Crosslinking of Gelatin in Bicomponent Electrospun Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning
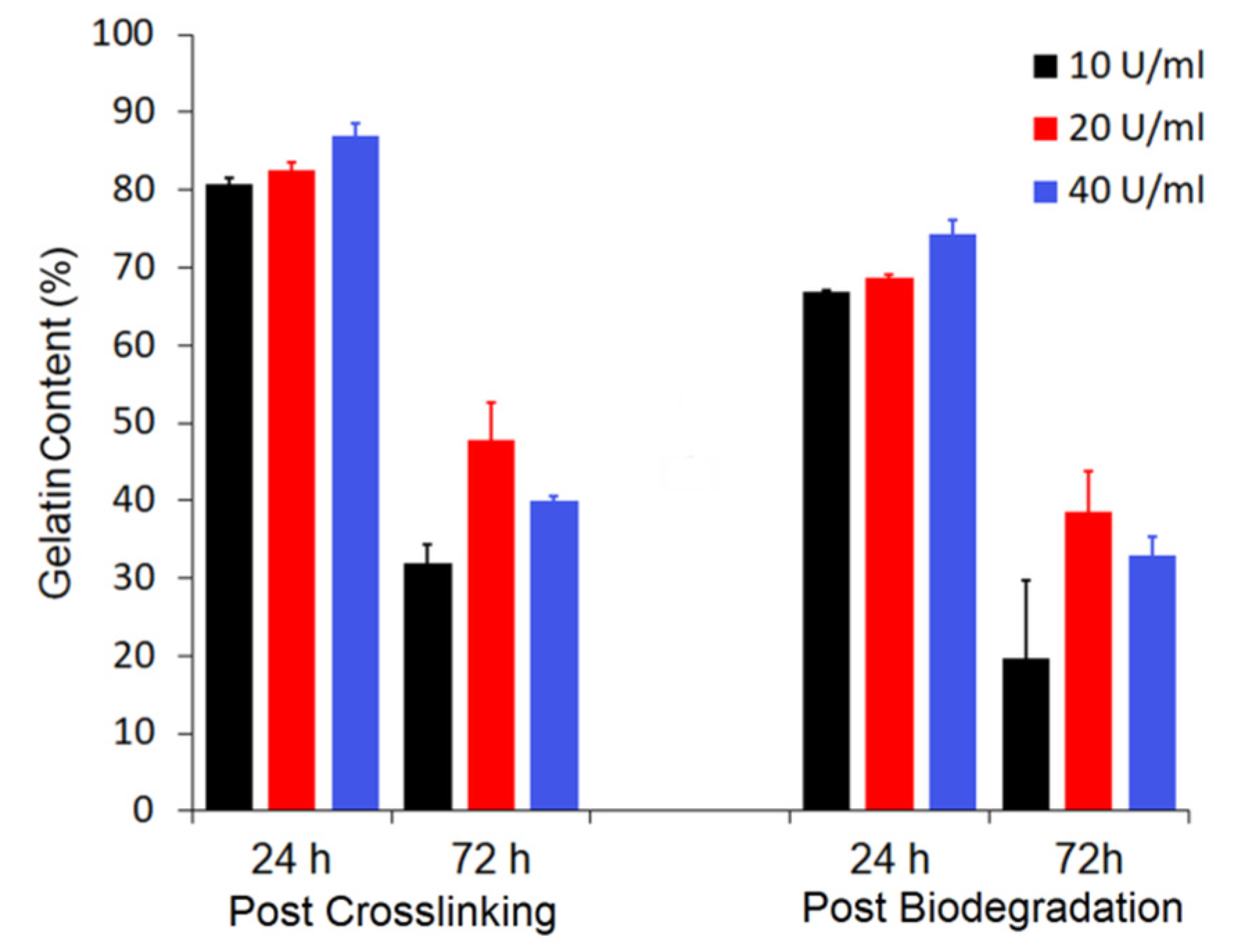
2.3. Crosslinking Methods
2.4. Fibre Biodegradation Test
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Imaging
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
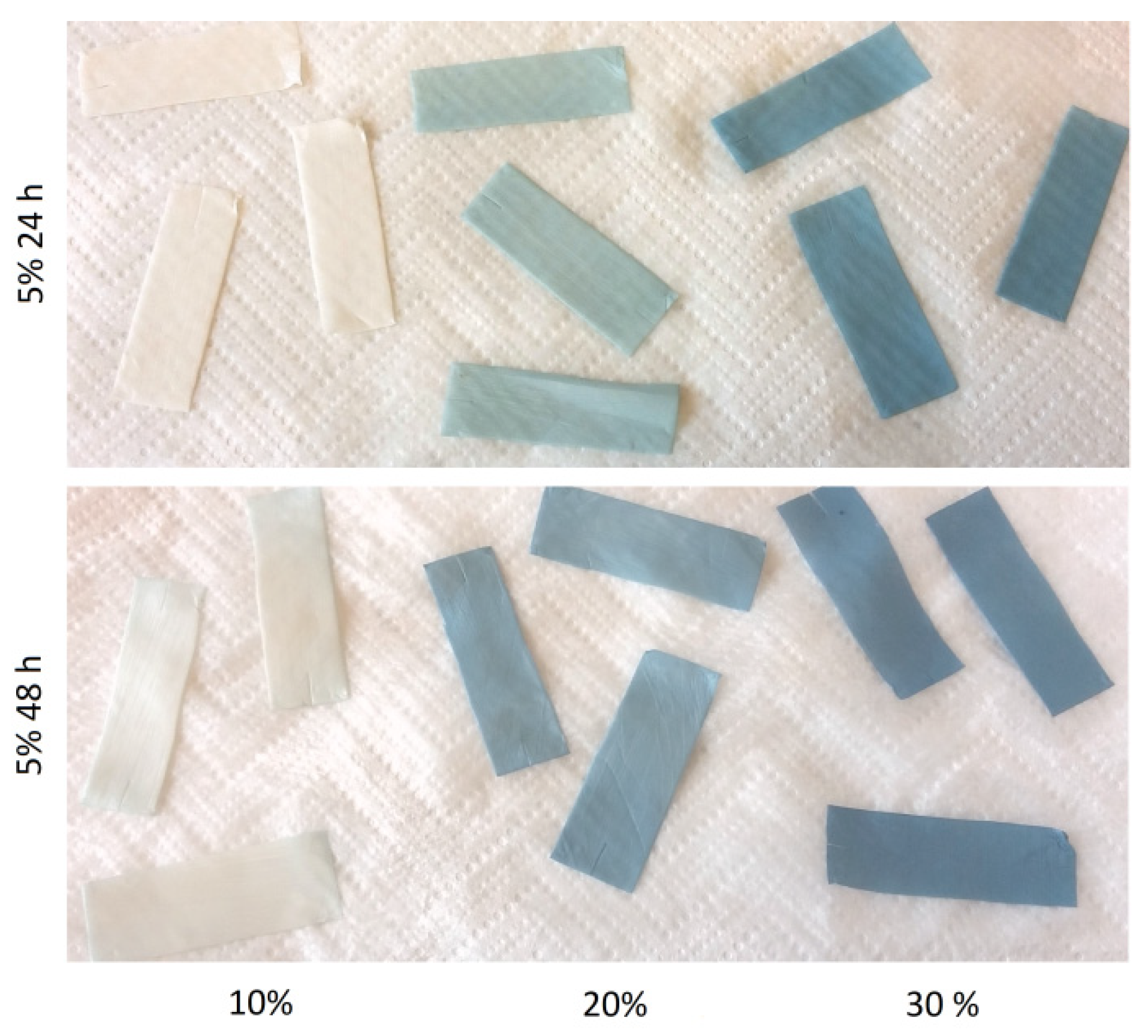
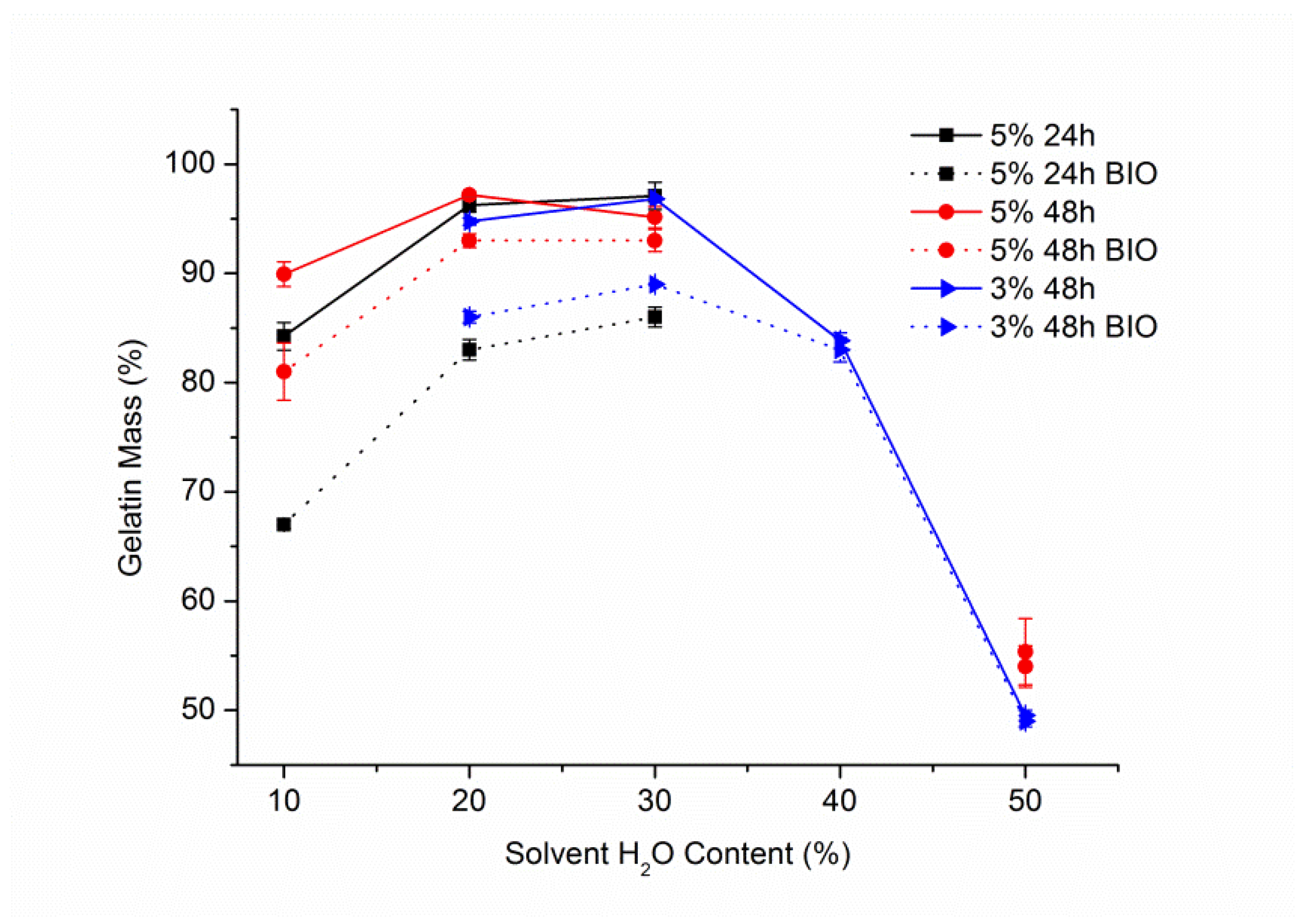
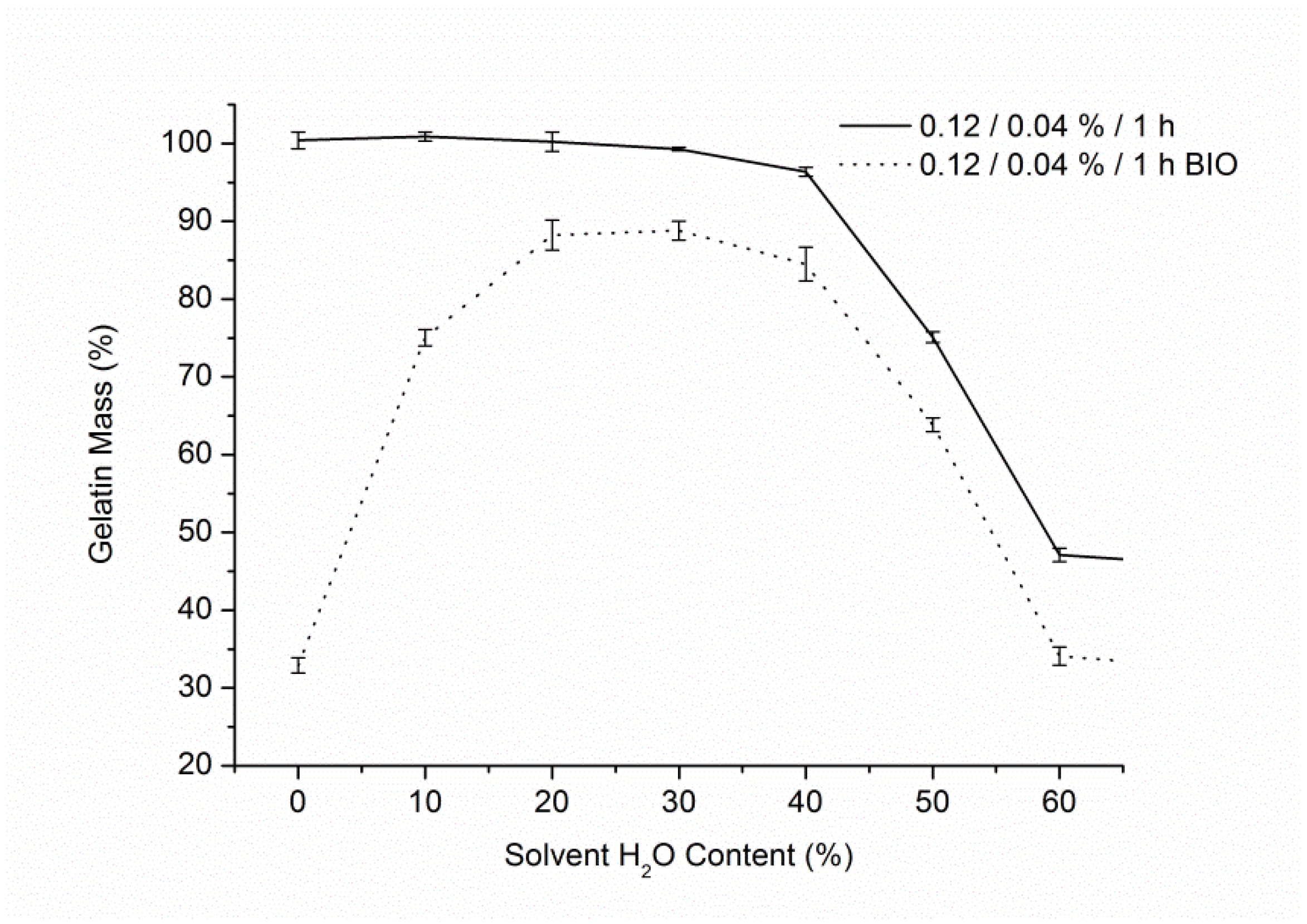
3.1. Solvent Optimisation
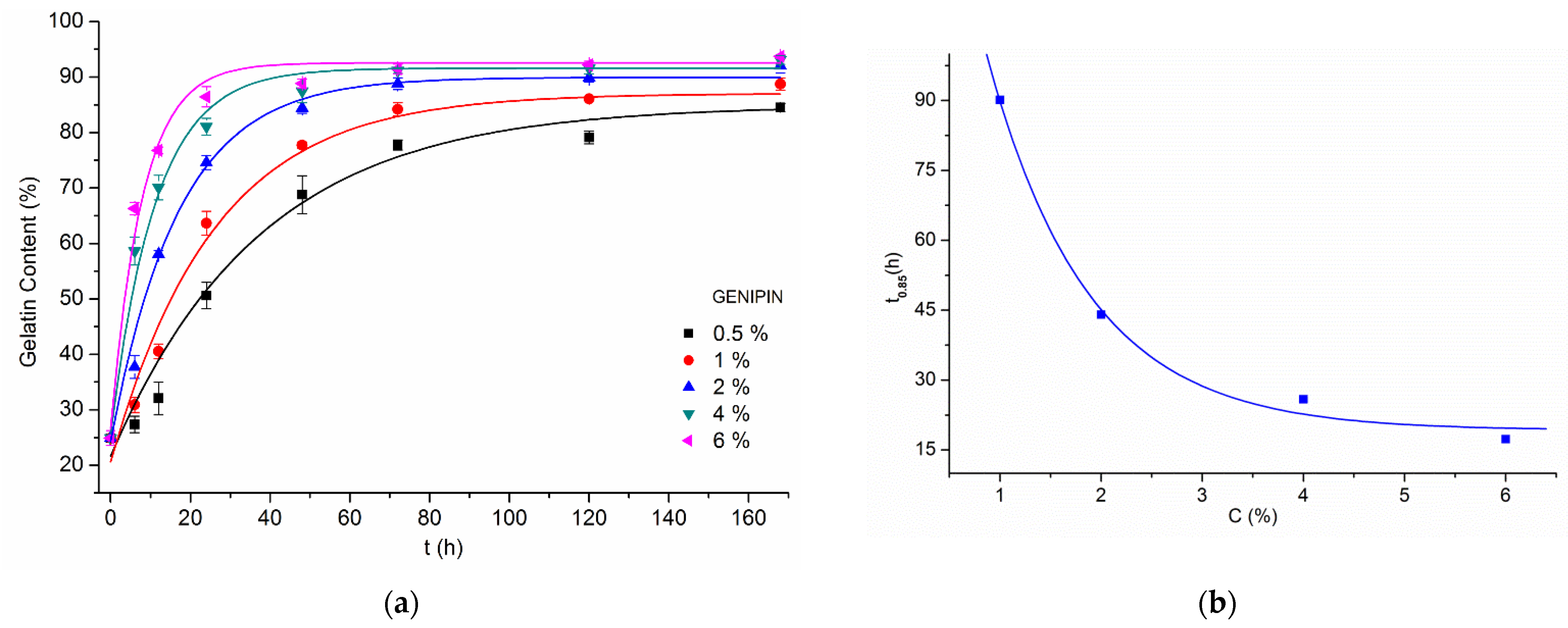
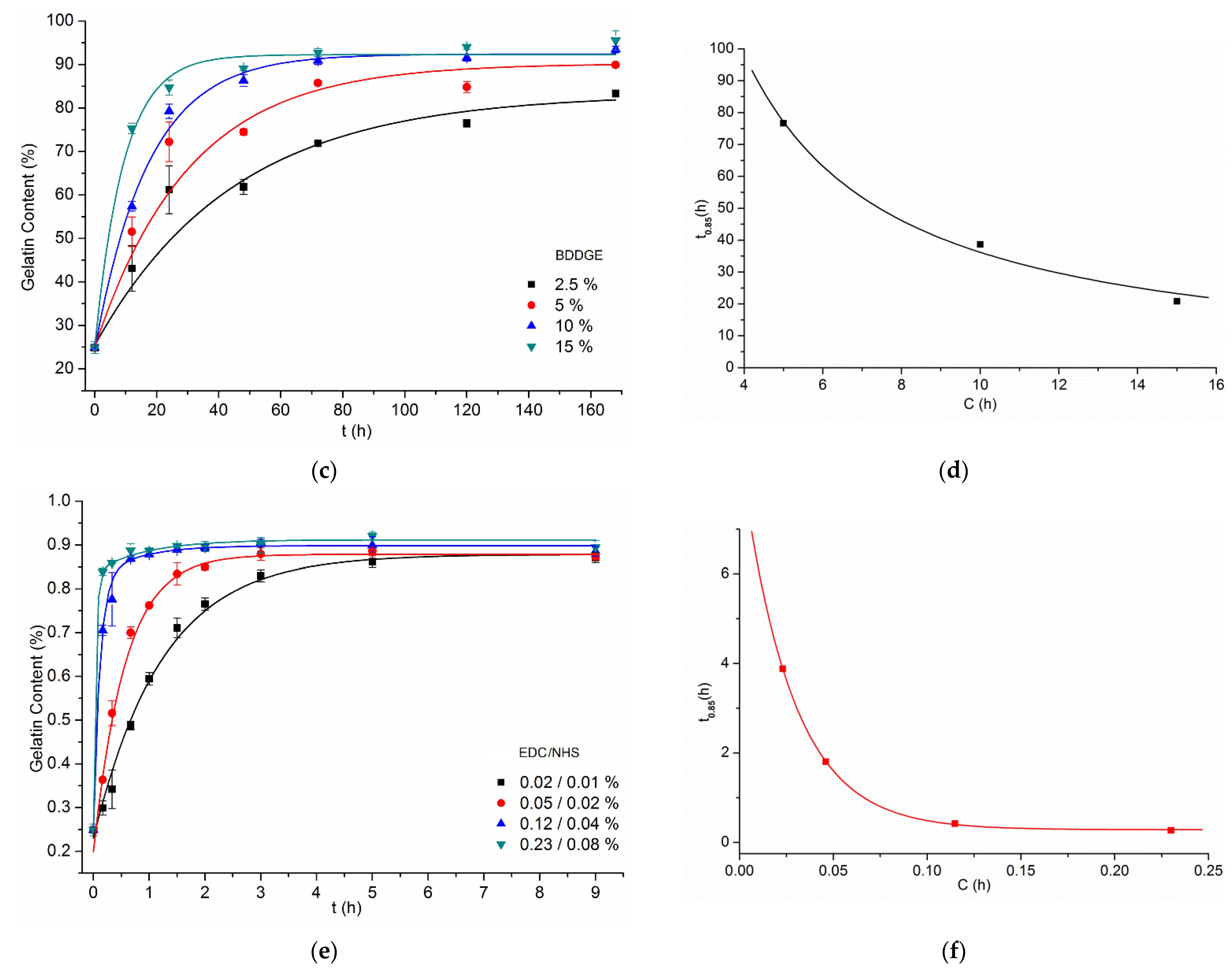
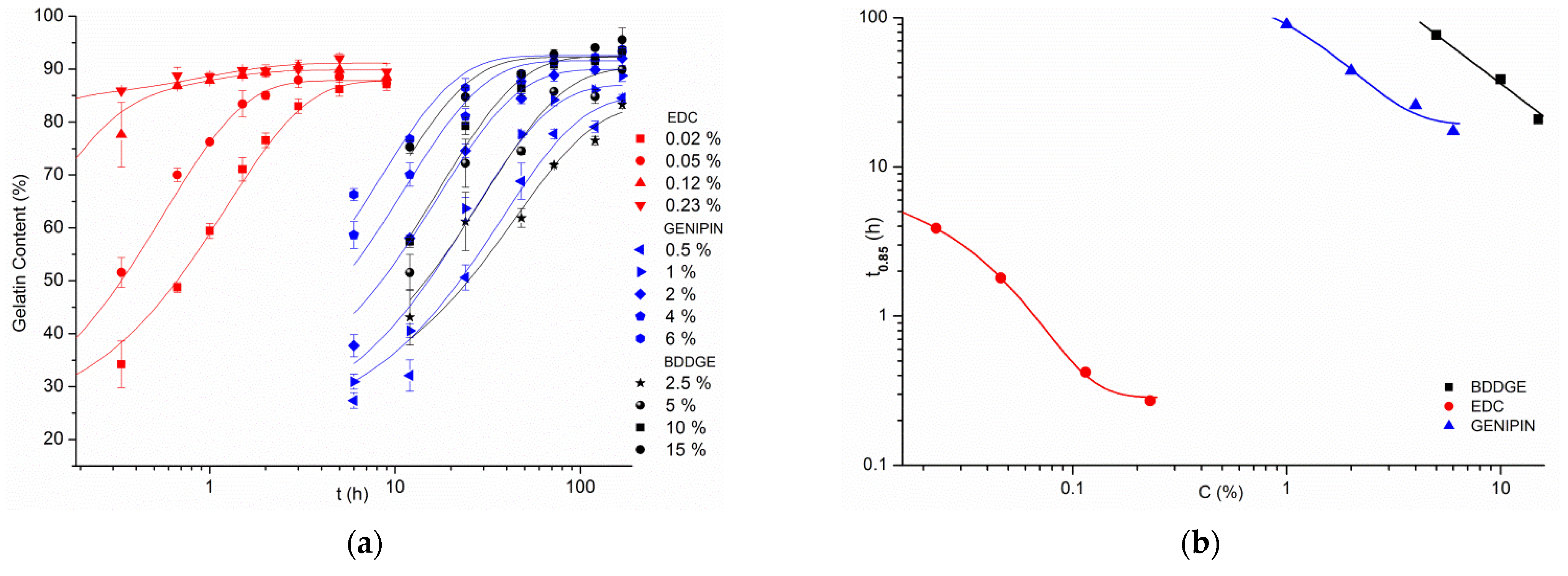
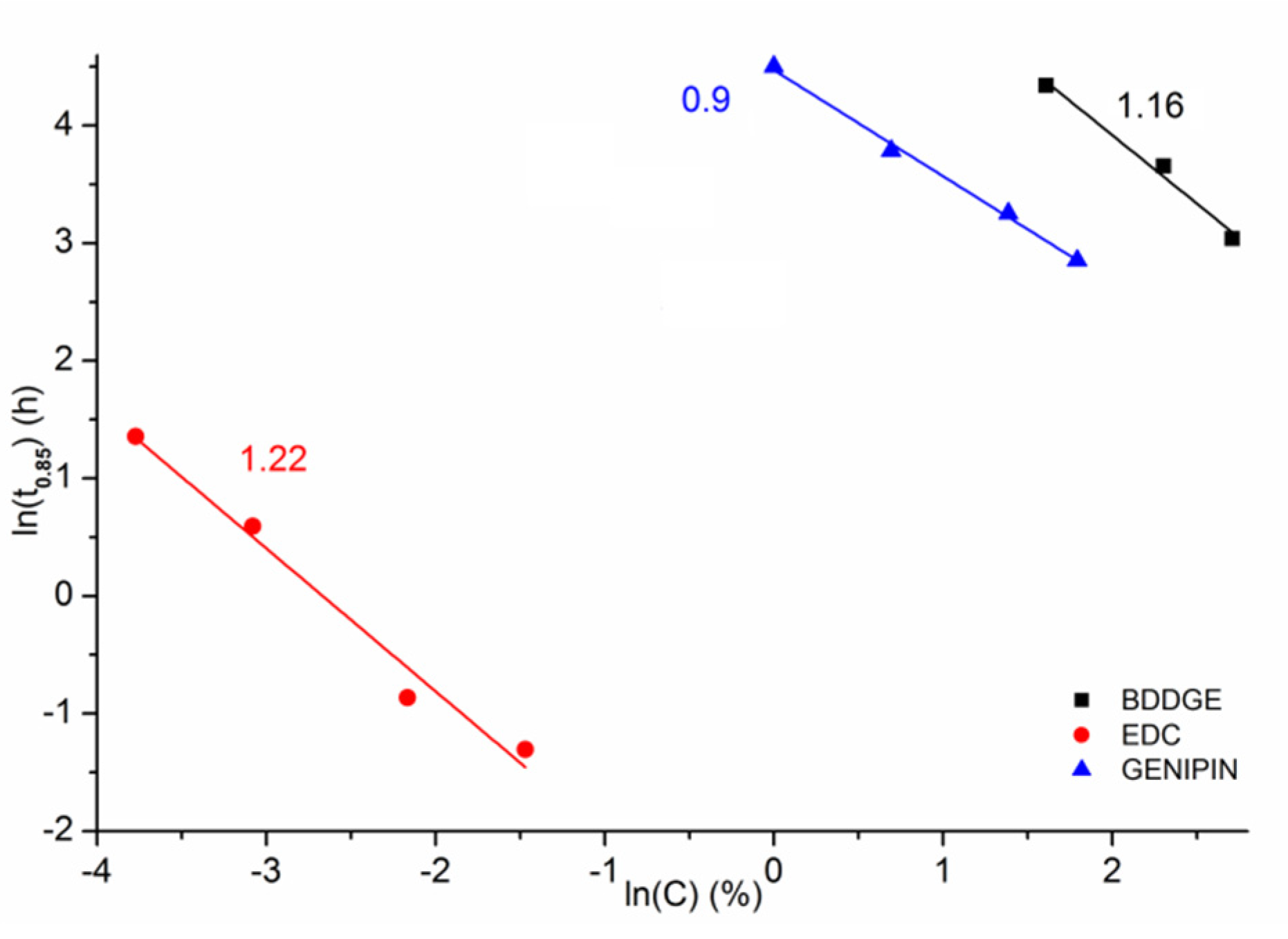
3.2. Gelatin Mass Change
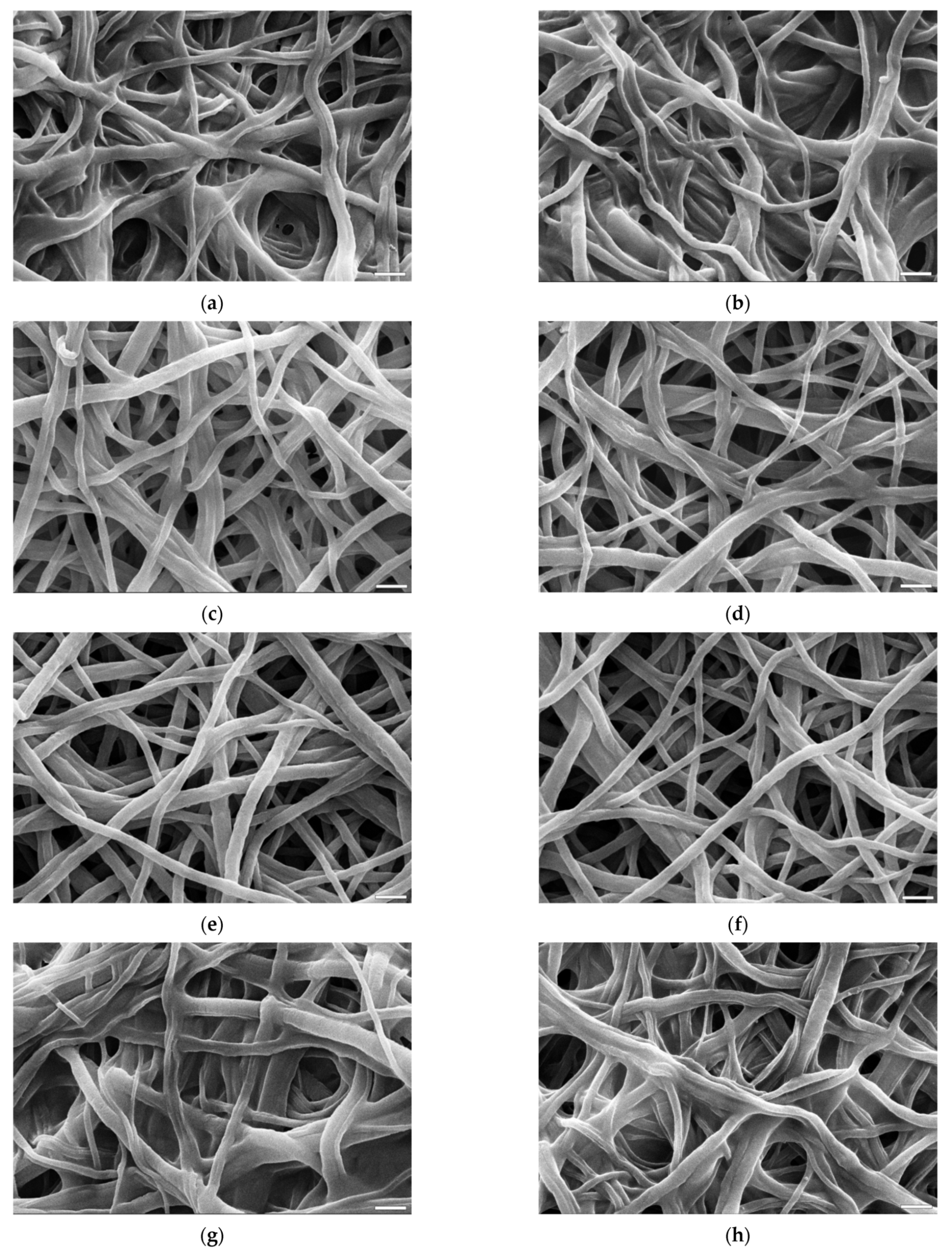
3.3. Morphology of the Fibres
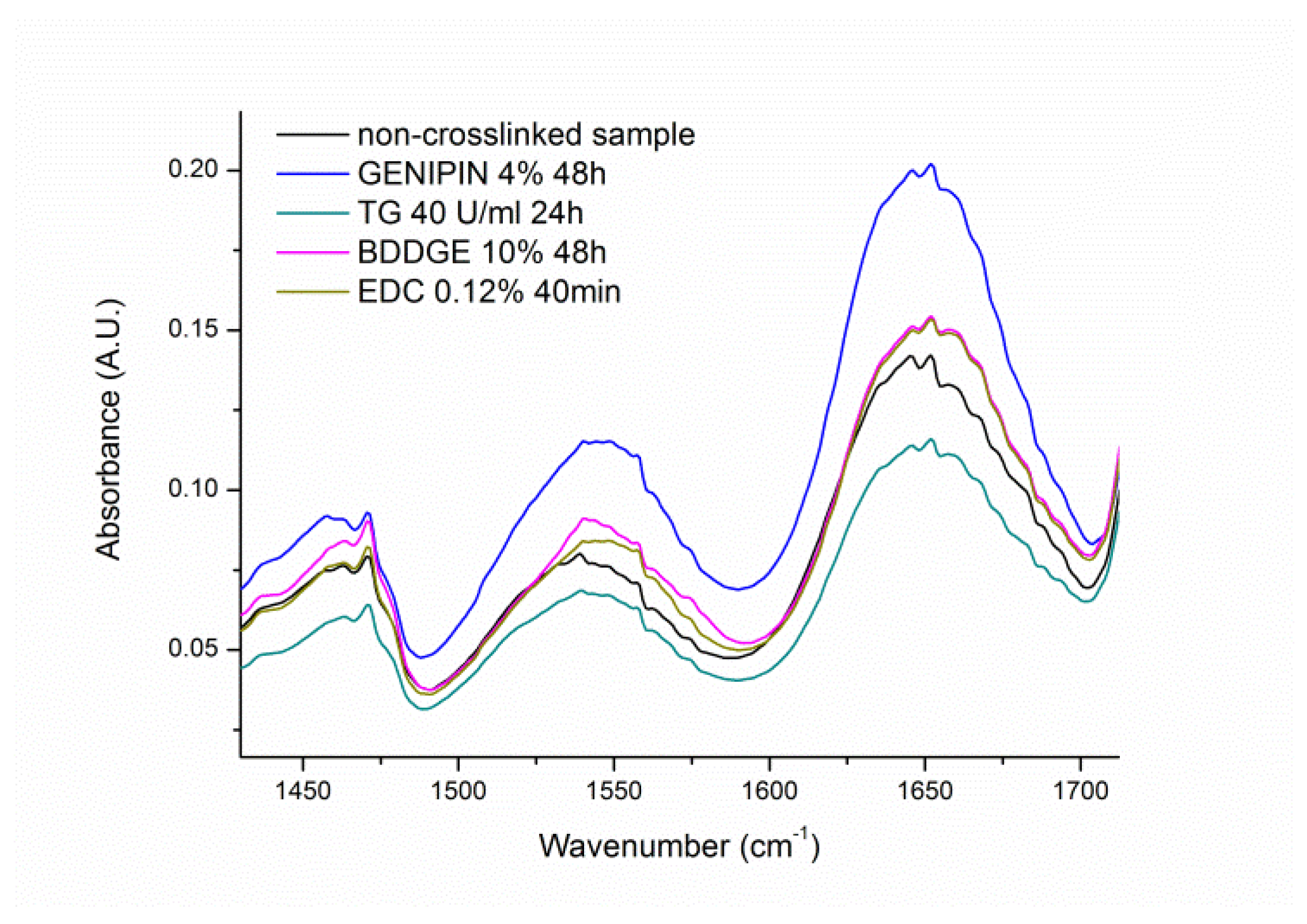
3.4. Gelatin FT-IR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.X. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, V.; Ko, F. Biomedical applications of nanofibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, P.; Dulnik, J.; Sajkiewicz, P. Electrospinning