Binary Self-Assembly of Nanocolloidal Arrays using Concurrent and Sequential Spin Coating Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
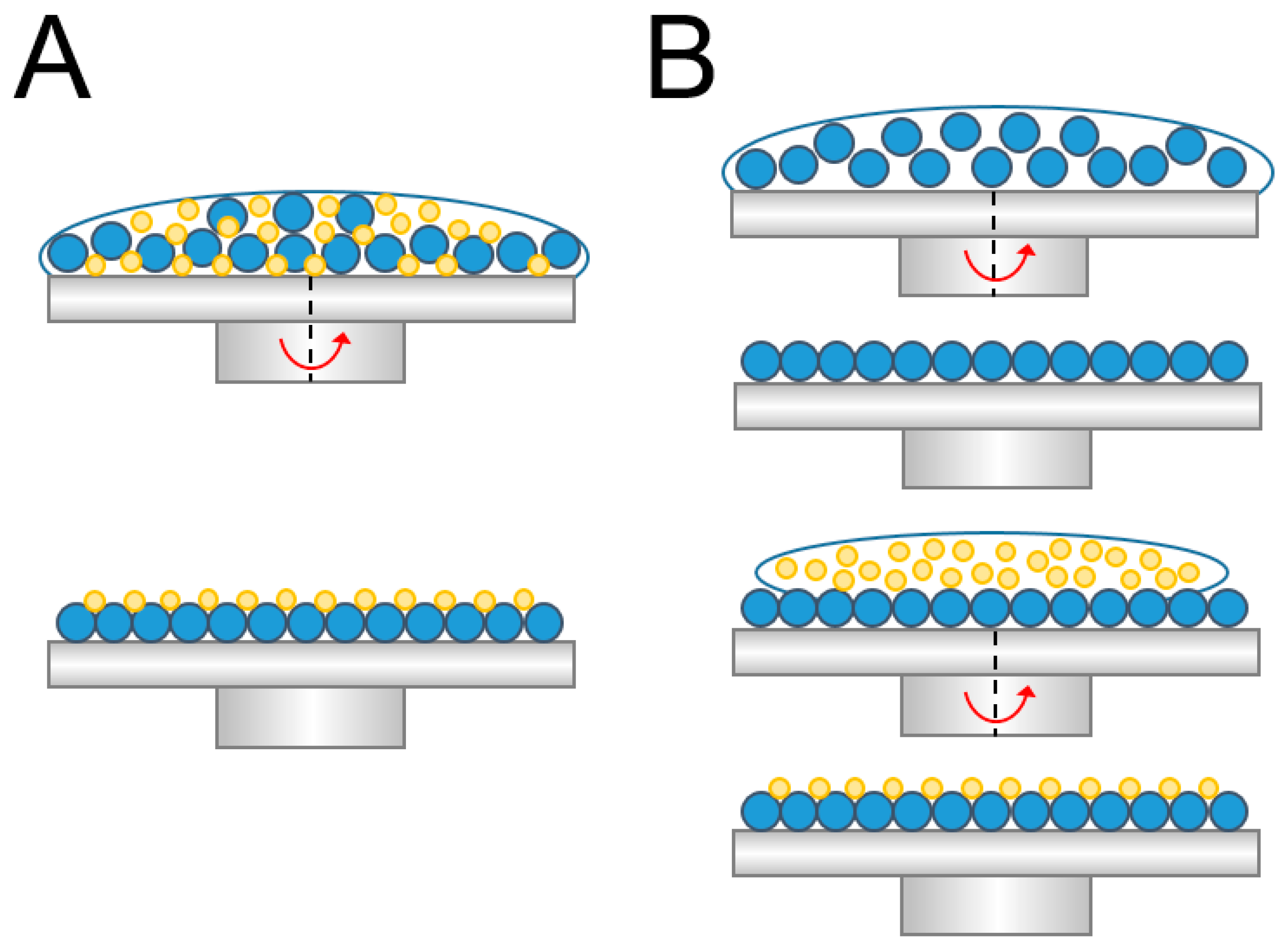
2.3. Concurrent Spin Coating
2.4. Sequential Spin Coating
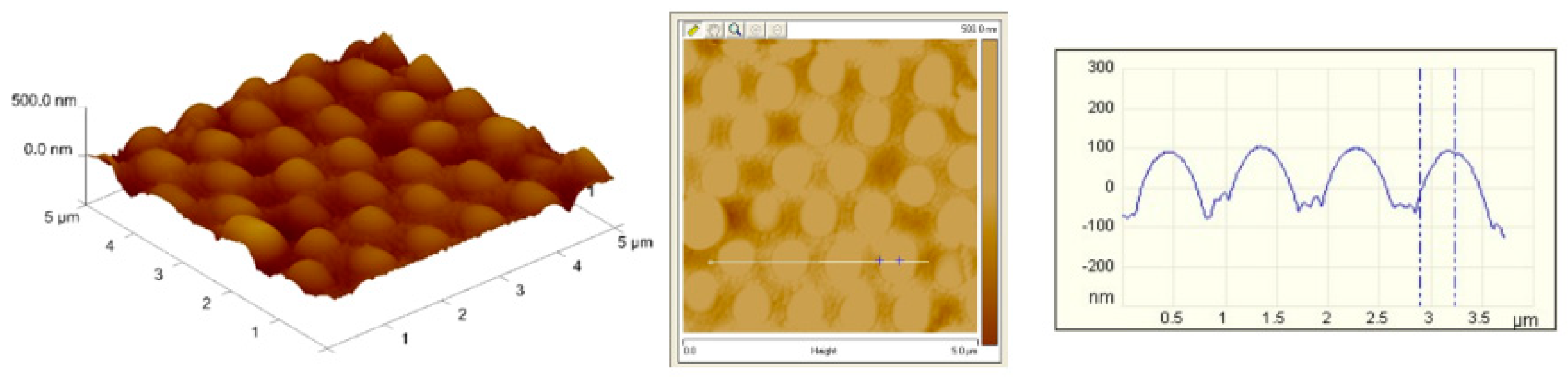
2.5. Characterization of Self-Assembled Binary Arrays
3. Results and Discussion
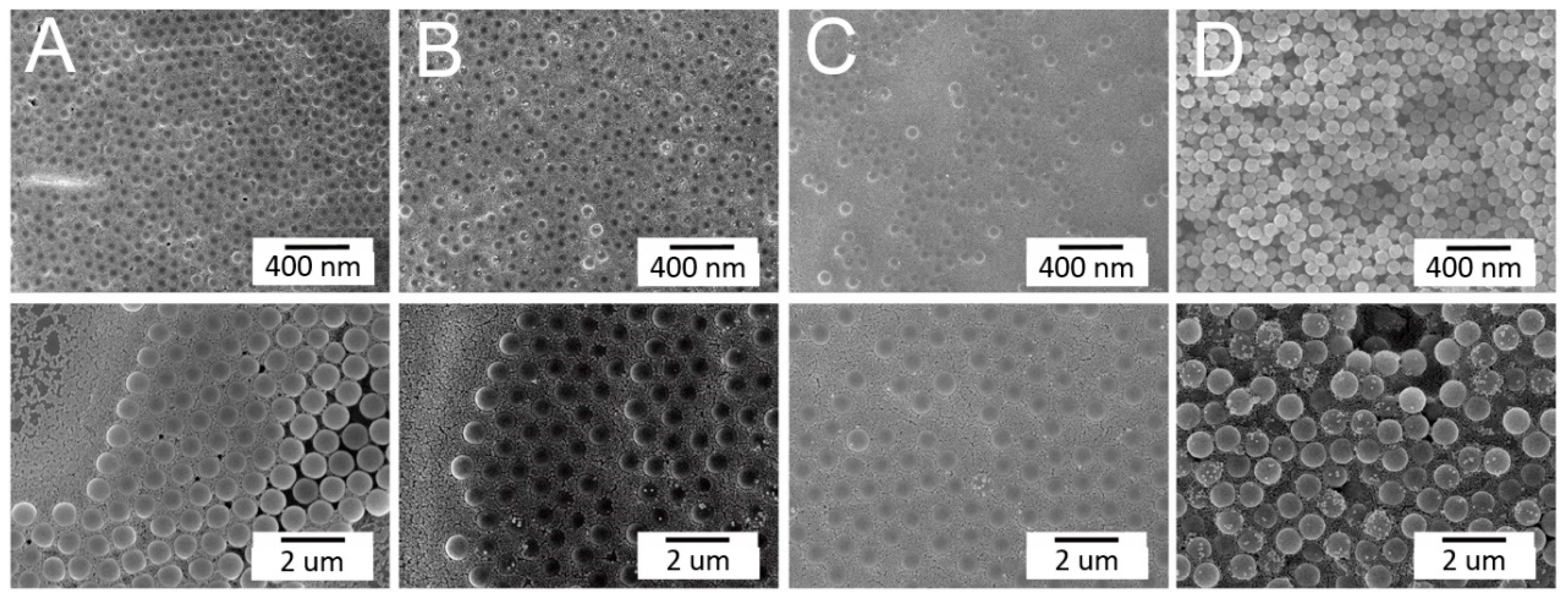
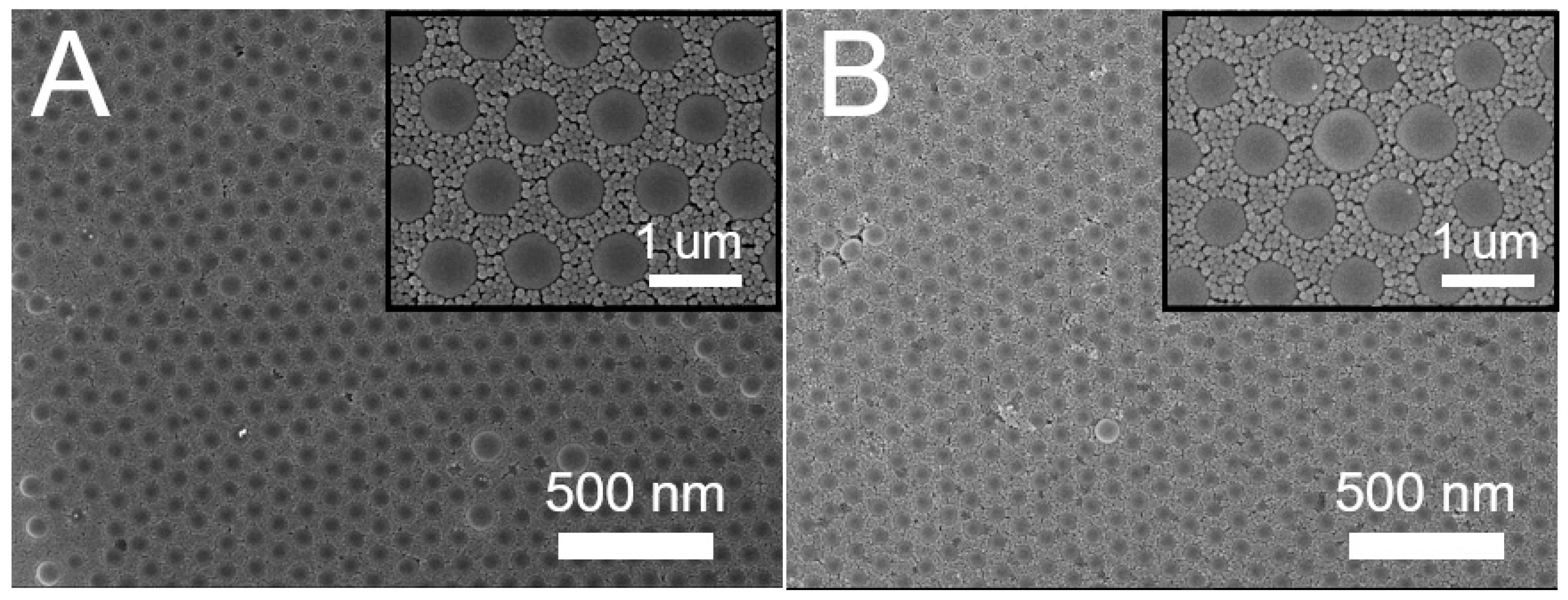
3.1. Concurrent Spin Coating of Binary Nanosphere Arrays
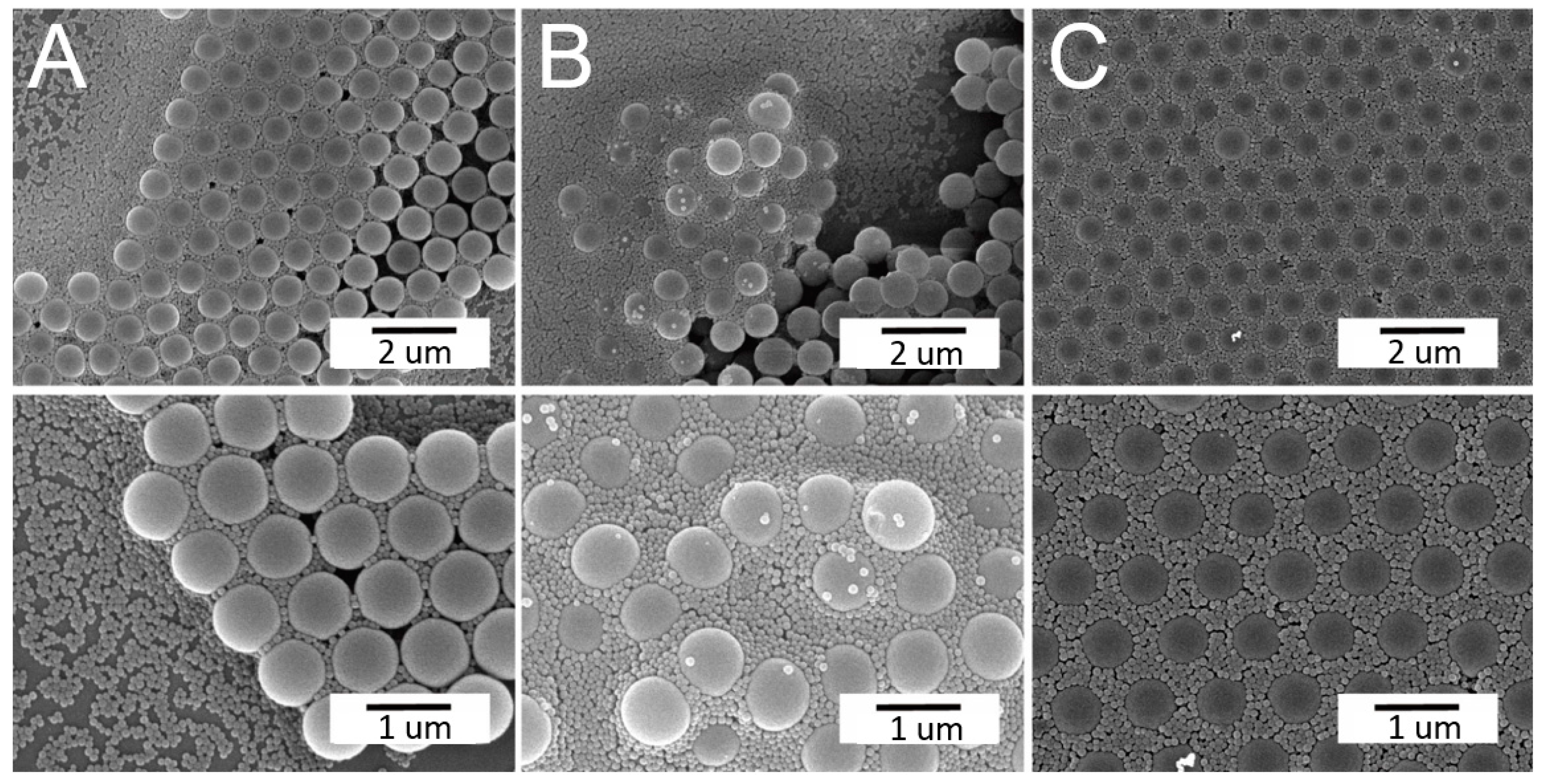
3.2. Sequential Spin Coating of Binary Nanosphere Arrays
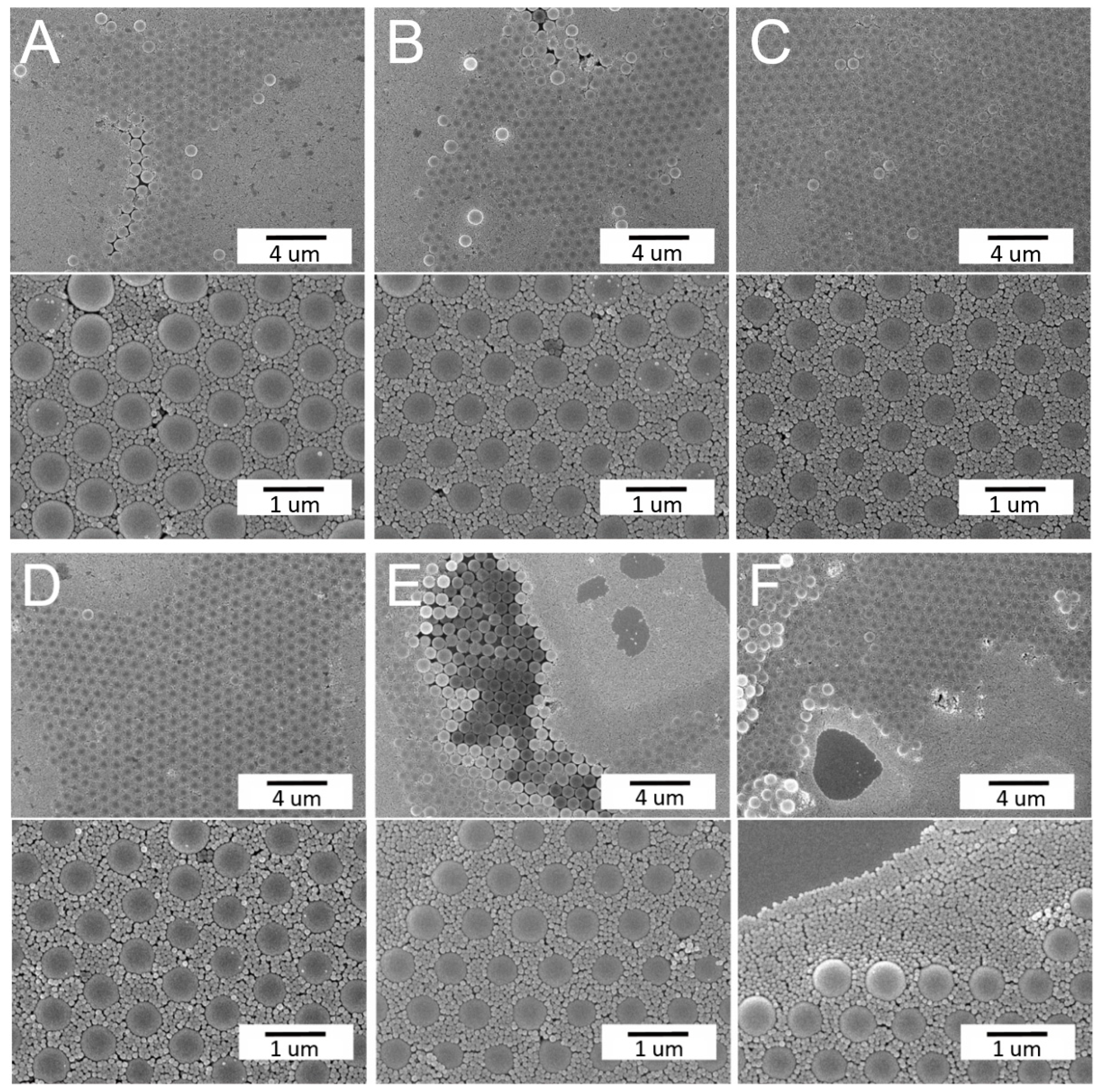
3.3. Self-Assembled Arrays using Optimum Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y. Effect of the Nano/Microscale Structure of Biomaterial Scaffolds on Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Amirthalingam, S.; Kim, S.L.; Lee, S.S.; Rangasamy, J.; Hwang, N.S. Biomimetic Materials and Fabrication Approaches for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 201700612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.H.; Kang, L.; Khademhosseini, A. Micro-And Nanoscale Technologies for Tissue Engineering and Drug Discovery Applications. