Vertical Discrepancy in Height of Morse Cone Abutments Submitted to Different Torque Forces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
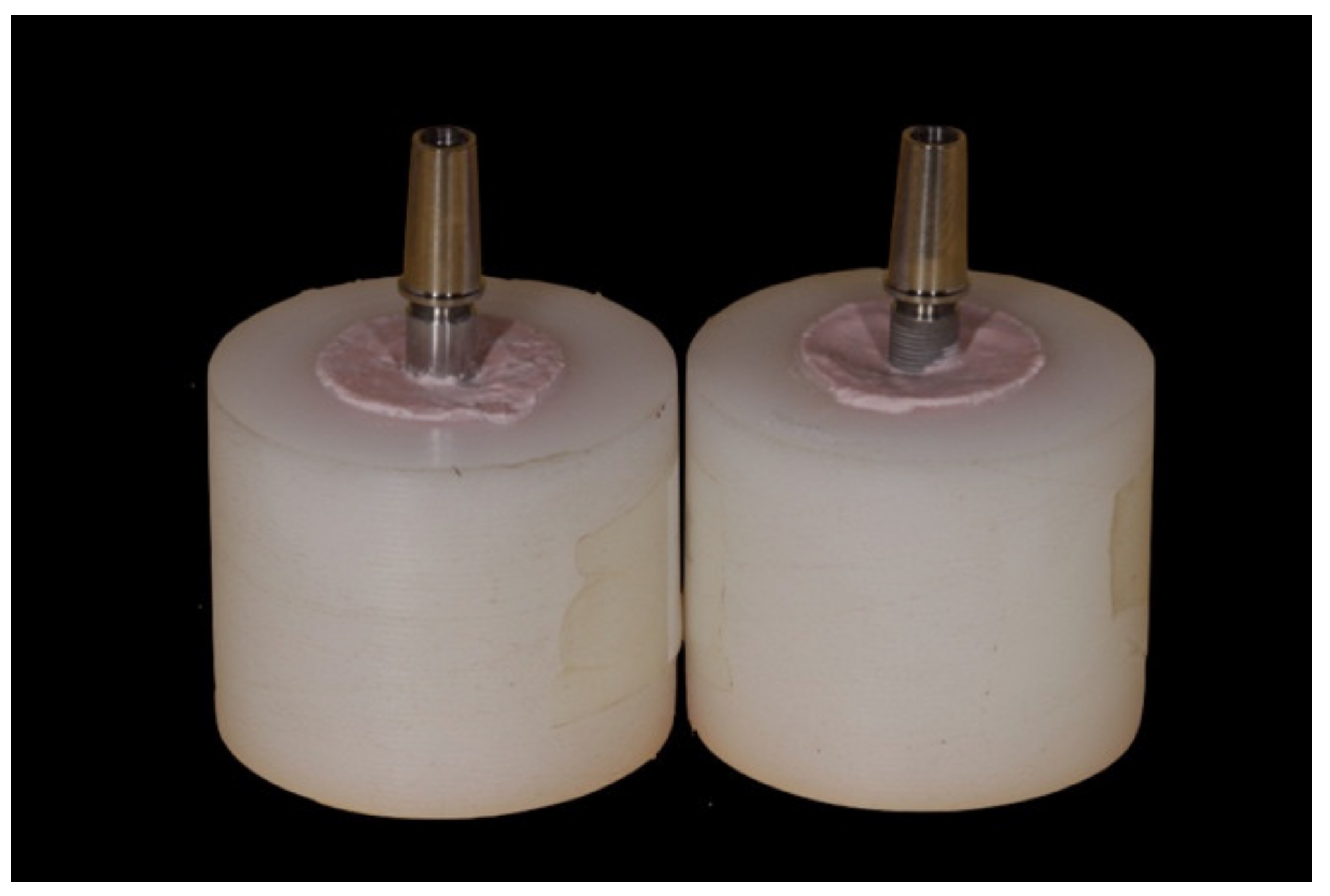
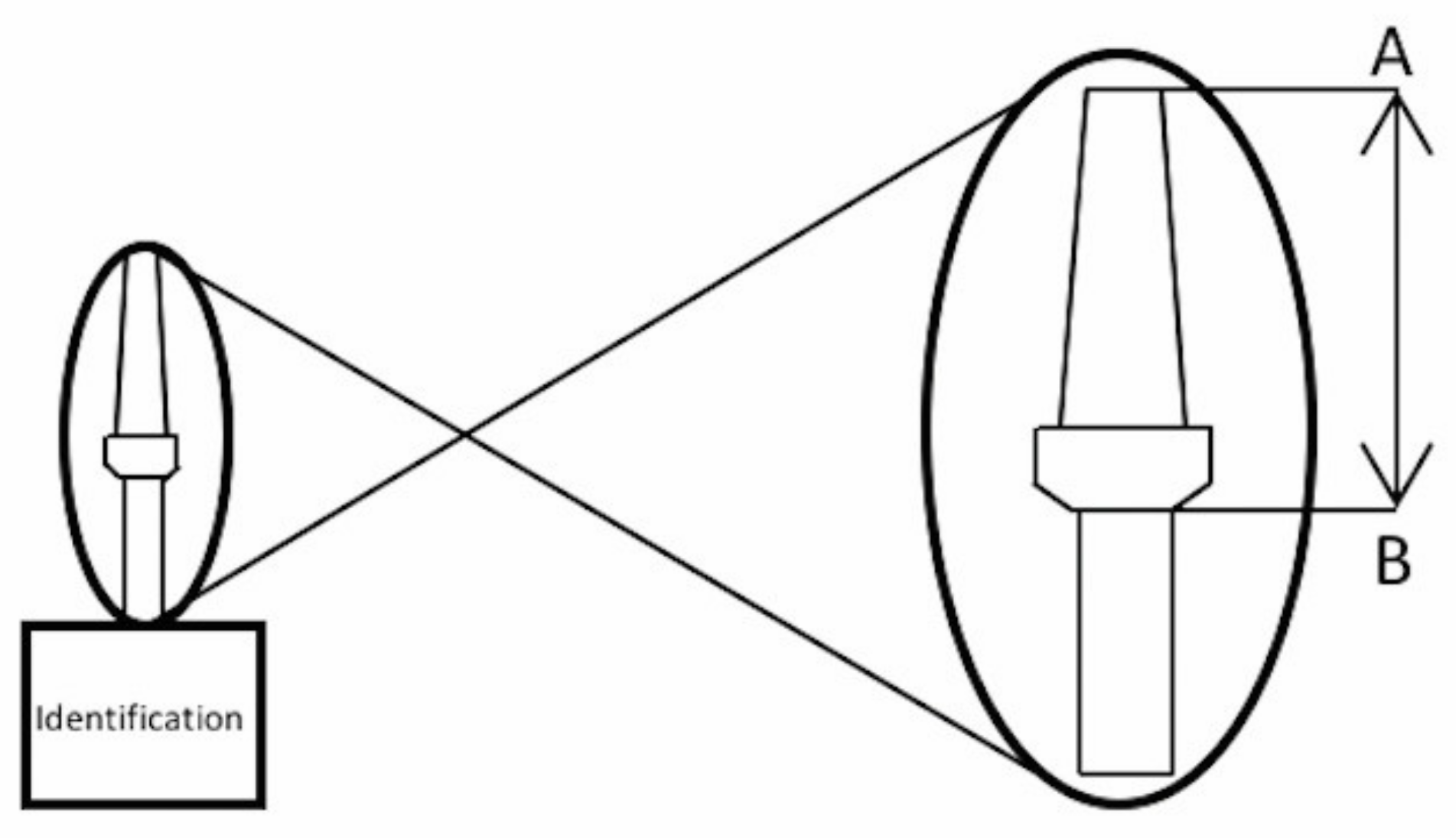
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
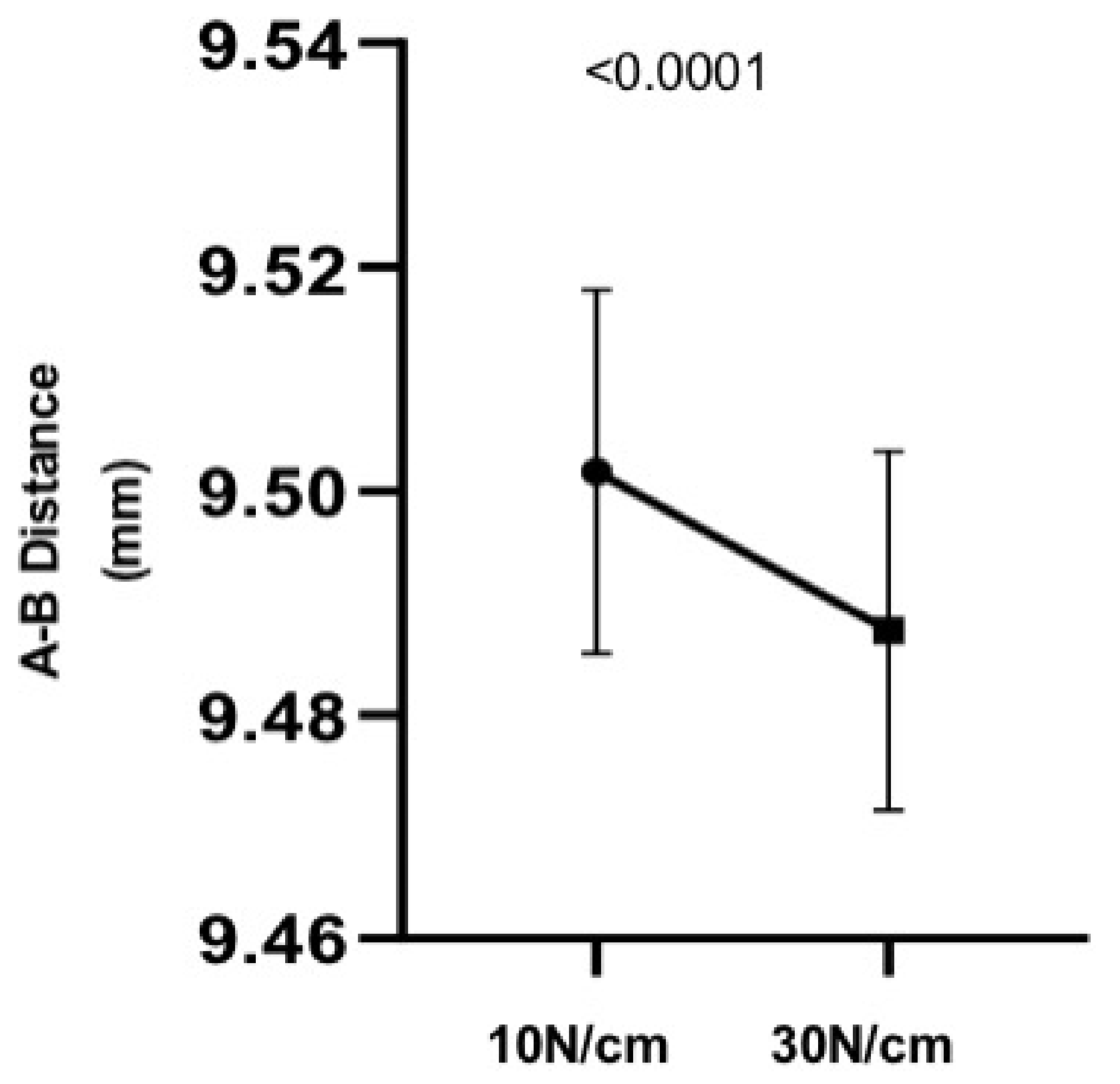
3.1. Analog Results
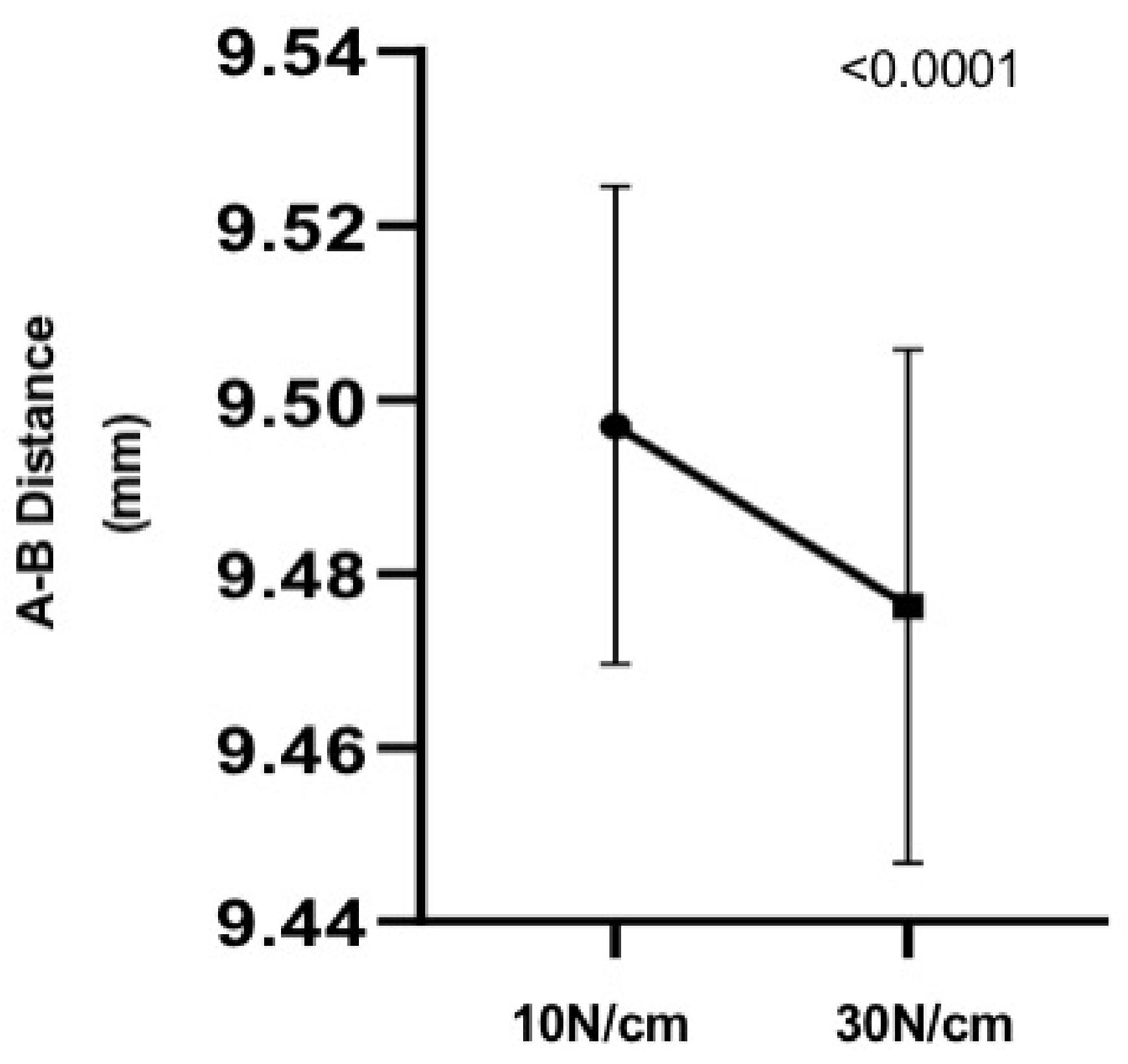
3.2. Implants Results
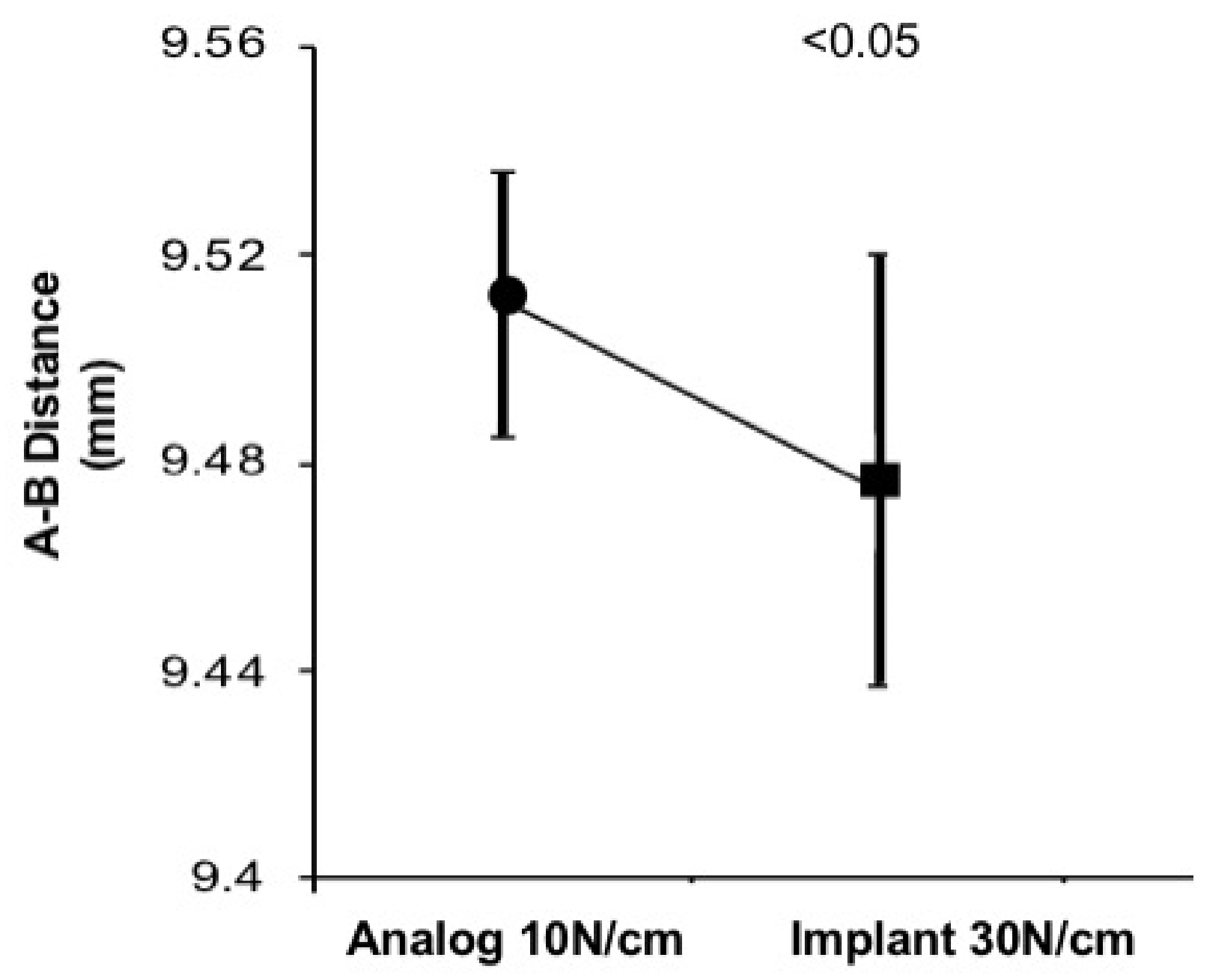
3.3. 10 Ncm Analog and 30 Ncm Implant Comparison
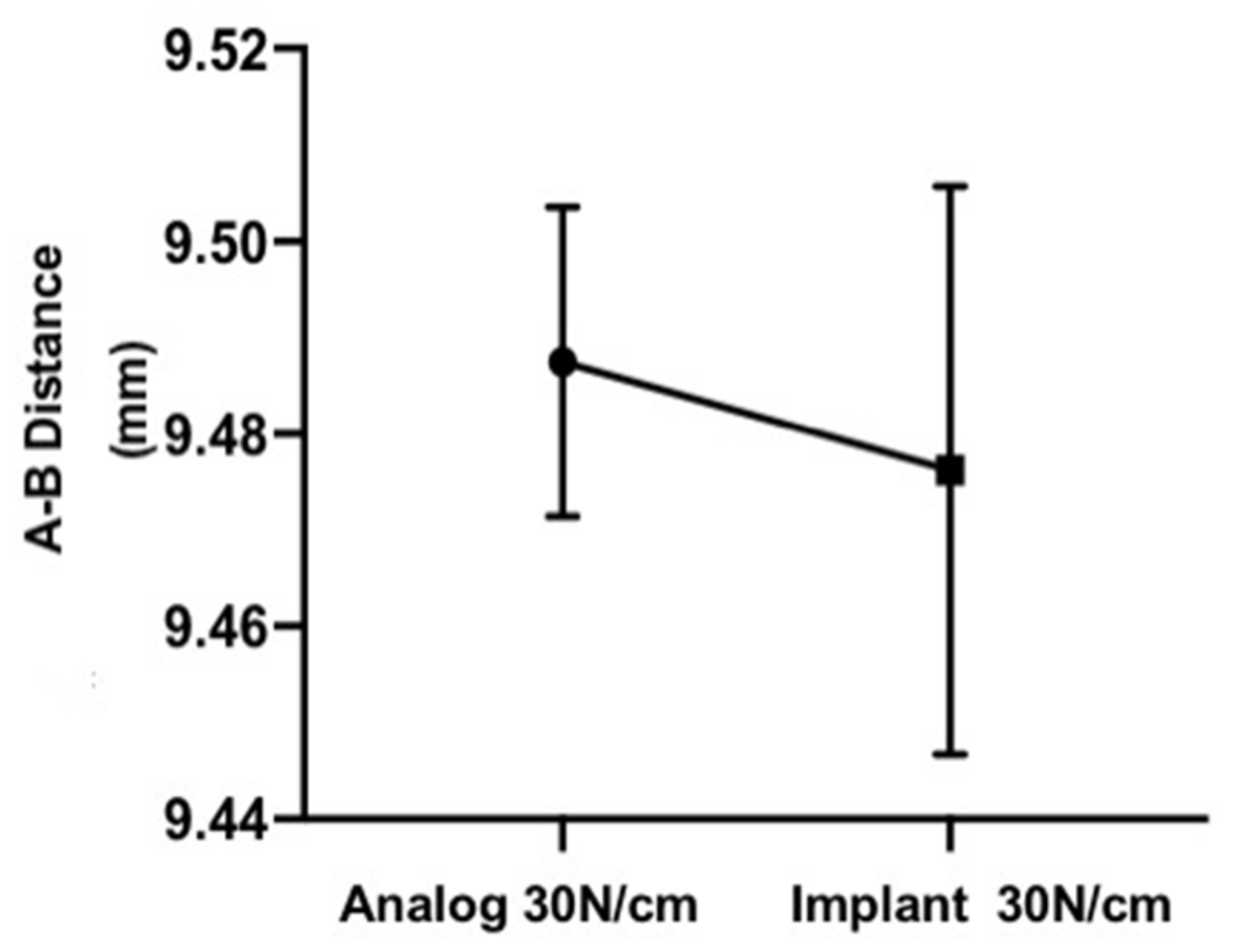
3.4. 30 N Analog and 30 N Implant Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezende, C.E.E.; Brisola, A.O.P. Conexões implante/pilar em implantodontia. Innov. Implant. J. Biomater. Esthet. 2014, 9, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dellinges, M.A.; Tebrock, O.C. A measurement of torque values obtained with hand-held drivers in a simulated clincal setting. J. Prosthodont. 