Introducing a Novel Experimental Model for Osseo-Disintegration of Titanium Dental Implants Induced by Monobacterial Contamination: An In-Vivo Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Protocol for Surface Contamination
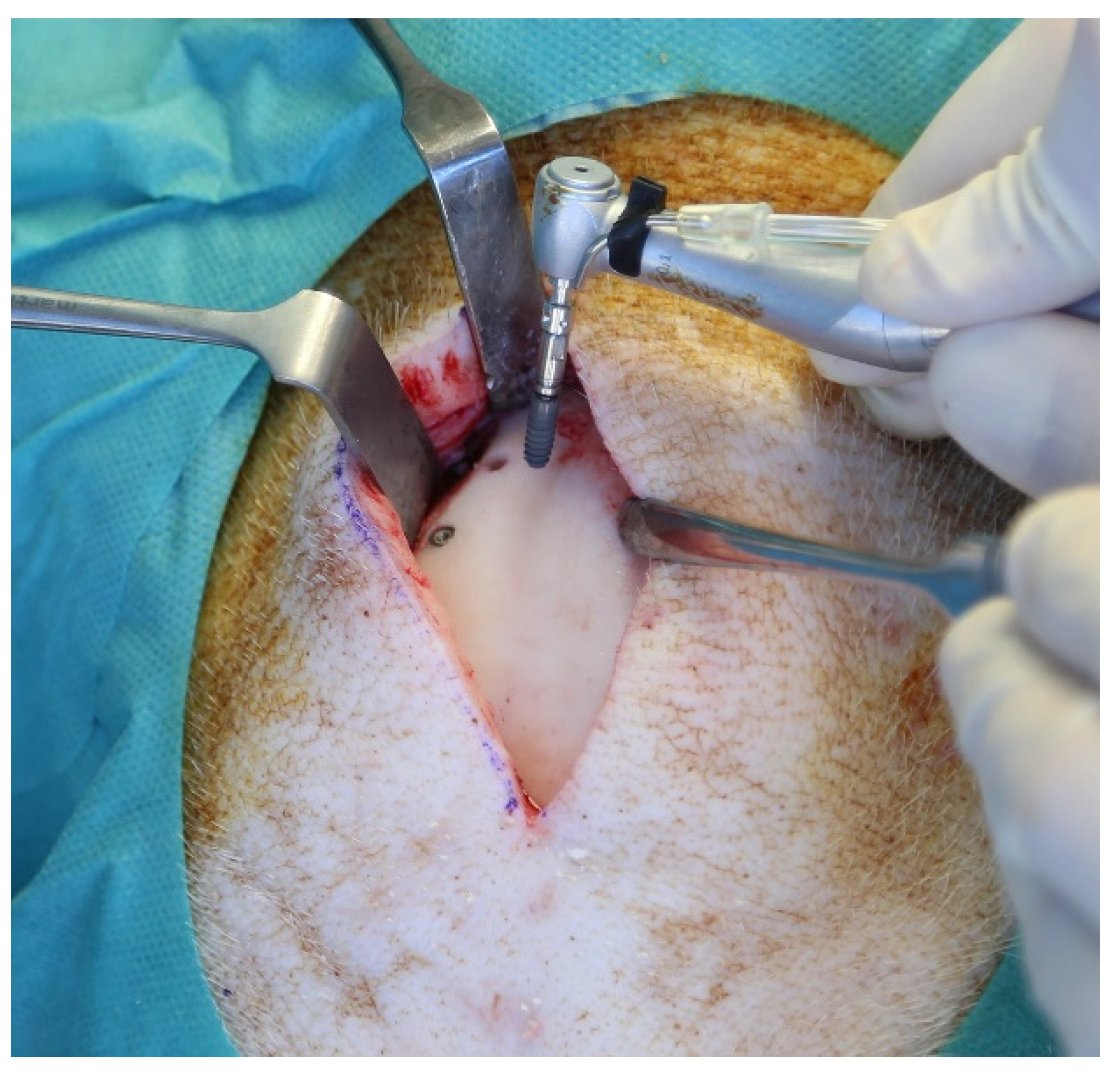
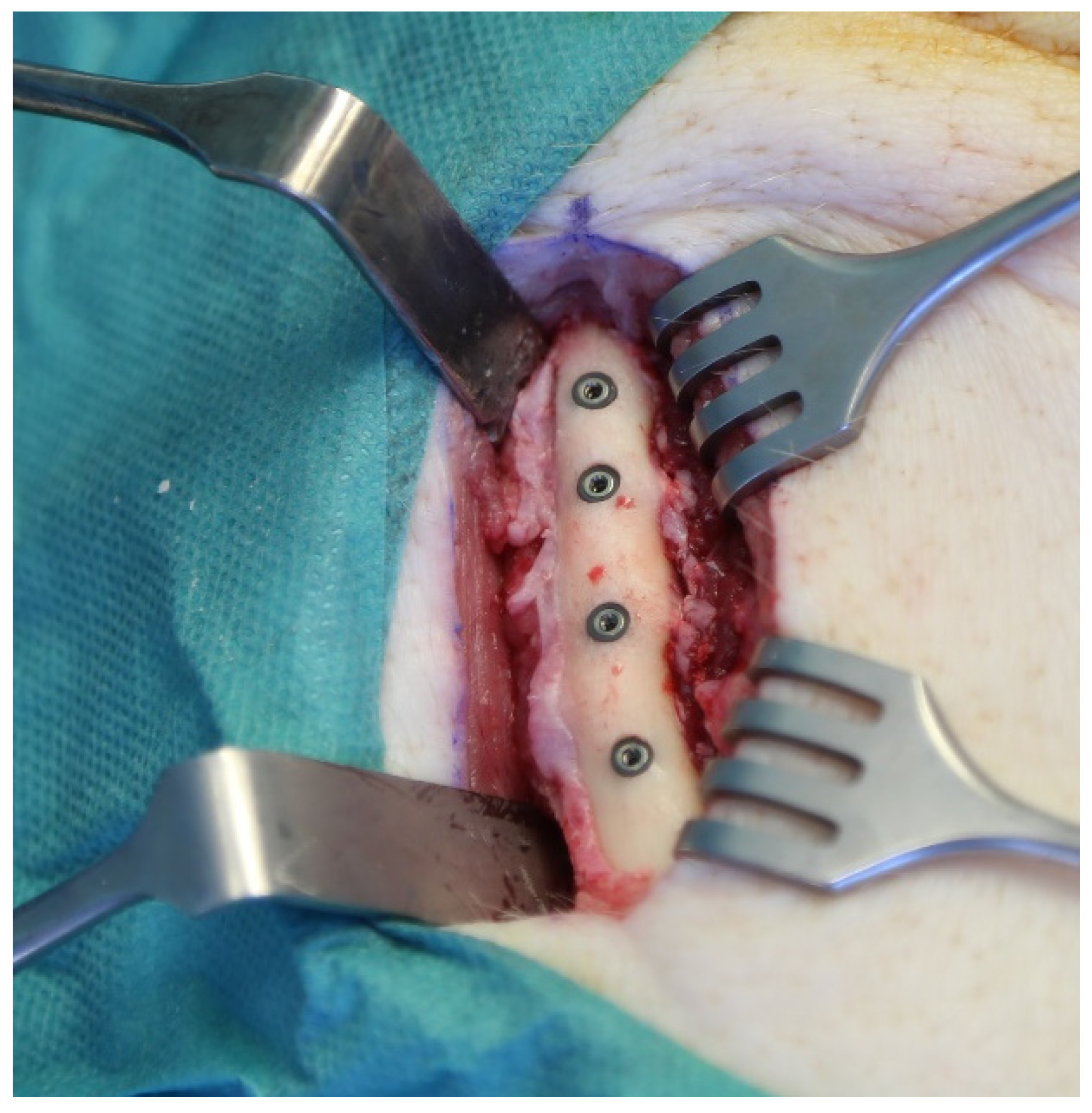
2.2. Surgical Procedure
- day 10: Xylenol-Orange (dosage 90 mg/kg bodyweight, solution 45 mg/mL)
- day 20: Calcein-Green (dosage 15 mg/kg bodyweight, solution 10 mg/mL)
- day 30: Alizarin-Complex (dosage 30 mg/kg bodyweight, solution 15 mg/mL)
- day 40: Tetracycline (dosage 30 mg/kg bodyweight, solution 15 mg/mL)
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Bone-to-Implant Contact, Interthread Bone Density, Peri-Implant Bone Density
2.5. Microradiography
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
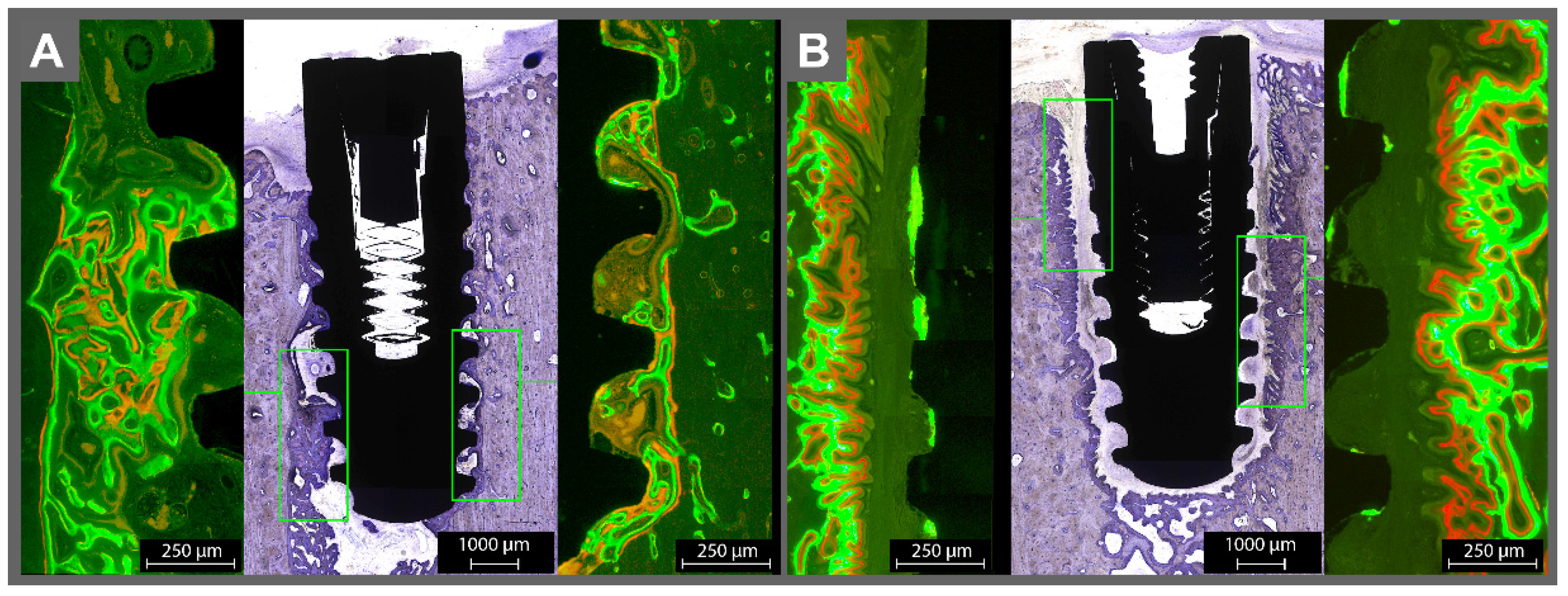
3.1. Histomorphometric Analysis
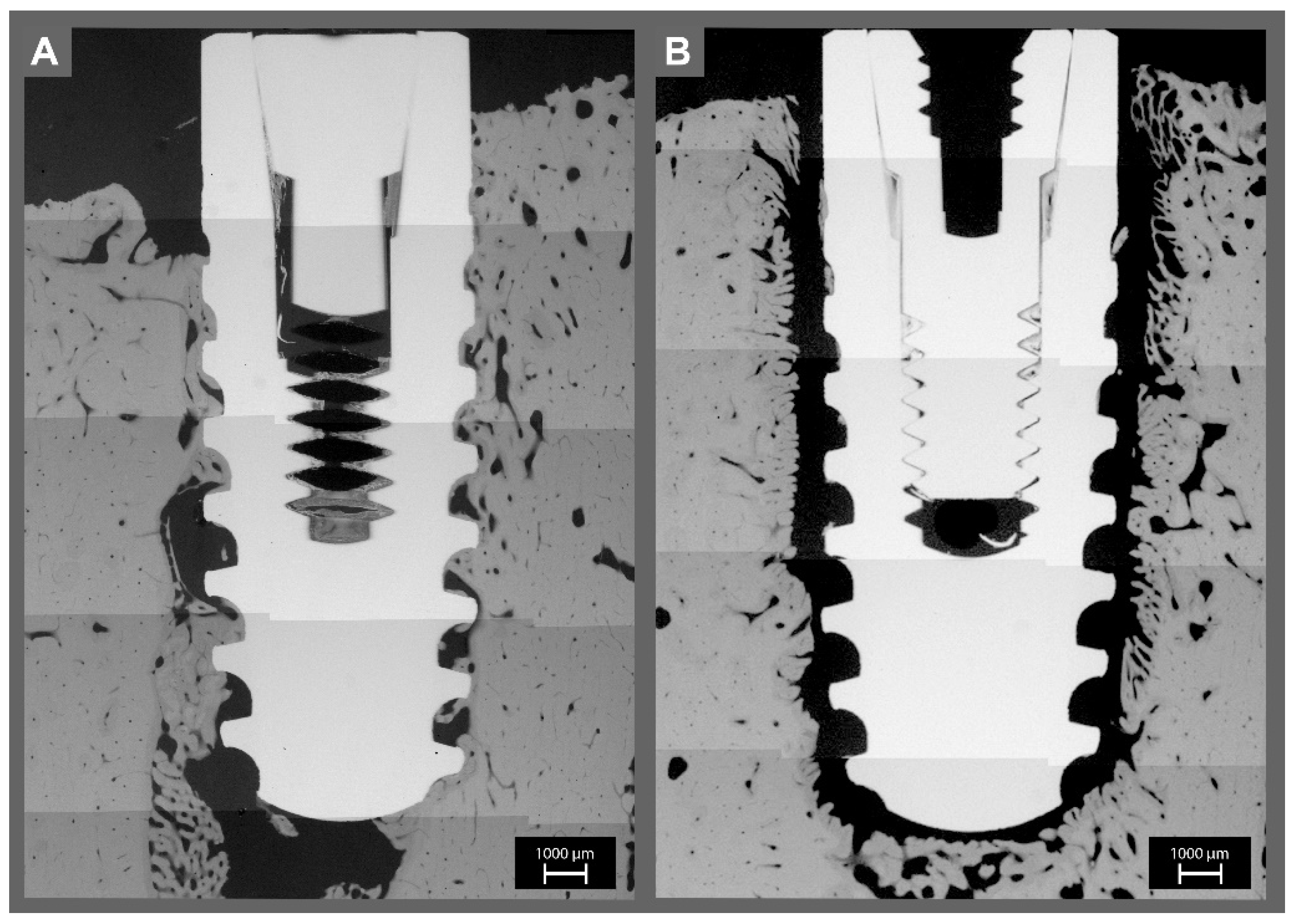
3.2. Micro-Radiographic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Aaboe, M.; Araujo, M.; Carrión, J.B.; Cavalcanti, R.; Cionca, N.; Cochran, D.; Darby, I.; Funakoshi, E.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C.; et al. Group 4 ITI Consensus Report: Risks and biologic complications associated with implant dentistry. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S16), 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. S16), S158–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.O.; Takenaka-Martinez, S.; Cota, L.O.; Ferreira, S.D.; Silva, G.L.; Costa, J.E. Peri-implant disease in subjects with and without preventive maintenance: A 5-year follow-up. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Berglundh, T. Periimplant diseases: Where are we now?—Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38 (Suppl. S11), 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rovin, S.; Costich, E.R.; Gordon, H.A. The influence of bacteria and irritation in the initiation of periodontal disease in germfree and conventional rats. J. Periodontal Res. 1966, 1, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhe, J.; Berglundh, T.; Ericsson, I.; Liljenberg, B.; Marinello, C. Experimental breakdown of peri-implant and periodontal tissues. A study in the beagle dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1992, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.T.; Föge, M.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.E.; Gavrilova, O.; Bolte, H.; Rosenstiel, P.; Wiltfang, J. Induction of periimplantitis in dental implants. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2013, 24, e15–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, B. Microbiological and immunological aspects of experimental periodontal disease in rats: A review article. J. Periodontol. 1991, 62, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.J.; Evans, R.T.; Roopenian, D.C. Oral infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and induced alveolar bone loss in immunocompetent and severe combined immunodeficient mice. Arch. Oral Biol. 1994, 39, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Eberhard, J.; Glage, S.; Held, N.; Voigt, H.; Schwabe, K.; Winkel, A.; Stiesch, M. Development of a peri-implantitis model in the rat. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berglundh, T.; Zitzmann, N.U.; Donati, M. Are peri-implantitis lesions different from periodontitis lesions? J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38 (Suppl. S11), 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayna, M.; Gulses, A.; Ziebart, T.; Neff, A.; Açil, Y. Histopathological and