Reasons for Reduced Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The processes of crystallization of sulfur in the volume of the sulfur-bitumen binder and the formation of capillaries that increase the permeability of asphalt concrete for liquid media (physical hypothesis).
2. Materials and Methods
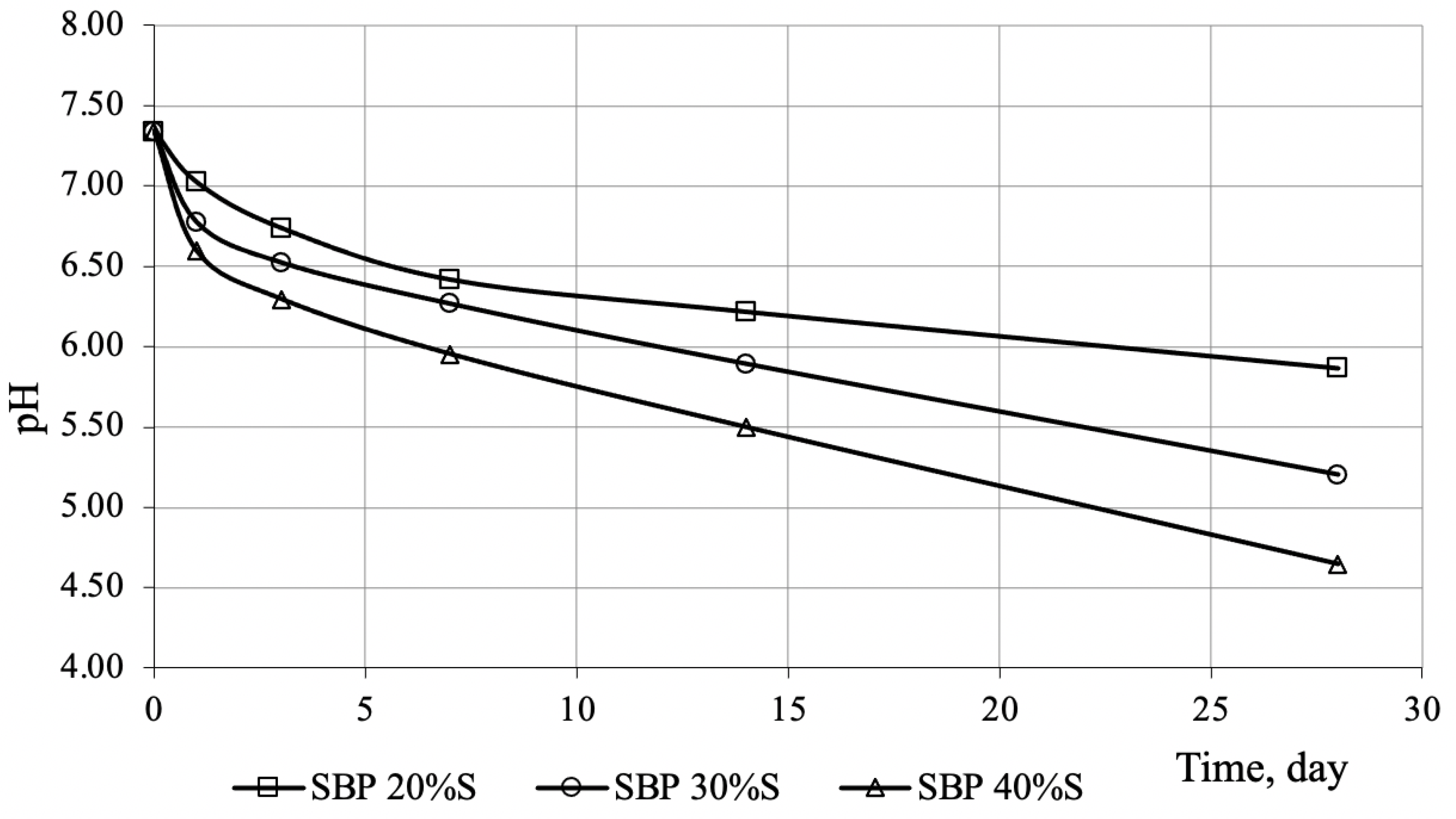
3. Results and Discussion
- In the first section, a classical exponential increase in concentration is observed, which clearly correlates with the depth of water penetration into the volume of the material sample and can be described by the function (1);
- In the second section, a linear increase in concentration is observed, which can only be explained by a significant increase in the permeability of the material.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Smirnov, V. Structure and physical properties of sulfur with nanoscale carbon modifiers. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 2019; Volume 91, p. 7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Husid, D.; Sukhachev, I.; Andreev, V. Properties of sulfur-extended asphalt concrete. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 2016; Volume 86, p. 4024. [Google Scholar]
- Alyami, A.M.; Toyogon, L. Field Performance Experience of Sulfur Extended Asphalt (SEA) pavement in Saudi Arabia. In Advances in Materials and Pavement Performance Prediction II; CRC Press: London, England, 2020; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Le, M.T.; Le, H.T.; Shukurov, I.; Slesarev, M. Sulfur-extended asphalt concrete with assessing the surface temperature of roads affecting urban heat island. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2020; Volume 869, p. 22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavussi, A.; Azarnia, M.; Ayar, P.; Pedram, M. The fatigue behavior of polymeric sulfur-modified asphalt mixtures subjected to freeze-thaw conditioning. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ozer, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Alarfaj, A.H.; Islam, K.; Khan, M.I.; Khan, K.M.; Shalabi, F.I. Life-Cycle Assessment of Using Sulfur-Extended Asphalt (SEA) in Pavements. In Airfield and Highway Pavements 2019: Innovation and Sustainability in Highway and Airfield Pavement Technology; American Society of Civil Engineers: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Gladkikh, V. Green sulfur-extended asphalt concrete: Mix design of the complex binder. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 2016; Volume 86, p. 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Gladkikh, V.; Sukhachev, I. Viscosity of plasticized sulfur-extended asphalt: Two-factor sequential optimization. In MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Science: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017; Volume 106, p. 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gladkikh, V.A.; Korolev, E.V. Suppressing the Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide Emission from Sulfur-Bituminous Concrete. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1040, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, V.A. Sulfur-Asphalt Concrete Modified with a Complex Additive Based on Technical Sulfur and Neutralizing Agents for the Emission of Toxic Gases. The Dissertation for the Degree of Candidate of Technical Sciences. Available online: https://www.dissercat.com/content/seroasfaltobeton-modifitsirovannyi-kompleksnoi-dobavkoi-na-osnove-tekhnicheskoi-sery-i-neitr (accessed on 2 October 2015).
- Turayev, F.T.; Beknazarov, K.S.; Dzhalilov, A.T. Study of the modification of road bitumen with elemental sulfur. Univers. Tech. Science. 2019, 2, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gladkikh, V.A.; Korolev, E.V.; Poddaeva, O.I.; Smirnov, V.A. Sulfur-Extended High-Performance Green Paving Materials. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1079–1080, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronov, S.Y.; Vasiliev, Y.E.; Timokhin, D.K.; Repin, A.M.; Repina, O.V.; Talalay, V.V. Production and use of sulfur-asphalt composite coatings on roads and bridges. Bull. Eurasian Sci. 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh, D.; Boon, K.H.; Jamaluddin, N. Exploratory study on the mechanical and physical properties of concrete containing sulfur. J. Teknol. 2015, 77, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faramarzi, M.; Golestani, B.; Lee, K.W. Improving moisture sensitivity and mechanical properties of sulfur extended asphalt mixture by nano-antistripping agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iii, S.B.C.; Mohammad, L.N.; Elseifi, M.A. Laboratory Performance Characteristics of Sulfur-Modified Warm-Mix Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1338–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Husid, D. Structure Formation and Phase Composition of Sulfur-Bitumen Systems. Mater. Sci. Forum 2016, 871, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.M.; Alla, E.-S.M.A.; El-Badawy, S.M. Phase angle master curves of sulfur-extended asphalt modified with recycled polyethylene waste. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Taylor, P.A. Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Modified Warm Mix. NCAT Report 11-07, National Center for Asphalt Technology, Auburn University. Available online: https://eng.auburn.edu/research/centers/ncat/files/technical-reports/rep11-07.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2011).
- Timm, D.H.; Robbins, M.; Willis, J.R.; Tran, N.; Taylor, A.J. Evaluation of Mixture Performance and Structural Capacity of Pavements Utilizing Shell Thiopave®, Phase II: Construction, Laboratory Evaluation and Full-Scale Testing of Thiopave® Test Sections–One Year Report. 2011. Available online: http://www.ncat.us/files/reports/2011/rep11-03.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2011).
