LTCC and Bulk Zn4B6O13–Zn2SiO4 Composites for Submillimeter Wave Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
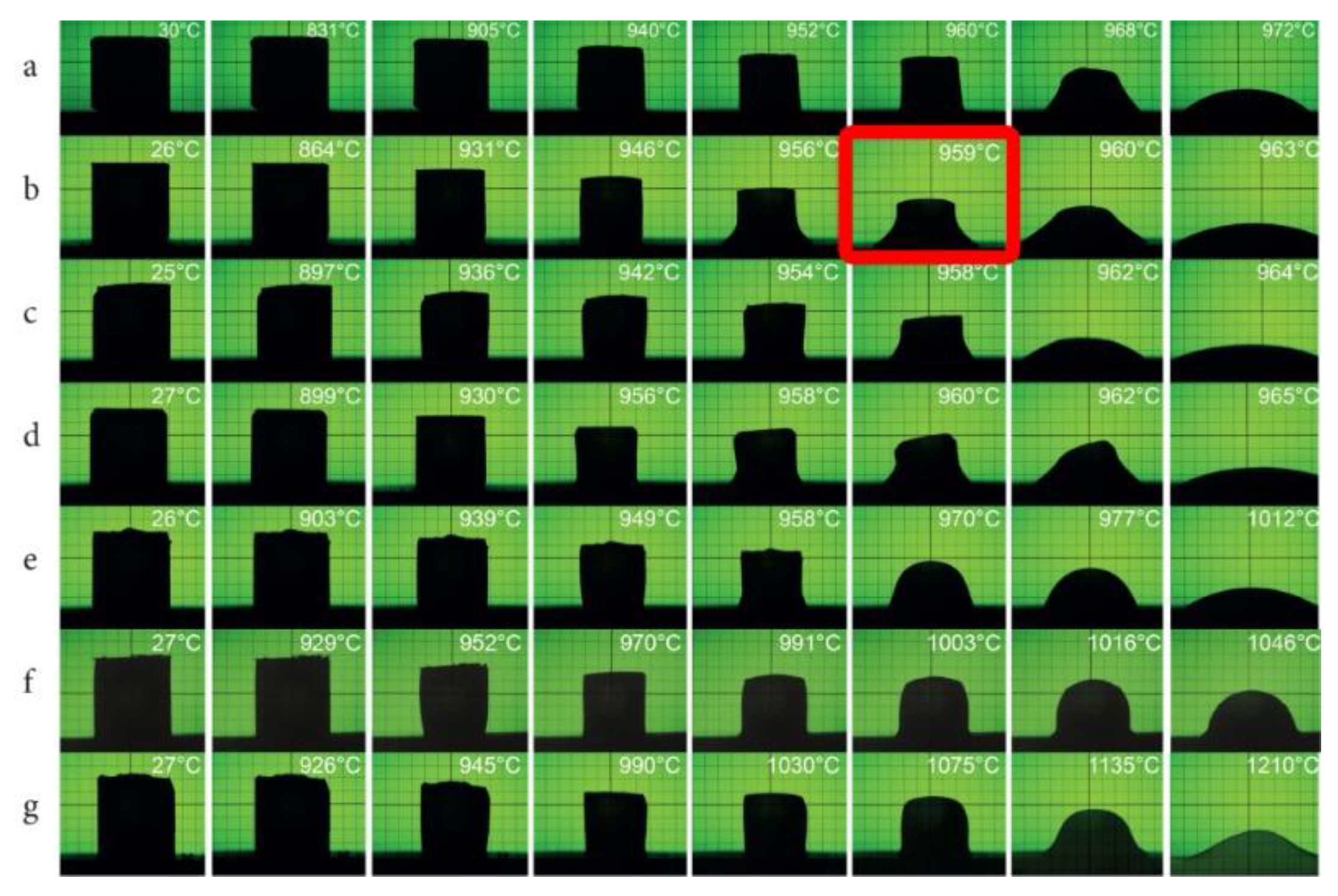
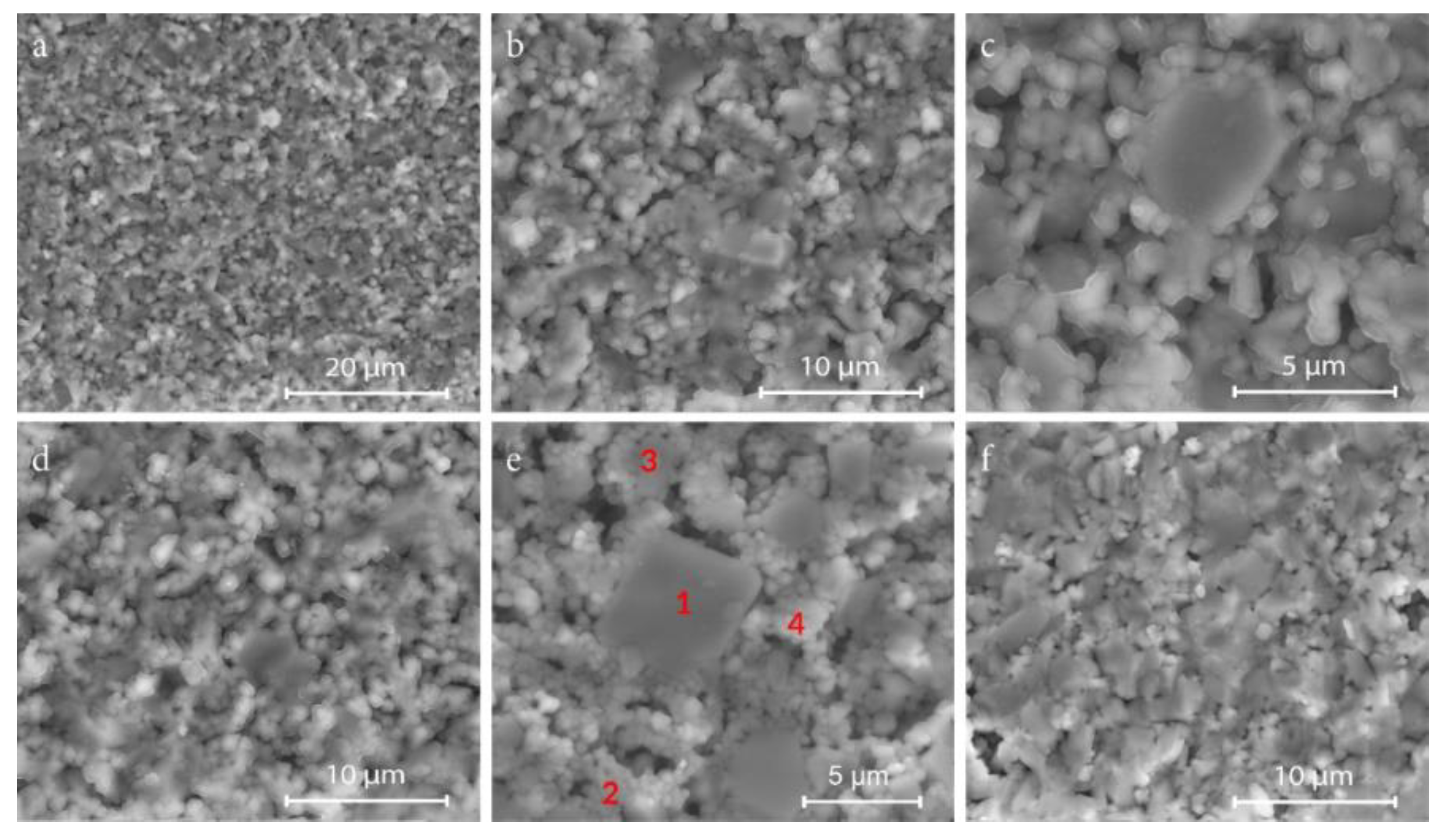
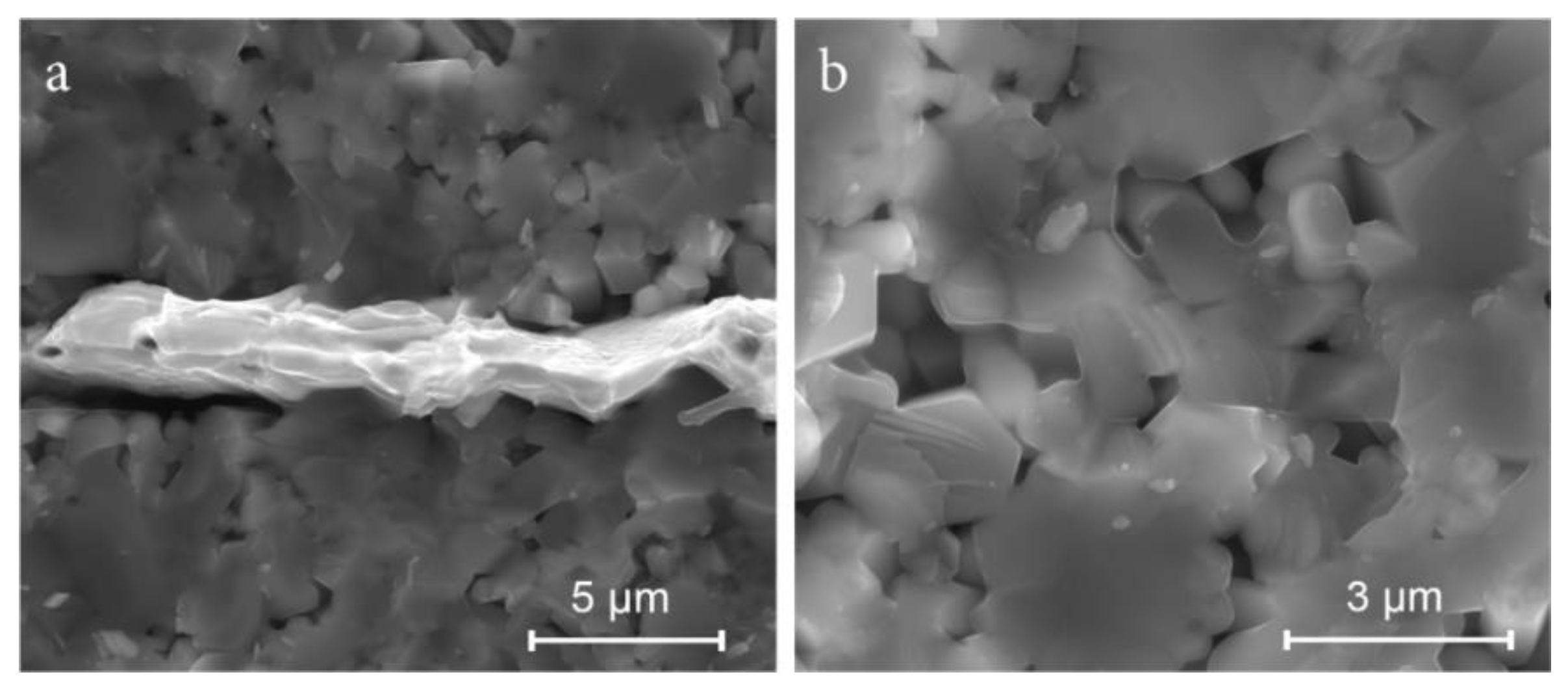
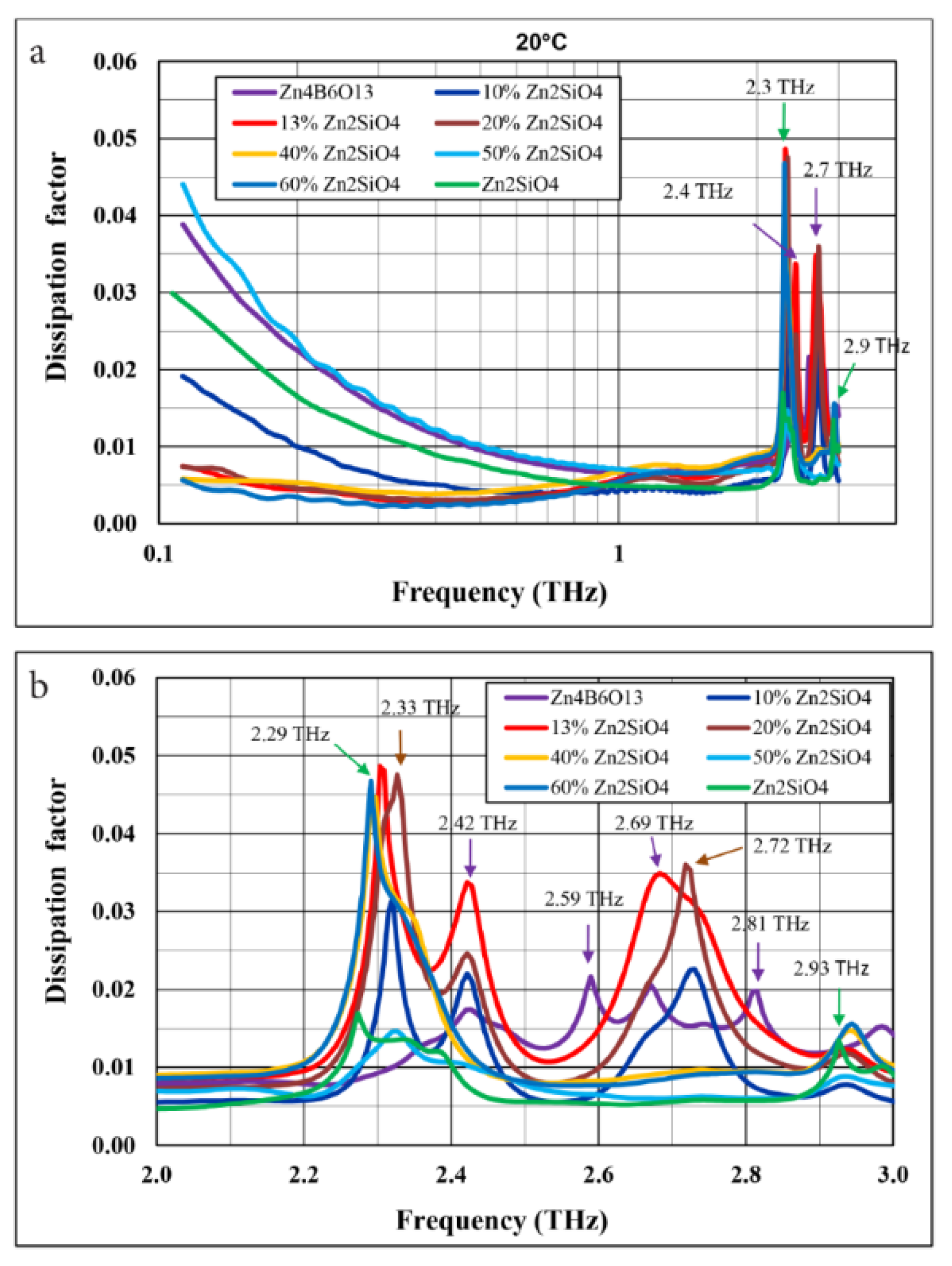
3.1. Composition, Microstructure, Sintering Behavior
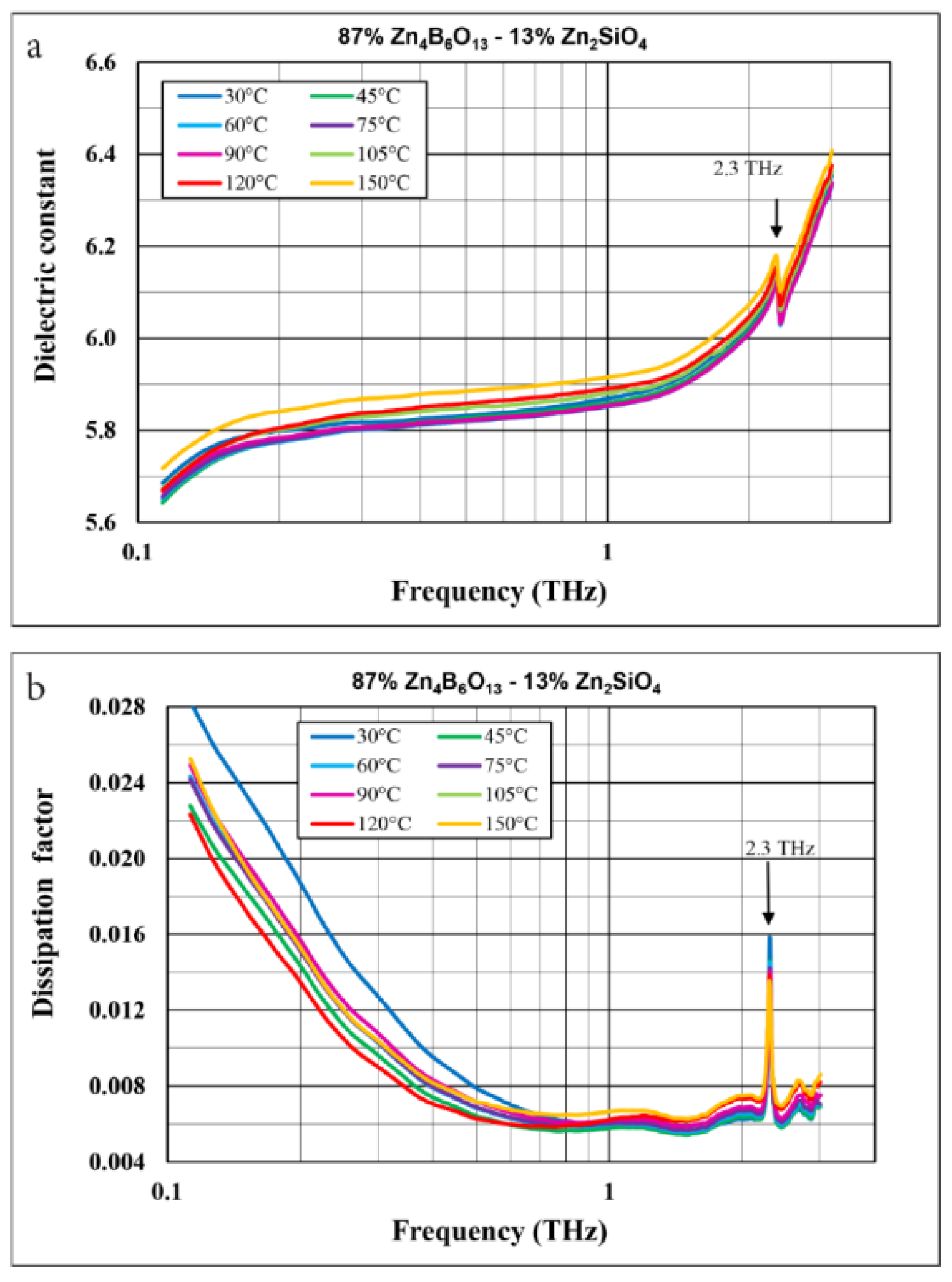
3.2. LTCC Structures
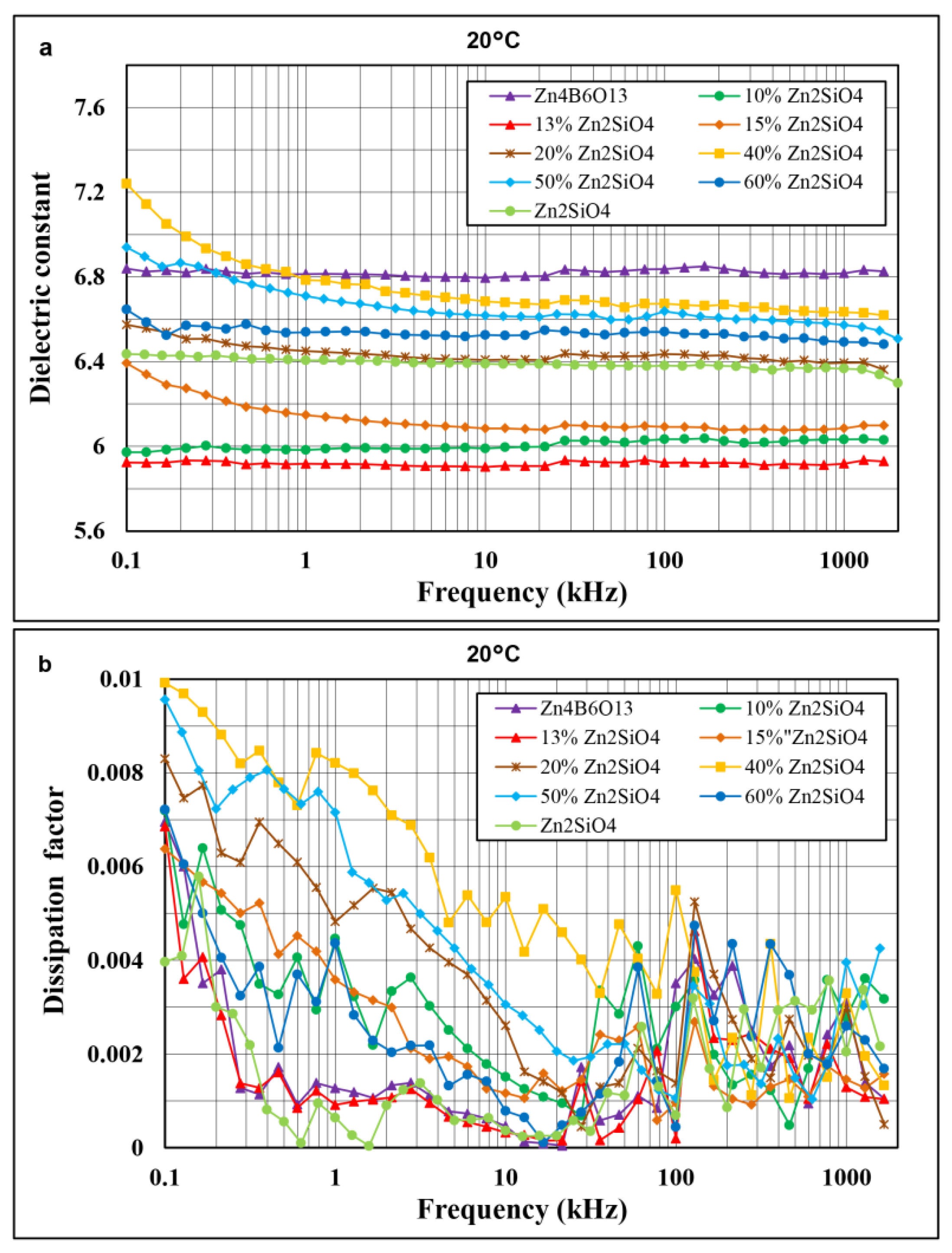
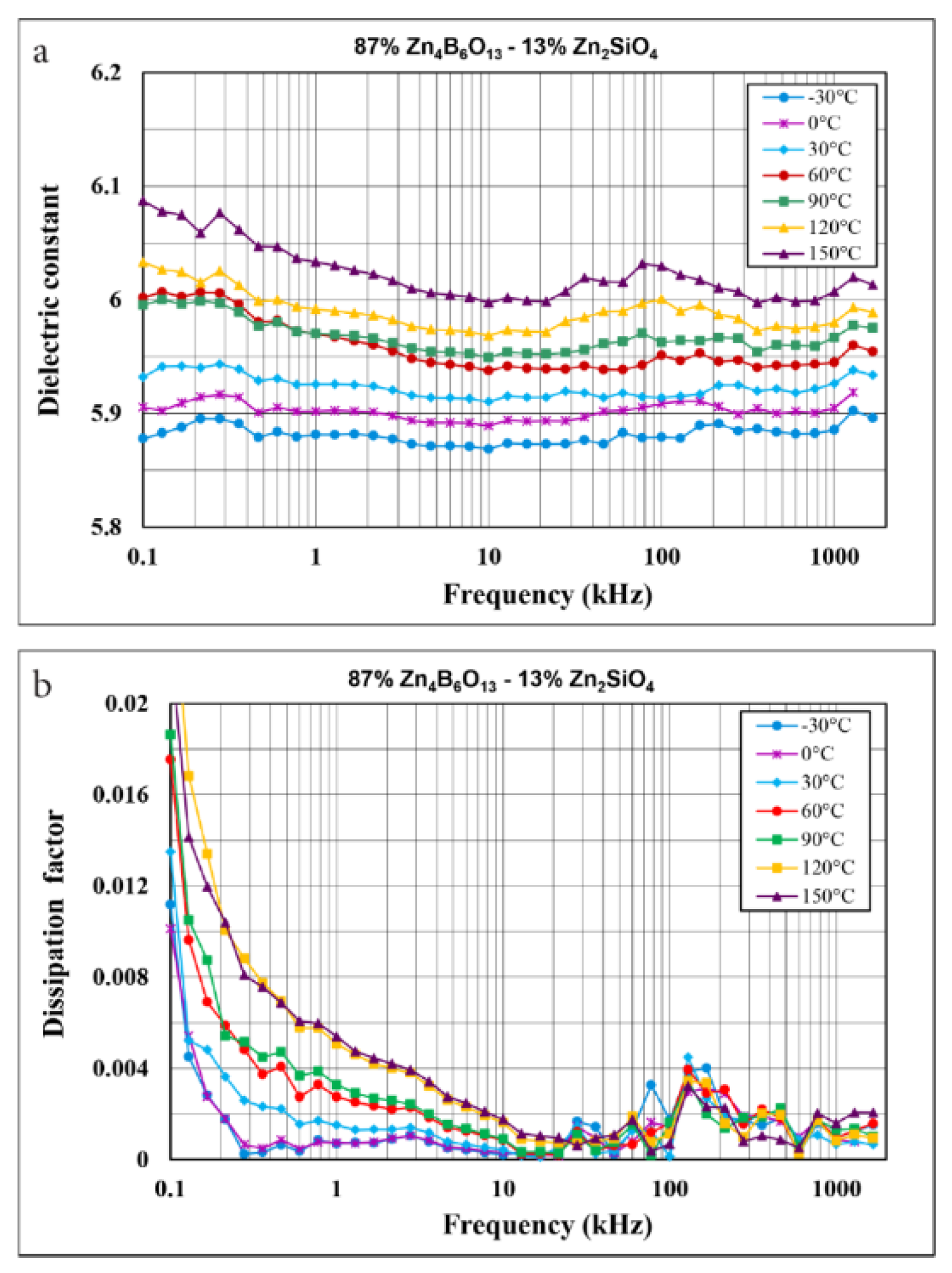
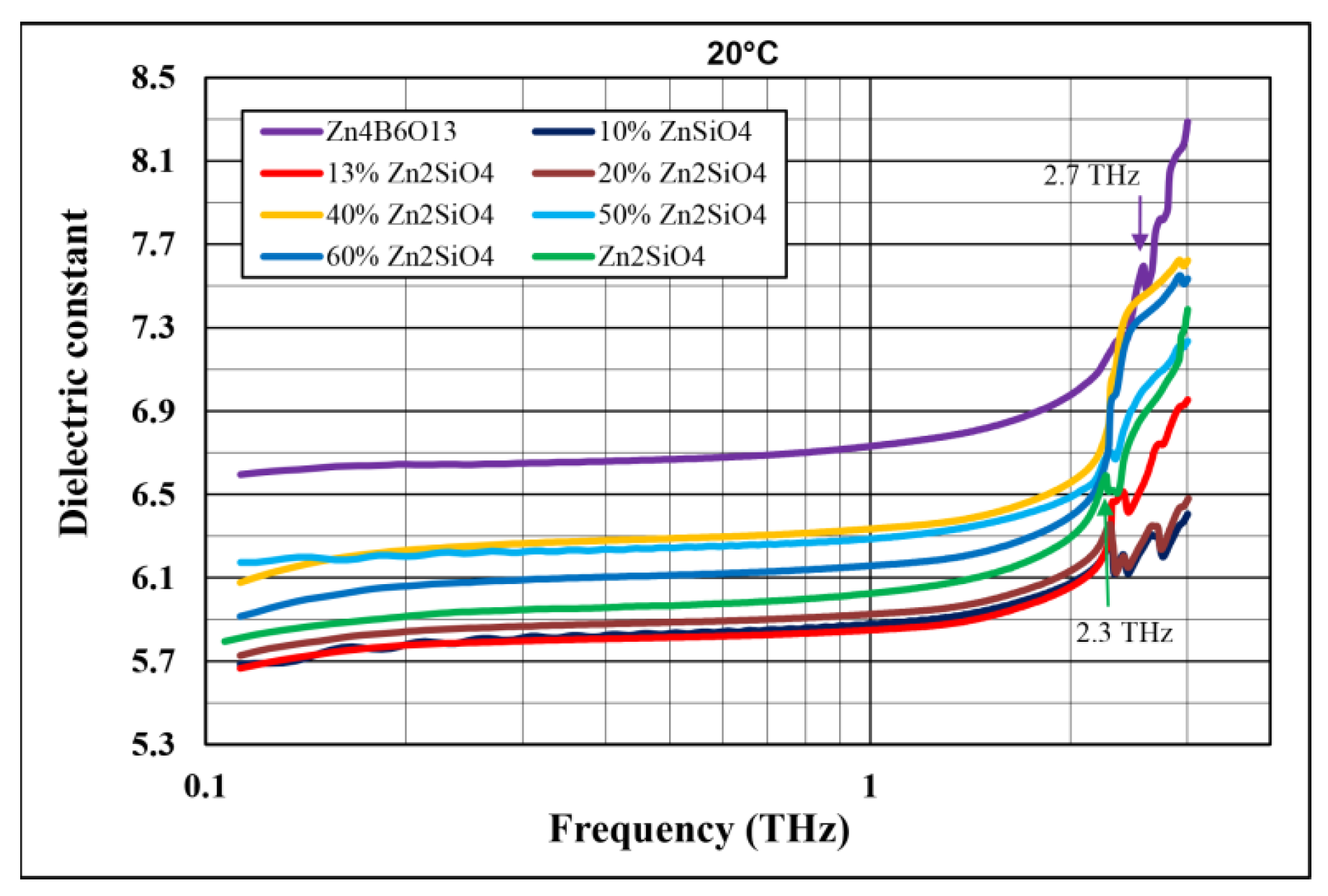
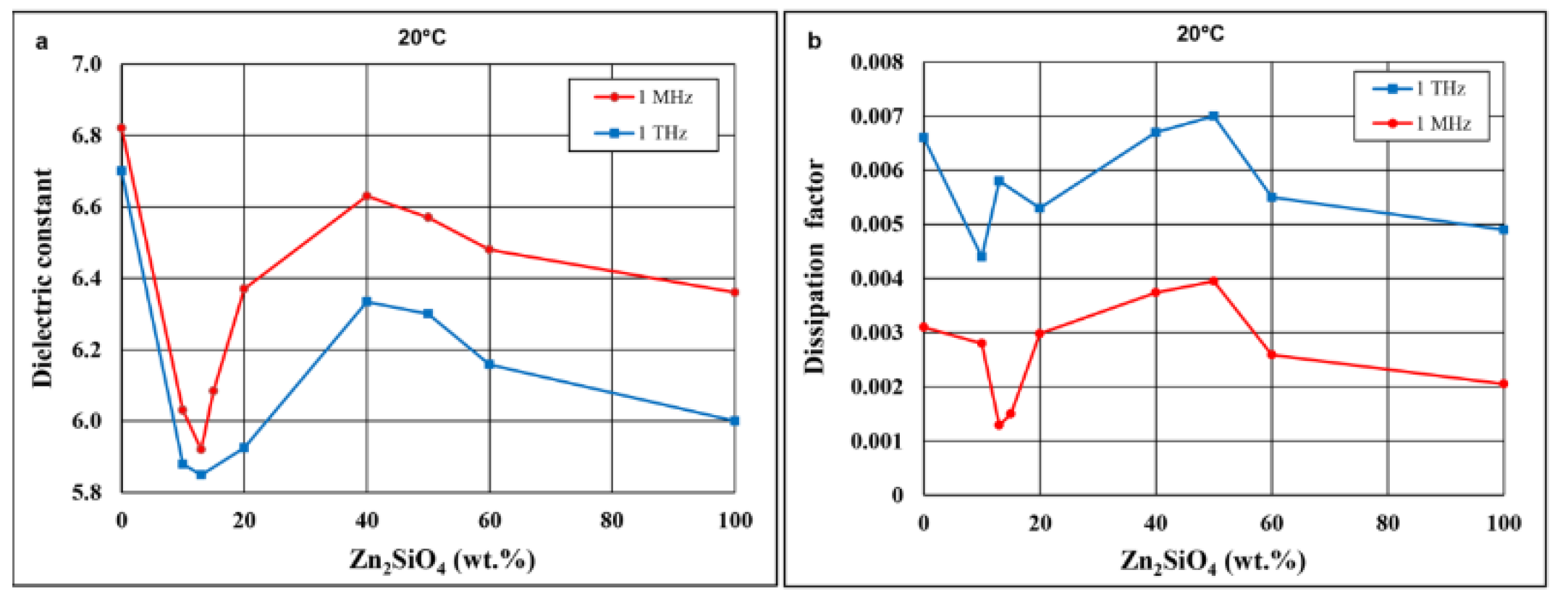
3.3. Dielectric Properties
4. Conclusions
- Lowering or broadening and stabilization of the sintering temperature range
- Improvement of the surface smoothness and uniformity of the substrates and consequently the quality and resolution of screen-printed patterns
- High-frequency dielectric constants for composites containing 10–15 wt% Zn2SiO4 are lower than those of the pure ceramic components
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, H.; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M.; Gutierrez, F. Millimeter Wave Mobile Communications for 5G Cellular: It Will Work! IEEE Access 2013, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, R.; Iqbal, Y.; Rambo, C.R.; Khan, H. Research trends in microwave dielectrics and factors affecting their properties: A review. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 105, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, M.T.; Ubic, R.; Jantunen, H. Low-loss dielectric ceramic materials and their properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2015, 60, 392–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, A.; Sebastian, M.T.; Raman, S. Applications of Microwave Materials: A Review. