Immobilization of Dextranase on Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Recyclable Catalyst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Immobilization of Dextranase on HA
2.3. Optimization of Immobilizing Parameters
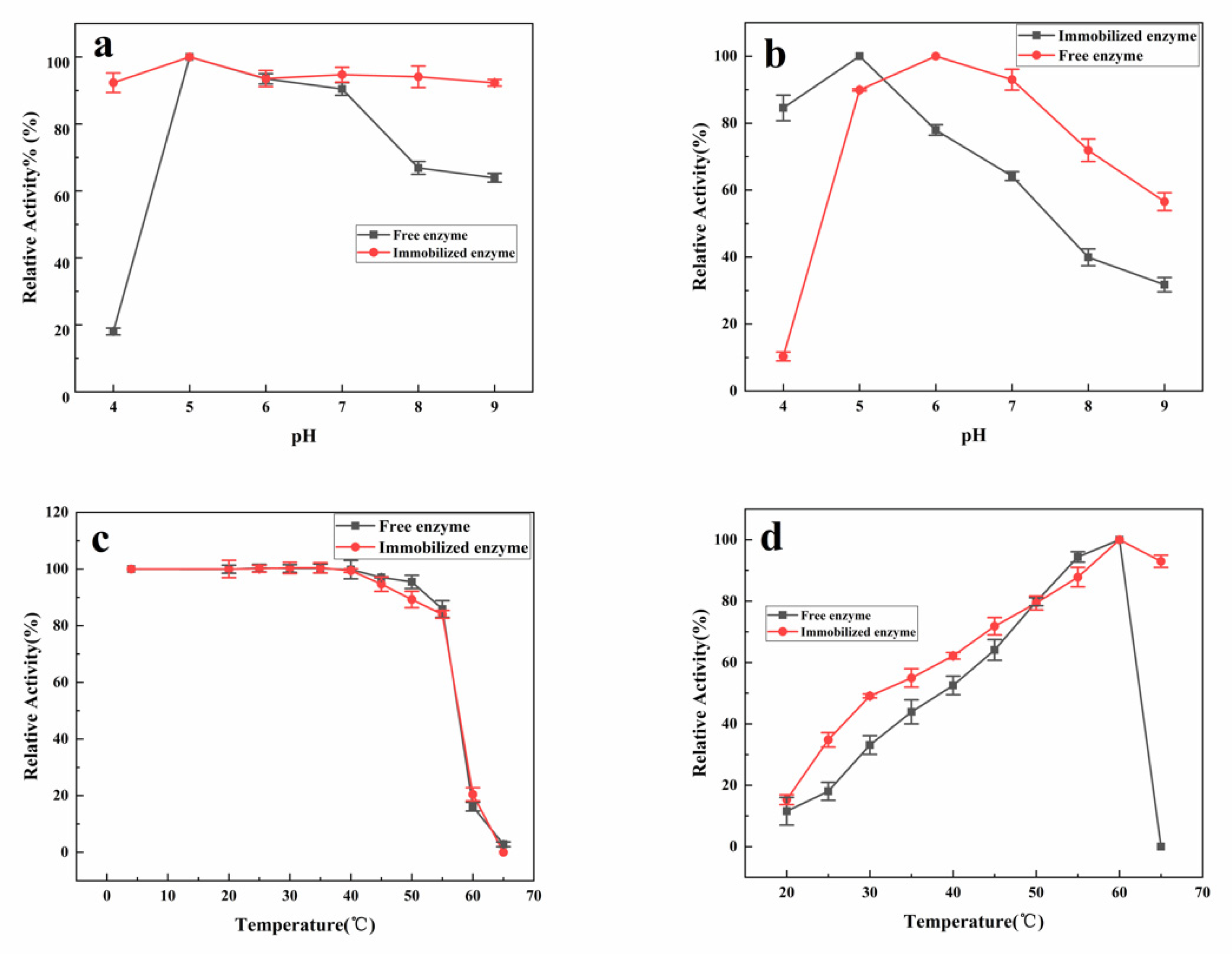
2.4. The Properties of Immobilized Dextranase
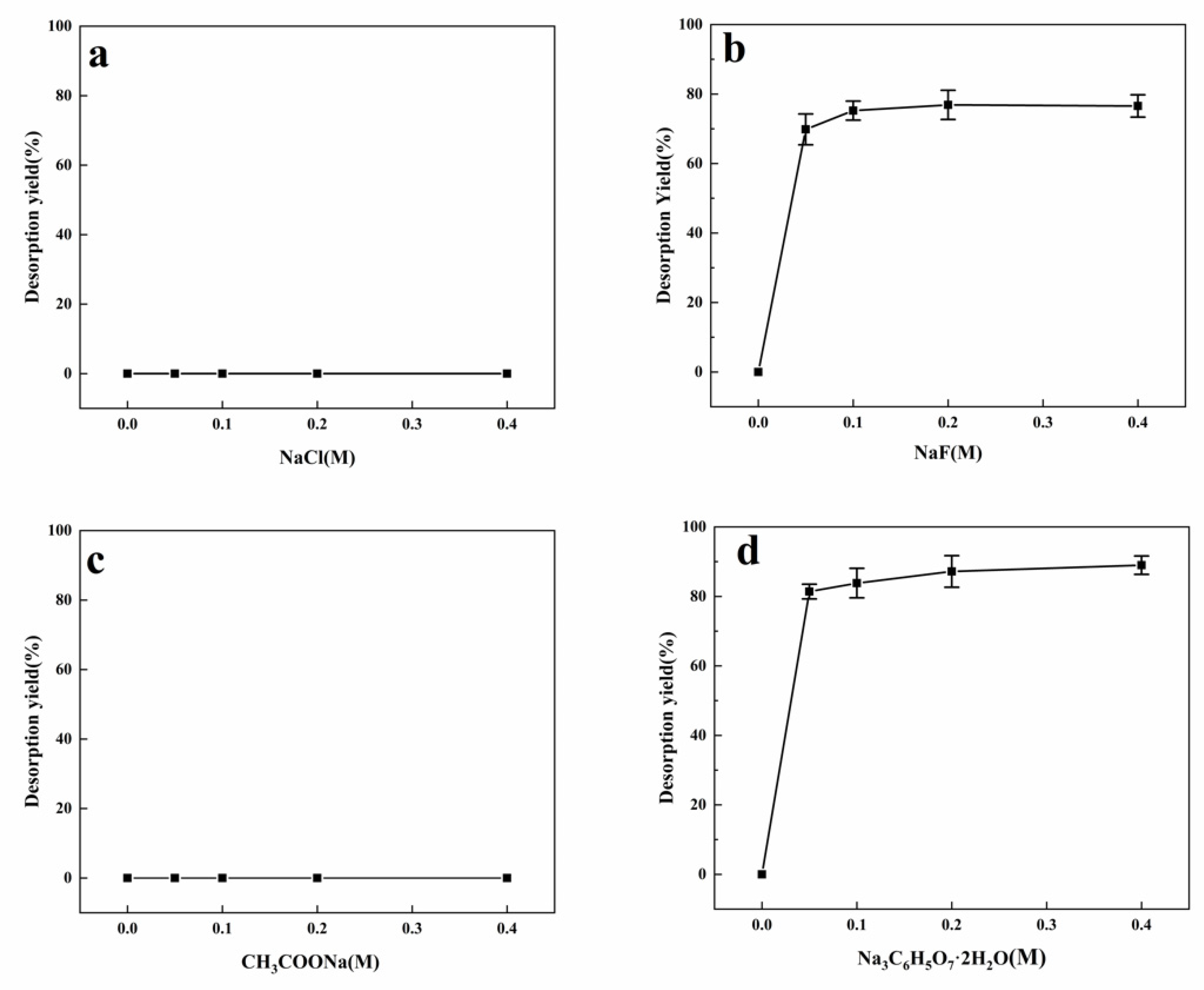
2.5. Desorption by Sodium Salts
2.6. Characterization Methods
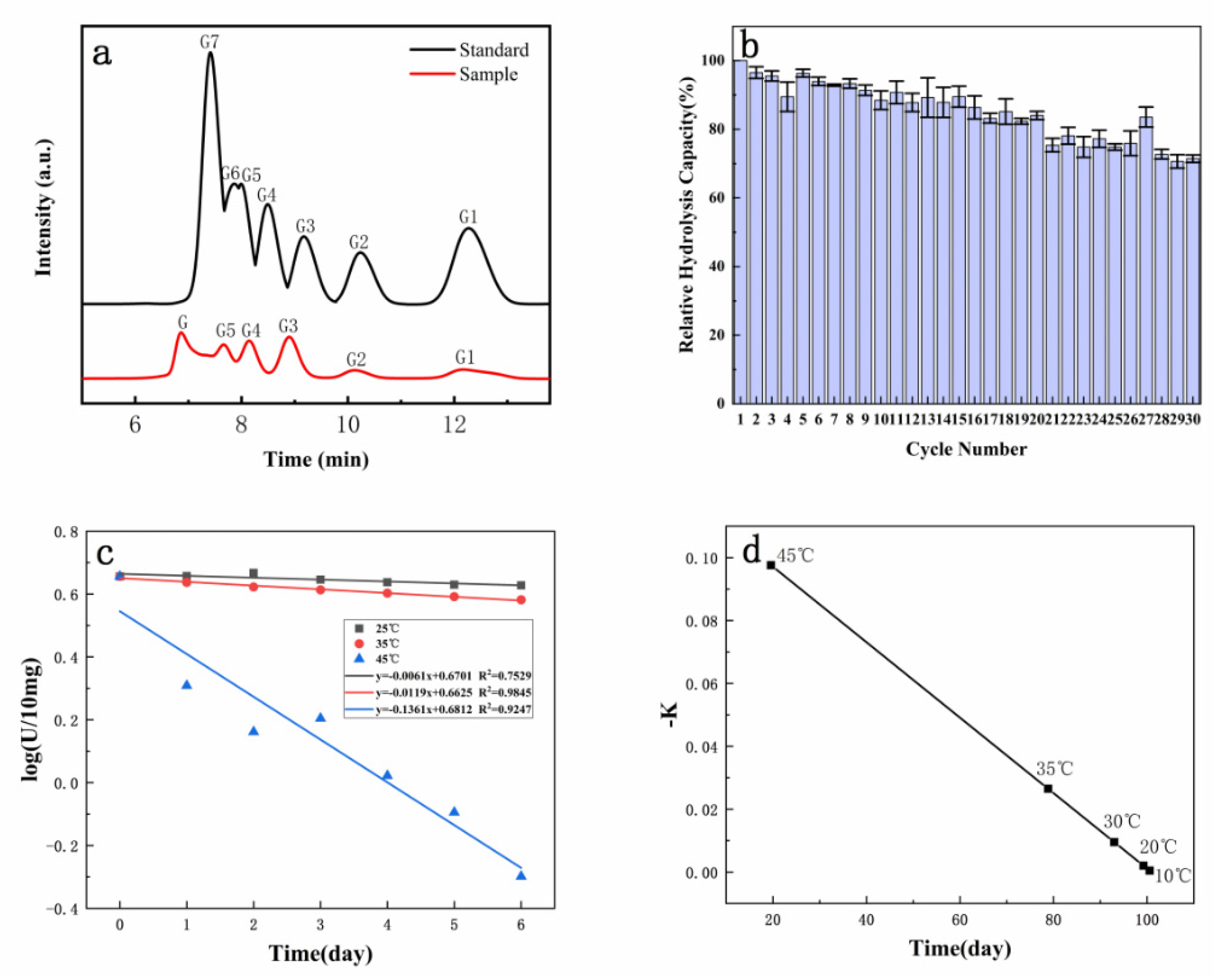
2.7. The Hydrolysates of Immobilized Dextranase
2.8. Stability of Reuse and Storage
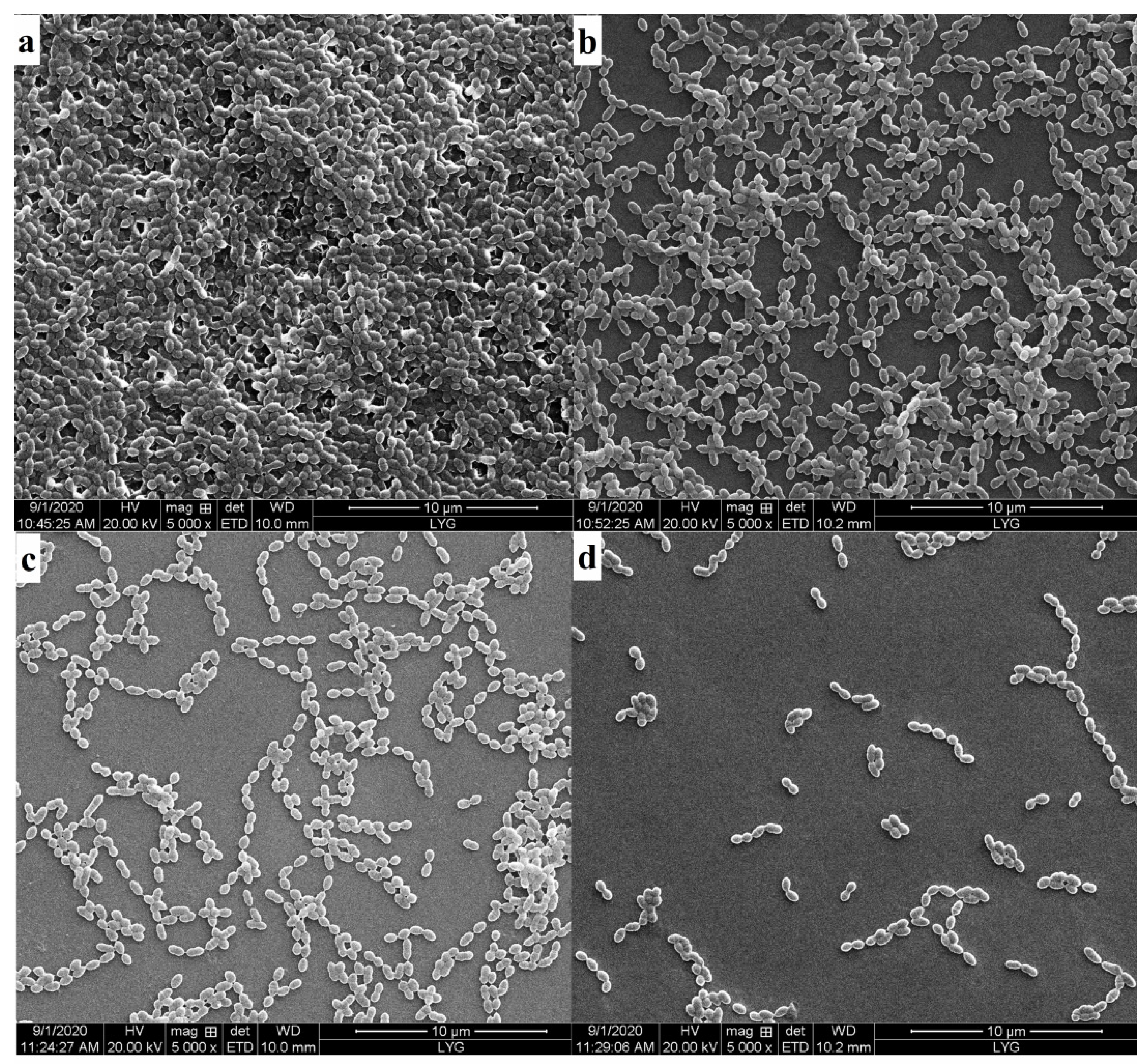
2.9. Removal of the Dental Plaque Biofilm
3. Results
3.1. Immobilization Condition
3.2. Characteristics of Immobilized Dextranase
3.3. Desorption by Sodium Salts
3.4. Detection of Immobilized Dextranase
3.5. The Hydrolysates and Recyclable Catalysts
3.6. Degradation of Dental Plaque Biofilm
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y. Expression, purification and characterization of a recombinant Lipomyces starkey dextranase in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 2008, 58, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, D. Characterization of novel thermostable dextranase from Thermotoga lettingae TMO. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kiso, Y.; Muraki, T.; Kang, M.S.; Nakai, H.; Saburi, W.; Lang, W.; Kang, H.K.; Okuyama, M.; Mori, H.; et al. Novel dextranase catalyzing cycloisomaltooligosaccharide formation and identification of catalytic amino acids and their functions using chemical rescue approach. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19927–19935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Seo, M.-Y.; Kang, H.-K.; Atsuo, K.; Kim, D. Construction of a fusion enzyme of dextransucrase and dextranase: Application for one-step synthesis of isomalto-oligosaccharides. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2009, 44, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkel, F.; Wefers, D. Fine structures of different dextrans assessed by isolation and characterization of endo-dextranase liberated isomalto-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Polym. 2019, 215, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.-J.; Jin, X.; Lee, J.-H.; Woo, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, G.J.; Seo, E.-S.; Kang, H.-K.; Kim, J.; Cho, D.-L.; et al. Optimal expression and characterization of a fusion enzyme having dextransucrase and dextranase activities. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2010, 47, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Zhao, Y.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Magnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers for enzymes immobilization: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2530–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, D.; Du, W.; Wang, Y. Progress & prospect of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for enzyme immobilization (enzyme/MOFs). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-M.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-P. Advances on methods and easy separated support materials for enzymes immobilization. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Torger, B.; Allertz, P.J.; Jähnichen, K.; Keßler, S.; Müller, M.; Simon, F.; Salchert, K.; Mäurer, H.; Pospiech, D. Multifunctional crosslinkable itaconic acid copolymers for enzyme immobilization. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 102, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadar, S.S.; Rathod, V.K. Magnetic-metal organic framework (magnetic-MOF): A novel platform for enzyme immobilization and nanozyme applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjana, S.; Medha, M.U.; Meghna, M.R.; Shruthi, T.S.; Srinivas, S.P.; Madhyastha, H.; Navya, P.N.; Daima, H.K. Enzyme immobilization on quercetin capped gold and silver nanoparticles for improved performance. Mater. Today: Proc. 2019, 10, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, W. Preparation of chitosan-based nanoparticles for enzyme immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, U.; Dogan, M.; Metin, A.U.; Baglar, S.; Turkoz, M.B.; Turk, M.; Nezir, S. Hydroxyapatite-based nanoparticles as a coating material for the dentine surface: An antibacterial and toxicological effect. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Labaki, M.; Giraudon, J.-M.; Lamonier, J.-F. Hydroxyapatite, a multifunctional material for air, water and soil pollution control: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasker, P.; Samanta, A.; Rudra, S.; Sinha, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Das, M. Effect of fluorine substitution on sintering behaviour, mechanical and bioactivity of hydroxyapatite. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 95, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, K.; Vidhya, G.; Girija, E.K.; Ashok, M. Fabrications of magnetic responsive hydroxyapatite platform: In vitro release of chemo drug for cancer therapy. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 3579–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, T.C.; Rojas, M.J.; Tardioli, P.W.; Paris, E.C.; Farinas, C.S. Nanoimmobilization of beta-glucosidase onto hydroxyapatite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, H.; Gyotoku, A.; Seto, H.; Ohto, K.; Harada, H.; Inoue, K. Dextran