Relevant Design Aspects to Improve the Stability of Titanium Dental Implants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindquist, L.W.; Rockler, B.; Carlsson, G.E. Bone resorption around fixtures in edentulous patients treated with mandibular fixed tissue-integrated prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1988, 59, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevins, M.; Langer, B. The successful application of osseointegrated implants to the posterior jaw: A long-term retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1993, 8, 428–432. [Google Scholar]
- Fugazzotto, P.A.; Gulbransen, H.J.; Wheeler, S.L.; Lindsay, J.A. The use of IMZ osseointegrated implants in partially and completely edentulous patients: Success and failure rates of 2,023 implant cylinders up to 60+ months in function. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1993, 8, 617–621. [Google Scholar]
- Buser, D.; Sennerby, L.; De Bruyn, H. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2016, 73, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Chappuis, V.; Belser, U.C.; Chen, S. Implant placement post extraction in esthetic single tooth sites: When immediate, when early, when late? Periodontol. 2000 2016, 73, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagter, K.W.; Hartog, L.D.; Bakker, N.A.; Vissink, A.; Meijer, H.J.; Raghoebar, G.M. Immediate Placement of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, e241–e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Carrion, J.; Carral, C.; Argibay, O.; Liñares, A. Implant placement in fresh extraction sockets. Periodontol. 2000 2019, 79, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Buser, D. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2009, 24, 186–217. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Polyzos, I.P.; Felice, P.; Worthington, H.V. Timing of implant placement after tooth extraction: Immediate, immediate-delayed or delayed implants? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur. J. Oral Implant. 2010, 3, 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, N.P.; Pun, L.; Lau, K.Y.; Li, K.Y.; Wong, M.C. A systematic review on survival and success rates of implants placed immediately into fresh extraction sockets after at least 1 year. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23 (Suppl. 