and Structure of Bicomponent Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Nanofibers Obtained Using Alternative Solvent System. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2015, 64, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The return of a forgotten polymer—Polycaprolactone in the 21st century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Griffith, M.; Venkatraman, S.S. Polycaprolactone-based biomaterials for tissue engineering and drug delivery: Current scenario and challenges. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2016, 65, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulnik, J.; Kołbuk, D.; Denis, P.; Sajkiewicz, P. The effect of a solvent on cellular response to PCL/gelatin and PCL/collagen electrospun nanofibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 104, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersel, U.; Dahmen, C.; Kessler, H. RGD modified polymers: Biomaterials for stimulated cell adhesion and beyond. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4385–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, J.A.; Fu, A.Y.; Choi, A.; Haq, N.A.; Kottke-Marchant, K.; Marchant, R.E. The influence of RGD-bearing hydrogels on the re-expression of contractile vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4127–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulnik, J.; Denis, P.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Kołbuk, D.; Choińska, E. Biodegradation of bicomponent PCL/gelatin and PCL/collagen nanofibers electrospun from alternative solvent system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 130, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, E.M.; Kinoshita, C.K.; Tanaka, T.T.; Ellison AK, D.; Yoza, B.A. Increasing Thermal Stability of Gelatin by UV-Induced Cross-Linking with Glucose. Int. J. Biomater. 