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 2601–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, C.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, X.M. B2O3-modified fused silica microwave dielectric materials with ultra-low dielectric constant. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagierczak, D.; Synkiewicz, B.; Kulawik, J. Low dielectric constant composites based on B2O3 and SiO2 rich glasses, cordierite and mullite. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 14495–14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.; Ramachandran, P.; Sobocinski, M.; Vahera, T.; Jantunen, H. ULTCC Glass Composites Based on Rutile and Anatase with Cofiring at 400 °C for High Frequency Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4274–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunooka, T.; Ando, M.; Suzuki, S.; Yasufuku, Y.; Ohsato, H. Research & Developments for Millimeter-Wave Dielectric Forsterite with Low Dielectric Constant, High Q, and Zero Temperature Coefficient of Resonant Frequency. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafrooei, H.B.; Liu, B.; Su, W.; Song, K.X. Ca3MgSi2O8: Novel low-permittivity microwave dielectric ceramics for 5G application. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Hu, M.; Lei, W.; Wang, X. A novel low-permittivity LiAl0.98(Zn0.5Si0.5)0.02O2 -based microwave dielectric ceramics for LTCC application. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2019, 17, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ohsato, H.; Kakimoto, K.-I. Characterization and dielectric behavior of willemite and TiO2-doped willemite ceramics at millimeter-wave frequency. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Yue, Z.; Zhuang, H.; Meng, S.; Li, L. Microstructure and Microwave Dielectric Properties of TiO2-Doped Zn2SiO4 Ceramics Synthesized Through the Sol-Gel Process. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 3981–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Song, M.-E.; Joung, M.-R.; Choi, J.-H.; Nahm, S.; Gu, S.-I.; Paik, J.-H.; Choi, B.-H. Effect of B2O3 addition on the sintering temperature and microwave dielectric properties of Zn2SiO4 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.-H.; Lim, J.-B.; Nahm, S.; Paik, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Effect of Zn/Si Ratio on the Microstructural and Microwave Dielectric Properties of Zn2SiO4 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 90, 3127–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Nguyen, N.-H.; Lim, J.-B.; Paik, D.-S.; Nahm, S.; Paik, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Low-Temperature Sintering and Microwave Dielectric Properties of the Zn2SiO4 Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 91, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Zhou, D.; Guo, M.; Gong, S. Low-temperature sintered Zn2SiO4–CaTiO3 ceramics with near-zero temperature coefficient of resonant frequency. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 513, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelcu, L.; Geambasu, C.D.; Banciu, M.G.; Iwamae, A.; Furuya, T.; Tani, M. Submillimeter-wave properties of Zn2SiO4 ceramics. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz 2015), Hong Kong, China, 23–28 August 2015; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, G.