Effect of Phenolic Resin on the Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber-Modified Asphalt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Asphalt Binder Preparation
2.2.2. Rheological Measurements
2.2.3. Aging Method
2.2.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.5. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
2.2.6. Fluorescence Microscope (FM)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Frequency Sweep Tests
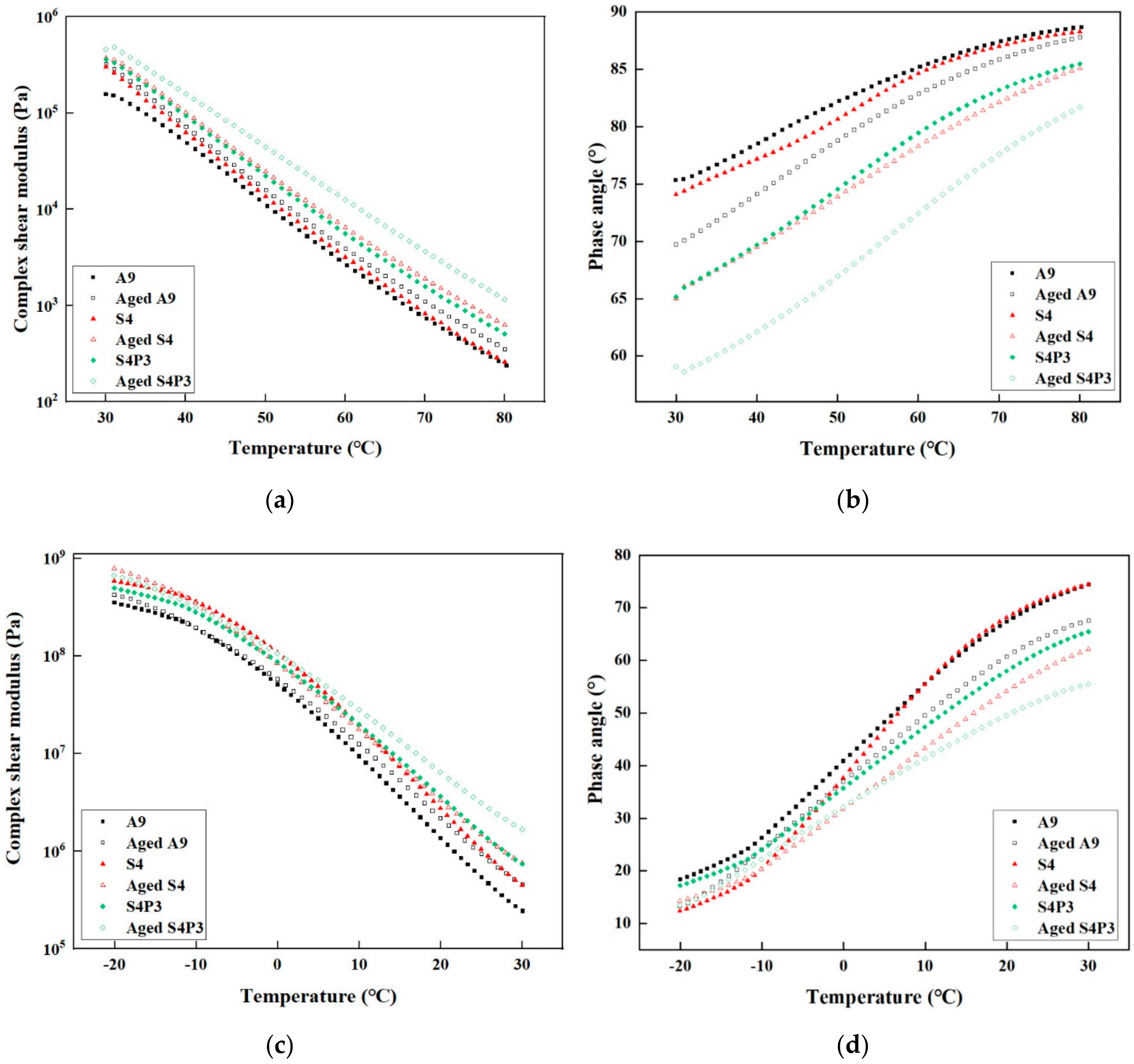
3.2. Temperature Sweep Tests
