Color Shift, Color Stability, and Post-Polishing Surface Roughness of Esthetic Resin Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Color Shift Determination
2.3. Staining Procedure
2.4. Color Stability after Storage in Beverages
2.5. Post-Polishing Surface Roughness
2.6. Statistical Testing
3. Results
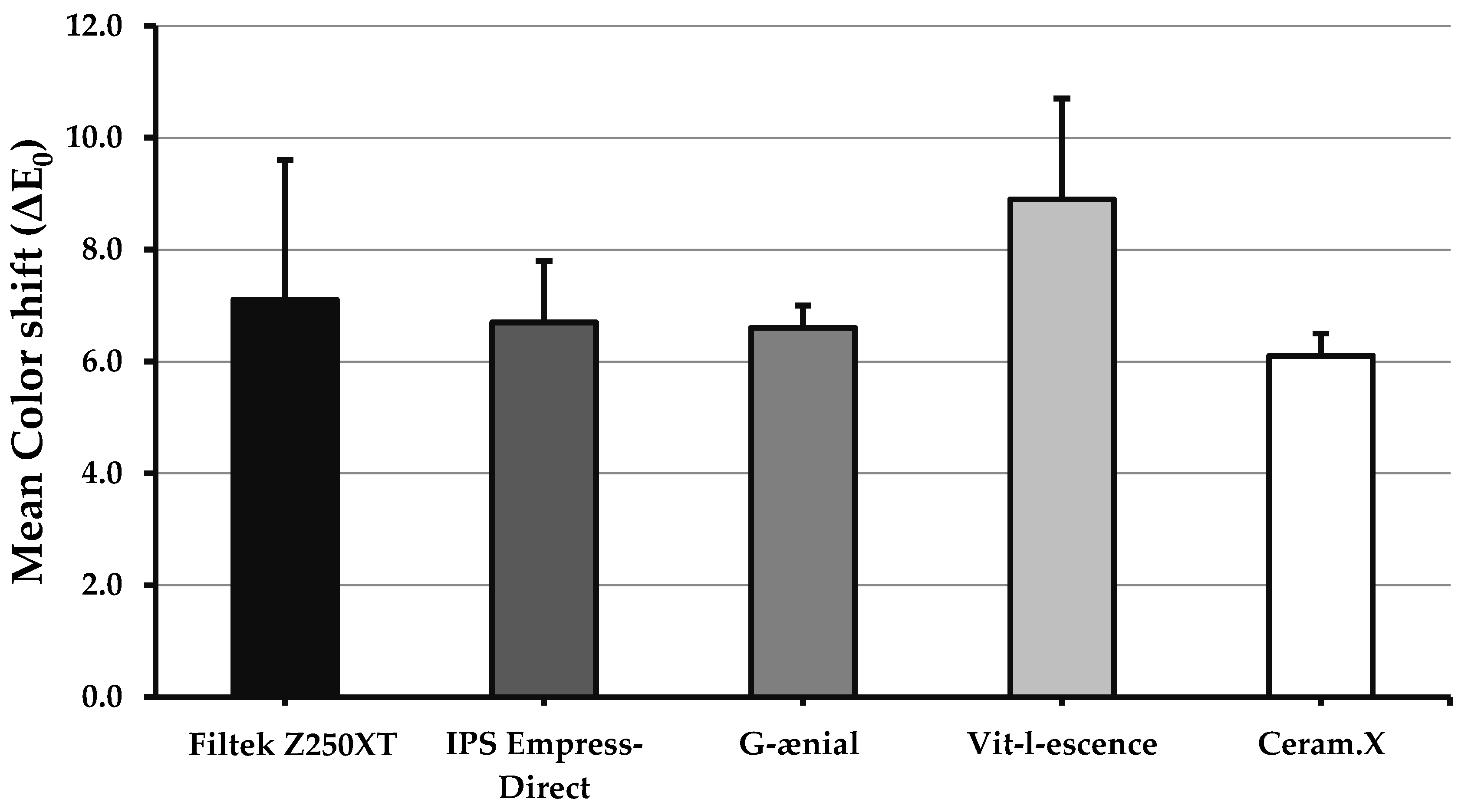
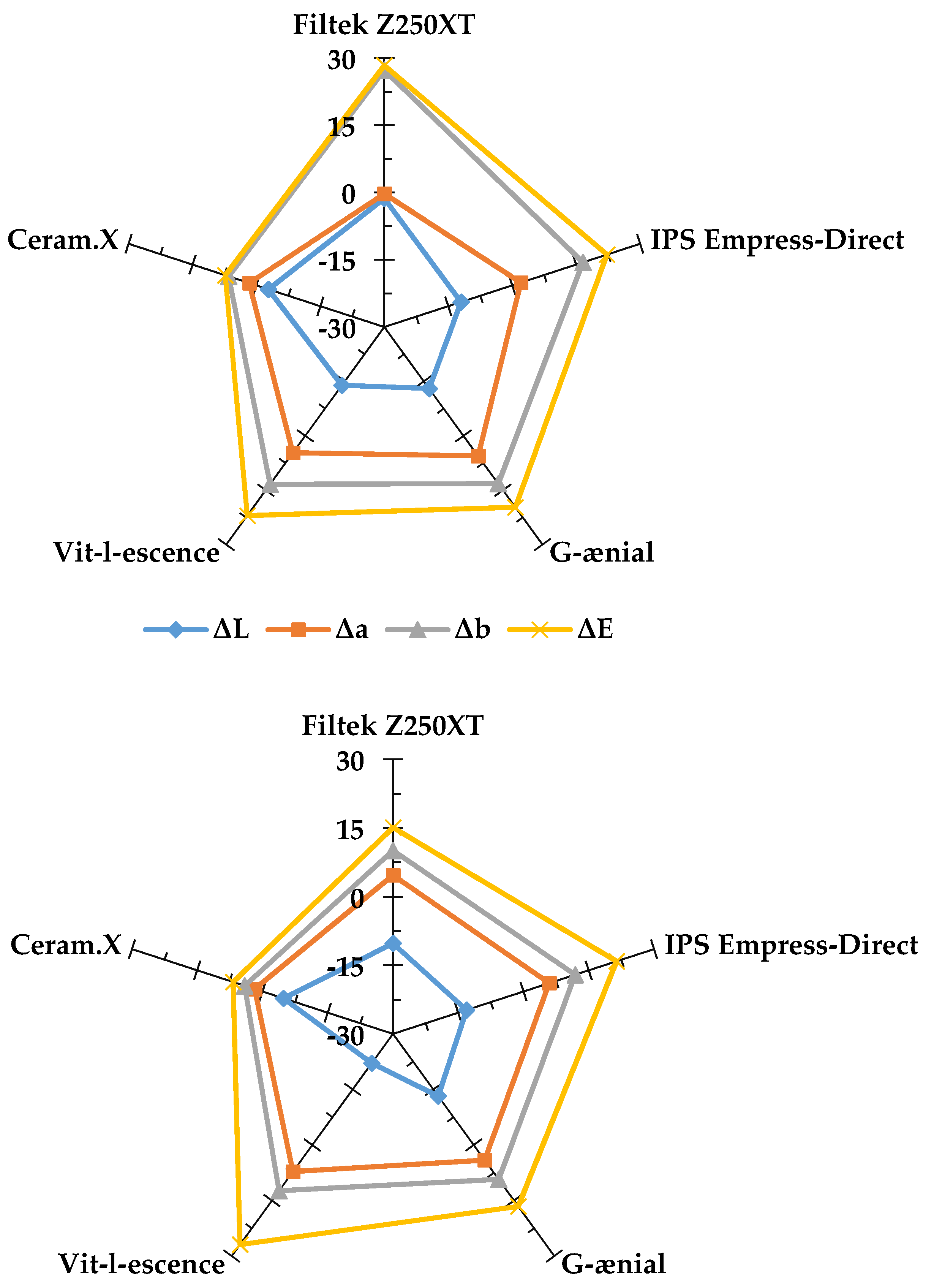
3.1. Color Shift (∆E0)
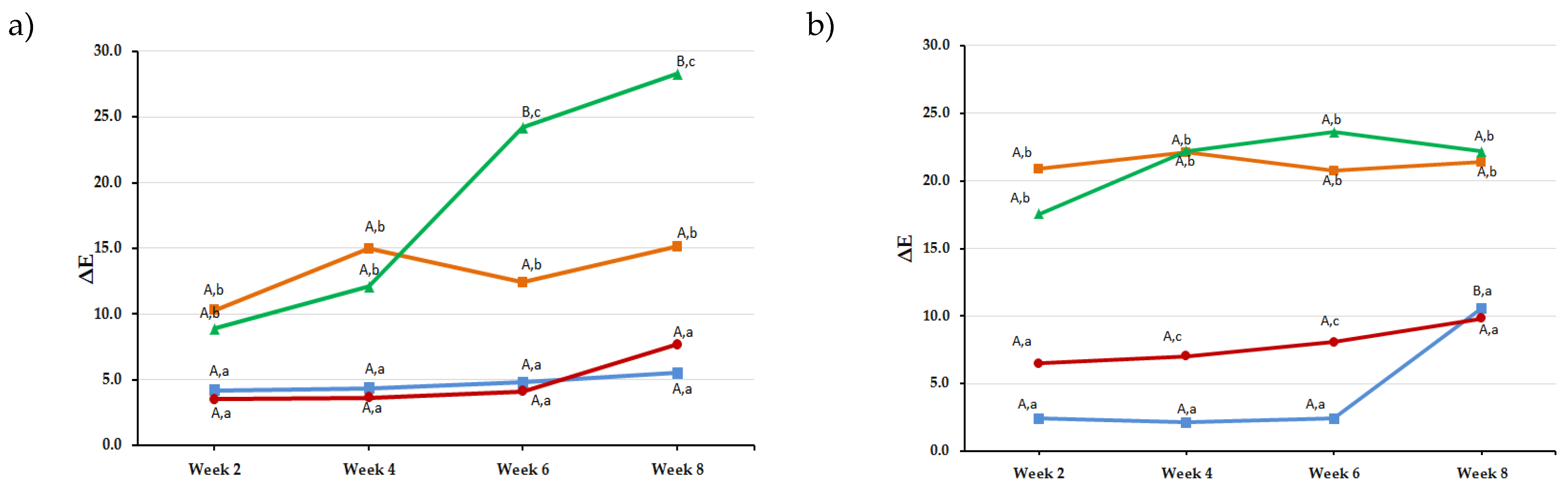
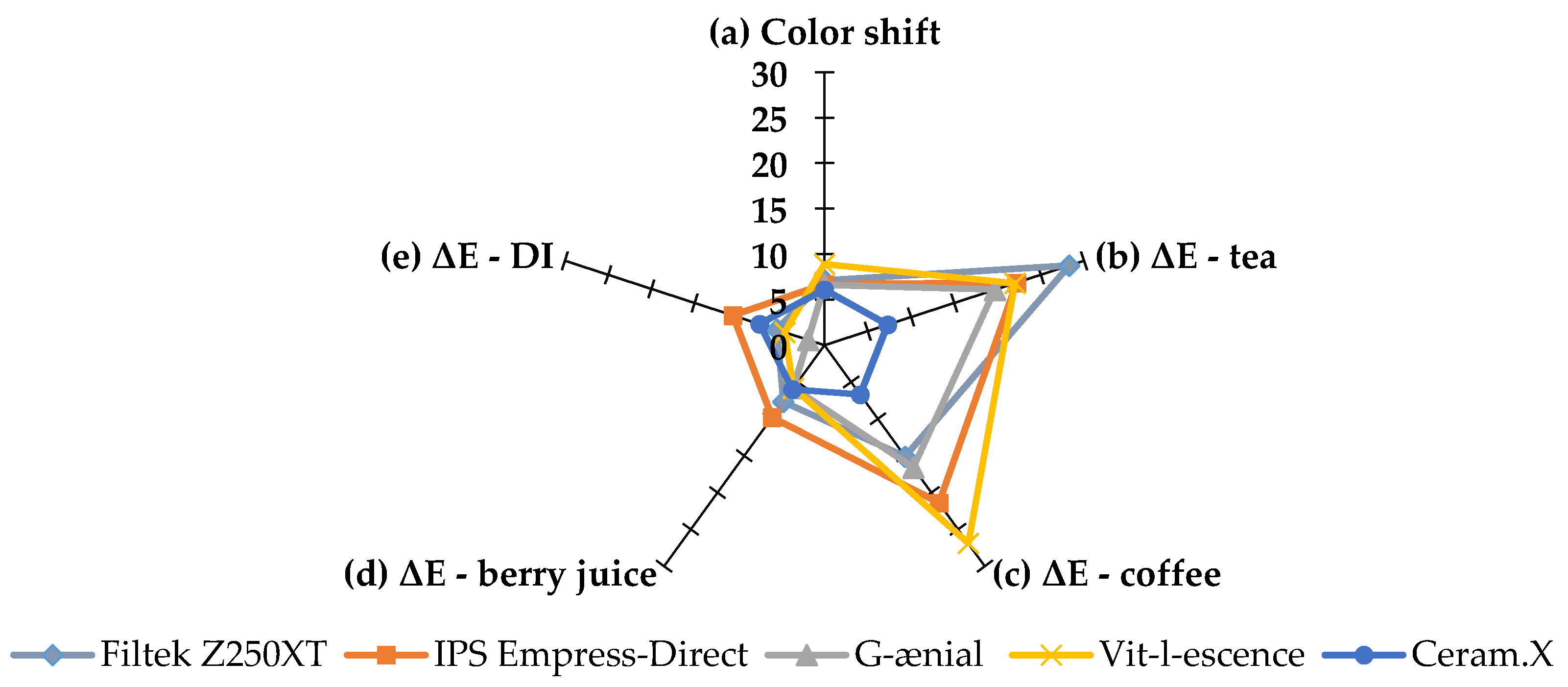
3.2. Color Stability after Storage in Staining Solutions (∆E2 − ∆E8)
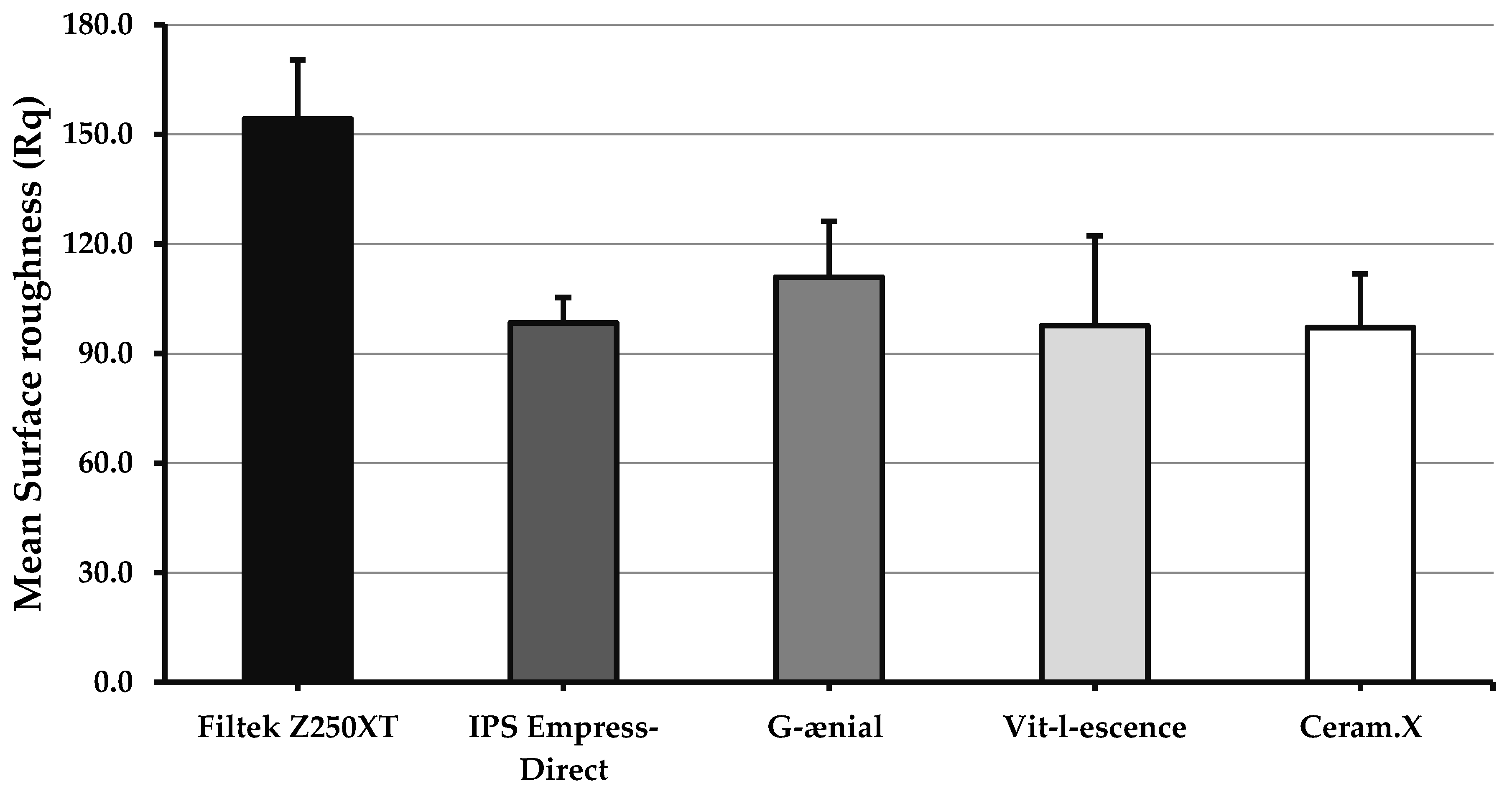
3.3. Post-Polishing Surface Roughness (Rq)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bis-GMA | bisphenolglycidyl methacrylate |
| Bis-EMA | ethoxylated bisphenol-A dimethacrylate |
| PEGDMA | polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| TEGDMA | triethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| UDMA | urethane dimethacrylate |
| wt.% | weight percentage |
| vol.% | volume percentage |
References
- De Oliveira, D.C.R.S.; Souza-Júnior, E.J.; Prieto, L.T.; Coppini, E.K.; Maia, R.R.; Paulillo, L.A.M.S. Color Stability and Polymerization Behavior of Direct Esthetic Restorations. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2014, 26, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ende, A.; De Munck, J.; Lise, D.P.; Van Meerbeek, B. Bulk-Fill Composites: A Review of the Current Literature. J. Adhes. Dent. 2017, 19, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demarco, F.F.; Correa, M.B.; Cenci, M.; De Moraes, R.R.; Opdam, N.J. Longevity of posterior composite restorations: Not only a matter of materials. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, C.; Vialba, L.; Berardengo, A.; Federico, R.; Colombo, M.; Beltrami, R.; Scribante, A. Color Stability of New Esthetic Restorative Materials: A Spectrophotometric Analysis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraç, D.; Saraç, Y.