Processing and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Reinforced AE44 Magnesium Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Fabrication Procedure
2.2. Microstructure Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Properties
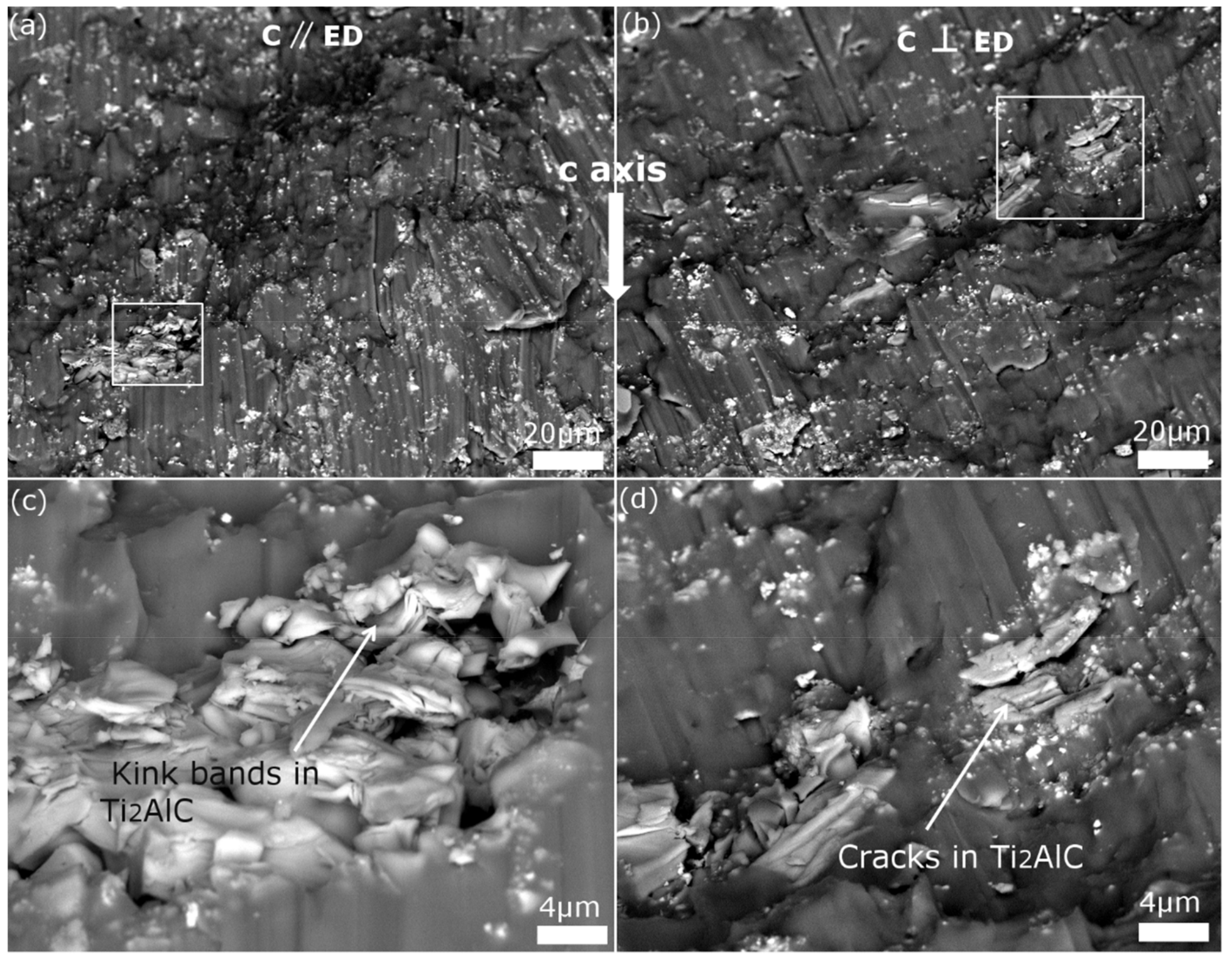
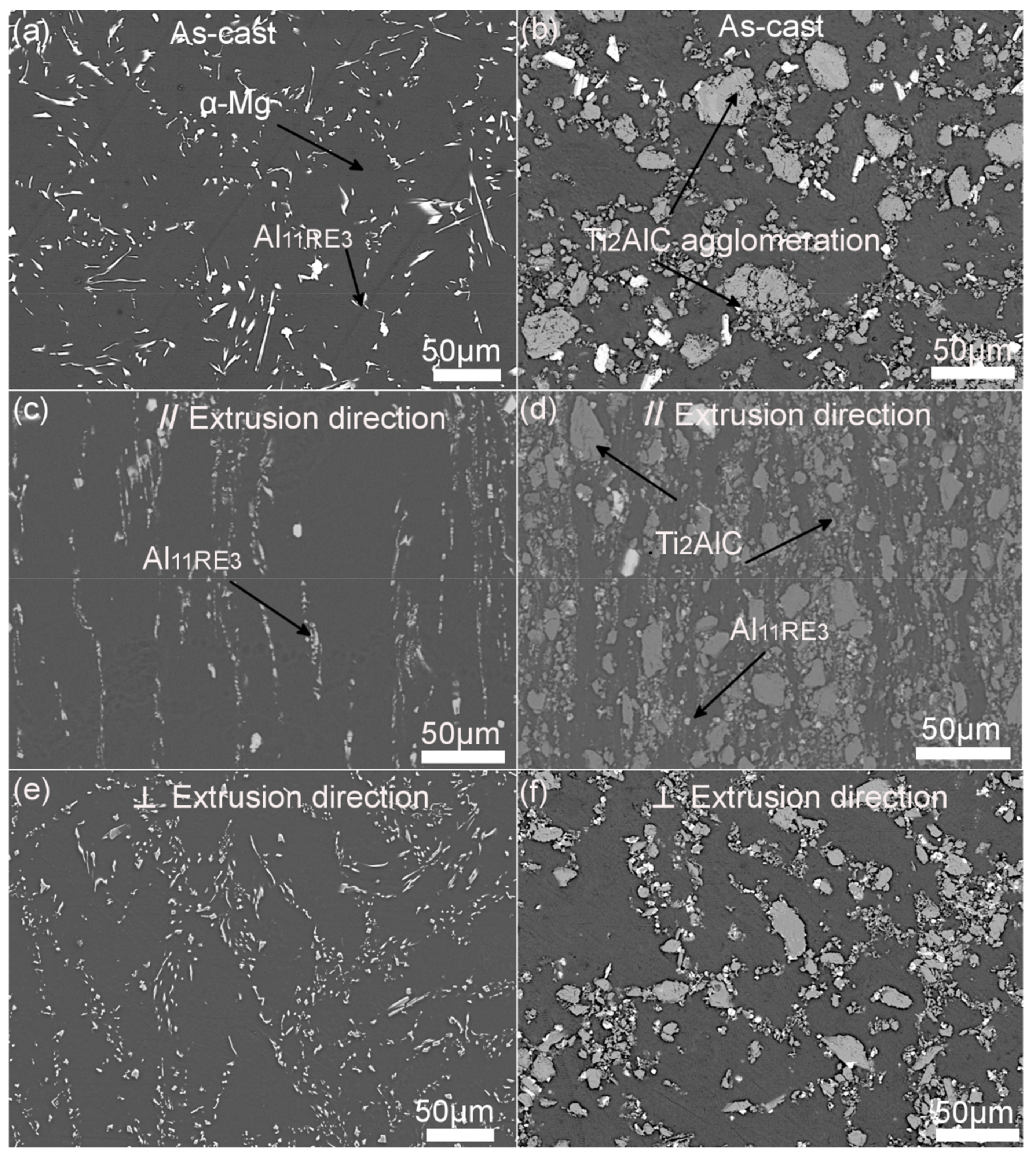
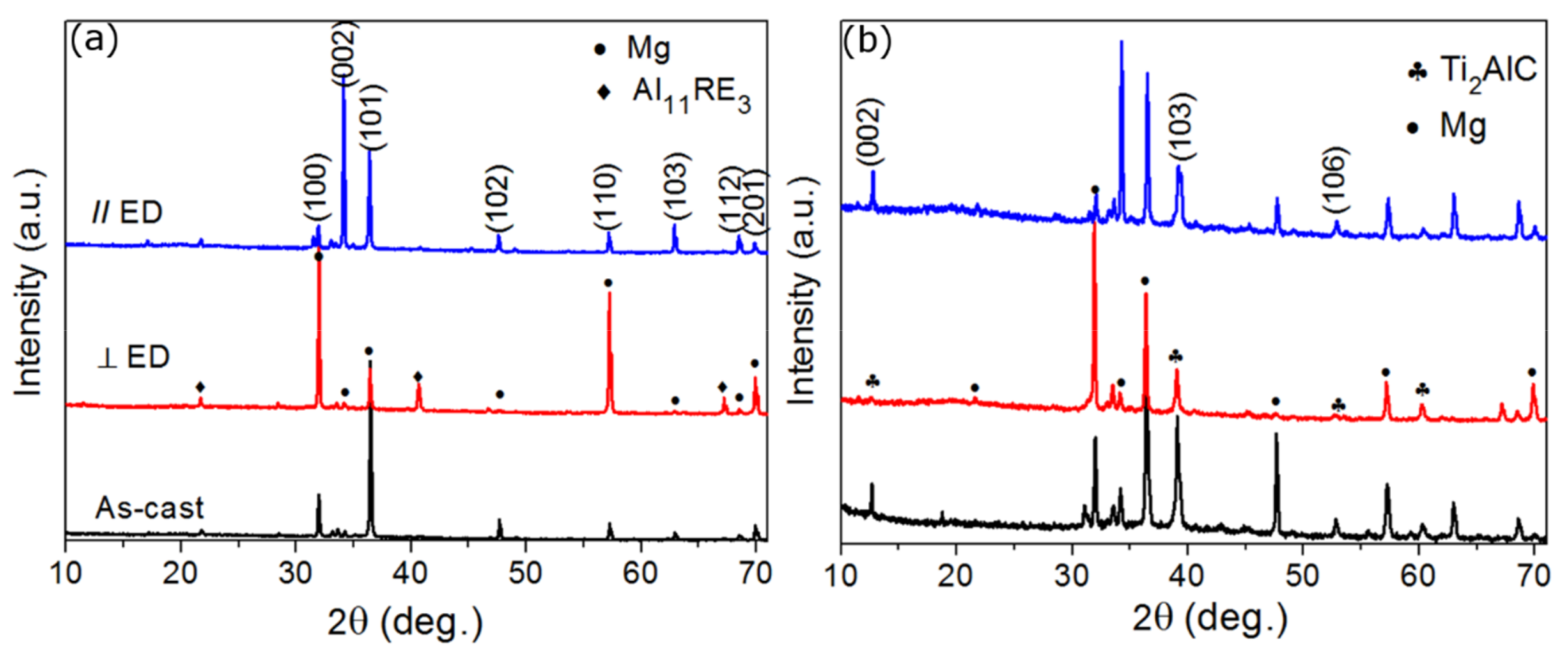
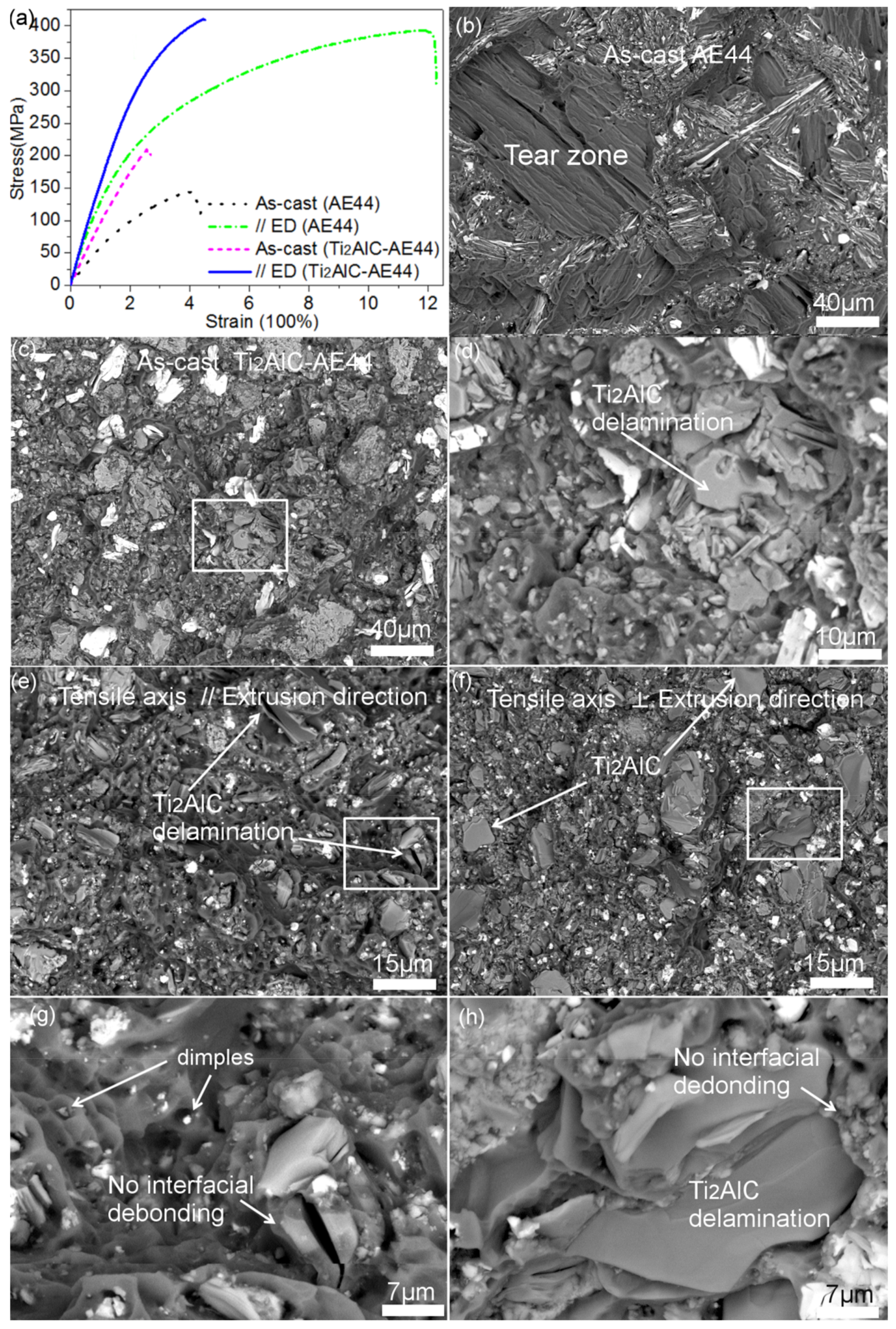
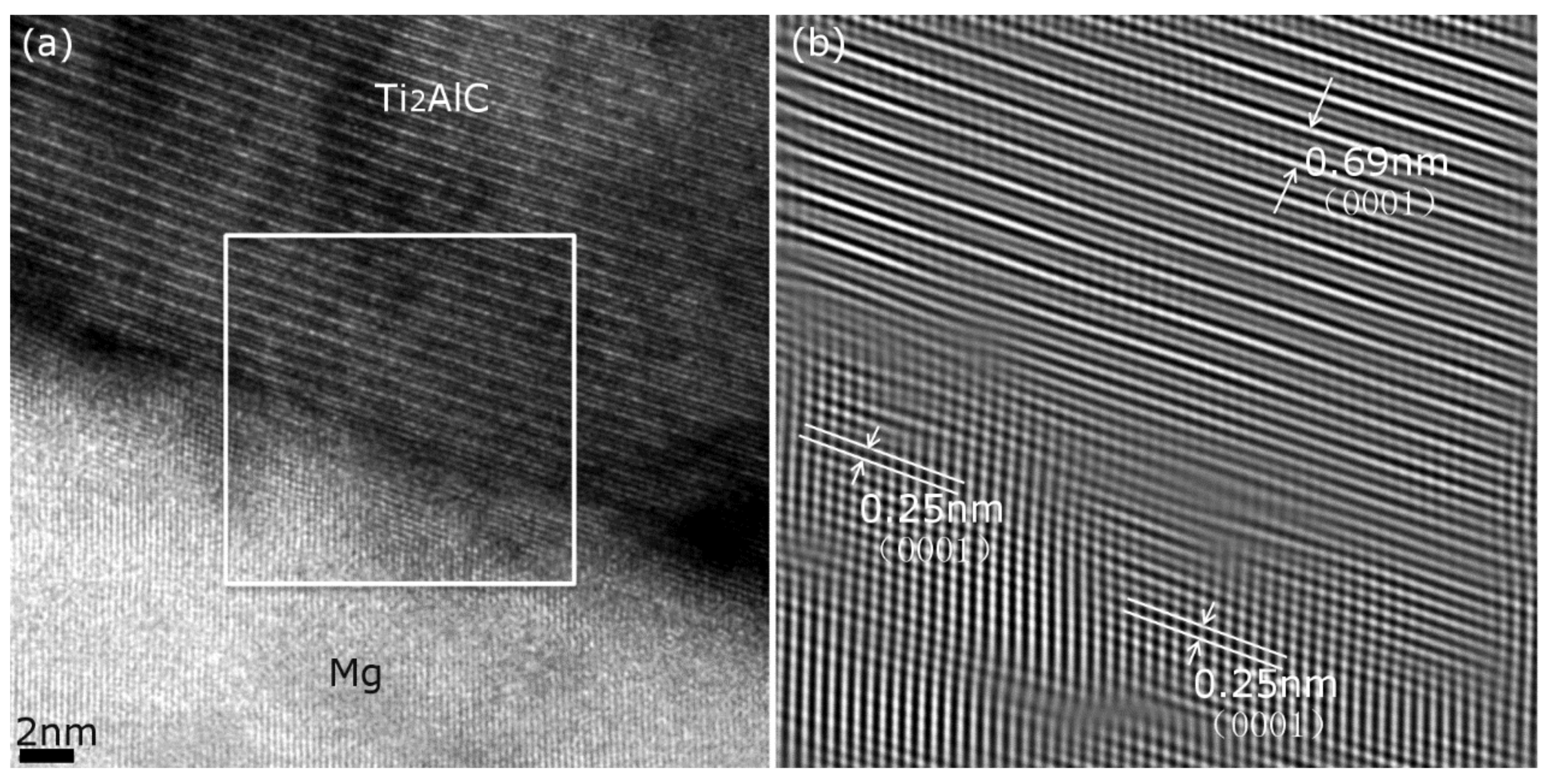
3. Results and Discussion
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pekguleryuz, M.O.; Kaya, A.A. Creep Resistant Magnesium Alloys for Powertrain Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 5, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.R.; Krajewski, P.E.; Luo, A.A. Magnesium alloys for lightweight powertrains and automotive structures. Mater. Design Manuf. Lightweight Veh. 2010, 80, 114–173. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Horstemeyer, M.F.; McDowell, D.L.; El Kadir, H.; Fan, J. Microstructure-based multistage fatigue modeling of a cast AE44 magnesium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wong, C.; Styles, M.J.; Abbott, T.B.; Nie, J.-F.; Easton, M.A. Revisiting the intermetallic phases in high-pressure die-cast Mg–4Al–4Ce and Mg–4Al–4La alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 156, 109839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Peng, L.M.; Powell, B.R.; Balough, M.P.; Kubic, R.C.; Sachdev, A.K. Interfacial and fracture behavior of short-fibers reinforced AE44 based magnesium matrix composites. J. Alloy Compd. 