The Research of Crystalline Morphology and Breakdown Characteristics of Polymer/Micro-Nano-Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Method
2.1. Main Raw Materials and Instrument
2.2. Preparation of Composites
2.3. Structure Characterization and Performance Testing of Composite
3. Results and Analysis
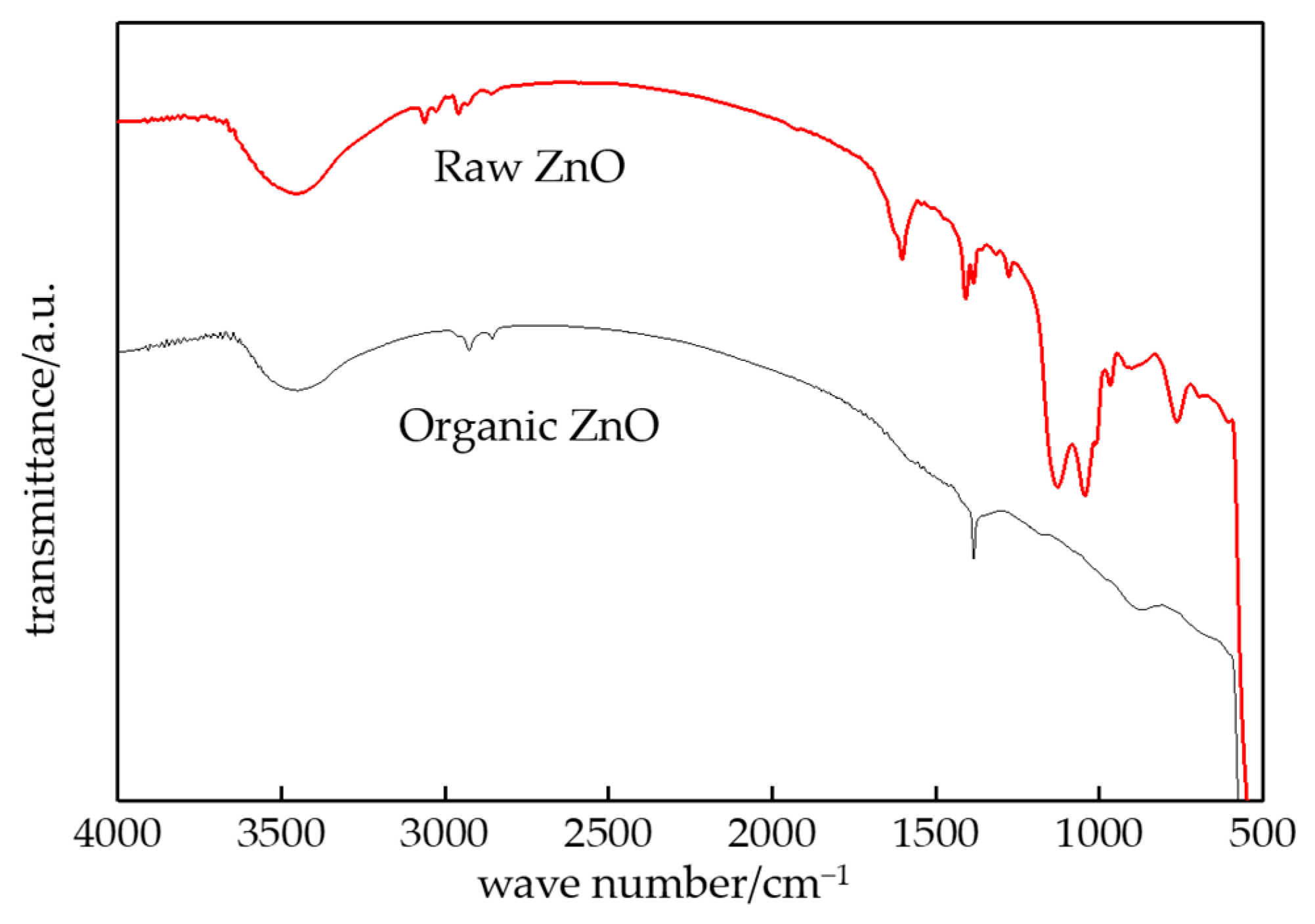
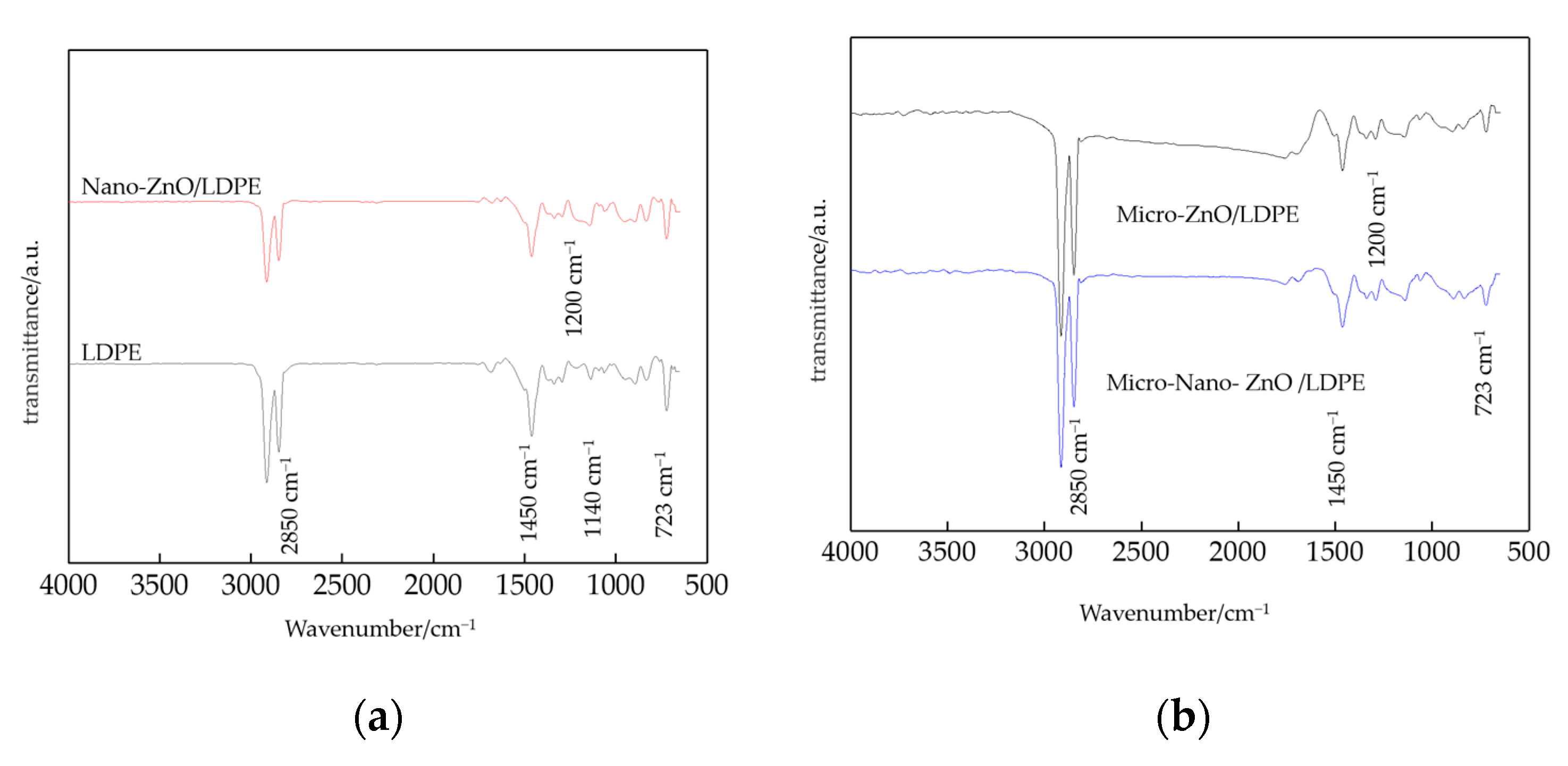
3.1. FTIR Characterization of Composites
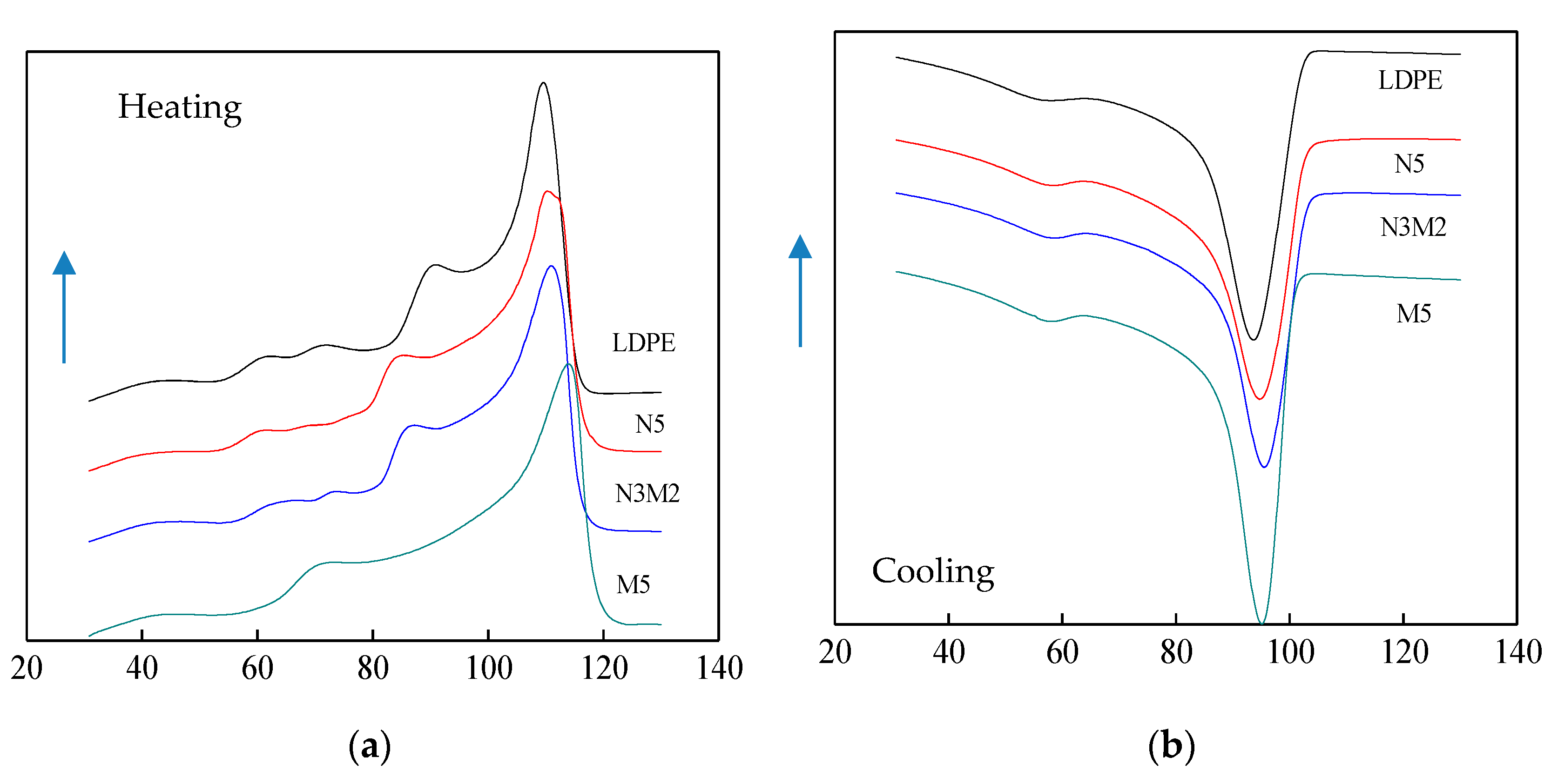
