Facile Preparation of Granular Copper Films as Cathode for Enhanced Electrochemical Degradation of Methyl Orange
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
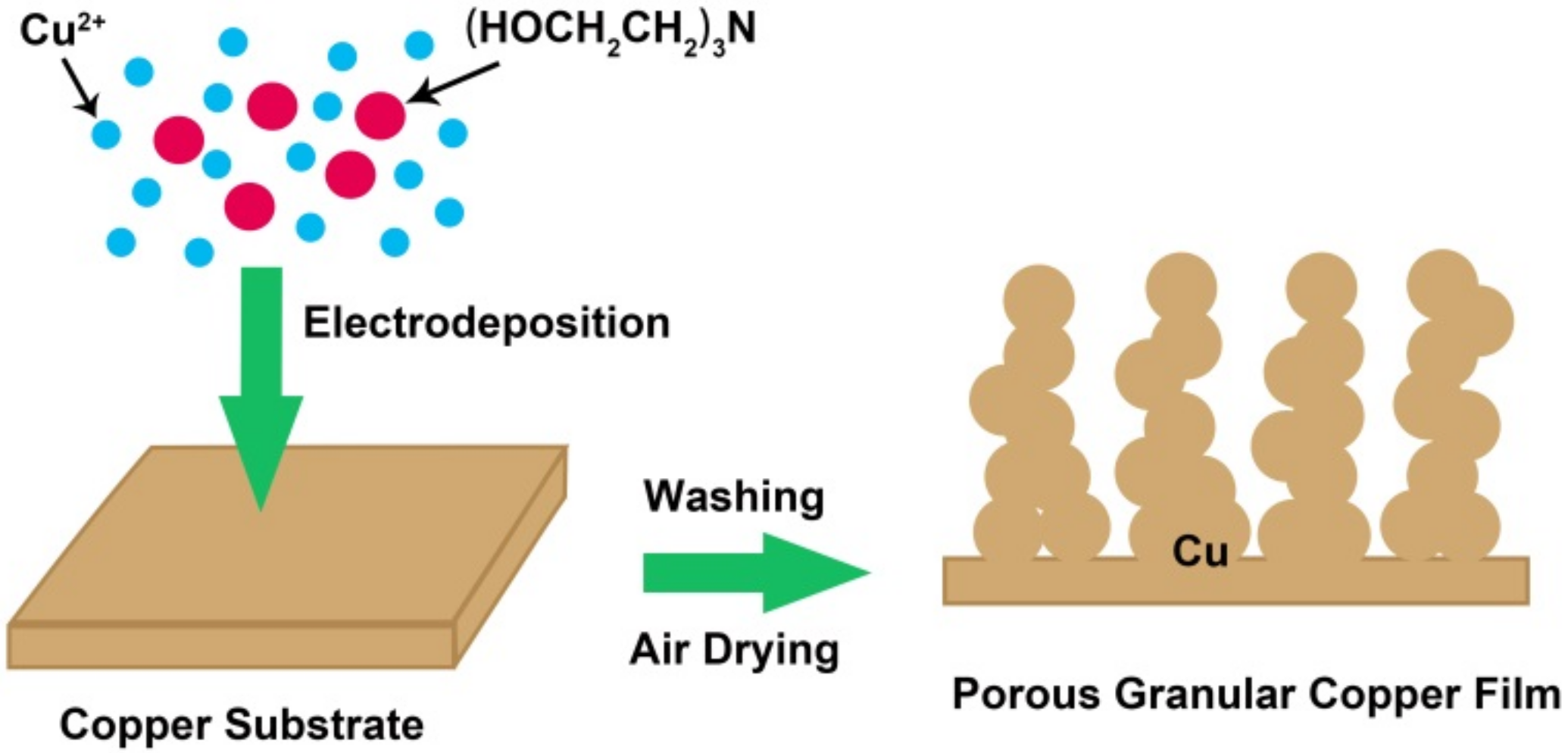
2.1. Preparation of Granular Copper Films
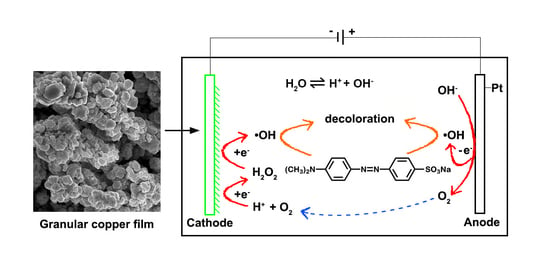
2.2. Electrochemical Degradation of MO
3. Results and Discussion
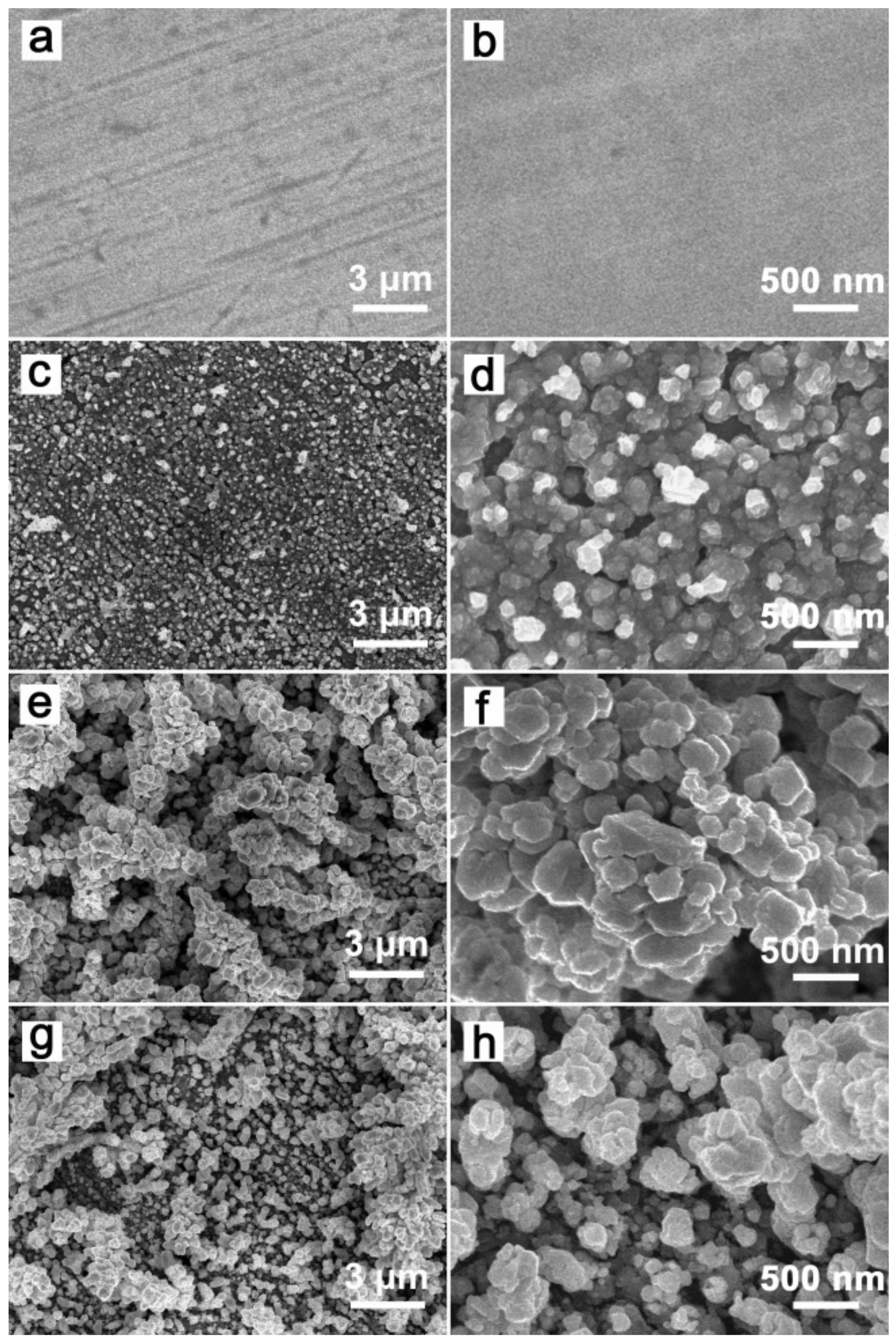
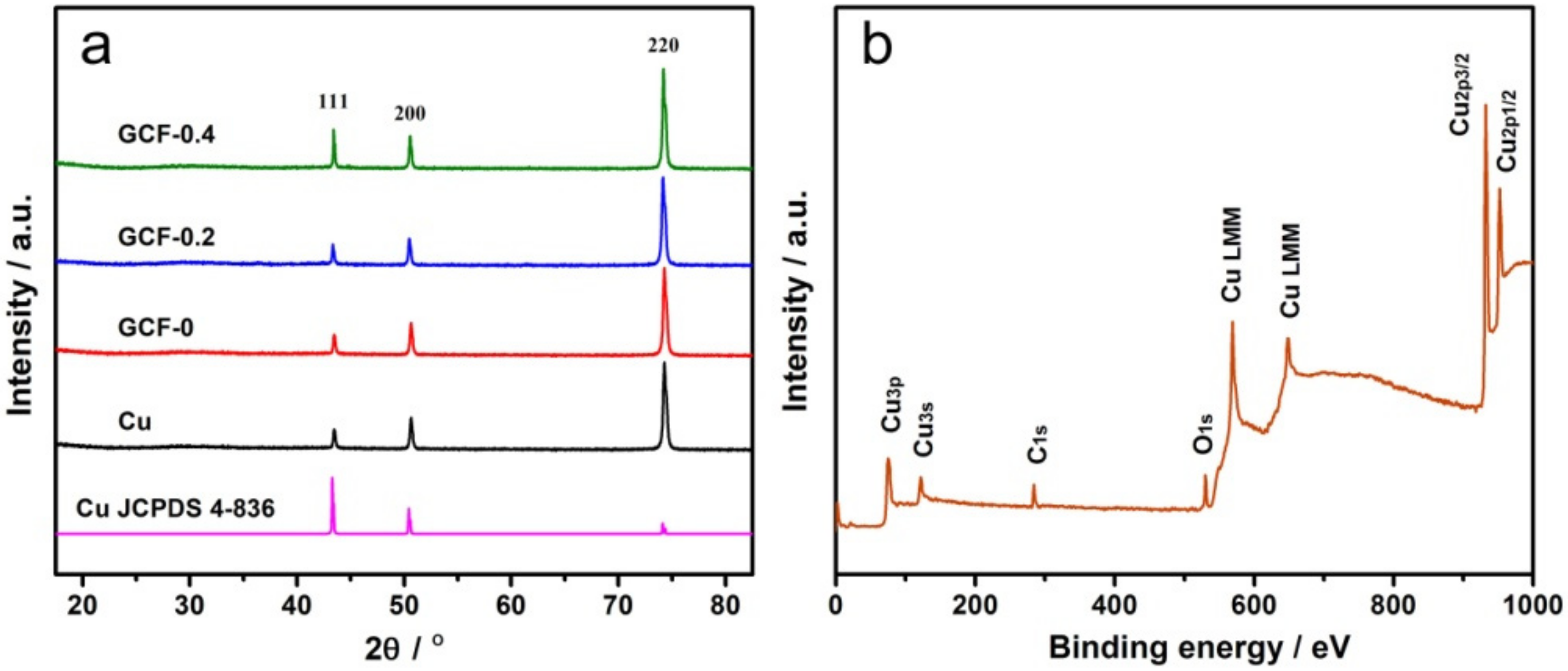
3.1. Morphologies and Structures
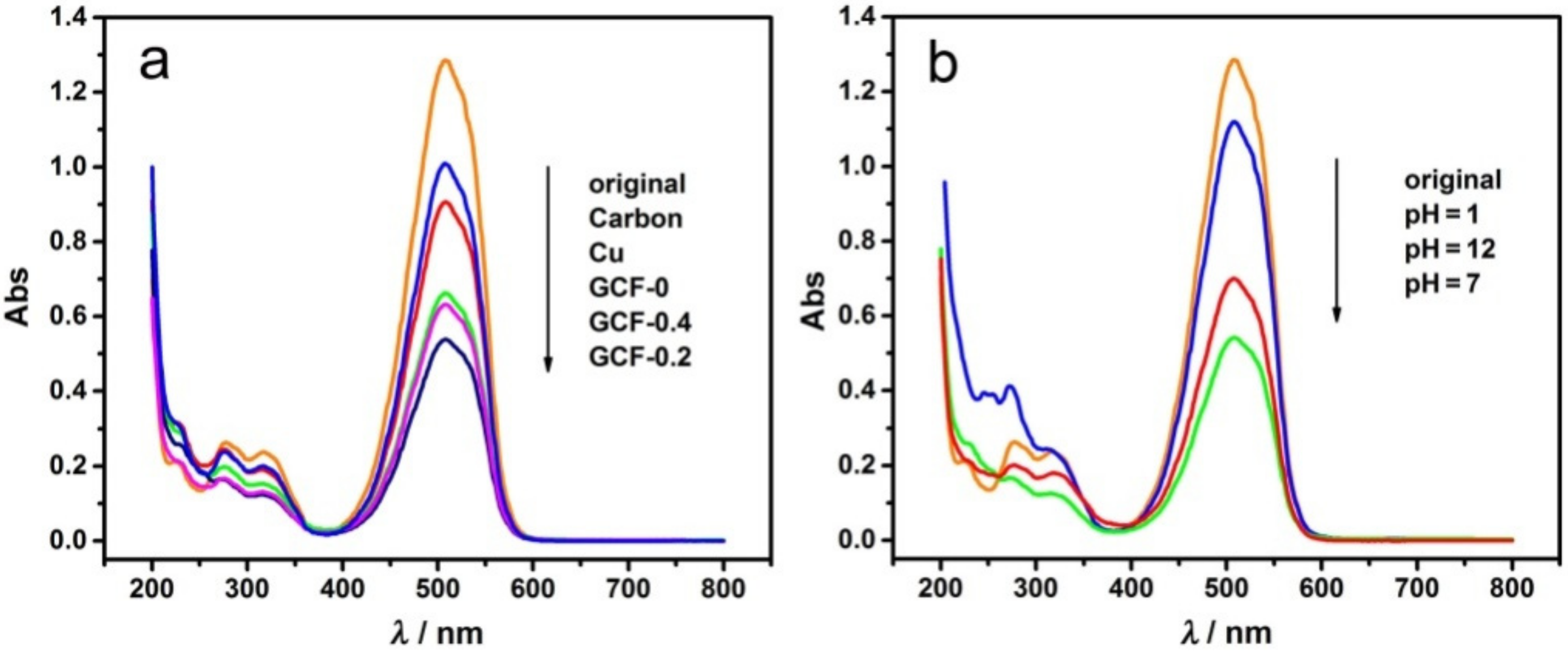
3.2. Effect of the Triethanolamine Dosage and pH Values
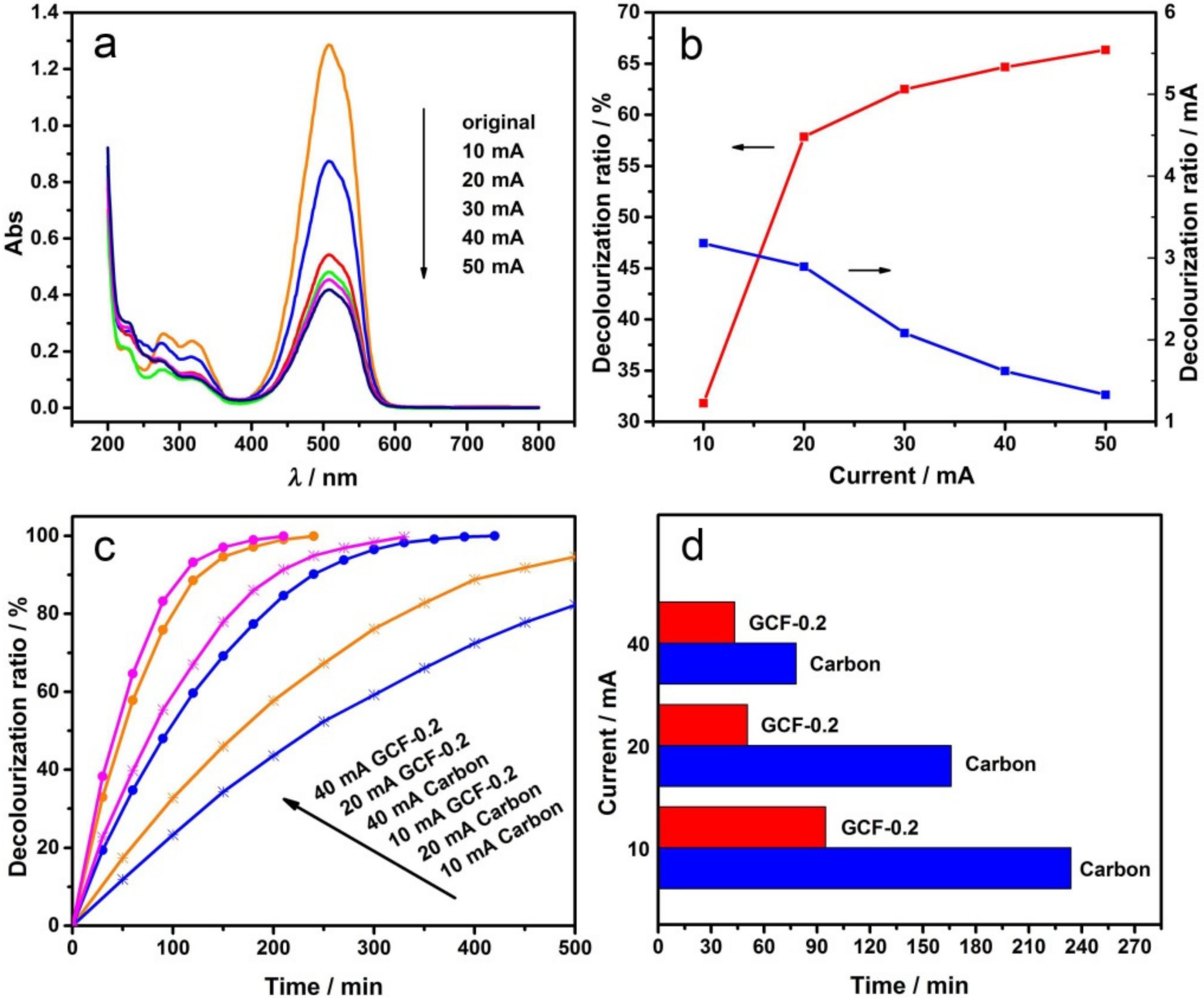
3.3. Effect of the Current Intensity
3.4. Effect of Degradation Temperatures
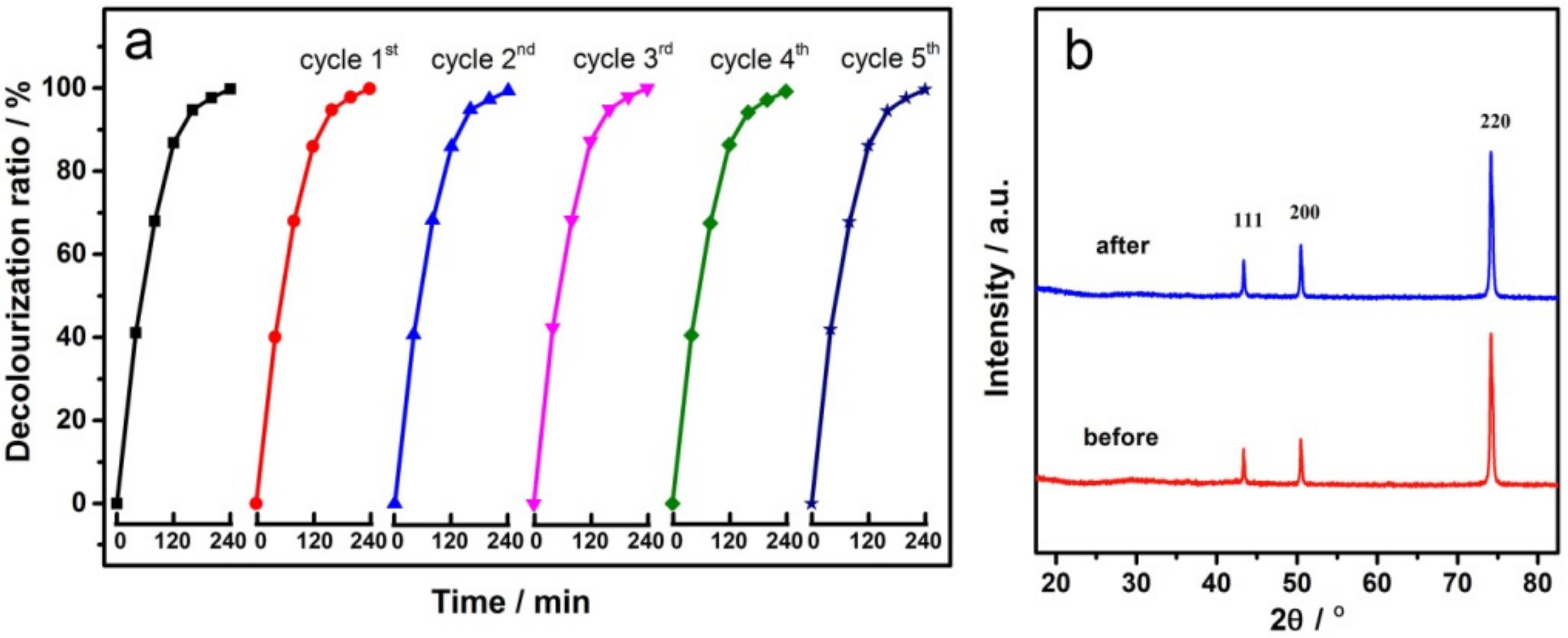
3.5. Recycling Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pavithra, K.G.; Kumar, P.S.; Jaikumar, V.; Rajan, P.S. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouk, B.; Gourich, B.; Madani, K.; Vial, C.; Sekki, A. Removal of a disperse red dye from synthetic wastewater by chemical coagulation and continuous electrocoagulation. A comparative study. Desalination 2011, 272, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Lin, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Enzymatic construction of antibacterial ultrathin membranes for dyes removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, D.; Kupka, D.; Vaclavikova, M.; Ivanicova, L.; Gallios, G. Degradation of reactive black 5 by electrochemical oxidation. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Rahim, W.M.; Moawad, H.; Abdel Azeiz, A.Z.; Sadowsky, M.J. Optimization of conditions for decolorization of azo-based textile dyes by multiple fungal species. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 260, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacan, E. Optimum BET surface areas for activated carbon produced from textile sewage sludges and its application as dye removal. J. Environ. Manage. 2016, 166, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; He, W.; Wang, A.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Huang, C.P. An activated carbon fiber cathode for the degradation of glyphosate in aqueous solutions by the Electro-Fenton mode: Optimal operational conditions and the deposition of iron on cathode on electrode reusability. Water Res. 2016, 105, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.; Fernández, J.; Del Río, A.I.; Bonastre, J.; Cases, F. Characterization of azo dyes on Pt and Pt/polyaniline/dispersed Pt electrodes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6246–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, L.; Xi, B. Efficient degradation of p-nitrophenol by electro-oxidation on Fe doped Ti/TiO2 nanotube/PbO2 anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Fan, J.; He, Z.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xu, X. Electrochemical degradation of azo dye C.I. Reactive red 195 by anodic oxidation on Ti/SnO2–Sb/PbO2 electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, A.I.D.; Benimeli, M.J.; Molina, J.; Bonastre, J.; Cases, F. Electrochemical treatment of C.I. Reactive black 5 solutions on stabilized doped Ti/SnO2 electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 7, 13074–13092. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Li, J. Preparation and electrochemical properties of Ce-Ru-SnO2 ternary oxide anode and electrochemical oxidation of nitrophenols. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Quiroz, M.A.; Comninellis, C.; Ferro, S.; Battisti, A.D. Electrochemical incineration of chloranilic acid using Ti/IrO2, Pb/PbO2 and Si/BDD electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyajjanavar, P.; Narayana, J.; Nayaka, Y.A. Degradation of textile dye C.I. Vat black 27 by electrochemical method by using carbon electrodes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, X.-R.; Sun, H.-Y.; Li, R.-P.; Fang, Y.-F.; Huang, Y.