Tuning of the Structure and Magnetocaloric Effect of Mn1−xZrxCoGe Alloys (Where x = 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.1)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Experimental Details
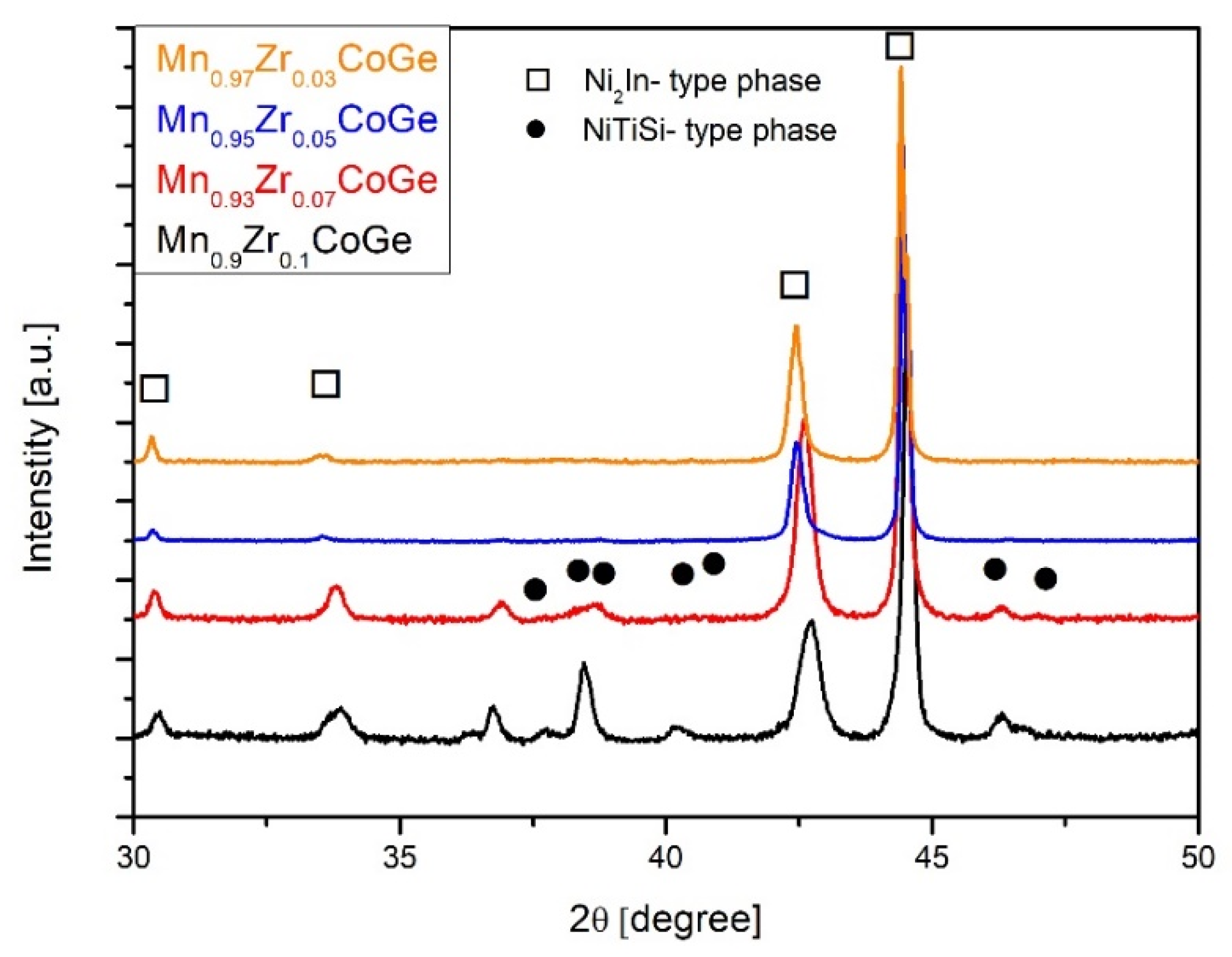
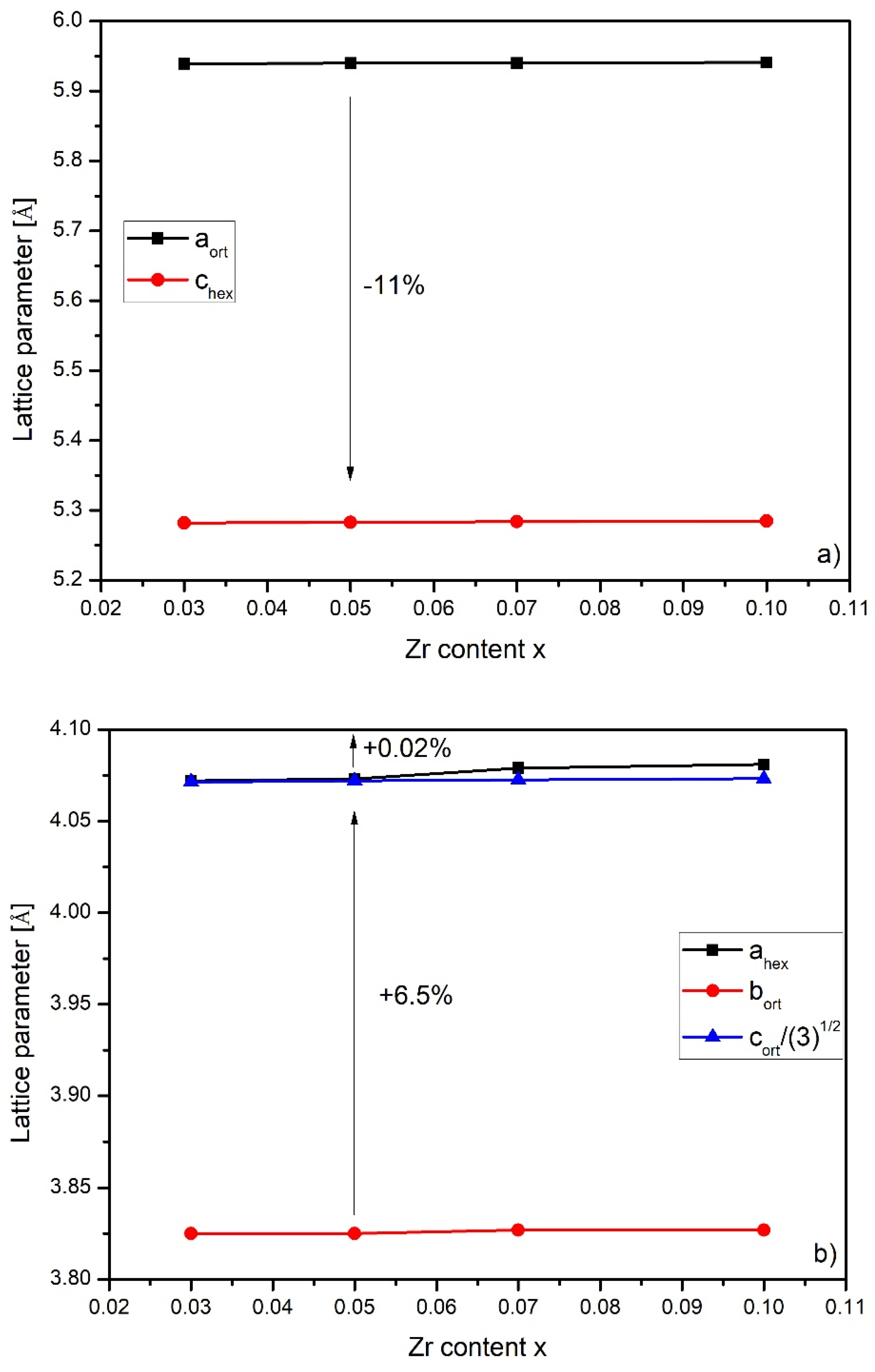
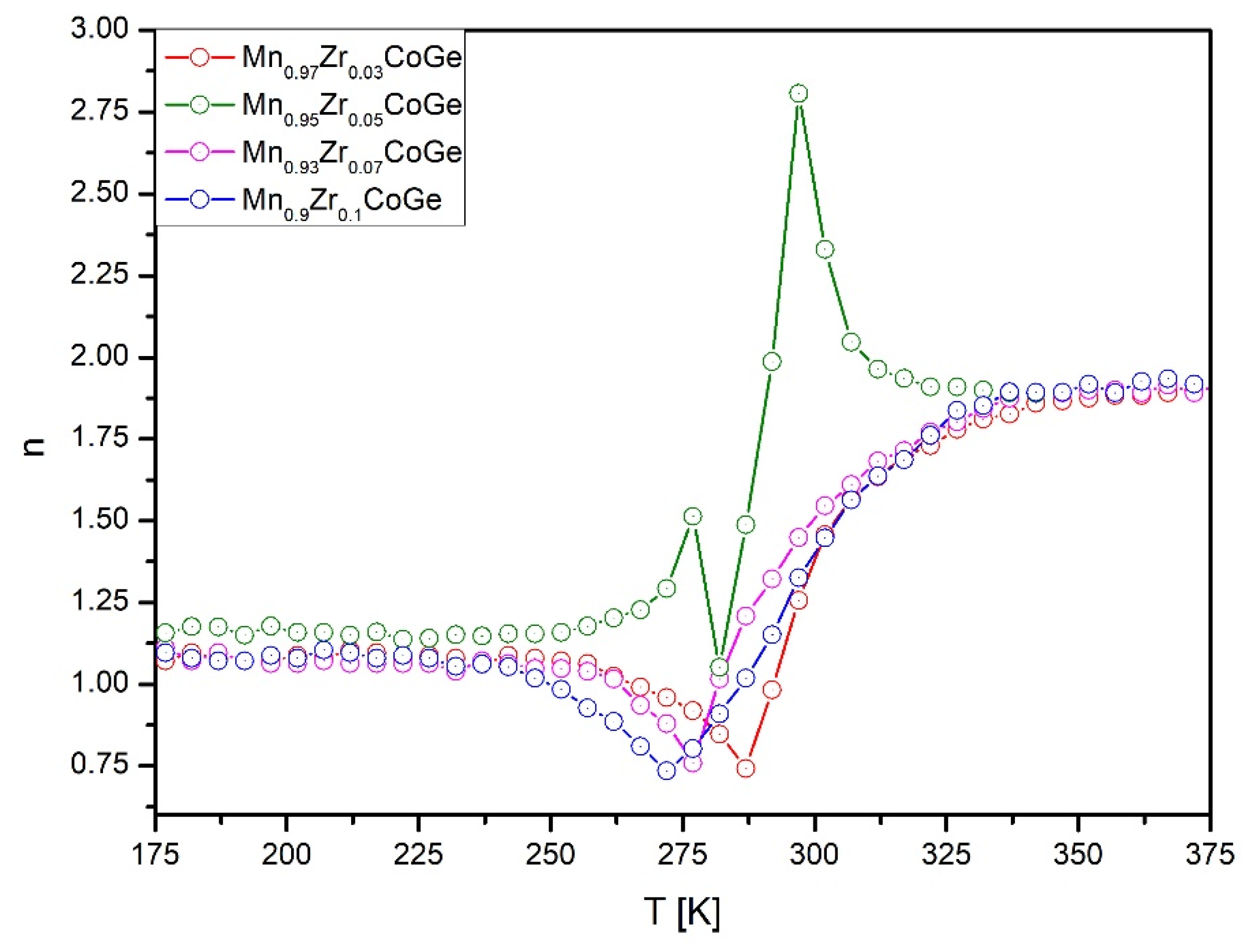
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tishin, A.M.; Spichkin, Y.I. The Magnetocaloric Effect and Its Applications; Institute of Physics Series in Condensed Matter Physics: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Magnetocaloric effect and magnetic refrigation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 200, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.B. Magnetocaloric effect in Gd5Si2Ge2/Gd composite materials. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08Q104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, A.; Akamatsu, Y.; Fukamichi, K. Itinerant electron metamagnetic transition in La(FexSi1−x)13 intermetallic compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 4756–47568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebara, P.; Kovac, J. The influence of partial substitution of La by Dy on structure and thermomagnetic properties of the LaFe11.0Co0.7Si1.3 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 454, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Cheng, W.; Ding, W.P.; Zhang, N.; Du, Y.W.; Yan, Q.J. Magnetocaloric properties of Na-Substituted perovskite-Type magnese oxides. Solid State Commun. 