microradiological features of peri-implantitis. A case report. Stomatologija 2017, 19, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barrak, I.; Baráth, Z.; Tián, T.; Venkei, A.; Gajdács, M.; Urbán, E.; Stájer, A. Effects of different decontaminating solutions used for the treatment of peri-implantitis on the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis-an in vitro study. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naujokat, H.; Harder, S.; Schulz, L.Y.; Wiltfang, J.; Flörke, C.; Açil, Y. Surface conditioning with cold argon plasma and its effect on the osseointegration of dental implants in miniature pigs. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2019, 47, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, A.I.; Richards, R.G.; Milz, S.; Schneider, E.; Pearce, S.G. Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: A review. Eur. Cells Mater. 2007, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerssens, J.; Boonen, S.; Lowet, G.; Dequeker, J. Interspecies differences in bone composition, density, and quality: Potential implications for in vivo bone research. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbro, M.D.; Taschieri, S.; Canciani, E.; Addis, A.; Musto, F.; Weinstein, R.; Dellavia, C. Osseointegration of Titanium Implants With Different Rough Surfaces: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in an Adult Minipig Model. Implant. Dent. 2017, 26, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkenke, E.; Lehner, B.; Weinzierl, K.; Thams, U.; Neugebauer, J.; Steveling, H.; Radespiel-Tröger, M.; Neukam, F.W. Bone contact, growth, and density around immediately loaded implants in the mandible of mini pigs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açil, Y.; Sievers, J.; Gülses, A.; Ayna, M.; Wiltfang, J.; Terheyden, H. Correlation