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.O.; Liu, X.H.; Smith, L.A.; Ma, P.X. Nano-Structured Polymer Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, A.; Bertacchini, J.; D’Avella, D.; Anselmi, L.; Maraldi, T.; Marmiroli, S.; Messori, M. Development of Solvent-Casting Particulate Leaching (SCPL) Polymer Scaffolds as Improved Three-Dimensional Supports to Mimic the Bone Marrow Niche. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, R.; Yousefi, A.-M. Effects of Processing Parameters in Thermally Induced Phase Separation Technique on Porous Architecture of Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, P.; Palka, K.; Przekora, A. Development and Optimization of the Novel Fabrication Method of Highly Macroporous Chi-Tosan/Agarose/Nanohydroxyapatite Bone Scaffold for Potential Regenerative Medicine Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, S.; Dong, B.; Li, C.Y. Mimicking Bone Nanostructure by Combining Block Copolymer Self-Assembly and 1D Crystal Nucleation. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8251–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzana, J.A.; Olvera, D.; Fuller, S.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Graeve, O.A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Kates, S.L.; Awad, H. 3D Printing of Composite Calcium Phosphate and Collagen Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4026–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Concepts, Materials, and Applications. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 1976–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Mathias, J.P.; Seto, C.T. Molecular Self-Assembly and Nanochemistry: A Chemical Strategy for the Synthesis of Nanostructures. Science 1991, 254, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, N.; Parija, B.; Panigrahi, S. Fundamental Understanding and Modeling of Spin Coating Process: A Review. Indian J. Phys. 2009, 83, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Chen, W.A. Nanofeatured Anti-Reflective Films Manufactured Using Hot Roller Imprinting and Self-Assembly Nanosphere Lithography. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 48, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Qi, L.; Guo, R.; Li, K.; Yin, Z.; Wu, D.; Zou, H. A Low-Cost Fabrication Method of Nanostructures by Ultraviolet Proximity Exposing Lithography. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 045221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, P.; Henrist, C.; Cloots, R. Nanosphere Lithography: A Powerful Method for the Controlled Manufacturing of Nanomaterials. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domonkos, M.; Demo, P.; Kromka, A. Nanosphere Lithography for Structuring Polycrystalline Diamond Films. Crystal 2020, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. Recent Developments in the Fabrication of Ordered Nanostructure Arrays Based on Nanosphere Lithography. Recent Patents Nanotechnol. 2010, 4, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Möhwald, H. Rapid Fabrication of Binary Colloidal Crystals by Stepwise Spin-Coating. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Al-Hanbali, O.; Pillai, S.; Hemmersam, A.G.; Meyer, R.L.; Hunter, A.C.; Rutt, K.J.; Besenbacher, F.; Moghimi, S.M.; Kingshott, P. Ordering of Binary Polymeric Nanoparticles on Hydrophobic Surfaces Assembled from Low Volume Fraction Dispersions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13390–13391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Griesser, H.J.; Bremmell, K.E.; Kingshott, P. Highly Ordered Nanometer-Scale Chemical and Protein Patterns by Binary Colloidal Crystal Lithography Combined with Plasma Polymerization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 21, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaev, V.; Ozin, G.A. Self-Assembled Surface Patterns of Binary Colloidal Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Gohri, V.; Pillai, S.; Arpanaei, A.; Foss, M.; Kingshott, P. Large-Area Protein Patterns Generated by Ordered Binary Colloidal as-Semblies as Templates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3542–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test No. | Surfactant:Solvent | Spin Speed (Spin Time) Unit: rpm (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TX-100:Methanol = 1:300 | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) |
| 2 | 500(30)/1500(60)/2000(60) | |
| 3 | 500(30)/1500(60)/2000(300) | |
| 4 | 500(30)/1500(60)/2000(100) | |
| 5 | TX-100:Methanol = 1:300 | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) |
| 6 | 500(5)/1000(30)/1500(300) | |
| 7 | 500(5)/1000(30)/2000(300) | |
| 8 | 500(5)/1500(30)/3000(300) | |
| 9 | TX-100:Methanol = 1:300 | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) |
| 10 | TX-100:Methanol = 1:400 | |
| 11 | DI water:Ethanol = 1:1 |
| Test No. | First Coating: 900 nm 900 nm: Surfactant = 0.7:1 | Second Coating: 100 nm 100 nm: Surfactant = 0.3:1 |
|---|---|---|
| Spin Speed (Spin Time) rpm (s) | Spin Speed (Spin Time) rpm (s) | |
| 1 | 500(30)/1500(30)/2000(60) | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) |
