Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Selective Laser Melting Processed Ni-Based Superalloy GTD222
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
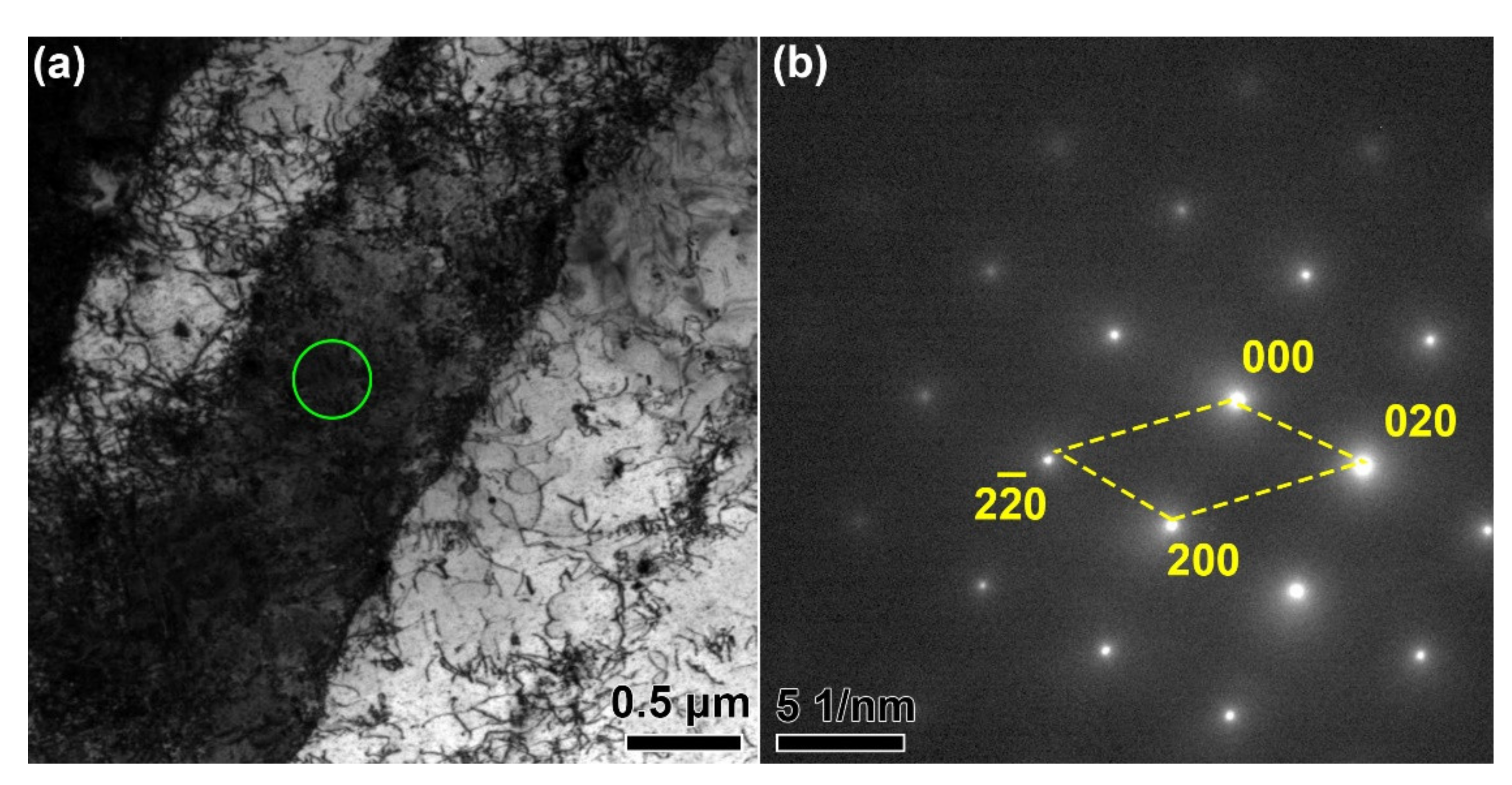
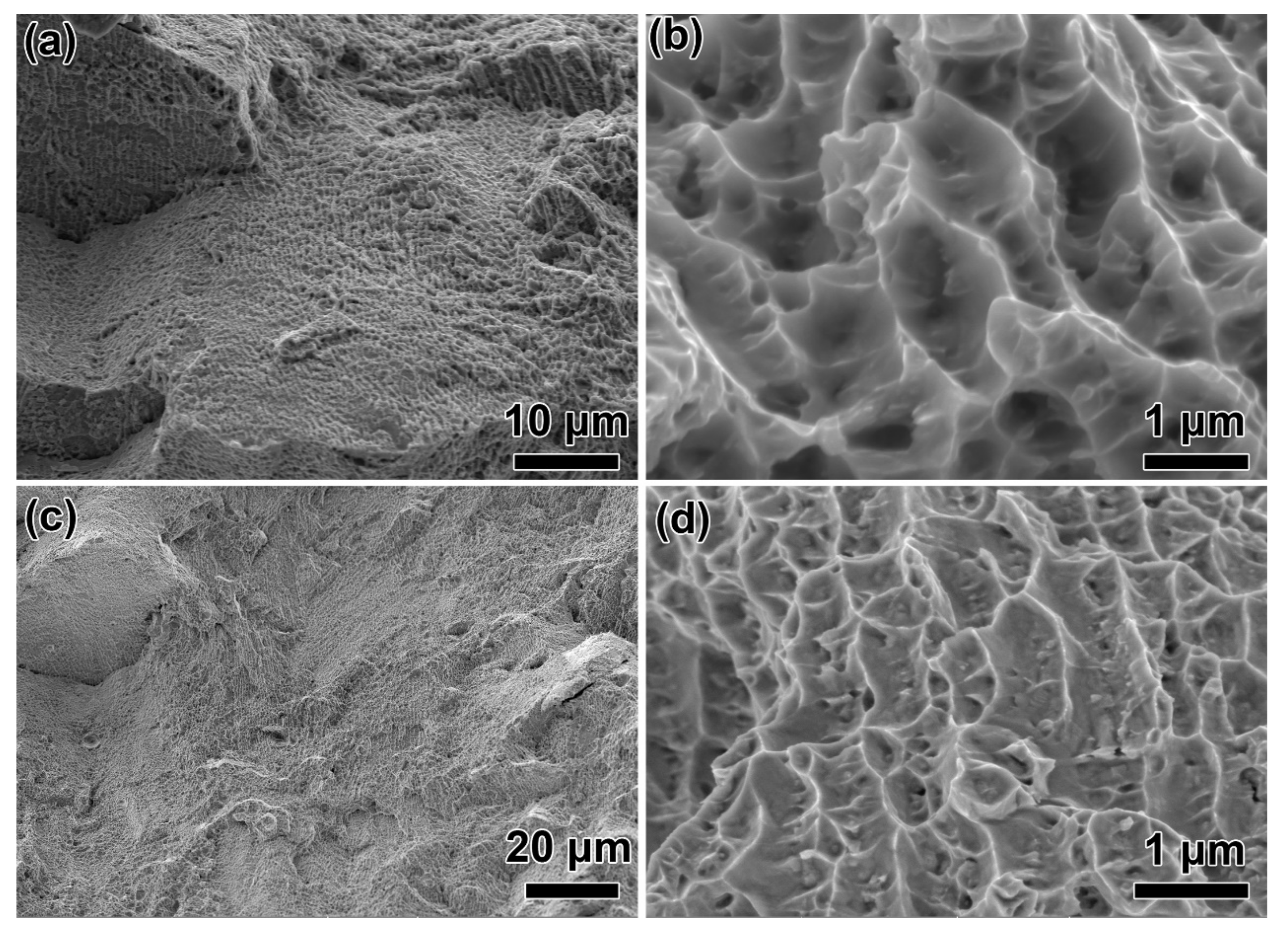
- The microstructure of the HTed GTD222 were consisting of columnar grains, 1170 °C solution + 800 °C aging 1170 °C.