Ş.; Külünk, Ş.; Ural, Ç.; Külünk, T. The effect of polishing techniques on the surface roughness and color change of composite resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 96, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, C.; Beltrami, R.; Scribante, A.; Colombo, M.; Chiesa, M. Surface discoloration of composite resins: Effects of staining and bleaching. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundim, F.M.; Garcia, L.D.F.R.; Pires-De-Souza, F.C.P. Effect of staining solutions and repolishing on color stability of direct composites. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2010, 18, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, P.; Lu, H.; Ökte, Z.; García-Godoy, F.; Powers, J.M. Effects of staining and bleaching on color change of dental composite resins. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2006, 95, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundim, F.M.; Pires-De-Souza, F.C.P.; Garcia, L.D.F.R.; Consani, S. Colour stability, opacity and cross-link density of composites submitted to accelerated artificial aging. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2010, 18, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ardu, S.; Braut, V.; Gutemberg, D.; Krejci, I.; Dietschi, D.; Feilzer, A.J. A long-term laboratory test on staining susceptibility of esthetic composite resin materials. Quintessence Int. 2010, 41, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Bahbishi, N.; Mzain, W.; Badeeb, B.; Nassar, H.M. Color Stability and Micro-Hardness of Bulk-Fill Composite Materials after Exposure to Common Beverages. Materials 2020, 13, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, S.T.; Fernández, M.R.; De Moura, C.M.; Meireles, S. Color stability of a nanofill composite: Effect of different immersion media. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2009, 17, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjan, A.H.; Chan, C.A. The polishability of posterior composites. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1989, 61, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Rai, R. In vitro evaluation of the effect of two finishing and polishing systems on four esthetic restorative materials. J. Conserv. Dent. 2013, 16, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaarslan, E.S.; Bulbul, M.; Yildiz, E.; Seçilmiş, A.; Sari, F.; Usumez, A. Effects of different polishing methods on color stability of resin composites after accelerated aging. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egilmez, F.; Ergun, G.; Cekic-Nagas, I.; Vallittu, P.K.; Lassila, L.V.J. Short and long term effects of additional post curing and polishing systems on the color change of dental nano-composites. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, S.; Schmalz, G. Reprinting the classic article on USPHS evaluation methods for measuring the clinical research performance of restorative materials. Clin. Oral Investig. 2005, 9, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.M. Color measurement in dentistry. J. Dent. 2009, 37, e2–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Pan, S.L.; Friedrich, K. Interfacial effects in polypropylene-silica nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürdal, P.; Akdeniz, B.G.; Sen, B.H. The effects of mouthrinses on microhardness and colour stability of aesthetic restorative materials. J. Oral Rehabil. 2002, 29, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yap, A.U.J.; Wang, X.; Gao, X. Effect of staining solutions on color of pre-reacted glass-ionomer containing composites. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, R.P.; Salomone, P.; Villetti, M.A.; Pozzobon, R.T. Effect of bleaching agents on the fluorescence of composite resins. Eur. J. Esthet. Dent. Off. J. Eur. Acad. Esthet. Dent. 2013, 8, 582–591. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Yap, A.; Ma, H.; Chew, J.; Tan, W. Effect of Beverages on Color and Translucency of New Tooth-Colored Restoratives. Oper. Dent. 2015, 40, E56–E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theobald, A.H.; Wong, B.K.J.; Quick, A.N.; Thomson, W.M. The impact of the popular media on cosmetic dentistry. N. Z. Dent. J. 2006, 102, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.-F.; Feng, L.; Serban, D.; Malmström, H.S. Effects of common beverage colorants on color stability of dental composite resins: The utility of a thermocycling stain challenge model in vitro. J. Dent. 2012, 40, e48–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llena, C.; Fernández, S.; Forner, L. Color stability of nanohybrid resin-based composites, ormocers and compomers. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 21, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.L.; Silva, F.D.S.D.C.M.E.; Meireles, S.S.; Duarte, R.M.; Andrade, A.K.M. The effect of drinks on color stability and surface roughness of nanocomposites. Eur. J. Dent. 2014, 8, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.M.; Kao, E. Assessment of Appearance Match by Visual Observation and Clinical Colorimetry. J. Dent. Res. 1989, 68, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, R.; Kumar, M.S.; Sahib, S.A.M.; Chittrarasu, M.; Navarasu, M.; Ragavendran, N.; Mohammed, O.F.B. Color stability assessment of two different composite resins with variable immersion time using various beverages: An In vitro study. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2017, 9, S161–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.K.; Sunarintyas, S.; Irnawati, D. Color stability of visible light cured composite resin after soft drink immersion. Dent. J. (Majalah Kedokt. Gigi) 2009, 42, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zidan, A.Z.; Mansouri, S.A. Effect of Water Sorption and Solubility on Color Stability of Bulk-Fill Resin Composite. J. Contemp. Dent. Pr. 2018, 19, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideridou, I. Study of water sorption, solubility and modulus of elasticity of light-cured dimethacrylate-based dental resins. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venz, S.; Dickens, B. NIR-spectroscopic investigation of water sorption characteristics of dental resins and composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 1231–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerby, R.E.; Knobloch, L.A.; Schricker, S.; Gregg, B. Synthesis and evaluation of modified urethane dimethacrylate resins with reduced water sorption and solubility. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekçe, N.; Tuncer, S.; Demirci, M.; Serim, M.E.; Baydemir, C. The effect of different drinks on the color stability of different restorative materials after one month. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2015, 40, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekipour, M.R.; Sharafi, A.; Kazemi, S.; Khazaei, S.; Shirani, F. Comparison of color stability of a composite resin in different color media. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Garoushi, S.; Lassila, L.; Hatem, M.; Shembesh, M.; Baady, L.; Salim, Z.; Vallittu, P.K. Influence of staining solutions and whitening procedures on discoloration of hybrid composite resins. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2012, 71, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadas, M. The effect of different beverages on the color and translucency of flowable composites. Scanning 2016, 38, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertaş, E.; Güler, A.U.; Yucel, A.C.; Köprülü, H.; Güler, E. Color stability of resin composites after immersion in different drinks. Dent. Mater. J. 2006, 25, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossam, A.E.; Rafi, A.T.; Ahmed, A.S.; Sumanth, P.C. Surface topography of composite restorative materials following ultrasonic scaling and its Impact on bacterial plaque accumulation. An in-vitro SEM study. J. Int. Oral Heal. 2013, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pettini, F.; Savino, M.; Corsalini, M.; Cantore, S.; Ballini, A. Cytogenetic genotoxic investigation in peripheral blood lymphocytes of subjects with dental composite restorative filling materials. J. Boil. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Sciammarella, C.A.; Lamberti, L.; Sciammarella, F.M.; Demelio, G.P.; Dicuonzo, A.; Boccaccio, A. Application of Plasmons to the Determination of Surface Profile and Contact Strain Distribution. Strain 2010, 46, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, C.; Yuzugullu, B.; Erkut, S.; Yamanel, K. Effects of Mouth Rinses on Color Stability of Resin Composites. Eur. J. Dent. 2008, 2, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettini, F.; Corsalini, M.; Savino, M.G.; Stefanachi, G.; Di