. Determination of the California Bearing Ratio of a Soil—Standard Laboratory Method for a Remoulded Specimen; Australian Standard: Sydney, Australia, 1998; Australian Standard 1289.6.1.1. [Google Scholar]
- Austroads. Commentary to AG:PT/T053, Determination of Permanent Deformation and Resilient Modulus Characteristics of Unbound Granular Materials Under Drained Conditions; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2007; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Saberian, M.; Li, J.; Boroujeni, M.; Law, D.W.; Li, C. Application of demolition wastes mixed with crushed glass and crumb rubber in pavement base/subbase. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, D.; Grenfell, J.R.; Collop, A.C. Comparison of Small and Large Scale Wheel Tracking Devices. Road Materials and Pavement Design. ICAM 2009, 10, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austroads. AGTP-T054: Determination of Permanent Deformation Characteristics of Unbound Granular Materials by the Wheel-Tracking Test; Austroads: Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- VicRoads. Guide to General Requirements for Unbound Pavement Materials; VicRoads: Melbourne, Australia, 1998; Volume 39. [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Arulrajah, A.; Maghool, F.; Newman, G.; Haghighi, H.; Horpibulsuk, S. Cement-treated recycled glass and crushed rock blends: Modulus of rupture and stiffness properties. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
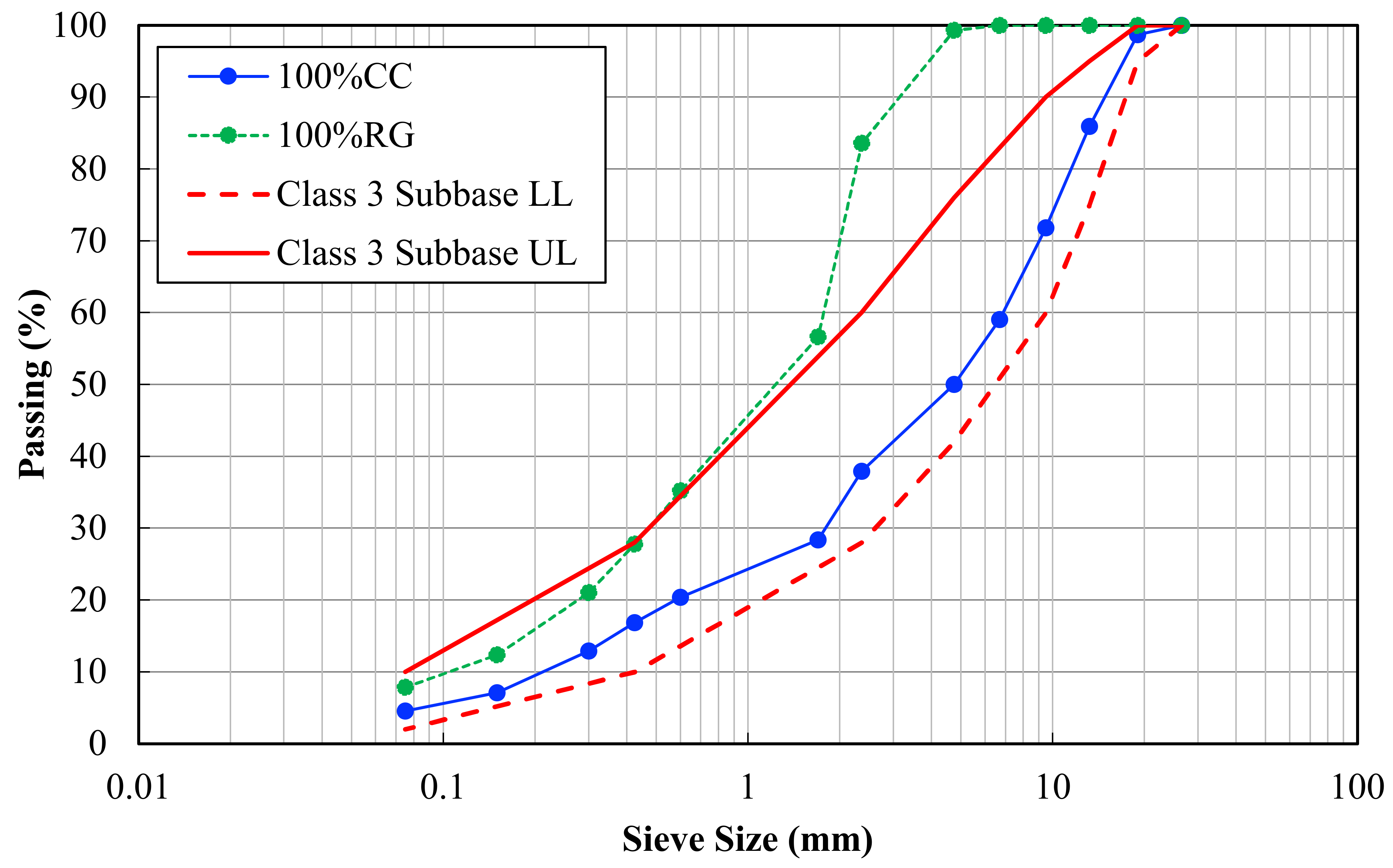
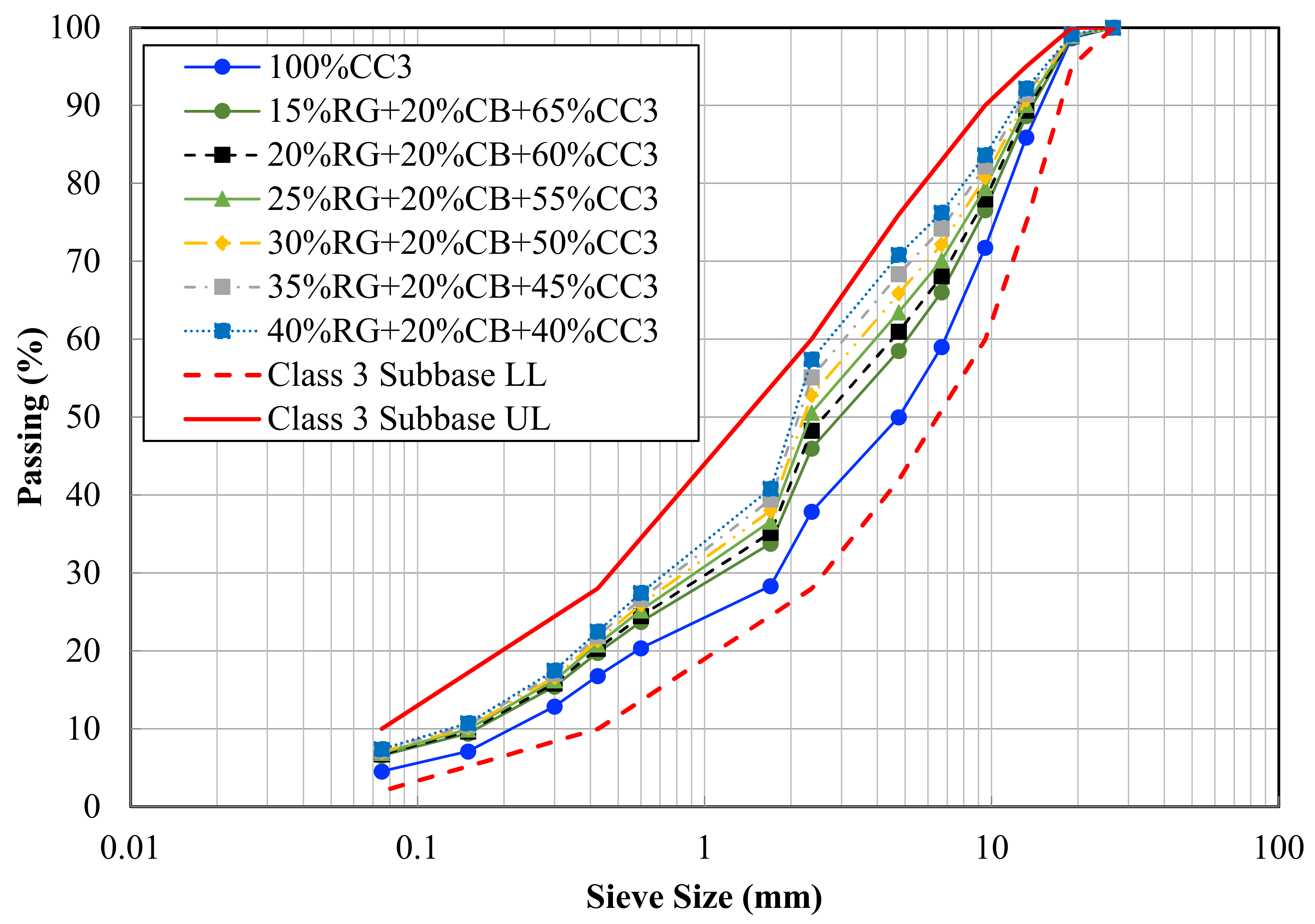