between resonance frequency, insertion torque and bone-implant contact in self-cutting threaded implants. Odontology 2017, 105, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokat, H.; Açil, Y.; Harder, S.; Lipp, M.; Böhrnsen, F.; Wiltfang, J. Osseointegration of dental implants in ectopic engineered bone in three different scaffold materials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, R.; Kuhlisch, E.; Schulz, M.C.; Eckelt, U.; Stadlinger, B. Comparison of bone-implant contact and bone-implant volume between 2D-histological sections and 3D-SRµCT slices. Eur. Cells Mater. 2012, 23, 237–247; discussion 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, D.; Stavropoulos, A.; Obrecht, M.; Pippenger, B.; Dard, M. A Comparison of Tapered and Nontapered Implants in the Minipig. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampakis, G.; Belibasakis, G.N. Microbiome of peri-implant infections: Lessons from conventional, molecular and metagenomic analyses. Virulence 2015, 6, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikolai, C.; Kommerein, N.; Ingendoh-Tsakmakidis, A.; Winkel, A.; Falk, C.S.; Stiesch, M. Early host-microbe interaction in a peri-implant oral mucosa-biofilm model. Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, R.; Amano, K.; Takahashi, S.W.; To, M.; Takahashi, S.; Matsuo, M. Changes in the microcirculation in periodontal tissue due to experimental peri-implantitis. J. Oral Biosci. 2021, 63, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.; Mardas, N.; Spratt, D.; Boniface, D.; Dard, M.; Donos, N. Experimental models for contamination of titanium surfaces and disinfection protocols. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.; Haas, R.; Dortbudak, O.; Watzek, G. Experimentally induced peri-implantitis: A review of differenttreatment methods described in the literature. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2000, 15, 533–544. [Google Scholar]