5), 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-Ba, G.; Oates, T.W.; Williams, M.A.H. Immediate loading vs. early/conventional loading of immediately placed implants in partially edentulous patients from the patients’ perspective: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallucci, G.O.; Hamilton, A.; Zhou, W.; Buser, D.; Chen, S. Implant placement and loading protocols in partially edentulous patients: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 106–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerle, C.H.F.; Glauser, R. Clinical evaluation of dental implant treatment. Periodontol. 2000 2004, 34, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.M.; Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Jensen, O.T. Minimum Criteria for Immediate Provisionalization of Single-Tooth Dental Implants in Extraction Sites: A 1-Year Retrospective Study of 100 Consecutive Cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Maghaireh, H.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: Different times for loading dental implants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD003878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Santos-García, R.; Jaramillo-Santos, R.; Romero-Ruiz, M.M.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Lázaro-Calvo, P.; Bullón, P.; Ríos-Santos, J.V. Assessment of Osstell ISQ’s reliability for implant stability measurement: A cross-sectional clinical study. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e877–e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, A.; Alvarez-Arenal, A.; Gil, F.J.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Prado, D.C.; Chento-Valiente, Y.; Diéguez, M. Relationship Between Insertion Torque and Resonance Frequency Measurements, Performed by Resonance Frequency Analysis, in Micromobility of Dental Implants. Implant. Dent. 2015, 24, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E.; Basha-Hijazi, A.; Gupta, B.; Ren, Y.F.; Malmstrom, H. Role of clinician’s experience and implant design on implant stability. An ex vivo study in artificial soft bones. Clin. Implant Dent Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.V.; Elias, C.N.; Lima, J.H.C. The Effects of Superficial Roughness and Design on the Primary Stability of Dental Implants. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 13, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Menjívar-Galán, A.M.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Rios-Carrasco, B.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Pérez, R.; Gil, F.J. Unravelling the effect of macro and microscopic design of dental implants on osseointegration: A randomised clinical study in minipigs. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, M.; Irastorza-Landa, A. Does implant design affect primary stability in extraction sites? Quintessence Int. 2017, 48, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L. Effects of occlusal forces on the peri-implant-bone interface stability. Periodontol. 2000 2019, 81, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila, E.; Ortiz-Hernández, M.; Perez, R.A.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Cerrolaza, M.; Gil, F.J. Crestal module design optimization of dental implants: Finite element analysis and in vivo studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trisi, P.; Berardini, M.; Falco, A.; Vulpiani, M.P. Effect of Implant Thread Geometry on Secondary Stability, Bone Density, and Bone-to-Implant Contact. Implant. Dent. 2015, 24, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.-H.; Du, J.-K.; Pan, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-E.; Chung, W.-H. Biomechanical analysis of alveolar bone stress around implants with different thread designs and pitches in the mandibular molar area. Clin. Oral Investig. 2011, 16, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.-S.; Namgung, C.; Lee, J.-H.; Lim, Y.-J. The influence of thread geometry on implant osseointegration under immediate loading: A literature review. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenga, J.T.; Al-Shammari, K.F.; Nociti, F.H.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.-L. Dental implant design and its relationship to long-term implant success. Implant. Dent. 2003, 12, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, F.; Ahmed, H.B.; Crespi, R.; Romanos, G.E. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2013, 5, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wu, G.; Hu, K.; Kong, L. Optimal design of thread height and width on an immediately loaded cylinder implant: A finite element analysis. Comput. Boil. Med. 2010, 40, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.G., Jr.; Miller, R.; Trushkowsky, R.; Dard, M. Tapered Implants in Dentistry. Adv. Dent. Res. 2016, 28, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, A.; Ćalasan, D.; Colic, S.; Stojcev-Stajcic, L.; Janjić, B.; Mišić, T. Implant stability in posterior maxilla: Bone-condensing versus bone-drilling: A clinical study. Oral Surgery, Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2011, 112, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Lazić, Z.; Gómez-Moreno, G.; Ćalasan, D.; Guardia, J.; Colic, S.; Dds, A.A.; Gacic, B.