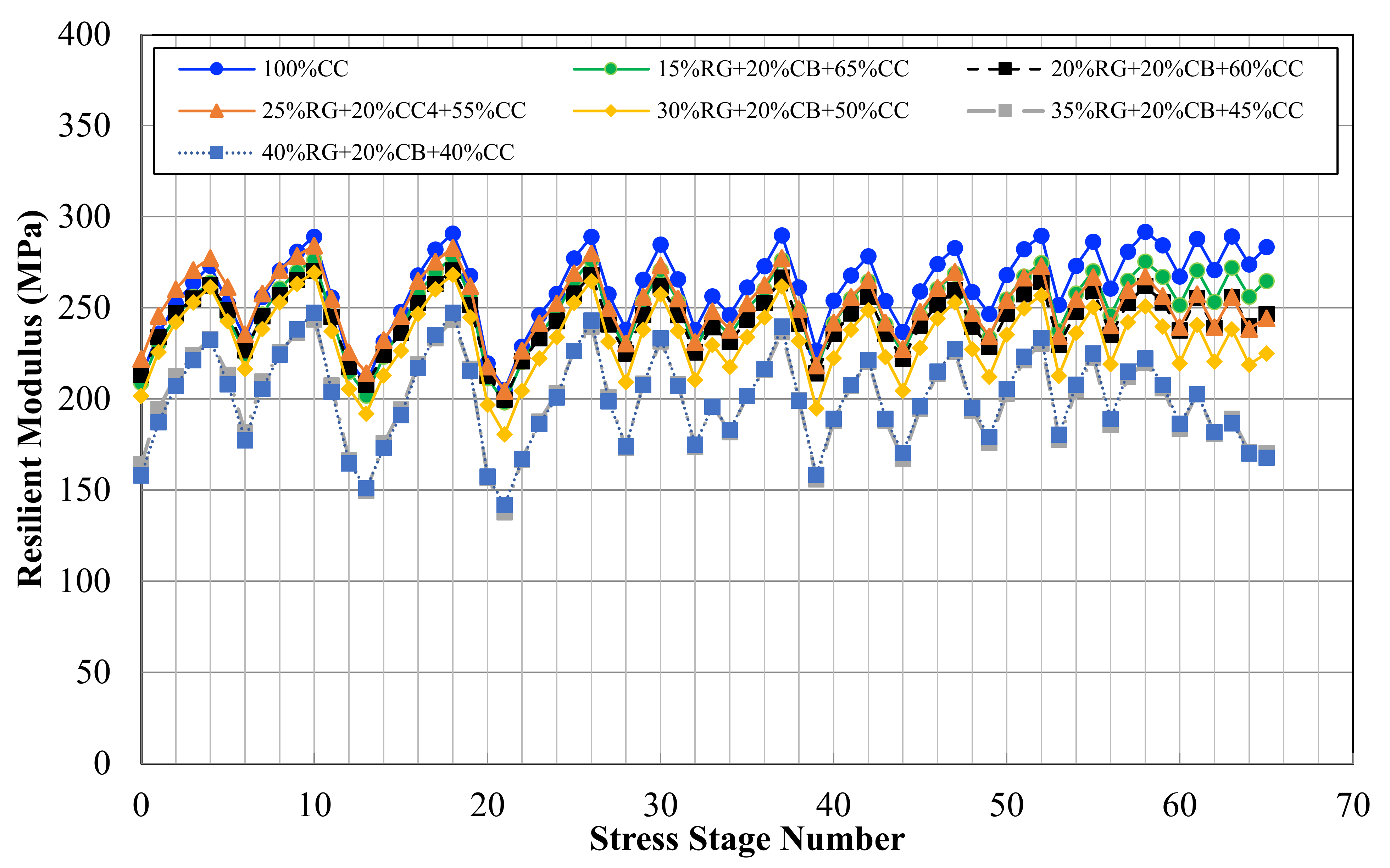

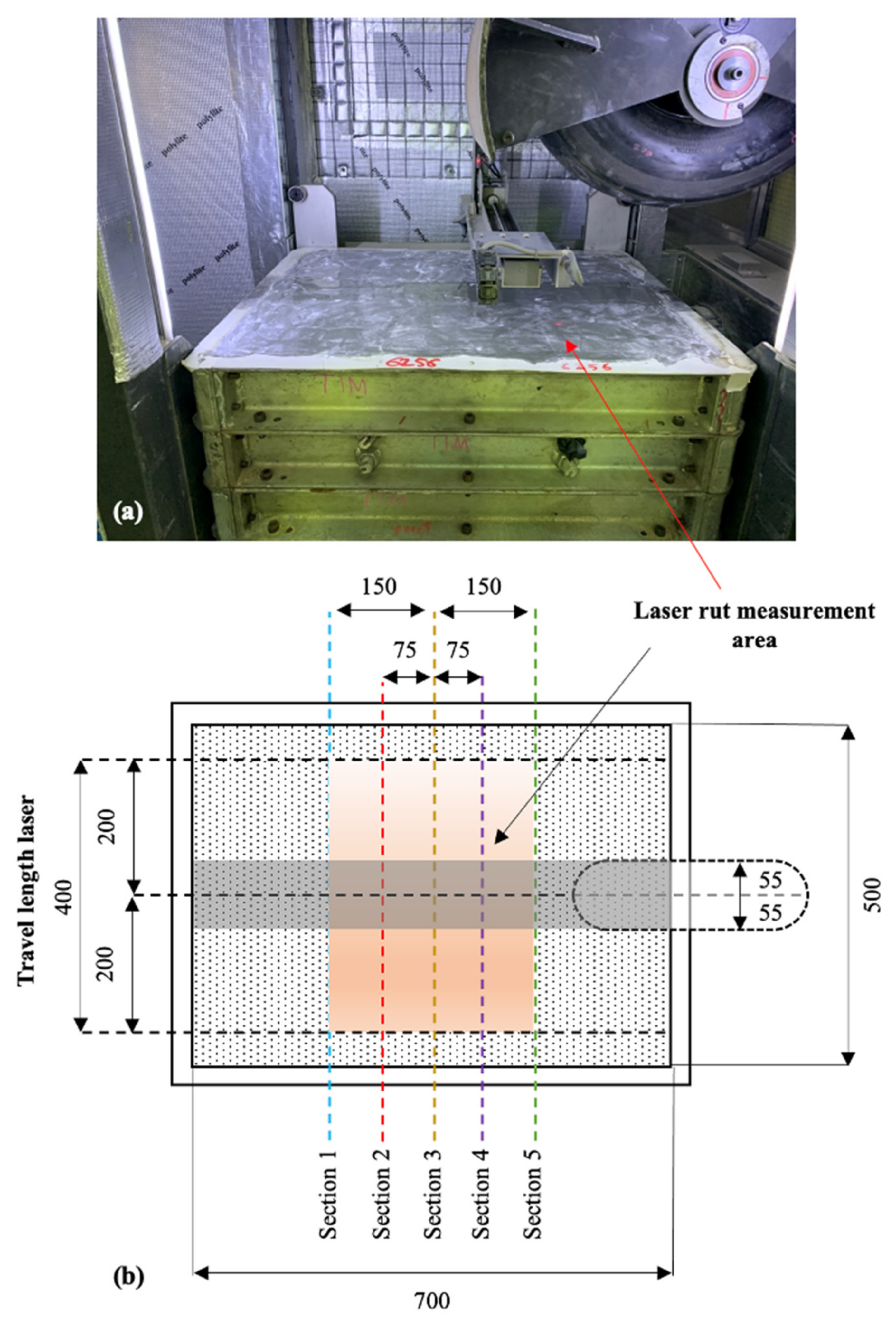

| Engineering Properties | 100% CC | 100% RG | Typical Quarry a Materials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine content | (%) | 4.5 | 7.8 | <10 |
| Sand content | (%) | 45.5 | 92 | 30–60 |
| Gravel content | (%) | 50 | 0.2 | 30–60 |
| Apparent particle density | (kN/m3) | 2.64 | 2.48 | >2 |
| Water absorption | (%) | 9.8 | <1 | 6–12 |
| Organic content | (%) | <1 | 1.2 | <5 |
| Flakiness index | 19.14 | - | <35 | |
| LA abrasion loss | (%) | 28 | - | <40 |
| California Bearing Ratio (CBR) | (%) | 239 | 20 | >80 |
| Resilient modulus (MR) | (MPa) | 205–292 | - | 125–300 |