3.2. DSC Characterization of Composites
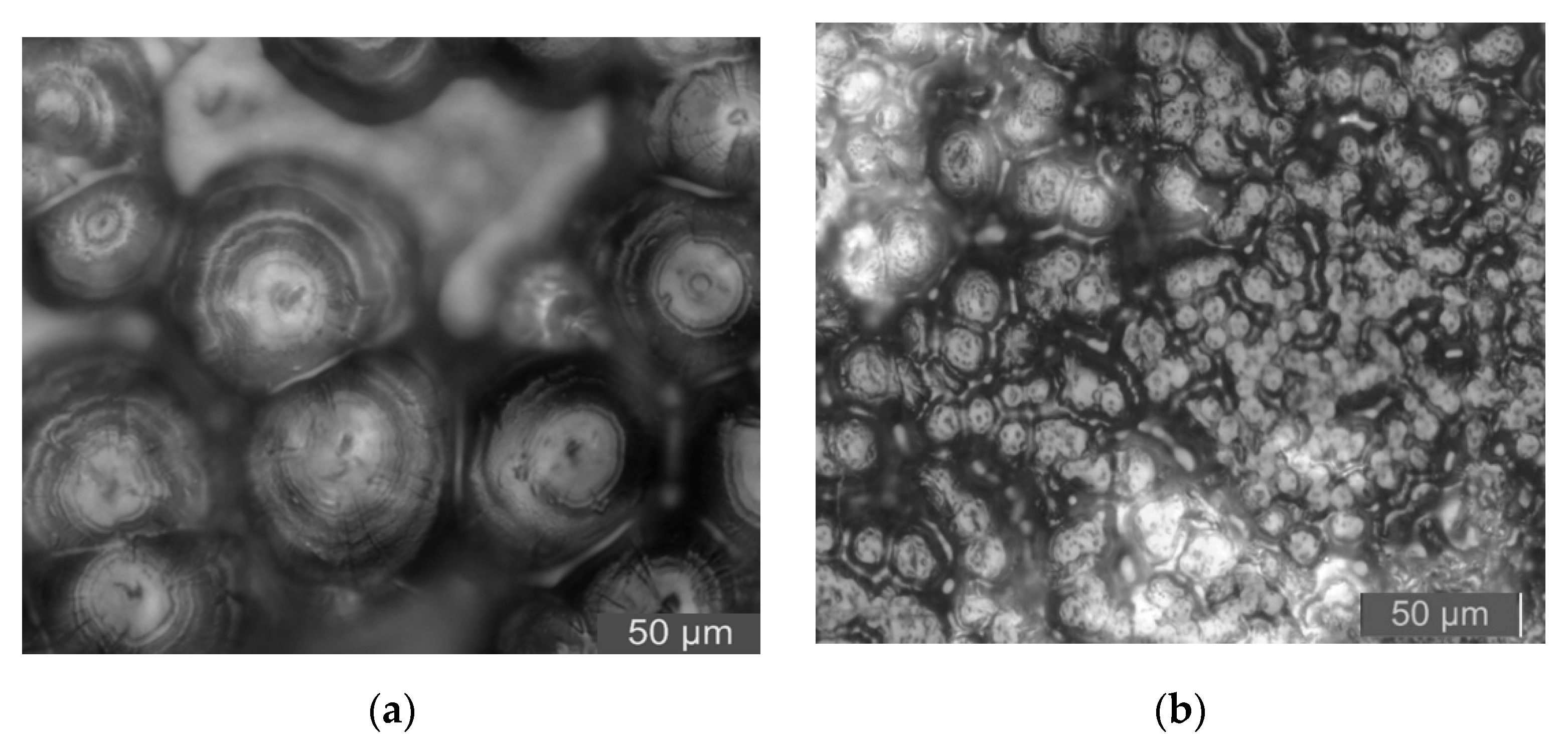
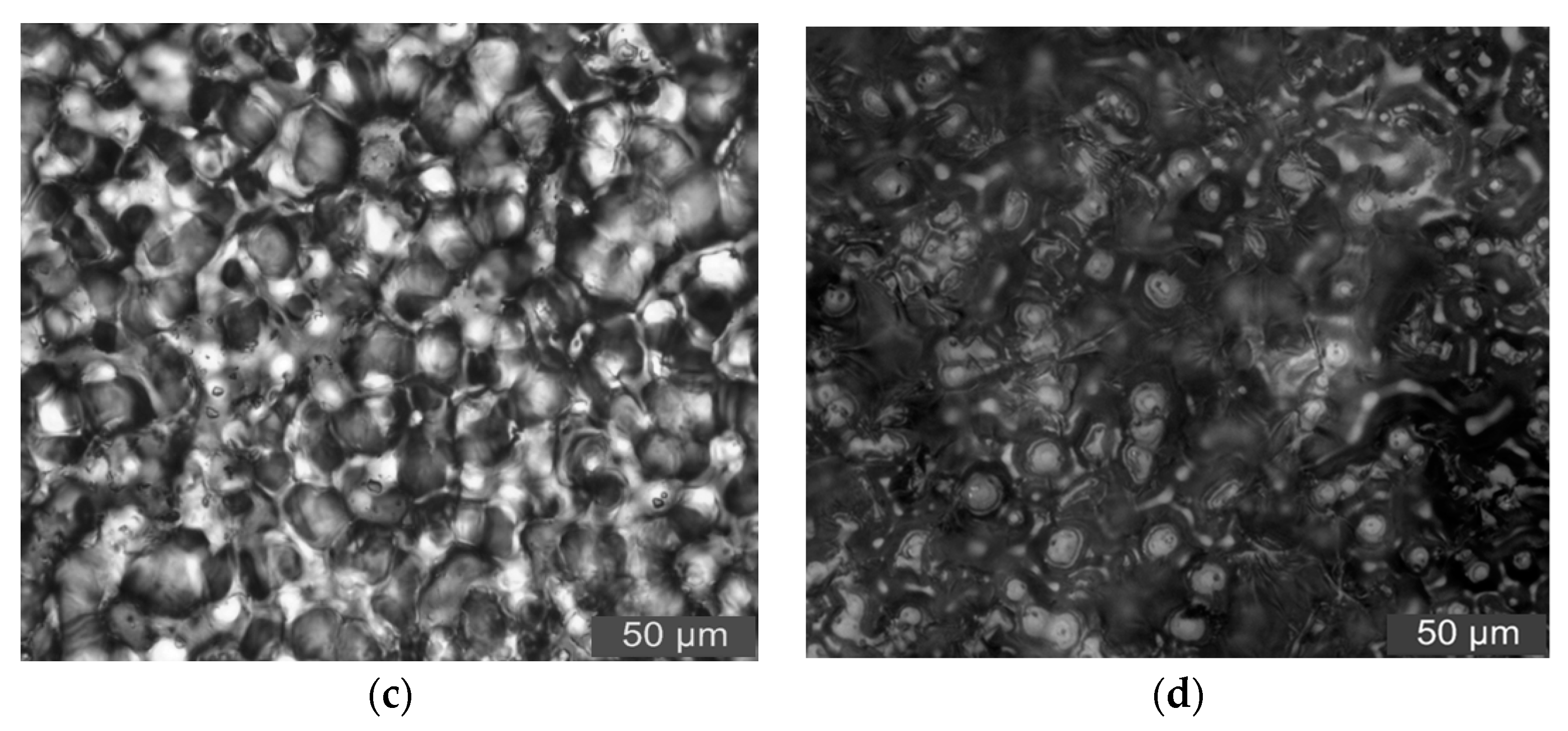
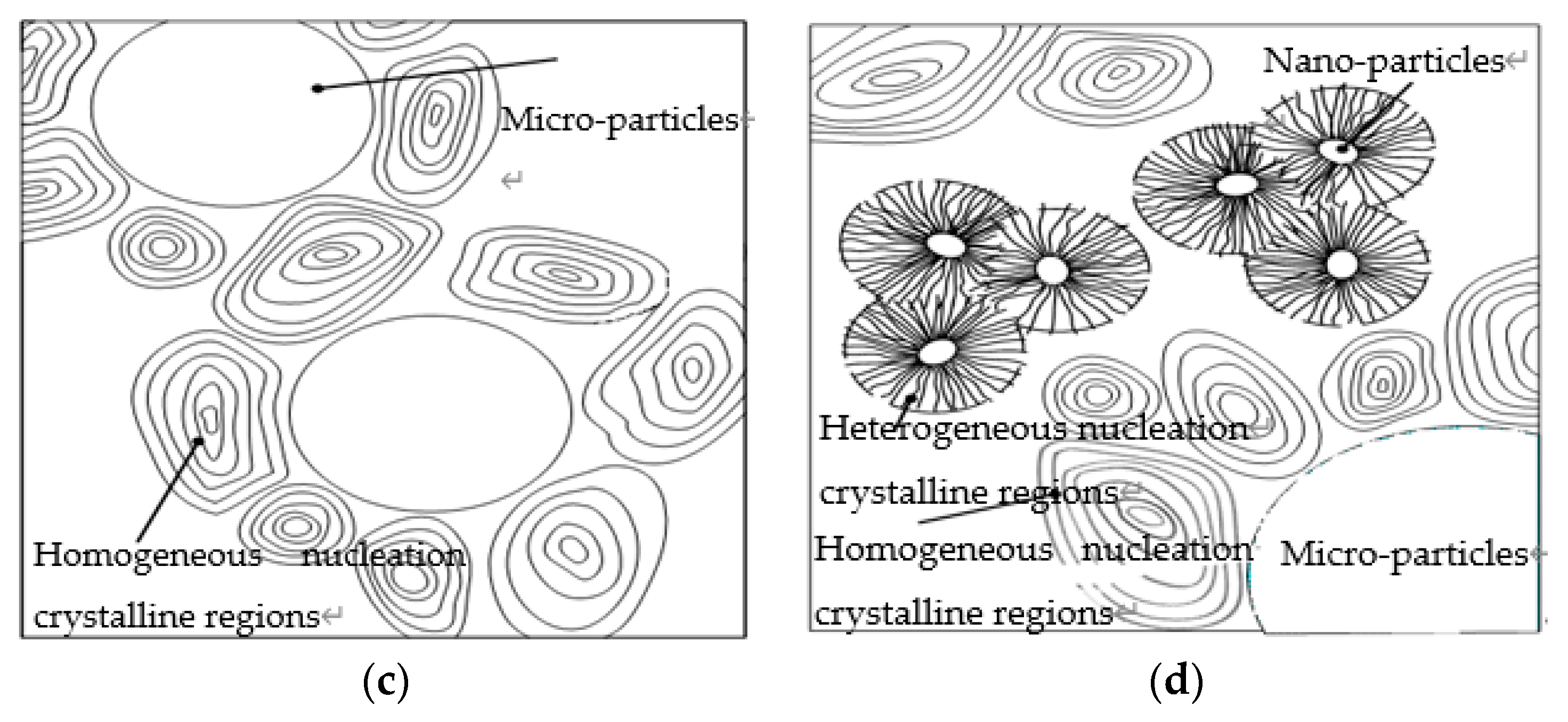
3.3. PLM Characterization of Composites
