The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Performance Test and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
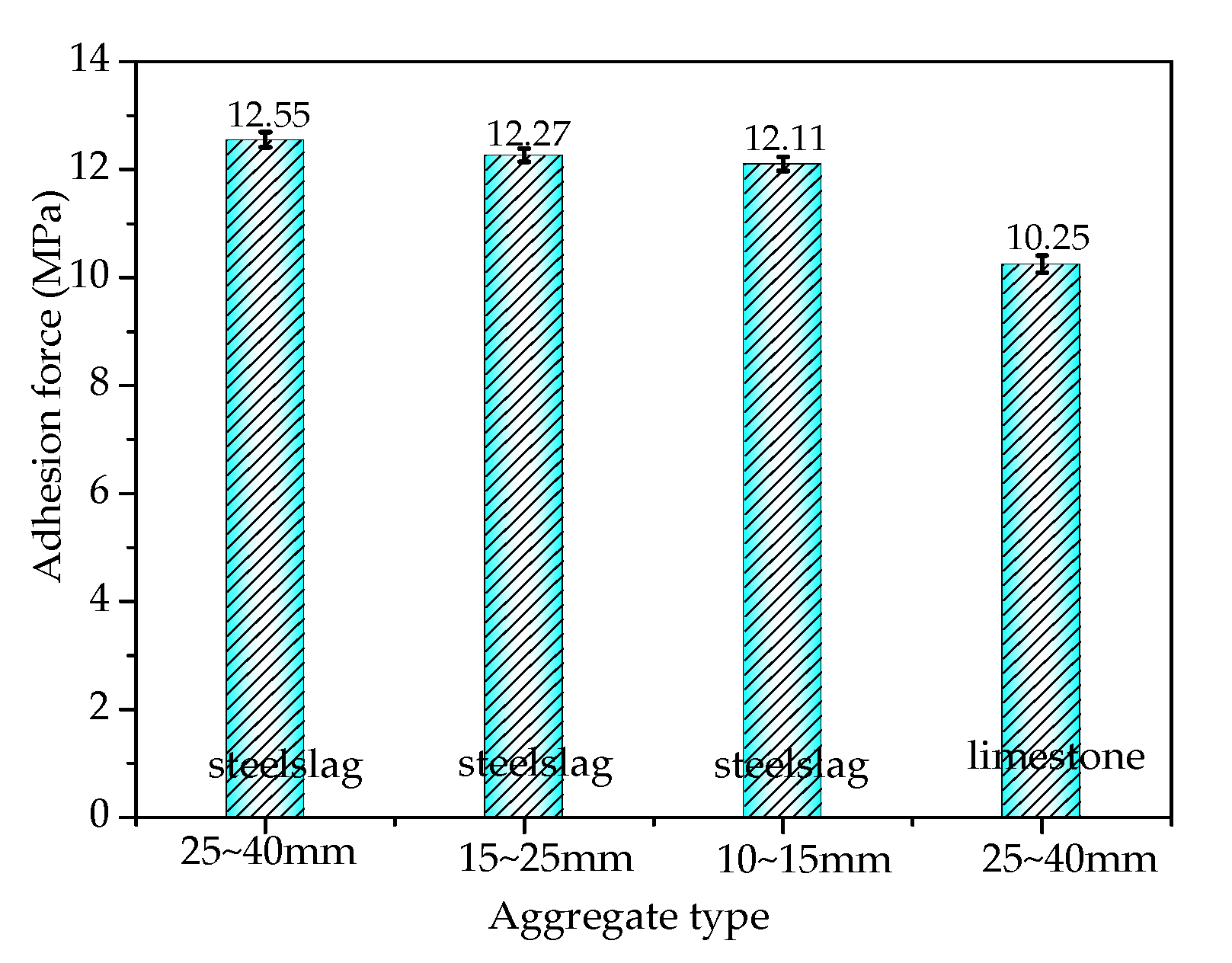
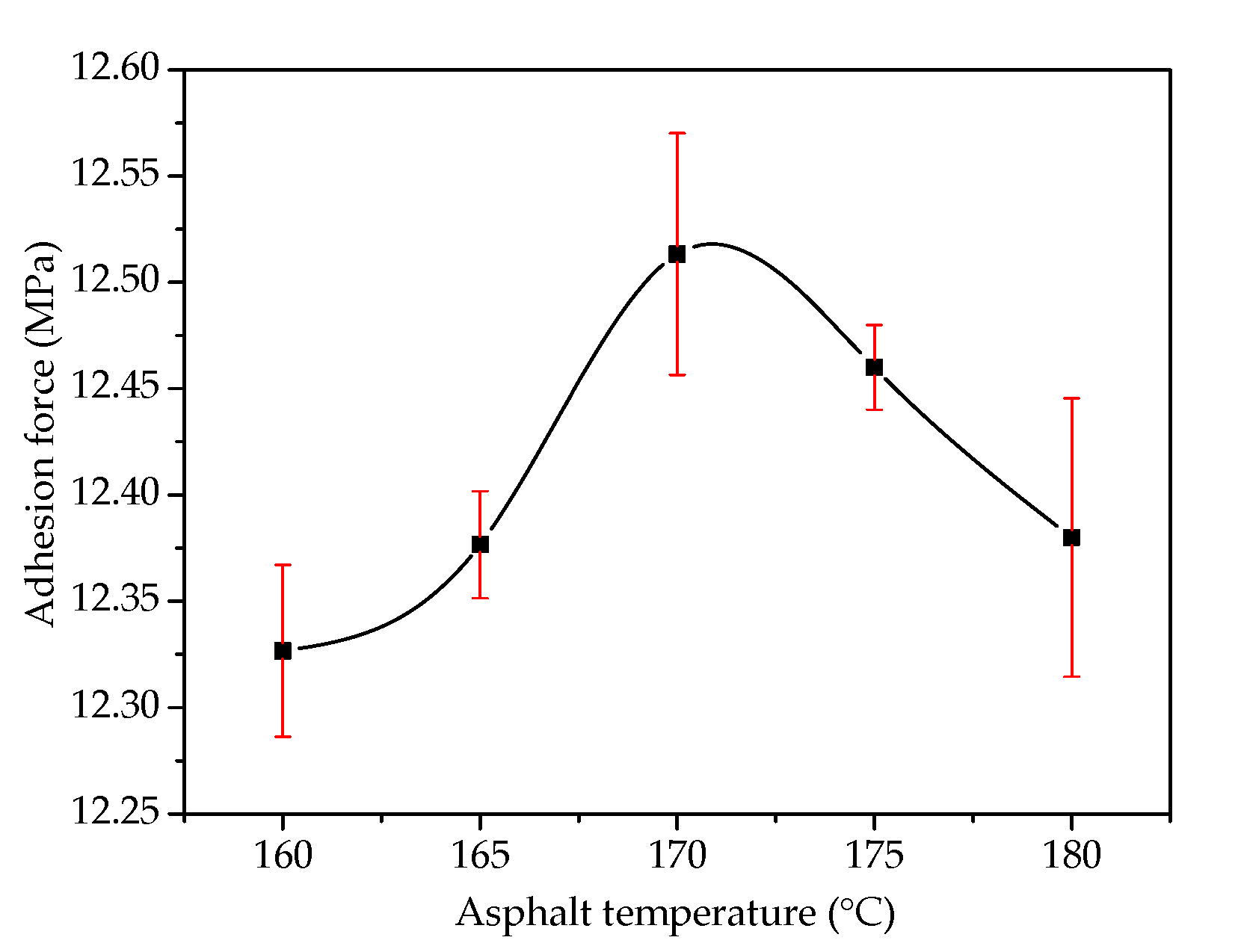
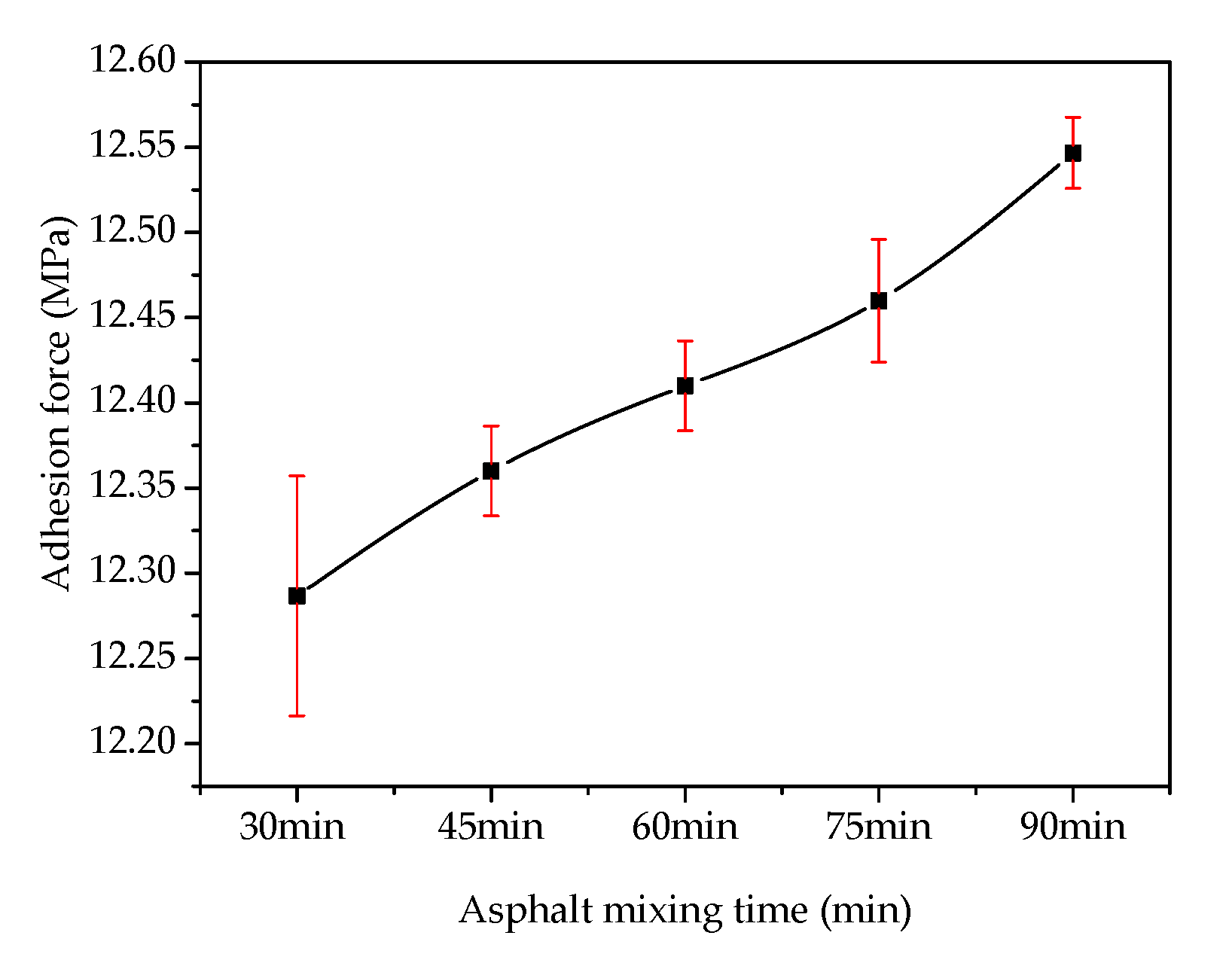
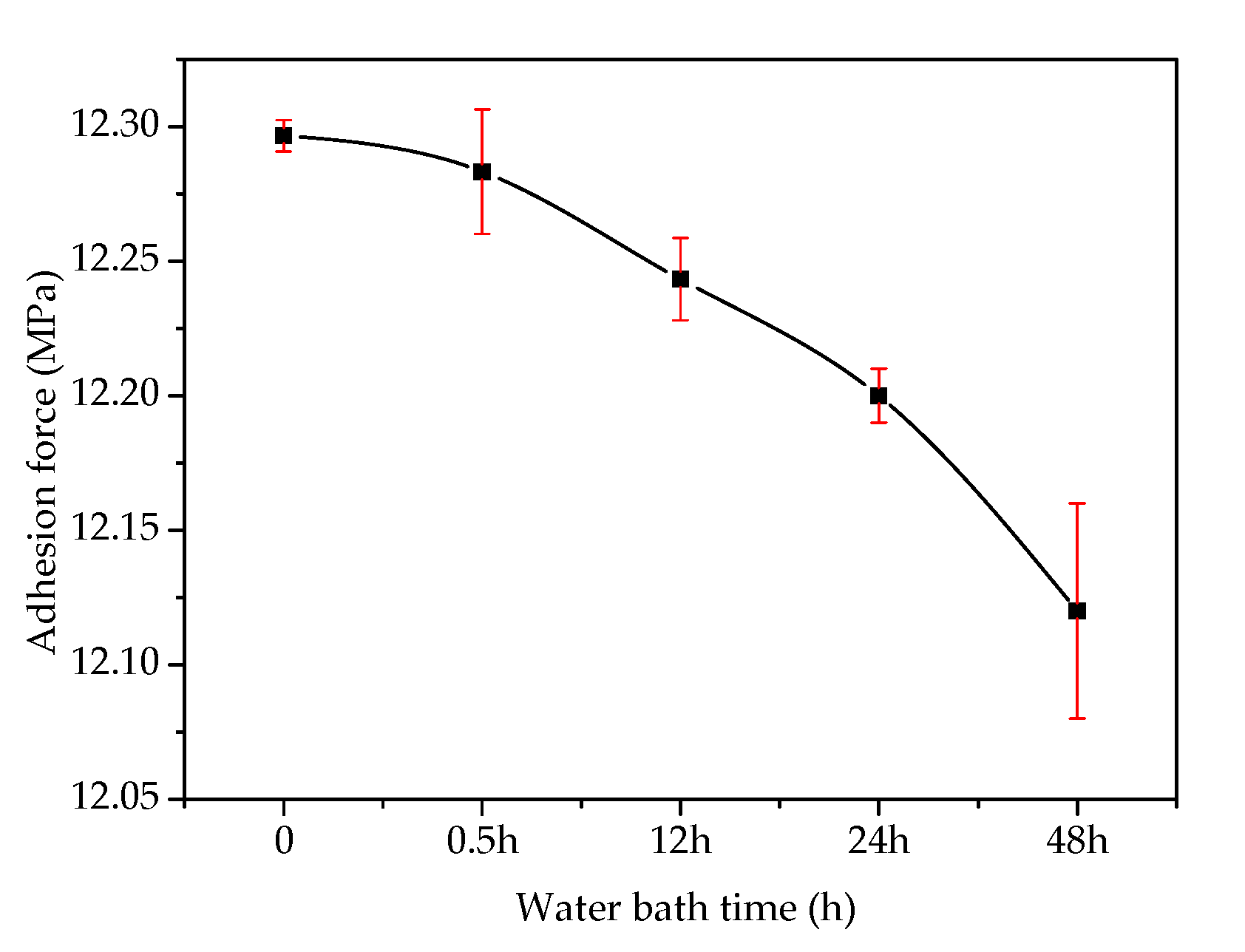
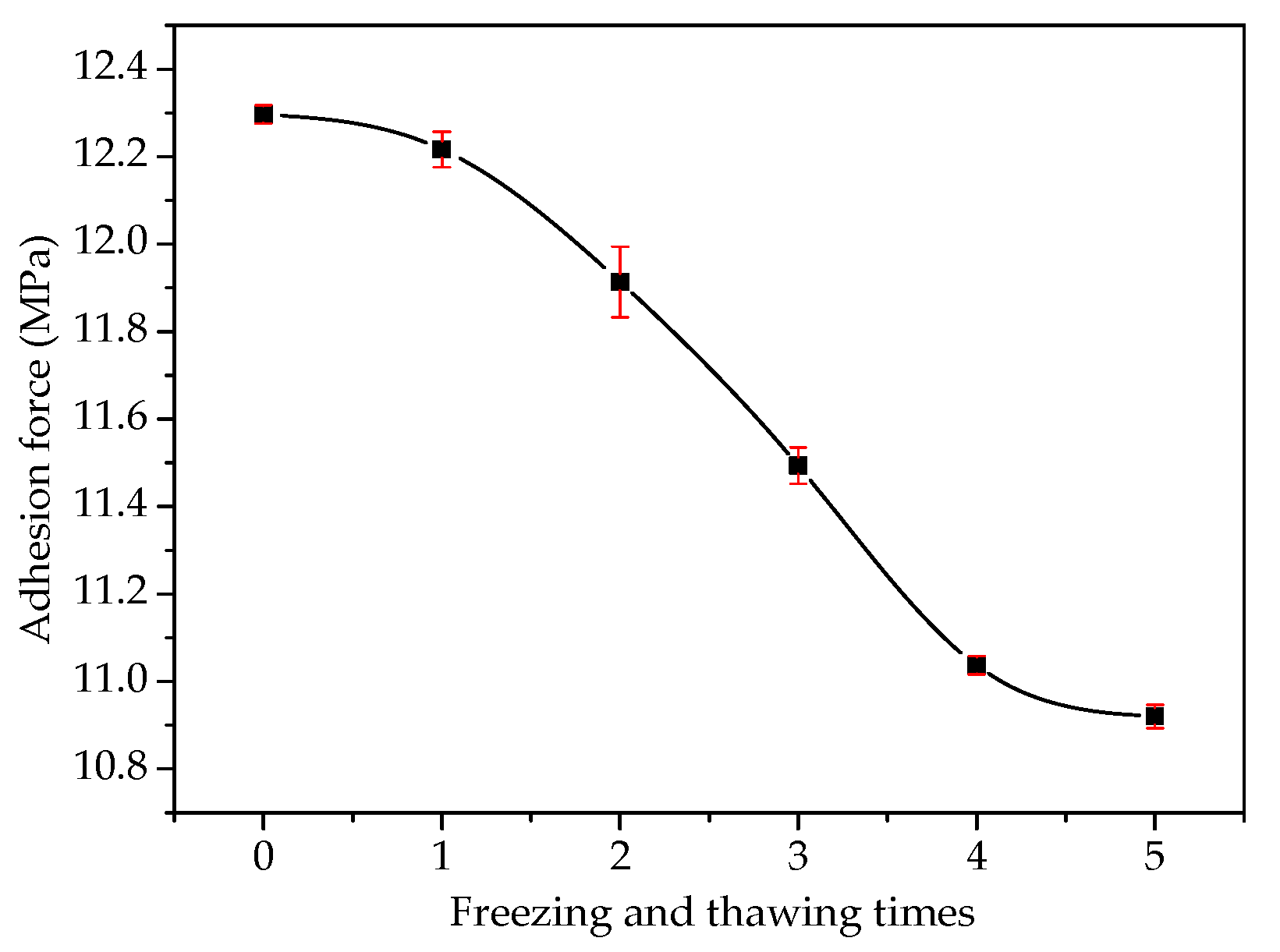
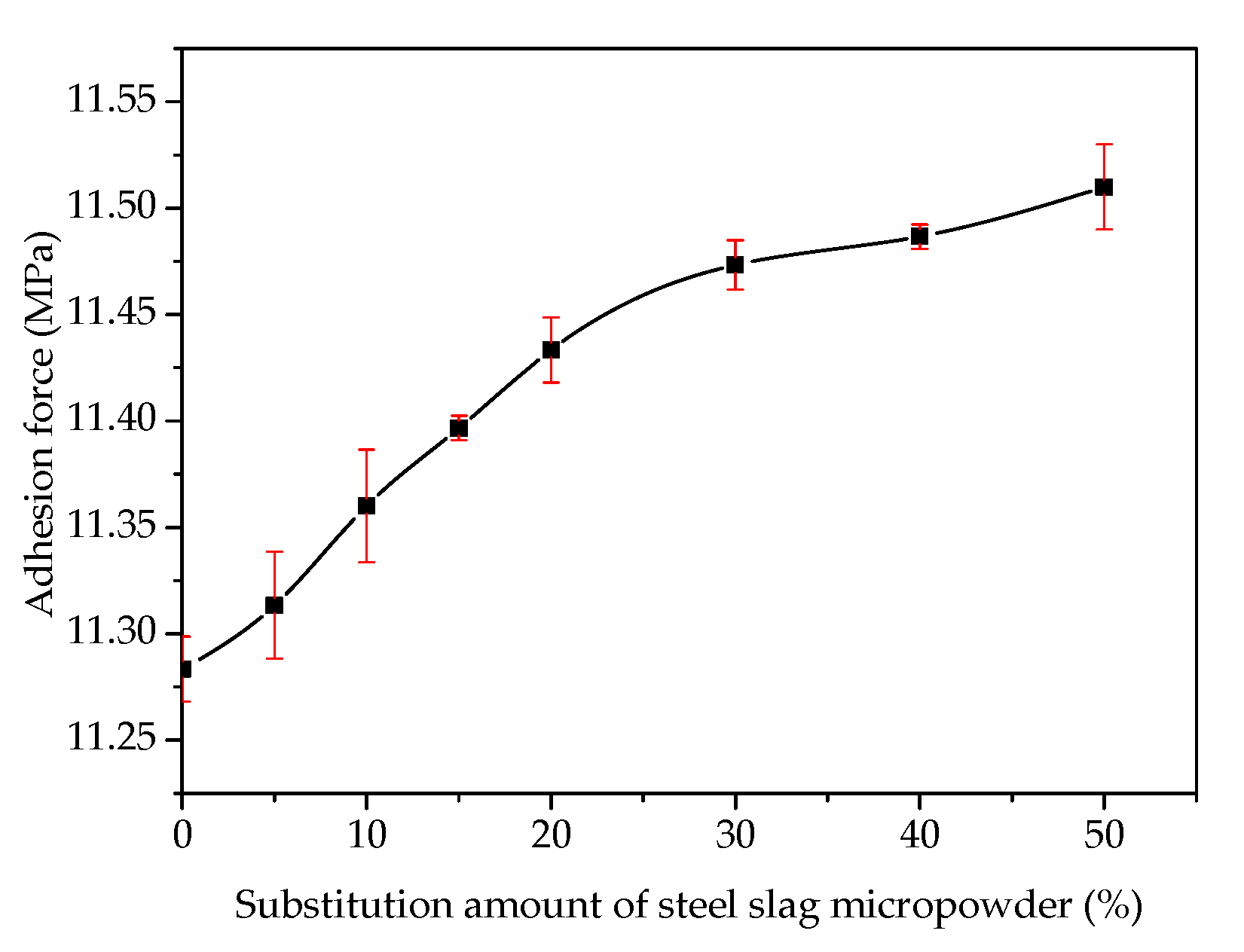
3.1. Adhesion Analysis of Steel Slag–Asphalt Interface
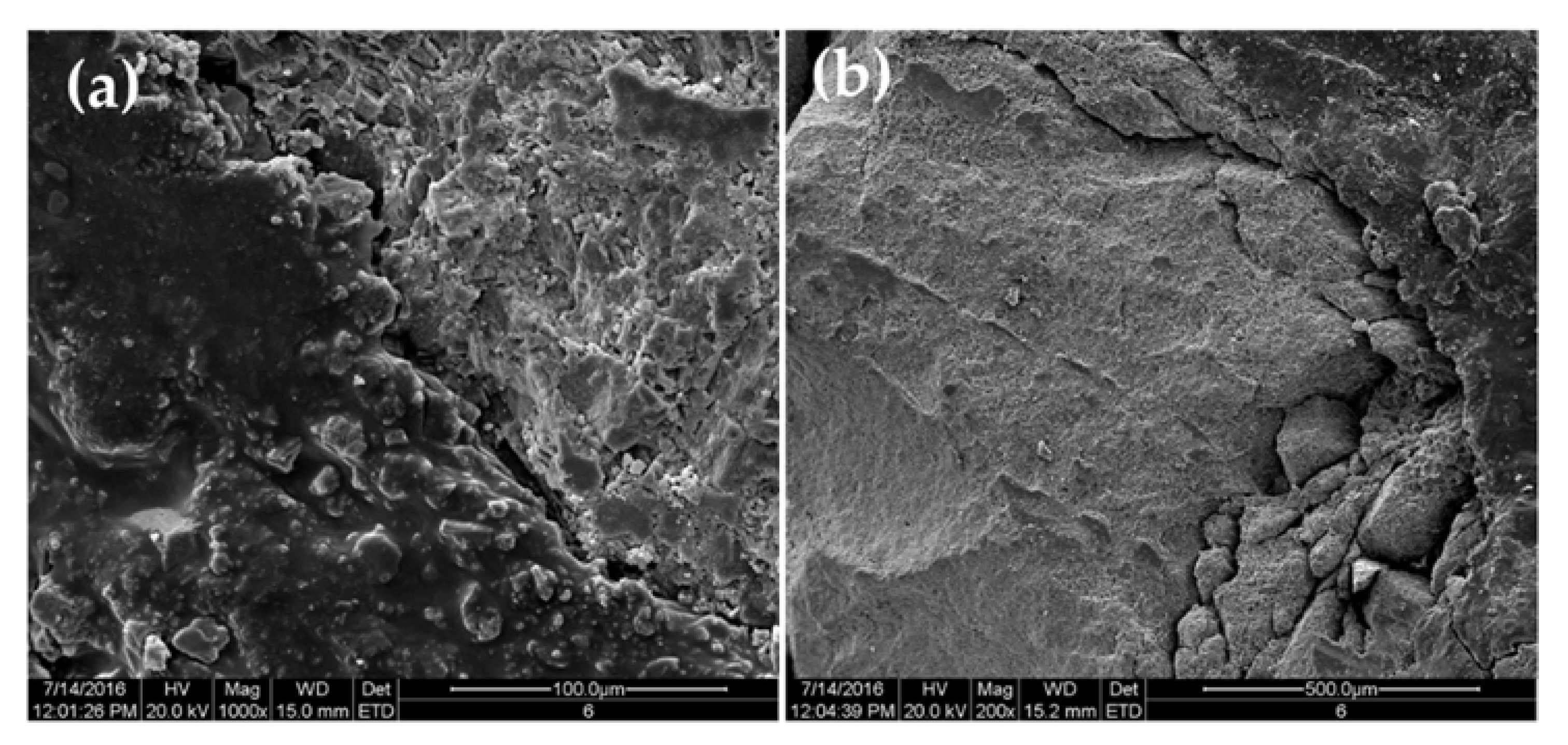
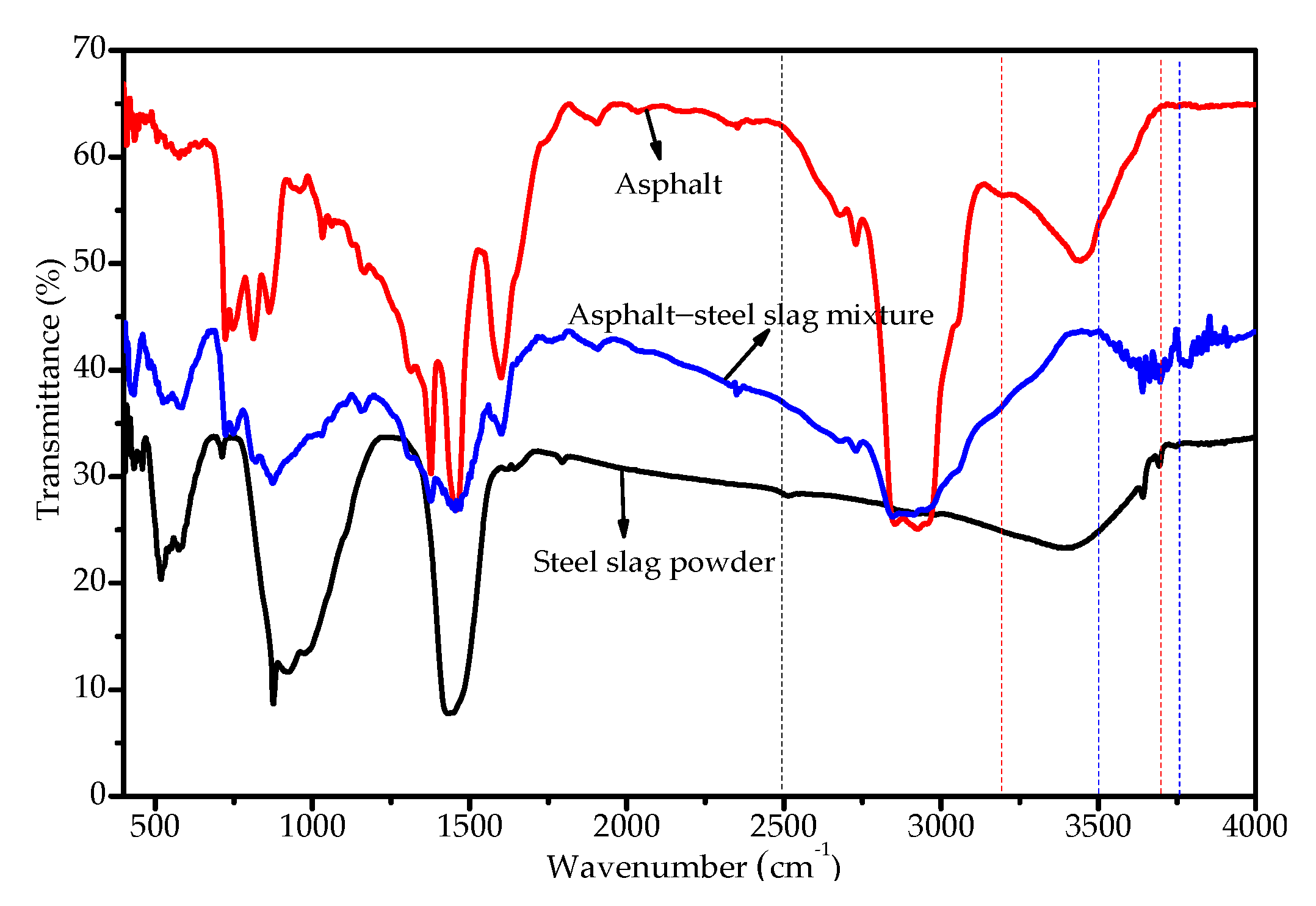
3.2. Microscopic Morphology of Asphalt–Aggregate Interface
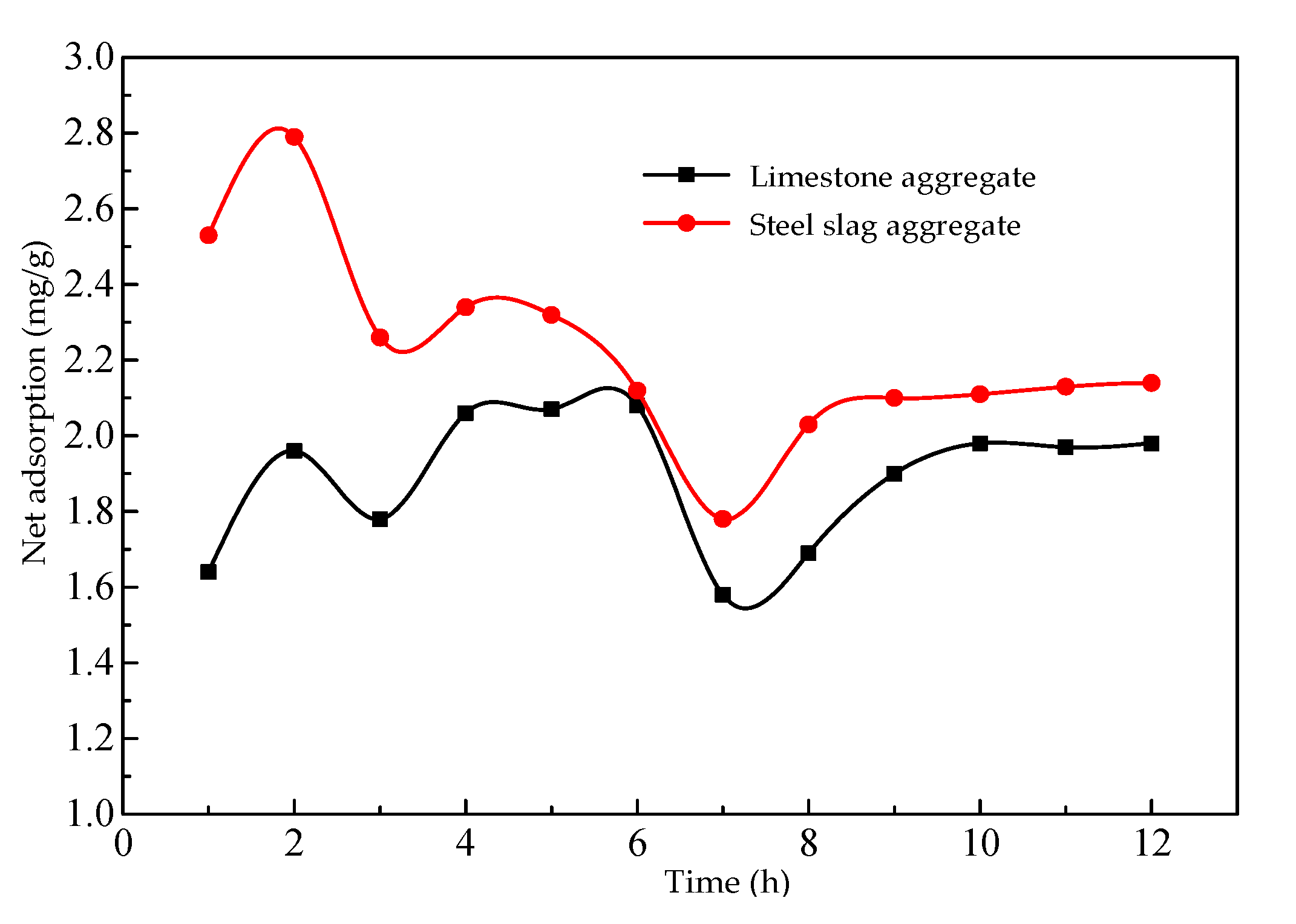
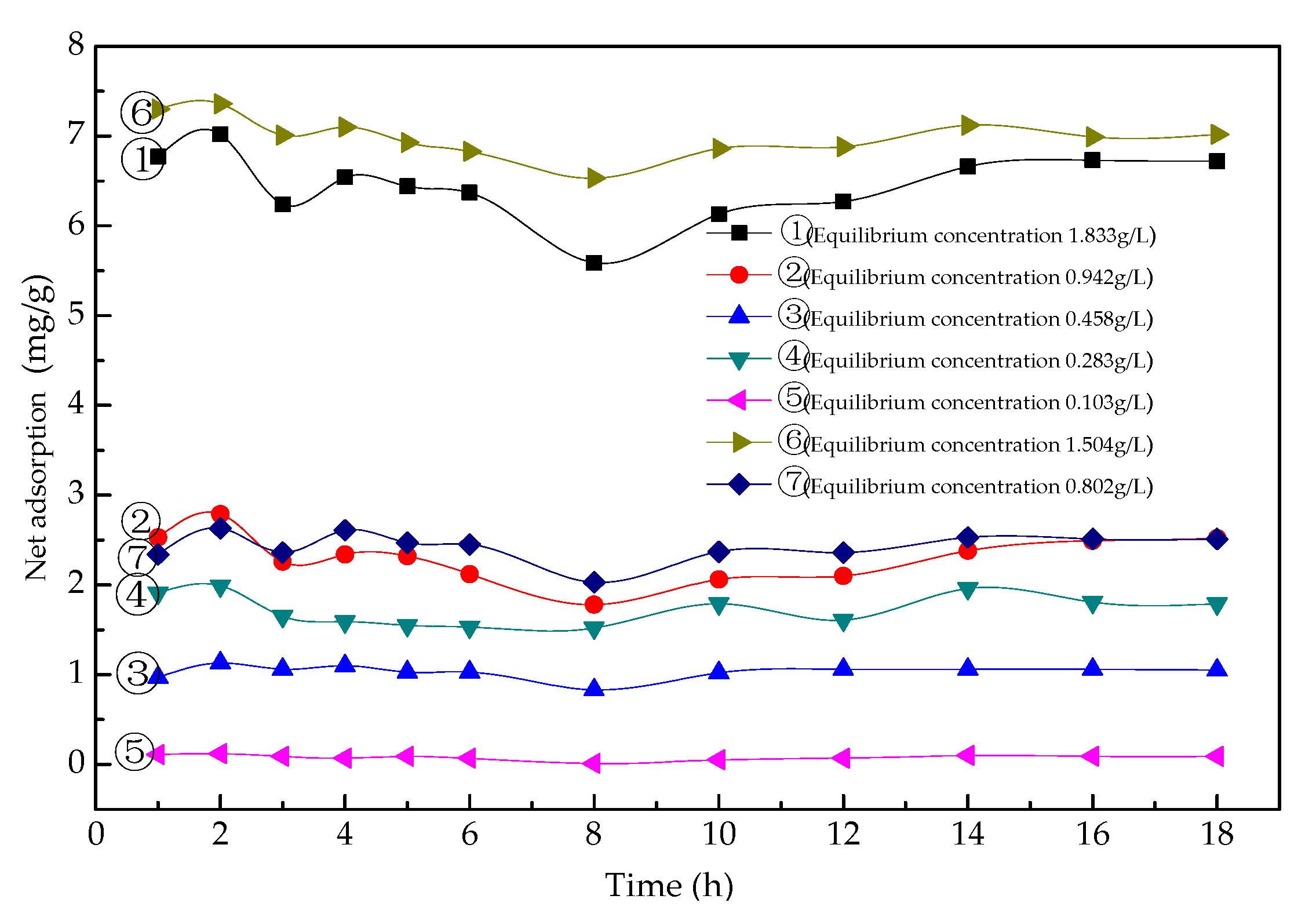
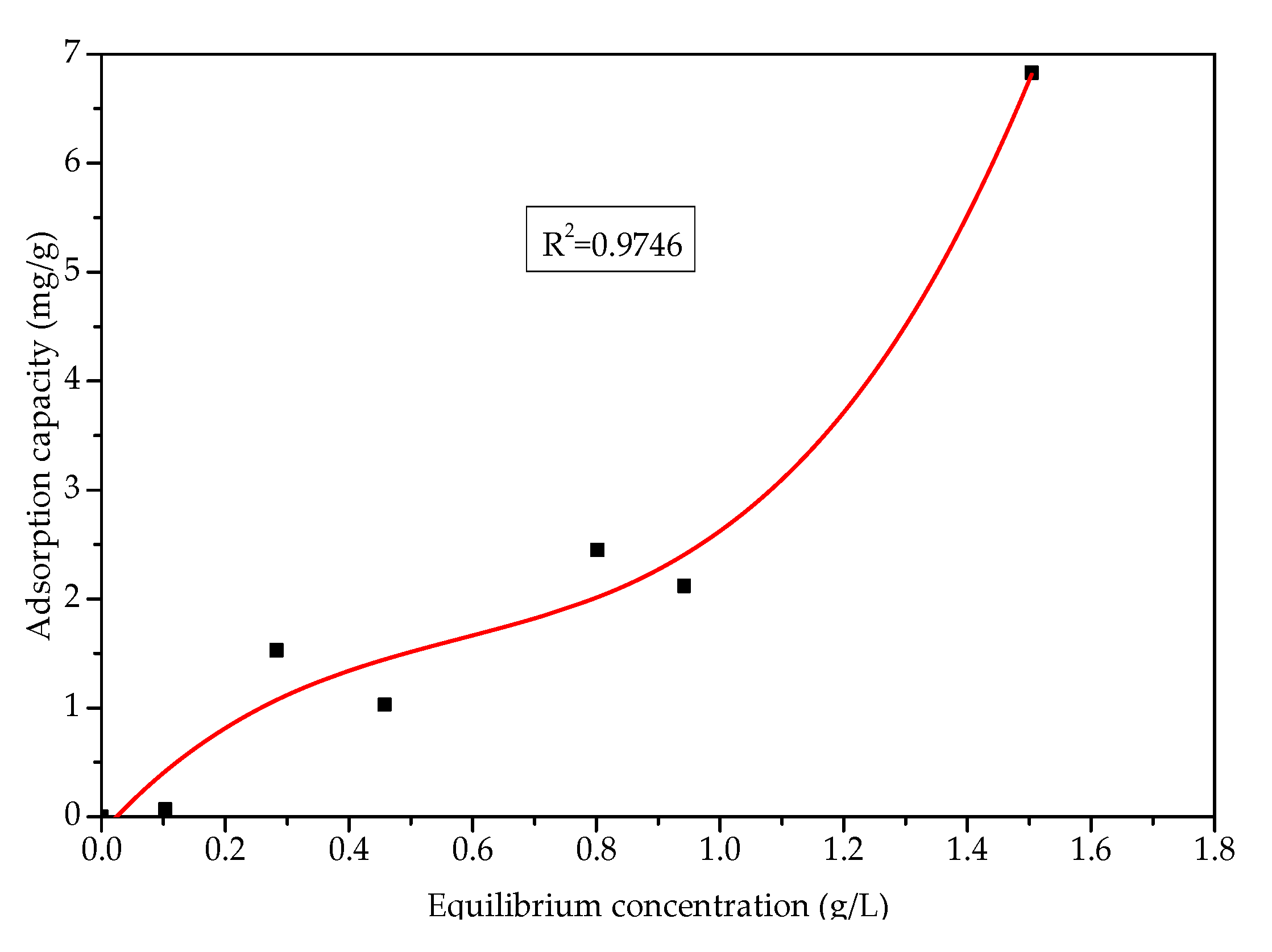
3.3. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics between Asphalt and Aggregate
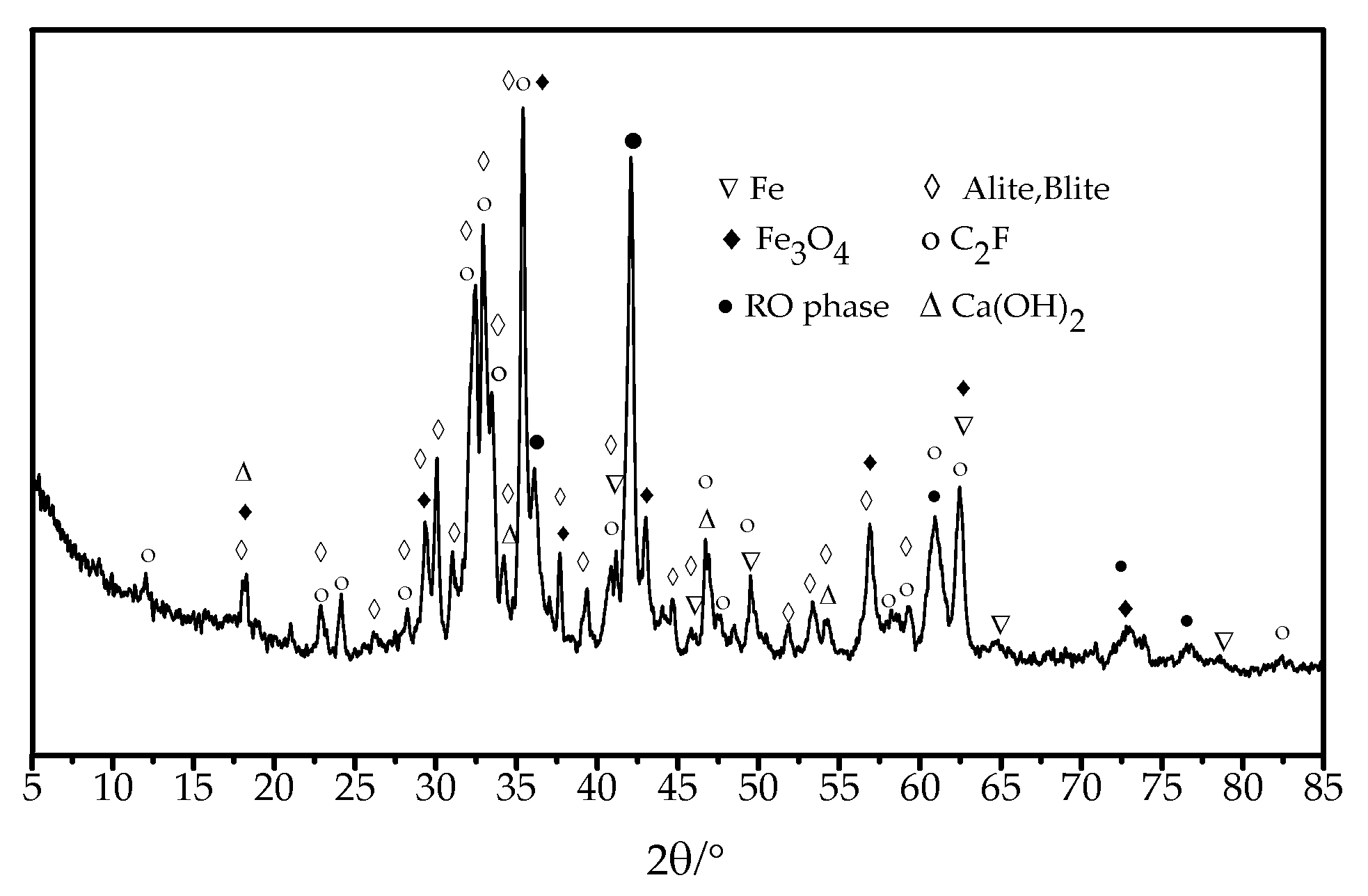
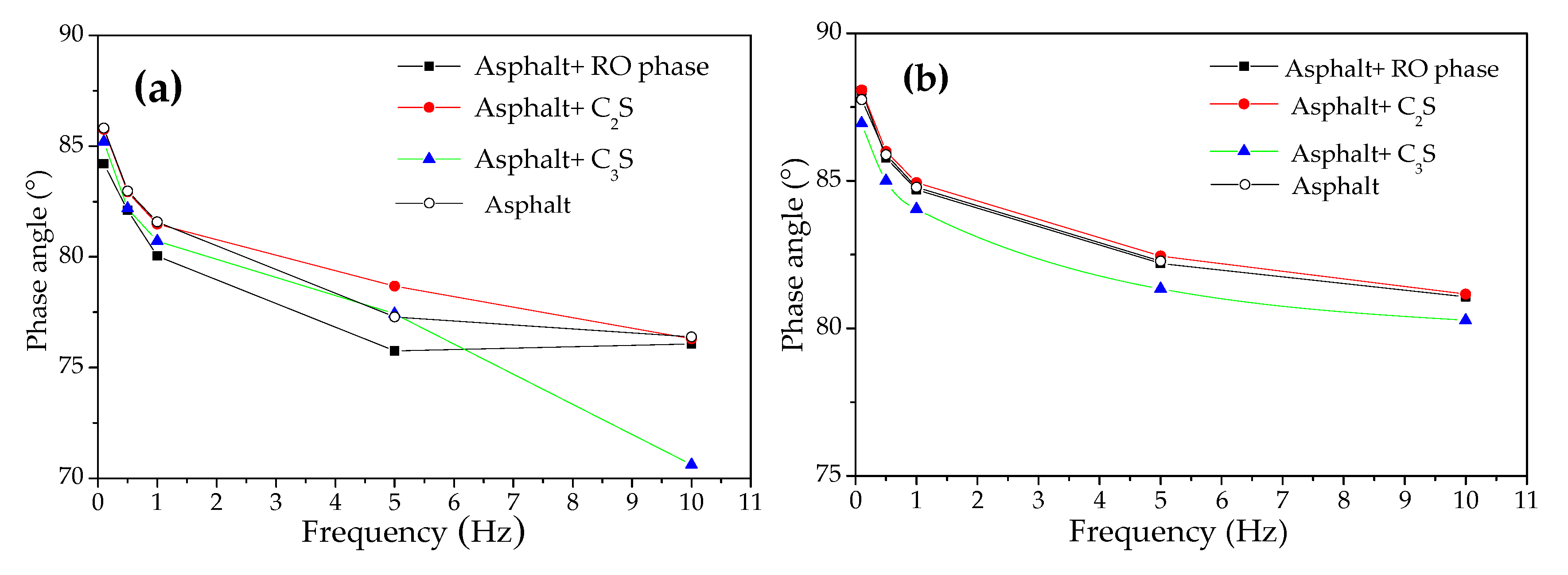
3.4. Analysis of Reaction Characteristics between Modified Asphalt and Steel Slag
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, H.; Dai, Q.; You, Z. Investigation of the asphalt–aggregate interaction using molecular dynamics. Petrol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.Y. Study on preparation stage and mechanism of modified desulfurization ash-based eco rubber by X-ray diffraction. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Romero, P.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y. Investigation on the low temperature property of asphalt fine aggregate matrix and asphalt mixture including the environmental factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F. Meso-scale analysis on shear failure characteristics of asphalt–aggregate interface. Mater. Struct. 2017, 50, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Park, D.; Singuranayo, J.L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Aggregate gradation theory, design and its impact on asphalt pavement performance: A review. Int. J. Pavement. Eng. 2019, 20, 1408–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habal, A.; Singh, D. Effects of warm mix asphalt additives on bonding potential and failure pattern of asphalt-aggregate systems using strength and energy parameters. Int. J. Pavement. Eng. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, P.; Zhu, H.; Xu, M. Study on the Application of Steel Slag in Porous Asphalt Concrete. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, L. Nano-mechanics modelling of deformation and failure behaviours at asphalt–aggregate interfaces. Int. J. Pavement. Eng. 2011, 12, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, E.; Xu, G. Molecular dynamics simulation of asphalt-aggregate interface adhesion strength with moisture effect. Int. J. Pavement. Eng. 2015, 18, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Darabi, M.K.; Little, D.N.; Al-Rub, R.K.A. Effect of the Realistic Tire Contact Pressure on the Rutting Performance of Asphaltic Concrete Pavements. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Long, H.M. Spectroscopic analysis of weak acid modified steel slag powder. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 3502–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, J.D.; Mun, S.H.; Huang, S.C. New Unified Viscoelastic Constitutive Equation for Asphalt Binders and Asphalt Aggregate Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, S.; Blankson, M.A. Environmental performance and mechanical analysis of concrete containing recycled asphalt pavement (RAP) and waste precast concrete as aggregate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podoll, R.T.; Becker, C.; Irwin, K.C. Surface Analysis by