| Blends | pH | OMC (%) | MDD (kN/m3) | CBR (%) | Permeability (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% CC | 12.4 | 11.5 | 1.96 | 230–248 | 1.05 × 10−7 |
| 15% RG + 20% CB + 65% CC | 11.87 | 10.6 | 1.98 | 220–257 | 4.57 × 10−7 |
| 20% RG + 20% CB + 60% CC | 11.78 | 10.7 | 1.97 | 192–228 | 1.39 × 10−7 |
| 25% RG + 20% CB + 55% CC | 11.64 | 10.7 | 1.97 | 167–182 | 2.15 × 10−7 |
| 30% RG + 20% CB + 50% CC | 11.51 | 10.5 | 1.96 | 165–202 | 9.76 × 10−7 |
| 35% RG + 20% CB + 45% CC | 11.37 | 10.4 | 1.96 | 131–157 | 1.78 × 10−6 |
| 40% RG + 20% CB + 40% CC | 11.23 | 10.0 | 1.96 | 116–147 | 4.34 × 10−6 |
| Blends | MR (MPa) | Permanent Strain at the End of Each Stage, Microstrain | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | ||
| 100% CC | 205–292 | 995 | 1282 | 1596 |
| 15% RG + 20% CB + 35% CC | 198–278 | 1082 | 1392 | 1703 |