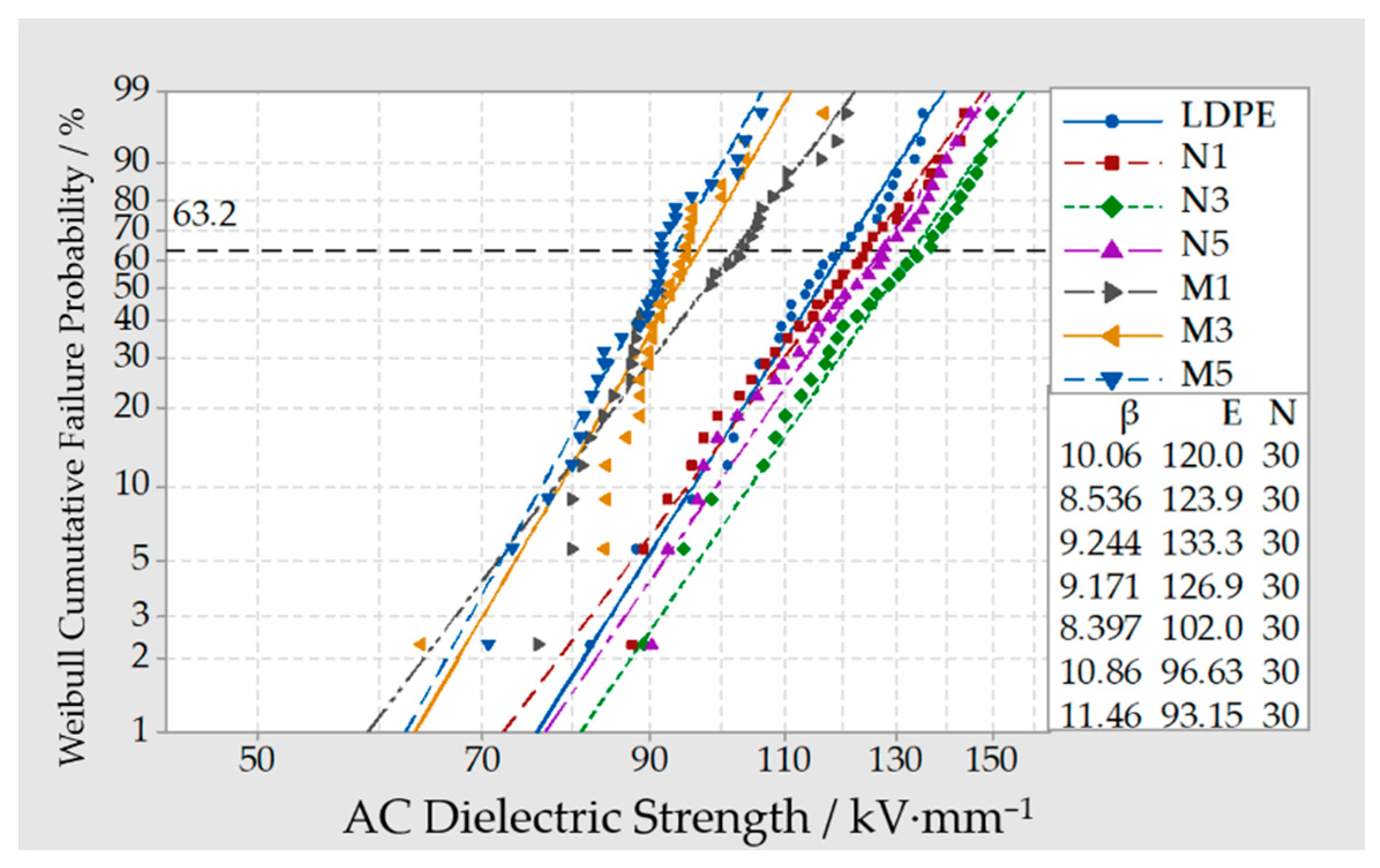
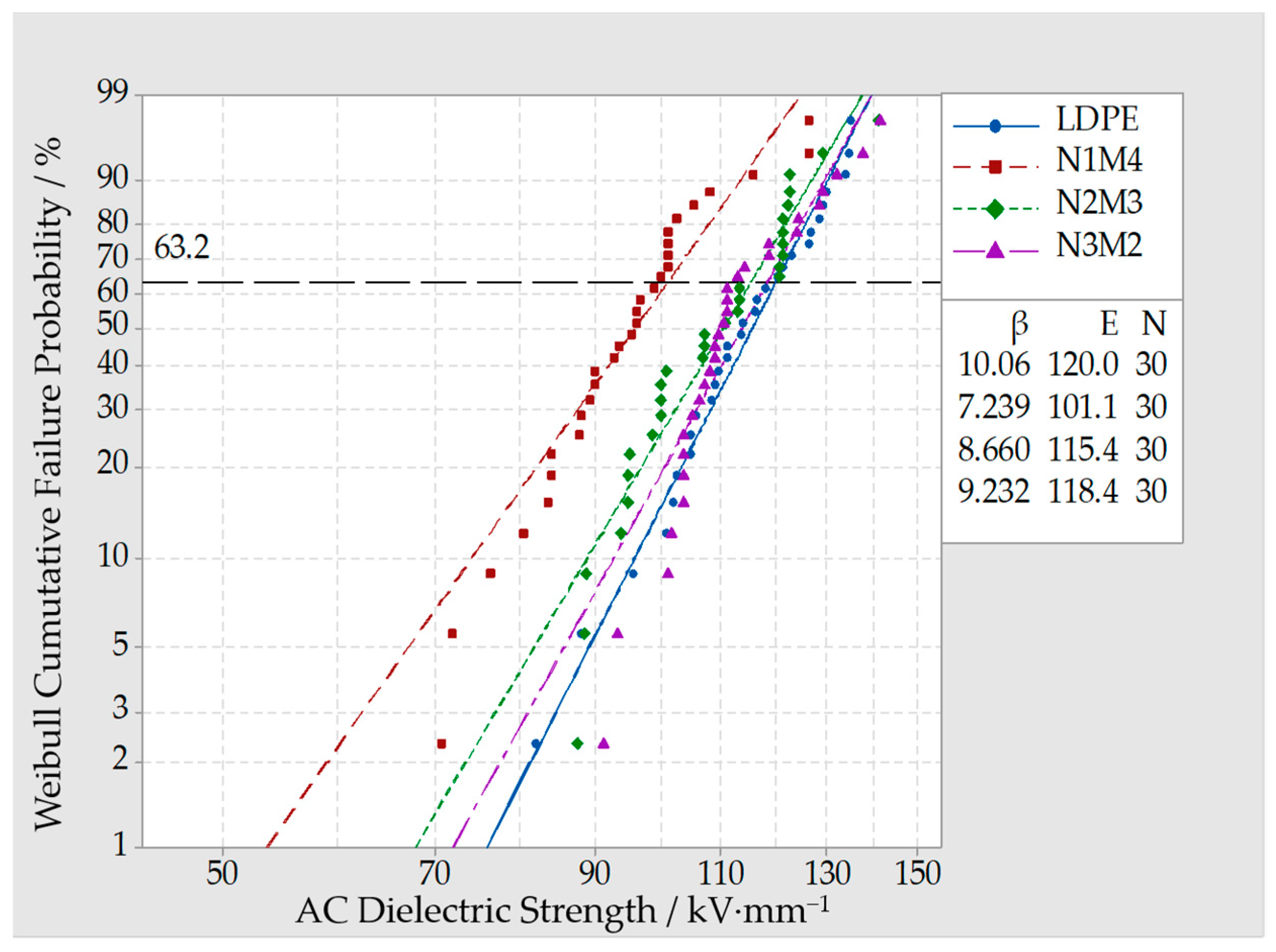
3.4. Breakdown Test of Composites
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- From the test result of FTIR, the chemical reaction happened between the organic nanoparticles and the coupling agent. Besides, the peaks value of composites in FTIR was lower than which of pure LDPE. From the test result of PLM, the inorganic ZnO-particles doping played the role of a nucleating agent, which would reduce the composite crystal size. The number of nucleation and the interfacial structure of the non-crystalline region increased obviously. At the same time, the grain arrangement was close inside the media.
