Optimum Operating Conditions for the Removal of Phosphate from Water Using of Wood-Branch Nanoparticles from Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Collection and Preparation
2.2. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Nanoparticles
2.3. Investigation of the Optimum Operating Conditions through Batch Bio-Sorption Experiments
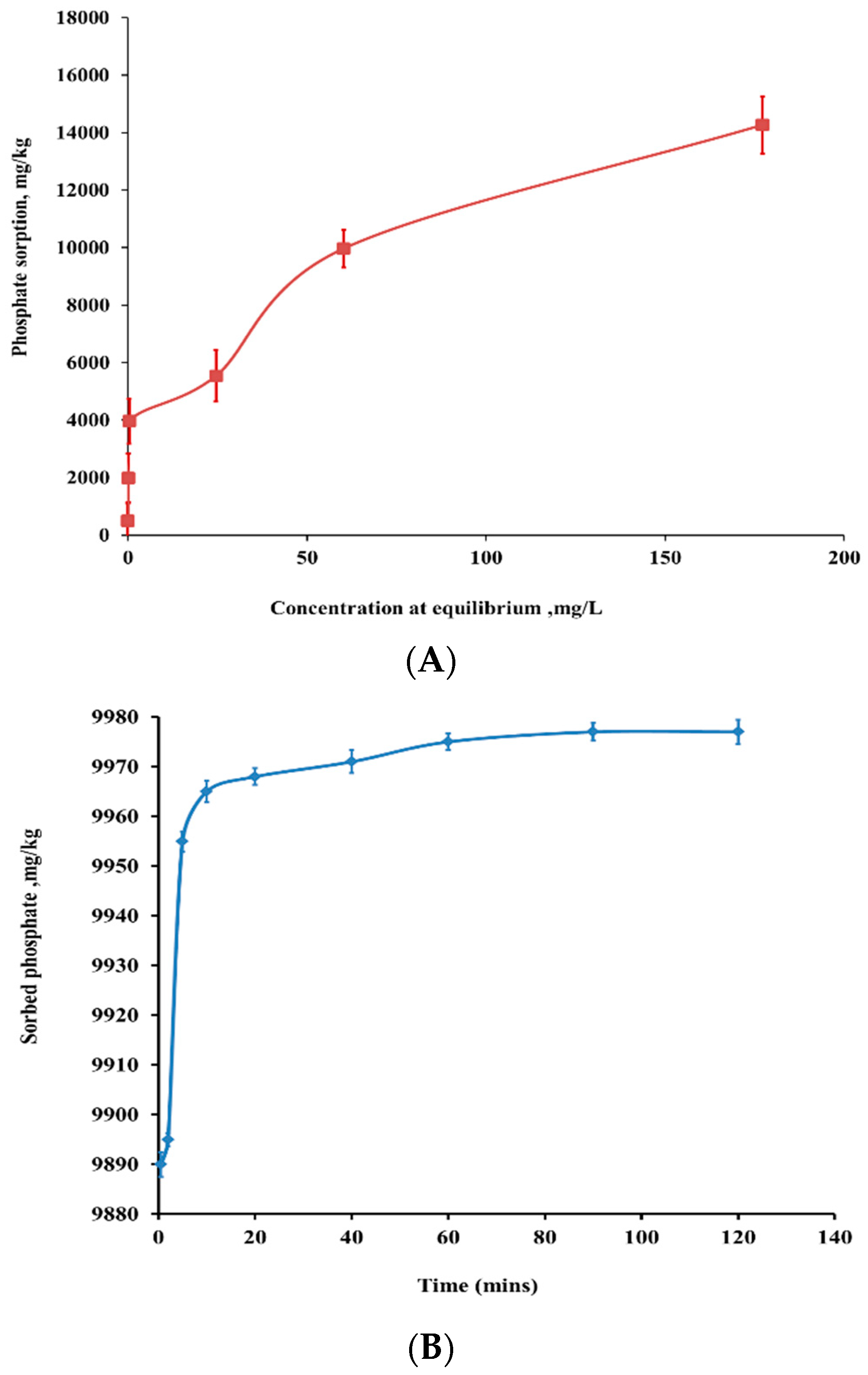
2.3.1. Initial Concentration and Bio-Sorption Kinetics
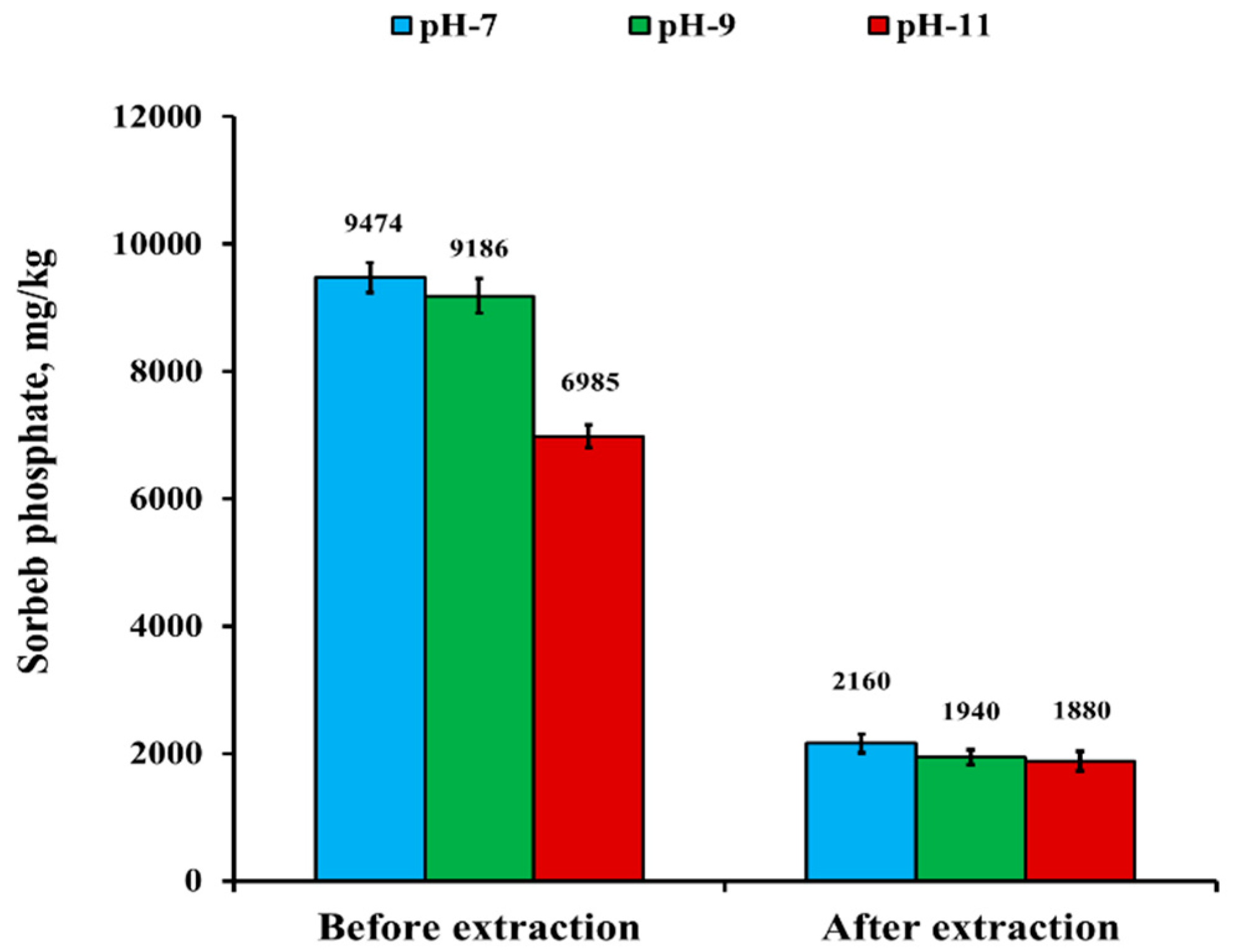
2.3.2. Hot-Water Extraction, pH Measurements, and FTIR Analysis
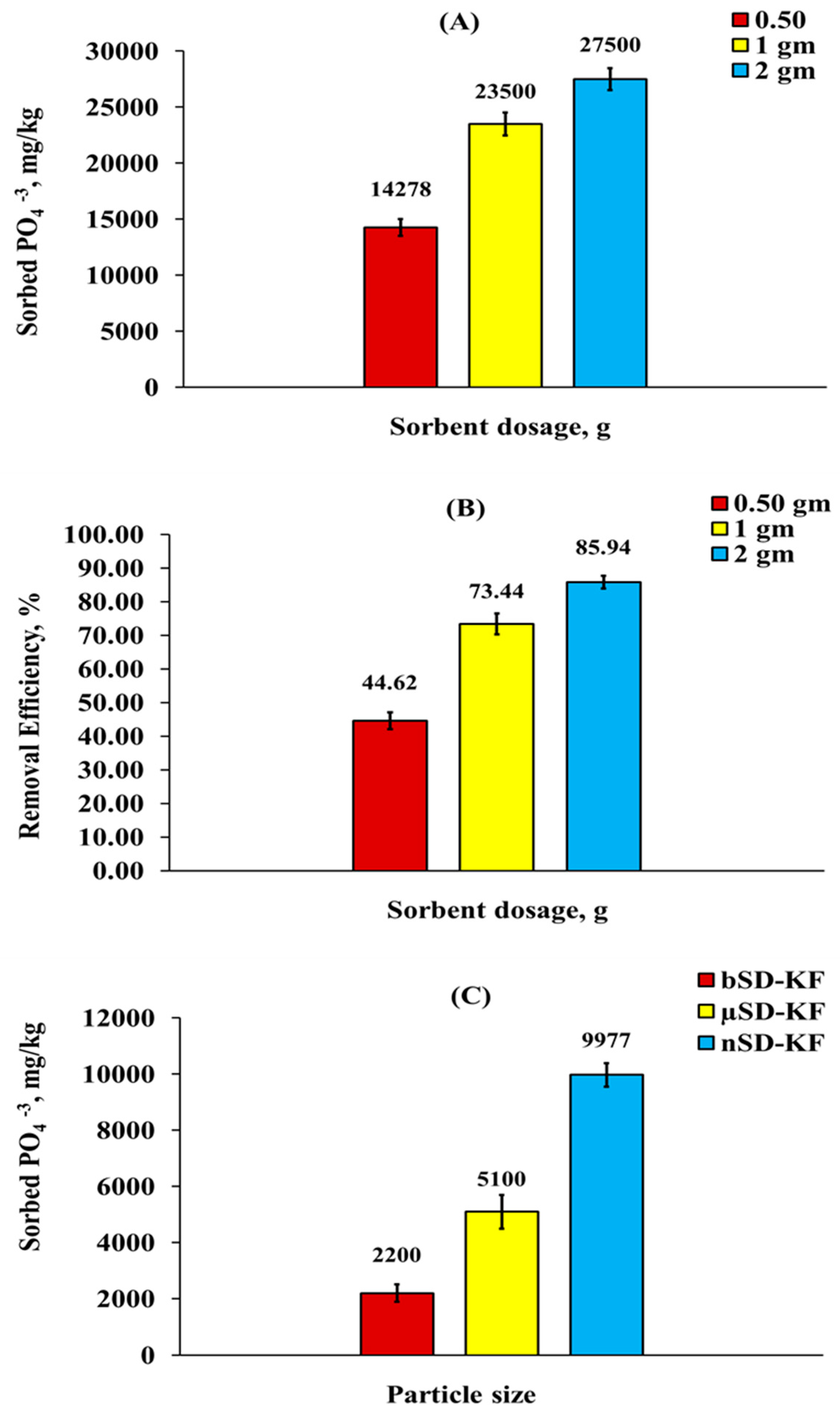
2.3.3. Bio-Sorbent Dose and Particle Size
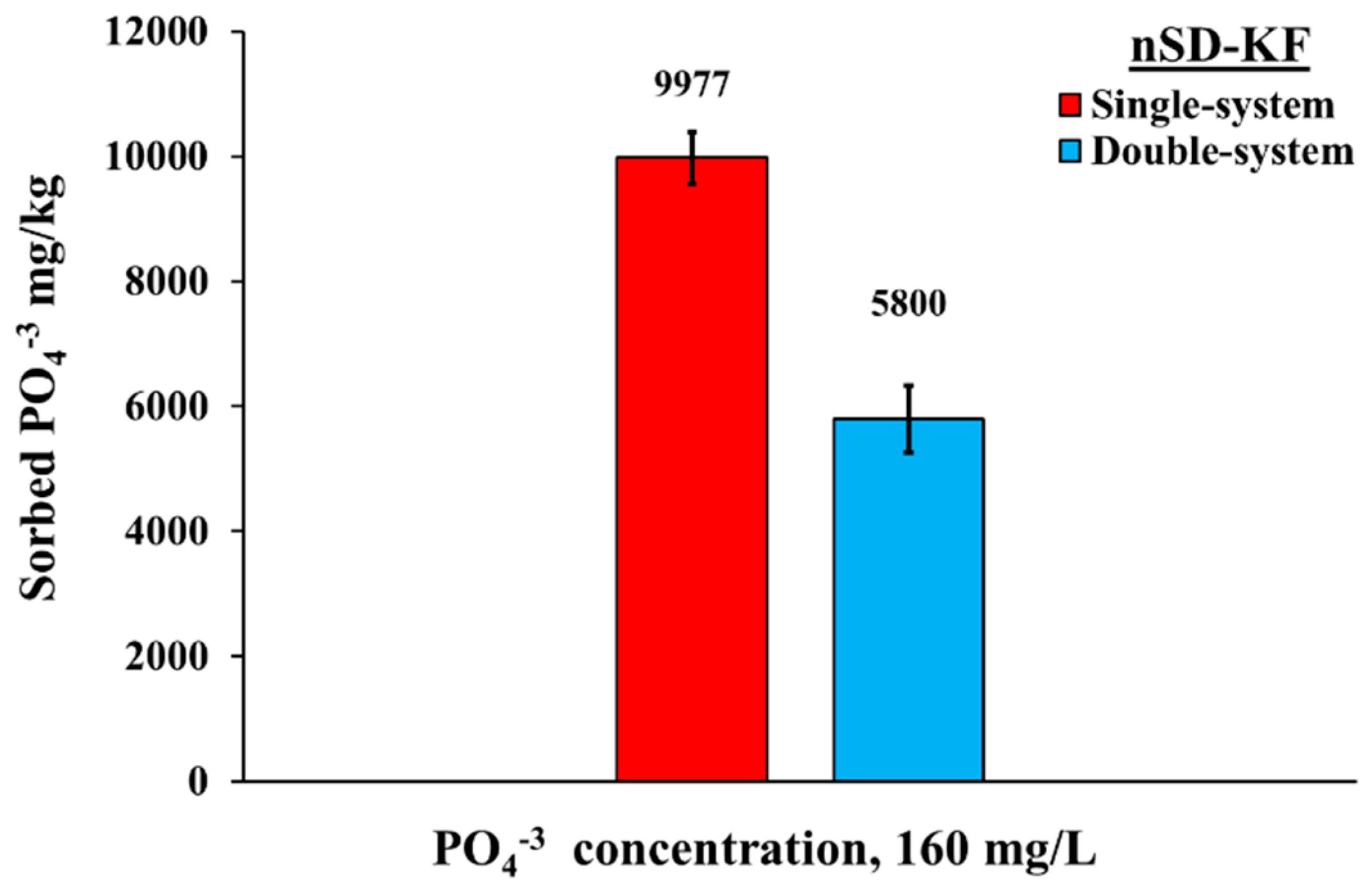
2.3.4. Phosphate Bio-Sorption in Double-System
2.3.5. Thermodynamics of Phosphate Bio-Sorption
2.3.6. Removal of Phosphate from Wastewater Effluents Using nSD-KF
Sample Collection
Performance of nSD-KF in Removing Phosphate from Actual Agricultural Wastewater Samples
2.3.7. Stability of Phosphate-Loaded nSD-KF
2.3.8. Regeneration and Reusability of nSD-KF
2.4. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
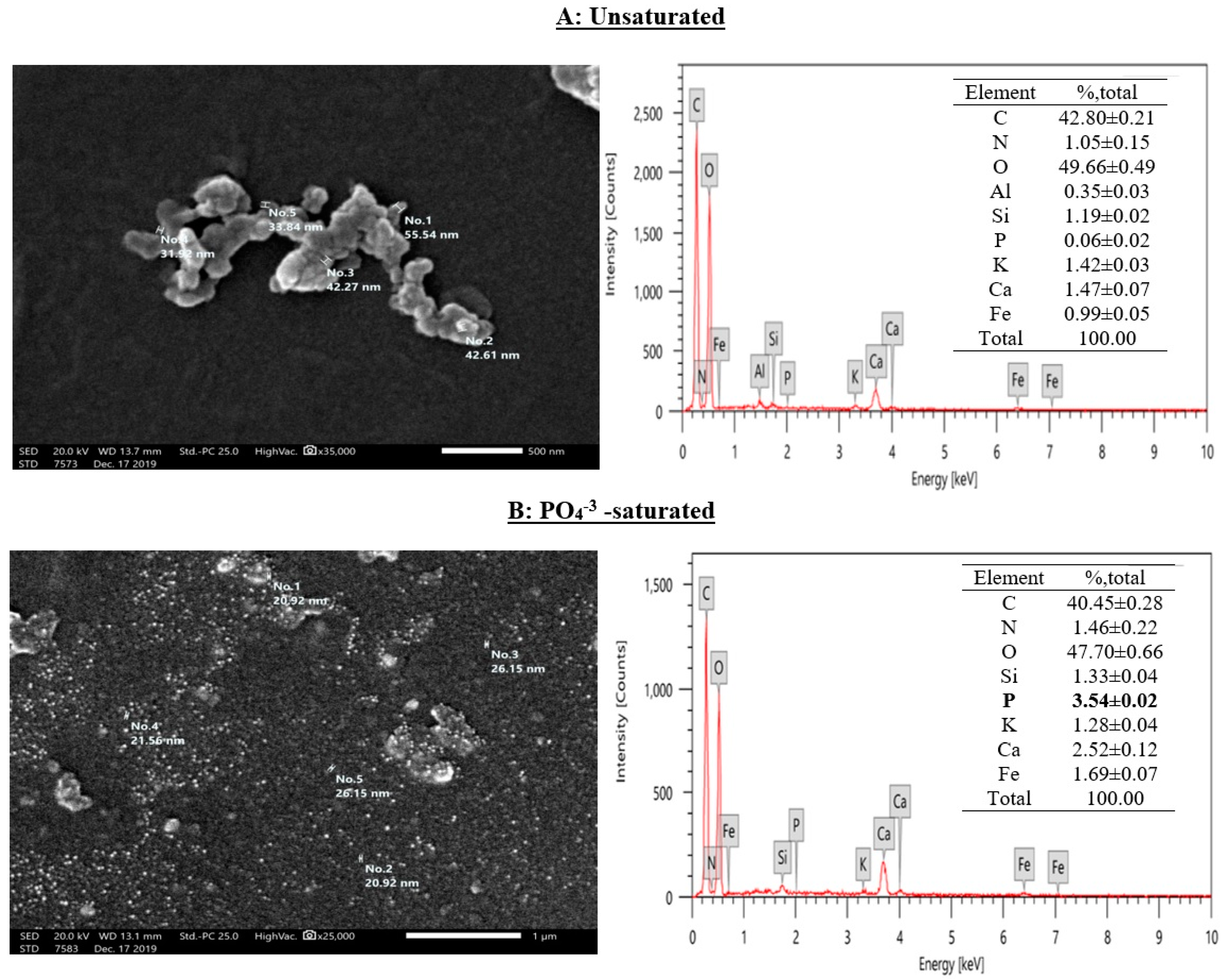
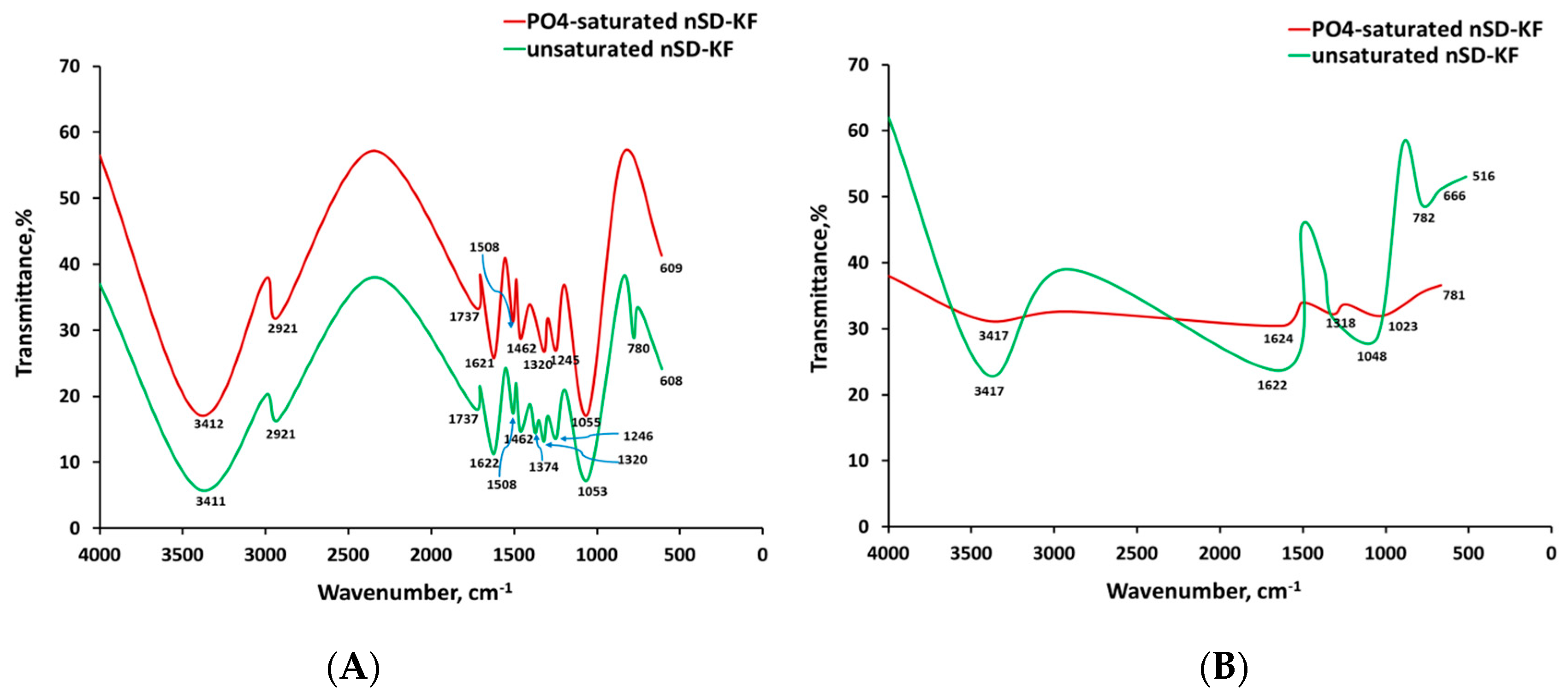
3.1. Characterization of nSD-KF Bio-Sorbent
3.2. Bio-Sorption Isotherm and Kinetics of Ammonium on nSD-KF
3.3. Factor Affecting Bio-Sorption Process
3.3.1. Effect of nSD-KF Dosage and Size of Particle
3.3.2. Effect of Hot Water-Extraction and Solution pH
3.3.3. Phosphate Bio-Sorption in Double-System
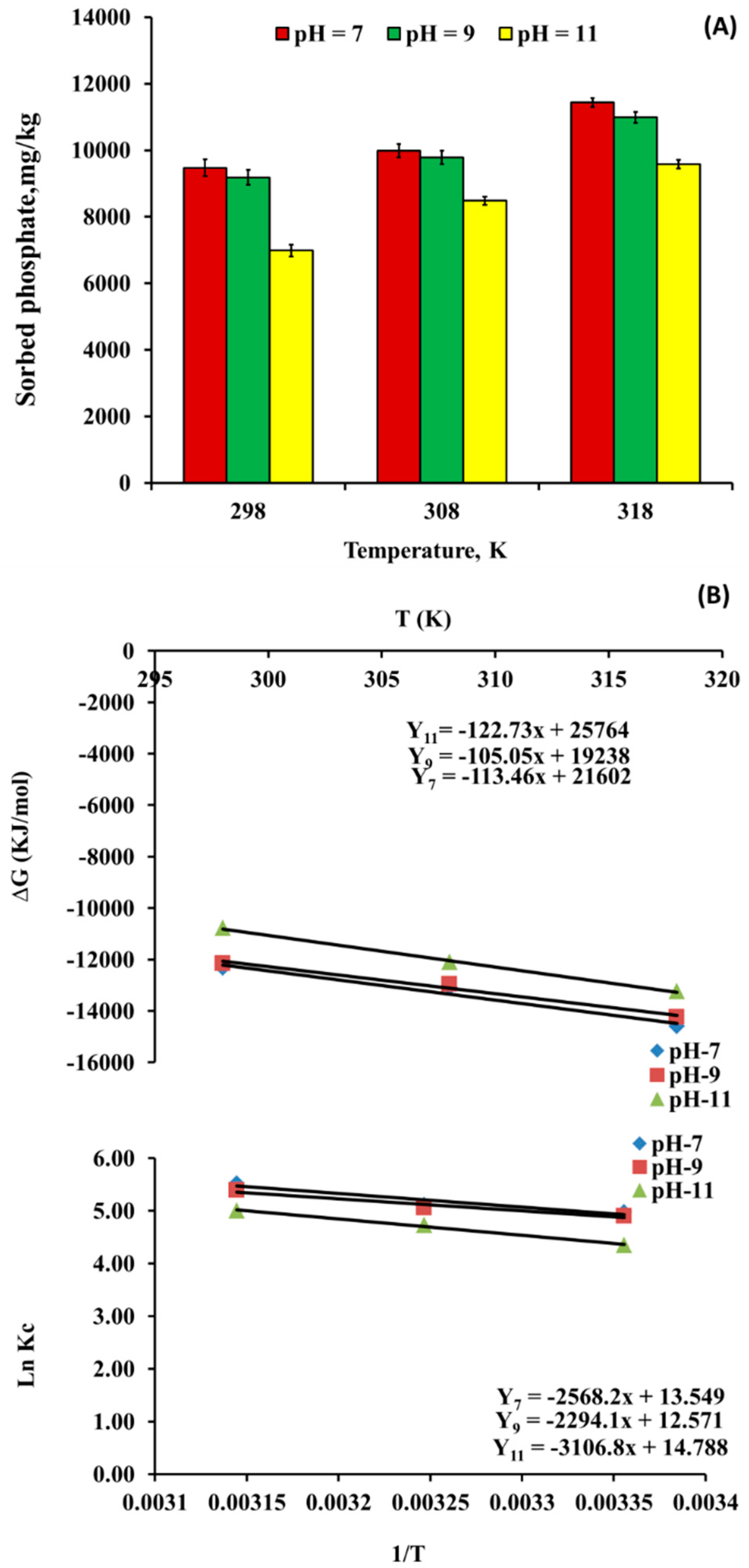
3.3.4. Effect of Temperatures on PO4−3 Sorption by nSD-KF
Thermodynamic Parameters of Phosphate Bio-Sorption on nSD-KF
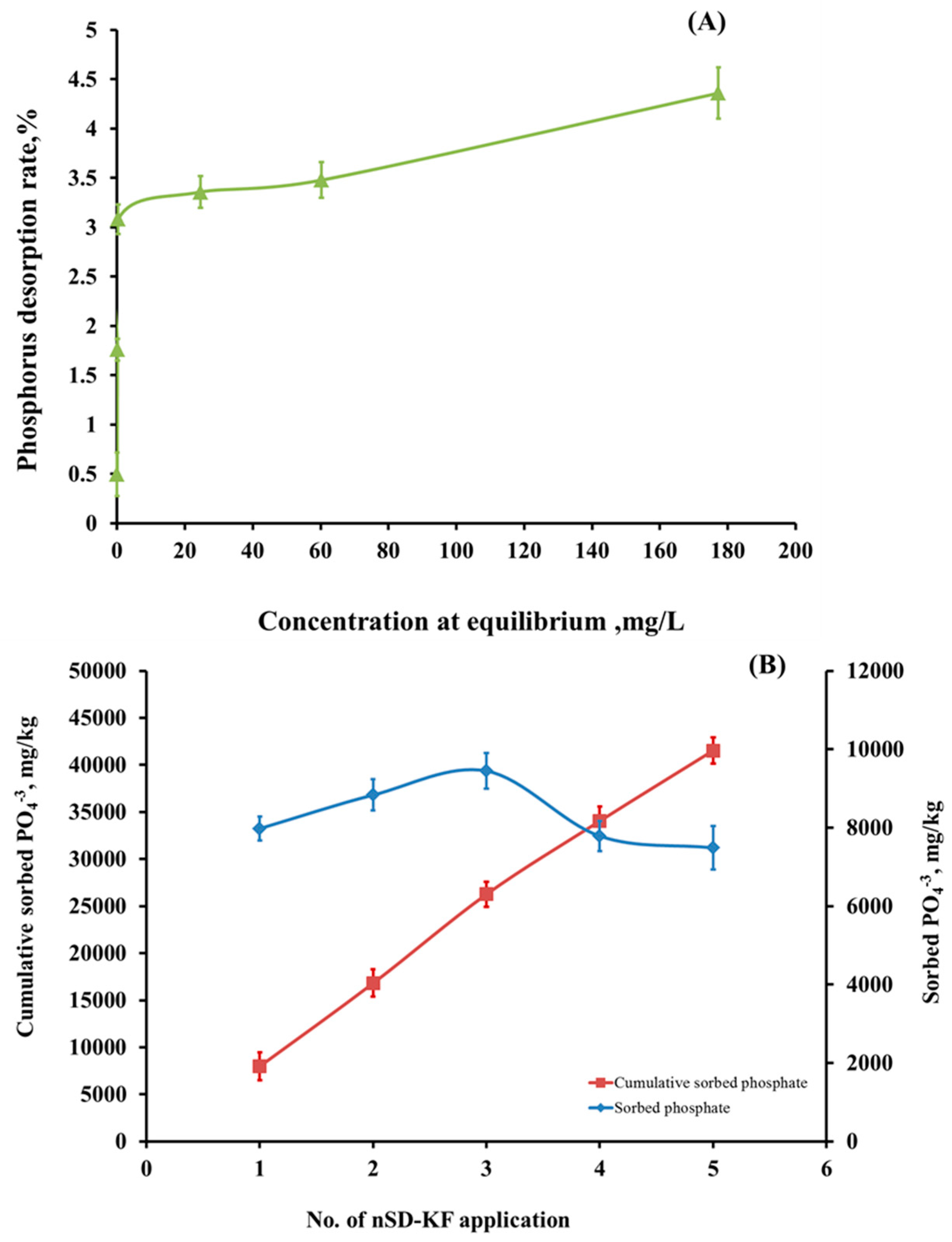
3.3.5. Desorption Behavior, Regeneration, and Reusability of nSD-KF Bio-Sorbent
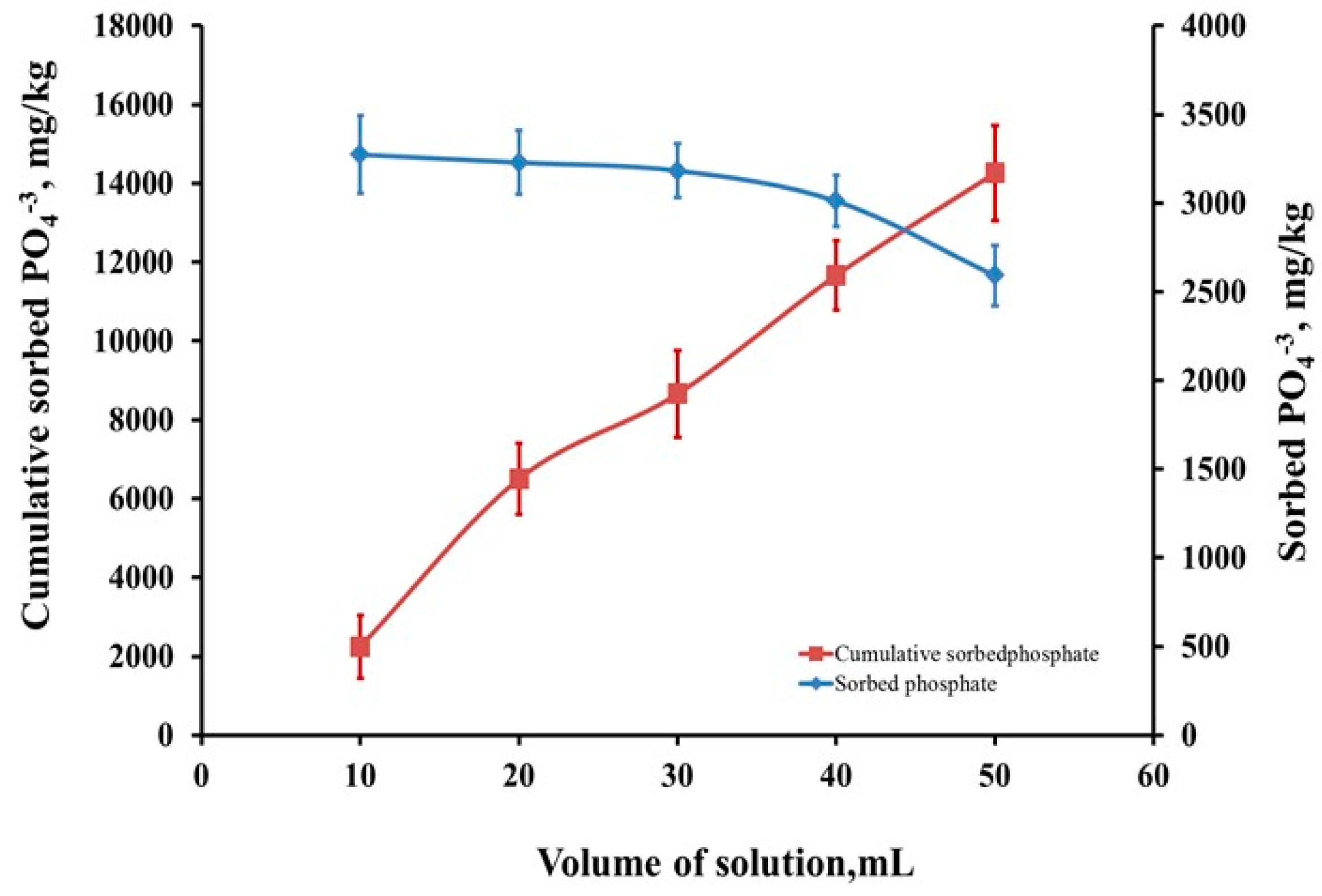
3.3.6. Application Study on Real Agricultural Wastewater
Batch Study
Backed-Column Study
