Effects of Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion of SN-9Zn Lead-Free Solders Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material Fabrication
2.2. Microstructural Observation
2.3. Wettability Measurements
2.4. Melting Point Test
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
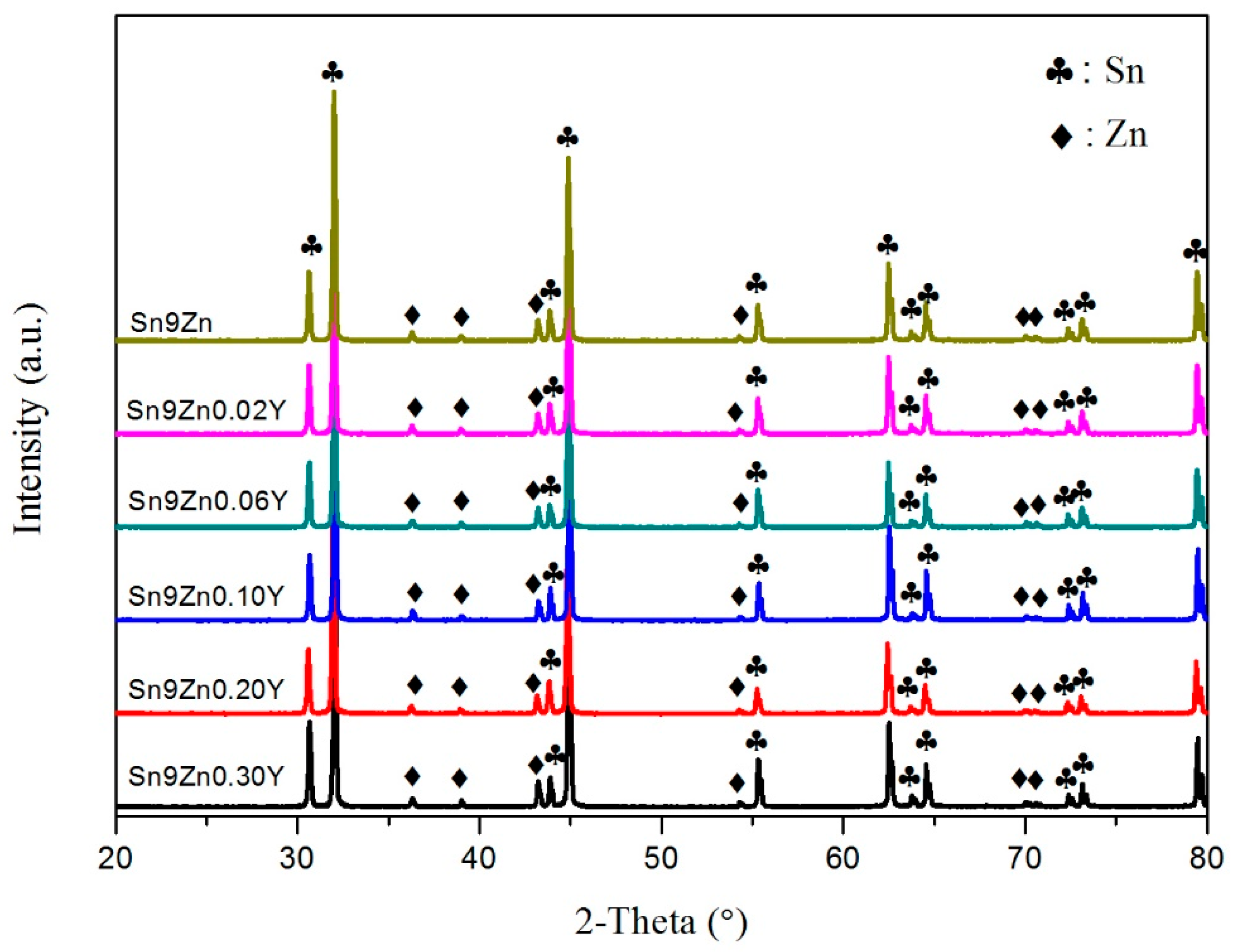
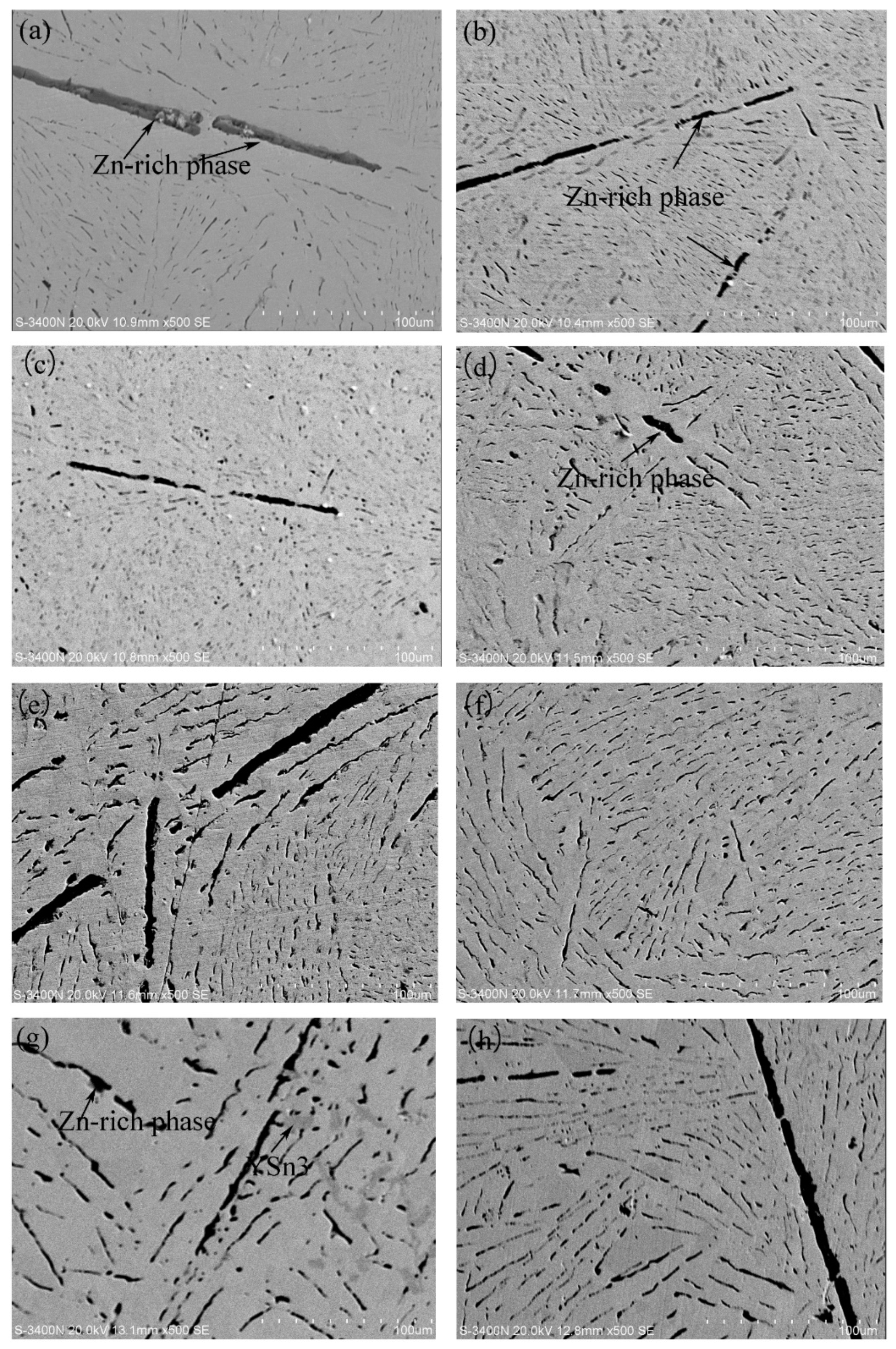
3.1. Microstructures of Sn-9Zn-xY Solder Alloys
