Progress in Sol-Gel Technology for the Coatings of Fabrics
Abstract
1. Introduction
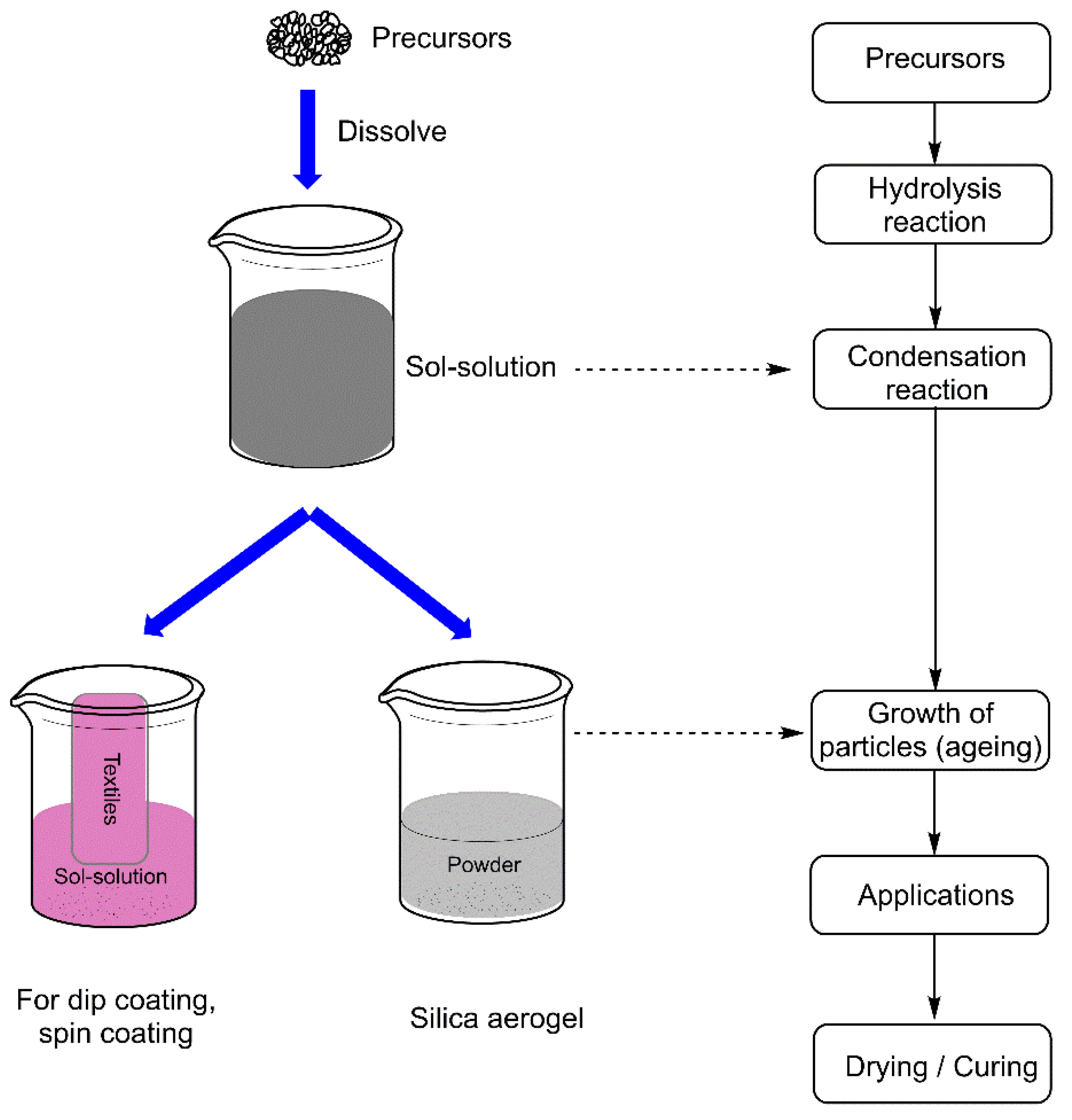
1.1. Sol-Gel Technology: History, Chemistry and Synthesis
Synthesis of Sol-Gels
- Solvation: the ionizable precursor-solvent unit (where z is the valence of the M ions) is formed by the metal cation Mz+ of the metal salt attracting the molecules of water and further H+ is released due to its strong tendency to maintain its coordination number:
- Hydrolysis: A non-ionized molecular precursor reacts with water, such as a metal alkoxide M(OR)n (n is the valence of the metal M, and R represents an alkyl group).
- Polycondensation:
1.2. Factors Affecting the Sol-Gel Reaction
1.2.1. Precursor Properties
1.2.2. Temperature and Time
1.2.3. Solvent
1.2.4. Properties and Concentrations of Catalyst
1.2.5. Ratio of Water to Metal Alkoxide
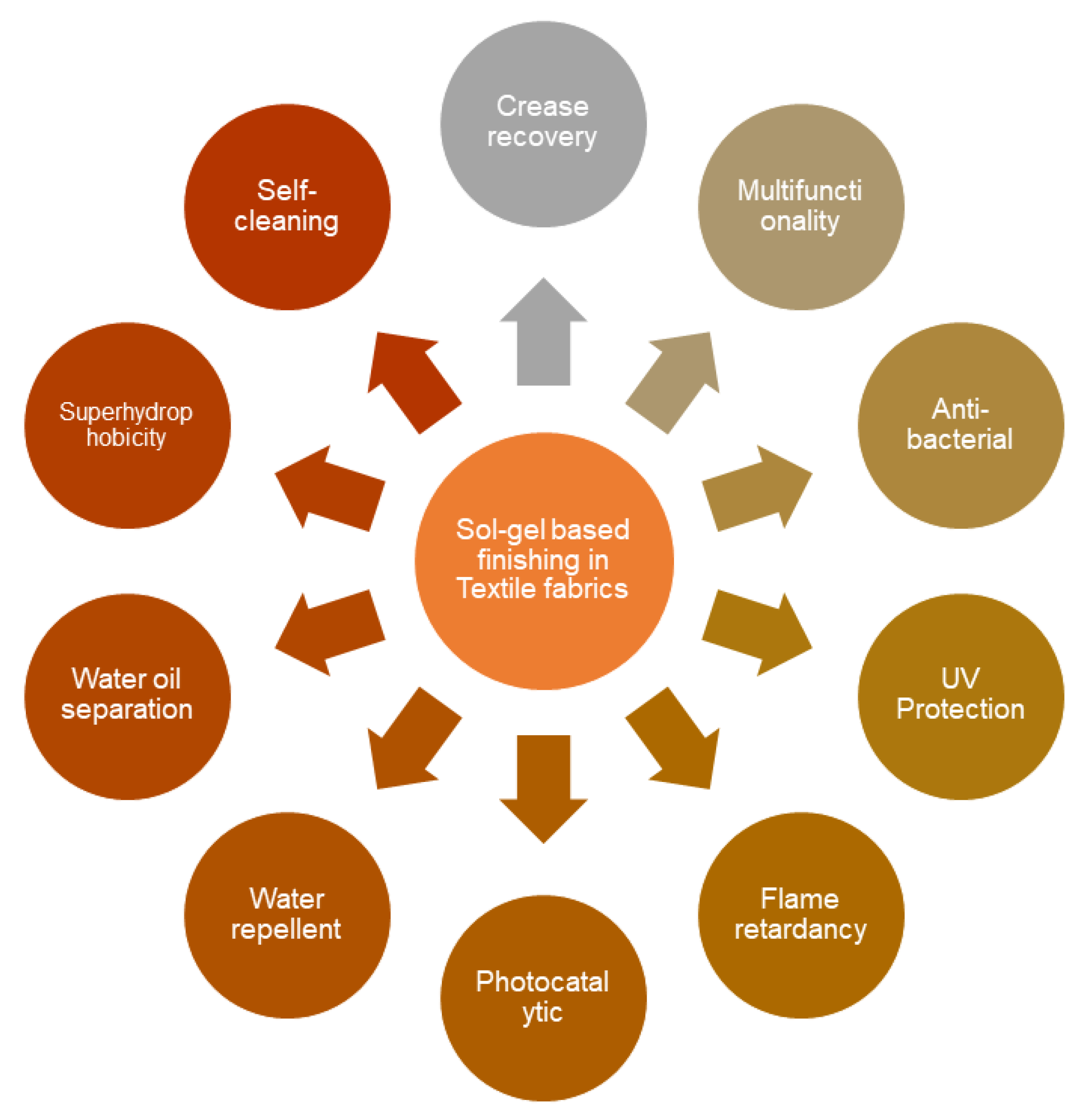
2. Progress in Sol-Gel Finishing on Fabrics
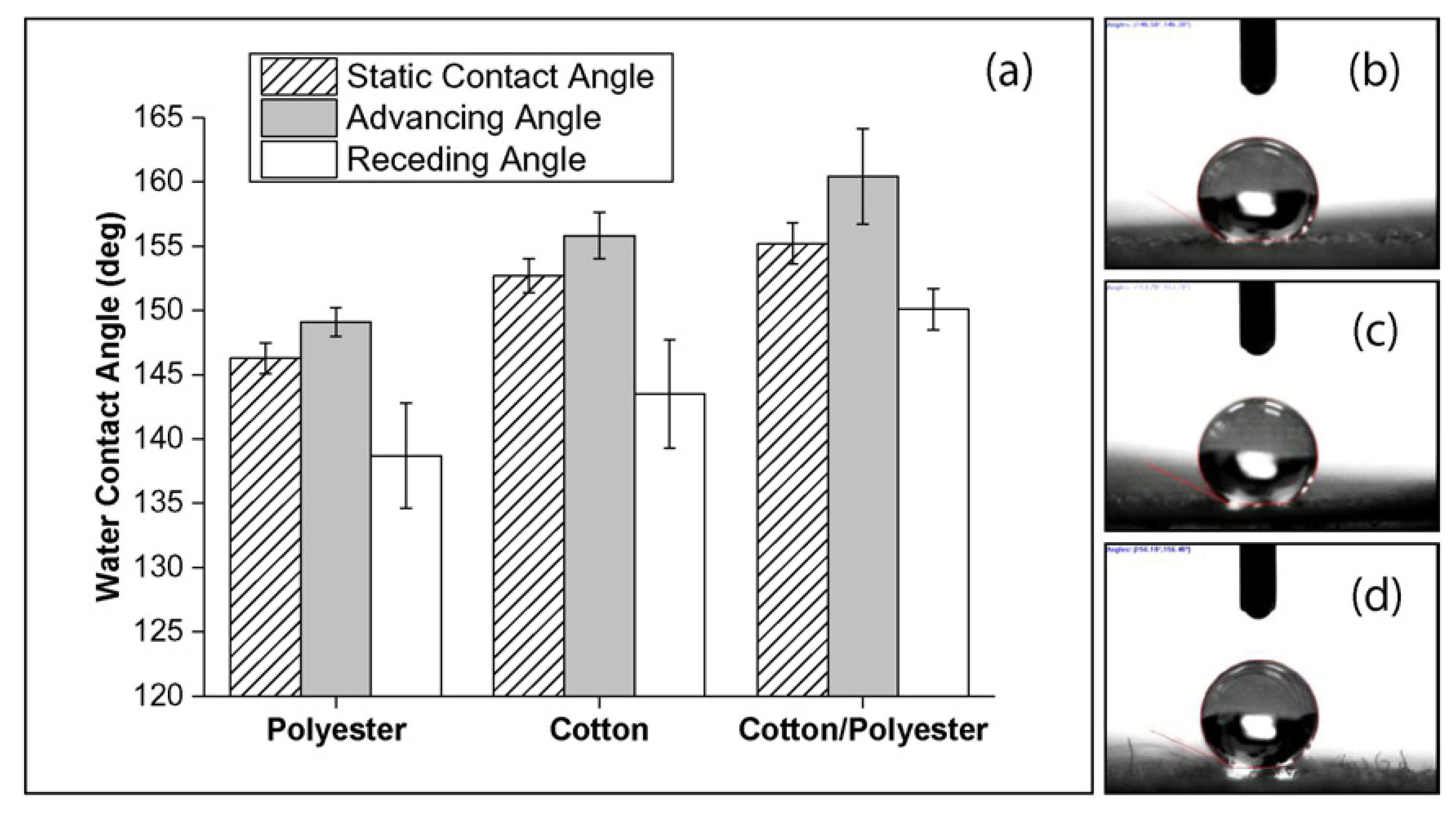
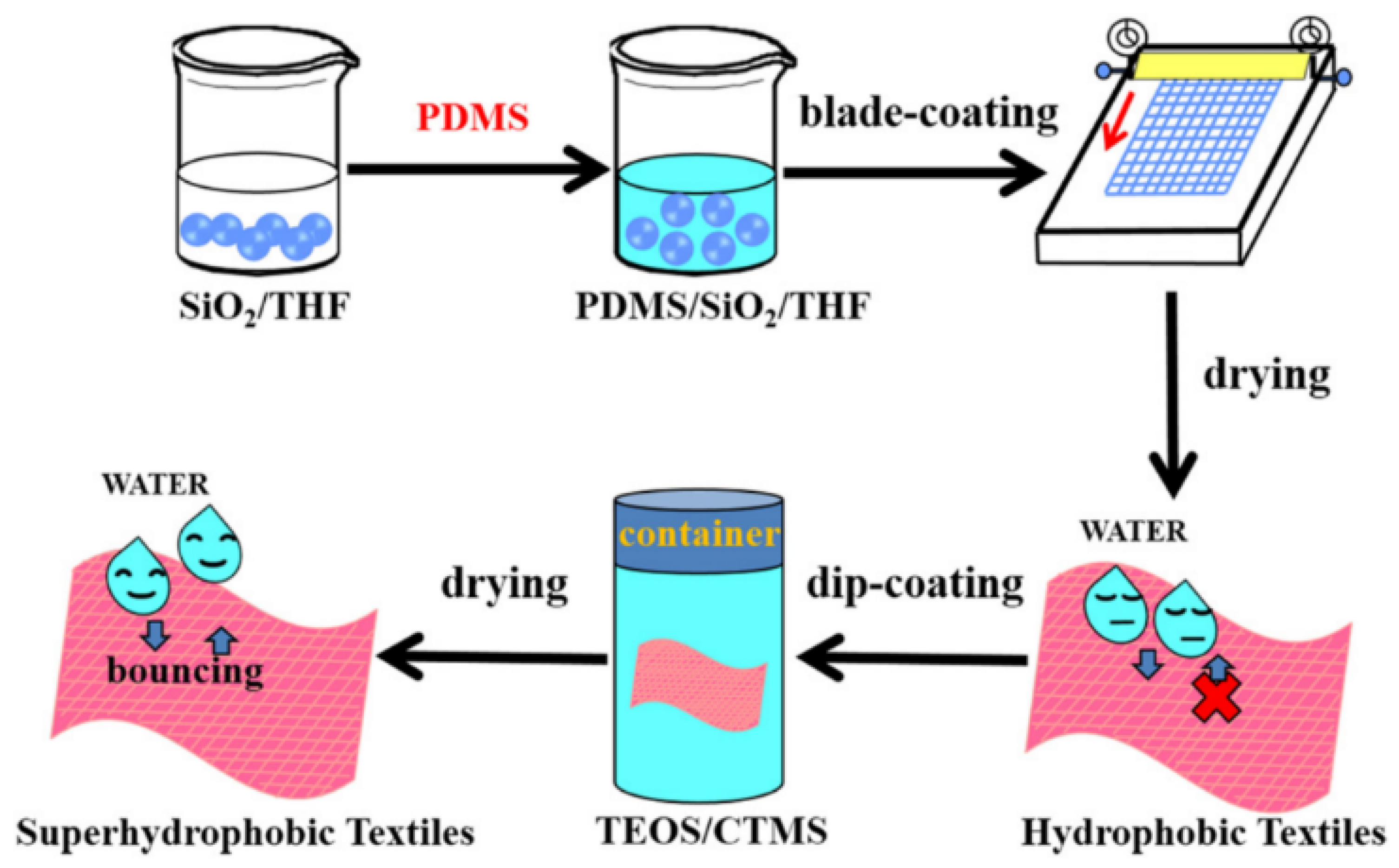
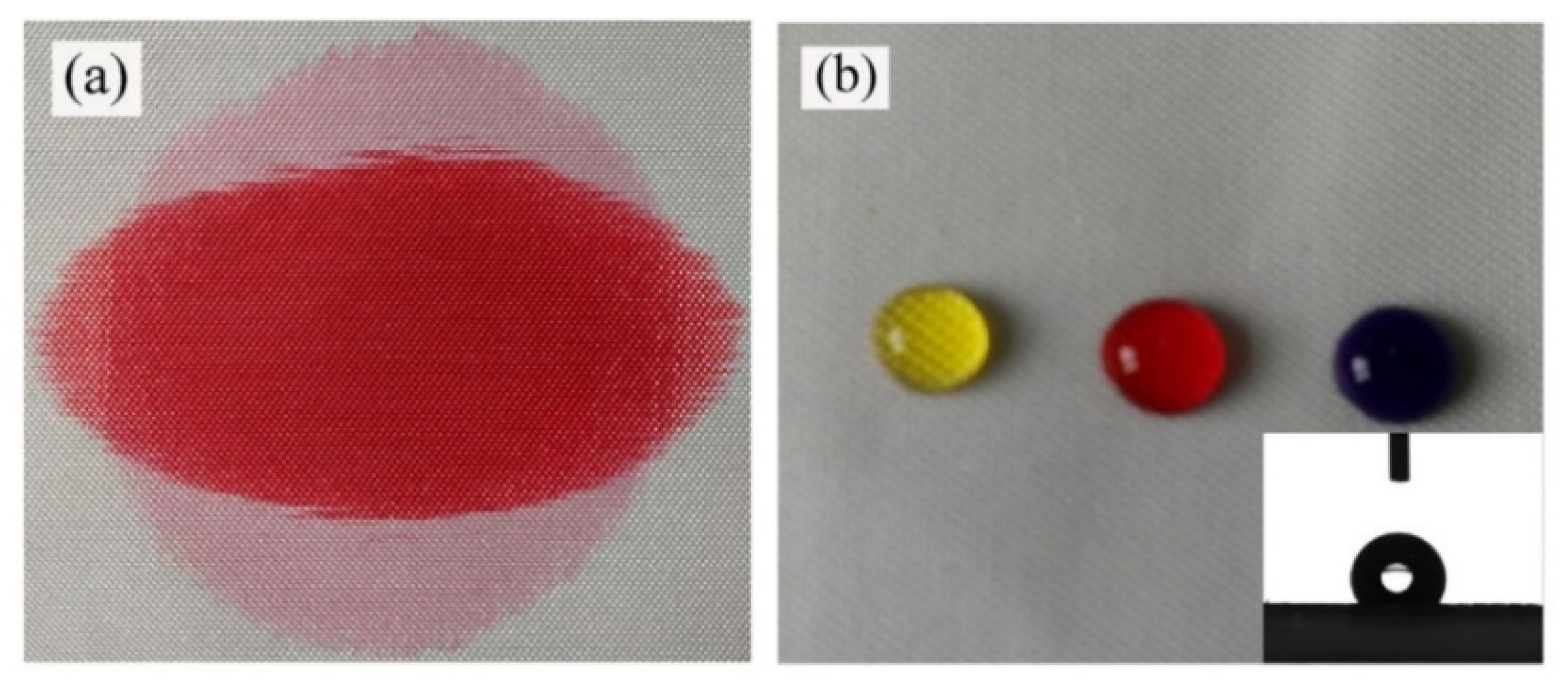
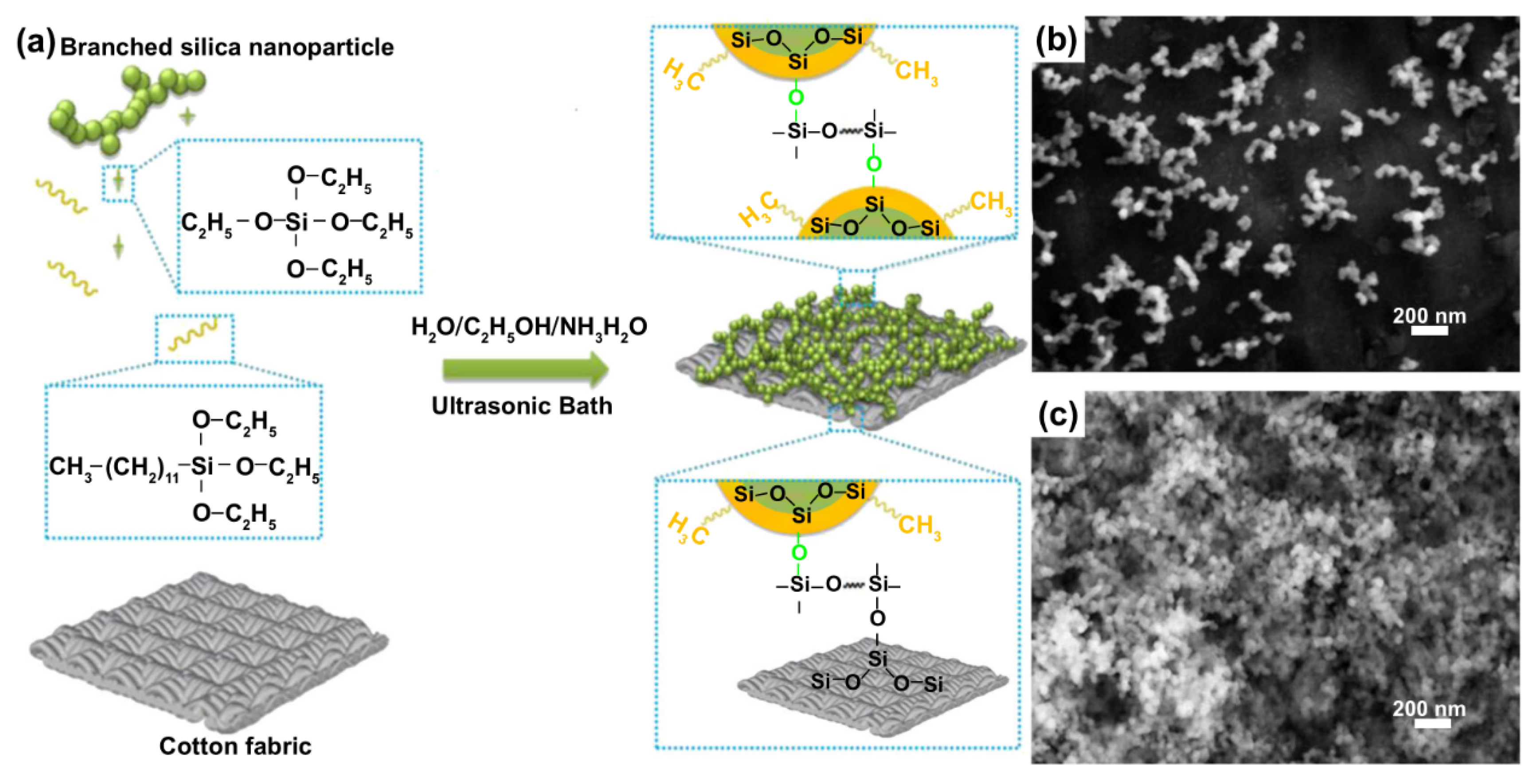
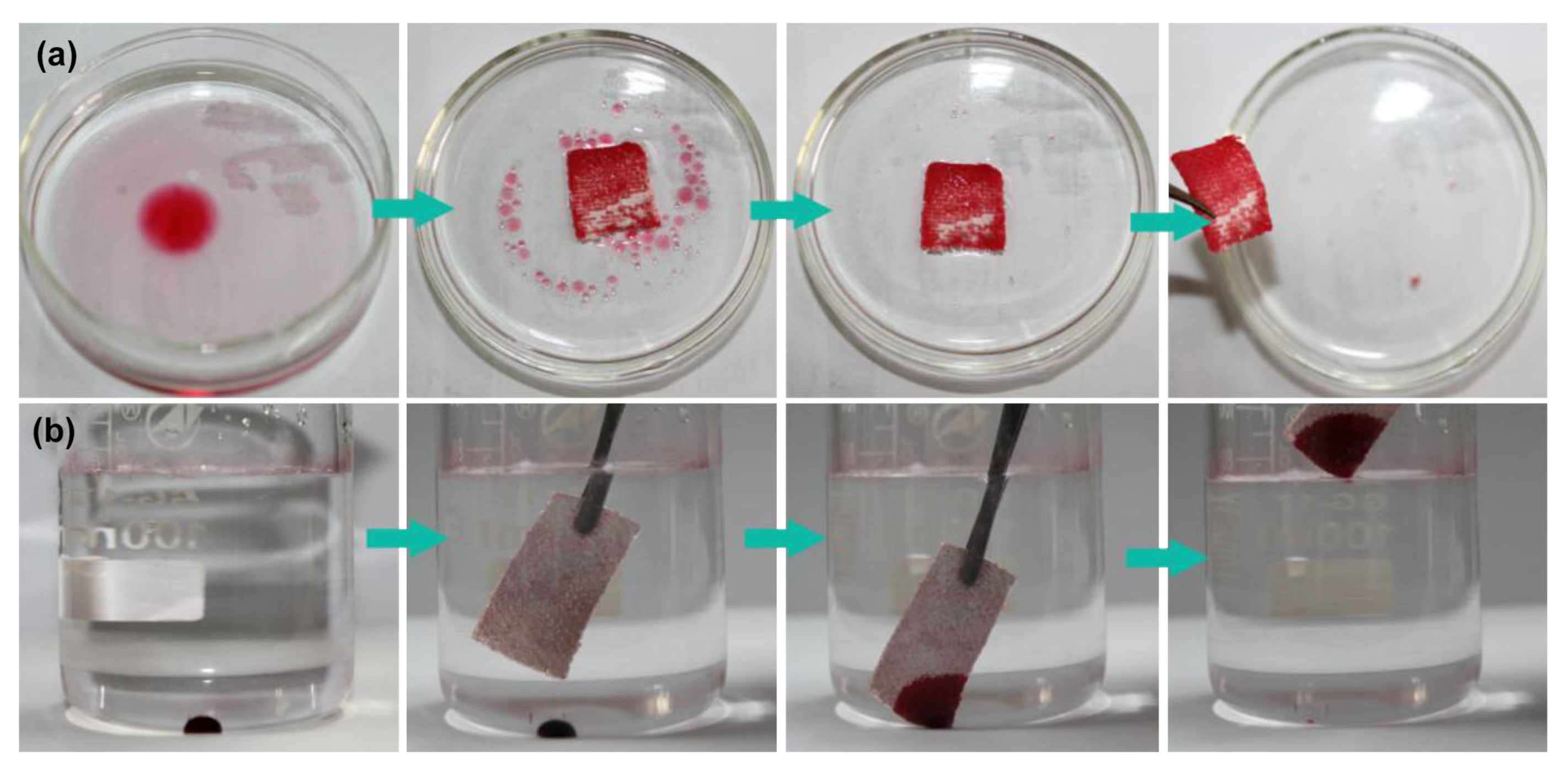
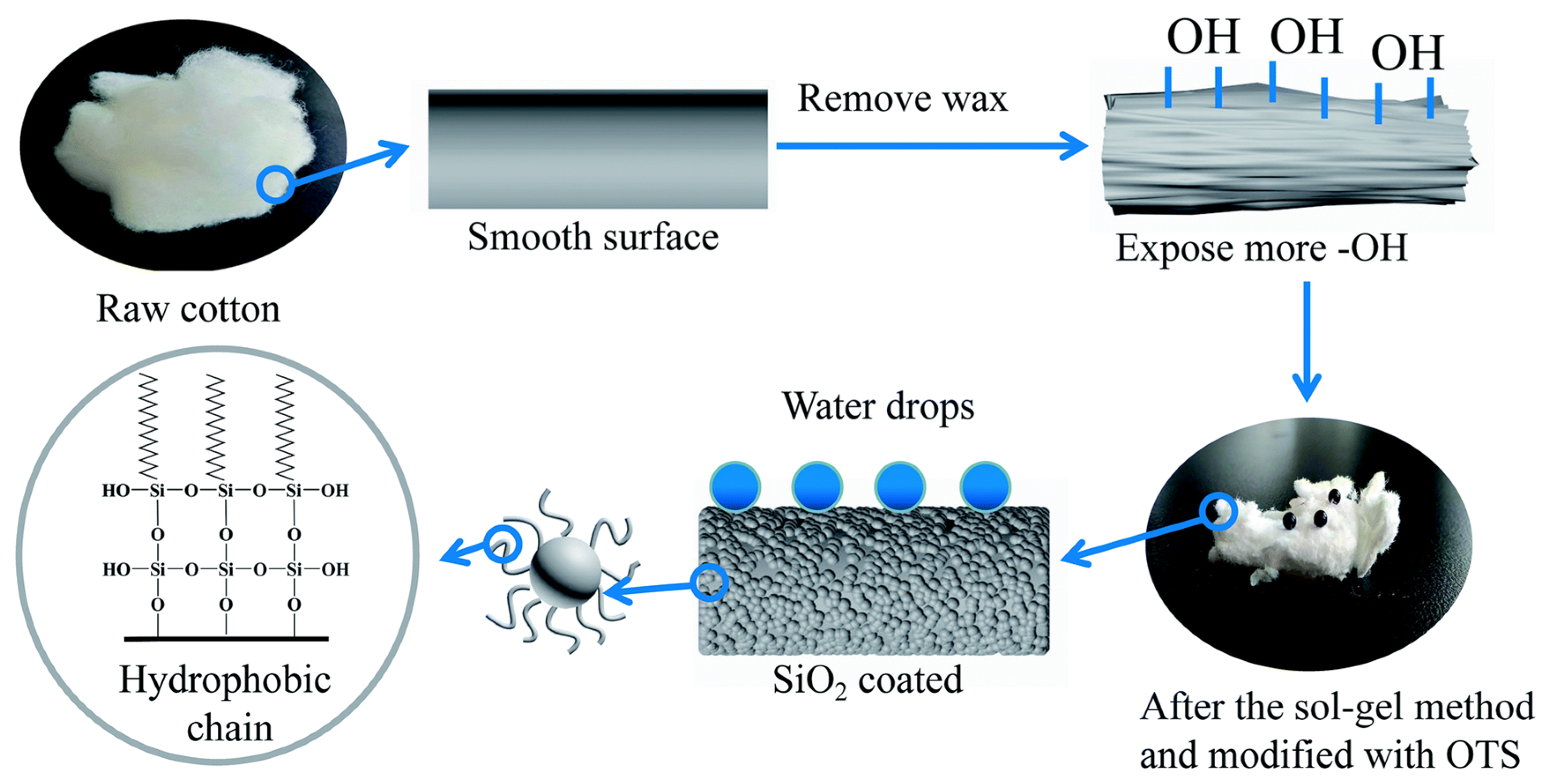
2.1. Water Repellent
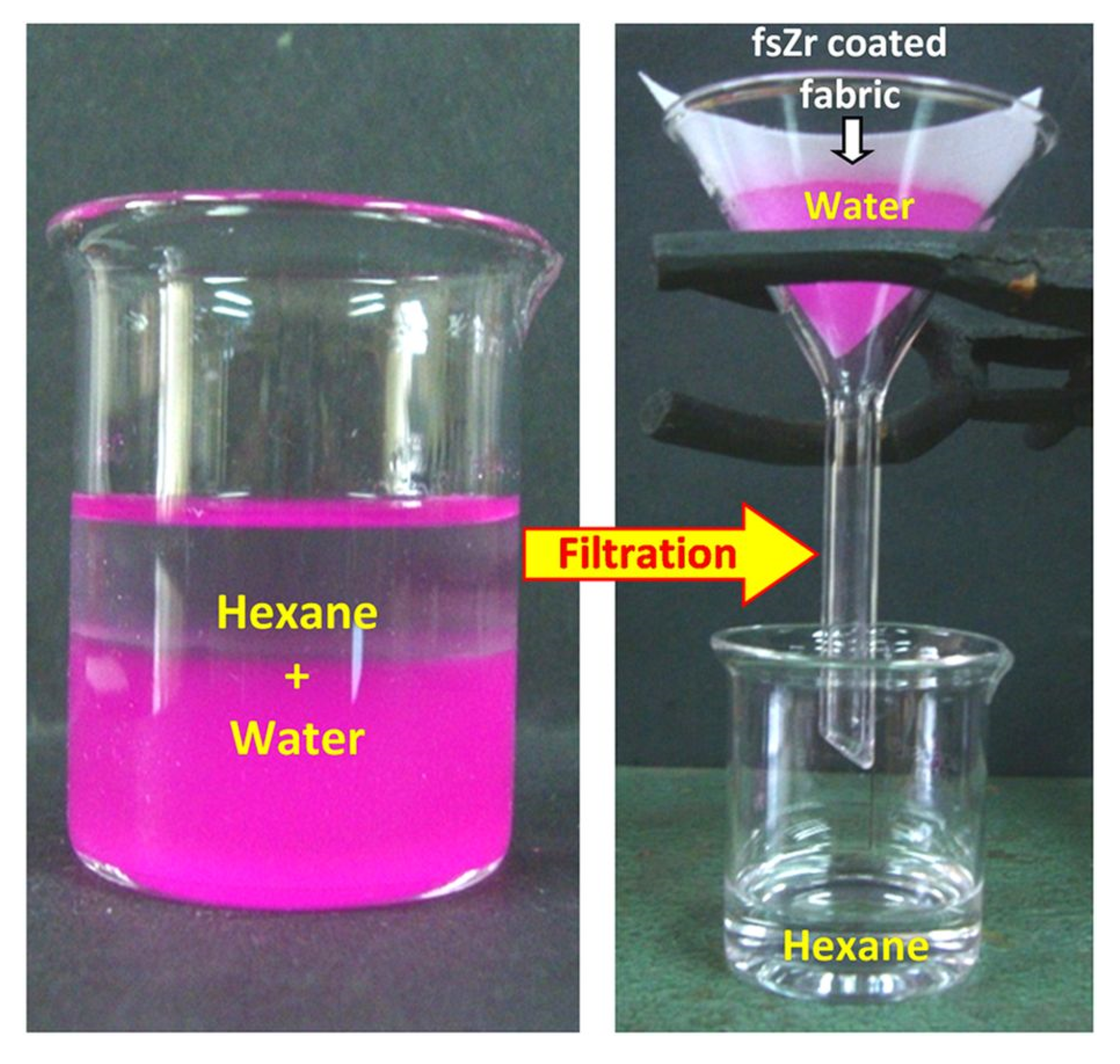
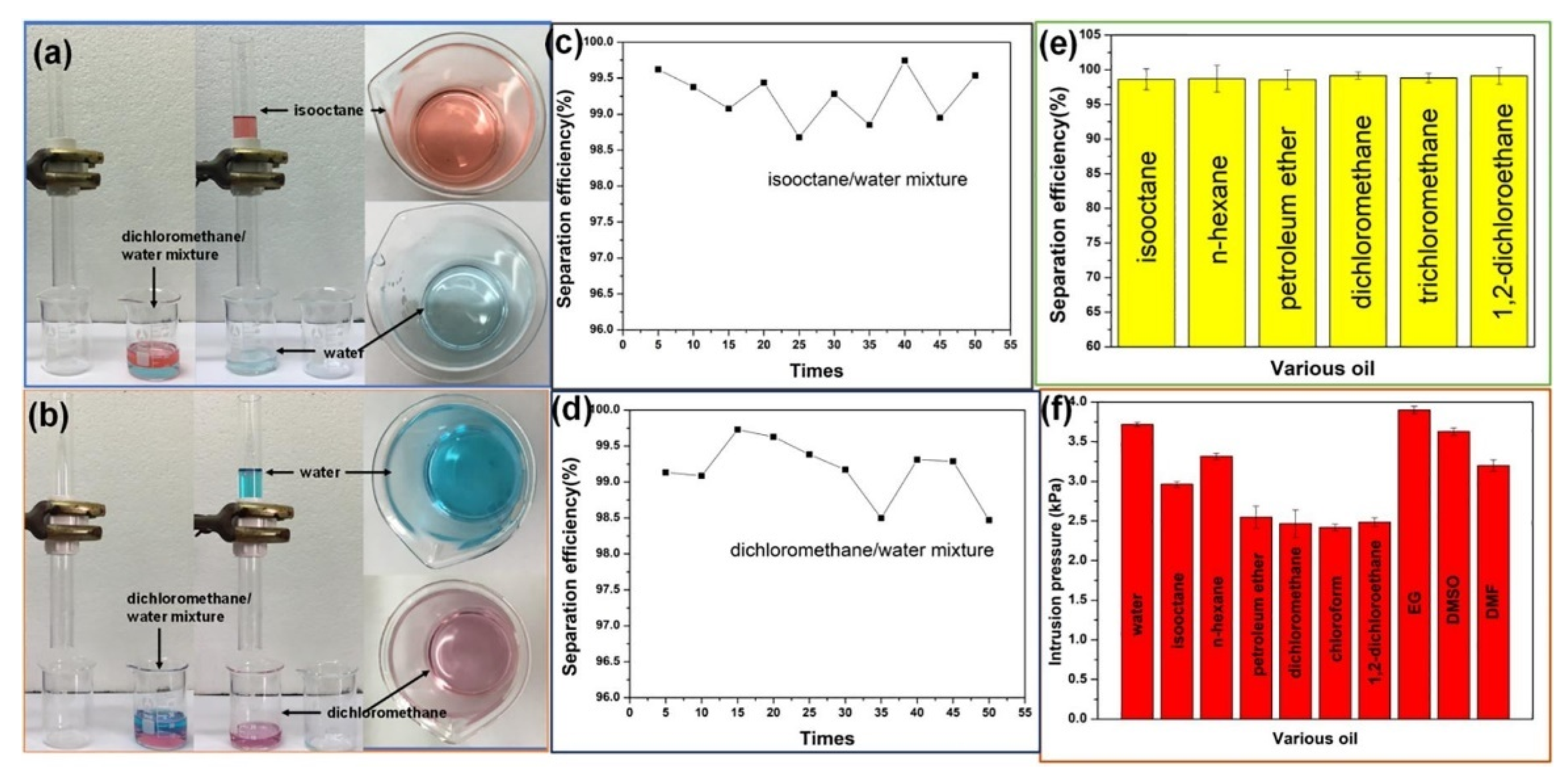
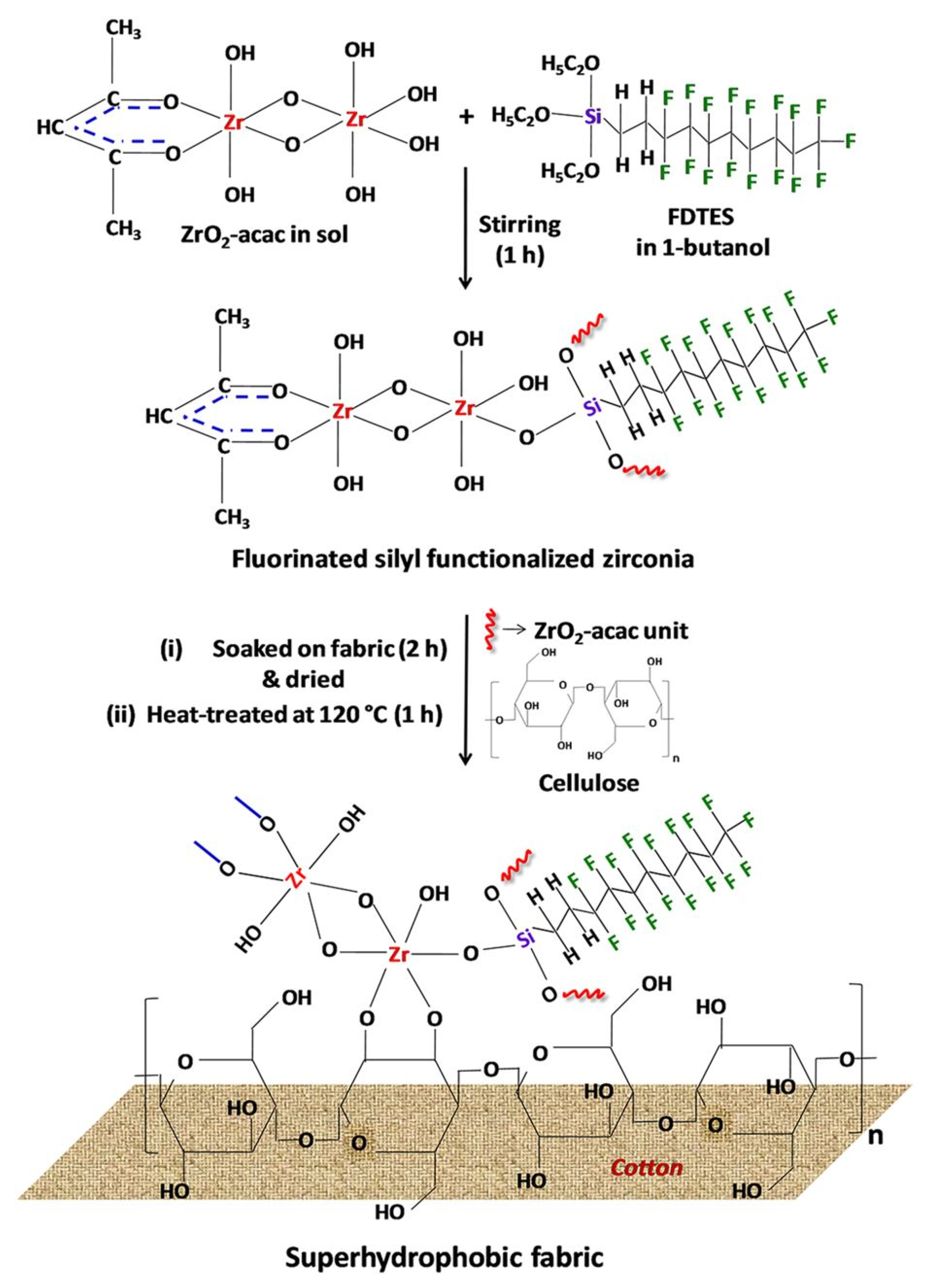
2.2. Oil and Water Separations
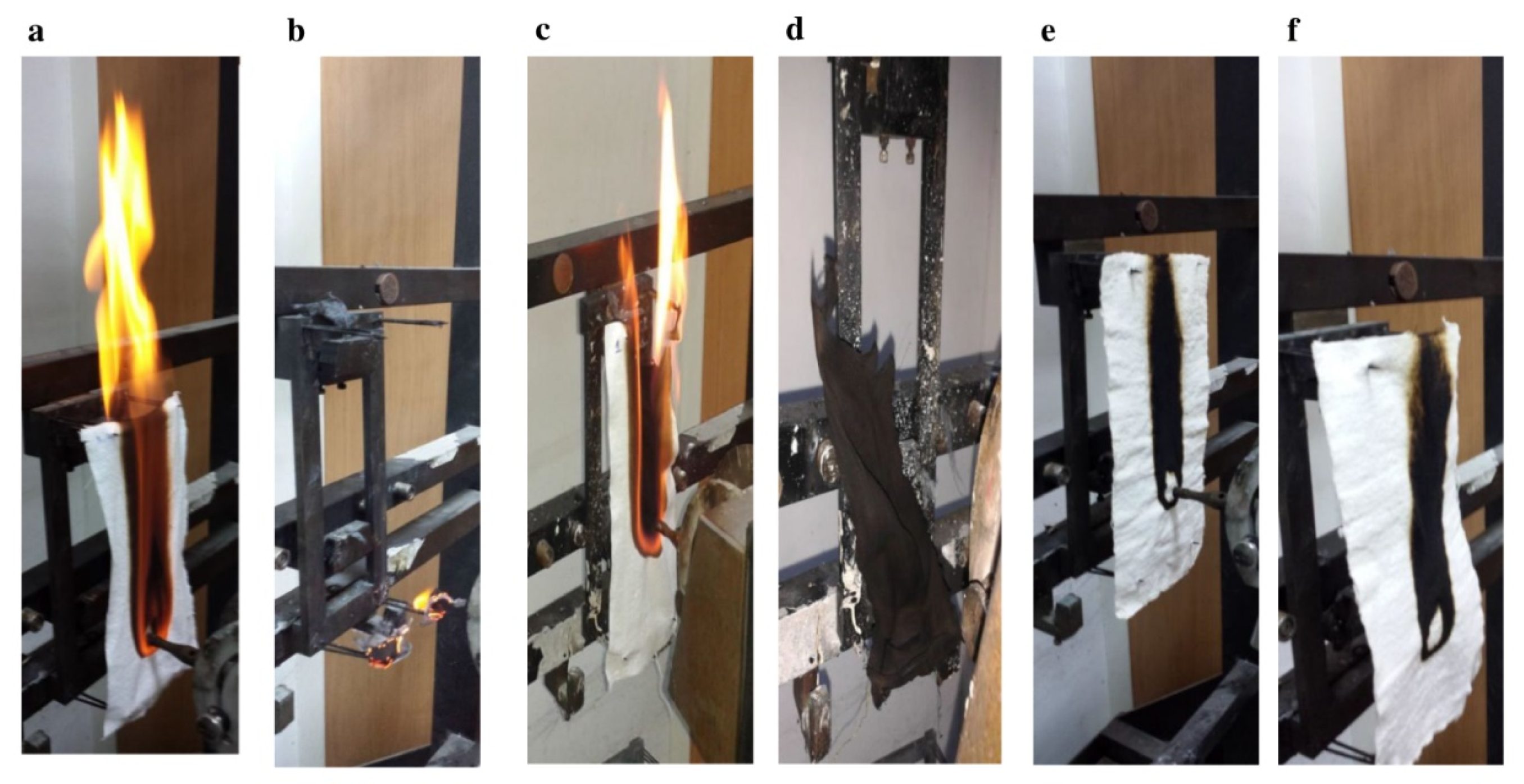
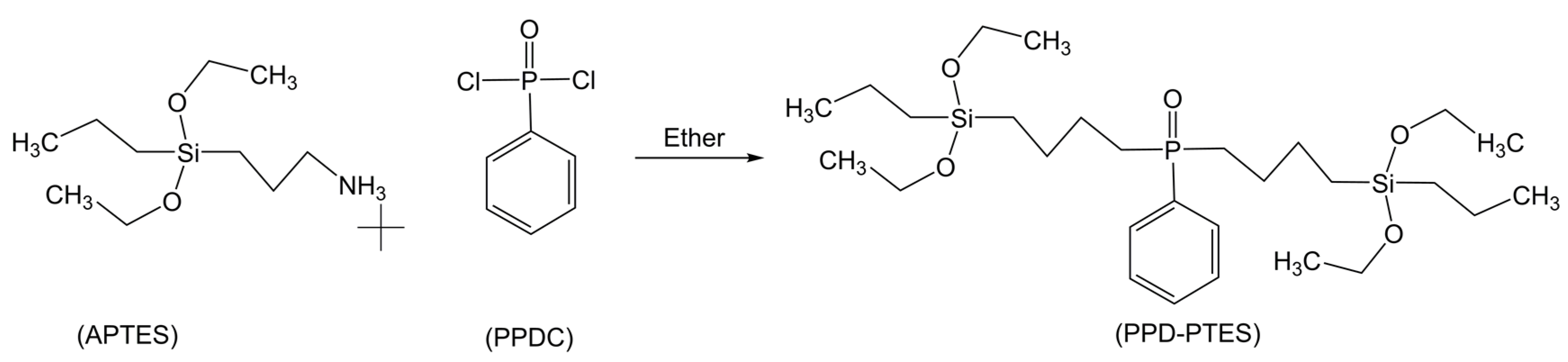
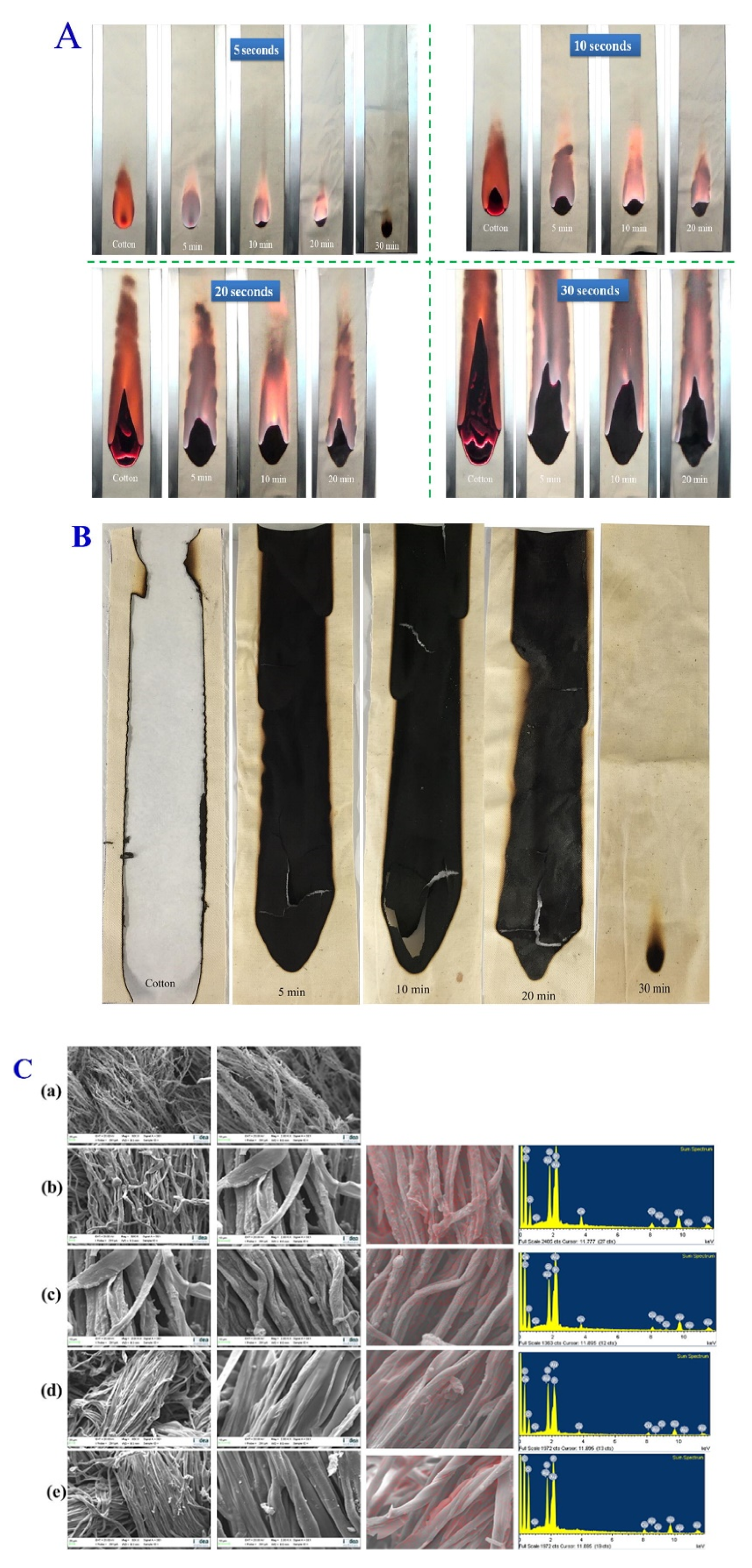
2.3. Flame Retardancy
2.4. UV Protection and Self-Cleaning
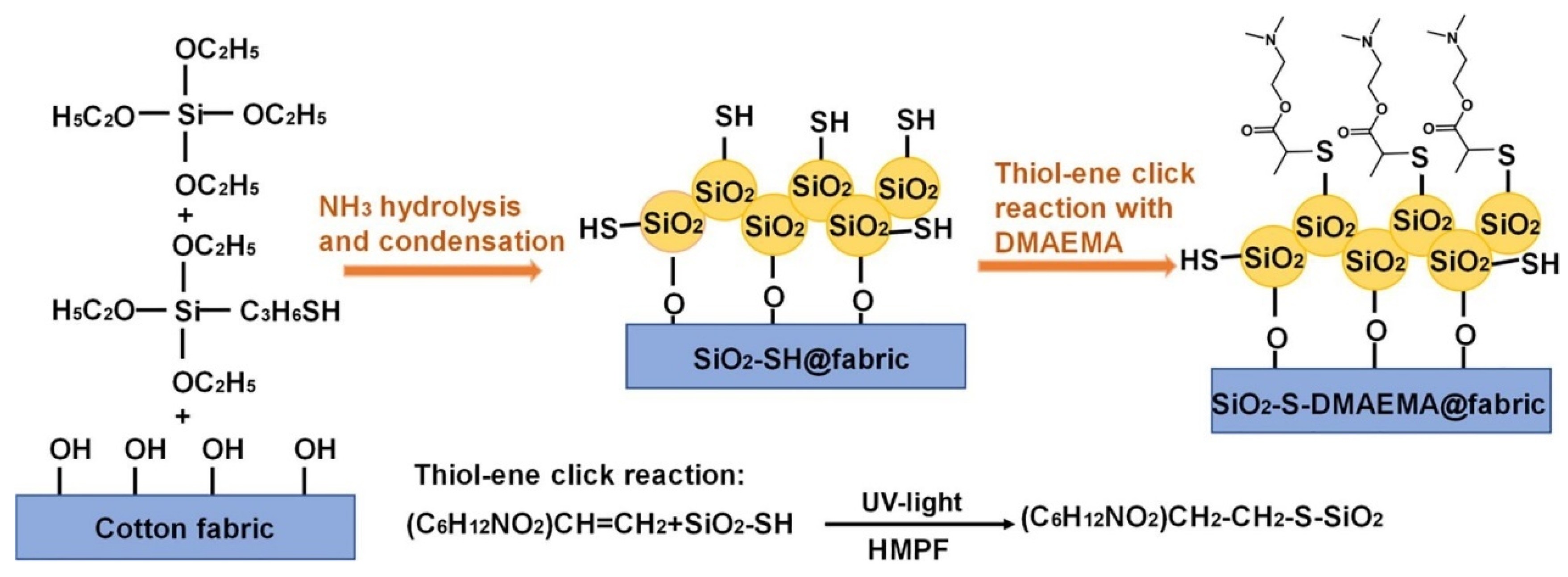
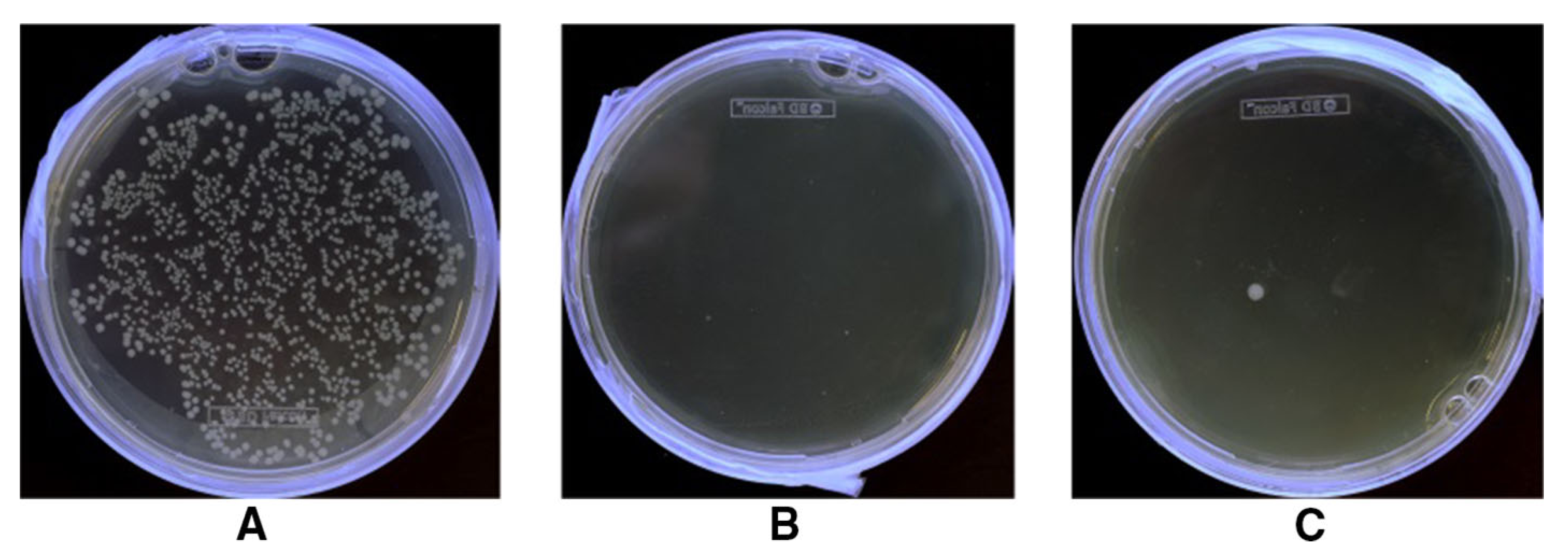
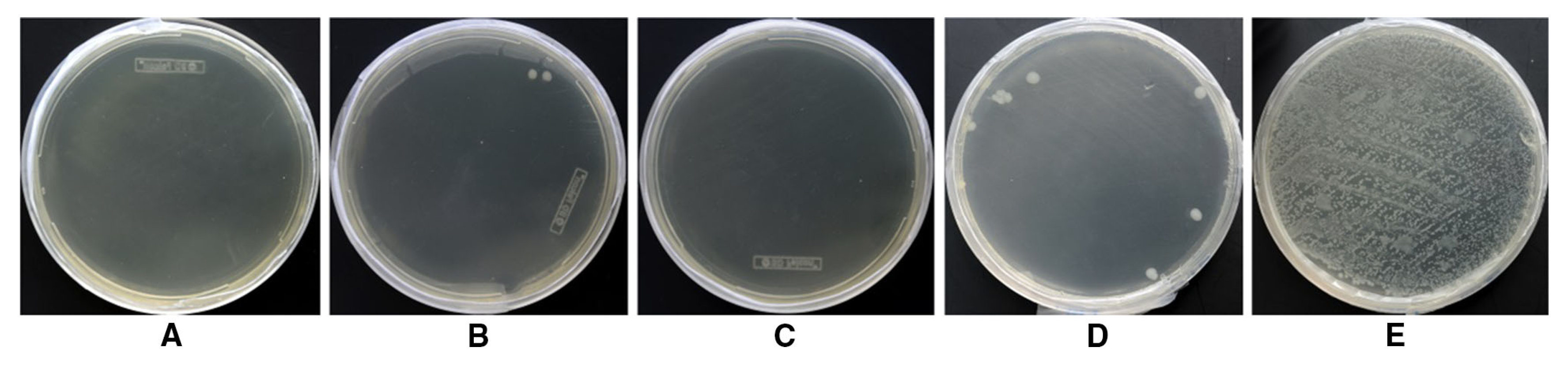
2.5. Antibacterial Finishes
2.6. Wrinkle-Resistance Finishing
2.7. Other Functional Finishing
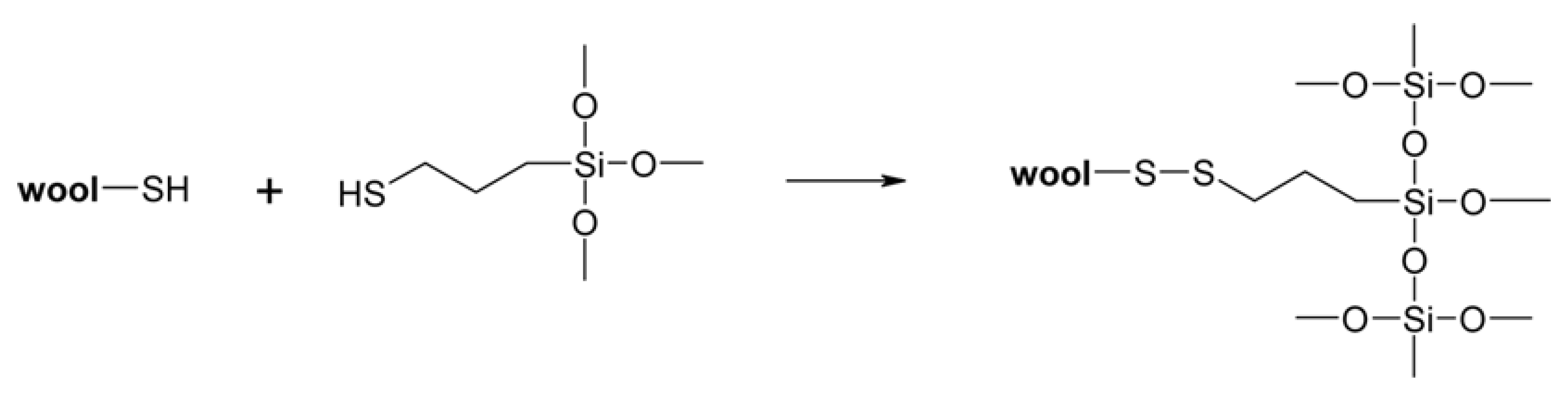
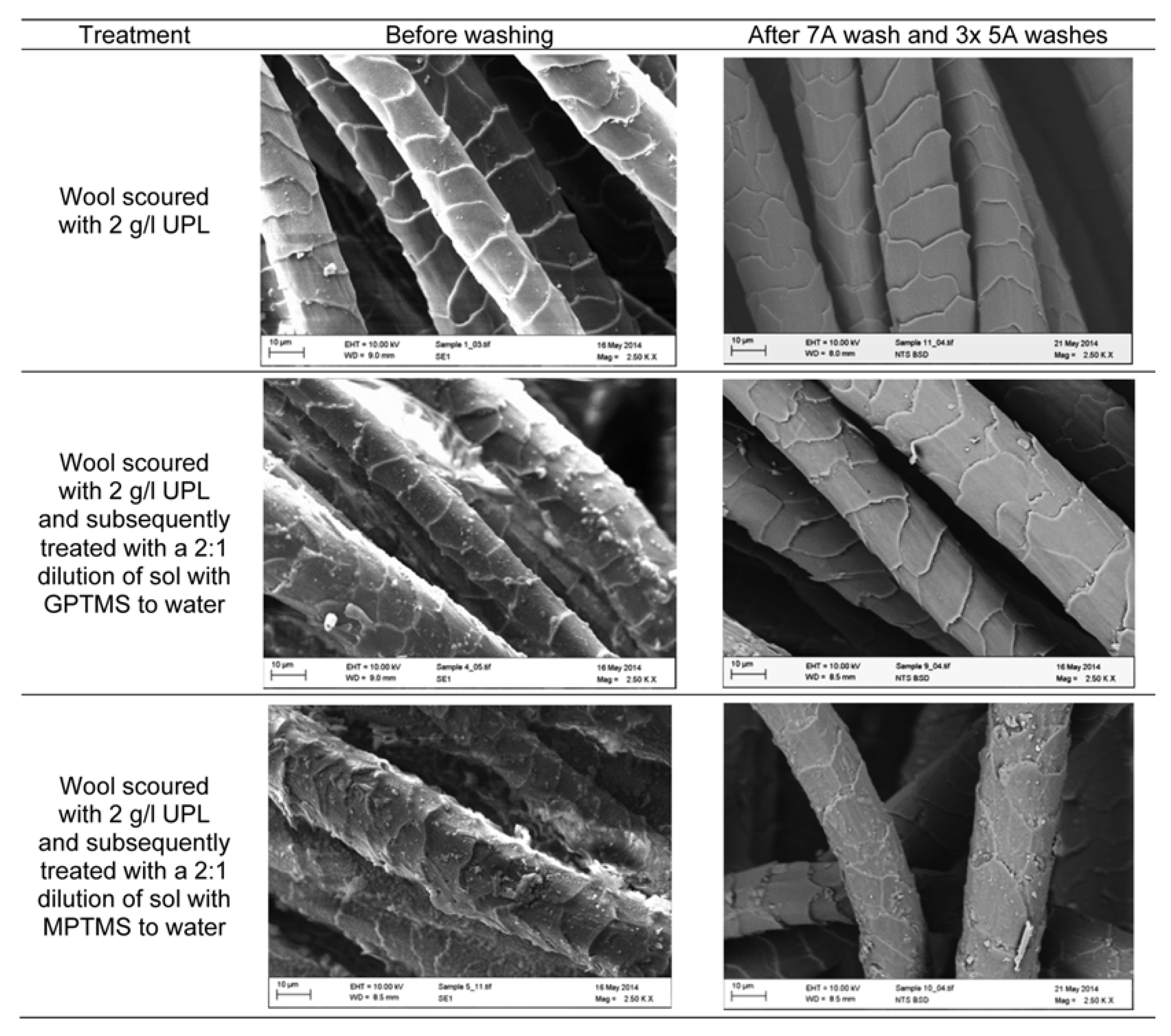
2.7.1. Anti-Felting Finishing on Wool
2.7.2. Heat Storage Temperature Adjustment
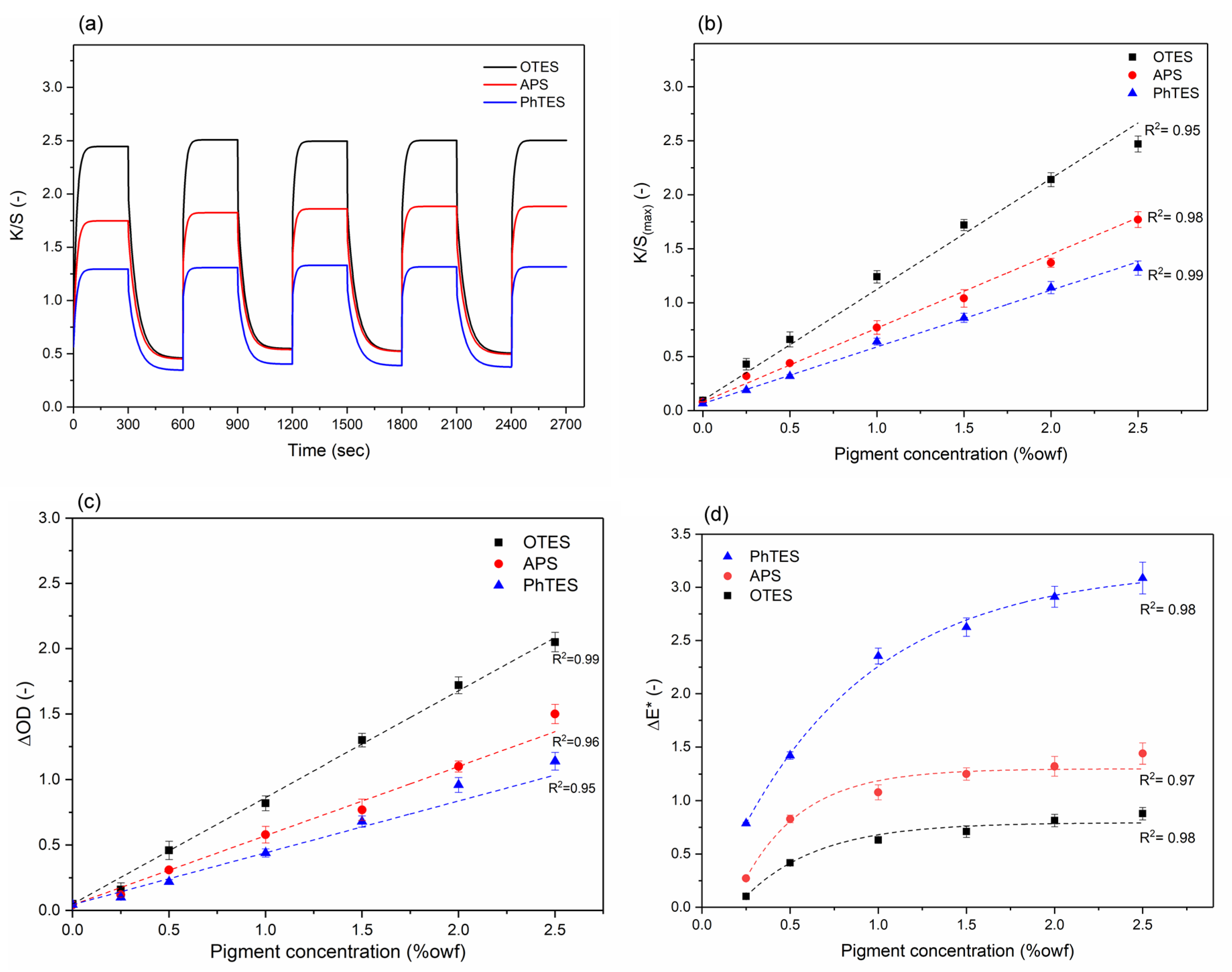
2.7.3. Photochromic/Thermochromic Color Change Finishing
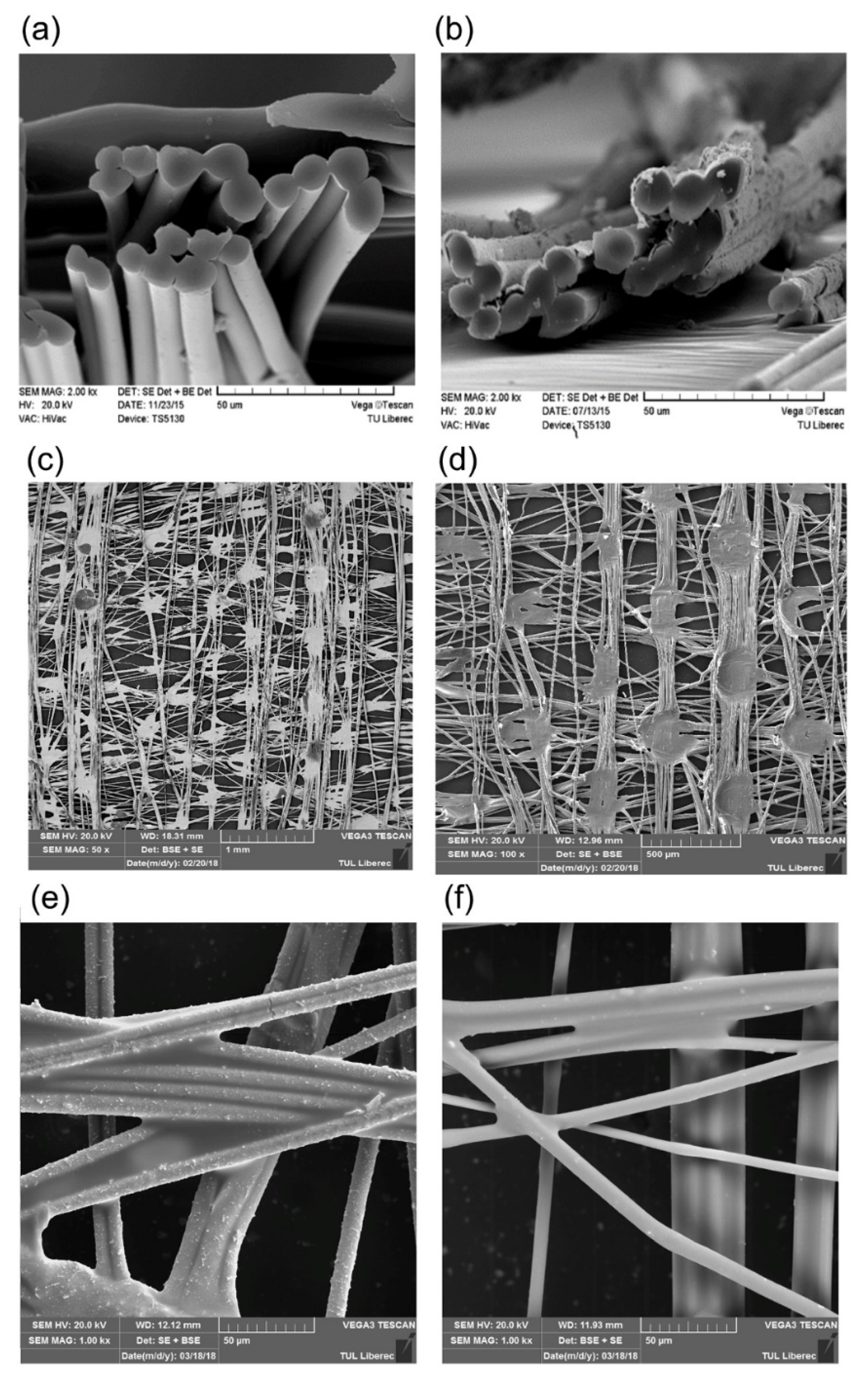
2.7.4. Improving the Durability/ Wear Resistance of Fabrics
2.8. Multifunctional Finishing
3. Future Trends and Challenges of Sol-Gel Finishing in Textiles
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J. Introduction to chemical finishing. In Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J. Chemical finishing processes. In Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 7–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, P. Fabric Finishing: Pretreatment/Textile wet processing. In Textiles and Fashion; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 459–473. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, P.R. Fabric Finishing: Dyeing and Colouring. In Textiles and Fashion: Materials, Design and Technology; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 475–505. ISBN 9780857095619. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Venkatesan, H. Eco-Materials in Textile Finishing; Springer: Cham/Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Lavate, S.S. Eco-Friendly Denim Processing; Springer: Cham/Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Routte, H.K. Encyclopedia of Textile Finishing; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 1995; ISBN 9781845690663. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J. Repellent finishes. In Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 74–86. [Google Scholar]
- Shabbir, M.; Sheikh, J.N. Introduction to Textiles and Finishing Materials. In Frontiers of Textile Materials; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bashari, A.; Shakeri, M.; Shirvan, A.R.; Najafabadi, S.A.N. Functional Finishing of Textiles via Nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials in the Wet Processing of Textiles; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, K.L.; Bahners, T. (Eds.) Textile Finishing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781119426790. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Rwahwire, S.; Zhao, Y. Environmental Friendly Textile Processing. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Springer: Cham/Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 3, ISBN 9783319682556. [Google Scholar]
- Panitz, J.-C.; Geiger, F. Leaching of the Anthraquinone Dye Solvent Blue 59 Incorporated into Organically Modified Silica Xerogels. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 1998, 13, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.P.; Yu, R.; Matijević, E. Well-defined colloidal pigments. ii: Monodispersed inorganic spherical particles containing organic dyes. Dyes Pigments 1992, 19, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuichi, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Onda, T.; Tsujii, K. Super Water- and Oil-Repellent Surfaces Resulting from Fractal Structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 208, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepte, J.; Böttcher, H. Improvement in the Leaching Behavior of Dye-Doped Modified Silica Layers Coated onto Paper or Textiles. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2000, 19, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Knittel, D.; Schollmeyer, E.; Böttcher, H. Incorporation of Triarylmethane Dyes into Sol-Gel Matrices Deposited on Textiles. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2004, 31, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Haufe, H.; Böttcher, H. Functionalisation of textiles by inorganic sol–gel coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4385–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Audenaert, F.; Böttcher, H. Hydrophobic silica sol coatings on textiles-the influence of solvent and sol concentration. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2005, 34, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghimaa, M.; Alharbi, S.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Curcuma longa L. and coating on the cotton fabrics for antimicrobial applications and wound healing activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 204, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Böttcher, H. Modified silica sol coatings for water-repellent textiles. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 27, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Fiedler, D.; Böttcher, H. Antimicrobial sol-gel coatings. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2004, 32, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Textor, T. Silver containing sol-gel coatings on polyamide fabrics as antimicrobial finish-description of a technical application process for wash permanent antimicrobial effect. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadvar, S.; Tavanai, H.; Dadvar, H.; Morshed, M.; Ghodsi, F.E. UV-protection and photocatalytic properties of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous mats coated with TiO2 nanofilm via sol-gel. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 59, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Fiedler, D.; Simon, P. Silver-containing sol-gel coatings on textiles: Antimicrobial effect as a function of curing treatment. J. Text. Inst. 2011, 102, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Fiedler, D.; Fischer, A.; Simon, P. Antimicrobial coatings on textiles-modification of sol-gel layers with organic and inorganic biocides. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2010, 55, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihodceva, S.; Kukle, S.; Muter, O. Antimicrobial Properties of the Modified Cotton Textiles by the Sol-Gel Technology. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1117, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Gu, Y. Phosphorus-doped organic-inorganic hybrid silicon coating for improving fire retardancy of polyacrylonitrile fabric. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, P.J.; Goicoechea, J. Sol-gel technology for antimicrobial textiles. In Antimicrobial Textiles; Sun, G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 47–72. ISBN 9780081005859. [Google Scholar]
- Trovato, V.; Teblum, E.; Kostikov, Y.; Pedrana, A.; Re, V.; Nessim, G.D.; Rosace, G. Sol-gel approach to incorporate millimeter-long carbon nanotubes into fabrics for the development of electrical-conductive textiles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Grethe, T.; Haase, H. Antimicrobial coatings obtained by sol-gel method. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology: Processing, Characterization and Applications; Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3461–3487. ISBN 9783319321011. [Google Scholar]
- Plutino, M.R.; Colleoni, C.; Donelli, I.; Freddi, G.; Guido, E.; Maschi, O.; Mezzi, A.; Rosace, G. Sol-gel 3-glycidoxypropyltriethoxysilane finishing on different fabrics: The role of precursor concentration and catalyst on the textile performances and cytotoxic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Yu, M.; Li, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Quan, M.; Liu, Z.; Shi, S.; Gong, Y. Synthesis of a fluorine-free polymeric water-repellent agent for creation of superhydrophobic fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, C.; He, S.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z. Fabrication of superhydrophobic cotton fabric with fluorinated TiO2 sol by a green and one-step sol-gel process. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, W.; Quan, M.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Shi, S.; Gong, Y. Positive effect of polymeric silane-based water repellent agents on the durability of superhydrophobic fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Lin, T. Recent Development in Durable Super-Liquid-Repellent Fabrics. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Mazzon, G.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Environmentally benign non-wettable textile treatments: A review of recent state-of-the-art. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 270, 216–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Textor, T.; Mahltig, B. A sol-gel based surface treatment for preparation of water repellent antistatic textiles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Shen, L.; Shang, S.; Xing, Y. Preparation of superhydrophobic and UV blocking cotton fabric via sol-gel method and self-assembly. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, L.Y.L.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y. Ambient-curable superhydrophobic fabric coating prepared by water-based non-fluorinated formulation. Mater. Des. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Wang, A. Facile preparation of durable and robust superhydrophobic textiles by dip coating in nanocomposite solution of organosilanes. Chem. Commun. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Li, M.; Guo, X.J.; Li, X.; An, Q.F.; Jia, S.T. Fabrication of superhydrophobic textiles with high water pressure resistance. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, M.D.; Annaldewar, B.N. Superhydrophobic and ultraviolet protective nylon fabrics by modified nano silica coating. J. Text. Inst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Jia, S.T.; Chen, H.Z.; Wang, M. Superhydrophobic cotton fabrics prepared by sol-gel coating of TiO2 and surface hydrophobization. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wen, G.; Guo, Z. Durable superhydrophobic and underwater superoleophobic cotton fabrics growing zinc oxide nanoarrays for application in separation of heavy/light oil and water mixtures as need. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 559, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lyu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Facile synthesis of fluorinated polydopamine/chitosan/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogel for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Shi, Z.; Ou, J.; Wang, F.; Xue, M.; Li, W.; Qiao, G.; Guan, X.; Zhang, J. Durable superhydrophobic cotton fabric for oil/water separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 533, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zeng, X.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Xie, H. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic filtration fabric with honeycomb structures for the separation of water and oil. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tu, W.; Wee, K.-H.; Bai, R. Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.-Y.; Zhao, X.-L.; Li, Y.-D.; Weng, Y.-X.; Zeng, J.-B. Robust and nanoparticle-free superhydrophobic cotton fabric fabricated from all biological resources for oil/water separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Zha, F.; Feng, H.; Hu, D. A photo-induced ZnO coated mesh for on-demand oil/water separation based on switchable wettability. Mater. Lett. 2016, 163, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y. One-pot fabrication of robust hydrophobia and superoleophilic cotton fabrics for effective oil-water separation. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, A.; Le Floch, S.; Reinert, L.; Ramos, S.M.M.; Tuaillon-Combes, J.; Soneda, Y.; Chaudet, P.; Baillis, D.; Blanchard, N.; Duclaux, L.; et al. Melamine-derived carbon sponges for oil-water separation. Carbon N. Y. 2016, 107, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Neisius, N.M.; Gaan, S. Recent developments in flame retardant polymeric coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1642–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleoni, C.; Donelli, I.; Freddi, G.; Guido, E.; Migani, V.; Rosace, G. A novel sol-gel multi-layer approach for cotton fabric finishing by tetraethoxysilane precursor. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, E.; Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Di Blasio, A.; Carosio, F.; Verelst, M.; Malucelli, G.; Rosace, G. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of polyester fabrics sol-gel treated in the presence of boehmite nanoparticles. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Ciobanu, M.; Malucelli, G. Sol-gel treatments on cotton fabrics for improving thermal and flame stability: Effect of the structure of the alkoxysilane precursor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Ciobanu, M.; Malucelli, G. Thermal stability, flame retardancy and mechanical properties of cotton fabrics treated with inorganic coatings synthesized through sol–gel processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, N.; Azhagurajan, A.; Natarajan, T.S.; Mohideen Abdul Khadir, M. Flame-retardant fabric systems based on electrospun polyamide/boric acid nanocomposite fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 126, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Ciobanu, M.; Tata, J.; Carosio, F.; Malucelli, G. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of polyester, cotton, and relative blend textile fabrics subjected to sol–gel treatments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Fang, S.; Ji, P.; Wang, H.; Ji, C. Durable flame-retardant and antidroplet finishing of polyester fabrics with flexible polysiloxane and phytic acid through layer-by-layer assembly and sol-gel process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, A.R. Flame Retardant Textile Finishes. In Textile Finishing: Recent Developments and Future Trends; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 69–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Williams, B.L.; Shrestha, S.B.; Nasir, Z.; Becher, E.M.; Lofink, B.J.; Santos, V.H.; Patel, H.; Peng, X.; Sun, L. Flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel and self-assembly techniques. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadil, B.; Amadine, O.; Essamlali, Y.; Cherkaoui, O.; Zahouily, M. A new route for the preparation of hydrophobic and antibacterial textiles fabrics using Ag-loaded graphene nanocomposite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Brzeziński, S.; Kamińska, I. Multifunctional bioactive and improving the performance durability nanocoatings for finishing PET/CO woven fabrics by the sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 649, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foksowicz-Flaczyk, J.; Walentowska, J.; Przybylak, M.; Maciejewski, H. Multifunctional durable properties of textile materials modified by biocidal agents in the sol-gel process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 304, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malucelli, G. Sol-Gel Flame Retardant and/or Antimicrobial Finishings for Cellulosic Textiles. In Handbook of Renewable Materials for Coloration and Finishing; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 501–519. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiljević, J.; Tomšič, B.; Jerman, I.; Orel, B.; Jakša, G.; Kovač, J.; Simončič, B. Multifunctional superhydrophobic/oleophobic and flame-retardant cellulose fibres with improved ice-releasing properties and passive antibacterial activity prepared via the sol-gel method. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vihodceva, S.; Kukle, S. Improvement of UV Protection Properties of the Textile from Natural Fibres by the Sol-gel Method. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 49, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Bautista, L.; De la Varga, M.; Botet, J.M.; Casals, E.; Puntes, V.; Marsal, F. Nano-cotton Fabrics with High Ultraviolet Protection. Text. Res. J. 2009, 80, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Butola, B.S. Development of Cotton Fabrics with Durable UV Protective and Self-cleaning Property by Deposition of Low TiO2 Levels through Sol-gel Process. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhatial, A.K.; Khatri, A.; Ali, S.; Babar, A.A. Sol-gel finishing of bamboo fabric with nanoparticles for water repellency, soil release and UV resistant characteristics. Cellulose 2019, 26, 6365–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Leong, H.J.; Noh, H.; Kang, T.; Kong, S.; Oh, S.G. Preparation of N-functionalized TiO2 particles using one-step sol-gel method and their photocatalytic activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 37, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Liu, K.; Ni, Y. Synthesis of mesoporous α-Fe2O3 via sol-gel methods using cellulose nano-crystals (CNC) as template and its photo-catalytic properties. Mater. Lett. 2015, 159, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeziński, S.; Kowalczyk, D.; Borak, B.; Jasiorski, M.; Tracz, A. Nanocoat finishing of polyester/cotton fabrics by the sol-gel method to improve their wear resistance. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 6, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, A.C. General Introduction. In Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing; Pierre, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-1-4615-5659-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sakka, S.; Kamiya, K. The sol-gel transition in the hydrolysis of metal alkoxides in relation to the formation of glass fibers and films. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.-Q. Sol-Gel Processes of Functional Powders and Films. In Chemical Reactions in Inorganic Chemistry; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dislich, H.; Hinz, P. History and principles of the sol-gel process, and some new multicomponent oxide coatings. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol–gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horizons 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycki, J. Gel→glass transformation. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, A.C. Gelation. In Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing; Pierre, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 169–204. ISBN 978-1-4615-5659-6. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, A.C. The Chemistry of Precursors Solutions. In Introduction to Sol-Gel Processing; Pierre, A.C., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 11–89. ISBN 978-1-4615-5659-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kursawe, M.; Hilarius, V.; Pfaff, G.; Anselmann, R. Sol-gel Coating Processes. In Modern Surface Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 205–220. ISBN 3527315322. [Google Scholar]
- Baccile, N.; Babonneau, F.; Thomas, B.; Coradin, T. Introducing ecodesign in silica sol-gel materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8537–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dislich, H. New Routes to Multicomponent Oxide Glasses. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.C.; Garvey, G.J. Monolithic dried gels. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordas, G. Sol-gel processing of ceramic superconductors. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1990, 121, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzini, P. High Performance Ceramic Films and Coatings; North-Holland Publishing, Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; ISBN 978-0444890580. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.K.; Kang, S.-J.; Choi, S.-K.; Min, Y.-H.; Yoon, C.-S. Highly Efficient Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Nonlinear Optic Materials via Sol-Gel Process: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Photobleaching for Channel Waveguides. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol-gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnir, D.; Braun, S.; Lev, O.; Ottolenghi, M. Enzymes and Other Proteins Entrapped in Sol-Gel Materials. Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayat, A.; Reinhardt, B.; Herwig, J.; Küster, C.; Uhlig, H.; Krenkel, S.; Raedlein, E.; Enke, D. Recent advances in the synthesis of hierarchically porous silica materials on the basis of porous glasses. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4095–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinle, A.; Elsaesser, M.S.; Hüsing, N. Sol-gel synthesis of monolithic materials with hierarchical porosity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3377–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livage, J. Inorganic Materials, Sol-Gel Synthesis of. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Buschow, K.H.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S., Veyssière, P.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 4105–4107. ISBN 978-0-08-043152-9. [Google Scholar]