3.3.7. Bio-Sorption Mechanism Investigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, J.; Patra, B.S.; Baliarsingh, N.; Parida, K.M. Adsorption of phosphate by layered double hydroxides in aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 32, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Chen, F.; Sheng, Y.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution onto modified palygorskites. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, S.; Abo-Shosha, M.H.; Ibrahim, N.A. Application of Starch Ion Exchange Composites II. Removal of Some Acid Dyestuffs Using Starch Methylenbis Acrylamide/Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate Anion Exchange Composite. Tinctoria 1994, 10, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Lahav, O.; Green, M. Ammonium removal using ion exchange and biological regeneration. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2019–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Quadros Melo, D.; de Oliveira Sousa Neto, V.; de Freitas Barros, F.C.; Raulino, G.S.C.; Vidal, C.B.; do Nascimento, R.F. Chemical modifications of lignocellulosic materials and their application for removal of cations and anions from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 43286, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Bolan, N.S. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water using sorption. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 847–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, M.; Zou, T.; Peng, N.; Zhao, M.; Gong, Z. Phosphate removal combined with acetate supplementation enhances lipid production from water hyacinth by Cutaneotrichosporon oleaginosum. Biotechnol. Biof. 2019, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Covey, G.H.; O’Connor, A.J. Silvichemicals from pulp mill wastes- bio-sorption of metal ions on ellagic acid. Appita Annu. Gen. Conf. 2000, 2, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of copper (II), chromium (III), nickel (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solutions by meranti sawdust. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, K.C.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Aluminum-based drinking-water treatment residuals: A novel sorbent for perchlorate removal. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 140, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Watts, D.W. Increasing the phosphorus sorption capacity of southeastern Coastal Plain soils using water treatment residuals. Soil Sci. 2004, 169, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, E.A.; Mahdy, A.M.; Sherif, F.K.; Salama, K.A. Water Treatment Residual Nanoparticles: A Novel Sorbent for Enhanced Phosphorus Removal from Aqueous Medium. Curr. Nanosci. 2015, 11, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soci. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B., Jr. Laboratory Guide for Conducting Soil Tests and Plant Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, R.; Ansari, T.M.; Khalid, A.M. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopic characterization and optimization of Pb (II) bio-sorption by fish (Labeo rohita) scales. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation (AWWA-EPHA-WEF): Denver, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, R.; Dan, M. Guidelines for Water Reuse 600/R-12/618; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Unnithan, M.R. Arsenic (V) removal from aqueous solutions using an anion exchanger derived from coconut coir pith and its recovery. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Abd-El Sayed, M.A.; Zikry, M.M. Nano sized Moringa oleifera an effective strategy for Pb (II) ions removal from aqueous solution. Chem. Mater. Res. 2016, 8, 8–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, M.A.; Jellali, S.; Jedidi, N. Effect of temperature and pH on the bio-sorption of ammonium onto Posidonia oceanica fibers: Equilibrium, and kinetic modeling studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, H.; Leiviskä, T.; Heiderscheidt, E.; Postila, H.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of metals from industrial wastewater and urban runoff by mineral and bio-based sorbents. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 209, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajav, E.A.; Fakayode, O.A. Physical properties of moringa (Moringa oleifera) seeds in relation to an oil expeller design. Agrosearch 2013, 13, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnisi, R.L.; Ndibewu, P.P. Surface and adsorptive properties of Moringa oleifera bark for removal of V (V) from aqueous solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Ppotential in Colloid Science-Principle and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, H. Zeta potential of a subbituminous coal and its effect on particle agglomeration. Min. Metall. Explor. 1996, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, N.; Duplay, J.; Jada, A.; Errais, E.; Ghazi, M.; Semhi, K.; Trabelsi-Ayadi, M. Removal of anionic dye from textile industries’ effluents by using Tunisian clays as adsorbents. Ζeta potential and streaming-induced potential measurements. C. R. Chim. 2019, 22, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Coll. Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.H. Removal of refractory compounds from stabilized landfill leachate using an integrated H2O2 oxidation and granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4079–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Thamaraiselvi, K.; Namasivayam, C. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from an agricultural solid waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhatib, E.A.; Hern, J.L. Kinetics of potassium desorption from Appalachian soils. Soil Sci. 1988, 145, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özacar, M.; Şengil, İ.A. Adsorption of metal complex dyes from aqueous solutions by pine sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, C.; Manju, G.N.; Anirudhan, T.S. Removal of heavy metal ions from water using sawdust-based activated carbon. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 1997, 4, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Chand, S.; Agarwal, V.K.; Kumar, P. Removal of hexavalent chromium form waste water by adsorption. Indian J. Environ. Health 1994, 36, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Mataka, L.M.; Henry, E.M.T.; Masamba, W.R.L.; Sajidu, S.M. Cadmium sorption by Moringa stenopetala and Moringa oleifera seed powders. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 3, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, J. Effects of pH and temperature on isotherm parameters of chlorophenols bio-sorption to anaerobic granular sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fávere, V.T.; Riella, H.G.; Rosa, S.D. Chitosan-n-2-hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride as adsorbent for the removal of the reactive dye from aqueous solutions. Química Nova 2010, 33, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellali, S.; Wahab, M.A.; Anane, M.; Riahi, K.; Jedidi, N. Bio-sorption characteristics of ammonium from aqueous solutions onto Posidonia oceanica (L.) fibers. Desalination 2011, 270, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Shen, F.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Deng, S. Biochar produced from oak sawdust by Lanthanum (La)-involved pyrolysis for adsorption of ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3−), and phosphate (PO43−). Chemosphere 2015, 119, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, M.; Khan, A.H.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, A. Role of sawdust in the removal of copper (II) from industrial wastes. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Fungal bio-sorption—An alternative treatment option for heavy metal bearing wastewaters: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 53, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Onyancha, D.; Mavura, W.; Ngila, J.C.; Ongoma, P.; Chacha, J. Studies of chromium removal from tannery wastewaters by algae bio-sorbents, Spirogyra condensata and Rhizoclonium hieroglyphicum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, W.P.; Kamari, A.; Yusoff, S.N.M.; Ishak, C.F.; Mohamed, A.; Hashim, N.; Isa, I.M. Bio-sorption of Cu (II), Pb (II) and Zn (II) ions from aqueous solutions using selected waste materials: Adsorption and characterisation studies. J. Encapsul. Adsorpt. Sci. 2014, 4, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Site, A. Factors affecting sorption of organic compounds in natural sorbent/water systems and sorption coefficients for selected pollutants. A review. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2001, 30, 187–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Abo-Shosha, M.H.; Farag, S. Application of Starch Ion Exchange Composites I. Use of Starch/N-Methylolacrylamide/Methacrylic Acid Cation Exchange Composites in the Removal of Some Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Tinctoria 1994, 9, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing ammonium from water and wastewater using cost-effective adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, P.S.; Petersen, J.N.; Lee, J.M.; Brouns, T.M. Sorption of heavy metals by untreated red fir sawdust. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1992, 34, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qambrani, N.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Won, S.; Shim, S.; Ra, C. Biochar properties and eco-friendly applications for climate change mitigation, waste management, and wastewater treatment: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Sreedhar, M.K. Adsorption thermodynamics of Co (II) on polysulphide treated sawdust. Ind. J. Chem. Technol. 1998, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.M.; Padrick, S.B.; Chen, B.; Umetani, J.; Rosen, M.K. The WAVE regulatory complex is inhibited. Nat. Sstruct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Anber, M.A. Thermodynamics approach in the adsorption of heavy metals. In Thermodynamics-Interaction Studies-Solids, Liquids and Gases; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, K.S.; Ramanathan, A.L.; Paul, J.; Subramanian, V.; Prasad, R. Bio-sorption of arsenite (As+ 3) and arsenate (As+5) from aqueous solution by Arthrobacter sp. biomass. Environ. Technol. 2014, 34, 2701–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadeer, R. Adsorption of ruthenium ions on activated charcoal: Influence of temperature on the kinetics of the adsorption process. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, X. Adsorption of Ni (II) from aqueous solution using oxidized multiwall carbon nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 9144–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefne, J.A.; Mekhemer, W.K.; Alandis, N.M.; Aldayel, O.A.; Alajyan, T. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of the adsorption of Pb (II) from aqueous solution to the natural and treated bentonite. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2008, 3, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, S.; Srivastava, V.C.; Mishra, I.M. Isotherm, thermodynamics, desorption, and disposal study for the adsorption of catechol and resorcinol onto granular activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 56, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, J.D. Inorganic and Organometallic Reaction Mechanisms; VCH Publishers: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzen, M.; Sarı, A.; Mendil, D.; Uluozlu, O.D.; Soylak, M.; Dogan, M. Characterization of bio-sorption process of as (III) on green algae Ulothrix cylindricum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Zhang, Y.H.; Dubey, P.; Margrave, J.L.; Shukla, S.S. The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 95, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, A.; Leiviskä, T.; Salakka, A.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of nickel and vanadium from ammoniacal industrial wastewater by ion exchange and adsorption on activated carbon. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasambandam, R.; Proctor, A. Determination of pectin degree of esterification by diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.M.; Hamed, S.A.E.K.M.; Mansour, M.M.A. Assessment of Efficacy and Effectiveness of Some Extracted Bio-Chemicals as Bio-Fungicides on Wood. Drvna Ind. 2019, 70, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 38–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, A.; Della Zassa, M.; Martin-Lara, M.A.; Calero, M.; Canu, P. Combustion of a Pb (II)-loaded olive tree pruning used as bio-sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Sorption and Bio-Sorption; BV Sorbex, Inc.: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2003; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Unit | Agricultural Wastewater | IWC ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | dS/m | 2.22 ± 0.17 * | 3.00 |