- (2)
- From the test result of DSC, the ZnO particles doping improved the crystallinity and crystallization rate of pure LDPE. Among them, the crystallinity of Micro-Nano-ZnO/LDPE was the highest, and nano-ZnO/LDPE took the second. On the other hand, the melting temperature and crystallization rate of Micro-ZnO/LDPE was the highest. Based on the analysis of crystallization kinetics theory and combining the experiment result of PLM and DSC, the crystalline morphology model of Micro-Nano-ZnO/LDPE was built, and the mechanisms of Micro-ZnO and Nano-ZnO particles doping to the crystallization properties of the polymer were explored.
- (3)
- From the breakdown test result of Micro-ZnO and Nano-ZnO composites, the breakdown field strength of Nano-ZnO/LDPE was the highest and 11% higher than which of pure LDPE. The breakdown field strength of Micro-ZnO/LDPE was the lowest and 15% lower than which of pure LDPE. The breakdown field strength order of different samples was as follows: Micro-ZnO/LDPE < Micro-Nano-ZnO/LDPE < Nano-ZnO/LDPE. While the inorganic particles showed a better dispersion in polymers since the microparticles doping.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Study on the development mode of national power grid of China. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2013, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Fan, J. Planning and Design of UHVDC Transmission System. High Volt. Eng. 2015, 41, 2545–2549. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Shaoqing, C.; Xia, W. In the process of polyethylene electrical aging, the influence of Nanometer ZnO for space charge and the breakdown characteristics. Insul. Mater. 2008, 41, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Key Technical Analysis and Prospect of High Voltage and Extra-high Voltage Power Cable. High Volt. Eng. 2014, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Lu, L.; Yu, L.; Yu, X.; Naito, K.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and Characterization of Epoxy/Alumina Nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 2694–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhen, X.; Peng, P. Nonlinear Conductivity Characteristics of Modified Polyimide Composite Materials with Inorganic Filler. High Volt. Eng. 2015, 41, 4137–4143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Ishizaka, T.; Kasai, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Furukawa, T.; Nakanishi, H.; Oikawa, H. Ultralow-Dielectric-Constant Films Prepared from Hollow Polyimide Nanoparticles Possessing Controllable Core Sizes. Chem. Mater. 2016, 21, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, G.; Peng, J.; Yiqiang, Z.; Huihui, X.; Peng, W. Research Progress on Interface Properties of Polymer Nanodielectrics. High Volt. Eng. 2012, 38, 2455–2464. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.Y.; Vaughan, A.S.; Chen, G.; Hosier, I.L.; Holt, A.F.; Ching, K.Y. On the space charge and DC breakdown behavior of polyethylene/silica nanocomposites. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, H.; Ji, C.; Jiaming, Y.; Wenlong, Z. Preparation of MgO/LDPE Nanocomposites and Its Space Charge Property. High Volt. Eng. 2012, 38, 684–690. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; Davies, A.E.; Vaughan, A.S.; Takada, T. Effect of additives on morphology and space charge accumulation in low density polyethylene. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2003, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Bulinski, A.; Castellon, J.; Frechette, M.; Gubanski, S.; Kindersberger, J.; Montanari, G.C.; Nagao, M.; Morshuis, P.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Dielectric properties of XLPE/SiO2 nanocomposites based on CIGRE WG D1. 24 cooperative test results. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1482–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Wu, K.; Wang, X.; Yonghong, C.; Tong, L.; Ruihai, L. Dependence of Charge Accumulation in Low Density Polyethylene Nanocomposites on Sample Thickness. High Volt. Eng. 2012, 38, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Yonghong, C.; Demin, T. Modified Low Density Polyethylene by Nano-fills as Insulating Material of DC Cable (II). High Volt. Eng. 2013, 39, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Nozomu, A.; Miyake, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeno, T. Space charge accumulation and electric breakdown in XLPE under DC high electric field. In Proceedings of the Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Shenzhen, China, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, G.; Duan, Z. Effect of Different Size ZnO Particle Doping on Dielectric Properties of Polyethylene Composites. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 9481415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Xia, N.; Gerhardt, R.A. Dielectric nanocomposite with high dielectric permittivity and low dielectric loss. In Proceedings of the Electrical Insulation Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 7–10 June 2015; pp. 442–445. [Google Scholar]