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. Effects of low melting point materials on sinterability and microwave dielectric properties of X2SiO4–CaTiO3 (X = Mg, Zn) for LTCC. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 9195–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, S.O.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Park, H. Microstructure, phase evolution and microwave dielectric properties of Li2O and Ga2O3 doped zinc orthosilicate. Ceram. Silikaty 2017, 61, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weng, Z.; Song, C.; Xiong, Z.; Xue, H.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B.; Reece, M.J.; Yan, H. Microstructure and broadband dielectric properties of Zn2SiO4 ceramics with nano-sized TiO2 addition. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 13251–13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Guan, R.; Xiong, Z. Effects of the ZBS addition on the sintering behavior and microwave dielectric properties of 0.95Zn2SiO4-0.05CaTiO3 ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 3517–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Ling, Z. Phase evolution and microwave dielectric properties of SrTiO3 added ZnAl2O4-Zn2SiO4-SiO2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7050–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synkiewicz-Musialska, B.; Szwagierczak, D.; Kulawik, J.; Pałka, N.; Bajurko, P. Impact of additives and processing on microstructure and dielectric properties of willemite ceramics for LTCC terahertz applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaware, V.; Deshmukh, R.; Sarode, C.; Gokhale, S.; Phatak, G. Low-Temperature Sintering and Microwave Dielectric Properties of Zn2SiO4 Ceramic Added with Crystalline Zinc Borate. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Molokeev, M.S.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Li, L.; et al. Near-Zero Thermal Expansion and High Ultraviolet Transparency in a Borate Crystal of Zn4B6O13. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7936–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwagierczak, D.; Synkiewicz-Musialska, B.; Kulawik, J.; Czerwińska, E.; Pałka, N.; Bajurko, P. Low temperature sintering of Zn4B6O13 based substrates, their microstructure and dielectric properties up to the THz range. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 819, 153025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ju, K.; Wang, K. A Novel Glass-Ceramic with Ultra-Low Sintering Temperature for LTCC Application. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.; Yu, H.; Ye, L.; Xu, G. Ultra-Low Temperature Sintering and Dielectric Properties of SiO2-Filled Glass Composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 3563–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Zhou, D. Synthesis and Microwave Dielectric Properties of Zn3B2O6 Ceramics for Substrate Application. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 1793–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Pang, L.-X.; Wang, D.-W.; Qi, Z.-M.; Reaney, I.M. High Quality Factor, Ultralow Sintering Temperature Li6B4O9 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics with Ultralow Density for Antenna Substrates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11138–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharanpillai, A.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Sebastian, M.T.; Kim, H.T. Environmental Friendly Approach for the Development of Ultra-Low-Firing Li2WO4 Ceramic Tapes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6849–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Fang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Shu, L.; Khaliq, J. NaCa4V5O17: A low-firing microwave dielectric ceramic with low permittivity and chemical compatibility with silver for LTCC applications. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Silva, R.; De Morais, J.; Batista, G.; Silva, M.; Goes, J.; De Andrade, H.; Júnior, I.Q.; Singh, C.; Sombra, A. Effects of CaTiO3 addition on the microwave dielectric properties and antenna properties of BiVO4 ceramics. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Varghese, J.; Teirikangas, M.; Sebastian, M.T.; Jantunen, H. Ultra-low sintering temperature ceramic composites of CuMoO4 through Ag2O addition for microwave applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 141, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faouri, S.S.; Mostaed, A.; Dean, J.S.; Wang, D.; Sinclair, D.C.; Zhang, S.; Whittow, W.G.; Vardaxoglou, Y.; Reaney, I.M. High quality factor cold sintered Li2MoO4BaFe12O19 composites for microwave applications. Acta Mater. 2019, 166, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Vardaxoglou, Y.; Whittow, W.; Cadman, D.; Zhou, D.; Song, K.; Reaney, I.M. Cold sintered CaTiO3-K2MoO4 microwave dielectric ceramics for integrated microstrip patch antennas. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Z.; Yuan, S.; Ding, X.; Ma, T.; Cui, S. Influence of CaO-B2O3-SiO2 crystallizable glass on microstructure and microwave dielectric of LiMg0.9Zn0.1PO4 ceramics for LTCC substrate applications. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 844, 156212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Kilpijärvi, J.; Myllymäki, S.; Yang, H.; Fang, L.; Jantunen, H. Spinel-olivine microwave dielectric ceramics with low sintering temperature and high quality factor for 5 GHz wi-fi antennas. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldem, M.A.; Orton, B.R.; Whitaker, A. Phase equilibria in the system ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 at 950 °C. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 4139–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamba, S.; Petzelt, J.; Buixaderas, E.; Haubrich, D.; Vanek, P.; Kuzel, P.; Jawahar, I.N.; Sebastian, M.T.; Mohanan, P. High frequency dielectric properties of A5B4O15 microwave ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3900–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Fan, X.C.; Chen, X.M. Analysis of Infrared Reflection Spectra of (Mg1-xZnx)Al2O4 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Chun, B.S.; Freer, R.; Cernik, R.J. Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+B6+O4 (A2+: Ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Y.; Qiu, T.; Jin, C. Effect of bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of (1 − x)CaTiO3-x(Li0.5La0.5)TiO3 ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Zhai, Y.; Duan, L.; Su, C.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Fang, L. A3Y2Ge3O12 (A = Ca, Mg): Two novel microwave dielectric ceramics with contrasting τf and Q × f. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3989–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