1998, 106, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Svitlyk, V.; Mozharivskyj, Y. Synthetic Approach for (Mn,Fe)2(Si,P) Magnetocaloric Materials: Purity, Structural, Magnetic, and Magnetocaloric Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.; Chraska, T.; Cinert, J.; Heczko, O.; Kopecek, J.; Landa, M.; Musalek, R.; Rames, M.; Siner, H.; Strasky, J.; et al. Mehcanical and magnetic properties of semi-Heusler/light-metal composites consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Des. 2017, 126, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Yang, B.; Hao, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Esling, C.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, L. Gigant low field magnetocaloric effect near room temperature in isostructurally alloyed MnNiGe-FeCoGe systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 506, 166782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, N.P.; Hung, L.T.; Hien, T.D.; Thuy, N.P.; Trung, N.T.; Bruck, E. Magnetic properties of half-metallic semi Heusler Co1−xCu xMnSb compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Hu, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Wu, G.; Sui, Y.; Qian, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. A new semi-Heusler ferromagnet NiFeSb: Electronic structure, magnetism and transport properties. Solid State Commun. 2003, 128, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, J.; Kaczmarska, K.; Tobola, J.; Skolozdra, R.V.; Melnyk, G.A. Location of Mn 3d states in semi-Heusler compounds. Physica B 1999, 261, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.K.; Kuang, A.L.; Chen, H. Effect of Nb doping on electronic and magnetic properties of half-metallic CoMnSb semi-Heusler compound from first-principles calculations. Phys. Status Solid B 2010, 247, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, S.; Balke, B.; Jakob, G. Hole localization in thermoelectric half-Heusler (Zr0.5Hf0.5)Co(Sb1−xSnx) thin films. Thin Solid Film 2019, 692, 137581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, E.; Ilyn, M.; Tishin, A.M.; Tegus, O. Magnetocaloric effects in MnFeP1−xAsx-based compounds. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 291, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.T.; Zhang, L.; Caron, L.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Bruck, E. Gigant magnetocaloric effect by tailoring the phase transitions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 172504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-López, J.; Rodriguez-Alba, R.; Aguilera-Granja, F. Modeling