Indentation Size Effect in CoCrFeMnNi HEA Prepared by Various Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization
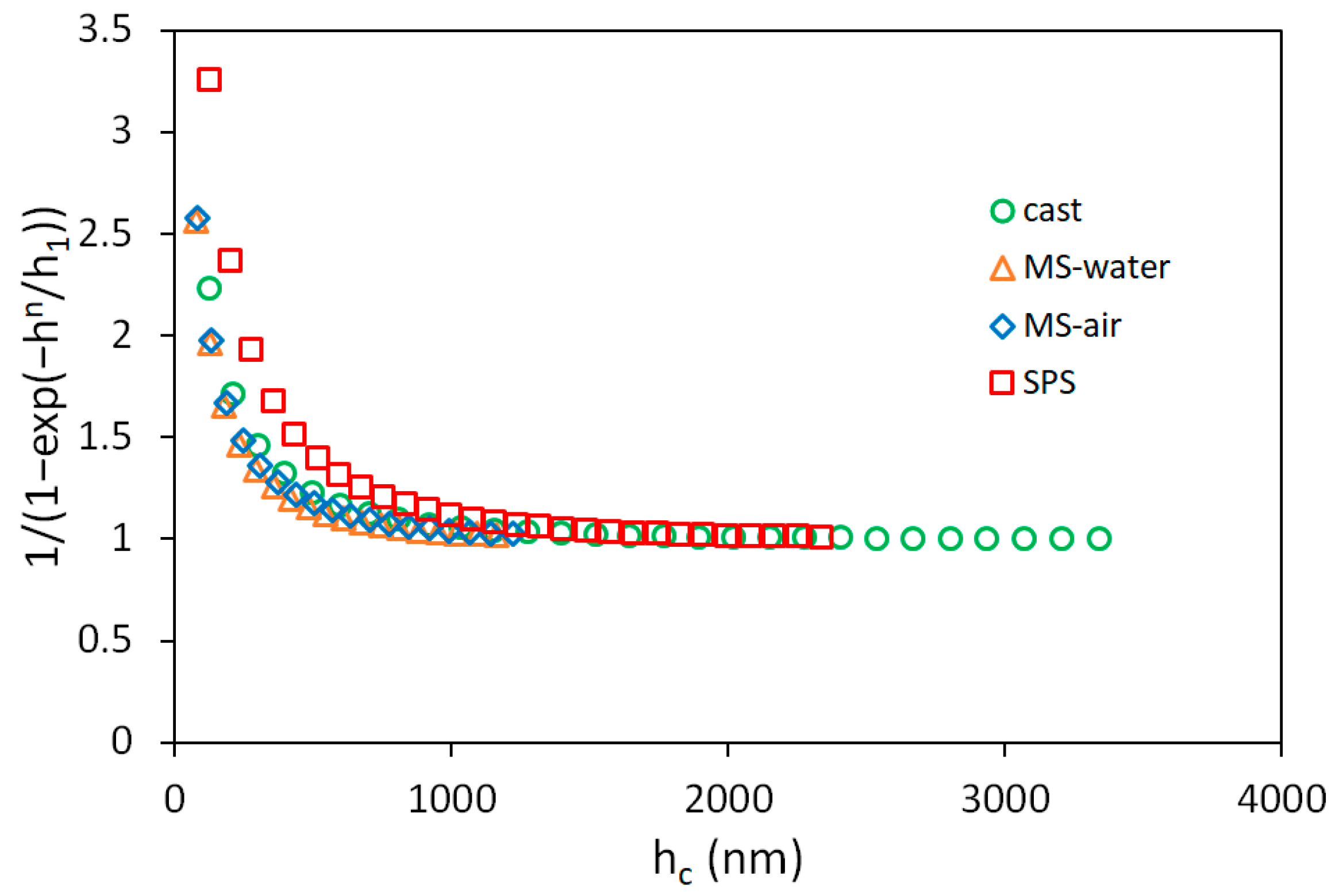
3.2. Indentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-Entropy Alloys: A Critical Review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Kim, W.T.; Bewlay, B.P.; Gillen, A.G. Microstructure-Cooling Rate Correlations in Melt-Spun Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1991, 26, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhani, R.C.; Goel, T.C.; Chopra, K.L. Melt-Spinning Technique for Preparation of Metallic Glasses. Bull. Mat. Sci. 1982, 4, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.D.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.; Hirata, A.; Fujita, T.; Nieh, T.G.; Liu, C.T.; Chen, M.W. Nanoscale Phase Separation in a Fcc-Based CoCrCuFeNiAl0.5 High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2015, 84, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wei, R.; Wang, T.; Zhang, T.; Li, F. A Novel Ultrafine-Grained High Entropy Alloy with Excellent Combination of Mechanical and Soft Magnetic Properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Sun, H.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Li, F. Effect of Cooling Rate on the Phase Structure and Magnetic Properties of Fe26.7Co28.5Ni28.5Si4.6B8.7P3 High Entropy Alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 435, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical Alloying and Milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Mechanically Alloyed Metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, R.; Licheri, R.; Locci, A.M.; Cincotti, A.; Cao, G. Consolidation/Synthesis of Materials by Electric Current Activated/Assisted Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2009, 63, 127–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nová, K.; Novák, P.; Průša, F.; Kopeček, J.; Čech, J. Synthesis of Intermetallics in Fe-Al-Si System by Mechanical Alloying. Metals 2019, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Průša, F.; Cabibbo, M.; Šenková, A.; Kučera, V.; Veselka, Z.; Školáková, A.; Vojtěch, D.; Cibulková, J.; Čapek, J. High-Strength Ultrafine-Grained CoCrFeNiNb High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Mechanical Alloying: Properties and Strengthening Mechanism. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 835, 155308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.-Y.; Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. Sluggish Diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni High-Entropy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.P.; Sathiaraj, G.D.; Zaid, M.; Gatti, J.R.; Lee, C.; Tsai, C.-W.; Yeh, J.-W. Microstructure and Texture Evolution During Annealing of Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 587, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Su, C.-H.; Wu, S.-K.; Lin, C. A Study on the Hall–Petch Relationship and Grain Growth Kinetics in FCC-Structured High/Medium Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2019, 21, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.H.; Wu, Y.; He, J.Y.