- Handbook of sol-gel science and technology: Processing, characterization, and applications. Choice Rev. Online 2013. [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L.; West, J.K. The Sol-Gel Process. Chem. Rev. 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Frye, G.C.; Hurd, A.J.; Ashley, C.S. Fundamentals of sol-gel dip coating. Thin Solid Films 1991, 201, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Particulate Sols and Gels. In Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; ISBN 9780080571034. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, J. Sol-Gel Technology in the Glass Industry. In Glass …Current Issues; Wright, A.F., Dupuy, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 224–231. ISBN 978-94-009-5107-5. [Google Scholar]
- Livage, J. Basic Principles of Sol-Gel Chemistry. In Sol-Gel Technologies for Glass Producers and Users; Aegerter, M.A., Mennig, M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 3–14. ISBN 978-0-387-88953-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.; Scholze, H. The Sol-Gel Process for Non-Metallic Inorganic Materials. In Aerogels; Fricke, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Livage, J. The Sol-Gel Process: Present and Future. In Transformation of Organometallics into Common and Exotic Materials: Design and Activation; Laine, R.M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 255–260. ISBN 978-94-009-1393-6. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmi, M.; Carturan, G. Precursors for sol-gel preparations. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corriu, R.J.P.; Leclercq, D. Recent Developments of Molecular Chemistry for Sol-Gel Processes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemistry, S. Sol-Gel Synthesis. In Encyclopedia of Electrochemical Power Sources; Garche, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 613–624. ISBN 978-0-444-52745-5. [Google Scholar]
- Brinker, C.J. Hydrolysis and condensation of silicates: Effects on structure. J. Non.-Cryst. Solids 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780080571034. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Orler, B.; Wilkes, G.L. Structure-Property Behavior of New Hybrid Materials Incorporating Oligomeric Species into Sol-Gel Glasses. 3. Effect of Acid Content, Tetraethoxysilane Content, and Molecular Weight of Poly(dimethylsiloxane). Macromolecules 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, M.; Mishra, R.; Yang, K.; Militky, J.; Kremenakova, D.; Zhu, G.; Yao, J. Preparation of Electrosprayed Microporous Membranes. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 460, 12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A.R. Waterproof breathable layers—A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 268, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylak, M.; Maciejewski, H.; Dutkiewicz, A. Preparation of highly hydrophobic cotton fabrics by modification with bifunctional silsesquioxanes in the sol-gel process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onar, N.; Mete, G. Development of water repellent cotton fabric with application of ZnO, Al2O3, TiO2 and ZrO2 nanoparticles modified with ormosils. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2016, 26, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Migani, V.; Rosace, G. Hydrophobic behaviour of non-fluorinated sol-gel based cotton and polyester fabric coatings. J. Ind. Text. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ferri, L.; Lorenzi, A.; Carcano, E.; Draghi, L. Silk fabrics modification by sol-gel method. Text. Res. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljević, J.; Zorko, M.; Tomšič, B.; Jerman, I.; Simončič, B. Fabrication of the hierarchically roughened bumpy-surface topography for the long-lasting highly oleophobic “lotus effect” on cotton fibres. Cellulose 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Niu, H.; Gestos, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Fluoroalkyl Silane Modified Silicone Rubber/Nanoparticle Composite: A Super Durable, Robust Superhydrophobic Fabric Coating. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2409–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Ge, M.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Deng, S.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Lai, Y. Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic PDMS–ormosil@ fabrics for highly effective self-cleaning and efficient oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12179–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrope, M. Oil cruise finds deep-sea plume. Nature 2010, 465, 274–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrope, M. The lost legacy of the last great oil spill. Nature 2010, 466, 304–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.K.; Dunderdale, G.J.; England, M.W.