the magnetic properties of Heusler alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1994, 131, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloufa, A.; Bakhti, B.; Bouguenna, D.; Chellali, M.R. Computational investigation of CrFeZ [Z = Si, Sn and Ge] half-Heusler compounds ferromagnets. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2019, 563, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Casper, F.; Winterlik, J.; Balke, B.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C. Crystal Structure of New Heusler Compounds. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2009, 635, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohl, H.; Ramirez, A.P.; Goldmann, C.; Ernst, G.; Wölfing, B.; Bucher, E. New Compounds with MgAgAs-type structure: NbIrSn and NbIrSb. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1998, 10, 7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębara, P.; Śniadecki, Z. Structure, magnetocaloric properties and thermodynamic modeling of enthalpies of formation of (Mn,X)-Co-Ge (X=Zr, Pd) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 796, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Zhu, Q.; Miao, X.; Fan, J.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H. Tailoring the magneto-structural coupling in Mn1−xZrxCoGe alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, W.; Nolze, G. PowderCell 2.0 for Windows. Powder Diffr. 1998, 13, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Bażela, W.; Szytuła, A.; Todorović, J.; Tomkowicz, Z.; Zieba, A. Crystal and magnetic structure of NiMnGe. Phys. Status Solid A 1976, 38, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V. Diffusionless orthorhombic to hexagonal transitions in ternary silicides and germanides. Inorg. Chem. 1975, 14, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Liu, E.K.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, J.L.; Wang, W.H.; Zhang, H.W.; Wu, G.H.; Yu, S.Y. Phase diagram, ferromagnetic martenstic transformation and magnetoresposive properties of Fe-doped MnCoGe alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 332, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A.J.; Mudryk, Y.; Pecharsky, V.K. On the nature of the magnetocaloric effect of the first-order magnetostructural transition. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, J.J.; Waszczak, J.V. Spin-glass transition in MnO. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 5167–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneider, K.A. Magnetocaloric effect from indirect measurements: Magnetization and heat capacity. Jr. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.E.; Potter, W.H. General analysis of magnetic refrigeration and its optimization using a new concept: Maximization of refrigerant capacity. Cryogenics 1985, 25, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A.; Karpenkov, D.Y.; Radulov, I.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. A quantitative criterion for determining the order of Magnetic phase transitions using the magnetocaloric effect. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Conde, A.; Provenzano, V.; Shull, R. Scaling analysis of the magnetocaloric effect in Gd5Si2Ge1.9X0.1 (X=Al, Cu, Ga, Mn,Fe,Co). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokov, K.P.; Müller, K.-H.; Moore, J.D.; Liu, J.; Karpenkov, Y.A.; Krautz, M.; Gutfleisch, O. Influence of thermal hysteresis and field cycling on themagnetocaloric effect in LaFe11.6Si1.4. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 552, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K.; Sandeman, K.G.; Cohen, L.F.; Sasso, C.P.; Basso, V.; Barcza, A.; Katter, M.; Moore, J.D.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Evaluation of the reliability of the measurement of key magnetocaloric properties: A round robin study of La(Fe,Si, Mn)Hdconducted by the SSEEC consortium of European laboratories. Int. J. Refrig. 2012, 35, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębara, P.; Hasiak, M. Determination of Phase Transition and Critical Behavior of the As-Cast GdGeSi-(X) Type Alloys (Where X = Ni, Nd and Pr). Materials 2021, 14, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