Venere, D.; Pappalettere, C.; Monno, G.; Boccaccio, A. Roughness Analysis on Composite Materials (Microfilled, Nanofilled and Silorane) After Different Finishing and Polishing Procedures. Open Dent. J. 2015, 9, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Sehr, K.; Klimek, J. Surface Texture of Four Nanofilled and One Hybrid Composite after Finishing. Oper. Dent. 2007, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.D.O.; Miotti, L.; Nicoloso, G.; Durand, L.; Susin, A. Color stability of a resin composite: Effect of the immersion method and surface treatments. Indian J. Dent. Res. 2016, 27, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Material, Abbreviation | Category | Resin Matrix | Main Fillers Type and Size | Filler Load (wt.%/vol.%) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtek Z250XT (Z250) | Nanohybrid | Bis-GMA, UDMA, Bis-EMA, PEGDMA, TEGDMA | Zirconia and silica (0.02–0.6 µm) | 78/68 | 3M ESPE, Dental Products, Saint Paul, Minnesota, USA |
| IPS Empress-Direct (ED) | Nanohybrid | UDMA, Bis-GMA, TEGDMA | Barium glass, ytterbium trifluoride, and mixed oxides (0.5 µm) | 75/52 | Ivoclar Vivadent, Zurich, Switzerland |
| G-ænial (GA) | Microhybrid | UDMA, dimethacrylate co-monomers | Silica, strontium, lanthanoid fluoride, fumed silica (0.1–17 µm) | 76/50 | GC Dental Products, Tokyo, Japan |
| Vit-l-escence (VL) | Microhybrid | Bis-GMA, TEGDMA | Silica (0.7 µm) | 75/52 | Ultradent Products, South Jordan, Utah, USA |
| Ceram.X (CX) | Nanoceramic | Methacrylate-modified polysiloxane, polyurethane methacrylate, Bis-EMA, TEGDMA | Barium-aluminum borosilicate glass, methacrylate functionalized silicon dioxide (0.01–1.5 µm) | 77/59 | Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany |
| Material | Solution | ΔE2 | ΔE4 | ΔE6 | ΔE8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtek Z250XT | Tea | 8.9 ± 4.1 A,b | 12.1 ± 4.4 A,b | 24.0 ± 1.9 B,c | 28.3 ± 4.5 B,c |
| Coffee | 10.3 ± 2.2 A,b | 15.0 ± 5.7 A,b | 12.4 ± 4.5 A,b | 15.1 ± 3.0 A,b | |
| Berry juice | 3.5 ± 1.2 A,a | 3.7 ± 1.0 A,a | 4.1 ± 2.3 A,a | 7.7 ± 6.2 A,a | |
| Distilled water | 4.2 ± 6.5 A,a | 4.4 ± 6.3 A,a | 4.8 ± 4.7 A,a | 5.5 ± 7.6 A,a | |