2010, 504, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondet, M.; Barraud, E.; Lemonnier, S.; Guyon, J.; Allain, N.; Grosdidier, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy developed by Spark Plasma Sintering. Acta Mater. 2016, 119, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C. Recent progress in the development and properties of novel metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2013, 74, 281–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Xu, D.K.; Wu, R.Z.; Chen, X.B.; Peng, Q.M.; Jin, L.; Xin, Y.C.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.H.; et al. What is going on in magnesium alloys? J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Deng, K.K.; Liang, W. High temperature damping behavior controlled by submicron SiCp in bimodal size particle reinforced magnesium matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 668, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.K.; Li, J.C.; Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Fan, J.F. High temperature damping behavior of as-deformed Mg matrix influenced by micron and submicron SiCp. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Harimkar, S.P. Effect of Graphene Nanoplate and Silicon Carbide Nanoparticle Reinforcement on Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Magnesium Matrix Composites. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Wu, K.; Nie, K.B.; Deng, K.K.; Hu, X.S.; Wang, X.J.; Zheng, M.Y. Damping capacities and tensile properties in Grp/AZ91 and SiCp/Grp/AZ91 magnesium matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Wu, K.; Deng, K.K.; Nie, K.B.; Wang, X.J.; Hu, X.S.; Zheng, M.Y. Damping capacities and tensile properties of magnesium matrix composites reinforced by graphite particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6816–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, S.; Torres, B.; Maroto, A.; López, A.J.; Otero, E.; Rams, J. Dry sliding wear behavior of globular AZ91 magnesium alloy and AZ91/SiCp composites. Wear 2017, 390–391, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.-j.; Deng, K.-k.; Nie, K.-b.; Li, J.-c.; Zhou, S.-s.; Xu, F.-j.; Fan, J.-f. Microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/Mg–Al–Zn composites containing Mg17Al12 phases processed by low-speed extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, P.; Srivastava, V.C.; De, P.K.; Sahoo, K.L. Processing and mechanical properties of SiC reinforced cast magnesium matrix composites by stir casting process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 460, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Amini, S.; Presser, V.; Barsoum, M.W. Nanocrystalline Mg-matrix composites with ultrahigh damping properties. Magnes. Technol. 