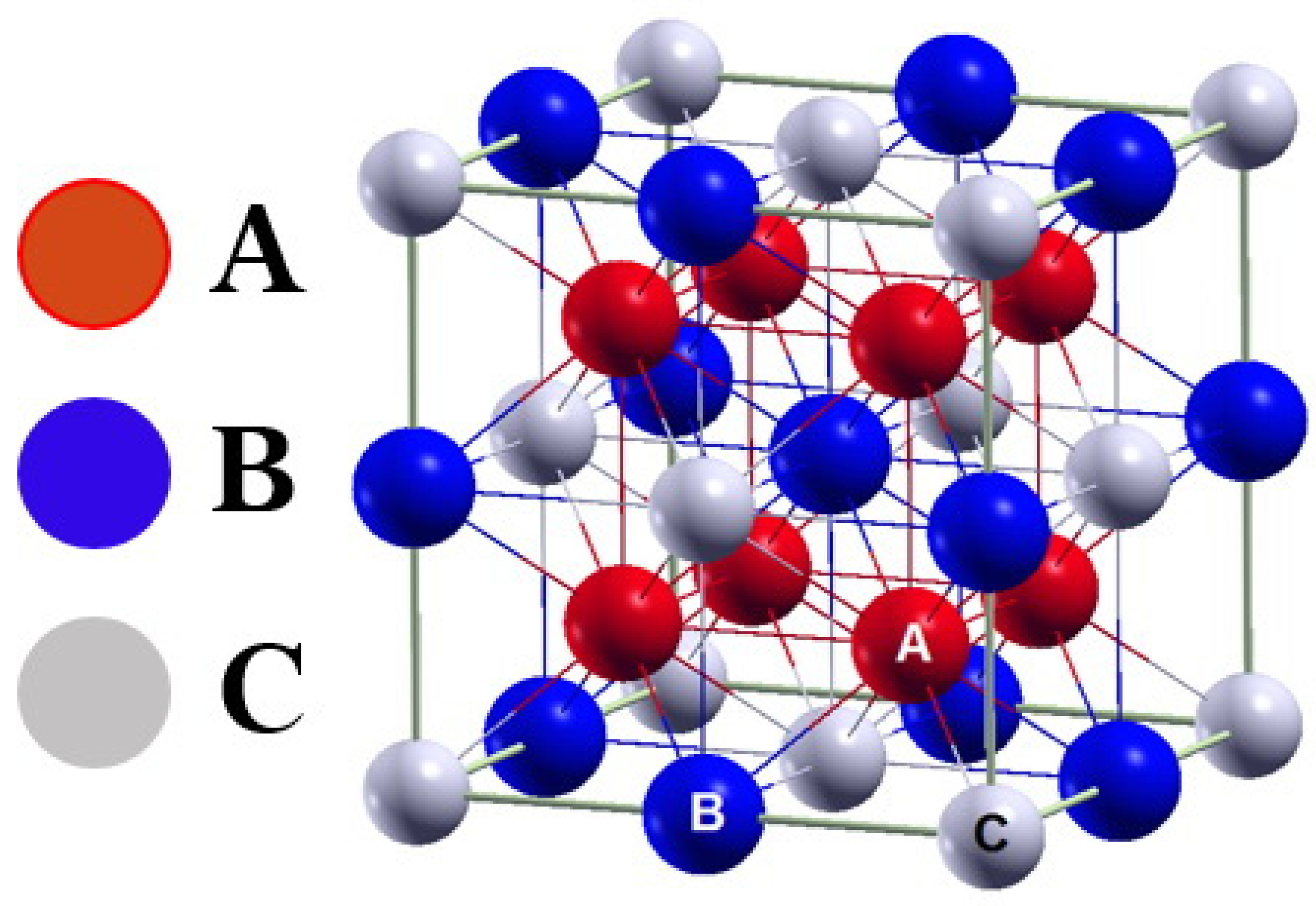
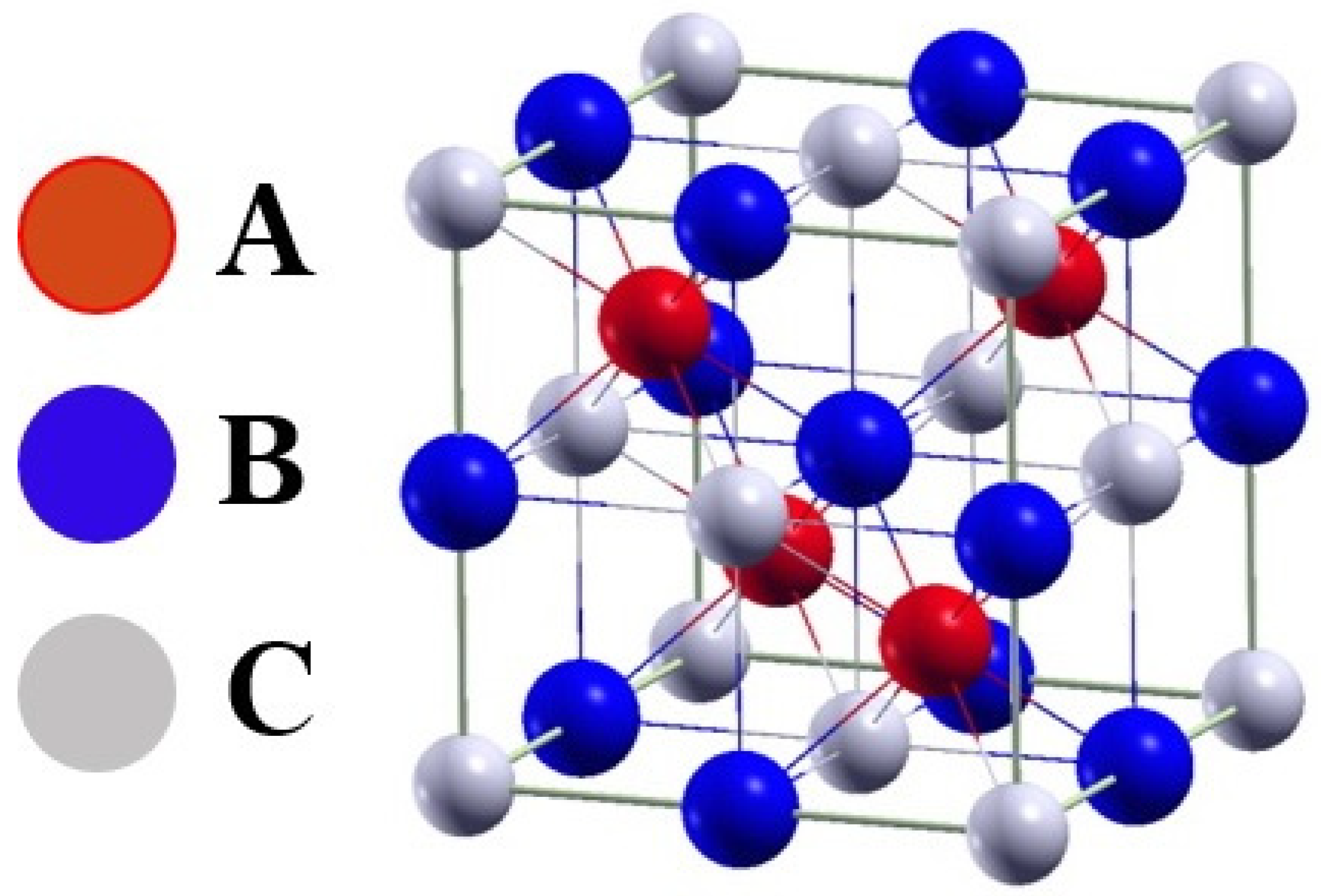

| Alloy | Crystalline Phase | Lattice Parameter [Å] ± 0.001 | Volume Fraction [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn0.97Zr0.03CoGe | hex Ni2In- type | a = 4.072 | 93 |
| c = 5.282 | |||
| ort NiTiSi- type | a = 5.939 | 7 | |
| b = 3.825 | |||
| c = 7.052 | |||
| Mn0.95Zr0.05CoGe | hex Ni2In- type | a = 4.073 | 92 |
| c = 5.283 | |||
| ort NiTiSi- type | a = 5.940 | 8 | |
| b = 3.825 | |||
| c = 7.053 | |||
| Mn0.93Zr0.0.07CoGe | hex Ni2In- type | a = 4.079 | 82 |
| c = 5.284 | |||
| ort NiTiSi- type | a = 5.940 | 18 | |
| b = 3.827 | |||
| c = 7.054 | |||
| Mn0.9Zr0.1CoGe | hex Ni2In- type | a = 4.081 | 72 |
| c = 5.285 | |||
| ort NiTiSi- type | a = 5.941 | 28 | |
| b = 3.827 | |||
| c = 7.055 |
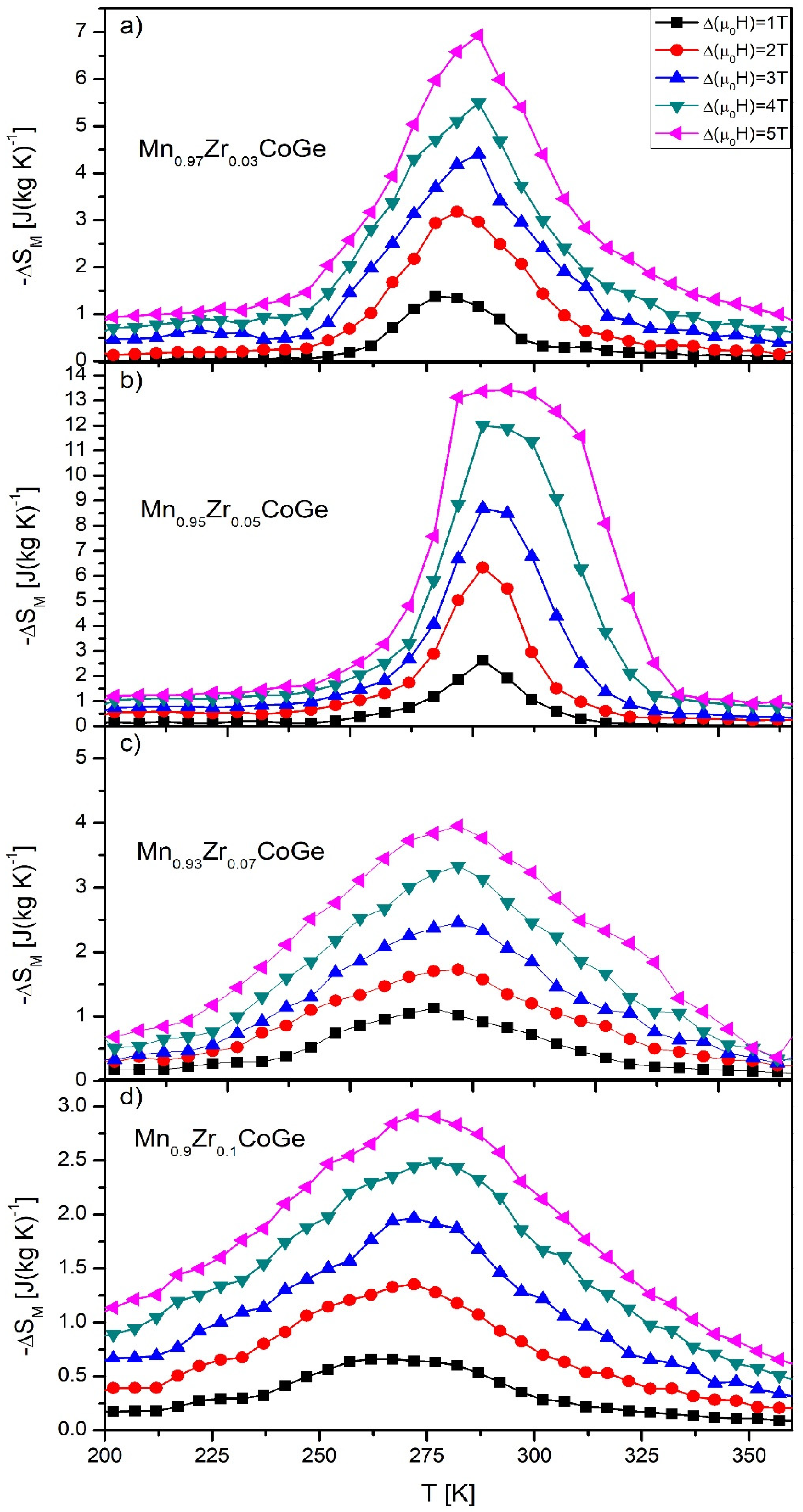
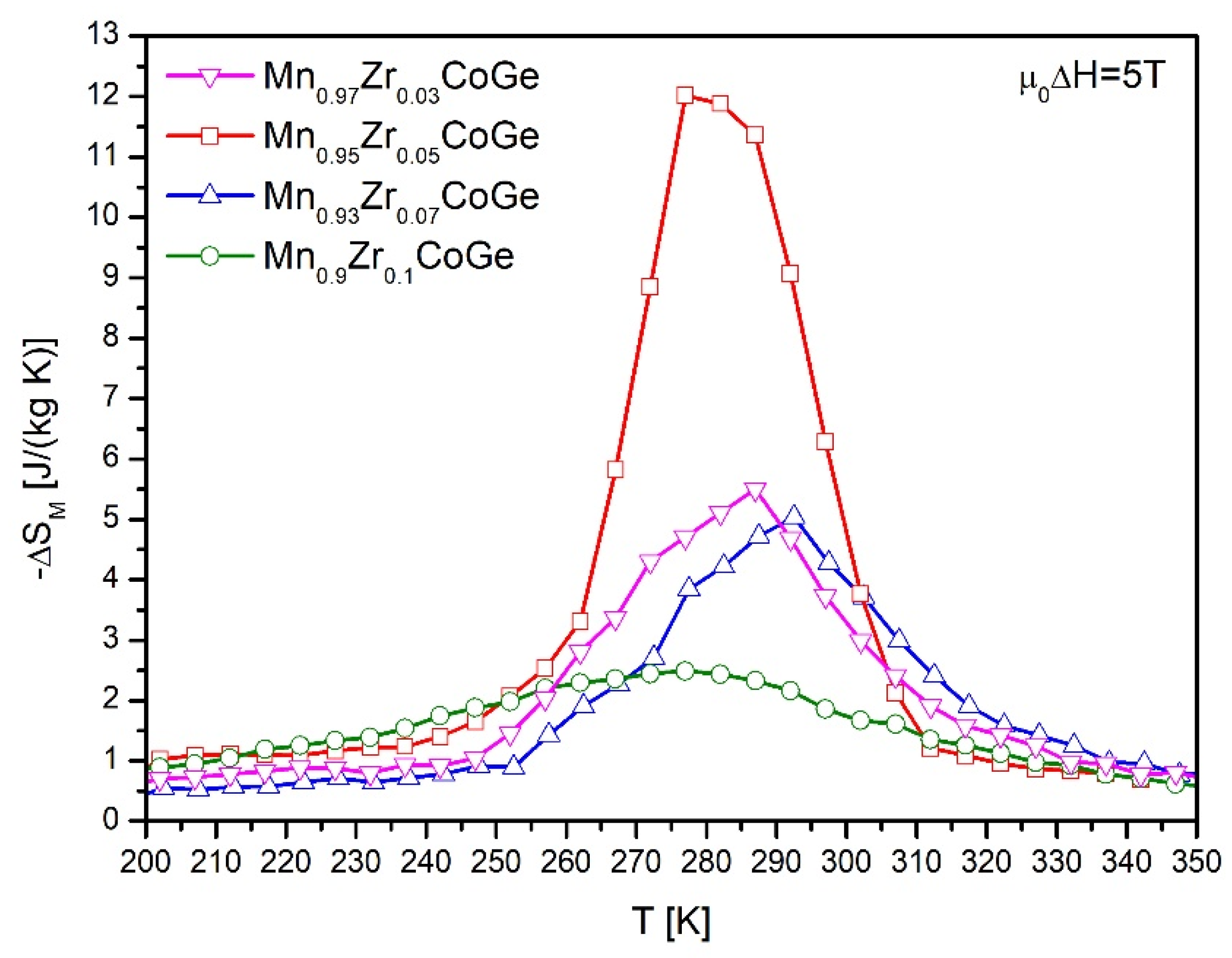
| Alloy | Δ(μ0H) [T] | ΔSM [J (kg K)−1] | RC [J kg−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn0.97Zr0.03CoGe | 1 | 1.38 | 29 |
| 2 | 3.18 | 67 | |
| 3 | 4.41 | 92 | |
| 4 | 5.51 | 139 | |
| 5 | 6.93 | 195 | |
| Mn0.95Zr0.05CoGe | 1 | 2.64 | 37 |
| 2 | 6.34 | 99 | |
| 3 | 8.71 | 174 | |
| 4 | 12.02 | 296 | |
| 5 | 13.42 | 425 | |