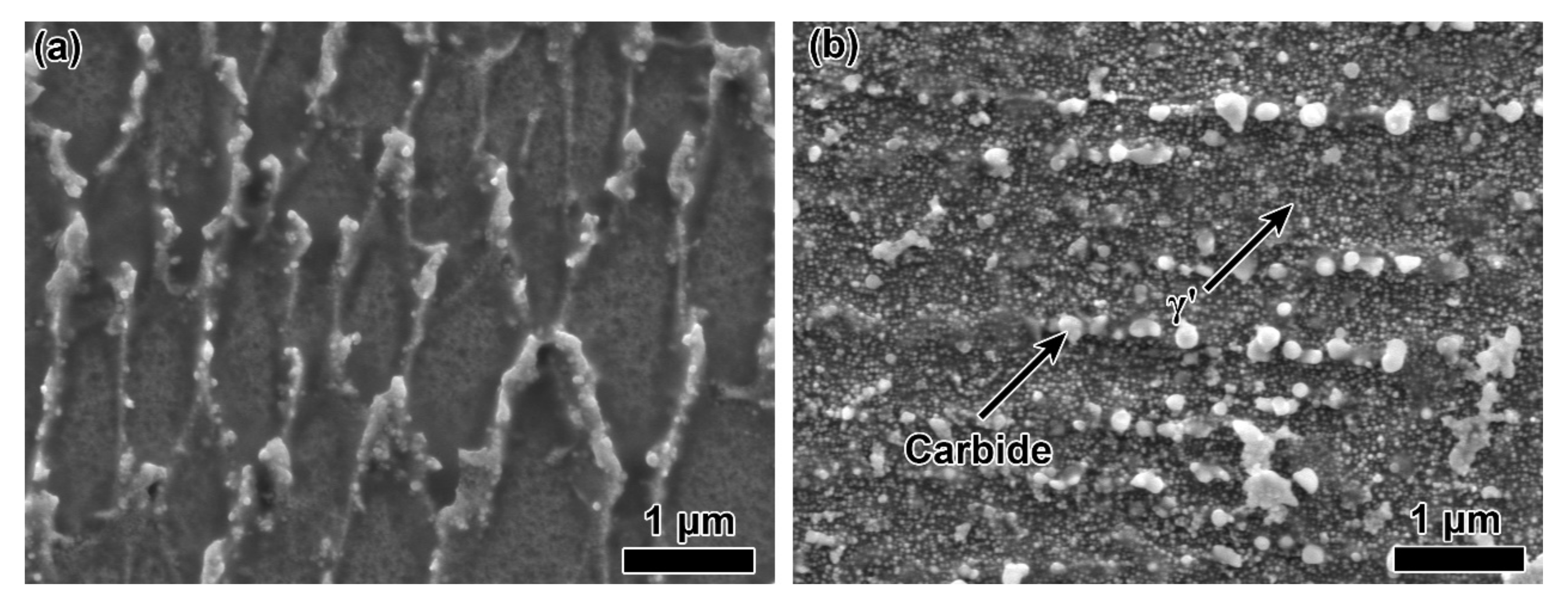
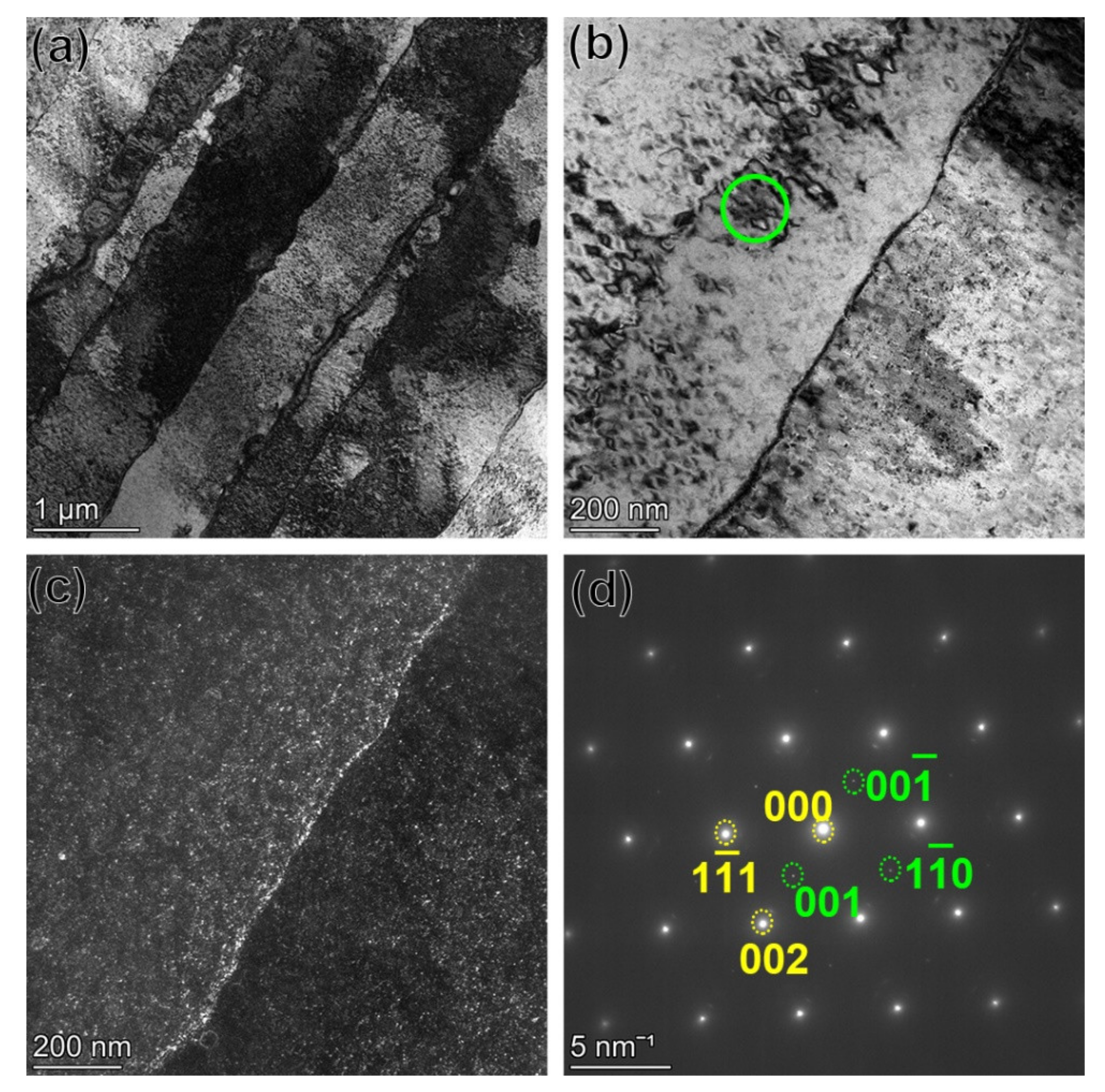
- A large amount of γ’ and nano-scaled carbides were precipitated in the HTed GTD222. The γ’ precipitates were homogeneously distributed in the matrix while the carbides were distributed along the boundaries of the columnar.
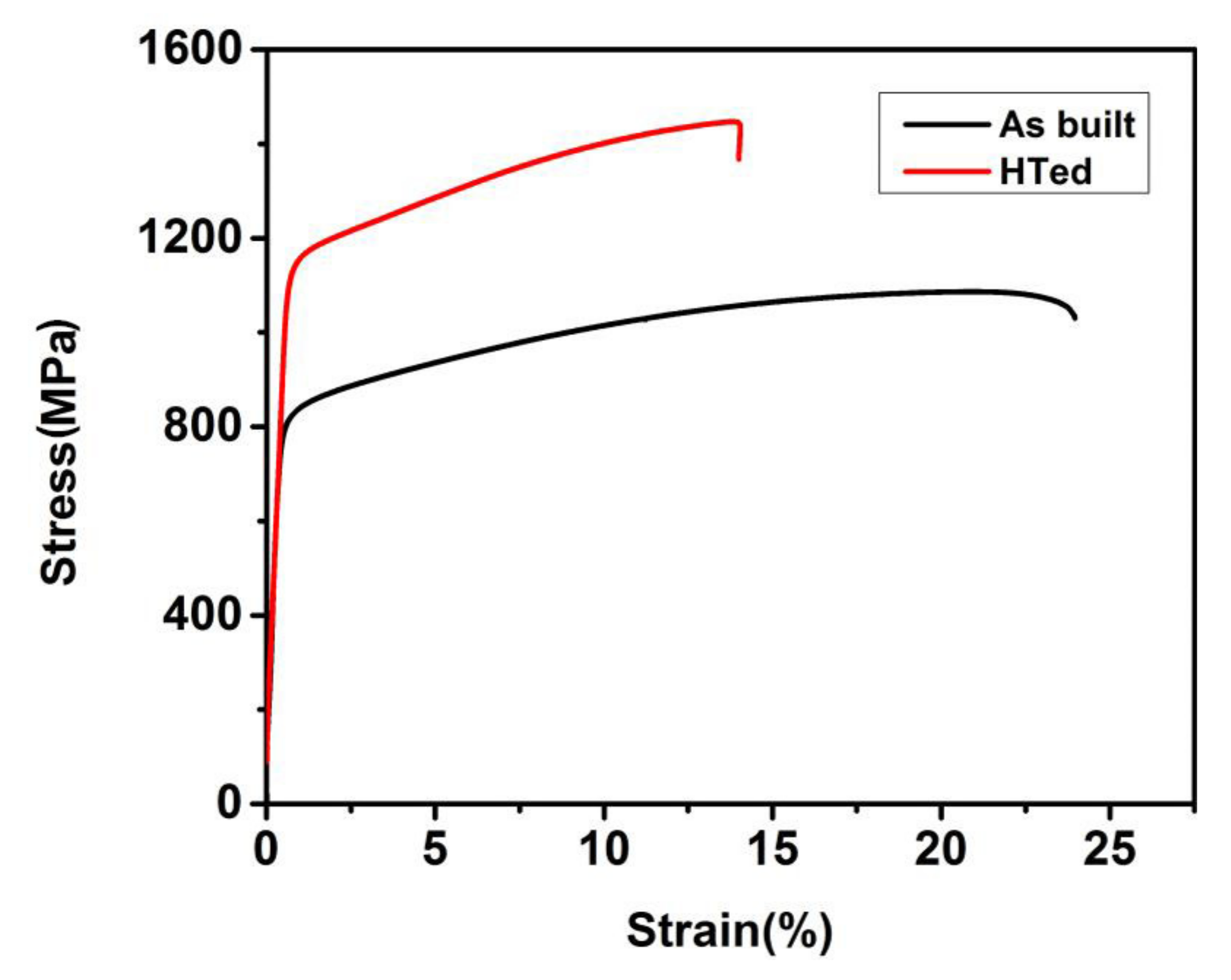
- The high yield strength of the HTed GTD222 was 1120 ± 6 MPa, which was caused by the precipitation of the γ’ and the nano-scaled carbides.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harte, A.; Atkinson, M.; Smith, A.; Drouven, C.; Zaefferer, S.; da Fonseca, J.Q.; Preuss, M. The effect of solid solution and gamma prime on the deformation modes in Ni-based superalloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 194, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, S.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, Z.; Fan, W.; Gasser, A.; Huang, W. The influence of Laves phases on the room temperature tensile properties of Inconel 718 fabricated by powder feeding laser additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2019, 164, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Huang, W. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of GH4099 additive-manufactured by directed energy deposition. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 800, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallmeyer, T.G.; Moorthy, S.; Kappes, B.B.; Mills, M.J.; Amin-Ahmadi, B.; Stebner, A.P. Knowledge of process-structure-property relationships to engineer better heat treatments for laser powder bed fusion additive manufactured Inconel 718. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messé, O.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Illston, T.; Baker, S.; Stone, H. Metastable carbides and their impact on recrystallisation in IN738LC processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, D.; Seyda, V.; Wycisk, E.; Emmelmann, C. Additive manufacturing of metals. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Schaak, C.; Nellesen, J.; Schaper, M.; Aydinöz, M.; Hoyer, K.-P. Hot isostatic pressing of IN718 components manufactured by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 13, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gruber, H.; Deng, D.; Peng, R.L.; Moverare, J.J. Short-term creep behavior of an additive manufactured non-weldable Nickel-base superalloy evaluated by slow strain rate testing. Acta Mater. 