2011, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Caspi, E.A.N.; Barsoum, M.W. Fabrication and mechanical properties of pressureless melt infiltrated magnesium alloy composites reinforced with TiC and Ti2AlC particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Wu, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties of micro-SiC particles reinforced magnesium matrix composites fabricated by stir casting assisted by ultrasonic treatment processing. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, X.; Vallet, M.; Tian, L. High temperature damping behavior and dynamic Youngs modulus of magnesium matrix composite reinforced by Ti2AlC MAX phase particles. Mech. Mater. 2019, 129, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Ding, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhai, H.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, S. Microstructure, mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of Ti2AlC reinforced AZ91D composites fabricated by stir casting. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 702, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W. The MN+1AXN phases: A new class of solids. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2000, 28, 201–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W.; Radovic, M. Elastic and Mechanical Properties of the MAX Phases. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 195–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhou, Y.C. Layered Machinable and Electrically Conductive Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 Ceramics: a Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 385–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Vallet, M.; Levraut, B.; Gauthier-Brunet, V.; Dubois, S. Oxidation mechanisms in bulk Ti2AlC: influence of the grain size. J. the Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, A.; Van Petegem, S.; Tromas, C.; Joulain, A.; Van Swygenhoven, H.; Thilly, L. Effect of microstructure anisotropy on the deformation of MAX polycrystals studied by in-situ compression combined with neutron diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, A.; Joulain, A.; Thilly, L.; Tromas, C. Dislocation analysis of Ti2AlN deformed at room temperature under confining pressure. Philos. Mag. 2012, 92, 4536–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitton, A.; Joulain, A.; Thilly, L.; Tromas, C. Evidence of dislocation cross-slip in MAX phase deformed at high temperature. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Mauchamp, V.; Cabioc’h, T.; Magne, D.; Gence, L.; Piraux, L.; Gauthier-Brunet, V.; Dubois, S. Solid solution effects in the Ti2Al(CxNy) MAX phases: Synthesis, microstructure, electronic structure and transport properties. Acta Mater. 2014, 80, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.P.; Huang, Z.Y.; Hu, W.Q.; Hao, S.M.; Zhai, H.X.; Zhou, Y. Fabrication, mechanical properties, and tribological behaviors of Ti2AlC and Ti2AlSn0.2C solid solutions. J. Adv. Ceram. 