Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instrumentation
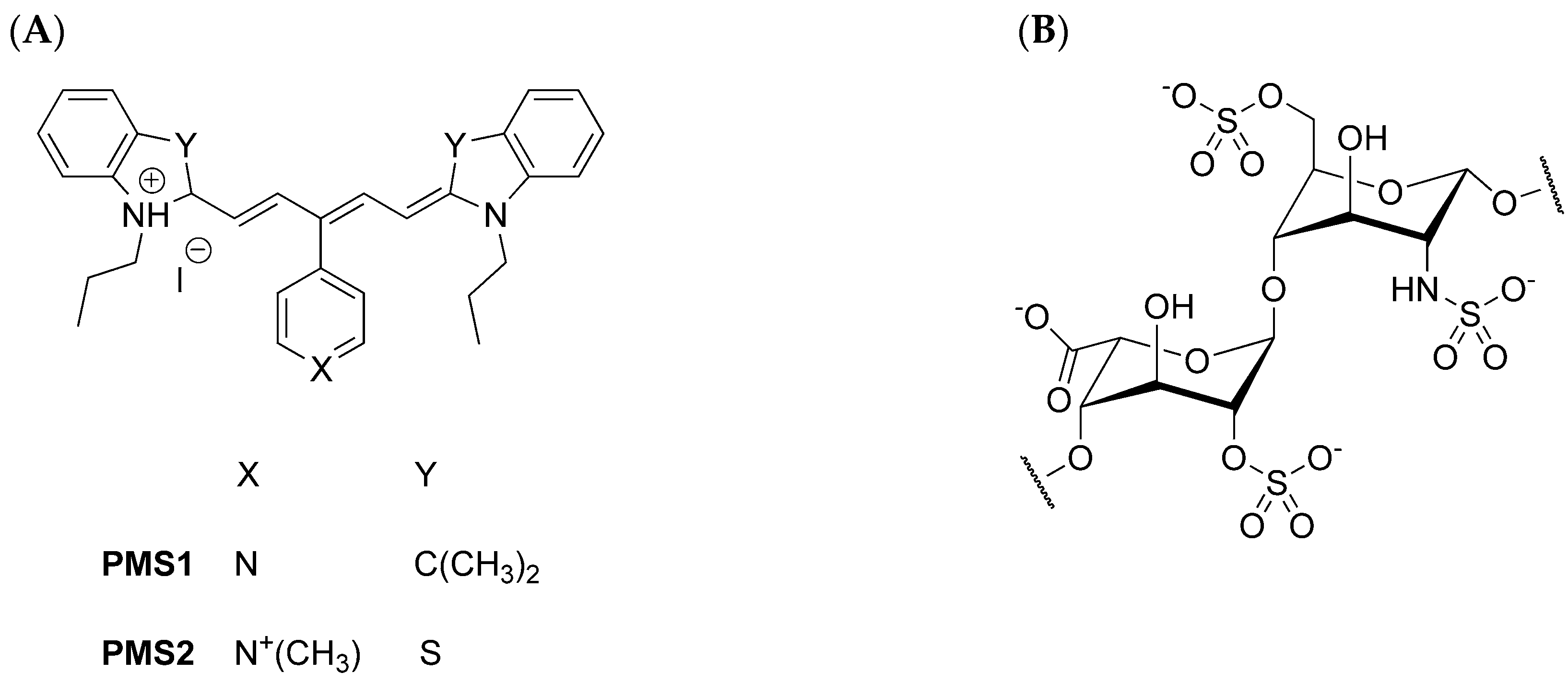
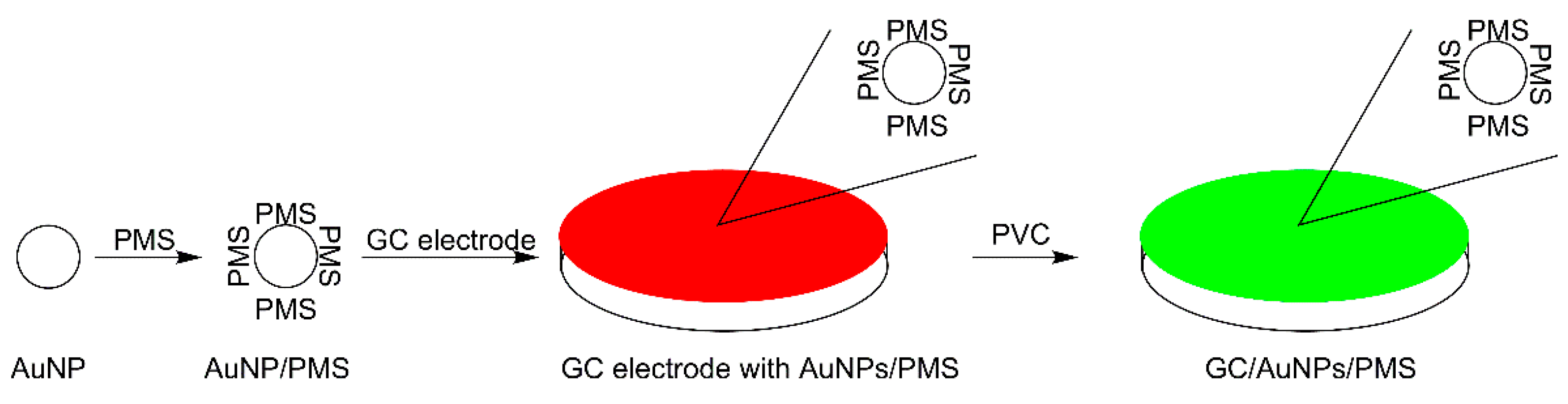
2.2. Preparation of Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite
2.3. Electrode Modification
2.4. Electrode Characterization and Electrochemical Binding Studies
3. Results
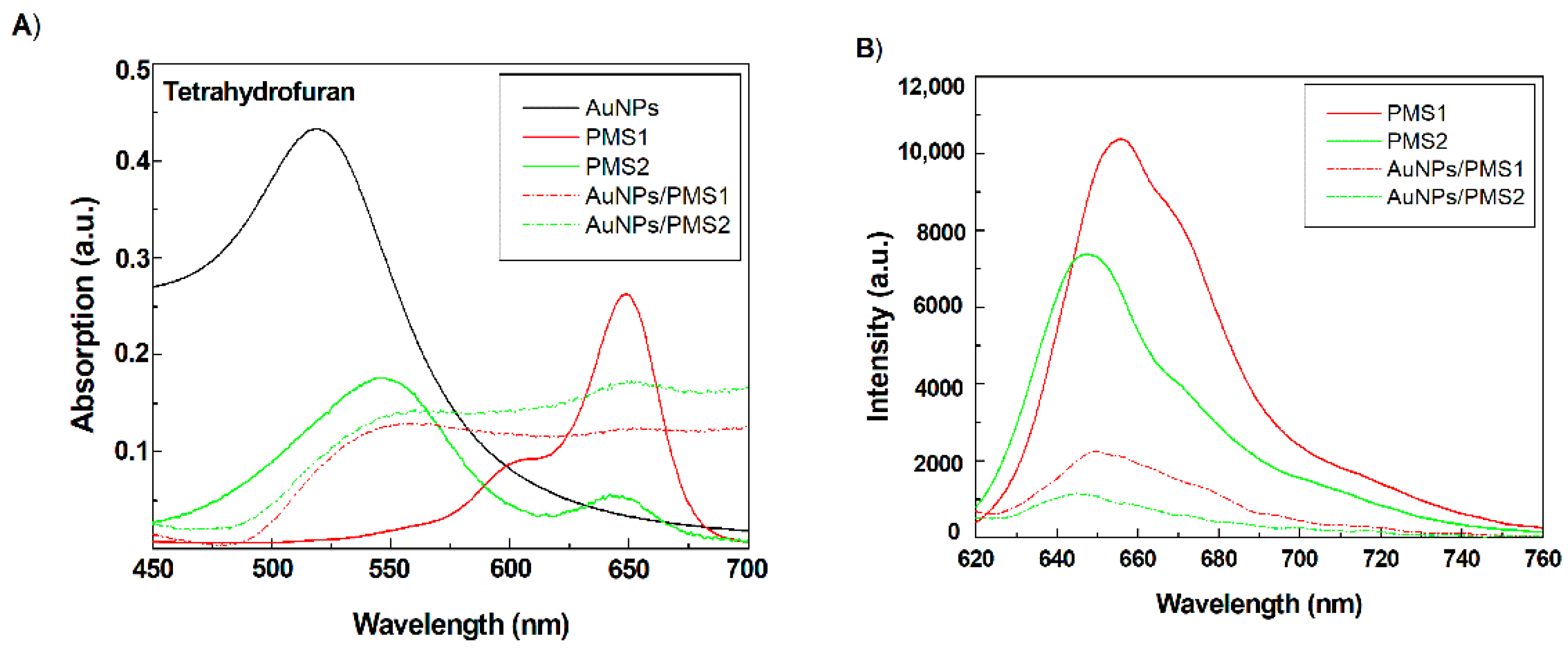
3.1. Characterization of Nanocomposites
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the Modified Electrode Surface
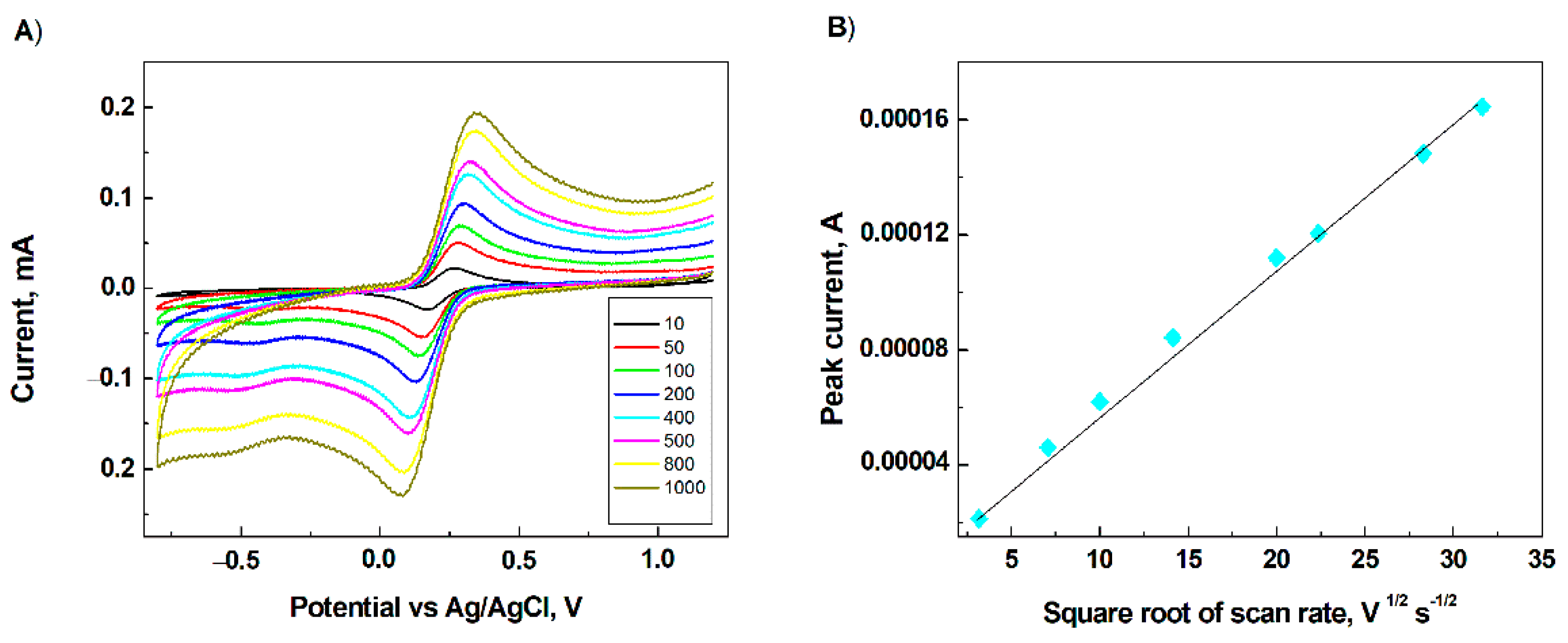
3.3. Electrochemical Behaviour of Heparin on the Modified Electrode Surface
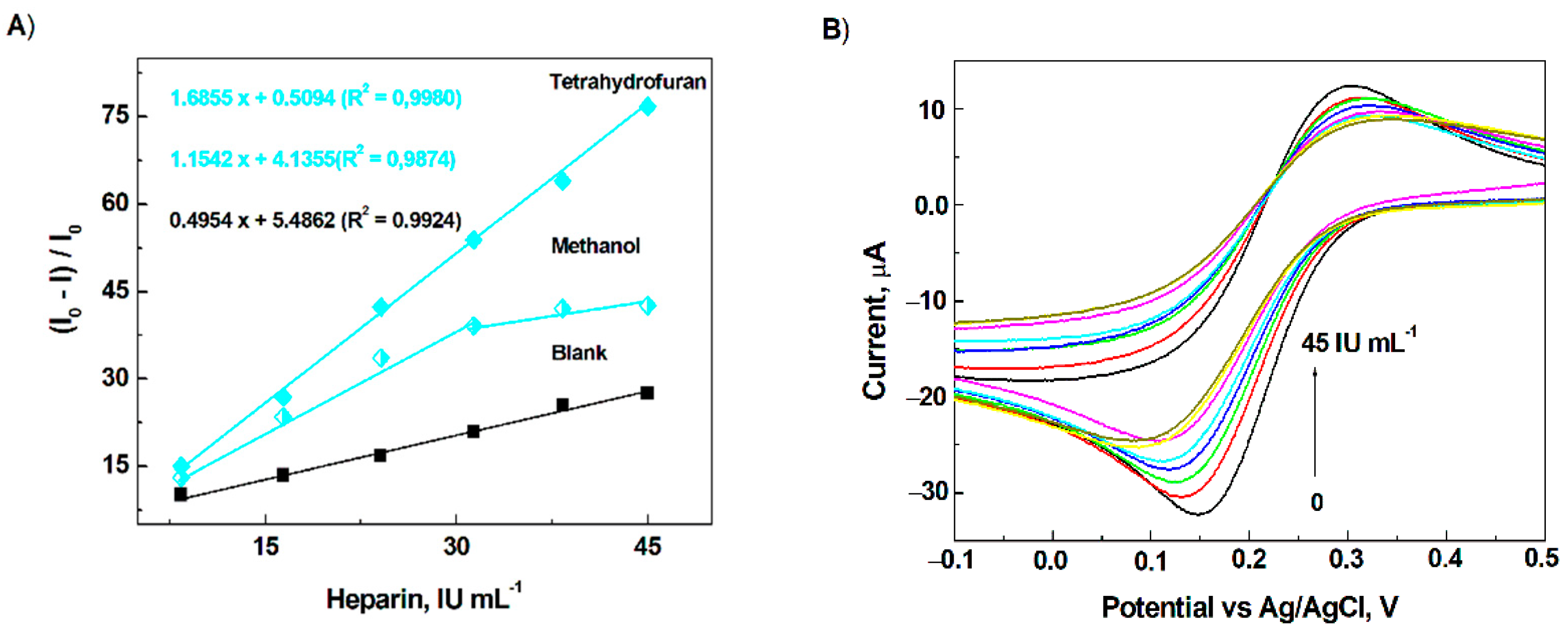
3.4. Detection of Heparin on the Modified Electrode Surface
3.5. Analytical Application
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Amemiya, S. Voltammetric Heparin-Selective Electrode Based on Thin Liquid Membrane with Conducting Polymer-Modified Solid Support. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6893–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Dong, S. Bioelectrochemical Interface Engineering: Toward the Fabrication of Electrochemical Biosensors, Biofuel Cells, and Self-Powered Logic Biosensors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Ju, H. Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Bu, L.