Mixed Manganese Dioxide on Magnetite Core MnO2@Fe3O4 as a Filler in a High-Performance Magnetic Alginate Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Investigated Fillers
2.3. Membrane Preparation
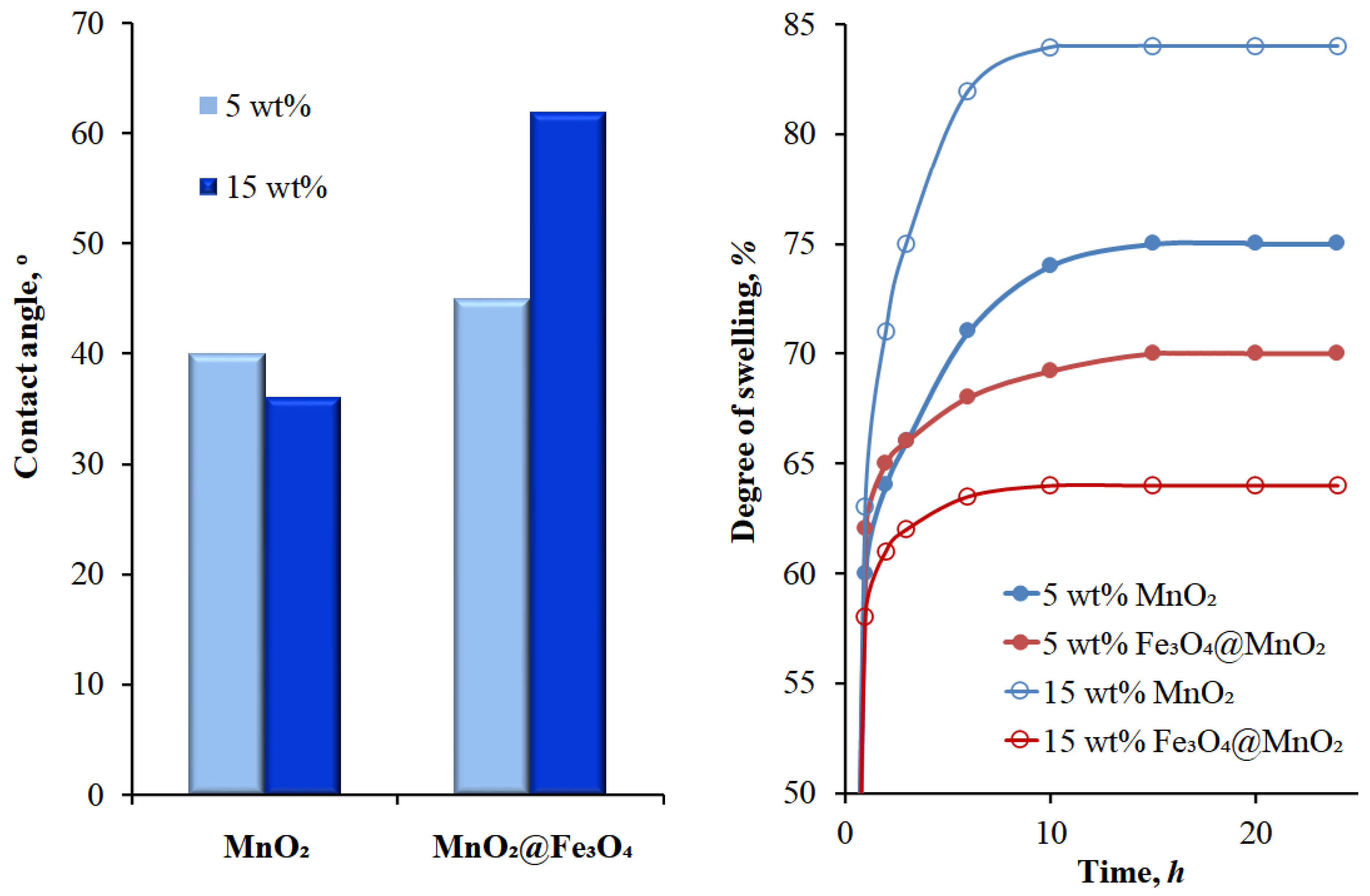
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization
2.5. Pervaporation Experiments
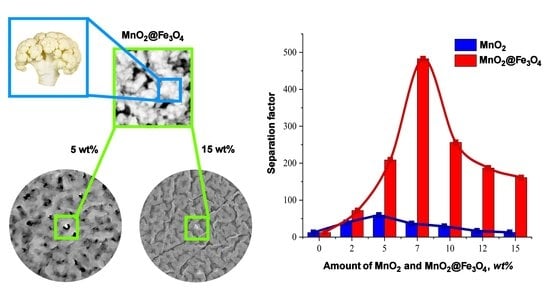
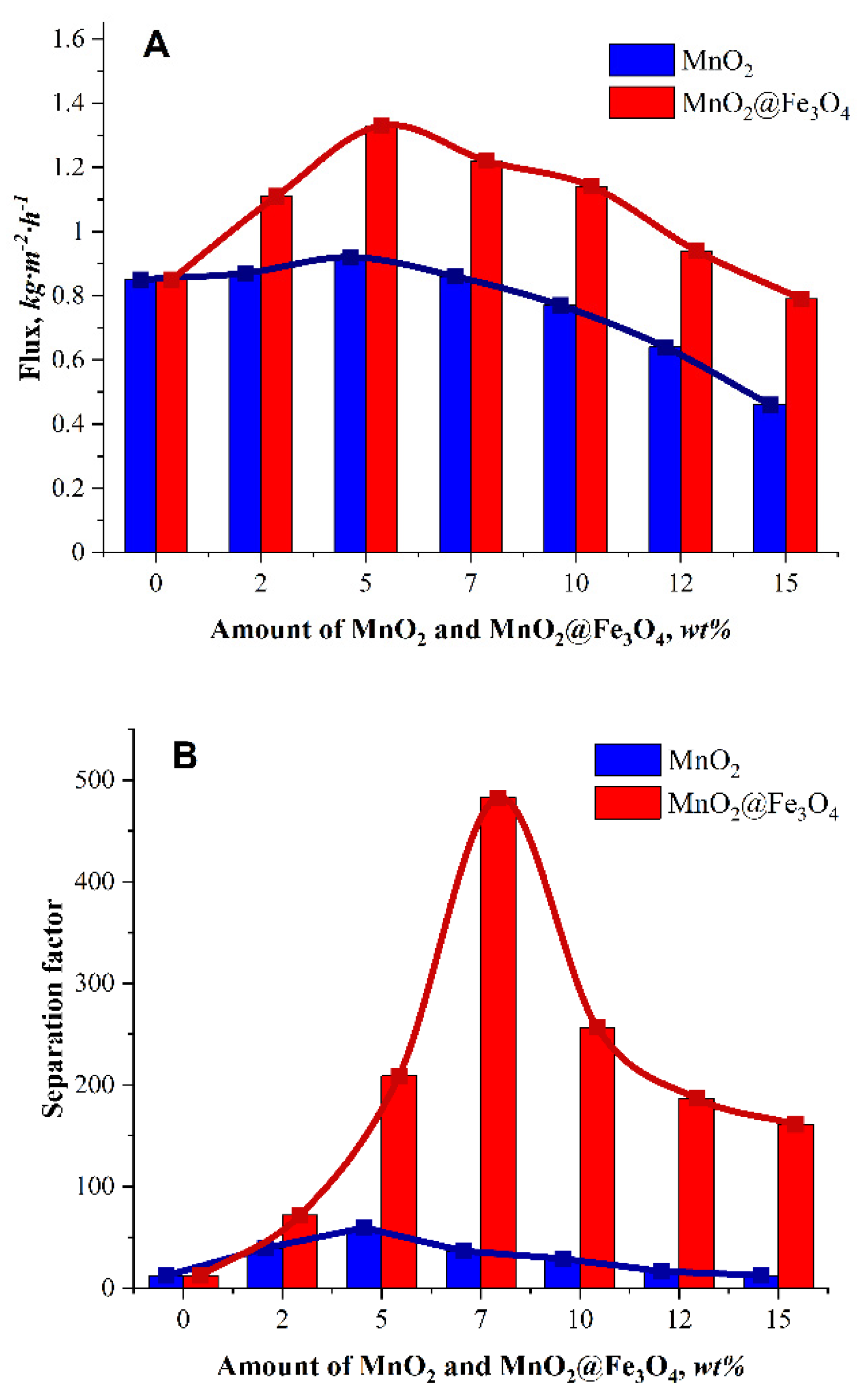
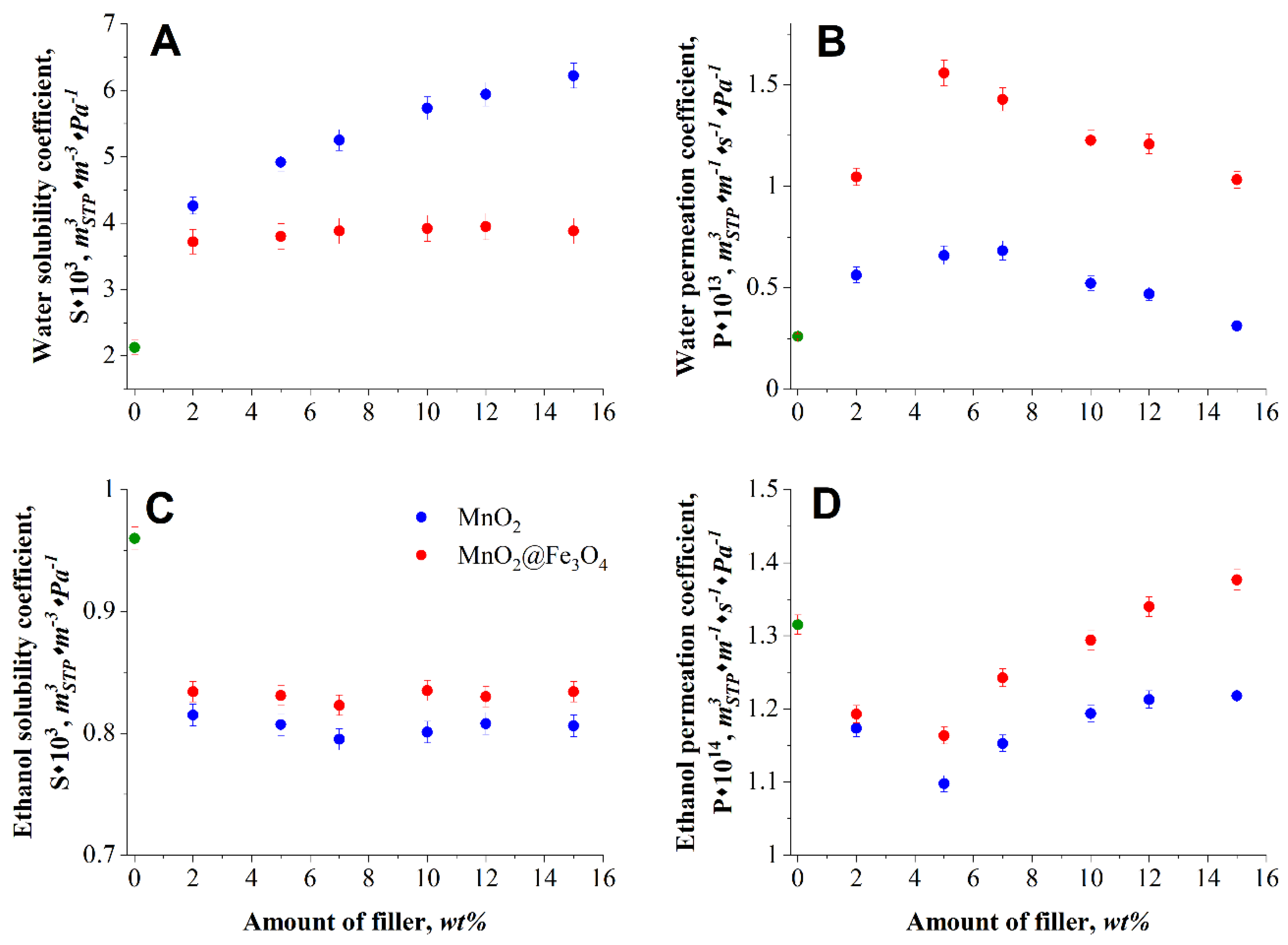
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membranes’ Morphology
3.2. Pervaporation Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, W.E. The Science of Ethanol, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, F.B. A Practical Handbook on the Distillation of Alcohol from Farm Products; Forgotten Books: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Onuki, S.; Koziel, J.A.; Jenks, W.S.; Cai, L.; Grewell, D.; van Leeuwen, J.H. Taking ethanol quality beyond fuel grade: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basile, A.; Figoli, A.; Khayet, M. Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sairam, M.; Naidu, B.V.K.; Nataraj, S.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Poly (vinyl alcohol)-iron oxide nanocomposite membranes for pervaporation, dehydration of isopropanol, 1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran. J. Memb. Sci. 2006, 283, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, F. High pervaporation dehydration performance of the composite membrane with an ultrathin alginate/poly(acrylic acid)-Fe3O4 active layer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Krasowska, M.; Turczyn, R.; Strzelewicz, A.; Djurado, D.; Pouget, S. Clustering analysis for pervaporation performance assessment of alginate hybrid membranes in dehydration of ethanol. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 144, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Gnus, M.; Turczyn, R.; Strzelewicz, A.; Krasowska, M. Pervaporation with chitosan membranes containing iron oxide nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Guo, S.; Tang, L.; Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; et al. Bimetallic metal-organic frameworks nanocages as multi-functional fillers for water-selective membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wu, G. Metal-organic frameworks based mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Nikolaeva, D.; Hartanto, Y.; Luis, P. MOF-based membranes for pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 278, 119233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Li, S.-H.; Zhang, A.-S.; Xu, L.-H.; Lu, J.-J.; Zhao, Z.-P. Novel MOF-capped halloysite nanotubes/PDMS mixed matrix membranes for enhanced n-butanol permselective pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; Buera-González, J.; de la Iglesia, Ó.; Galiano, F.; Fíla, V.; Malankowska, M.; Rubio, C.; Figoli, A.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Towards the dehydration of ethanol using pervaporation cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecaros, R.L.G.; Bismonte, M.E.; Doma, B.T.; Hung, W.-S.; Hu, C.-C.; Tsai, H.-A.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Alcohol dehydration performance of pervaporation composite membranes with reduced graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots homostructured filler. Carbon 2020, 162, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhas, D.P.; Raghu, A.V.; Jeong, H.M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Graphene-loaded sodium alginate nanocomposite membranes with enhanced isopropanol dehydration performance via a pervaporation technique. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17120–17130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, A.A.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Aralaguppi, M.I.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Preparation and characterization of novel pervaporation membranes for the separation of water–isopropanol mixtures using chitosan and NaY zeolite. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 247, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittur, A.A.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y.; Toti, U.S.; Ramesh, K.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of water-isopropanol mixtures using ZSM-5 zeolite incorporated poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nigiz, F.U.; Dogan, H.; Hilmioglu, N.D. Pervaporation of ethanol/water mixtures using clinoptilolite and 4A filled sodium alginate membranes. Desalination 2012, 300, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Turczyn, R.; Konieczny, K. Robust poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes containing chitosan/chitosan derivatives microparticles for pervaporative dehydration of ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Yang, H.; He, J.; Zhu, W. The effects of magnetic fields on water molecular hydrogen bonds. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 938, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksimentyeva, O.I.; Savchyn, V.P.; Dyakonov, V.P.; Piechota, S.; Horbenko, Y.Y.; Opainych, I.Y.; Demchenko, P.Y.; Popov, A.; Szymczak, H. Modification of Polymer-Magnetic Nanoparticles by Luminescent and Conducting Substances. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 590, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Turczyn, R.; Gnus, M.; Konieczny, K. Pervaporative dehydration of ethanol/water mixture through hybrid alginate membranes with ferroferic oxide nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 193, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Turczyn, R.; Djurado, D. Collation Effciency of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Alginate Membranes with Iron-Based Magnetic Organic/Inorganic Fillers in Pervaporative Dehydration of Ethanol. Materials 2020, 13, 4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serga, V.; Burve, R.; Maiorov, M.; Krumina, A.; Skaudžius, R.; Zarkov, A.; Kareiva, A.; Popov, A.I. Impact of Gadolinium on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline Powders of Iron Oxides Produced by the Extraction-Pyrolytic Method. Materials 2020, 13, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Superparamagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 Heterogeneous Nanoparticles with Enhanced Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetrivel, S.; Rana, D.; Saraswathi, M.S.S.A.; Divya, K.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Nagendran, A. Cellulose acetate nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes tailored with hydrous manganese dioxide nanoparticles for water treatment applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, C.L.; Chouyyok, W.; Mackie, K.E.; Neiner, D.; Saraf, L.V.; Droubay, T.C.; Warner, M.G.; Addleman, R.S. Manganese Doping of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Tailoring Surface Reactivity for a Regenerable Heavy Metal Sorbent. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3931–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.T.; Nah, H.