| pH | − | 8.03–8.11 | 6.50–9.00 |
| Cl | meq/L | 11.35 ± 1.88 | 10.00 |
| HCO3− | meq/L | 2.13 ± 0.11 | 1.50 |
| NO3− | meq/L | 4.13 ± 0.44 | 10 |
| PO4− | meq/L | 5.61 ± 0.54 | 10 |
| NH4+ | meq/L | 3.22 ± 0.24 | 10 |
| SAR | − | 7.18 ± 0.91 | 6–12 |
| Initial Concentration (mg/L) | pH | T (K) | ΔG° (k J/mol) | ΔS° (k J/mol/K) | ΔH° (k J/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 160 | 7 | 298 | −12.19 | 0.11 | 21.35 |
| 308 | −13.32 | ||||
| 318 | −14.45 | ||||
| 9 | 298 | −12.07 | 0.10 | 19.07 | |
| 308 | −13.12 | ||||
| 318 | −14.16 | ||||
| 11 | 298 | −10.81 | 0.12 | 25.83 | |
| 308 | −12.04 | ||||
| 318 | −13.27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdy, A.M.; Salem, M.Z.M.; Ali, A.M.; Ali, H.M. Optimum Operating Conditions for the Removal of Phosphate from Water Using of Wood-Branch Nanoparticles from Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Materials 2020, 13, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081851
Mahdy AM, Salem MZM, Ali AM, Ali HM. Optimum Operating Conditions for the Removal of Phosphate from Water Using of Wood-Branch Nanoparticles from Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Materials. 2020; 13(8):1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081851
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdy, Ahmed M., Mohamed Z. M. Salem, Asmaa M. Ali, and Hayssam M. Ali. 2020. "Optimum Operating Conditions for the Removal of Phosphate from Water Using of Wood-Branch Nanoparticles from Eucalyptus camaldulensis" Materials 13, no. 8: 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081851
APA StyleMahdy, A. M., Salem, M. Z. M., Ali, A. M., & Ali, H. M. (2020). Optimum Operating Conditions for the Removal of Phosphate from Water Using of Wood-Branch Nanoparticles from Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Materials, 13(8), 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081851