| 20% RG + 20% CB + 40% CC | 200–271 | 1194 | 1492 | 1804 |
| 25% RG + 20% CB + 35% CC | 204–284 | 1154 | 1443 | 1755 |
| 30% RG + 20% CB + 30% CC | 181–270 | 1220 | 1534 | 1867 |
| 35% RG + 20% CB + 25 %CC | 138–244 | 1406 | 1746 | 2110 |
| 40% RG + 20% CB + 20% CC | 142–247 | 1383 | 1723 | 2086 |
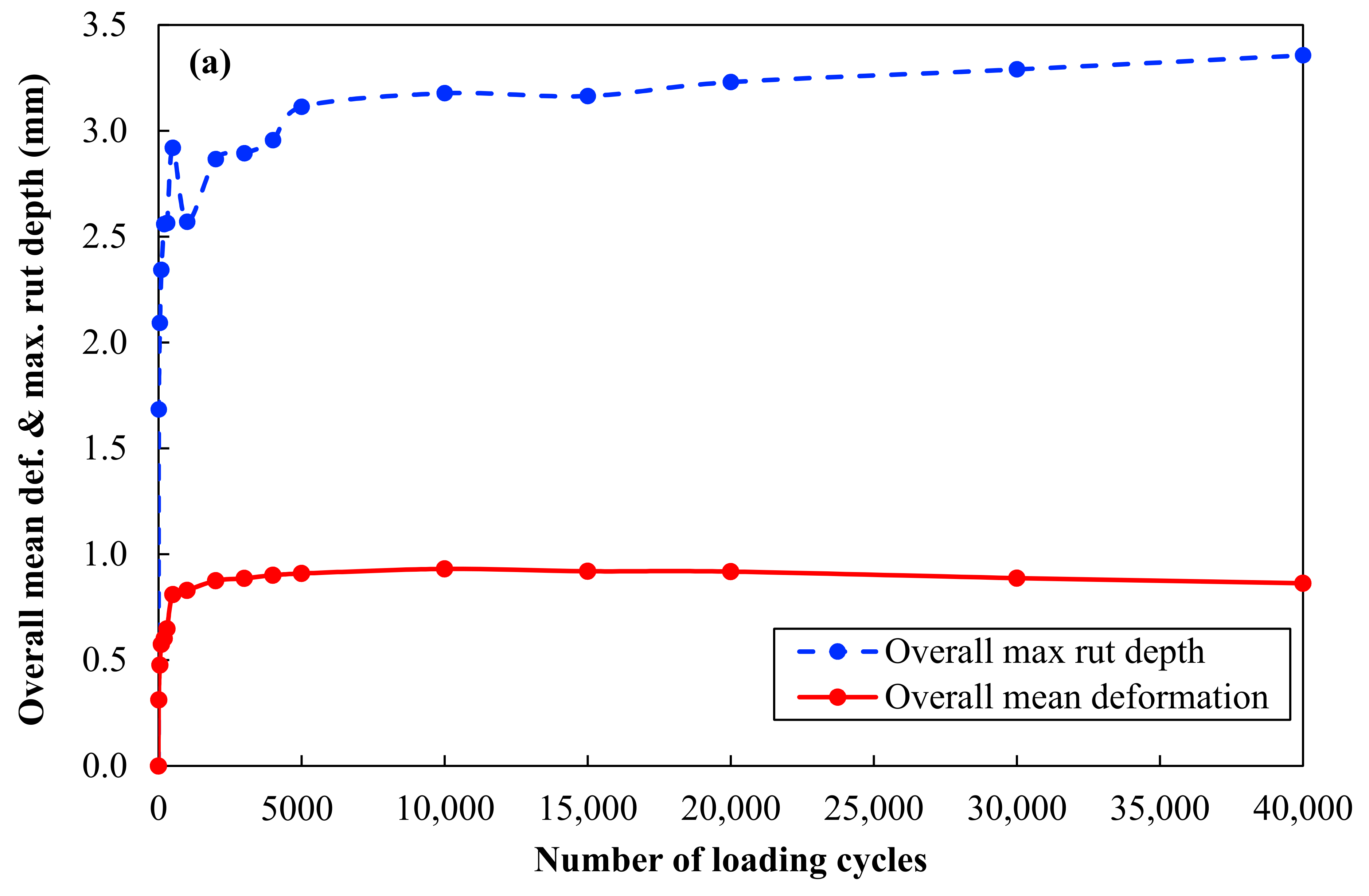
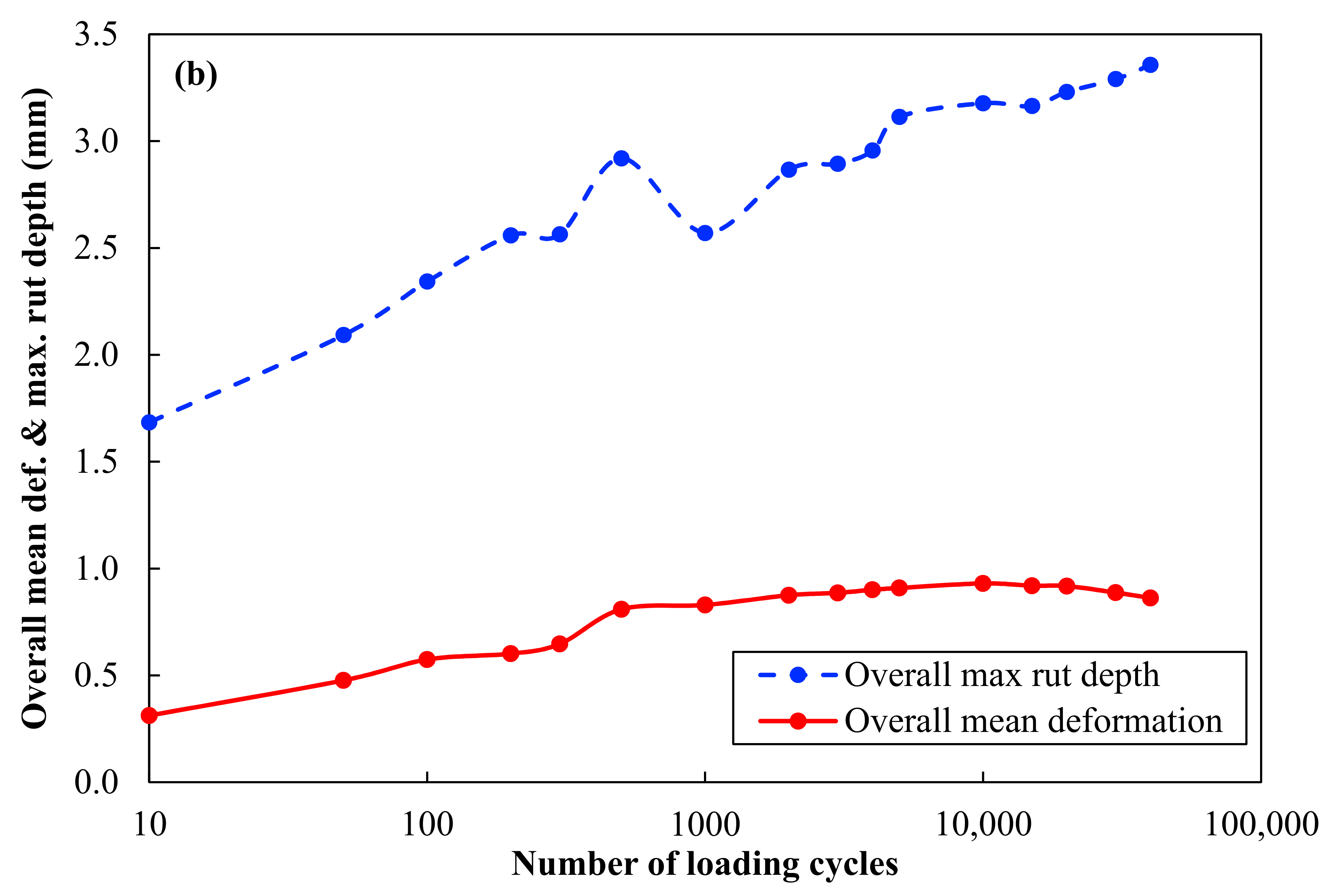
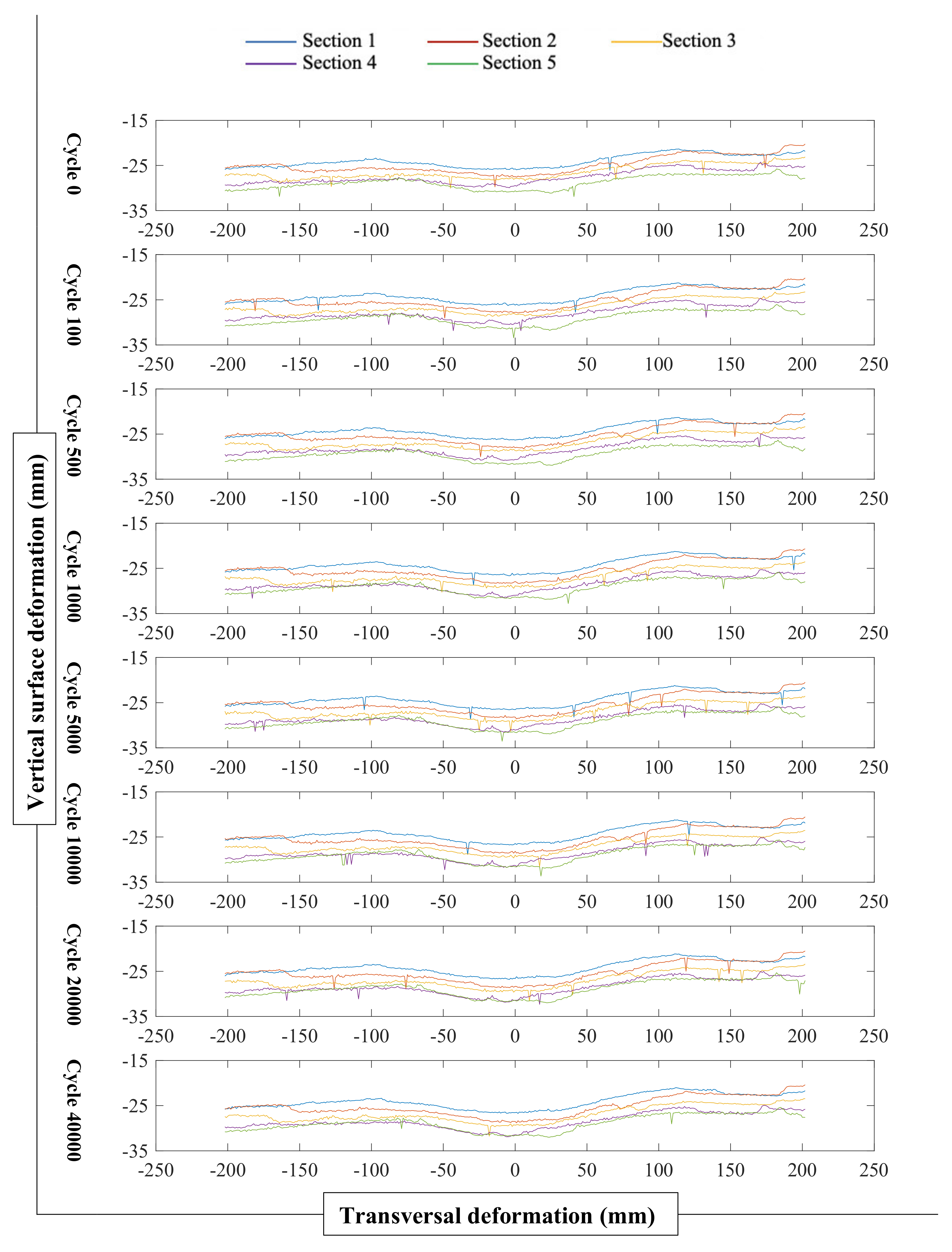
| Number of Cycles (N) | Mean Surface Deformation | Mean overall | Maximum Rut Depth | Mean overall | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross Section | Cross Section | |||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| −150 mm | −75 mm | 0 mm | +75 mm | +150 mm | −150 mm | −75 mm | 0 mm | +75 mm | +150 mm | |||