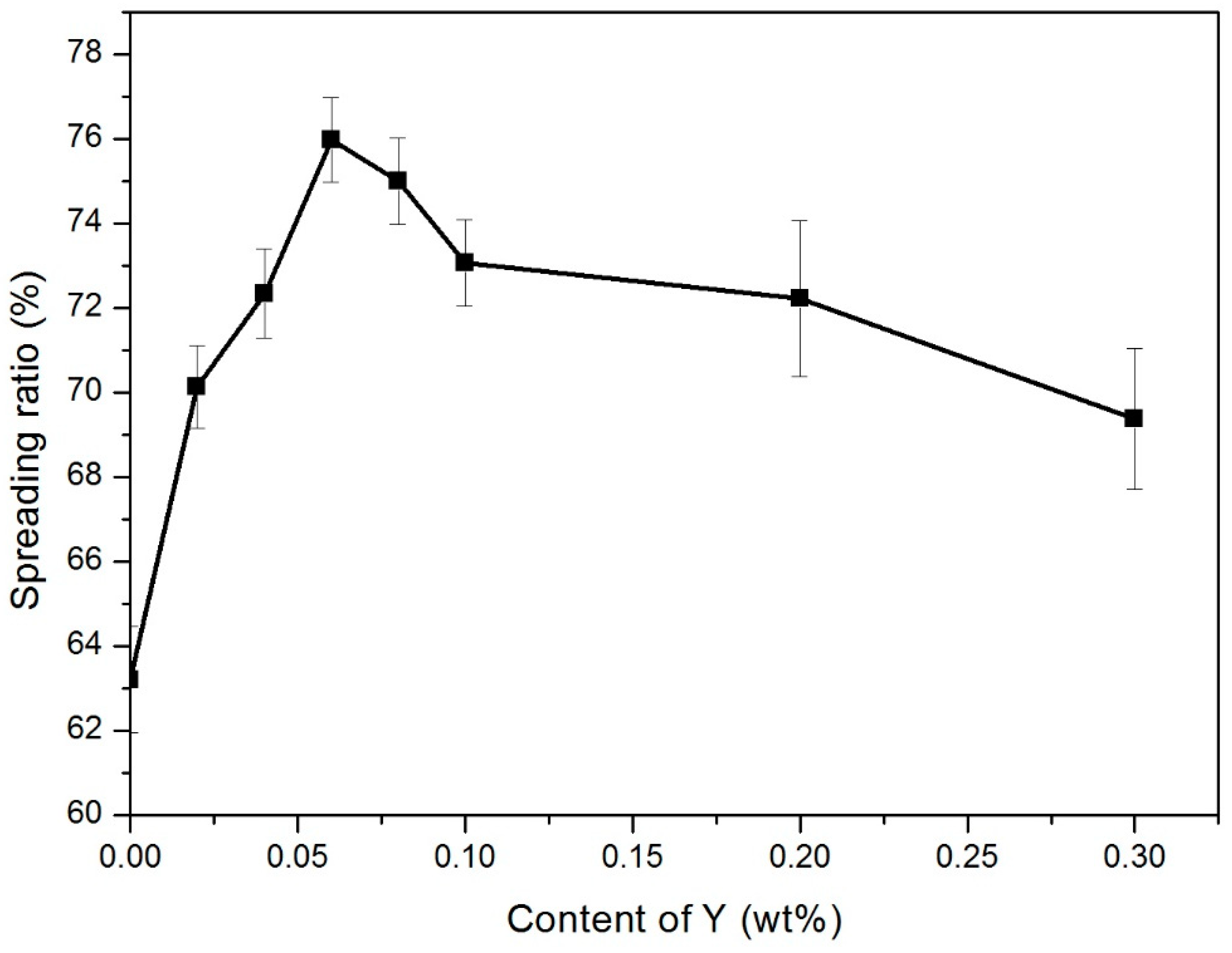
3.2. Wettability Analysis
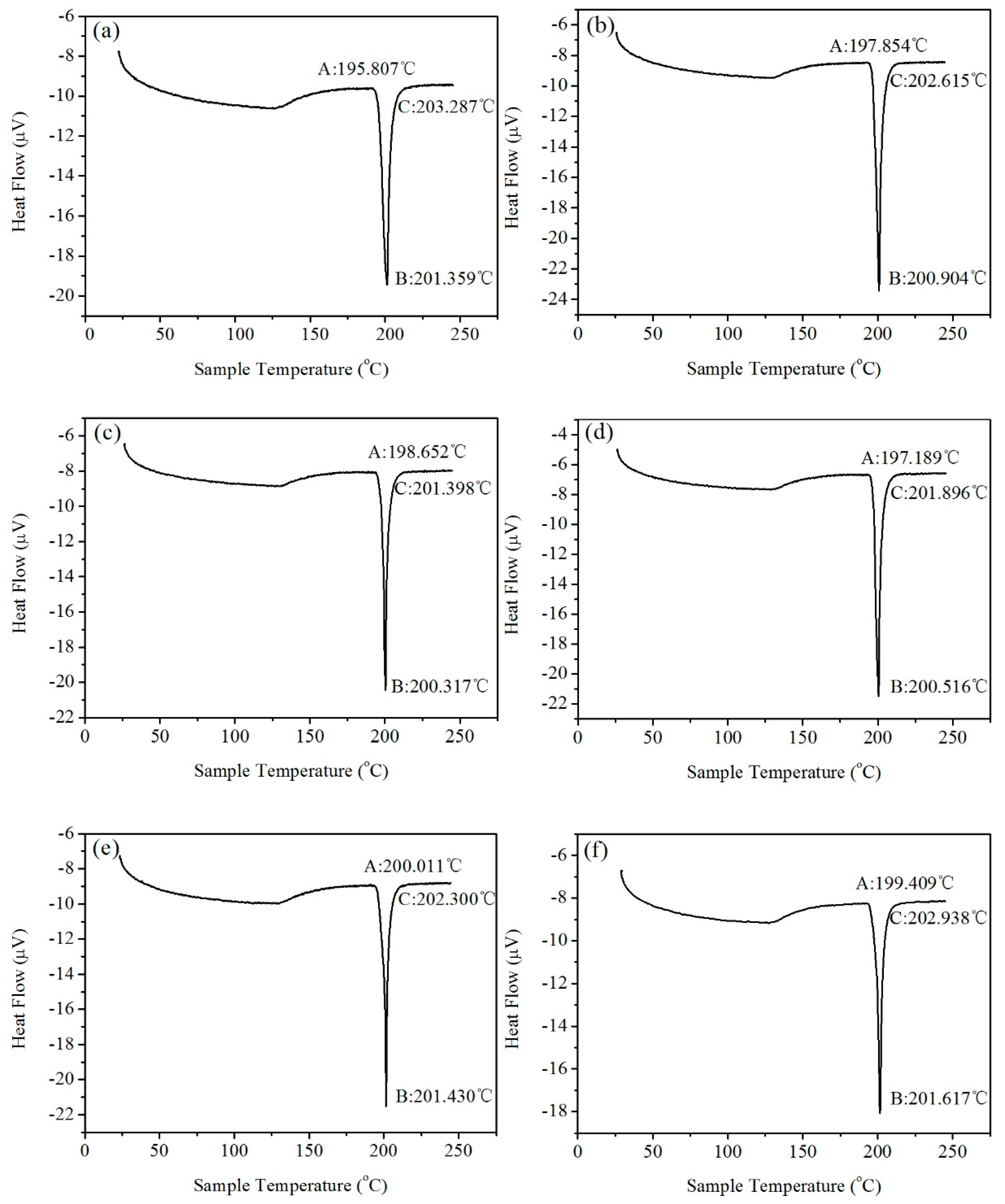
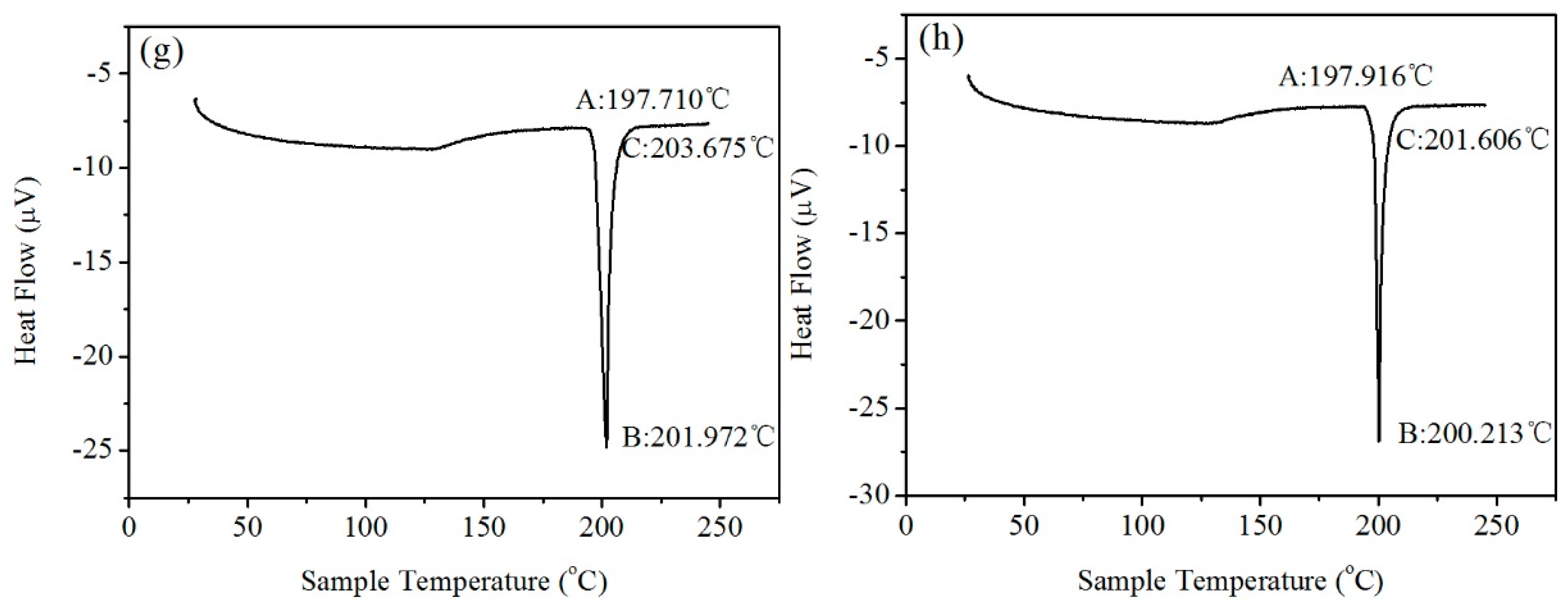
3.3. Melting Temperature
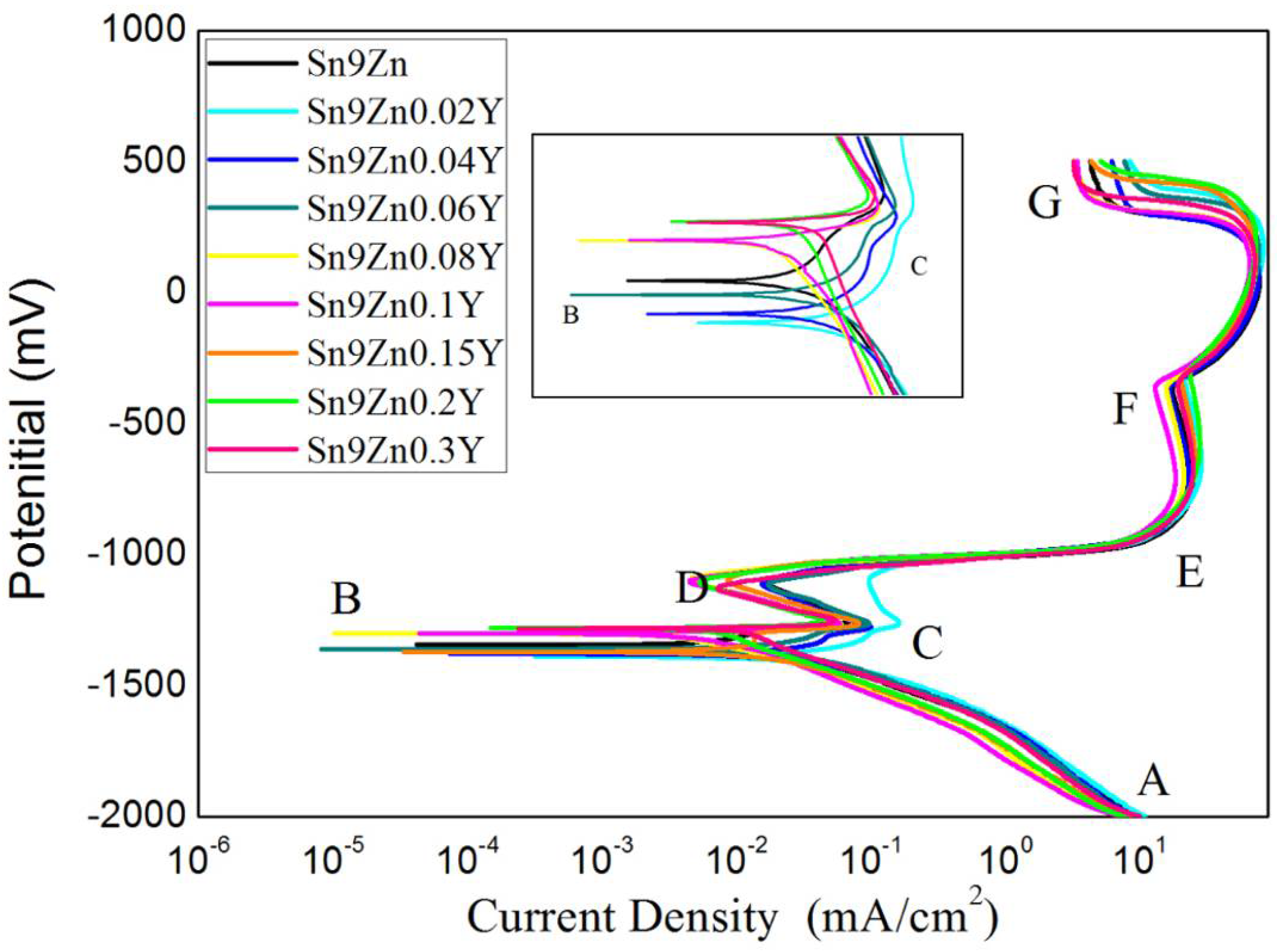