formation on hydroxyapatite by immobilized dextransucrase to control protein adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zang, X. Covalent immobilization of lipase onto aminopropyl-functionalized hydroxyapatite-encapsulated-gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: A magnetic biocatalyst for interesterification of soybean oil. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakoolwannachai, V.; Kheolamai, P.; Ummartyotin, S. Development of hydroxyapatite from eggshell waste and a chitosan-based composite: In vitro behavior of human osteoblast-like cell (Saos-2) cultures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turlybekuly, A.; Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Sukhodub, L.F.; Sukhodub, L.B.; Kistaubayeva, A.S.; Savitskaya, I.S.; Shokatayeva, D.H.; Bondar, O.V.; Shaimardanov, Z.K.; Plotnikov, S.V.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro biocompatibility and antibacterial properties study of nanocomposite materials based on hydroxyapatite-biphasic ZnO micro- and nanoparticles embedded in Alginate matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. CMater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Wunder, A.; Auschill1, T.M.; Follo, M.; Braun, G.; Hellwig, E.; Arweiler, N. The in vivo dynamics of Streptococcus spp., Actinomyces naeslundii, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Veillonella spp. in dental plaque biofilm as analysed by five-colour multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization. J. Med Microbiol. 2007, 56, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lyu, M. Dextranase from Arthrobacter oxydans KQ11: Identifification of key residues in catalysis. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Deka, J.R.; Saikia, D.; Lai, Y.