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.; et al. Evaluation of Primary Stability of Self-Tapping and Non-Self-Tapping Dental Implants. A 12-Week Clinical Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 15, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoshima, T.; Wagner, W.; Klein, M.O.; Stender, E.; Wieland, M.; Al-Nawas, B. Primary Stability of a Hybrid Self-Tapping Implant Compared to a Cylindrical Non-Self-Tapping Implant with Respect to Drilling Protocols in an Ex Vivo Model. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 13, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irinakis, T.; Wiebe, C. Initial Torque Stability of a New Bone Condensing Dental Implant. A Cohort Study of 140 Consecutively Placed Implants. J. Oral Implant. 2009, 35, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, D.; Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Influence of implant taper on the primary and secondary stability of osseointegrated titanium implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yi, Y.-J. A randomized controlled clinical trial of two types of tapered implants on immediate loading in the posterior maxilla and mandible. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.S.W.; Yeung, S.C.H.; Zee, K.Y.; Hell, P.; Tumuluri, V.; Curtis, B. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of NobelActiveTM dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 24, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waechter, J.; Madruga, M.D.M.; Filho, L.C.D.C.; Leite, F.R.M.; Schinestsck, A.R.; Faot, F. Comparison between tapered and cylindrical implants in the posterior regions of the mandible: A prospective, randomized, split-mouth clinical trial focusing on implant stability changes during early healing. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1999, 11, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Swami, V.; Vijayaraghavan, V.; Swami, V. Current trends to measure implant stability. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2016, 16, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Castro, M.C.; Falcao, A.; López-Jarana, P.; Falcao, C.; Ríos-Santos, J.-V.; Fernández-Palacín, A.; Herrero-Climent, M. Repeatability of the resonance frequency analysis values in implants with a new technology. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, e636–e642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Falcão, A.; López-Jarana, P.; Díaz-Castro, C.M.; Ríos-Carrasco, B.; Ríos-Santos, J.V. In vitro comparative analysis of two resonance frequency measurement devices: Osstell implant stability coefficient and Penguin resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Lee, J.M.; Maniatopoulos, C. Observations on the Effect of Movement on Bone Ingrowth into Porous-Surfaced Implants. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1986, 1986, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msc, F.S.L.; Douglas-De-Oliveira, D.W.; Costa, F.O. Relationship between implant stability measurements obtained by insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis: A systematic review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 20, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padrós, A. Fracture and fatigue behavior of shot-blasted titanium dental implants. Implant. Dent. 2002, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Sevilla, P. Fatigue Life of Bioactive Titanium Dental Implants Treated by Means of Grit-Blasting and Thermo-Chemical Treatment. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Albertini, M.; Rios-Santos, J.V.; Lazaro-Calvo, P.; Fernandez-Palacin, A.; Bullon, P. Resonance frequency analysis-reliability in third generation instruments: Osstell mentor(R). Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e801–e806. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, R.; Al-Nawas, B.; Araujo, M.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Barter, S.; Brodala, N.; Chappuis, V.; Chen, B.; De Souza, A.; Faria-Almeida, R.; et al. Group 1 ITI Consensus Report: The influence of implant length and design and medications on clinical and patient-reported outcomes. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanos, G.E.; Ciornei, G.; Jucan, A.; Malmstrom, H.; Gupta, B. In vitro assessment of primary stability of Straumann(R) implant designs. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Shiota, M.; Munakata, M.; Kasugai, S.; Ozeki, M. Effect of implant design on primary stability using torque-time curves in artificial bone. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2015, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
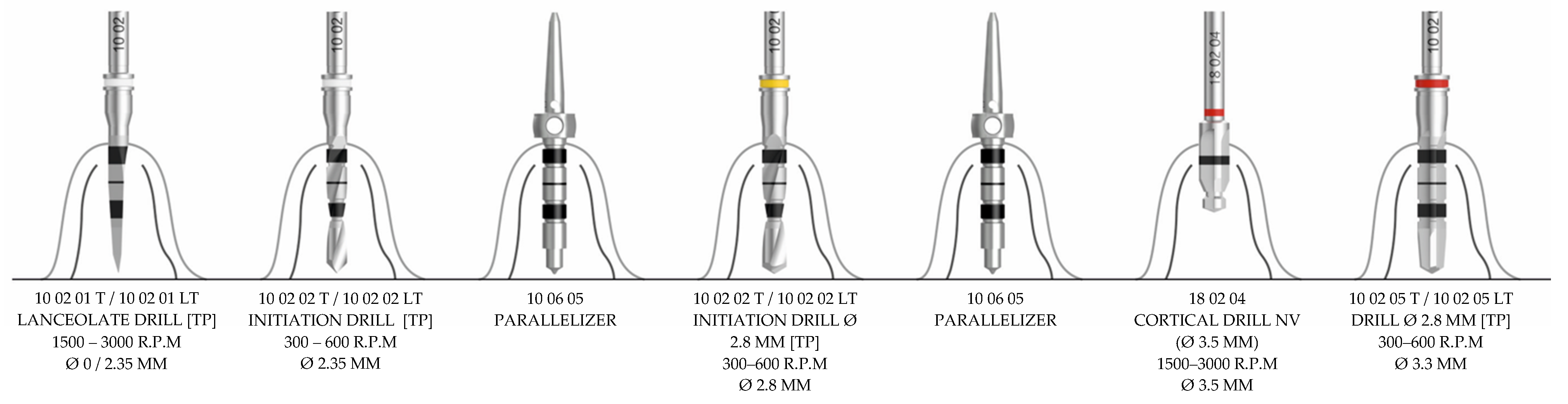
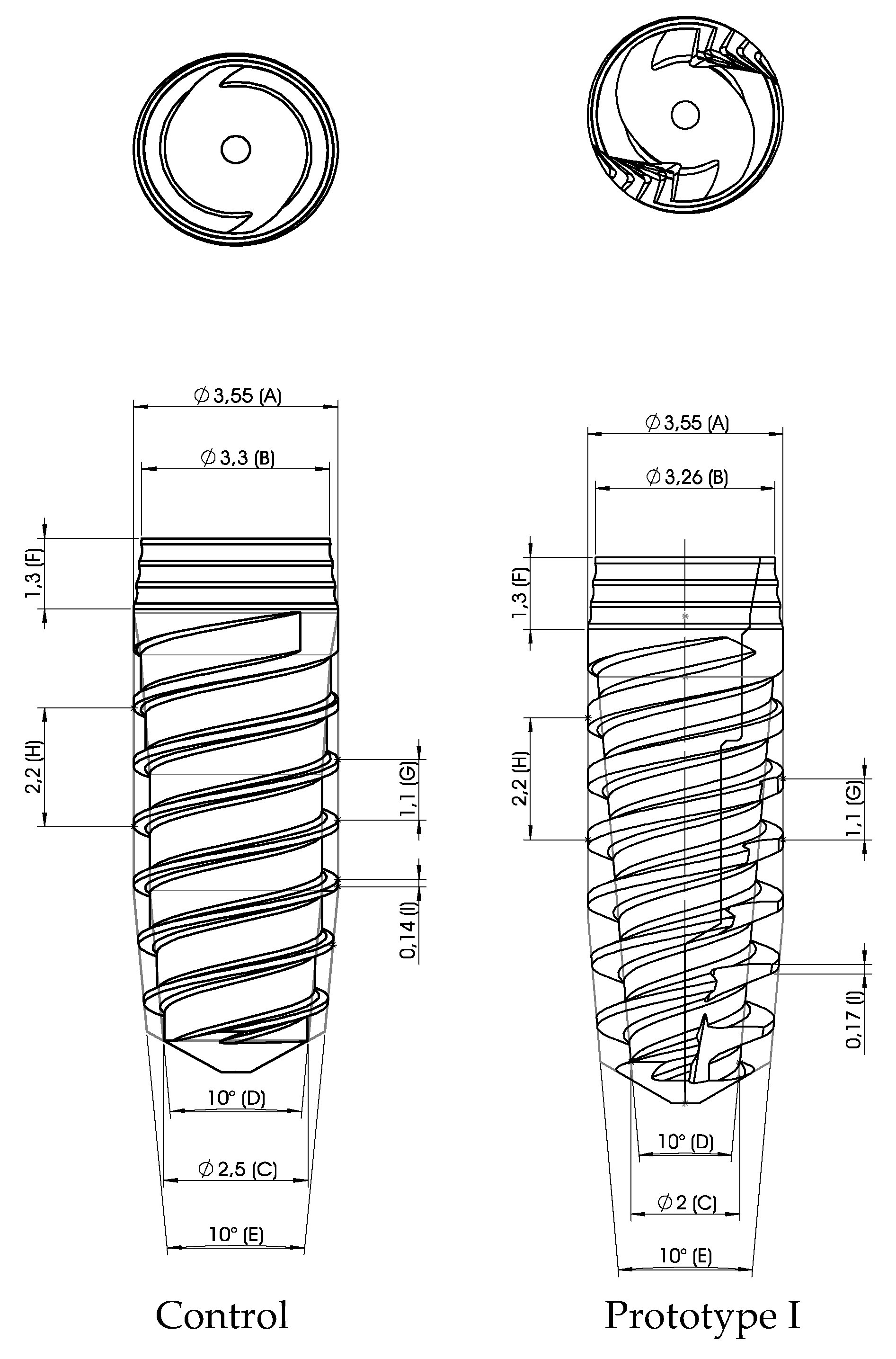
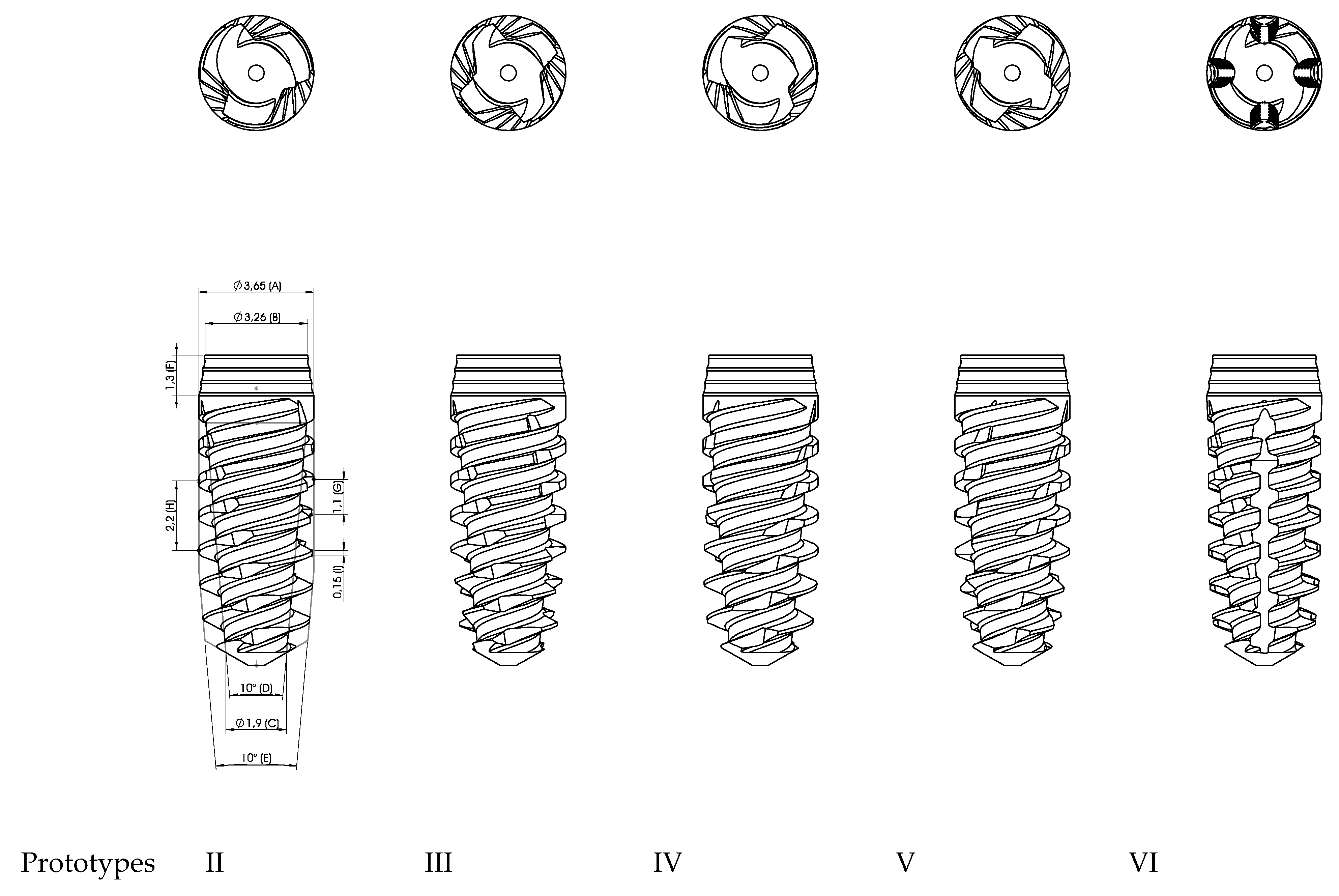
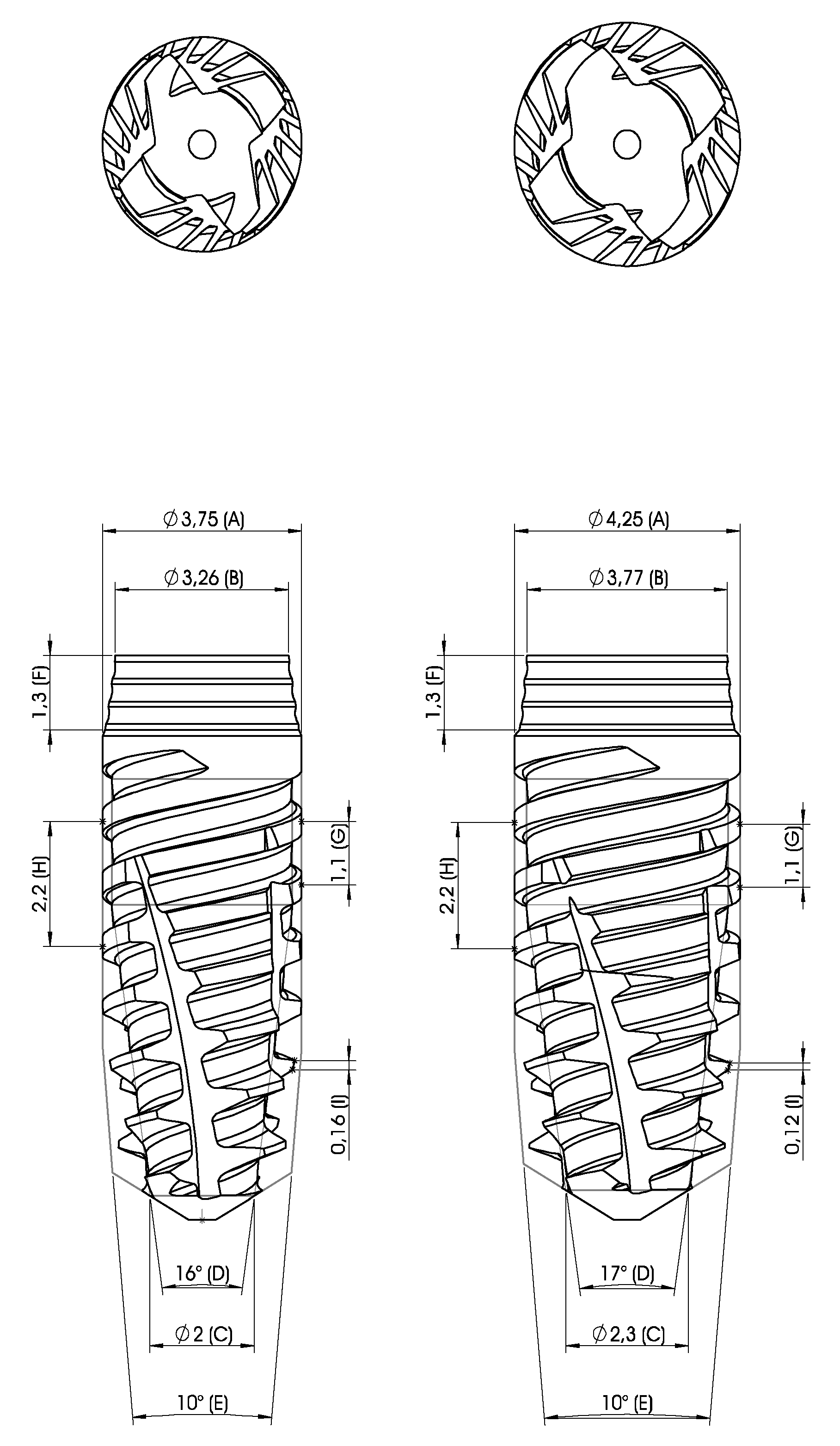
| Implant | IT – N/cm | ISQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | p Value | SD | Mean | p Value | SD | |
| VEGA—3.5 | 30.1 | 0.025 | 16.3 | 71.4 | 0.6841 | 7.8 |