2017, 6, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.D.; Zhu, D.G.; Grasso, S.; Suzuki, T.; Kasahara, A.; Tosa, M.; Kim, B.n.; Sakka, Y.; Zhu, M.H.; Hu, C.F. Effect of texture microstructure on tribological properties of tailored Ti3AlC2 ceramic. J. Adv. Ceram. 2017, 6, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chen, D.; Tian, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X. Self-lubricate and anisotropic wear behavior of AZ91D magnesium alloy reinforced with ternary Ti2AlC MAX phases. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenny, J., Jr. Replacing the Cast Iron Liners for Aluminum Engine Cylinder Blocks: A Comparative Assessment of Potential Candidates. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.698.7932&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Xiong, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, H. Synthesis and characterization of textured Ti2AlC reinforced magnesium composite. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 730, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahador, A.; Umeda, J.; Hamzah, E.; Yusof, F.; Li, X.; Kondoh, K. Synergistic strengthening mechanisms of copper matrix composites with TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 772, 138797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Nie, K.B.; Deng, K.K.; Shang, S.J.; Zhou, S.S.; Xu, F.J.; Fan, J.F. Microstructure stability of as-extruded bimodal size SiCp/AZ91 composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Z.; Cai, L.; Lei, C.; Zhai, H.; Hao, S.