Evaluation of Reducing NO and SO2 Concentration in Nano SiO2-TiO2 Photocatalytic Concrete Blocks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
Photocatalyst
3. Materials and Experiment Method
3.1. Materials
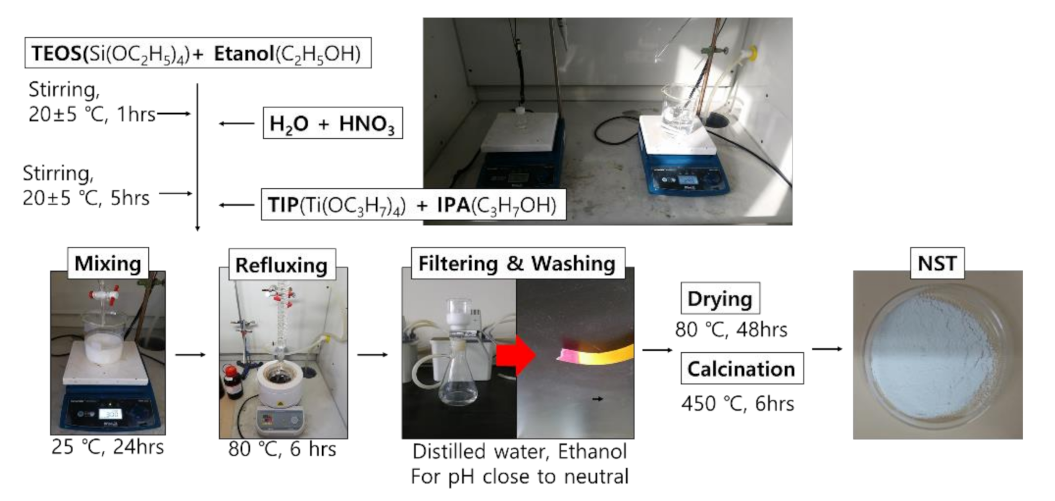
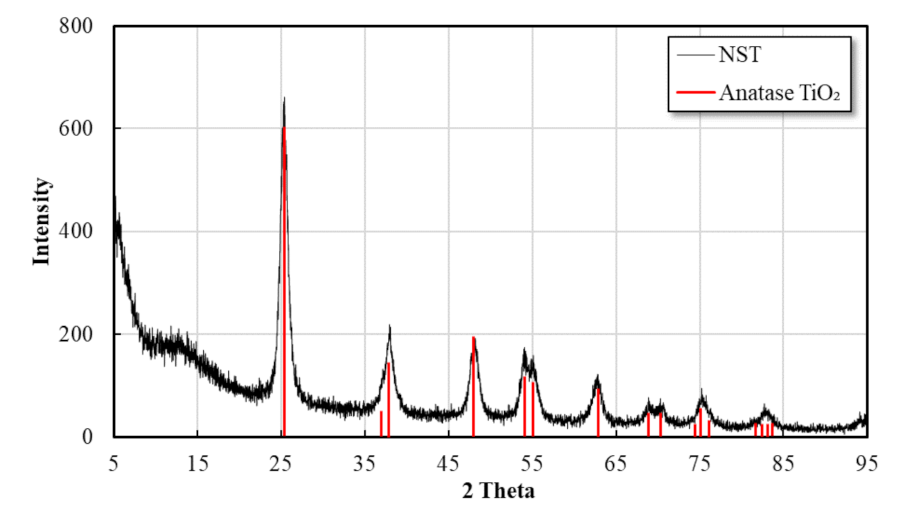
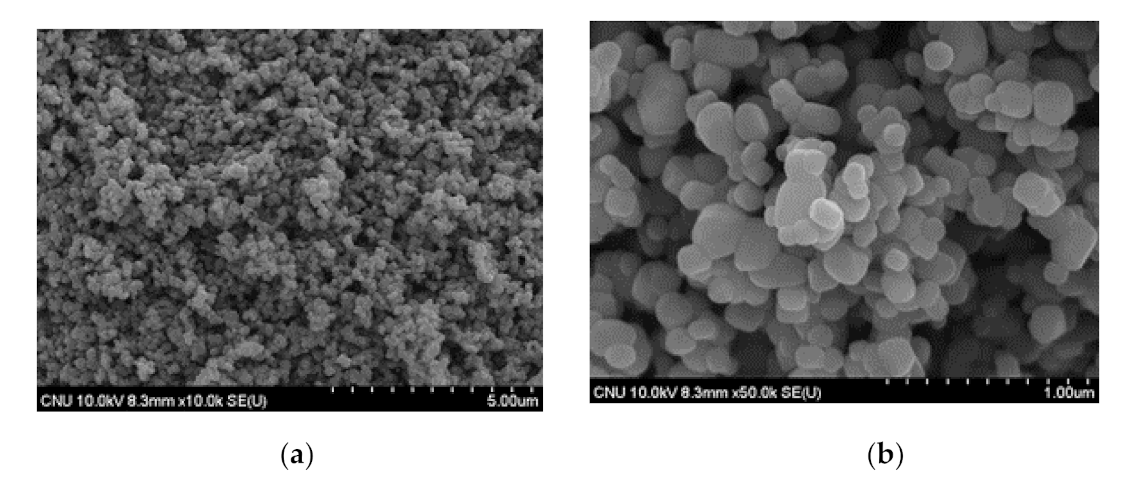
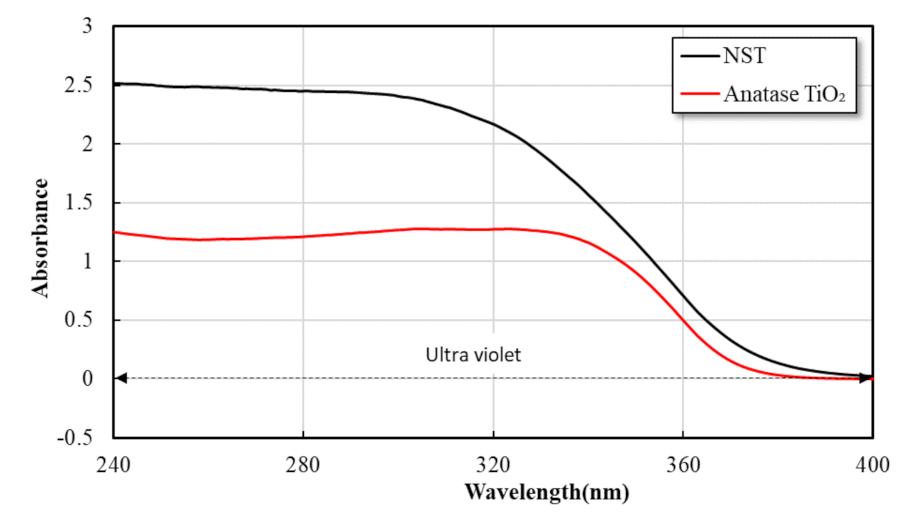
3.1.1. Nano SiO2-TiO2
- TEOS and EtOH were stirred at a molar ratio of 1:1, at 600 rpm or higher, for one hour.
- HNO3 and distilled water were stirred at a molar ratio of 1:150, at 600 rpm or higher, for one hour.
- The solutions prepared in steps 1 and 2 were stirred at 600 rpm or higher for five hours.
- TIP and IPA were stirred at a molar ratio of 1:1 at 600 rpm or higher for one hour.
- The solutions prepared in steps 3 and 4 were mixed and stirred at 800 rpm for 24 hours.
- The mixture prepared in step 5 was refluxed at 80 °C for six hours.
- The prepared NST slurry was washed and filtered for neutralization.
- The NST slurry was dried at 80 °C for 48 hours.
- Heat treatment was applied to the dried NST at 450 °C for six hours.
- The heat-treated NST was ground.