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, M.G.; Cheon, J. Critical enhancements of MRI contrast and hyperthermic effects by dopant-controlled magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Chi, X.; Yang, L.; Yang, R.; Ren, B.W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J. Cation Exchange of Anisotropic-Shaped Magnetite Nanoparticles Generates High-Relaxivity Contrast Agents for Liver Tumor Imaging. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, P.; Sathiyamurthy, K. Effect of Temperatures on Structural, Morphological and Magnetic Properties of Zinc Ferrite Nanoparticles. Can. Chem. Trans. Year 2016, 4, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Kalska-Szostko, B.; Kropiewnicka, K. The influence of the transition metal substitution on chemically prepared ferrite nanoparticles—Mossbauer studies. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, C.A.C.; Franzreb, M.; Valenzuela, F.; Höll, W.H. Magnetic manganese dioxide as an amphoteric adsorbent for removal of harmful inorganic contaminants from water. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafalla, S.E.; Reimers, G.W. Preparation of dilution-stable aqueous magnetic fluids. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1980, 16, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geankoplis, C.J. Transport Processes and Separation Process Principles; Prentice-Hall International: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 696. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, G.; Borys, P. A Simple Methodology to Estimate the Diffusion Coefficient in Pervaporation-Based Purification Experiments. Polymers 2019, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudek, G.; Krasowska, M.; Turczyn, R.; Gnus, M.; Strzelewicz, A. Structure, morphology and separation efficiency of