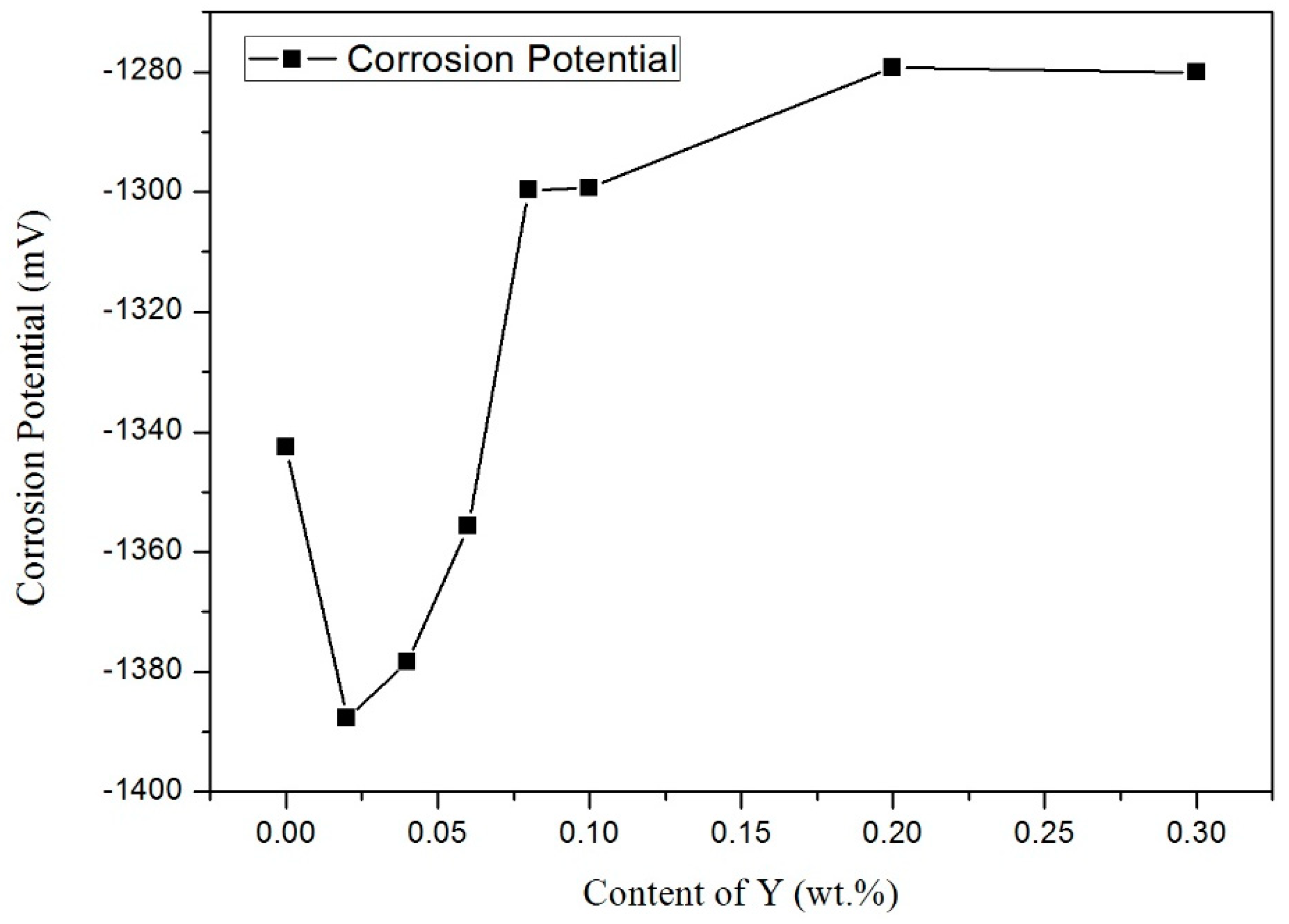
3.4. Electrochemical Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The addition of Y refined the Zn-rich phase of the matrix and made the Zn phase narrow and uniformly distributed. When the addition of Y was 0.06 wt.%, it showed the most significant refinement effect. However, when the content of Y continued to increase, YSn3 was unstable at high temperature in the matrix.
- The spreading rate of Sn-9Zn solder increased with the addition of Y. When the Y content was 0.06 wt.%, the wettability was the best. However, when the amount of Y added continued to increase, the wetting performance dropped sharply.