3.1.2. Cement
3.1.3. Silica Sand
3.1.4. Aggregate
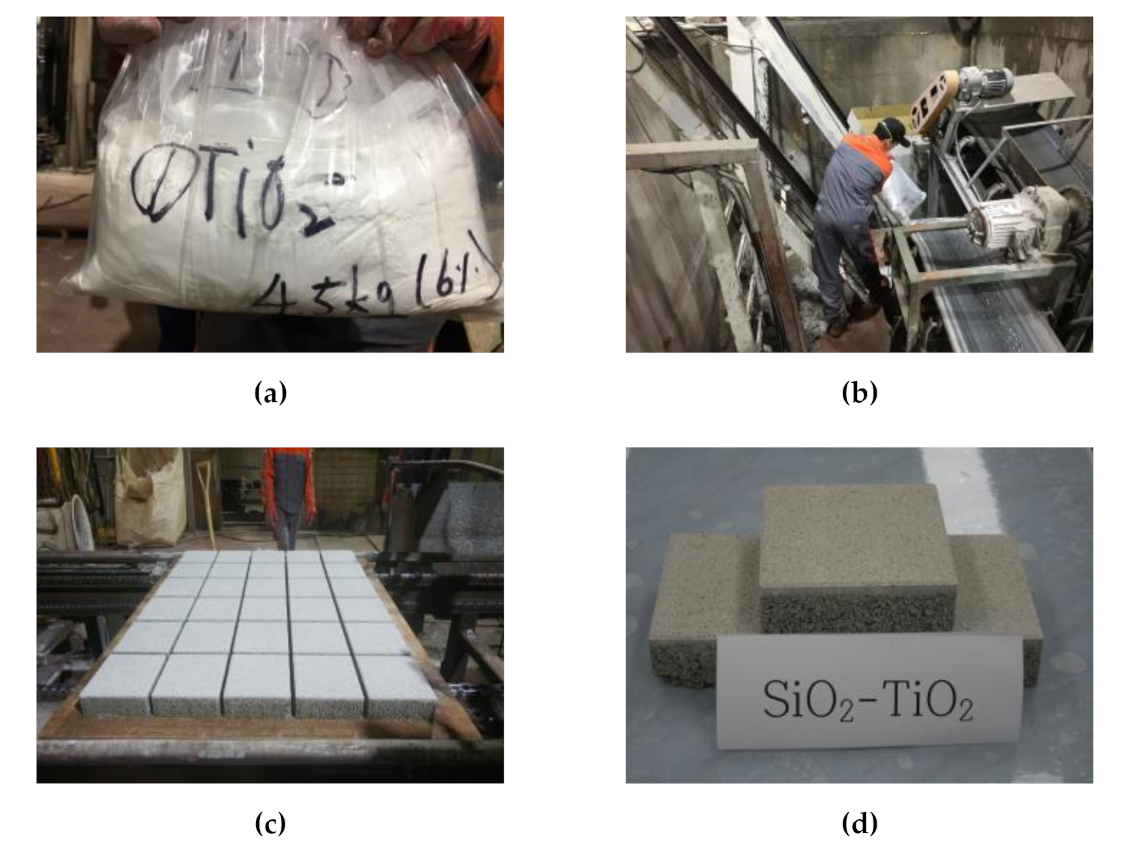
3.2. Production of Concrete Block
3.3. Experimental Program
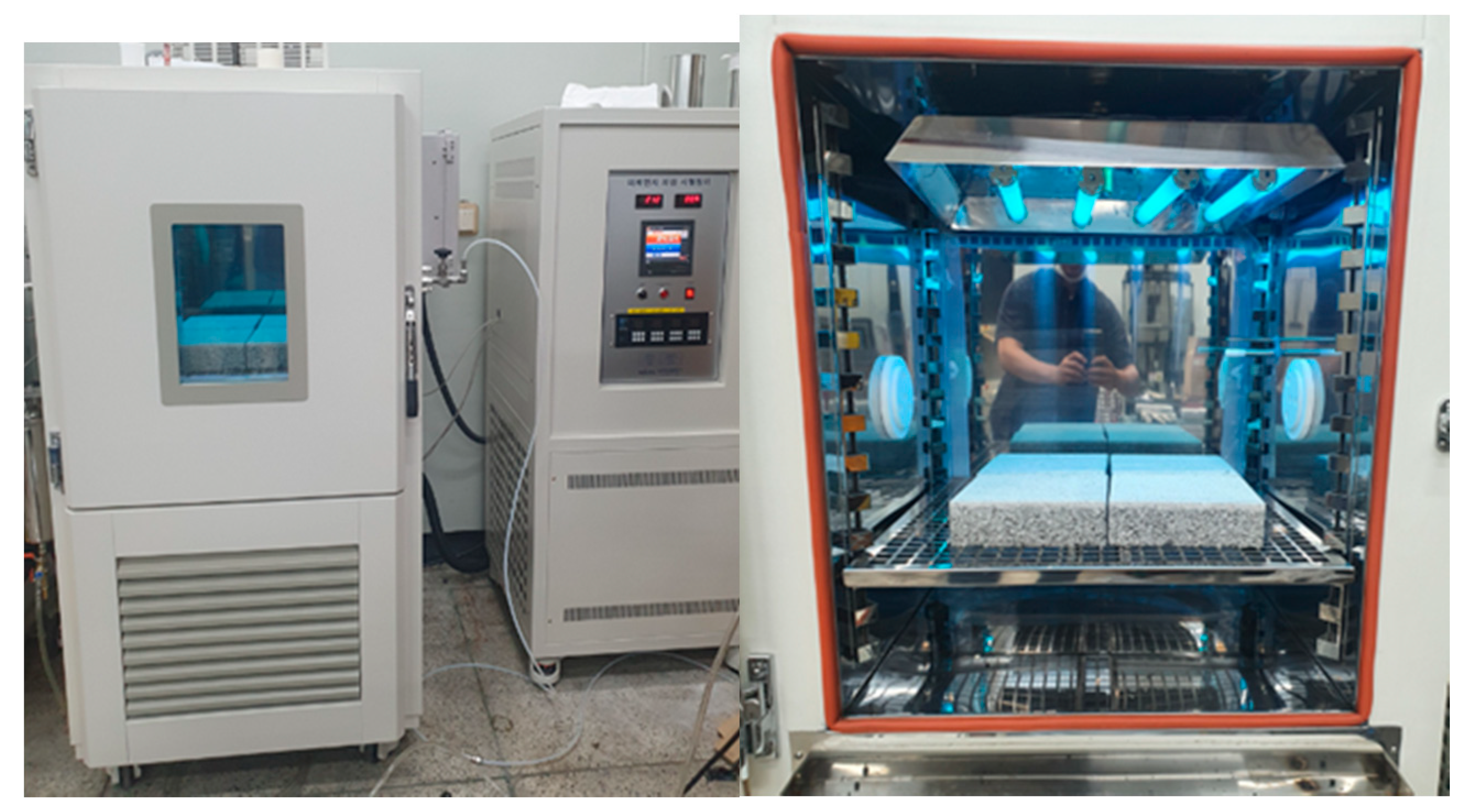
3.3.1. Laboratory Experiment
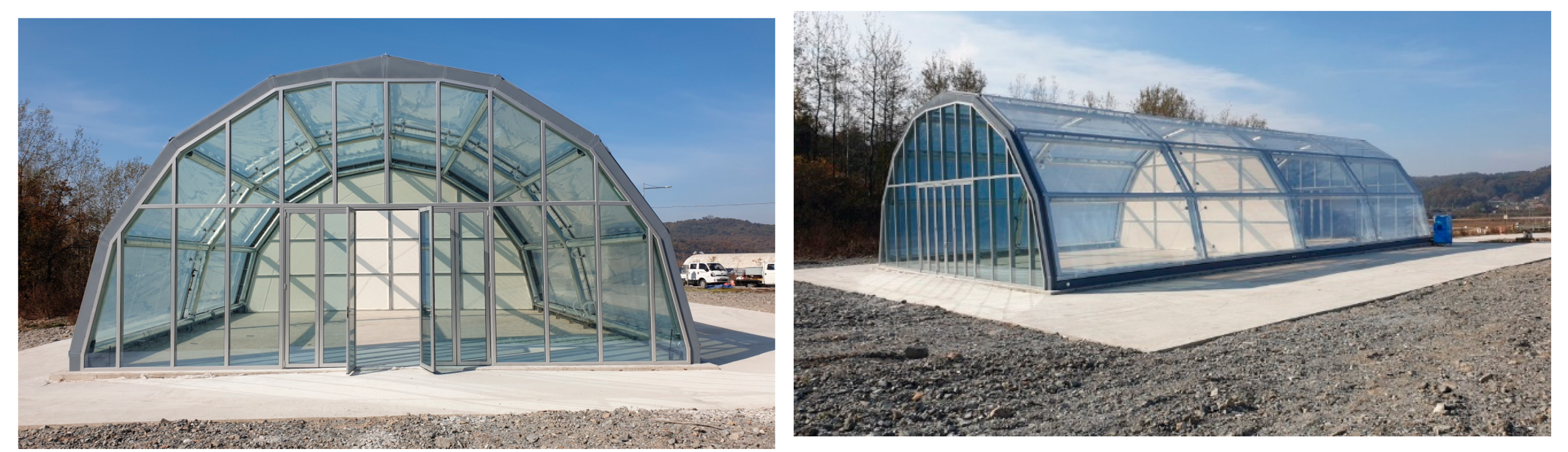
3.3.2. Full-Scale Environment Chamber Experiment
4. Test result
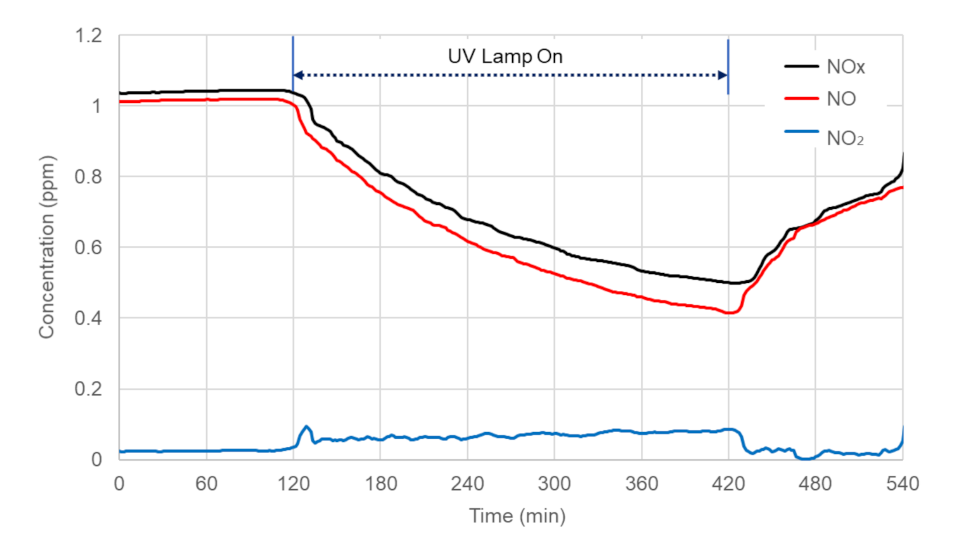
4.1. Laboratory Experiment
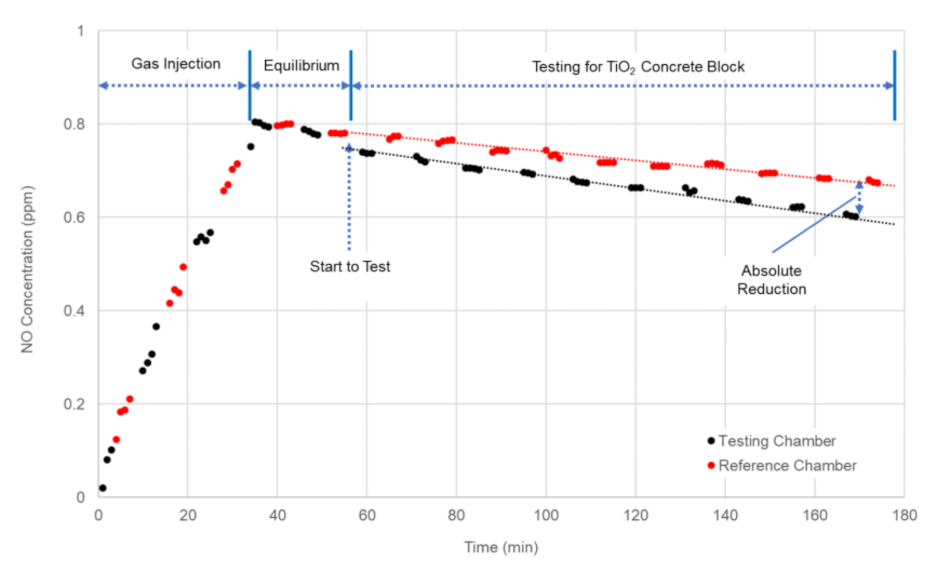
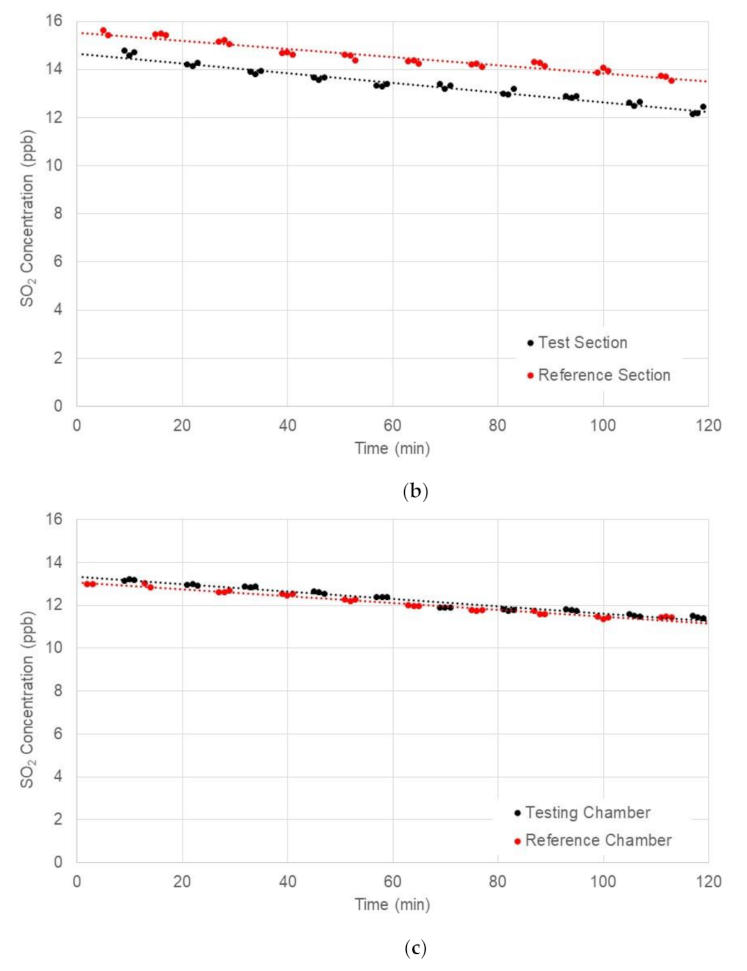
4.2. Full-Scale Environment Chamber Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kan, H.; London, S.J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Song, G.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, L.; Chen, B. Season, sex, age, and education as modifiers of the effects of outdoor air pollution on daily mortality in Shanghai, China: The Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA) study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hong, C.; Kan, H. Exposures and health outcomes from outdoor air pollutants in China. Toxicology 2004, 198, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. National Air Pollutants Emission 2015; National Institute of Environmental Research, Ministry of Environment: Seoul, Korea, 2018. (In Korean)
- Kim, Y.K.; Hong, S.J.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, S.W. Evaluation of NOx removal efficiency of photocatalytic concrete for road structure. Int. J. Highw. Eng. 2014, 16, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Tan, X.; Fang, C. Analysis of NOx pollution characteristics in the atmospheric environment in Changchun city. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, I.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Roh, Y.S. Sensitivity of NOx Removal on Recycled TiO2 in Cement Mortar. J. Rec. Const. Res. 2016, 4, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balbuena, J.; Sánchez, L.; Cruz-Yusta, M. Use of Steel Industry Wastes for the Preparation of Self-Cleaning Mortars. Materials 2019, 12, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, C.S.; Cheung, E. NO removal efficiency of photocatalytic paving blocks prepared with recycled materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Poon, C. Photocatalytic construction and building materials: From fundamentals to applications. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Poon, C.S. Photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide modified concrete materials Influence of utilizing recycled glass cullets as aggregates. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3436–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.Z.; Poon, C.S. Photocatalytic NO removal of concrete surface layers intermixed with TiO2. Build. Environ. 2013, 70, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeldens, A. An environmental friendly solution for air purification and self-cleaning effect: The application of TiO2 as photocatalyst in concrete. In Proceedings of the Transport Research Arena Europe–TRA, Göteborg, Sweden, 12–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.M.; Dylla, H.; Mohammad, L.N.; Rupnow, T. Evaluation of the durability of titanium dioxide photocatalyst coating for concrete pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, D.; Hassan, M.; Asadi, S.; White, J.R. Durability quantification of TiO2 surface coating on concrete and asphalt pavements. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Kamitani, K.; Takeuchi, K. Air purifying blocks based on photocatalysis. In Proceedings of the Japan Interlocking Block Pavement Engineering Association World Congress, Tokyo, Japan, 16–19 July 2000. (In Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-Z.; Ling, T.-C.; Poon, C.S. Photocatalytic NOx degradation of concrete surface layers intermixed and spray-coated with nano-TiO2: Influence of experimental factors. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 83, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Afshar, S. Improved photodegradation of organic contaminants using nano-TiO2 and TiO2–SiO2 deposited on Portland cement concrete blocks. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, K.M.; Kai, M.F.; Zhang, L.W. Mechanical and damping properties of CNT-reinforced cementitious composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 160, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Nam, I.W.; Lee, H.K. Enhanced effect of carbon nanotube on mechanical and electrical properties of cement composites by incorporation of silica fume. Compos. Struct. 