hybrid Alg/Fe3O4 membranes in pervaporative dehydration of ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 182, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewniak, A.; Forajter, A.; Szymańska, K. Mesoporous silica-supported ionic liquids as catalysts for styrene carbonate synthesis from CO2. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, K.; Zhang, T.; Ding, S.; Wang, X. High-performance polyamide composite membranes via double-interfacial polymerizations on a nanofibrous substrate for pervaporation dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, M.L.; Liu, L.; Feng, X. Sericin/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend membranes for pervaporation separation of ethanol/water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 295, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuga, T.; Tatsuoka, H. Magnetic-field transfer of water molecules. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 094311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gomaa, H.; Pan, F. Enhanced pervaporative performance of hybrid membranes containing Fe3O4@CNT nanofillers. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.F. The conductivity properties of protons in ice and mechanism of magnetization of liquid water. Eur. Phys. J. B 2006, 49, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubski, Ł.; Grzybek, P.; Chrobak, A.; Haye, E.; Colomer, J.-F.; Konieczny, K.; Turczyn, R.; Dudek, G. Single-molecule magnets as novel fillers with superior dispersibility–First application of a tetranuclear iron(III) molecular magnet [Fe4(acac)6(Br-mp)2] for pervaporative dehydration of ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, X. Chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite pervaporation membranes for ethanol dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