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrope, M. Oil spill: Deep wounds. Nature 2011, 472, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, S.B. Deepwater Horizon, 5 years on. Science 2015, 349, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B.K. Aerostat Sampling of PCDD/PCDF Emissions from the Gulf Oil Spill In Situ Burns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Jiang, P.; Ke, Q.; Cheng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polydimethylsiloxane-coated cotton for oil–water separation process: An evidence of the relationship between its loading capacity and oil absorption ability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Han, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Seo, H.O.; Kim, Y.D. Oil absorption capacity of bare and PDMS-coated PET non-woven fabric; dependency of fiber strand thickness and oil viscosity. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefelová, J.; Slovák, V.; Siqueira, G.; Olsson, R.T.; Tingaut, P.; Zimmermann, T.; Sehaqui, H. Drying and Pyrolysis of Cellulose Nanofibers from Wood, Bacteria, and Algae for Char Application in Oil Absorption and Dye Adsorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.R.; Maurya, R.; Balani, K. Superhydrophobic self-floating carbon nanofiber coating for efficient gravity-directed oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2936–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Tai, N.-H. Carbon materials as oil sorbents: A review on the synthesis and performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1550–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Tzeng, F.-S.; Chen, H.-G.; Chang, C.-J. Ultraviolet-Durable Superhydrophobic Zinc Oxide-Coated Mesh Films for Surface and Underwater–Oil Capture and Transportation. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10015–10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, D.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Nanowire-Haired Inorganic Membranes with Superhydrophilicity and Underwater Ultralow Adhesive Superoleophobicity for High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4192–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Lang, J.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Dai, J. One-step facile fabrication of sustainable cellulose membrane with superhydrophobicity via a sol-gel strategy for efficient oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 361, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wen, X.; Xu, S.; Cheng, J.; Pi, P. A durable underwater superoleophobic and underoil superhydrophobic fabric for versatile oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Long, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Hu, J. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic glass-fiber fabric for water-in-oil emulsion separation. Text. Res. J. 2018, 89, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, I.; De, G. Zirconia based superhydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics exhibiting excellent durability for versatile use. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z. Fabrication of durable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic cotton fabric with fluorinated silica sol via sol-gel process. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Luo, L.; Zhou, R. Superhydrophobic/superoleophilic cotton-oil absorbent: Preparation and its application in oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 30257–30264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G. Phosphorus- and nitrogen-doped silica coatings for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton: Synergisms or additive effects? Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G. Sol-gel derived architectures for enhancing cotton flame retardancy: Effect of pure and phosphorus-doped silica phases. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 99, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Q. Flame resistant cotton. In Handbook of Fire Resistant Textiles; Kilinc, F.S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013; pp. 177–220. ISBN 9780857098931. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiljević, J.; Hadžić, S.; Jerman, I.; Černe, L.; Tomšič, B.; Medved, J.; Godec, M.; Orel, B.; Simončič, B. Study of flame-retardant finishing of cellulose fibres: Organic-inorganic hybrid versus conventional organophosphonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, T. Modification of textile surfaces using the sol-gel technique. In Surface Modification of Textiles; Wei, Q.B., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 185–213. ISBN 9781845694197. [Google Scholar]