2019, 179, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.; Sarosi, P.; Henry, M.; Whitis, D.; Milligan, W.; Mills, M. Investigation of creep deformation mechanisms at intermediate temperatures in René 88 DT. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, F.; Ngai, S.; Fricke, K.; McKechnie, M.; Wanderka, N.; Hentrich, T.; Banhart, J.; Thompson, G. Tracing the three-dimensional nanochemistry of phase separation in an inverse Ni-based superalloy. Acta Mater. 2018, 157, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Nategh, S.; Isac, M.; Zebarjad, S.M. Tensile deformation mechanisms at different temperatures in the Ni-base superalloy GTD-111. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 155–156, 1900–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaver, D.W.; Beltran, A.M. Nickel-Base Alloy GTD-222, a New Gas Turbine Nozzle Alloy. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1993, 115, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, G.; Yang, C.; Zhou, W.; Wang, D.; Dong, A.; Shu, D.; Sun, B. Novel selective laser melting processed in-situ TiC particle-reinforced Ni matrix composite with excellent processability and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 797, 140145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, G.; Yang, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Dong, A.; Shu, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B. Nano-size carbide-reinforced Ni matrix composite prepared by selective laser melting. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Gu, Y.; Setchi, R.; Lacan, F.; Johnston, R.; Evans, S.L.; Yang, S. Additive manufacturing of high-strength crack-free Ni-based Hastelloy X superalloy. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Galilea, I.; Ruttert, B.; He, J.; Hammerschmidt, T.; Drautz, R.; Gault, B.; Theisen, W. Additive manufacturing of CMSX-4 Ni-base superalloy by selective laser melting: Influence of processing parameters and heat treatment. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, J.-R.; Kreitcberg, A.; Terriault, P.; Brailovski, V. Long fatigue crack propagation behavior of laser powder bed-fused inconel 625 with intentionally-seeded porosity. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 127, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkin, D.B.; Patel, D.; Albright, T.V.; Bean, G.E.; McLouth, T. Influence of surface conditions and specimen orientation on high cycle fatigue properties of Inconel 718 prepared by laser powder bed fusion. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 132, 105392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Shen, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Yan, M. Selective laser melting of the hard-to-weld IN738LC superalloy: Efforts to mitigate defects and the resultant microstructural and mechanical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 807, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, A.; Dinda, G.P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of direct laser metal deposited Haynes 282 superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 748, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, G.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, D.; Dong, A.; Shu, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B. Effect of high temperature aging on microstructures and tensile properties of a selective laser melted GTD222 superalloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 853, 157226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, A.; Dinda, G.P. Direct laser metal deposition of Inconel 738. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 740, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, G.; Dasgupta, A.; Mazumder, J. Laser aided direct metal deposition of Inconel 625 superalloy: Microstructural evolution and thermal stability. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 509, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, P.; Lu, B.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, Y. Anisotropy of nickel-based superalloy K418 fabricated by selective laser melting. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2018, 28, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debroy, T.; Wei, H.L.; Zuback, J.S.; Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Milewski, J.O.; Beese, A.M.; Wilson-Heid, A.D.; De, A.; Zhang, W. Additive manufacturing of metallic components—Process, structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 92, 112–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešička, J.; Kuzel, R.; Dronhofer, A.; Eggeler, G. The evolution of dislocation density during heat treatment and creep of tempered martensite ferritic steels. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4847–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Sui, Y.; Wang, H.; Zou, C.; Wei, Z.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y. Effects of Cooling Rate on the Solidification and Microstructure of Nickel-Based Superalloy GTD222. Materials 2019, 12, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Li, L.; He, D.-G.; Chen, M.-S.; Liu, G.-Q. Effects of pre-treatments on mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of a nickel-based superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Guo, S.; Yang, G.; Song, X. Tensile deformation behavior of a new Ni-base superalloy at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 655, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, P.; Zhang, S.; Lu, B.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Huang, K.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Q. Graphene reinforced nickel-based superalloy composites fabricated by additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 769, 138484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-built GTD222 | 831 ± 5 | 1100 ± 7 | 24.3 ± 2.5 |
| HTed GTD222 | 1120 ± 6 | 1424 ± 7 | 13.7 ± 1.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, T.; Wang, R.; Bi, Z.; Zhu, G.; Tan, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Selective Laser Melting Processed Ni-Based Superalloy GTD222. Materials 2021, 14, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133668
Xia T, Wang R, Bi Z, Zhu G, Tan Q, Wang R, Zhang J. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Selective Laser Melting Processed Ni-Based Superalloy GTD222. Materials. 2021; 14(13):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133668
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Tian, Rui Wang, Zhongnan Bi, Guoliang Zhu, Qingbiao Tan, Rui Wang, and Ji Zhang. 2021. "Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Selective Laser Melting Processed Ni-Based Superalloy GTD222" Materials 14, no. 13: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133668
APA StyleXia, T., Wang, R., Bi, Z., Zhu, G., Tan, Q., Wang, R., & Zhang, J. (2021). Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Selective Laser Melting Processed Ni-Based Superalloy GTD222. Materials, 14(13), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14133668