| 0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 10 | 0.8 | 0.8 | −0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.7 |
| 50 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 2.1 |
| 100 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.3 |
| 200 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.6 |
| 300 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.6 |
| 500 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 2.9 |
| 1000 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.6 |
| 2000 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 3.7 | 2.2 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 2.9 |
| 3000 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 2.9 |
| 4000 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 3.0 |
| 5000 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 3.1 |
| 10,000 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 3.2 |
| 15,000 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 3.2 |
| 20,000 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.1 | 3.2 |
| 30,000 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 3.9 | 4.3 | 2.8 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 3.3 |
| 40,000 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maghool, F.; Senanayake, M.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Permanent Deformation and Rutting Resistance of Demolition Waste Triple Blends in Unbound Pavement Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040798
Maghool F, Senanayake M, Arulrajah A, Horpibulsuk S. Permanent Deformation and Rutting Resistance of Demolition Waste Triple Blends in Unbound Pavement Applications. Materials. 2021; 14(4):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040798
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaghool, Farshid, Muditha Senanayake, Arul Arulrajah, and Suksun Horpibulsuk. 2021. "Permanent Deformation and Rutting Resistance of Demolition Waste Triple Blends in Unbound Pavement Applications" Materials 14, no. 4: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040798
APA StyleMaghool, F., Senanayake, M., Arulrajah, A., & Horpibulsuk, S. (2021). Permanent Deformation and Rutting Resistance of Demolition Waste Triple Blends in Unbound Pavement Applications. Materials, 14(4), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040798