1993, 2, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, B.; Jordan, L.; Blind, O.; Tavernier, B. Axial displacement of abutments into implants and replicas, with the tapered cone-screw internal connection, as a function of tightening torque. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ceruso, F.M.; Barnaba, O.; Mazzoleni, S.; Ottria, L.; Gargari, M.; Zuccon, A.; Bruno, G.; Di Fiore, A. Implant-Abutment connection on single crowns: A systematic review. Oral Implantol. 2017, 10, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degidi, M.; Daprile, G.; Piattelli, A. Marginal bone loss around implants with platform-switched Morse-cone connection: A radiographic cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, D.; Nagata, M.J.; Bosco, A.F.; de Melo, L.G. Influence of microgap location and configuration on radiographic bone loss around submerged implants: An experimental study in dogs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2011, 26, 941–946. [Google Scholar]
- Saber, F.S.; Abolfazli, N.; Ataei, S.J.; Motlagh, M.T.; Gharekhani, V. The effect of repeated torque tightening on total lengths of implant abutments in different internal implant‒abutment connections. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2017, 11, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Otaibi, H.N.; Almutairi, A.; Alfarraj, J.; Algesadi, W. The effect of torque application technique on screw preload of implant-supported prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.S.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kwon, H.B.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Yim, S.H. Variation in the total lengths of abutment/implant assemblies generated with a function of applied tightening torque in external and internal implant–abutment connection. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhasi, M.; Kazemi, M.; Jalali, H.; Hashemzadeh, S.; Dodangeh, H.; Yilmaz, B. Clinician-generated torque on abutment screws using different hand screwdrivers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2017, 118, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Chen, C.J.; Singh, M.; Weber, H.P.; Gallucci, G.O. Success