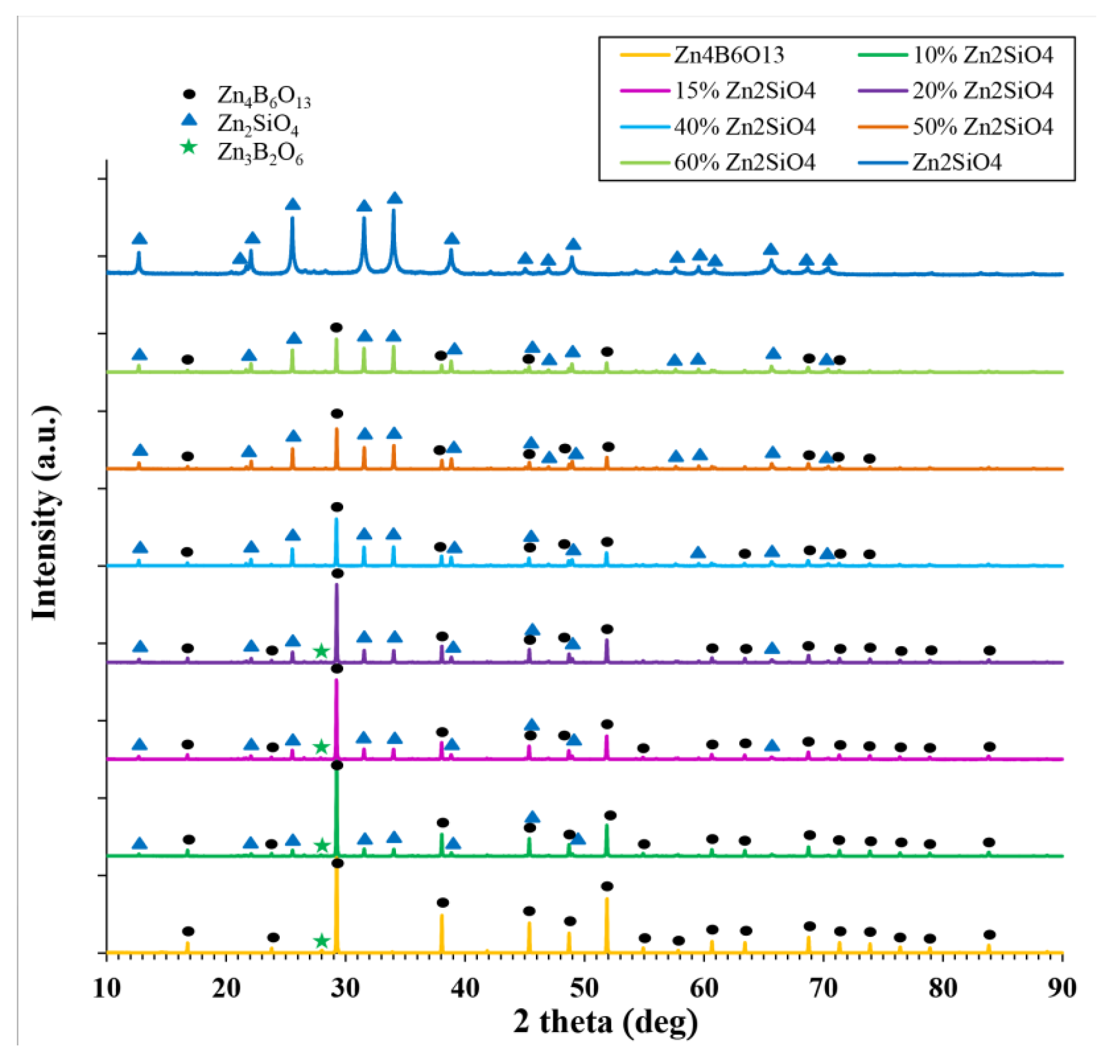
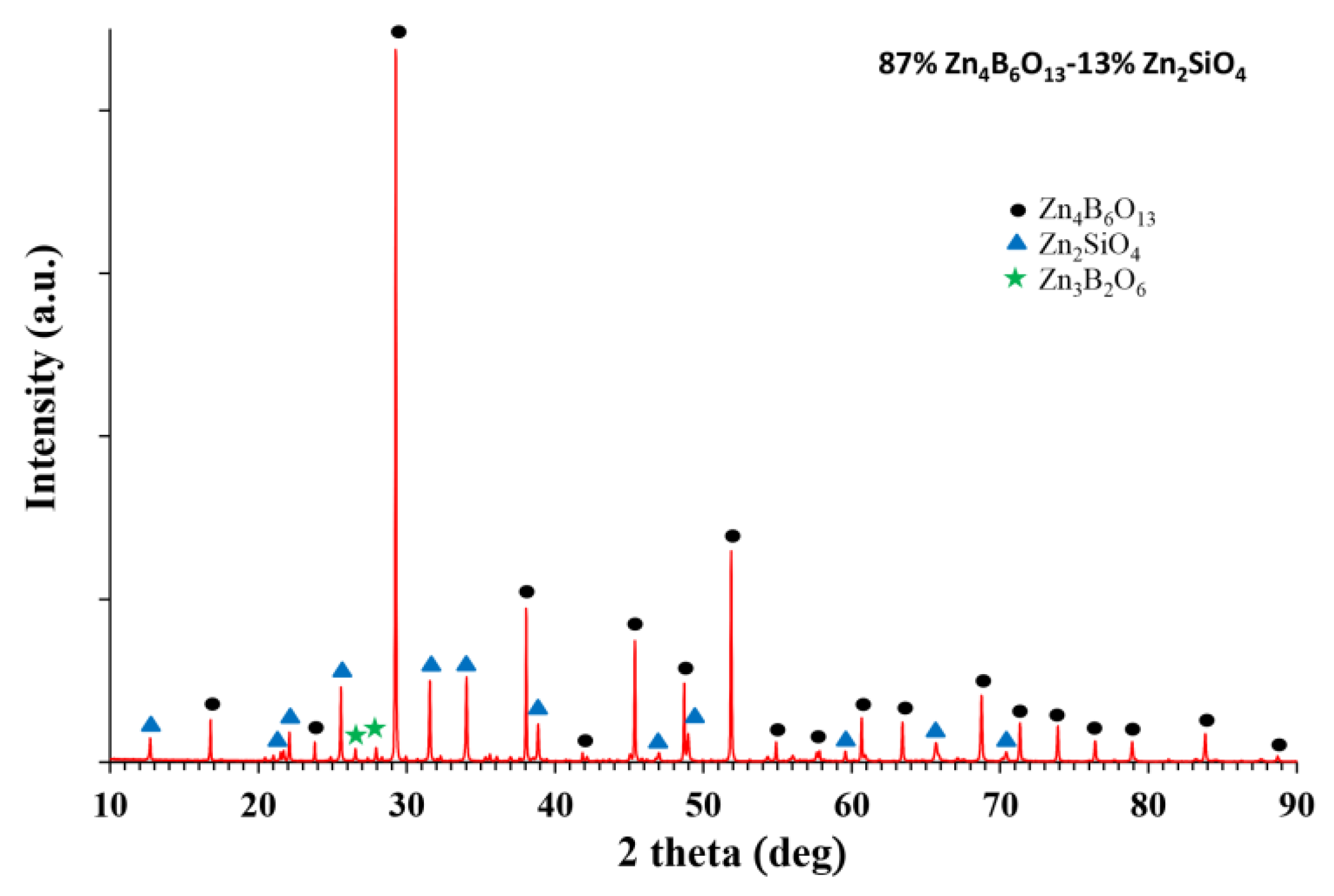


| Lattice Parameters | Zn2SiO4 Content (wt %) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |
| “a” Zn4B6O13 (Å) | 7.4746 | 7.4749 | 7.4749 | 7.4748 | 7.4745 | 7.4743 |
| “a” Zn2SiO4 (Å) | 13.9326 | 13.9352 | 13.9350 | 13.9351 | 13.9303 | 13.9324 |
| “c” Zn2SiO4 (Å) | 9.3066 | 9.3066 | 9.3067 | 9.3081 | 9.3043 | 9.3060 |
| Element | at % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | Point 2 | Point 3 | Point 4 | |
| B | 50.66 | 38.37 | 30.19 | 0.00 |
| O | 27.15 | 39.06 | 29.05 | 37.03 |
| Si | 1.05 | 3.72 | 5.32 | 19.11 |
| Zn | 21.15 | 18.85 | 35.44 | 43.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szwagierczak, D.; Synkiewicz-Musialska, B.; Kulawik, J.; Pałka, N. LTCC and Bulk Zn4B6O13–Zn2SiO4 Composites for Submillimeter Wave Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041014
Szwagierczak D, Synkiewicz-Musialska B, Kulawik J, Pałka N. LTCC and Bulk Zn4B6O13–Zn2SiO4 Composites for Submillimeter Wave Applications. Materials. 2021; 14(4):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzwagierczak, Dorota, Beata Synkiewicz-Musialska, Jan Kulawik, and Norbert Pałka. 2021. "LTCC and Bulk Zn4B6O13–Zn2SiO4 Composites for Submillimeter Wave Applications" Materials 14, no. 4: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041014
APA StyleSzwagierczak, D., Synkiewicz-Musialska, B., Kulawik, J., & Pałka, N. (2021). LTCC and Bulk Zn4B6O13–Zn2SiO4 Composites for Submillimeter Wave Applications. Materials, 14(4), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14041014