| IPS Empress Direct | Tea | 17.6 ± 8.0 A,b | 22.2 ± 3.4 A,b | 23.6 ± 5.9 A,b | 22.2 ± 6.0 A,b |
| Coffee | 20.9 ± 4.9 A,b | 22.1 ± 2.4 A,b | 20.8 ± 4.8 A,b | 21.4 ± 2.9 A,b | |
| Berry juice | 6.5 ± 3.0 A,a | 7.0 ± 3.1 A,c | 8.1 ± 1.6 A,c | 9.8 ± 1.7 A,a | |
| Distilled water | 2.5 ± 0.6 A,a | 2.2 ± 1.2 A,a | 2.4 ± 0.5 A,a | 10.6 ± 5.5 B,a | |
| G-ænial | Tea | 6.6 ± 0.5 A,a | 10.2 ± 4.0 A,c | 16.5 ± 2.3 B,b | 19.7 ± 4.7 B,b |
| Coffee | 13.8 ± 0.6 A,b | 15.7 ± 1.9 A,b | 18.5 ± 1.1 A,b | 16.6 ± 0.9 A,b | |
| Berry juice | 3.8 ± 0.8 A,a | 5.1 ± 0.8 A,a | 5.9 ± 2.5 A,a | 5.8 ± 1.2 A,a | |
| Distilled water | 2.8 ± 0.5 A,a | 2.9 ± 1.0 A,a | 3.1 ± 0.9 A,a | 1.9 ± 0.7 A,a | |
| Vit-l-escence | Tea | 12.1 ± 6.8 A,b | 12.2 ± 2.4 A,b | 21.6 ± 7.2 B,c | 22.0 ± 6.9 B,c |
| Coffee | 10.1 ± 1.3 A,b | 11.8 ± 2.9 A,b | 17.4 ± 4.0 B,b | 26.9 ± 8.2 C,b | |
| Berry juice | 7.5 ± 4.7 A,b | 6.3 ± 4.3 A,a | 7.5 ± 4.9 A,c | 5.8 ± 3.7 A,a | |
| Distilled water | 1.8 ± 1.1 A,a | 2.0 ± 1.3 A,a | 2.1 ± 0.8 A,a | 4.6 ± 1.8 A,a | |
| Ceram.X | Tea | 5.5 ± 2.6 A,a | 8.7 ± 4.2 A,b | 9.2 ± 2.2 A,b | 7.3 ± 2.0 A,a |
| Coffee | 6.2 ± 3.2 A,a | 7.5 ± 4.2 A,a,b | 9.2 ± 1.8 A,b | 6.7 ± 4.3 A,a | |
| Berry juice | 2.6 ± 0.7 A,a | 2.4 ± 1.5 A,a | 3.2 ± 1.7 A,a | 6.0 ± 2.0 A,a | |
| Distilled water | 3.3 ± 1.5 A,a | 2.9 ± 1.1 A,a | 3.4 ± 1.0 A,a | 7.5 ± 1.3 A,a |
| Material | Solution | ΔL | Δa | Δb | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filtek Z250XT | Tea | −1.3 ± 8.5 | −0.3 ± 2.1 | 27.3 ± 3.7 | 28.3 ± 4.5 * |
| Coffee | −10.2 ± 2.6 | 4.7 ± 1.8 | 10.1 ± 1.3 | 15.1 ± 3.0 * | |
| Berry juice | −3.4 ± 8.3 | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | 7.7 ± 6.2 * | |
| Distilled water | 4.7 ± 8.1 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | −1.0 ± 1.3 | 5.5 ± 7.6 * | |
| IPS Empress-Direct | Tea | −12.0 ± 9.1 | 2.0 ± 4.0 | 16.6 ± 4.8 | 22.2 ± 6.0 * |
| Coffee | −13.1 ± 3.9 | 5.9 ± 1.1 | 11.9 ± 2.5 | 21.4 ± 2.9 * | |
| Berry juice | 0.5 ± 6.0 | 3.3 ± 0.5 | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 9.8 ± 1.7 * | |
| Distilled water | 10.5 ± 5.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | −0.8 ± 0.9 | 10.6 ± 5.5 * | |