| Mn0.93Zr0.07CoGe | 1 | 1.13 | 41 |
| 2 | 1.73 | 71 | |
| 3 | 2.46 | 114 | |
| 4 | 3.33 | 165 | |
| 5 | 3.96 | 246 | |
| Mn0.9Zr0.1CoGe | 1 | 0.66 | 33 |
| 2 | 1.35 | 78 | |
| 3 | 1.97 | 121 | |
| 4 | 2.42 | 177 | |
| 5 | 2.94 | 219 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutynia, K.; Gębara, P. Tuning of the Structure and Magnetocaloric Effect of Mn1−xZrxCoGe Alloys (Where x = 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.1). Materials 2021, 14, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113129
Kutynia K, Gębara P. Tuning of the Structure and Magnetocaloric Effect of Mn1−xZrxCoGe Alloys (Where x = 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.1). Materials. 2021; 14(11):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113129
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutynia, Karolina, and Piotr Gębara. 2021. "Tuning of the Structure and Magnetocaloric Effect of Mn1−xZrxCoGe Alloys (Where x = 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.1)" Materials 14, no. 11: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113129
APA StyleKutynia, K., & Gębara, P. (2021). Tuning of the Structure and Magnetocaloric Effect of Mn1−xZrxCoGe Alloys (Where x = 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.1). Materials, 14(11), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14113129







