Improving ANFO: Effect of Additives and Ammonium Nitrate Morphology on Detonation Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Properties of ANFO
3. Modification of ANFO Properties
3.1. Modification of AN
3.2. Fuel Modification and Alternative Fuels
3.3. Additives to ANFO
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaturvedi, S.; Dave, P.N. Review on thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate. J. Energetic Mater. 2013, 31, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Mohamed, S.; Alaa, M. Blast Loads on Structures; CSCE: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2018; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, P.W. Explosives Engineering; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, R.; Köhler, J.; Homburg, A. Explosives, 5th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, S.I.; Kiyanda, C.B.; Short, M. Experimental observations of detonation in ammonium-nitrate-fuel-oil (ANFO) surrounded by a high-sound-speed, shockless, aluminum confiner. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2219–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruhe, T.C.; Bajpayee, T.S. Thermal stabilty of ANFO made with recycled oil. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Explosives and Blasting Technique, Nashville, TN, USA, 7–10 February 1999; International Society of Explosives Engineers: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Damon, G.H. Safety Recommendations for Sensitized Ammonium Nitrate Blasting Agents; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Damon, G.H.; Mason, C.M.; Hanna, N.E.; Forshey, D.R. Safety Recommendations for Ammonium Nitrate-Based Blasting Agents. Revision of Information Circular 8179; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Labor, Mine Safety and Health Administration. Hazardous Waste Fuels in Mining. IR 1195; U.S. Department of Labor, Mine Safety and Health Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Vandermeulen, J.H.; Fonda, A.; Stuttard, C. Toxicity vs. mutagenicity of some crude oils, distillates and their water soluble fractions. Water Res. 1985, 19, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.A. The Science of Industrial Explosives; IRECO Chemicals: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1974; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, H.; Ogata, Y.; Wada, Y.; Miyake, A.; Jung, W.; Nakamura, J.; Ogawa, T. Detonation behavior of ANFO in resin tubes. Sci. Techno. Energetic Mat. 2004, 65, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Mertuszka, P.; Cenian, B.; Kramarczyk, B.; Pytel, W. Influence of explosive charge diameter on the detonation velocity based on emulinit 7L and 8L bulk emulsion explosives. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2018, 15, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.L.; Drive, G.B. Multi-Valued Normal Shock Velocity versus Curvature Relationships for Highly Non-Ideal Explosives. In Proceedings of the Detonation Symposia, Snowmass, CO, USA, 30 August–4 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, E.B.; Kostitsin, O.V.; Koval, A.V.; Akhlyustin, I.A. Model of non-ideal detonation of condensed high explosives. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 774, 012076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahedavan, E.G. Ammonium Nitrate Explosives for Civil Application; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cetner, Z.; Maranda, A. Wybrane parametry materiałów wybuchowych typu heavy-ANFO. Mater. Wysokoenergetyczne 2014, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Maranda, A. Przemysłowe Materiały Wybuchowe; Wojskowa Akademia Techniczna: Warsaw, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kramarczyk, B.; Pytlik, M.; Mertuszka, P. Effect of aluminium additives on selected detonation parameters of a bulk emulsion explosive. High Energy Mater. 2020, 12, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szastok, M. Comparative Study of Anfo’s and Dynamite’s Capability to Perform Work Determined with Lead Block and Ballistic Pendulum; Zeszyty Naukowe: Krakow, Poland, 2018; pp. 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zapp, K.H.; Wostbrock, K.H.; Schäfer, M.; Sato, K.; Seiter, H.; Zwick, W.; Leiter, H. Ammonium Compounds. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; VCH: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2000; Volume 3, pp. 264–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammonium Nitrate (AN)—Production. Available online: https://knoema.com//atlas/topics/Agriculture/Fertilizers-Production-Quantity-in-Nutrients/Ammonium-nitrate-production (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Hainer, R.M. The application of kinetics to the hazardous behavior of ammonium nitrate. In Symposium on Combustion, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1954; pp. 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykes, W.G.; Johnson, R.H.; Hanier, R.M. An explosion hazard. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1963, 59, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt, B.; Buczkowski, D. Influence of ammonium nitrate prills’ properties on detonation velocity of ANFO. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2007, 32, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktorov, S.D.; Frantov, A.E.; Lapikov, I.N.; Andreev, V.V.; Starshinov, A.V. Effect of the microstructure of ammonium nitrate granules on the detonability of composite propellants based on it. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 2016, 52, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presles, H.N.; Vidal, P.; Khasainov, B. Experimental study of the detonation of technical grade ammonium nitrate. C. R. Mec. 2009, 337, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt, B.; Buczkowski, D. Agriculture grade ammonium nitrate as the basic ingredient of massive explosive charges. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2012, 37, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitkiewicz-Wołodko, R.; Maranda, A.; Paszula, J.P. Modification of ANFO detonation parameters by addition of ground of ammonium nitrate(V) and aluminium powder. Central Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2019, 16, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhova, N.O.; Krmela, J. Nanoporous structure of the ammonium nitrate granules at the final drying: The effect of the dryer operation mode. J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 2019, 11, 04006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhova, N.O. Morphological features of the nanoporous structure in the ammonium nitrate granules at the final drying stage in multistage devices. J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 2020, 12, 04036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxley, J.C.; Kaushik, S.M.; Gilson, N.S. Thermal stability and compatibility of ammonium nitrate explosives on a small and large scale. Thermochim. Acta 1992, 212, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinditskii, V.P.; Egorshev, V.Y.; Levshenkov, A.I.; Serushkin, V.V. Ammonium nitrate: Combustion mechanism and the role of additives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2005, 30, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.W. Particulate Ammonium Nitrate Sensitized with a Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuel Containing Calcium Chloride as Anti-Caking Agent. U.S. Patent 3,368,929A, 13 February 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Sachdeva, S.; Papadaki, M.I.; Mannan, M.S. Ammonium nitrate thermal decomposition with additives. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2015, 35, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sachdeva, S.; Papadaki, M.I.; Mannan, S. Effects of inhibitor and promoter mixtures on ammonium nitrate fertilizer explosion hazards. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 624, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-R.; Koseki, H. Study on the contamination of chlorides in ammonium nitrate. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2005, 83, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, I.; Kaljuvee, T.; Türn, L.; Bender, V.; Trikkel, A.; Kuusik, R. Interactions of ammonium nitrate with different additives. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xia, L.-H.; Wu, Q.-J.; Xu, S.; Liu, D.-B. Detonation characteristics of ammonium nitrate and activated fertilizer mixtures. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 2016, 52, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Pingua, B.M.P.; Dey, A.; Roy, M.P.; Singh, P.K. Surface functionalized ammonium nitrate prills with enhanced water resistance property: Characterizations and its application as commercial explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2021, 46, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhu, M.; Ma, Y.; Millin, N. Homogeneous combustion catalysts for efficiency improvements and emission reduction in diesel engines. In Proceedings of the 7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Combustion, Taipei, Taiwan, 24–27 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Biessikirski, A.; Czerwonka, D.; Biegańska, J.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Ziąbka, M.; Dworzak, M.; Twardosz, M. Research on the possible application of polyolefin waste-derived pyrolysis oils for ANFO manufacturing. Energies 2020, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, S.A.; Costa e Silva, V.; de Lima, H.M. Study of non-conventional fuels for explosives mixes. REM Rev. Esc. Minas 2014, 67, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, D. Explosive properties of mixtures of ammonium nitrate(V) and materials of plant origin—danger of unintended explosion. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2014, 11, 115–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khawaja, M.A.; Aban, M.M. Characteristics of used lubricating oils, their environmental impact and survey of disposal methods. Environ. Manag. Health 1996, 7, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Roy, M.P.; Pingua, B.M.P.; Mukherjee, R.; Agarwal, L.; Singh, P.K. Utilization of Waste lubricant oil in fuel phase of ANFO explosives: Its field applications and environmental impact. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2021, 46, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feustel, M.; Krull, M.; Collins, C.R.; Tolliday, I.J.; Franjic, M.; Roy, T. Water Resistance Additive Foer Ammonium Nitrate–Fuel Oil (Anfo) Explosives. Patent No. EP3239120A1, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Maranda, A.; Paszula, J.; Zawadzka-Małota, I.; Kuczyńska, B.; Witkowski, W.; Nikolczuk, K.; Wilk, Z. Aluminum powder infuence on ANFO detonation parameters. Cent. Eur. J. Energetic Mater. 2011, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar]