2014, 2014, 979636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Lan, P. The Review on Electrospun Gelatin Fiber Scaffold. J. Res. Updates Polym. Sci. 2012, 1, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weadock, K.S.; Miller, E.J.; Keuffel, E.L.; Dunn, M.G. Effect of physical crosslinking methods on collagen-fiber durability in proteolytic solutions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K. Relationship between triple-helix content and mechanical properties of gelatin films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5675–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OldeDamink, L.H.H.; Dijkstra, P.J.; van Luyn, M.J.A.; van Wachem, P.B.; Nieuwenhuis, P.; Feijen, J. Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1995, 6, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi-Hiep, N.; Byong-Taek, L. Fabrication and characterization of cross-linked gelatin electro-spun nano-fibers. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, S.-M.; Li, W.-T.; Huang, T.-J. Genipin-crosslinked gelatin scaffolds for articular cartilage tissue engineering with a novel crosslinking method. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2008, 28, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clercq, K.D.; Schelfhout, C.; Bracke, M.; Wever, O.D.; Bockstal, M.V.; Ceelen, W.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. Genipin-crosslinked gelatin microspheres as a strategy to prevent postsurgical peritoneal adhesions: In vitro and in vivo characterization. Biomaterials 2016, 96, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidenko, N.; Schuster, C.F.; Bax, D.V.; Raynal, N.; Farndale, R.W.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Control of crosslinking for tailoring collagen-based scaffolds stability and mechanics. Acta Biomater. 2015, 25, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, H.; Jadidi, K.; Pourmotabed, S.; Sharifi, E.; Aghamollaei, H. Preparation and in vitro characterization of cross-linked collagen–gelatin hydrogel using EDC/NHS for corneal tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiabbas, M.; Alemzadeh, I.; Vossoughi, M. A porous hydrogel-electrospun composite scaffold made of oxidized alginate/gelatin/silk fibroin for tissue engineering application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, A.; Gualandi, C.; Panseri, S.; Montesi, M.; Marcacci, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Bigi, A. Comparative performance of collagen nanofibers electrospun from different solvents and stabilized by different crosslinkers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.R.; Baptista-Silva, S.; Oliveira CM, T.; Sousa, A.; Oliveira, A.L.; Bártolo, P.J.; Granja, P.L. In situ crosslinked electrospun gelatin nanofibers for skin regeneration. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, D.Y.S.; Collighan, R.J.; Verderio, E.A.M.; Addy, V.L.; Griffin, M. The cellular response to transglutaminase-cross-linked collagen. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6518–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, F.; Barbani, N.; Giusti, P.; Ciardelli, G. Transglutaminase reactivity with gelatine: Perspective applications in tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collighan, R.J.; Griffin, M. Transglutaminase 2 cross-linking of matrix proteins: Biological significance and medical applications. Amino Acids 2009, 36, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Venugopal, J.; Huang, Z.-M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, J.E. The amino acid composition of mammalian collagen and gelatin. Biochem. J. 1955, 61, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabotyagova, O.S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Collagen Structural Hierarchy and Susceptibility to Degradation by Ultraviolet Radiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2008, 28, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Crosslinking Agent | Concentration (% w/w) | Process Duration | Solvent (w/w Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genipin | 0.5–6% | 6–168 h | EtOH:H2O (7:3) |
| Transglutaminase | 10–40 U/mL | 24–72 h | H2O |
| EDC/ NHS | 0.02–0.23% 0.01–0.08% | 10 min–9 h | EtOH:H2O (7:3) |
| BDDGE | 2.5–15% | 12–168 h | EtOH:H2O (7:3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulnik, J.; Sajkiewicz, P. Crosslinking of Gelatin in Bicomponent Electrospun Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123391
Dulnik J, Sajkiewicz P. Crosslinking of Gelatin in Bicomponent Electrospun Fibers. Materials. 2021; 14(12):3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123391
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulnik, Judyta, and Paweł Sajkiewicz. 2021. "Crosslinking of Gelatin in Bicomponent Electrospun Fibers" Materials 14, no. 12: 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123391
APA StyleDulnik, J., & Sajkiewicz, P. (2021). Crosslinking of Gelatin in Bicomponent Electrospun Fibers. Materials, 14(12), 3391. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123391