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Preparation and mechanical properties of TiCx-Ni3(Al,Ti)/Ni composites synthesized from Ni alloy and Ti3AlC2 powders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 697, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramfitt, B.L. The effect of carbide and nitride additions on the heterogeneous nucleation behavior of liquid iron. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1970, 1, 19871995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D.; Vonnegut, B. Nucleation Catalysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhao, H.; Hu, X. Anisotropic mechanical and physical properties in textured Ti2AlC reinforced AZ91D magnesium composite. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 732, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xin, R.; Huang, G.; Liu, Q. Effect of crystal orientation on the mechanical properties and strain hardening behavior of magnesium alloy AZ31 during uniaxial compression. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 534, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
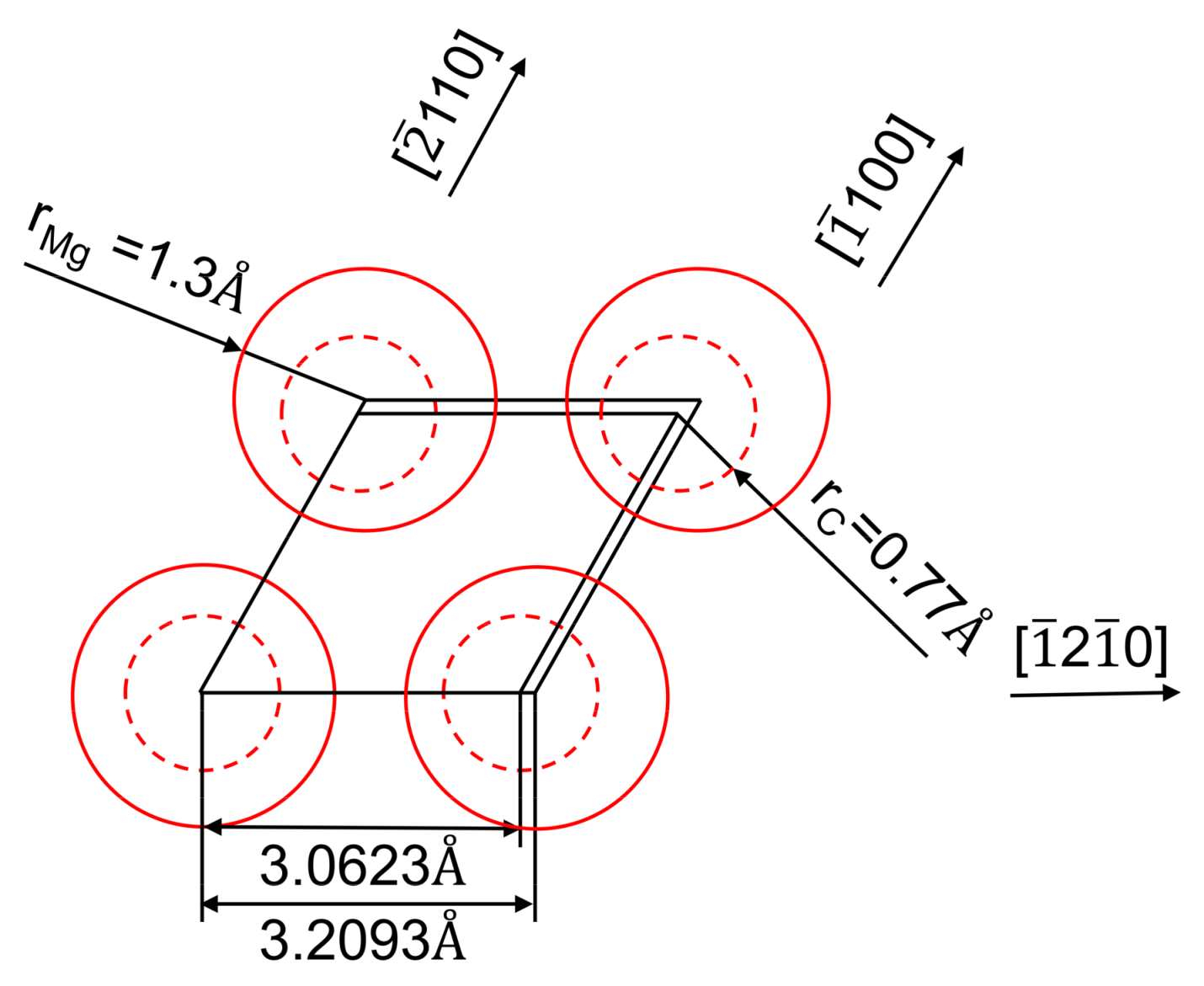
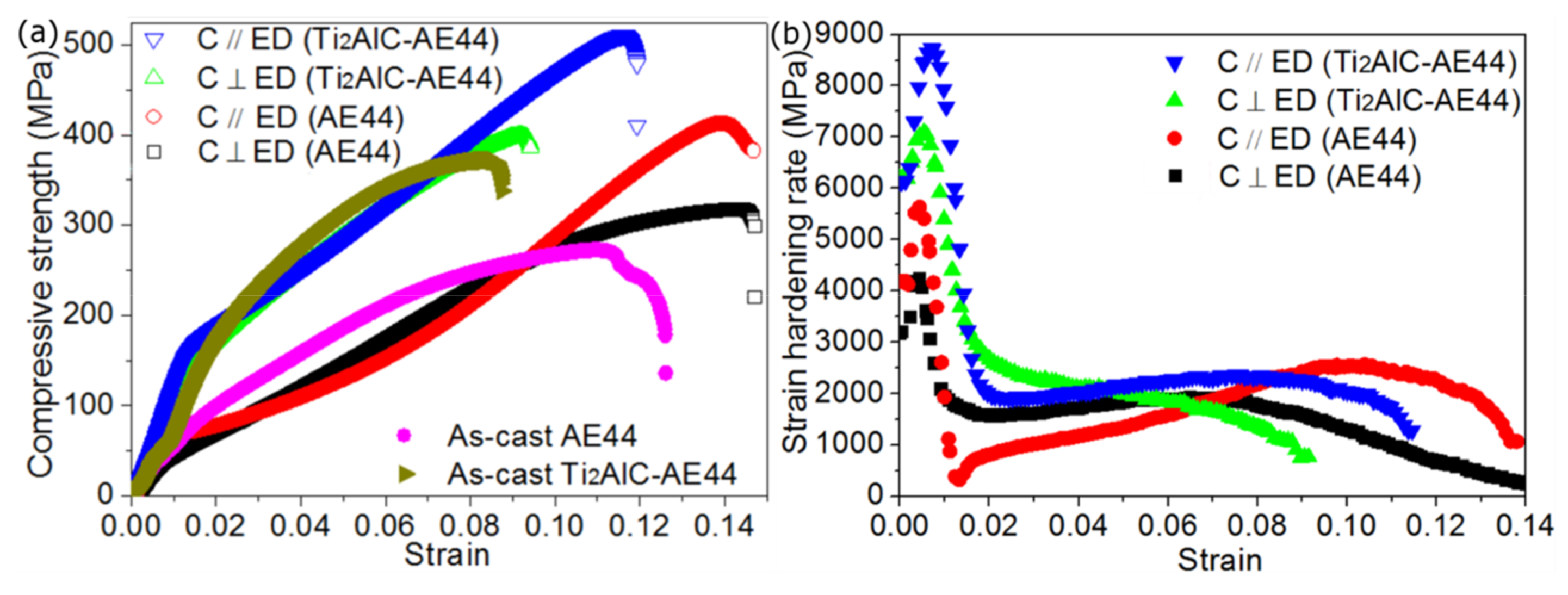

| Materials | Density (g/cm3) | TYS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | UCS (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast AE44 | 1.81 | 88 ± 20 | 149 ± 20 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 264 ± 5 |