- Araos, M.; Onederra, I. Preliminary detonation study of dry, wet and aluminised ANFO using high-speed. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2019, 16, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, R.K.; Royle, H.J. Factors that affect the impact sensitiveness of ammonium nitrate—fuel oil (ANFO) explosives containing aluminium. J. Energetic Mater. 2000, 18, 177–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranchimeg, E.; Narantsetseg, M.; Purev, L. Modification of ANFO detonation parameters by biowaste addition. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1019, p. 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessikirski, A.; Barański, K.; Pytlik, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Biegańska, J.; Słowiński, K. Application of silicon dioxide as the inert component or oxide component enhancer in ANFO. Energies 2021, 14, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
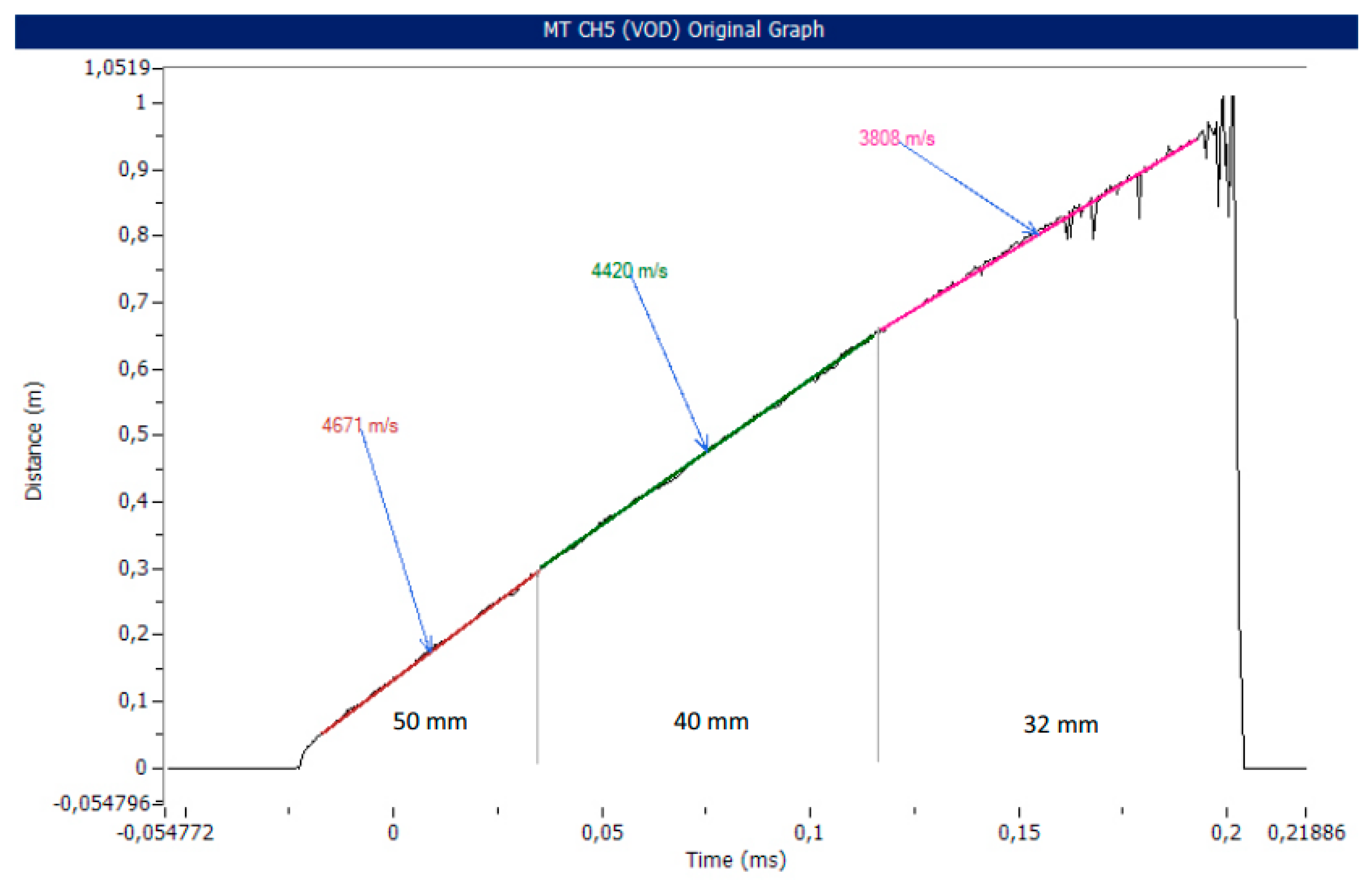
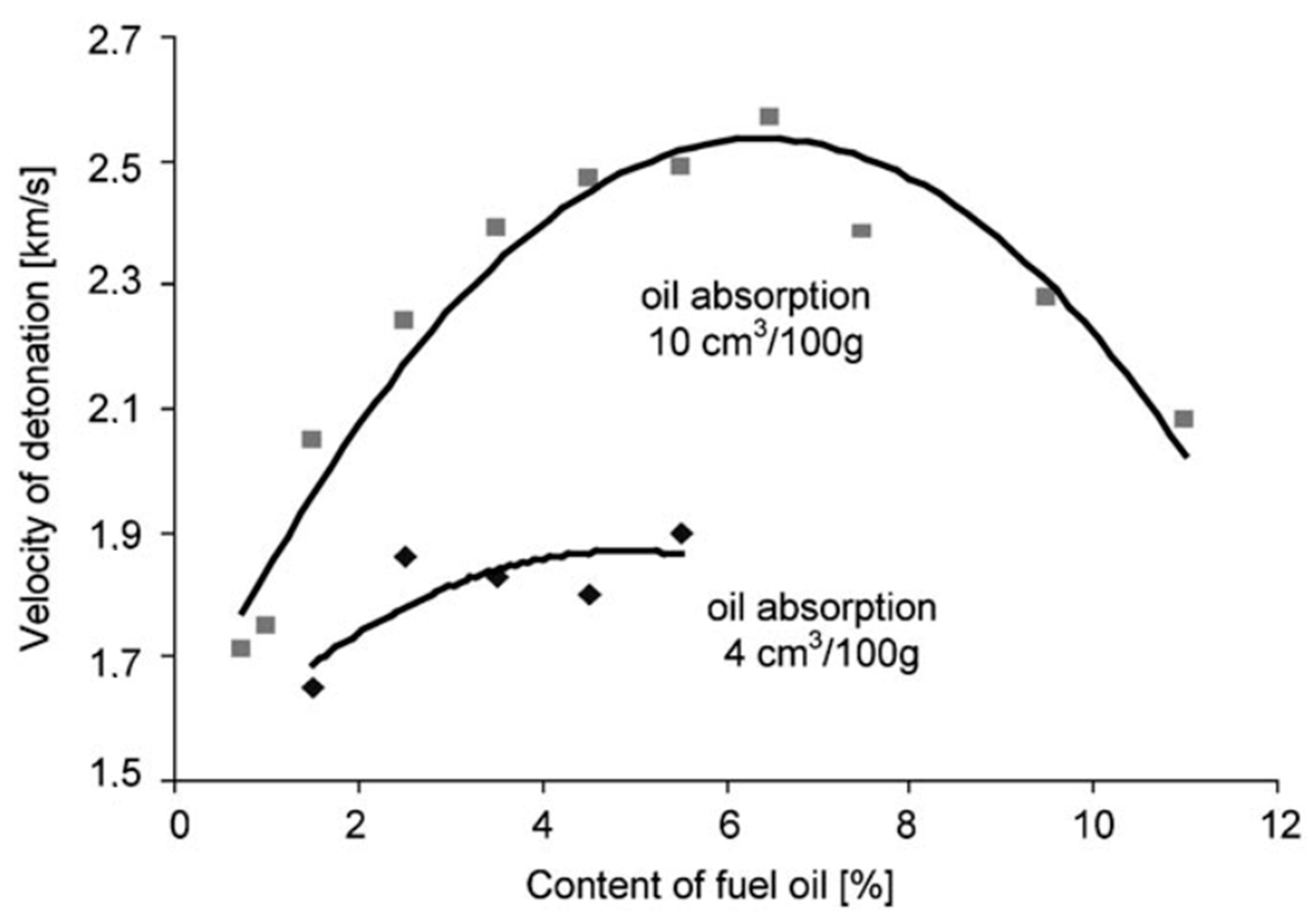

| Parameter | Explosive | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ANFO | ANNMAL | Amatol | |
| Composition (wt%) | AN-94 FO-6 | AN-66 NM(nitromethane)-25 Al-5 C-3 TETA (triethylenetetramine)-1 | AN-50 TNT-50 |
| Density (kg/m3) | 917.86 | 1158.13 | 1496.12 |
| Typical detonation velocity (km/s) | 5269.93 | 5359.94 | 6289.91 |
| Parameter | ANFO | EE |
|---|---|---|
| Critical diameter (mm) | 50–80 | 16–46 |
| Loading density (g∙cm−3): | 0.75–0.85 | 0.90–1.20 |
| Detonation model: | Non-ideal | Ideal (provided it contains no stable components) |
| Detonation velocity (m∙s−1): | 1800–3300 | 3800–5100 |
| Water-resistance | No | Yes |
| Components | Ammonium nitrate (>90 wt%), FO (1–10) wt% | Oxidising agents, organic fuels, inorganic fuels, water, emulsifying agents, sensitizing agents, modifying agents |
| Manufacturing technology | Uncomplicated | Complicated |
| Price | Low | High |
| Trauzl lead block test (cm3/10 gPb) | 211.83 | 360 |
| Ballistic mortar test (%) | 51.09 | 80.4–84.4 |
| Granule Size (mm) | ANFO Density (g/cm3) | Detonation Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.00–1.20 | 1.02 | No detonation |
| 0.63–1.00 | 1.01 | 2330 |
| 0.50–0.63 | 1.02 | 2500 |
| 0.20–0.50 | 0.98 | 2960 |
| 0.20–0.50 | 0.86 | 3440 |
| ANFO Symbol | Weight ANFO Composition (%) | Density (g/cm3) | Detonation Velocity (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANgranular porous | ANmilled | Fuel Oil | |||
| ANFO-10 | 10 | 84.5 | 5.5 | 0.88 | 1210 |
| ANFO-15 | 15 | 79.5 | 0.90 | 2200 | |
| ANFO-20 | 20 | 74.5 | 0.90 | 2360 | |
| ANFO-30 | 30 | 64.5 | 0.92 | 2570 | |
| ANFO-40 | 40 | 54.5 | 0.93 | 2660 | |
| ANFO-50 | 50 | 44.5 | 0.97 | 2680 | |
| ANFO-60 | 60 | 34.5 | 0.98 | 2620 | |