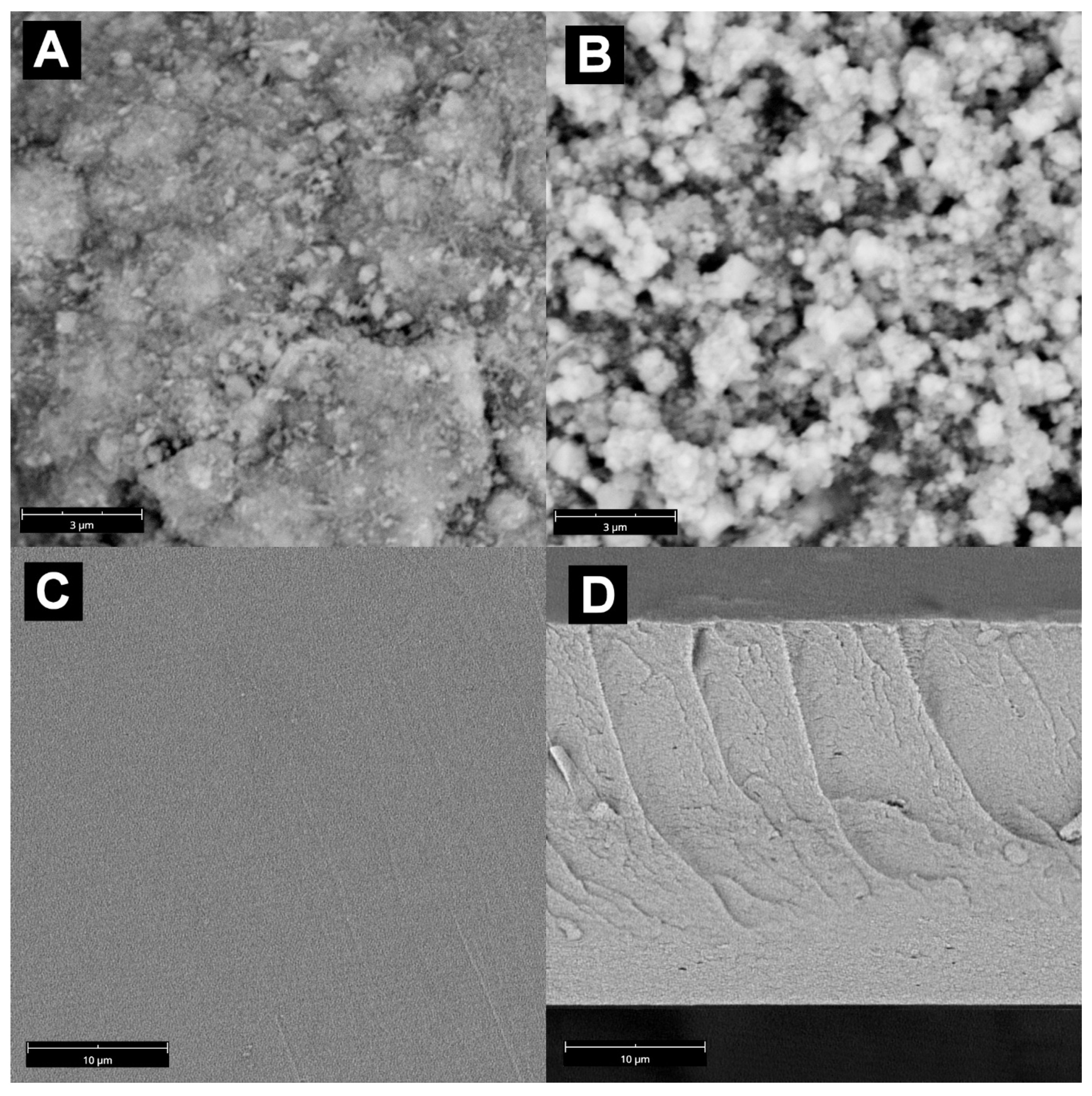
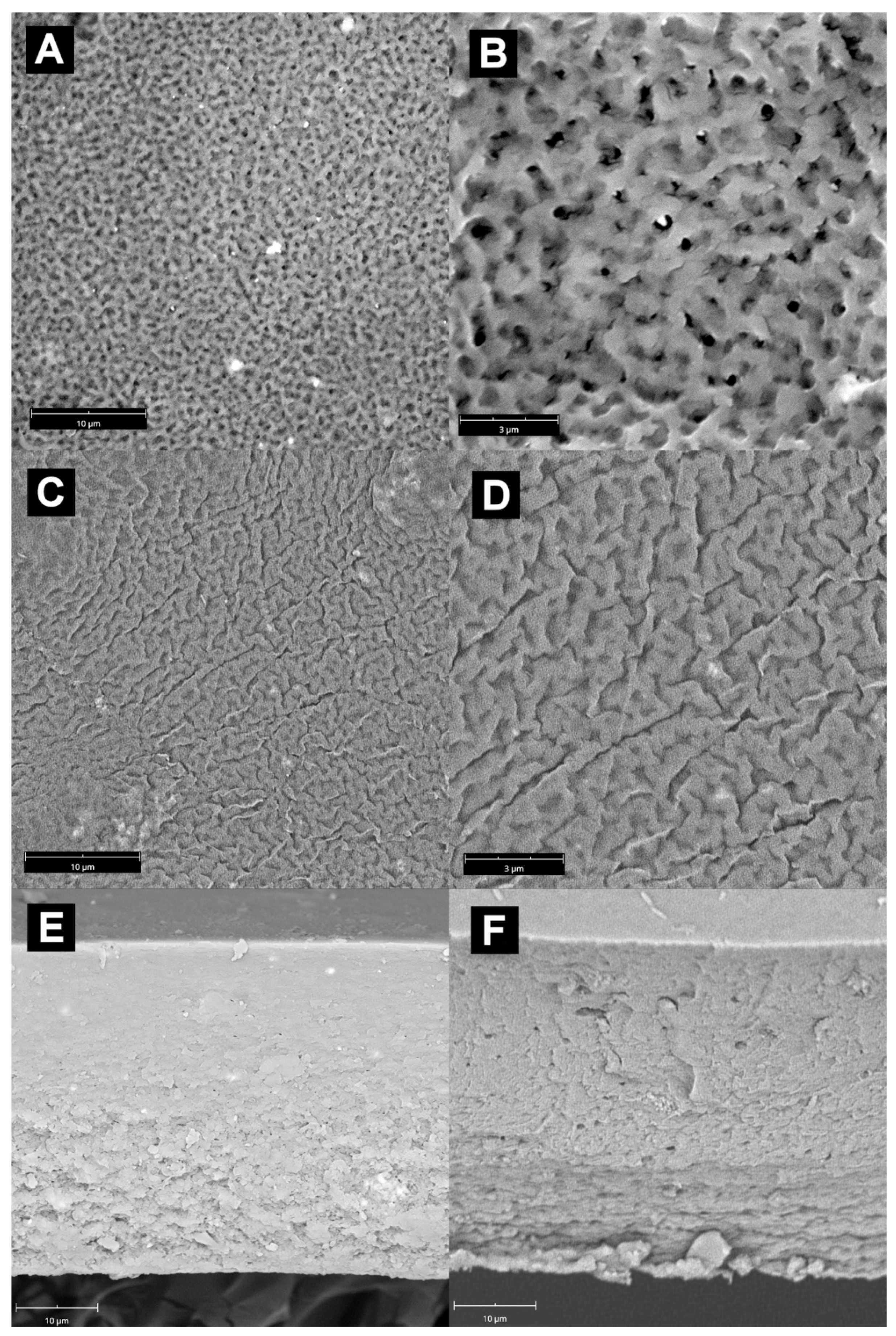



| Polymer Matrix | Filler | Flux kg·m−2·h−1 | Separation Factor | Temperature °C | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA/PAN | 8 wt.% PAA/Fe3O4 | 1.63 0.121 | 1044.0 101.1 | 77 30 | [7] |
| CHIT | TiO2 | 0.34 | 196.0 | 80 | [46] |
| CHIT | Fe3O4 | - | 3.3 | 25 | [9] |
| SA | Fe3O4 | 1.38 | 58.8 | 25 | [24] |
| SA | Ag2O | 0.81 | 33.8 | 25 | [8] |
| SA | TiO2 | 0.85 | 33.3 | 25 | [8] |
| SA | Cr2O3 | 1.09 | 28.3 | 25 | [8] |
| SA | ZnO | 1.28 | 30.3 | 25 | [8] |
| SA | 5 wt.% MnO2 | 0.91 | 59.8 | 25 | Present work |
| SA | 7 wt.% MnO2@Fe3O4 | 1.22 | 483.0 | 25 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grzybek, P.; Turczyn, R.; Dudek, G. Mixed Manganese Dioxide on Magnetite Core MnO2@Fe3O4 as a Filler in a High-Performance Magnetic Alginate Membrane. Materials 2021, 14, 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247667
Grzybek P, Turczyn R, Dudek G. Mixed Manganese Dioxide on Magnetite Core MnO2@Fe3O4 as a Filler in a High-Performance Magnetic Alginate Membrane. Materials. 2021; 14(24):7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247667
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrzybek, Paweł, Roman Turczyn, and Gabriela Dudek. 2021. "Mixed Manganese Dioxide on Magnetite Core MnO2@Fe3O4 as a Filler in a High-Performance Magnetic Alginate Membrane" Materials 14, no. 24: 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247667
APA StyleGrzybek, P., Turczyn, R., & Dudek, G. (2021). Mixed Manganese Dioxide on Magnetite Core MnO2@Fe3O4 as a Filler in a High-Performance Magnetic Alginate Membrane. Materials, 14(24), 7667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247667