-S.; Tsai, C.-H.; Chang, W.-C.; Kao, H.-M. Roles of nanostructures and carboxylic acid functionalization of ordered cubic mesoporous silicas in lysozyme immobilization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 213, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wang, Z.; Peng, D.; Shen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Cheng, S.; Li, B.; Huang, Q. Effect of linear charge density of polysaccharides on interactions with α-amylase: Self-Assembling behavior and application in enzyme immobilization. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornecki, J.F.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Siar, E.H.; Kashefi, S.; Chafiaa, M.; Arana-Peña, S.; Rios, N.S.; Gonçalves, L.R.B.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Influence of phosphate anions on the stability of immobilized enzymes. Effect of enzyme nature, immobilization protocol and inactivation conditions. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Song, S.; Gu, W. Biomimetic mineralization of calcium carbonate/carboxymethylcellulose microspheres for lysozyme immobilization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1982–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.J.F.; Comunian, T.A.; Kasemodel, M.G.C.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Microencapsulation of lactase by W/O/W emulsion followed by complex coacervation: Effects of enzyme source, addition of potassium and core to shell ratio on encapsulation efficiency, stability and kinetics of release. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Verma, A.; Satlewal, A. Application of nanoparticle-immobilized thermostable beta-glucosidase for improving the sugarcane juice properties. Innovative Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade Neto, D.M.; Carvalho, E.V.; Rodrigues, E.A.; Feitosa, V.P.; Sauro, S.; Mele, G.; Carbone, L.; Mazzetto, S.E.; Rodrigues, L.K.; Fechine, P.B. Novel hydroxyapatite nanorods improve anti-caries efficacy of enamel infiltrants. Dent. Mater. Off. Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuma, K.; Yamagishi, K.; Oyane, A. Nucleation and growth of hydroxyapatite nanocrystals for nondestructive repair of early caries lesions. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 282, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Additives | Biofilm Removal Rate |
|---|---|
| Control | 0.00 ± 8.66 |
| Free Enzyme | 14.32 ± 12.29 |
| HA | 52.56 ± 9.64 |
| Immobilized Enzyme | 86.44 ± 1.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zu, H.; Wang, C.; Dong, D.; Lyu, M.; Wang, S. Immobilization of Dextranase on Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Recyclable Catalyst. Materials 2021, 14, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010130
Ding Y, Zhang H, Wang X, Zu H, Wang C, Dong D, Lyu M, Wang S. Immobilization of Dextranase on Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Recyclable Catalyst. Materials. 2021; 14(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yanshuai, Hao Zhang, Xuelian Wang, Hangtian Zu, Cang Wang, Dongxue Dong, Mingsheng Lyu, and Shujun Wang. 2021. "Immobilization of Dextranase on Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Recyclable Catalyst" Materials 14, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010130
APA StyleDing, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Zu, H., Wang, C., Dong, D., Lyu, M., & Wang, S. (2021). Immobilization of Dextranase on Nano-Hydroxyapatite as a Recyclable Catalyst. Materials, 14(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010130