| Lp. | ANFO Composition (wt%) | Density (g/cm3) | Detonation Velocity (m/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANgranular porous | ANmilled | FO | Al | Alatomized | Alflaked | ||
| 1 | 44.5 | 50 | 5.5 | - | 0.97 | 2680 | 2680 |
| 2 | 42.3 | 47.5 | 5.2 | 5 | 0.97 | 2680 | 2710 |
| 3 | 40.1 | 45.0 | 4.9 | 10 | 0.96 | 2990 | 2840 |
| 4 | 35.6 | 40.0 | 4.4 | 20 | 0.88 | 2400 | 2300 |
| 5 | 31.2 | 35.0 | 3.8 | 30 | 0.83 | ND | 1490 |
| Experimental Results for Pure AN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4NO3(g) | Tonset (°C) | Ponset (MPa) | (dT/dt)max (°C s−1) | (dP/dt)max (MPa s−1) | Tmax (°C) | |
| 3.5 | 190 | 1.59 | 65 | 1.1 | 318 | |
| 200 | 1.45 | 82 | 1.43 | 343 | ||
| 210 | 1.45 | 98 | 2.02 | 381 | ||
| Average | 200 (±10) | 1.50 (±0.1) | 82 (±17) | 1.52 (±0.50) | 347 (±42) | |
| Experimental Results for AN/Na2SO4 Mixture at Different Concentrations | ||||||
| Na2SO4 wt% | Na2SO4 (g) | Tonset (°C) | Ponset (MPa) | (dT/dt)max (°C s−1) | (dP/dt)max (MPa s−1) | Tmax (°C) |
| 1.13 | 0.04 | 240 (±7) | 1.45 (±0.02) | 166 (±12) | 3.50 (±0.44) | 394 (±4) |
| 1.69 | 0.06 | 248 (±7) | 1.46 (±0.03) | 119 (±20) | 3.39 (±0.36) | 387 (±6) |
| 2.78 | 0.1 | 250 (±10) | 1.45 (±0.02) | 115 (±16) | 2.74 (±1.13) | 381 (±4) |
| 5.41 | 0.2 | 255 (±5) | 1.45 (±0.03) | 132 (±22) | 2.92 (±1.05) | 392 (±8) |
| 10.26 | 0.4 | 263 (±4) | 1.48 (±0.05) | 113 (±19) | 1.65 (±0.21) | 379 (±12) |
| 12.50 | 0.5 | 268 (±1) | 1.47 (±0.03) | 107 (±8) | 1.57 (±0.10) | 388 (±5) |
| 36.36 | 2 | 276 (±2) | 1.54 (±0.12) | 19 (±17) | 0.36 (±0.14) | 377 (±10) |
| Experimental Results for KCl Mixture at Different Concentrations | ||||||
| KCl wt% | KCl(g) | Tonset (°C) | Ponset (MPa) | (dT/dt)max (°C s−1) | (dP/dt)max (MPa s−1) | Tmax (°C) |
| 2.78 | 0.1 | 194 (±2) | 1.41 (±0.08) | 332 (±35) | 5.39 (±1.92) | 301 (±2) |
| 5.41 | 0.2 | 196 (±3) | 1.43 (±0.03) | 290 (±65) | 4.77 (±2.11) | 323 (±18) |
| 7.89 | 0.3 | 196 (±2) | 1.43 (±0.01) | 373 (±32) | 10.02 (±2.43) | 309 (±10) |
| 11.39 | 0.45 | 180 (±5) | 1.42 (±0.01) | 420 (±20) | 8.87 (±0.84) | 292 (±6) |
| 12.50 | 0.5 | 152 (±9) | 1.40 (±0.01) | 490 (±96) | 7.82 (±2.03) | 295 (±15) |
| 22.22 | 1 | 145 (±8) | 1.39 (±0.01) | 503 (±65) | 7.36 (±1.83) | 302 (±3) |
| Experimental Results for AN/Na2SO4/KCl Mixture at Different Concentrations | ||||||
| Na2SO4 + KCl | Tonset (°C) | Ponset (MPa) | (dT/dt)max (°C s−1) | (dP/dt)max (MPa s−1) | Tmax (°C) | |
| Mass (g) | Mol% | |||||
| 0.25 + 0.25 | 3.61 + 6.87 | 231 (±3) | 1.50 (±0.01) | 468 (±86) | 1.50 (±0.01) | 344 (±35) |
| 0.5 + 0.5 | 6.53 + 12.44 | 237 (±3) | 1.50 (±0.01) | 637 (±144) | 1.50 (±0.01) | 343 (±1) |
| 0.5 + 0.0 | 7.45 + 0 | 268 (±1) | 1.60 (±0.10) | 107 (±8) | 1.60 (±0.10) | 388 (±5) |