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Guo, M.; Li, Y.; Ying, Y.; Yao, S. Bio-Inspired Preparation of Fibrin-Boned Bionanocomposites of Biomacromolecules and Nanomaterials for Biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5011–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y. Functional Three-Dimensional Porous Conductive Polymer Hydrogels for Sensitive Electrochemiluminescence in Situ Detection of H2O2 Released from Live Cells. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8462–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Doepke, A.; Cho, W.; Likodimos, V.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Back, T.; Heineman, W.R.; Halsall, H.B.; Shanov, V.N.; Schulz, M.J.; et al. A Multiwalled-Carbon-Nanotube-Based Biosensor for Monitoring Microcystin-LR in Sources of Drinking Water Supplies. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1807–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Dong, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, B.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Zou, G. Use of Triangular Silver Nanoplates as Low Potential Redox Mediators for Electrochemical Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3295–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, T.; Kumar, D. Recent progress in the development of nano-structured conducting polymers/nanocomposites for sensor applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 136, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Benny, L.; Cherian, A.R.; Narahari, S.Y.; Varghese, A.; Hegde, G. Electrochemical sensors using conducting polymer/noble metal nanoparticle nanocomposites for the detection of various analytes: A review. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2021, 11, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimpelová, S.; Bříza, T.; Králová, J.; Záruba, K.; Kejík, Z.; Císařová, I.; Martásek, P.; Ruml, T.; Král, V. Rational Design of Chemical Ligands for Selective Mitochondrial Targeting. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimkin, T.M.; Tatikolov, A.S.; Panova, I.G.; Yarmoluk, S.M. Spectral study of the noncovalent interaction of thiacarbocyanine dyes with hyaluronic acid. High Energy Chem. 2011, 45, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, N. Therapeutic applications of glycosaminoglycans. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köwitsch, A.; Zhou, G.; Groth, T. Medical application of glycosaminoglycans: A review. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e23–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, H.; Panitch, A. Glycosaminoglycans in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, U. ‘Heparin’—From anticoagulant drug into the new biology. Glycoconj. J. 2000, 17, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H.; Han, I.S.; Chang, L.-C.; Ramamurthy, N.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Yang, V.C. Electrochemical sensors for polyionic macromolecules: Development and applications in pharmaceutical research. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capila, I.; Linhardt, R.J. Heparin—Protein interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.A.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Advances in electrochemical and optical polyion sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 272, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bříza, T.; Kejík, Z.; Císařová, I.; Králová, J.; Martásek, P.; Král, V. Optical sensing of sulfate by polymethinium salt receptors: Colorimetric sensor for heparin. Chem. Commun. 2008, 16, 1901–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bříza, T.; Rimpelová, S.; Králová, J.; Záruba, K.; Kejík, Z.; Ruml, T.; Martásek, P.; Král, V. Pentamethinium fluorescent probes: The impact of molecular structure on photophysical properties and subcellular localization. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 107, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bříza, T.; Králová, J.; Rimpelová, S.; Havlík, M.; Kaplánek, R.; Kejík, Z.; Martásek, P.; Mikula, I.; Džubák, P.; Hajdúch, M.; et al. Pentamethinium salts as ligands for cancer: Sulfated polysaccharide co-receptors as possible therapeutic target. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanka, P.; Navrátilová, K.; Žvátora, P.; Sýkora, D.; Matějka, P.; Miksik, I.; Kašička, V.; Kral, V. Cyclodextrin modified gold nanoparticles-based open-tubular capillary electrochromatographic separations of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 5947–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.L.; Formisano, N.; Estrela, P.; Carrara, S.; Tkac, J. Electrochemical biosensors and nanobiosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casu, B. Methods of Structural analysis. In Heparin, Chemical and Biological Properties, Clinical Applications; Lane, D.A., Lindahl, U., Eds.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1989; pp. 25–51. [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski, I.X. General physical properties of heparin. In Heparin, Chemical and Biological Properties, Clinical Applications; Lane, D.A., Lindahl, U., Eds.; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1989; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bromfield, S.M.; Wilde, E.; Smith, D.K. Heparin sensing and binding—Taking supramolecular chemistry towards clinical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9184–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanka, P.; Záruba, K.; Král, V. A change in nucleotide selectivity pattern of porphyrin derivatives after immobilization on gold nanoparticles. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 6448–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Videnská, K.; Antonova, S.G.; Krondak, M.; Fitl, P.; Kopecký, D.; Vrňata, M.; Kral, V. Application of polyaniline for potentiometric recognition of salicylate and its analogues. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Xiong, L.; Barros, A.A.; Compton, R.G. Controlling voltammetric responses by electrode modification; using adsorbed acetone to switch graphite surfaces between adsorptive and diffusive modes. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9037–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerhoff, M.E.; Yang, V.C.; Wahr, J.A.; Lee, L.M.; Yun, J.H. Potentiometric Polyion Sensors: New Measurement Technology for Monitoring Blood Heparin Concentrations During Open Heart Surgery. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1355–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Yuan, D.; Wang, L.; Bakker, E. Separating boundary potential changes at thin solid contact ion transfer voltammetric membrane electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 880, 114800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.C.; Yang, V.C.; Fu, B.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Electrochemical sensor for heparin: Further characterization and bioanalytical applications. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H.; Ma, S.-C.; Fu, B.; Yang, V.C.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Direct potentiometric membrane electrode measurements of heparin binding to macromolecules. Electroanalisys 1993, 5, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
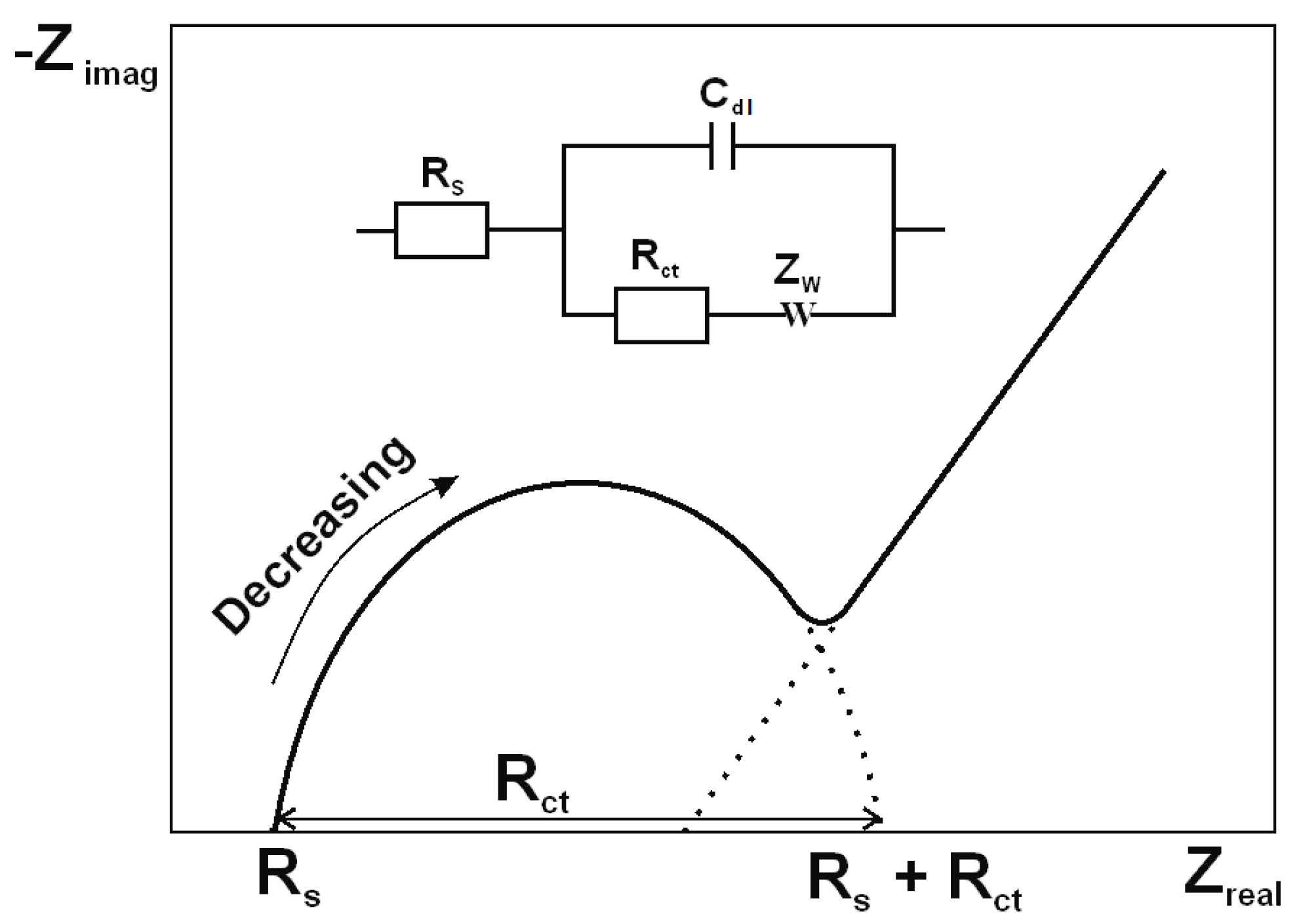
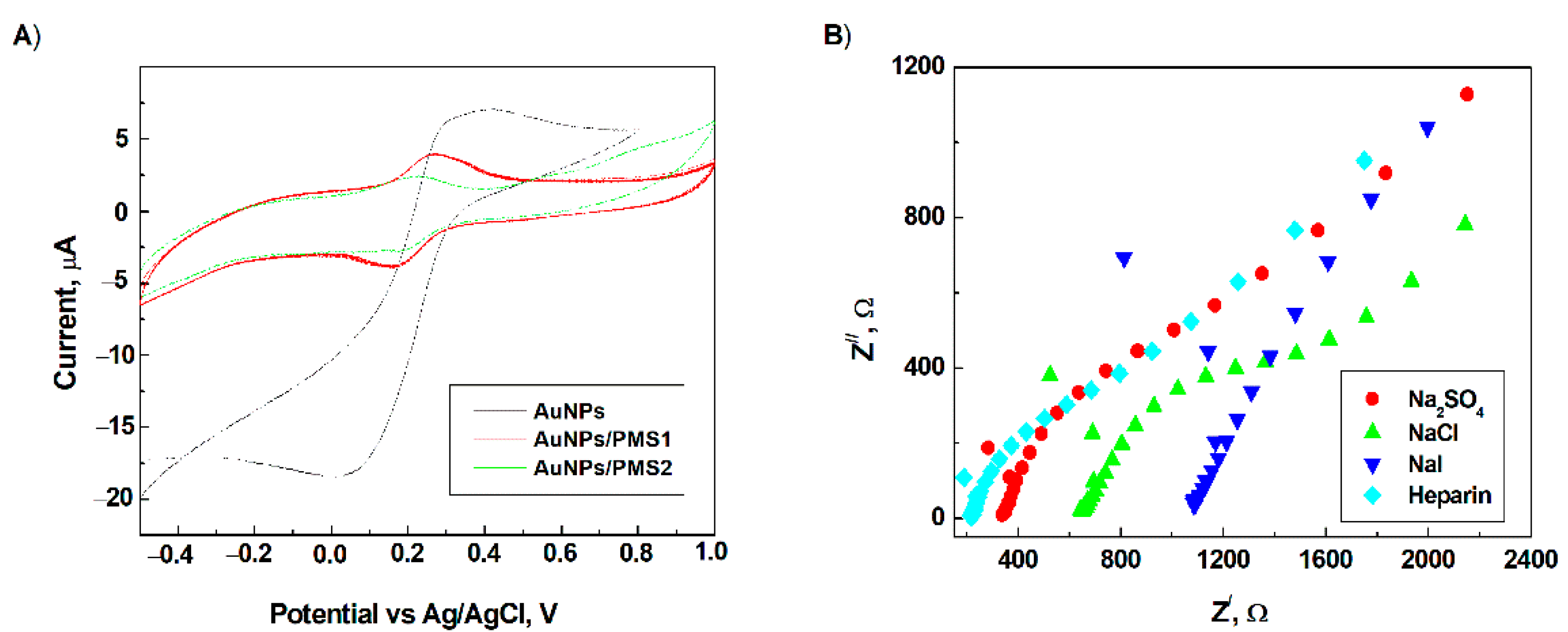