| Prototype I—3.5 | 22.2 | 8.2 | 71.5 | 6.1 | ||
| VEGA—4.0 | 17.9 | 0.0695 | 10.8 | 64.8 | 0.454 | 10.7 |
| Prototype I—4.0 | 21.3 | 11.2 | 66.6 | 7.9 | ||
| Implant | IT – N/cm | ISQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | p Value | SD | Mean | p Value | SD | |
| VEGA—3.5 | 28.7 | - | 14.9 | 71.9 | - | 8.9 |
| Prototype II—3.5 | 27.9 | 0.267 | 13.5 | 75.4 | 0.051 | 4.9 |
| Prototype III—3.5 | 26.7 | 16.9 | 74.6 | 4.7 | ||
| Prototype IV—3.5 | 25.8 | 14.2 | 74.8 | 5.5 | ||
| Prototype V—3.5 | 23.2 | 11.8 | 72.1 | 6.9 | ||
| Prototype VI—3.5 | 22.3 | 12.7 | 71.4 | 7.8 | ||
| VEGA—4.0 | 37.8 | - | 20.4 | 73.8 | - | 6.8 |
| Prototype II—4.0 | 36.7 | 0.625 | 19.7 | 76.3 | 0.012 | 6.1 |
| Prototype III—4.0 | 30.2 | 13.5 | 75.0 | 7.7 | ||
| Prototype IV—4.0 | 37.8 | 17.9 | 78.0 | 3.7 | ||
| Prototype V—4.0 | 35.6 | 15.7 | 75.7 | 5.4 | ||
| Prototype VI—4.0 | 34.4 | 17.8 | 75.5 | 6.2 | ||
| Implant | IT – N/cm | ISQ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | p Value | SD | Mean | p Value | SD | |
| VEGA—3.5 | 34.6 | 0.000 | 9.9 | 74.9 | 0.0001 | 5.3 |
| Prototype VII—3.5 | 54.2 | 22.6 | 78.2 | 7.5 | ||
| VEGA—4.0 | 43.6 | 0.0004 | 25.5 | 76.0 | 0.0192 | 5.0 |
| Prototype VII—4.0 | 64.7 | 22.8 | 78.5 | 3.2 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrero-Climent, M.; López-Jarana, P.; Lemos, B.F.; Gil, F.J.; Falcão, C.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Ríos-Carrasco, B. Relevant Design Aspects to Improve the Stability of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials 2020, 13, 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081910
Herrero-Climent M, López-Jarana P, Lemos BF, Gil FJ, Falcão C, Ríos-Santos JV, Ríos-Carrasco B. Relevant Design Aspects to Improve the Stability of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials. 2020; 13(8):1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081910
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrero-Climent, M., P. López-Jarana, B. F. Lemos, F. J. Gil, C. Falcão, J. V. Ríos-Santos, and B. Ríos-Carrasco. 2020. "Relevant Design Aspects to Improve the Stability of Titanium Dental Implants" Materials 13, no. 8: 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081910
APA StyleHerrero-Climent, M., López-Jarana, P., Lemos, B. F., Gil, F. J., Falcão, C., Ríos-Santos, J. V., & Ríos-Carrasco, B. (2020). Relevant Design Aspects to Improve the Stability of Titanium Dental Implants. Materials, 13(8), 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081910