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Grain Growth and the Hall–Petch Relationship in a High-Entropy FeCrNiCoMn Alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 68, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Somsen, C.; Bei, H.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. The Influences of Temperature and Microstructure on the Tensile Properties of a CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.F.; Xiao, D.H.; Li, G.; Song, M. Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy under Different High-Pressure Torsion Deformations. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.-H.; Kato, H.; Jang, M.J.; Moon, J.; Kim, E.B.; Hong, S.-J.; Kim, H.S. Structure and Properties of Ultrafine-Grained CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Produced by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 698, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Průša, F.; Šenková, A.; Kučera, V.; Čapek, J.; Vojtěch, D. Properties of a High-Strength Ultrafine-Grained CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Prepared by Short-Term Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Anupam, A.; Bharadwaj, J.V.; Srivastava, C.; Murty, B.S. Grain Growth Kinetics in CoCrFeNi and CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloys Processed by Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 791, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of Superfine-Grained High Entropy Alloy by Spark Plasma Sintering Gas Atomized Powder. Intermetallics 2016, 68, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nix, W.D.; Gao, H. Indentation Size Effects in Crystalline Materials: A Law for Strain Gradient Plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swadener, J.G.; George, E.P.; Pharr, G.M. The Correlation of the Indentation Size Effect Measured with Indenters of Various Shapes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Backes, B.; Goken, M. Indentation Size Effect in Metallic Materials: Correcting for the Size of the Plastic Zone. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1093–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, K.; Backes, B.; Franke, O.; Goken, M. Indentation Size Effect in Metallic Materials: Modeling Strength from Pop-in to Macroscopic Hardness Using Geometrically Necessary Dislocations. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 2547–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Nix, W.D. Indentation Size Effect in MgO. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haung, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hwang, K.C.; Nix, W.D.; Pharr, G.M.; Feng, G. A Model of Size Effects in Nano-Indentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 1668–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haušild, P. On the Breakdown of the Nix-Gao Model for Indentation Size Effect. Philos. Mag. 2021, 101, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Volz, T.; Weygand, S.M.; Schwaiger, R. The Indentation Size Effect of Single Crystalline Tungsten. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Metallic Materials—Instrumented Indentation Test for Hardness and Material Parameters; ISO 14577; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Moravcik, I.; Kubicek, A.; Moravcikova-Gouvea, L.; Adam, O.; Kana, V.; Pouchly, V.; Zadera, A.; Dlouhy, I. The Origins of High-Entropy Alloy Contamination Induced by Mechanical Alloying and Sintering. Metals 2020, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siska, F.; Cech, J.; Hausild, P.; Hadraba, H.; Chlup, Z.; Husak, R.; Stratil, L. Twinning in CoCrFeNiMn High Entropy Alloy Induced by Nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 784, 139297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehm, G.; Jaya, B.N.; Raghavan, R.; Kirchlechner, C. Overview on Micro- and Nanomechanical Testing: New Insights in Interface Plasticity and Fracture at Small Length Scales. Acta Mater. 2018, 142, 248–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczel, A.; Kawasaki, M.; Ugi, D.; Jang, J.; Langdon, T.G.; Gubicza, J. The Influence of Chemical Heterogeneities on the Local Mechanical Behavior of a High-Entropy Alloy: A Micropillar Compression Study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 721, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Co | Cr | Fe | Mn | Ni | Si | O | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cast | 22.4 ± 0.2 | 15.0 ± 0.2 | 22.1 ± 0.2 | 20.3 ± 0.2 | 19.5 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | ||
| MS-water | 20.4 ± 0.2 | 19.9 ± 0.2 | 20.6 ± 0.2 | 18.3 ± 0.2 | 18.7 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | |
| MS-air | 20.0 ± 0.2 | 20.0 ± 0.2 | 20.4 ± 0.2 | 19.5 ± 0.2 | 18.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | |
| SPS | 18.4 ± 0.1 | 19.3 ± 0.1 | 20.3 ± 0.1 | 18.3 ± 0.1 | 17.9 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.03 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.03 |
| H0 (MPa) | h* (nm) | h1 (nm) | n (-) | E (GPa) | Structural Unit Size (nm) | Structural Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cast | 1252 | 3761 | 73 | 0.78 | 204.4 | 4908 ± 542 | cell or subgrain |
| MS-water | 2080 | 1239 | 60 | 0.78 | 193.1 | 1083 ± 88 | grain (direction of ribbon axis) |
| MS-air | 1931 | 1274 | 57 | 0.75 | 194.8 | 1078 ± 141 | grain (direction of ribbon axis) |
| SPS | 3399 | 523 | 201 | 0.89 | 218.8 | 502 ± 38 | grain |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čech, J.; Haušild, P.; Karlík, M.; Čapek, J.; Průša, F. Indentation Size Effect in CoCrFeMnNi HEA Prepared by Various Techniques. Materials 2021, 14, 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237246
Čech J, Haušild P, Karlík M, Čapek J, Průša F. Indentation Size Effect in CoCrFeMnNi HEA Prepared by Various Techniques. Materials. 2021; 14(23):7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237246
Chicago/Turabian StyleČech, Jaroslav, Petr Haušild, Miroslav Karlík, Jiří Čapek, and Filip Průša. 2021. "Indentation Size Effect in CoCrFeMnNi HEA Prepared by Various Techniques" Materials 14, no. 23: 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237246
APA StyleČech, J., Haušild, P., Karlík, M., Čapek, J., & Průša, F. (2021). Indentation Size Effect in CoCrFeMnNi HEA Prepared by Various Techniques. Materials, 14(23), 7246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237246