| EIS–Parameters | Anionic Species | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfate | Chloride | Iodide | Heparin | |
| Cdl, μF | 12.7 | 16.7 | 21.1 | 15.4 |
| Rct, kΩ | 1.48 | 1.773 | 7.583 | 1.275 |
| Sample | Introduced, IU mL−1 | Found, IU mL−1 | Recovery, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saline | 1.72 | 1.66 ± 0.20 | 96.5 |
| 8.42 | 8.29 ± 0.98 | 98.5 | |
| 16.43 | 15.63 ± 1.09 | 95.1 | |
| Human serum | 1.93 | 1.93 ± 0.37 | 99.7 |
| 7.50 | 7.57 ± 0.86 | 100.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shishkanova, T.V.; Bříza, T.; Řezanka, P.; Kejík, Z.; Jakubek, M. Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin. Materials 2021, 14, 5357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185357
Shishkanova TV, Bříza T, Řezanka P, Kejík Z, Jakubek M. Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin. Materials. 2021; 14(18):5357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185357
Chicago/Turabian StyleShishkanova, Tatiana V., Tomáš Bříza, Pavel Řezanka, Zdeněk Kejík, and Milan Jakubek. 2021. "Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin" Materials 14, no. 18: 5357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185357
APA StyleShishkanova, T. V., Bříza, T., Řezanka, P., Kejík, Z., & Jakubek, M. (2021). Pentamethinium Salts Nanocomposite for Electrochemical Detection of Heparin. Materials, 14(18), 5357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14185357