criteria in implant dentistry: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, M.R. Assessment of cold welding properties of the internal conical interface of two commercially available implant systems. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1999, 81, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenza, B.; Tripodi, D.; Scarano, A.; Perrotti, V.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G.; D’Ercole, S. Bacterial leakage in implants with different implant-abutment connections: An in vitro study. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsini, G.; Fanali, S.; Scarano, A.; Petrone, G.; di Silvestro, S.; Piattelli, A. Tissue reactions, fluids, and bacterial infiltration in implants retrieved at autopsy: A case report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 283–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta, K.; Ayukawa, Y.; Matsuzaki, T.; Kihara, M.; Koyano, K. The influence of implant-abutment connection on the screw loosening and microleakage. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyle, J.; Casado, P.; Fourmousis, I.; Kumar, P.; Quirynen, M.; Salvi, G.E. General genetic and acquired risk factors, and prevalence of peri-implant diseases—Consensusreport of working group 1. Int. Dent. J. 2019, 69, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lang, N.P.; Berglundh, T. Periimplant diseases: Where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on periodontology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallee, M.C.; Conrad, H.J.; Basu, S.; Seong, W.J. Accuracy of friction-style and spring-style mechanical torque limiting devices for dental implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, M.S.; Mitchell, L.; Hegde, R.; Mavalli, M.D. Variability of mechanical torque-limiting devices in clinical service at a US dental school. J. Prosthodont. 2010, 19, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 10 Ncm | 30 Ncm | |
|---|---|---|
| Analogs (Group 1) | 9.507 | 9.497 |
| 9.497 | 9.479 | |
| 9.485 | 9.470 | |