- Al Boukhari, J.; Khalaf, A.; Awad, R. Structural analysis and dielectric investigations of pure and rare earth elements (Y and Gd) doped NiO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 820, 153381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Guo, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.H. Effects of nano-ZnO and nano-montmorillonte on dielectric properties of low density polyethylene. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2015, 32, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X. The Dielectric Properties Improvement of Cable Insulation Layer by Different Morphology Nanoparticles Doping into LDPE. Coatings 2019, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bai, L.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X. Effect of Particles Size on Dielectric Properties of Nano-ZnO/LDPE Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Cheng, Y. Study on electrical properties of micro-nano structured epoxy composites. In Proceedings of the Conference International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials, Niigata, Japan, 1–5 June 2014; pp. 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X. Effects of Cooling Methods on Dielectric Properties of MMT/LDPE. J. Inorg. Mater. 2015, 30, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Yu, L.; Zheng, J.; Gao, J.G.; Zhang, X.H. Crystallization morphology and electrical tree resistance characteristics of montmorillonite/polypropylene composites. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2015, 32, 76–84. [Google Scholar]
- Green, C.D.; Vaughan, A.S. Morphology and crystallisation kinetics of polyethylene/montmorillonite nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Solid Dielectrics, Winchester, UK, 8–13 July 2007; pp. 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Liu, L.; Kong, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, P. The effect of LDPE crystal morphology on the aging characteristics of water treeing. High Volt. Eng. 2010, 36, 678–684. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Lu, B.; Quan, Y.; Quan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C. Interfacial Crystallization of Semi-crystalline Polymer-Based Composites. Shanghai Plast. 2013, 163, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Lu, B.; Quan, Y.; Zheng, G. Study on the Nano Hybrid Shish-kebabs Formed in Polymer Composites. China Plast. Ind. 2012, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hosier, I.L.; Praeger, M.; Holt, A.F.; Vaughan, A.S.; Swingler, S.G. On the effect of functionalizer chain length and water content in polyethylene/silica nanocomposites: Part I—Dielectric properties and breakdown strength. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, K.F.T.A.; Eusoff, N.; Lau, K.Y.; Piah, M.A.M.; Ching, K.Y. DC and AC breakdown behaviors of polyethylene/silica nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy, Melaka, Malaysia, 28–29 November 2017; pp. 591–594. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, B.T.; Liu, Y.N. The Trap Theory of Breakdown in Polymer and its Verification in Polypropylene. Electr. Eng. Mag. 1993, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Min, D.; Li, S. Understanding the conduction and breakdown properties of polyethylene nanodielectrics: effect of deep traps. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Torque rheometer | RM-200A | Harbin Hapro Electrical Technology Co., Ltd. (Harbin, Heilongjiang, China) |
| Plate vulcanization machine | XLB | Haimen Jinma Rubber & Plastics Machinery Technology Co., Ltd. (Haimen, Jiangsu, China) |
| Fourier transform infrared | EQUINOX55 | Bruker (Karlsruhe, Baden-Wuerttemberg, Germany) |
| Polarization microscope | LeicaDM2500 | Leica Microsystems Co., Ltd. (Frankfurt, Hesse-Darmstadt, Germany) |
| Differential scanning calorimeter | DSC-1 | Mettler Toledo (Zurich, Zurich canton, Swizerland) |
| Ultrasonic cleaner | KQ5200DE | Kunshan Ultrasonic Instruments Co., Ltd. (Kunshan, Jiangsu, China) |
| Electric blender | JJ-1 | Jincheng Guosheng Laboratory Instrument Work (Jincheng, Shanxi, China) |
| Thermostat water bath | DZKW-A | Shanghai Shuli Instrument and Meter Factory (Shanghai, China) |
| Vacuum oven | DZF-6020 | Shanghai Boxun Industrial Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| AC high voltage experimental console | JG-5 | Shanghai Pujing Electrical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Sample | LDPE (wt%) | Mass Fraction of Nano-ZnO (wt%) | Mass Fraction of Micro-ZnO (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| N1 | 99 | 1 | 0 |
| N3 | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| N5 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| M1 | 99 | 0 | 1 |
| M3 | 97 | 0 | 3 |
| M5 | 95 | 0 | 5 |
| N1M4 | 95 | 1 | 4 |
| N2M3 | 95 | 2 | 3 |
| N3M2 | 95 | 3 | 2 |
| Sample | Tc (°C) | Tcon (°C) | ΔTc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 93.67 | 102.31 | 8.64 | 109.75 | 34.90 |
| N5 | 95.15 | 102.65 | 7.50 | 109.84 | 36.18 |
| N3M2 | 95.89 | 102.97 | 7.08 | 110.46 | 37.79 |
| M5 | 95.65 | 100.66 | 5.03 | 113.66 | 36.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B. The Research of Crystalline Morphology and Breakdown Characteristics of Polymer/Micro-Nano-Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061432
Cheng Y, Yu G, Zhang X, Yu B. The Research of Crystalline Morphology and Breakdown Characteristics of Polymer/Micro-Nano-Composites. Materials. 2020; 13(6):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061432
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yujia, Guang Yu, Xiaohong Zhang, and Boyang Yu. 2020. "The Research of Crystalline Morphology and Breakdown Characteristics of Polymer/Micro-Nano-Composites" Materials 13, no. 6: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061432
APA StyleCheng, Y., Yu, G., Zhang, X., & Yu, B. (2020). The Research of Crystalline Morphology and Breakdown Characteristics of Polymer/Micro-Nano-Composites. Materials, 13(6), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061432