-P. The degradation of tetracycline in a photo-electro-Fenton system. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Bi, Z.; Yang, J. Electro-Fenton degradation of p-nitrophenol using the anodized graphite felts. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Rajic, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Qin, Y.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Rates of H2O2 electrogeneration by reduction of anodic O2 at RVC foam cathodes in batch and flow-through cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 277, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-T.; Chou, W.-L.; Chung, M.-H.; Kuo, Y.-M. COD removal from real dyeing wastewater by electro-Fenton technology using an activated carbon fiber cathode. Desalination 2010, 253, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, M.; Hu, Z.; Bi, Z.; Serrano, K.G. Chemically modified graphite felt as an efficient cathode in electro-Fenton for p-nitrophenol degradation. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 140, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gao, J.; Kou, K.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wu, S.; Qin, Y. Highly efficient H2O2 electrogeneration from O2 reduction by pulsed current: Facilitated release of H2O2 from porous cathode to bulk. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 83, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, M.; Oturan, N.; Oturan, M.A. Removal of methyl parathion from water by electrochemically generated Fenton’s reagent. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Ye, P.; Li, H.; Yan, Y. Novel flexible Fenton-like catalyst: Unique CuO nanowires arrays on copper mesh with high efficiency across a wide pH range. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L. Fabrication of novel nanoporous copper powder catalyst by dealloying of ZrCuNiAl amorphous powders for the application of wastewater treatments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Pan, Y.; Wu, S. Relationship between dealloying conditions and coarsening behaviors of nanoporous copper fabricated by dealloying Cu-Ce metallic glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liao, P.; Yuan, S.; Tong, M.; Luo, M.; Xie, W. Cu-catalytic generation of reactive oxidizing species from H2 and O2 produced by water electrolysis for electro-fenton degradation of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 233, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X. Cost-effective electro-Fenton using modified graphite felt that dramatically enhanced on H2O2 electro-generation without external aeration. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 163, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.M.; Lee, J.J. One-pot synthesis of copper nanoparticles on glass: Applications for non-enzymatic glucose detection and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 23, 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- Whang, T.-J.; Hsieh, M.-T.; Kao, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-J. A study of electrodeposition of CuInSe2 thin films with triethanolamine as the complexing agent. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4600–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Kanan, M.W. CO2 reduction at low overpotential on Cu electrodes resulting from the reduction of thick Cu2O films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7231–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszczuk, P.; Zelenay, P.; Sobkowski, J. Surface interaction of benzoic acid with a copper electrode. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oturan, M.A.; Oturan, N.; Lahitte, C.; Trevin, S. Production of hydroxyl radicals by electrochemically assisted Fenton’s reagent application to the mineralization of an organic micropollutant, pentachlorophenol. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 507, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Sires, I.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Rodriguez, R.M.; Garrido, J.A. Mineralization of paracetamol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, J.; Song, M.; Yang, M.; Tan, X.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Facile Preparation of Granular Copper Films as Cathode for Enhanced Electrochemical Degradation of Methyl Orange. Materials 2021, 14, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112697
Xing J, Song M, Yang M, Tan X, Li F, Wang X, Zhao J. Facile Preparation of Granular Copper Films as Cathode for Enhanced Electrochemical Degradation of Methyl Orange. Materials. 2021; 14(11):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112697
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Jiajie, Min Song, Mengyao Yang, Xu Tan, Fenglin Li, Xixin Wang, and Jianling Zhao. 2021. "Facile Preparation of Granular Copper Films as Cathode for Enhanced Electrochemical Degradation of Methyl Orange" Materials 14, no. 11: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112697
APA StyleXing, J., Song, M., Yang, M., Tan, X., Li, F., Wang, X., & Zhao, J. (2021). Facile Preparation of Granular Copper Films as Cathode for Enhanced Electrochemical Degradation of Methyl Orange. Materials, 14(11), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14112697