- Malucelli, G. Surface-Engineered Fire Protective Coatings for Fabrics through Sol-Gel and Layer-by-Layer Methods: An Overview. Coatings 2016, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancaric, A.M.; Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Botteri, L.; Rosace, G. Thermal behaviour and flame retardancy of monoethanolamine-doped sol-gel coatings of cotton fabric. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhriss, A.; Gmouh, S.; Hannach, H.; Roblin, J.P.; Cherkaoui, O.; Boyer, D. Treatment of cotton fabrics by ionic liquid with PF6−anion for enhancing their flame retardancy and water repellency. Cellulose 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Gu, J.; Chen, G.Q.; Xing, T.L. Durable flame retardant finish for silk fabric using boron hybrid silica sol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šehić, A.; Tomšič, B.; Jerman, I.; Vasiljević, J.; Medved, J.; Simončič, B. Synergistic inhibitory action of P- and Si-containing precursors in sol-gel coatings on the thermal degradation of polyamide 6. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deh, S.; Gähr, F.; Buchmeiser, M.R. Synergistic effects in the pyrolysis of phosphorus-based flame-retardants: The role of Si- and N-based compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.T.; Wang, X.; Acuña, P.; Zhu, P.; Wagenknecht, U.; Heinrich, G.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.Y. Effect of phosphorus-containing inorganic-organic hybrid coating on the flammability of cotton fabrics: Synthesis, characterization and flammability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, H. Surface modification of TiO2/SiO2 composite hydrosol stabilized with polycarboxylic acid on Kroy-process wool fabric. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhineshbabu, N.R.; Arunmetha, S.; Manivasakan, P.; Karunakaran, G.; Rajendran, V. Enhanced functional properties of cotton fabrics using TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposites. J. Ind. Text. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.; Textor, T.; Schollmeyer, E.; Tarbuk, A.; Grancacic, A.M. Sol-gel-derived inorganic-organic hybrid polymers filled with zno nanoparticles as an ultraviolet protection finish for textiles. Autex Res. J. 2010, 10, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rilda, Y.; Fadhli, F.; Syukri, S.; Alif, A.; Aziz, H.; Chandren, S.; Nur, H. Self-cleaning TiO2-SiO2 clusters on cotton textile prepared by dip-spin coating process. J. Teknol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, H. Thermal crystallization of low-temperature prepared anatase nano-TiO2 and multifunctional finishing of cotton fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.; Abdallah, S.; Khalek, A.A. Characterization and photocatalytic properties of cotton fibers modified with ZnO nanoparticles using sol-gel spin coating technique. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, R.; Colleoni, C.; Calvimontes, A.; Polášková, H.; Dutschk, V.; Rosace, G. Innovative sol-gel route in neutral hydroalcoholic condition to obtain antibacterial cotton finishing by zinc precursor. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Yi, S.C.; Oh, S.G. Preparation and antibacterial effects of Ag-SiO2 thin films by sol-gel method. Biomaterials 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.O.; Yeh, K. Effects of Silicone Softeners and Silane Coupling Agents on the Performance Properties of Cotton Fabrics. Text. Res. J. 1993, 63, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazer, M.; Harifi, T. Nanocrosslinking. In Nanofinishing of Textile Materials; Montazer, M., Harifi, T.B., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 109–125. ISBN 978-0-08-101214-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, C.; Binder, W.H.; Tessadri, R. Durable press finishing of cotton fabric with 1,2,3,4-butanetetracarboxylic acid and TEOS/GPTMS. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guise, G.B.; Jones, F.W. Shrink-Resisting Wool with Poly(Dimethylsiloxane)-α, ω-Diols and Aminofunctional Silane Crosslinking Agents: Part II: Influence of Crosslinking Agent Structure. Text. Res. J. 1978, 48, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Smith, E.; Chizyuka, M.; Prajapati, C. Development of durable shrink-resist coating of wool with sol-gel polymer processing. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, A.; Xu, G.; Ni, C. High-Performance Phase Change Composite of Acetamide/Silica-Network for Thermal Storage. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lin, T.; Brady, R.; Wang, X. Fast response photochromic textiles from hybrid silica surface coating. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lin, T.; Fang, J.; Brady, R. Photochromic Wool Fabrics from a Hybrid Silica Coating. Text. Res. J. 2007, 77, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lin, T.; Fang, J.; Brady, R. Photochromic Wool Fabrics from a Hybrid Silica Coating. In Proceedings of the China International Wool Textile Conference & IWTO Wool Forum, Xian, China, 19–21 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Roe, B.; Zhang, X. Durable Hydrophobic Textile Fabric Finishing Using Silica Nanoparticles and Mixed Silanes. Text. Res. J. 2009, 79, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Vikova, M.; Vik, M. Spectral and physical properties organo-silica coated photochromic poly-ethylene terephthalate (PET) fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, R.; Zayat, M.; Levy, D. Effect of the chemical environment on the light-induced degradation of a photochromic dye in ormosil thin films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 198, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo Martínez, C.I. Energy use and energy efficiency development in the German and Colombian textile industries. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2010, 14, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, R.; Zayat, M.; Levy, D. Stability against photodegradation of a photochromic spirooxazine dye embedded in amino-functionalized sol-gel hybrid coatings. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, R.; Zayat, M.; Levy, D. Temperature dependence of the photochromism of naphthopyrans in functionalized sol-gel thin films. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, R.; Zayat, M.; Levy, D. Photochromic organic-inorganic hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhizkar, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Photostability and Durability Properties of Photochromic Organosilica Coating on Fabric. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2014, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X. Handbook of Smart Textiles; Springer: Singapore, 2015; ISBN 978-981-4451-44-4. [Google Scholar]