- Le, H.; Gladkikh, V.; Korolev, E.; Grishina, A. Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete. Results of the Study and Features of Definition. Stroit. Mater. 2021, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reducing H2S-Emission from Hot Cast Sulfur-Asphalt Mixtures. 1976. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3960585A/en (accessed on 1 June 1976).
- Evstifeeva, I.Y. Structure and Properties of Corrosion-Resistant Sulfur Composites on Sized Quartz Filler. The Dissertation for the Degree of Candidate of Technical Sciences. 2007. Available online: http://www.dslib.net/stroj-materialy/struktura-i-svojstva-korrozionno-stojkih-sernyh-kompozitov-na-appretirovannom.html (accessed on 15 November 2007).
- Tumanova, N.N. Analysis of Kinetic Processes to Assess the Structure and Properties of Composite Building Materials. The Dissertation for the Degree of Candidate of Technical Sciences. RGB OD, 61:04-5/3220. 2004. Available online: https://www.dissercat.com/content/analiz-kineticheskikh-protsessov-dlya-otsenki-struktury-i-svoistv-kompozitnykh-stroitelnykh- (accessed on 13 May 2004).
- Korovkin, M.V.; Ananyeva, L.G. Infrared Spectroscopy of Carbonate Rocks and Minerals—TPU Publishing House. 2016. Available online: https://www.iprbookshop.ru/84013.html (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Gorshkov, B.C.; Timoshev, V.V.; Saveliev, V.G. Methods of Physical and Chemical Analysis of Binders. 1981. Available online: https://www.iprbookshop.ru/14351.html (accessed on 31 October 2021).





| Index | Actual Values |
|---|---|
| Penetration depth of the needle at 25 °C, 0.1 mm | 69 |
| Depth of needle penetration at 0 °C, 0.1 mm | 34 |
| Elongation at 20 °C, cm | 82.7 |
| Elongation at 0 °C, cm | 3.7 |
| Softening point, °C | 53 |
| Brittleness temperature, °C | −20 |
| Change in softening temperature after heating, °C | 5 |
| Penetration index | −0.6 |
| Flash point, °C | 254 |
| Material | Content, % by Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaCO3 + MgCO3 | |
| Dolomite | 7.64 | 0.34 | 1.12 | 90.9 |
| Indicator Name | Actual Values |
|---|---|
| Appearance | yellow granules |
| True density, g/cm3 | 2.07 |
| Bulk density, g/cm3 | 1.05 |
| Mechanical pollution (paper, wood, sand, etc.) | absent |
| Composition | Dependence | Coefficient Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||
| Sulfuric mastic for MP-1 | −6.85 | 0.1515 | −0.0006 | |
| −0.39 | 0.0032 | −0.00001 | ||
| Sulfuric mastic on fly ash | 40.03 | −0.5333 | 0.0019 | |
| −6.43 | 0.0895 | −0.0003 | ||
| Sulfur Content in SBB, % | Empirical Coefficients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area I | Area II | ||||
| 20 | 0.34 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.039 | 0.083 |
| 30 | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.079 | 0.005 |
| 40 | 1.26 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.111 | 0.500 |
| Sulfur Content in SBB, % | Empirical Coefficients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area I | Area II | ||||
| 20 | 6.21 | 0.18 | 2.04 | −0.026 | 6.59 |
| 30 | 6.10 | 0.18 | 2.22 | −0.050 | 6.56 |
| 40 | 5.95 | 0.23 | 2.22 | −0.062 | 6.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, H.T.; Korolev, E.V.; Grishina, A.N.; Gladkikh, V.A. Reasons for Reduced Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 7218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237218
Le HT, Korolev EV, Grishina AN, Gladkikh VA. Reasons for Reduced Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete. Materials. 2021; 14(23):7218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237218
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Huu Tuan, Evgenij V. Korolev, Anna N. Grishina, and Vitaly A. Gladkikh. 2021. "Reasons for Reduced Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete" Materials 14, no. 23: 7218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237218
APA StyleLe, H. T., Korolev, E. V., Grishina, A. N., & Gladkikh, V. A. (2021). Reasons for Reduced Moisture Resistance of Sulfur-Extended Asphalt Concrete. Materials, 14(23), 7218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237218