2014, 107, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Kwon, E. A self-sensing carbon nanotube/cement composite for traffic monitoring. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Materazzi, A.L.; Ubertini, F.; D’Alessandro, A. Carbon nanotube cement-based transducers for dynamic sensing of strain. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Sun, S.; Ding, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Review of nanocarbon-engineered multifunctional cementitious composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 70, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Kundalwal, S.I.; Kumar, S. Gas barrier performance of graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Carbon 2016, 98, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Ding, S.; Yu, X. Intrinsic self-sensing concrete and structures: A review. Measurement 2015, 59, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Multifunctional and smart carbon nanotube reinforced cement-based materials. In Nanotechnology in Civil Infrastructure; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Self-Sensing Concrete in Smart Structures; Butterworth-Heinemann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.L.; Wang, T.J.; Jin, Y. Surface characteristics of hydrous silica-coated TiO2 particles. Powder Technol. 2002, 123, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroenworaluck, A.; Sunsaneeyametha, W.; Kosachan, N.; Stevens, R. Characteristics of silica-coated TiO2 and its UV absorption for sunscreen cosmetic applications. Surf. Interface Anal. 2006, 38, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Xu, W.Z.; Charpentier, P.A. The effect of silica thickness on nano TiO2 particles for functional polyurethane nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 115–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Mao, S.S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2891–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Du, X.; Wei, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Shah, S.P. Influence of nano-silica agglomeration on microstructure and properties of the hardened cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, N.