- Brzeziński, S.; Kowalczyk, D.; Borak, B.; Jasiorski, M.; Tracz, A. Applying the sol-gel method to the deposition of nanocoats on textiles to improve their abrasion resistance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Yang, K.; Xiong, X.; Venkataraman, M.; Militky, J.; Mishra, R.; Kremenakova, D. Effect of silanization on copper coated milife fabric with improved EMI shielding effectiveness. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 122008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, M.; Yang, K.; Periyasamy, A.P.; Xiong, X.; Militky, J.; Mishra, R. Modification of electromagnetic property of copper coated milife fabrics. In Proceedings of the 10th Anniversary International Conference on Nanomaterials Research and Application (NANOCON 2018), Brno, Czech Republic, 17–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Yang, K.; Xiong, X.; Venkataraman, M.; Militky, J.; Rajesh, M.; Kremenakova, D. Influence of sılanızatıon on copper coated nonwoven fabrıc and theır electrıcal conductıvıty. In Proceedings of the 19th World Textile Conference on Textiles (AUTEX2019), Ghent, Belgium, 11–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Periyasamy, A.P.; Yang, K.; Xiong, X.; Venkatraman, M.; Militky, J.; Mishra, R.; Kremenakova, D. Influence of EMI Shielding on Silane-coated Conductive Fabric. In Proceedings of the 12th Textile Bioengineering and Informatics Symposium (TBIS 2019), Suzhou, China, 8–11 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Onar, N.; Mete, G. Development of water-, oil-repellent and flame-retardant cotton fabrics by organic-inorganic hybrid materials. J. Text. Inst. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, H.; Yasin, S.; Khoso, N.; Memon, S. Study of Wrinkle Resistant, Breathable, Anti-UV Nanocoated Woven Polyester Fabric. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simončič, B.; Tomšič, B.; Černe, L.; Orel, B.; Jerman, I.; Kovač, J.; Žerjav, M.; Simončič, A. Multifunctional water and oil repellent and antimicrobial properties of finished cotton: Influence of sol-gel finishing procedure. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Fischer, A. Inorganic/organic polymer coatings for textiles to realize water repellent and antimicrobial properties—A study with respect to textile comfort. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafei, A.; Elshemy, M.; Abou-Okeil, A. Eco-friendly finishing agent for cotton fabrics to improve flame retardant and antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Hao, B.; Mu, L.; Chen, L.; Ma, P.C. Development of multi-functional cotton fabrics with Ag/AgBr-TiO2 nanocomposite coating. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Shaheen, T.I.; Zaghloul, S.; El-Rafie, M.H.; Hebeish, A. Antibacterial Activities and UV Protection of the in Situ Synthesized Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles on Cotton Fabrics. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, A.; Murugan, R.; Periyasamy, S. Evaluation of multifunctional properties of polyester/cotton blend treated with unmodified and modified nano-TiO2 particles. Mater. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadnia, A.; Montazer, M.; Mahmoudi Rad, M. In Situ Photo Sonosynthesis of Organic/Inorganic Nanocomposites on Wool Fabric Introducing Multifunctional Properties. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.L.; Zhang, Q.H.; Chen, Y.B.; Chen, G.Q.; Xing, T.L. Thermal properties and water repellency of cotton fabric prepared through sol-gel method. Therm. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Gao, T.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, X. Preparation of crosslinked polysiloxane/SiO2 nanocomposite via in-situ condensation and its surface modification on cotton fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Periyasamy, A.P.; Venkataraman, M.; Kremenakova, D.; Militky, J.; Zhou, Y. Progress in Sol-Gel Technology for the Coatings of Fabrics. Materials 2020, 13, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081838
Periyasamy AP, Venkataraman M, Kremenakova D, Militky J, Zhou Y. Progress in Sol-Gel Technology for the Coatings of Fabrics. Materials. 2020; 13(8):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081838
Chicago/Turabian StylePeriyasamy, Aravin Prince, Mohanapriya Venkataraman, Dana Kremenakova, Jiri Militky, and Yan Zhou. 2020. "Progress in Sol-Gel Technology for the Coatings of Fabrics" Materials 13, no. 8: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081838
APA StylePeriyasamy, A. P., Venkataraman, M., Kremenakova, D., Militky, J., & Zhou, Y. (2020). Progress in Sol-Gel Technology for the Coatings of Fabrics. Materials, 13(8), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13081838