| Extruded AE44 | 1.83 | 250 ± 10 | 397 ± 10 | 12.2 ± 1.0 | 414 ± 5 (c // ED axis) |
| 313 ± 5 (c ⊥ ED axis) | |||||
| As-cast Ti2AlC-AE44 | 2.14 | 179 ± 20 | 200 ± 20 | 2.6 ± 1.2 | 371 ± 5 |
| Extruded Ti2AlC-AE44 | 2.16 | 316 ± 10 | 416 ± 10 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 516 ± 5 (c // ED axis) |
| 394 ± 5 (c ⊥ ED axis) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pi, X.; Yu, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Xiong, S.; Guitton, A. Processing and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Reinforced AE44 Magnesium Composite. Materials 2020, 13, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040995
Pi X, Yu W, Ma C, Wang X, Xiong S, Guitton A. Processing and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Reinforced AE44 Magnesium Composite. Materials. 2020; 13(4):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040995
Chicago/Turabian StylePi, Xufeng, Wenbo Yu, Chaosheng Ma, Xiaojun Wang, ShouMei Xiong, and Antoine Guitton. 2020. "Processing and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Reinforced AE44 Magnesium Composite" Materials 13, no. 4: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040995
APA StylePi, X., Yu, W., Ma, C., Wang, X., Xiong, S., & Guitton, A. (2020). Processing and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Reinforced AE44 Magnesium Composite. Materials, 13(4), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13040995