| G-ænial | Tea | −13.0 ± 5.4 | 5.6 ± 2.6 | 13.2 ± 1.5 | 19.7 ± 4.7 * |
| Coffee | −13.2 ± 1.0 | 4.1 ± 0.4 | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 16.6 ± 0.9 * | |
| Berry juice | −2.9 ± 1.2 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | 5.8 ± 1.2 * | |
| Distilled water | 0.1 ± 1.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | −1.4 ± 0.9 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | |
| Vit-l-escence | Tea | −13.9 ± 9.8 | 4.7 ± 5.7 | 13.4 ± 5.8 | 22.0 ± 6.9 * |
| Coffee | −22.1 ± 9.8 | 7.2 ± 2.8 | 12.4 ± 1.6 | 26.9 ± 8.2 * | |
| Berry juice | 12.8 ± 20.6 | 0.6 ± 1.3 | 3.0 ± 3.5 | 5.8 ± 3.7 * | |
| Distilled water | 4.5 ± 1.8 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 1.8 * | |
| Ceram.X | Tea | −2.8 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 6.5 ± 1.7 | 7.3 ± 2.0 * |
| Coffee | −4.8 ± 3.9 | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 4.1 ± 2.1 | 6.7 ± 4.3 * | |
| Berry juice | 4.0 ± 2.8 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 1.7 | 6.0 ± 2.0 * | |
| Distilled water | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 1.2 | 7.5 ± 1.3 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhadim, Y.K.; Hulbah, M.J.; Nassar, H.M. Color Shift, Color Stability, and Post-Polishing Surface Roughness of Esthetic Resin Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061376
Alkhadim YK, Hulbah MJ, Nassar HM. Color Shift, Color Stability, and Post-Polishing Surface Roughness of Esthetic Resin Composites. Materials. 2020; 13(6):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061376
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhadim, Yara Khalid, Malak Jameel Hulbah, and Hani Mohammad Nassar. 2020. "Color Shift, Color Stability, and Post-Polishing Surface Roughness of Esthetic Resin Composites" Materials 13, no. 6: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061376
APA StyleAlkhadim, Y. K., Hulbah, M. J., & Nassar, H. M. (2020). Color Shift, Color Stability, and Post-Polishing Surface Roughness of Esthetic Resin Composites. Materials, 13(6), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13061376