| 2 | 500(30)/1500(30)/2000(60) | 500(30)/1500(30)/2000(60) |
| 3 | 500(30)/1500(30)/2000(60) | 500(30)/3000(60)/1000(60) |
| 4 | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) |
| 5 | 500(5)/1500(30)/2000(300) | 500(30)/3000(60)/1000(60) |
| 6 | 500(30)/3000(60)/1000(60) | 500(30)/3000(60)/1000(60) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, S.-J.; Lee, D.; Wu, Y.-C.; Liu, S.-J. Binary Self-Assembly of Nanocolloidal Arrays using Concurrent and Sequential Spin Coating Techniques. Materials 2021, 14, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020274
Shen S-J, Lee D, Wu Y-C, Liu S-J. Binary Self-Assembly of Nanocolloidal Arrays using Concurrent and Sequential Spin Coating Techniques. Materials. 2021; 14(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Shih-Jyun, Demei Lee, Yu-Chen Wu, and Shih-Jung Liu. 2021. "Binary Self-Assembly of Nanocolloidal Arrays using Concurrent and Sequential Spin Coating Techniques" Materials 14, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020274
APA StyleShen, S.-J., Lee, D., Wu, Y.-C., & Liu, S.-J. (2021). Binary Self-Assembly of Nanocolloidal Arrays using Concurrent and Sequential Spin Coating Techniques. Materials, 14(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14020274