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Cui, X.; Yu, X.; Ou, J. Study on the reinforcing mechanisms of nano silica to cement-based materials with theoretical calculation and experimental evidence. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 4135–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnström, J.; Martinelli, A.; Matic, A.; Börjesson, L.; Panas, I. Accelerating effects of colloidal nano-silica for beneficial calcium–silicate–hydrate formation in cement. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 392, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, S.; Dong, S.; Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Ou, J. Nano-core effect in nano-engineered cementitious composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 95, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, D.; Yu, X.; Cui, X.; Ou, J. Properties and modification mechanisms of nano-zirconia filled reactive powder concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, M.K.; Park, H.M. An Analysis on the Effectiveness of Nitrogen Oxide Reduction from Applying Titanium Dioxide on Urban Roads Using a Statistical Method. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; Le Hunte, S. An overview of semiconductor photocatalysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1997, 108, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devahasdin, S.; Fan Jr, C.; Li, K.; Chen, D.H. TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of nitric oxide: Transient behavior and reaction kinetics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 156, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, G. Study on the photocatalytic oxidation of NO2–ions using TiO2 beads as a photocatalyst. Desalination 2006, 194, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, J.; Yu, Y.H.; Wu, J.C. Removal of NOx by photocatalytic processes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2013, 14, 29–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, J.S.; Janes, P.A.; Jones, N.G.; Nicholson, J.A.; Hallam, K.R.; Allen, G.C. Photocatalytic oxidation of NOx gases using TiO2: A surface spectroscopic approach. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Yoon, H.N.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, S.J.; Jang, D.I.; Kil, T.K.; Park, S.M.; Lee, H.K. An overview on the physicochemical properties and photocatalytic pollutant removal performances of TiO2-incorporated cementitious composites. Compos. Res. 2020, 33, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Jang, Y.I.; Park, W.S.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, B.J. Photocatalytic and pozzolanic properties of nano-SiO2/Al2O3-TiO2 powder for functional mortar. Materials 2019, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlteich, J.; Steiner, C.; Schiller, N.; Miesbauer, O.; Noller, K.; Deichmann, K.-J.; Mirza, M.; Amberg-Schwab, S. Roll-to-roll thin film coating on fluoropolymer webs status, challenges and applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 314, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamnatou, C.; Moreno, A.; Chemisana, D.; Reitsma, F.; Clariá, F. Ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (ETFE) material: Critical issues and applications with emphasis on buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2186–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Ban, J.H.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.M. Preliminary Study on Small-Scale Environment Chambers for Simulating Formation of Fine Particulate Matter at Roadsides. Int. J. Highw. Eng. 2020, 22, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Density (g/cm3) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Particle Size (nm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (Å) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4 | 337 | 6.3~11.5 | 0.31 | 52 | 6~6.5 |
| Density (g/cm3) | Blaine Fineness (cm2/g) | Chemical Properties (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | Ig.loss | ||
| 3.14 | 3,492 | 21.1 | 4.65 | 3.14 | 62.8 | 2.81 | 2.1 | 2.18 |
| Type | Density (g/cm3) | Diameter of Particle (mm) | Absorption (%) | SiO2 Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #4 | 2.61 | 0.8∼1.18 | 0.8 | 97.2 |
| Grading (mm) | Density (g/cm3) | Unit Weight (kg/m3) | Absorption (%) | Ratio of Absolute Volume (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5~8 | 2.75 | 1.510 | 0.84 | 52 |