- The amount of Y added had no significant influence on the melting point and melting range of the alloy.
- Adding Y to Sn-9Zn improved the corrosion resistance of solder. When a small amount of Y was added, the corrosion resistance of the alloy was lower than that of Sn-9Zn. However, with the increase of Y content, the corrosion potential increased. When Y content was 0.06 wt.%, the corrosion potential of the alloy was close to that of the Sn-9Zn alloy. The corrosion potential increased with the increase of Y content, which was higher than that of Sn-9Zn, and tended to a stable value. The addition of Y can refine the Zn-rich phase of Sn-9Zn system and improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suganuma, K. Advances in lead-free electronics soldering. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2001, 5, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtew, M.; Selvaduray, G. Lead-free solders in microelectronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2000, 27, 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.O.; Chan, Y.C.; Tu, K.N. Effect of reaction time and P content on mechanical strength of the interface formed between eutectic Sn–Ag solder and Au/electroless Ni (P)/Cu bond pad. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 4108–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chada, S.; Fournelle, R.A.; Laub, W.; Shuangguan, D. Copper substrate dissolution in eutectic Sn-Ag solder and its effect on microstructure. J. Electron. Mater. 2000, 29, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumaan, M.S.; Shalaby, R.M.; Ali, E.A.M.; Kamal, M. Copper effects in mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of rapidly solidified eutectic Sn–Ag alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 8886–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Ho, C.E.; Kao, C.R. Effect of Cu concentration on the interfacial reactions between Ni and Sn–Cu solders. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.; Guo, F.; Xia, Z.D.; Lei, Y.P.; Yan, Y.F.; Liu, J.P.; Shi, Y.W. Processing and creep properties of Sn-Cu composite solders with small amounts of nanosized Ag reinforcement additions. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Xiong, M.-Y.; Sun, L. Structure and properties of Sn-Cu lead-free solders in electronics packaging. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Duh, J.G.; Chiou, B.S. The effect of substrate surface roughness on the wettability of Sn-Bi solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2000, 11, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yu, A.; Wang, J.; Liang, S.; Wei, M.; Zhan, Y.; et al. Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure and Properties of Non-Eutectic Sn-20Bi Solder Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Morris, J.W. Characterization of eutectic Sn-Bi solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 1992, 21, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, M.; Ren, X.X.; Hu, A.M.; Mao, D.L. Effect of small additions of alloying elements on the properties of Sn-Zn eutectic alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 2006, 35, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, K.; Kim, K.S. Sn-Zn low temperature solder. In Lead-Free Electronic Solders; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xue, S.-B.; Gao, L.-L.; Sheng, Z.; Ye, H.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Zeng, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, S.-L. Development of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, W.; Ma, Y.; Tang, C.; Tang, H.; Zhan, Y. The electrochemical corrosion behavior of Pb–free Sn–8.5 Zn–XCr solders in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 168, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Huh, S.H.; Suganuma, K. Effects of intermetallic compounds on properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free soldered joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 352, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Zhang, L. Interface reaction and intermetallic compound growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder joints on different substrates in electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 1741–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.L.; Liu, T.P. High-temperature oxidation of a Sn-Zn-Al solder. Oxid. Met. 1998, 50, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Xue, F. Properties of low melting point Sn–Zn–Bi solders. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 397, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Lan, G.F.; Lui, T.S.; Chen, L.H. Microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–9Zn–xAg lead-free solder alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Zhong, L. On the microstructure and mechanical property of as-extruded Mg-Sn-Zn alloy with Cu addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 744, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Tiwary, C.S.; Chattapadhyay, K. Effects of minute addition of Ni on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn-Zn eutectic alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 5468–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, T.; Bobrowski, P.; Pawlak, S.; Schell, N.; Chulist, R.; Janik, K. Wetting of Sn-Zn-Ga and Sn-Zn-Na Alloys on Al and Ni substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-E.; Kim, K.