| 9.515 | 9.498 | |
| 9.491 | 9.478 | |
| 9.511 | 9.494 | |
| 9.487 | 9.470 | |
| 9.503 | 9.505 | |
| 9.485 | 9.470 | |
| 9.536 | 9.514 | |
| Minimum value | 9.485 | 9.470 |
| Maximum value | 9.536 | 9.514 |
| Mean ± SD | 9.5017 ± 0.016 | 9.487 ± 0.016 |
| Implants (Group 2) | 9.503 | 9.480 |
| 9.487 | 9.468 | |
| 9.493 | 9.474 | |
| 9.463 | 9.437 | |
| 9.485 | 9.47 | |
| 9.466 | 9.441 | |
| 9.527 | 9.504 | |
| 9.488 | 9.462 | |
| 9.555 | 9.538 | |
| 9.503 | 9.488 | |
| Minimum value | 9.463 | 9.437 |
| Maximum value | 9.555 | 9.538 |
| Mean ± SD | 9.497 ± 0.027 | 9.476 ± 0.029 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cordeiro, B.Q.S.; Mourão, C.F.d.A.B.; Carvalho, W.R.; Fonseca, E.M.; Montemezzi, P.; Javid, K.; Martins, C.C.P.; Quinelato, V.; Moreno, M.D.; Casado, P.L. Vertical Discrepancy in Height of Morse Cone Abutments Submitted to Different Torque Forces. Materials 2021, 14, 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174950
Cordeiro BQS, Mourão CFdAB, Carvalho WR, Fonseca EM, Montemezzi P, Javid K, Martins CCP, Quinelato V, Moreno MD, Casado PL. Vertical Discrepancy in Height of Morse Cone Abutments Submitted to Different Torque Forces. Materials. 2021; 14(17):4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174950
Chicago/Turabian StyleCordeiro, Bruno Q. S., Carlos Fernando de Almeida Barros Mourão, Waldimir R. Carvalho, Edgard M. Fonseca, Pietro Montemezzi, Kayvon Javid, Cintia C.P. Martins, Valquiria Quinelato, Mylena D. Moreno, and Priscila L. Casado. 2021. "Vertical Discrepancy in Height of Morse Cone Abutments Submitted to Different Torque Forces" Materials 14, no. 17: 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174950
APA StyleCordeiro, B. Q. S., Mourão, C. F. d. A. B., Carvalho, W. R., Fonseca, E. M., Montemezzi, P., Javid, K., Martins, C. C. P., Quinelato, V., Moreno, M. D., & Casado, P. L. (2021). Vertical Discrepancy in Height of Morse Cone Abutments Submitted to Different Torque Forces. Materials, 14(17), 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14174950