| Type | Grading of Agg. | W/B (%) | Thickness (mm) | Mix Proportioning (Ratio) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | NST | Aggregate | ||||
| Surface Layer | Silica sand No. 4 | 25 | 8 | 1 | 0.04 | 3 |
| Type | Grading of Agg. | W/B (%) | Target Void Ratio (%) | Unit Weight (kg/0.7m3) | ||
| OPC | Water | Aggregate | ||||
| Concrete Layer | 5∼8 mm | 25 | 6 | 413 | 95 | 1876 |
| Test ID | Average Solar Radiation (W/m2) | Average UV Intensity (W/m2) | NO Concentration (ppm) | Absolute Reduction (ppm) | Reduction Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Chamber | Testing Chamber | |||||
| 1 | 564 | 30.2 | 0.6508 | 0.5056 | 0.1452 | 22.3 |
| 2 | 358 | 19.8 | 0.5883 | 0.5247 | 0.0636 | 10.8 |
| 3 | 67 | 2.9 | 0.5802 | 0.5768 | 0.0034 | 0.6 |
| Test ID | Average Solar Radiation (W/m2) | Average UV Intensity (W/m2) | NO Concentration (ppm) | Absolute Reduction (ppm) | Reduction Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Chamber | Testing Chamber | |||||
| 1 | 564 | 30.2 | 13.106 | 11.22 | 1.886 | 14.4 |
| 2 | 358 | 19.8 | 11.668 | 11.155 | 0.513 | 10.0 |
| 3 | 67 | 2.9 | 11.145 | 11.259 | −0.114 | −1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.H.; Jang, Y.I.; Park, H.M. Evaluation of Reducing NO and SO2 Concentration in Nano SiO2-TiO2 Photocatalytic Concrete Blocks. Materials 2021, 14, 7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237182
Lee JW, Lee SH, Jang YI, Park HM. Evaluation of Reducing NO and SO2 Concentration in Nano SiO2-TiO2 Photocatalytic Concrete Blocks. Materials. 2021; 14(23):7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237182
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jong Won, Sang Hyuk Lee, Young Il Jang, and Hee Mun Park. 2021. "Evaluation of Reducing NO and SO2 Concentration in Nano SiO2-TiO2 Photocatalytic Concrete Blocks" Materials 14, no. 23: 7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237182
APA StyleLee, J. W., Lee, S. H., Jang, Y. I., & Park, H. M. (2021). Evaluation of Reducing NO and SO2 Concentration in Nano SiO2-TiO2 Photocatalytic Concrete Blocks. Materials, 14(23), 7182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14237182