Laser Ionization of the Asphalt Aggregate Bond; March Progress Report SHRP-87-AIIR-07; SRI International: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, C.H. Phased Evaluation Theory and Study on Adhesion between Asphalt and Stone Based on Surface Energy Theory. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 723, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrer, A.R.; Wagh, V. The Effect of the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Aggregate on Bonding; Strategic Highway Research Program; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.C.; Turner, T.F.; Pauli, A.T.; Miknis, F.P.; Branthaver, J.F.; Robertson, R.E. Evaluation of different techniques for adhesive properties of asphalt-filler systems at interfacial region. J. ASTM Int. 2005, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Huang, X. Study on combustion mechanism of asphalt binder by using TG–FTIR technique. Fuel 2010, 89, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W. Impacts of Aggregate Characteristics on Asphalt/Aggregates Interface Properties. Available online: http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10710-1013017492.htm (accessed on 7 June 2012).
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Y. Study on physical excitation mechanism of steel slag tailings by XRD and SEM. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 937–941. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, S.C.; Berge, P.A.; Berryman, J.G. Using two-point correlation functions to characterize microgeometry and estimate permeabilities of sandstones and porous glass. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1996, 101, 20359–20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Miknis, F.P. The Effect of Antistrip Treatments on Asphalt-Aggregate Systems: An Environmental Scanning Electron Microscope Study. J. Elastom. Plast. 1998, 30, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasong, W.A.; Lynsdale, C.J.; Cripps, J.C. Aggregate-cement paste interface: Part I. Influence of aggregate geochemistry. Cement. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, Y. Temperature dependent photoluminescence of surfactant assisted electrochemically synthesized ZnSe nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.M.; Xu, P.J. Properties of a Steel Slag–Permeable Asphalt Mixture and the Reaction of the Steel Slag–Asphalt Interface. Materials 2019, 12, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Long, H.M. Study on composite activating mechanism of alkali steel slag cementations materials by XRD and FTIR. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2018, 38, 2302–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Standard Service Net Home Page. Available online: http://www.cssn.net.cn/cssn/cssn/MandStandard/gyDetail.jsp?bz_code=NjU1OTgzMw==&db_info=VF9OX1RSU19TVEFOREFSRF9XRUI=&A100=Q0pKL1QgMTkwLTIwMTI=&A101=MjAxMi0wOC0yMw==&price= (accessed on 23 August 2012).

| CaO | Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | MnO | P2O5 | TiO2 | SO3 | Na2O | K2O | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 44.83 | 21.65 | 14.38 | 5.48 | 3.42 | 1.94 | 0.83 | 0.57 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 6.58 |
| Test Item | Steel Slag | Limestone | Request | Normative References of the Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent relative density (g/cm3) | 3.39 | 2.93 | ≥2.90 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Water absorption (%) | 1.83 | 0.80 | ≤3.0 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Needle particle content (%) | 4.56 | 3.62 | ≤12 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Aggregate crushing value (%) | 13.9 | 13.9 | ≤26 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Water washing method <0.075 mm (%) | 0.2 | 0.1 | ≤1.0 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Los Angeles abrasion loss (%) | 13.2 | 16.2 | ≤26 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Incorruptibility (%) | 2.6 | 1.2 | ≤12 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Soaking expansion rate (%) | 1.2 | 0.9 | ≤2.0 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Adhesion to asphalt (%) | 5 | 5 | ≥4 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| f–CaO (%) | 1.7 | / | ≤3.0 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Test Item | Measured Value | Request | Normative References of the Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s) (0.1 mm) | 50.2 | ≥40 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 10 °C) (cm) | 42 | ≥30 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| softening point | 85 | ≥80 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Flash point (COC) (°C) | 275 | ≥260 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| 60 °C dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) | 32,000 | ≥20,000 | CJJT 190–2012 |
| Test Item | Steel Slag | Limestone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity (by volume) (%) | 14.5413 | 10.6205 | |
| BET surface area (m2·g−1) | 4.181 | 0.193 | |
| Proportion of apertures of different size (μm) | >10 | 19.784 | 99.273 |
| 1~10 | 15.479 | 0.023 | |
| 0.1~1 | 19.397 | 0 | |
| 0.01~0.1 | 36.570 | 0.203 | |
| 0.001~0.01 | 8.770 | 0.501 | |
| Medium pore diameter (μm) | 0.0138 | 0.0071 | |
| Average pore diameter (μm) | 0.0396 | 1.1821 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, P. The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate. Materials 2020, 13, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051180
Liu W, Li H, Zhu H, Xu P. The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenhuan, Hui Li, Huimei Zhu, and Pinjing Xu. 2020. "The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate" Materials 13, no. 5: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051180
APA StyleLiu, W., Li, H., Zhu, H., & Xu, P. (2020). The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate. Materials, 13(5), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051180