-S.; Inoue, M.; Jiang, J.; Suganuma, K. Effects of Ag and Cu addition on microstructural properties and oxidation resistance of Sn-Zn eutectic alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 454, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-C.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.-S.; Suganuma, K. Ti addition to enhance corrosion resistance of Sn–Zn solder alloy by tailoring microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 644, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Luo, T.; Hu, A.; Li, M.; Mao, D. Electrochemical corrosion behaviors of Sn-9Zn-3Bi-xCr solder in 3.5% NaCl solution. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Han, J.-G.; Guo, Y.-H.; He, C.-W. Properties of SnZn lead free solders bearing rare earth Y. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Hu, B.; Du, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, P.; Zheng, F.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J. Thermodynamic modeling of the Hf-Sn and Sn-Y systems. Calphad 2012, 39, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, Y.W.; Lei, Y.P.; Guo, F.; Xia, Z.D.; Zong, B. Effect of rare earth element addition on the microstructure of Sn–Ag–Cu solder joint. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.L.; Wong, Y.W. Rare-earth additions to lead-free electronic solders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2007, 18, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M.; Franklin, J.A. Potential-pH diagrams. (Book reviews: Atlas of electrochemical equilibria in aqueous solutions). Science 1966, 154, 1537. [Google Scholar]
- Latimer, W.M. Oxidation Potentials. Second Edition. Soil Sci. 1952, 74, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Tian, J.; Shi, Y.W.; Lei, Y.P.; Xia, Z.D. Properties of Sn3.8Ag0.7Cu solder alloy with trace rare earth element Y additions. J. Electron. Mater. 2007, 36, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayarathna, D.; Hale, E.; O’Keefe, T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Radovic, D. Effects of sample orientation on the corrosion of zinc in ammonium sulfate and sodium hydroxide solutions. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N.; Davies, C.H.J. Revealing the relationship between grain size and corrosion rate of metals. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osório, W.R.; Garcia, L.R.; Peixoto, L.C.; Garcia, A. Electrochemical behavior of a lead-free SnAg solder alloy affected by the microstructure array. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4763–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Solder Alloy | Sn (wt.%) | Zn (wt.%) | Y (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sn9Zn | 91.00 | 9 | 0 |
| Sn9Zn0.02Y | 90.98 | 9 | 0.02 |
| Sn9Zn0.04Y | 90.96 | 9 | 0.04 |
| Sn9Zn0.06Y | 90.94 | 9 | 0.06 |
| Sn9Zn0.08Y | 90.92 | 9 | 0.08 |
| Sn9Zn0.10Y | 90.90 | 9 | 0.1 |
| Sn9Zn0.20Y | 90.80 | 9 | 0.2 |
| Sn9Zn0.30Y | 90.70 | 9 | 0.3 |
| Solder Alloy | Solid Phase Line, °C | Melting Point, °C | Melting Range, °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sn9Zn | 195.8 | 201.4 | 5.6 |
| Sn9Zn0.02Y | 197.8 | 200.9 | 3.1 |
| Sn9Zn0.04Y | 198.7 | 200.3 | 1.6 |
| Sn9Zn0.06Y | 197.2 | 200.5 | 3.3 |
| Sn9Zn0.08Y | 200.0 | 201.4 | 1.4 |
| Sn9Zn0.10Y | 199.4 | 201.6 | 2.2 |
| Sn9Zn0.20Y | 197.7 | 201.9 | 4.2 |
| Sn9Zn0.30Y | 197.9 | 200.2 | 2.3 |
| Y (wt.%) | Icorr (mA/cm2) × 10−3 | Ecorr (mV) | Corrosion Rate (mm/a) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3.81 | −1342.6 | 0.096 |
| 0.02 | 39.6 | −1387.7 | 0.996 |
| 0.04 | 21.6 | −1378.3 | 0.548 |
| 0.06 | 7.43 | −1355.7 | 0.188 |
| 0.08 | 2.09 | −1299.7 | 0.053 |
| 0.1 | 3.27 | −1299.3 | 0.083 |
| 0.2 | 4.39 | −1279.3 | 0.111 |
| 0.3 | 5.27 | −1280.1 | 0.133 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, W.; Mao, J.; Ma, Y.; Yu, S.; He, H.; Qi, D.; Zhan, Y. Effects of Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion of SN-9Zn Lead-Free Solders Alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102549
Yang W, Mao J, Ma Y, Yu S, He H, Qi D, Zhan Y. Effects of Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion of SN-9Zn Lead-Free Solders Alloy. Materials. 2021; 14(10):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102549
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Wenchao, Jun Mao, Yueyuan Ma, Shuyuan Yu, Hongping He, Da Qi, and Yongzhong Zhan. 2021. "Effects of Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion of SN-9Zn Lead-Free Solders Alloy" Materials 14, no. 10: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102549
APA StyleYang, W., Mao, J., Ma, Y., Yu, S., He, H., Qi, D., & Zhan, Y. (2021). Effects of Yttrium Addition on the Microstructure Evolution and Electrochemical Corrosion of SN-9Zn Lead-Free Solders Alloy. Materials, 14(10), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14102549