| 0.0 + 0.5 | 0 + 13.31 | 152 (±9) | 1.50 (±0.10) | 596 (±92) | 1.50 (±0.10) | 295 (±15) |
| Sample | Chloride Concentration in Samples | Tonset (°C) | Ponset (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AN | - | 280 | 44.82 |
| AN-BaCl2 | 0.1% | 228 | 30.34 |
| 0.5% | 222 | 34.47 | |
| 1% | 215 | 32.41 | |
| AN-NH4Cl | 0.5% | 231 | 37.23 |
| 2% | 216 | 77.91 | |
| AN-CaCl2 | 0.1% | 226 | 31.03 |
| 0.5% | 220 | 32.41 | |
| 1% | 213 | 37.23 | |
| AN-NaCl | 0.1% | 231 | 33.78 |
| 0.5% | 213 | 35.85 | |
| AN-KCl | 0.1% | 230 | 40.68 |
| 0.5% | 224 | 45.51 | |
| 1% | 215 | 53.09 |
| Sample | Mixing Method | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AN/KCl | In solution | 0.68 | 420–841 |
| AN/KCl | Mechanically | 0.76 | 250–420 |
| AN/NH4H2PO4 | In solution | 0.55 | 177–250 |
| AN/NH4H2PO4 | Mechanically | 0.70 | 149–177 |
| Material | Composition of Materials (wt%) | Decomposition Temperature (°C) | Critical Diameter (mm) | Detonation Velocity (km/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | Onset | |||||
| AN | - | ca.203 | ca.250 | 45 | 1.65 | |
| ANFO | AN 94.5 | Fuel oil 5.5 | 203 | 227 | 35 | 3.56 |
| ANWF | AN 85 | Wheat flour 15 | 165 | 170 | 45 | 3.14 |
| ANHC | AN 90 | Coal 10 | 182 | 196 | 40 | 2.84 |
| Properties | ANFO | 20 wt% LO in D/O | 30 wt% LO in D/O | 40 wt% LO in D/O | 50 wt% LO in D/O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cc) | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 0.8 |
| VOD (m/s) | 4579 | 4537 | 4375 | 4247 | 4137 |
| Detonation pressure (GPa) | 4.14 | 4.01 | 3.78 | 3.56 | 3.42 |
| SO2 (g) (um/m3) | 7.95 | 7.12 | 6.98 | 8.11 | 7.19 |
| NOx (g) (um/m3) | 18.2 | 18.2 | 15.6 | 16.5 | 14.9 |
| Particulate matter 2.5 (um/m3) | 42.6 | 42.4 | 44.9 | 42.9 | 45.9 |
| Particulate matter 10 (um/m3) | 64.2 | 63.5 | 66.3 | 65.9 | 63.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabin, M.; Jarosz, T. Improving ANFO: Effect of Additives and Ammonium Nitrate Morphology on Detonation Parameters. Materials 2021, 14, 5745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195745
Fabin M, Jarosz T. Improving ANFO: Effect of Additives and Ammonium Nitrate Morphology on Detonation Parameters. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195745
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabin, Magdalena, and Tomasz Jarosz. 2021. "Improving ANFO: Effect of Additives and Ammonium Nitrate Morphology on Detonation Parameters" Materials 14, no. 19: 5745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195745
APA StyleFabin, M., & Jarosz, T. (2021). Improving ANFO: Effect of Additives and Ammonium Nitrate Morphology on Detonation Parameters. Materials, 14(19), 5745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195745