- Reinedahl, D.; Chrcanovic, B.; Albrektsson, T.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Ligature-Induced Experimental Peri-Implantitis-A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, D. Enterococcus faecalis and Dental Implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stájer, A.; Kajári, S.; Gajdács, M.; Musah-Eroje, A.; Baráth, Z. Utility of Photodynamic Therapy in Dentistry: Current Concepts. Dent. J. 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzis, S.; Veziroglu, S.; Kohlhaas, T.; Flörke, C.; Mishra, Y.K.; Wiltfang, J.; Açil, Y.; Faupel, F.; Aktas, O.; Gülses, A. Early osteoblastic activity on TiO2 thin films decorated with flower-like hierarchical Au structures. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 28935–28940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es-Souni, M.; Es-Souni, M.; Bakhti, H.; Gülses, A.; Fischer-Brandies, H.; Açil, Y.; Wiltfang, J.; Flörke, C. A Bacteria and Cell Repellent Zwitterionic Polymer Coating on Titanium Base Substrates towards Smart Implant Devices. Polymers 2021, 13, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sterile | Contaminated | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BIC [%] | 58.8 ± 3.4 | 7.61 ± 2.2 | p < 0.001 |
| ITBD [%] | 61.4 ± 4.4 | 8.7 ± 3.4 | p < 0.001 |
| PBD [%] | 78.6 ± 2.4 | 40.6 ± 2.9 | p < 0.001 |
| Fb Sterile | Fb Contaminated | p-Value | |
| BIC [%] | 64.2 ± 2.4 | 8.2 ± 5.2 | p < 0.001 |
| ITBD [%] | 73.6 ± 6.7 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | p < 0.001 |
| PBD [%] | 63.9 ± 5.9 | 22.8 ± 4.5 | p < 0.001 |
| M Sterile | M Contaminated | p-Value | |
| BIC [%] | 56.2 ± 4.7 | 7.2 ± 1.7 | p < 0.001 |
| ITBD [%] | 53.2 ± 4.9 | 14.0 ± 5.2 | p < 0.001 |
| PBD [%] | 86.0 ± 1.5 | 54.2 ± 3.1 | p < 0.001 |
| Frontal Bone | Mandible | p-Value | |
| BIC [%] | 30.01 ± 4.2 | 29.03 ± 2.7 | p > 0.001 |
| ITBD [%] | 34.9 ± 4.7 | 35.48 ± 1.4 | p > 0.001 |
| PBD [%] | 61.82 ± 2.4 | 62.0 ± 4.6 | p >0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flörke, C.; Eisenbeiß, A.-K.; Metz, U.; Gülses, A.; Acil, Y.; Wiltfang, J.; Naujokat, H. Introducing a Novel Experimental Model for Osseo-Disintegration of Titanium Dental Implants Induced by Monobacterial Contamination: An In-Vivo Feasibility Study. Materials 2021, 14, 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14227076
Flörke C, Eisenbeiß A-K, Metz U, Gülses A, Acil Y, Wiltfang J, Naujokat H. Introducing a Novel Experimental Model for Osseo-Disintegration of Titanium Dental Implants Induced by Monobacterial Contamination: An In-Vivo Feasibility Study. Materials. 2021; 14(22):7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14227076
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlörke, Christian, Anne-Katrin Eisenbeiß, Ulla Metz, Aydin Gülses, Yahya Acil, Jörg Wiltfang, and Hendrik Naujokat. 2021. "Introducing a Novel Experimental Model for Osseo-Disintegration of Titanium Dental Implants Induced by Monobacterial Contamination: An In-Vivo Feasibility Study" Materials 14, no. 22: 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14227076
APA StyleFlörke, C., Eisenbeiß, A.-K., Metz, U., Gülses, A., Acil, Y., Wiltfang, J., & Naujokat, H. (2021). Introducing a Novel Experimental Model for Osseo-Disintegration of Titanium Dental Implants Induced by Monobacterial Contamination: An In-Vivo Feasibility Study. Materials, 14(22), 7076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14227076