3.3. Aging Index (AI)
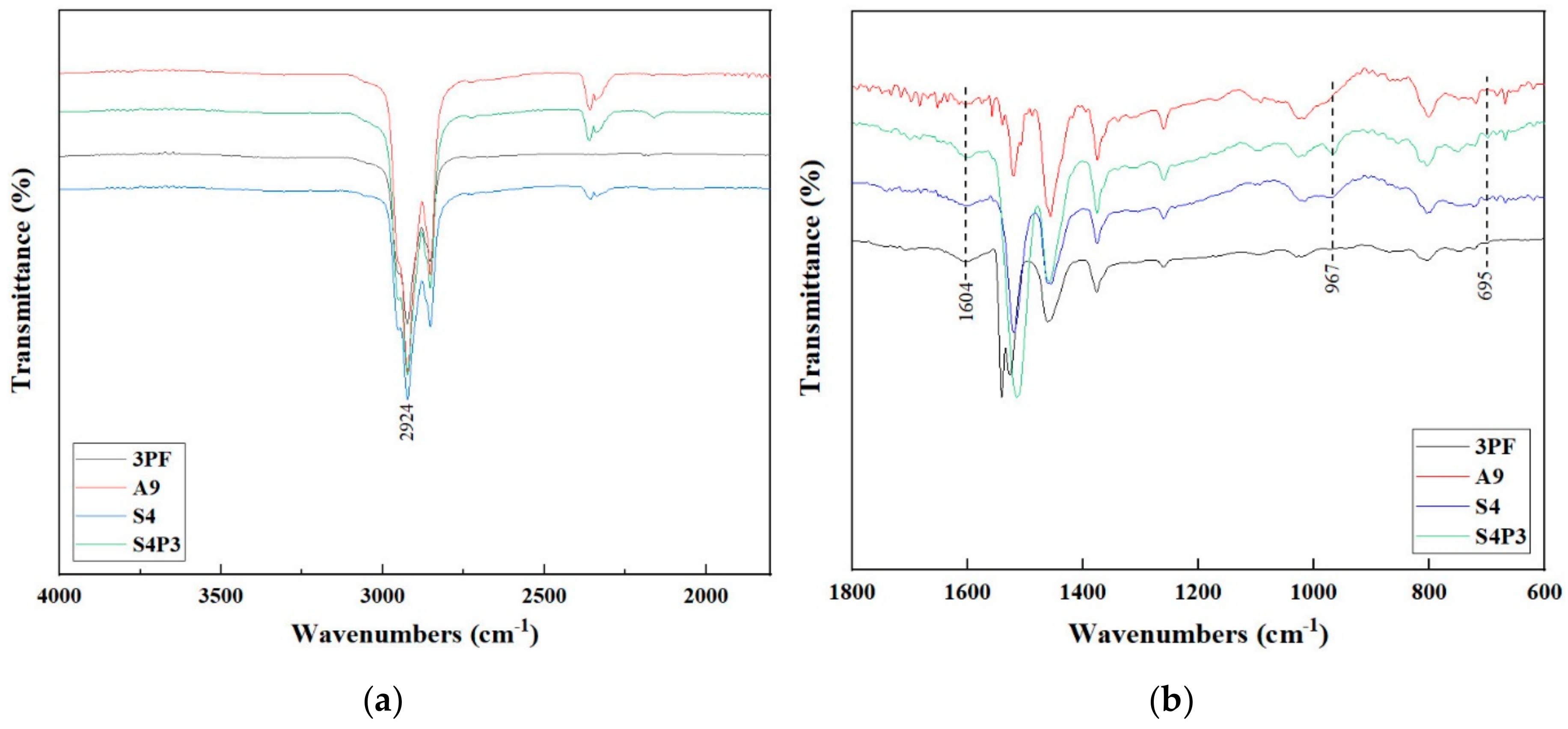
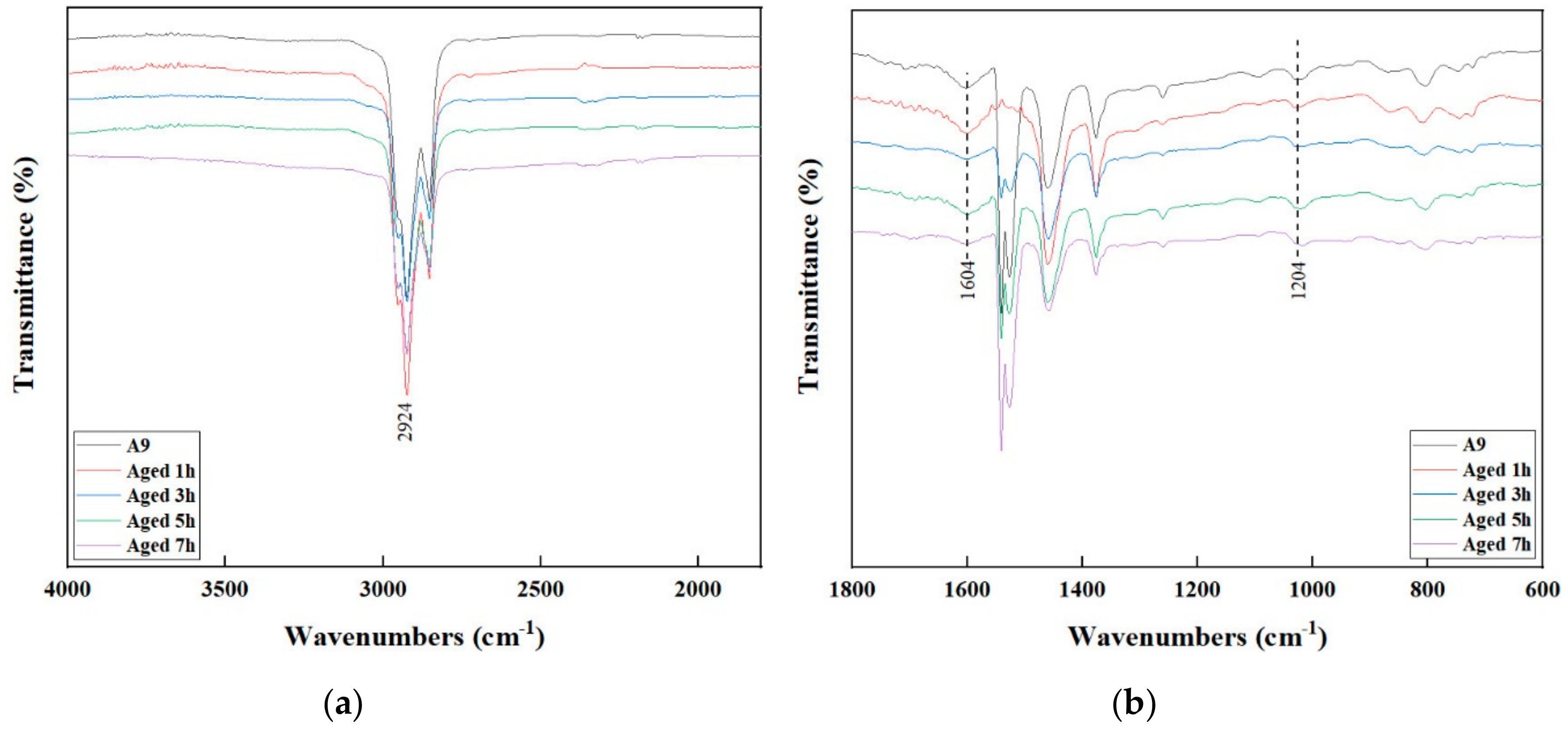
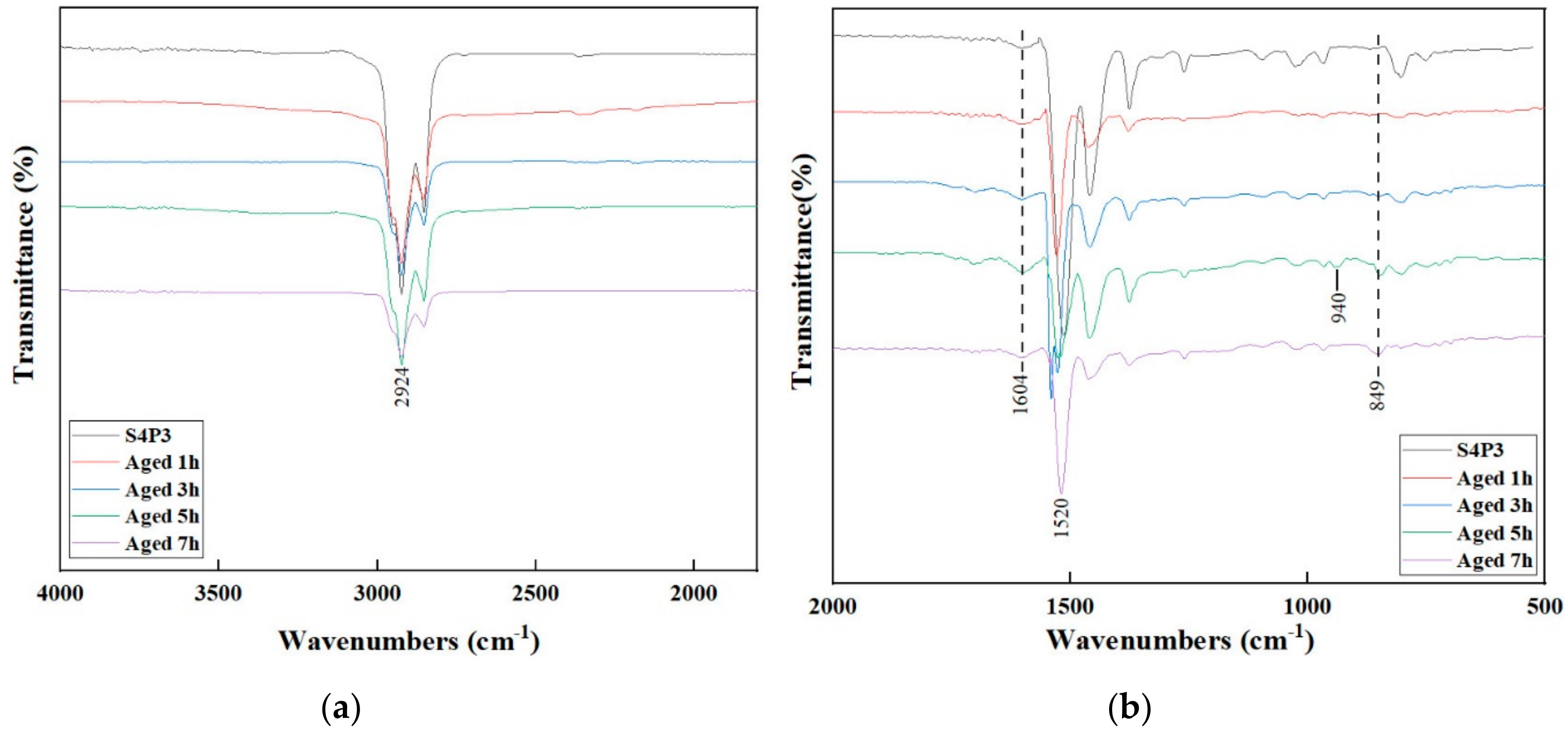
3.4. FTIR Analysis
3.5. GPC Analysis
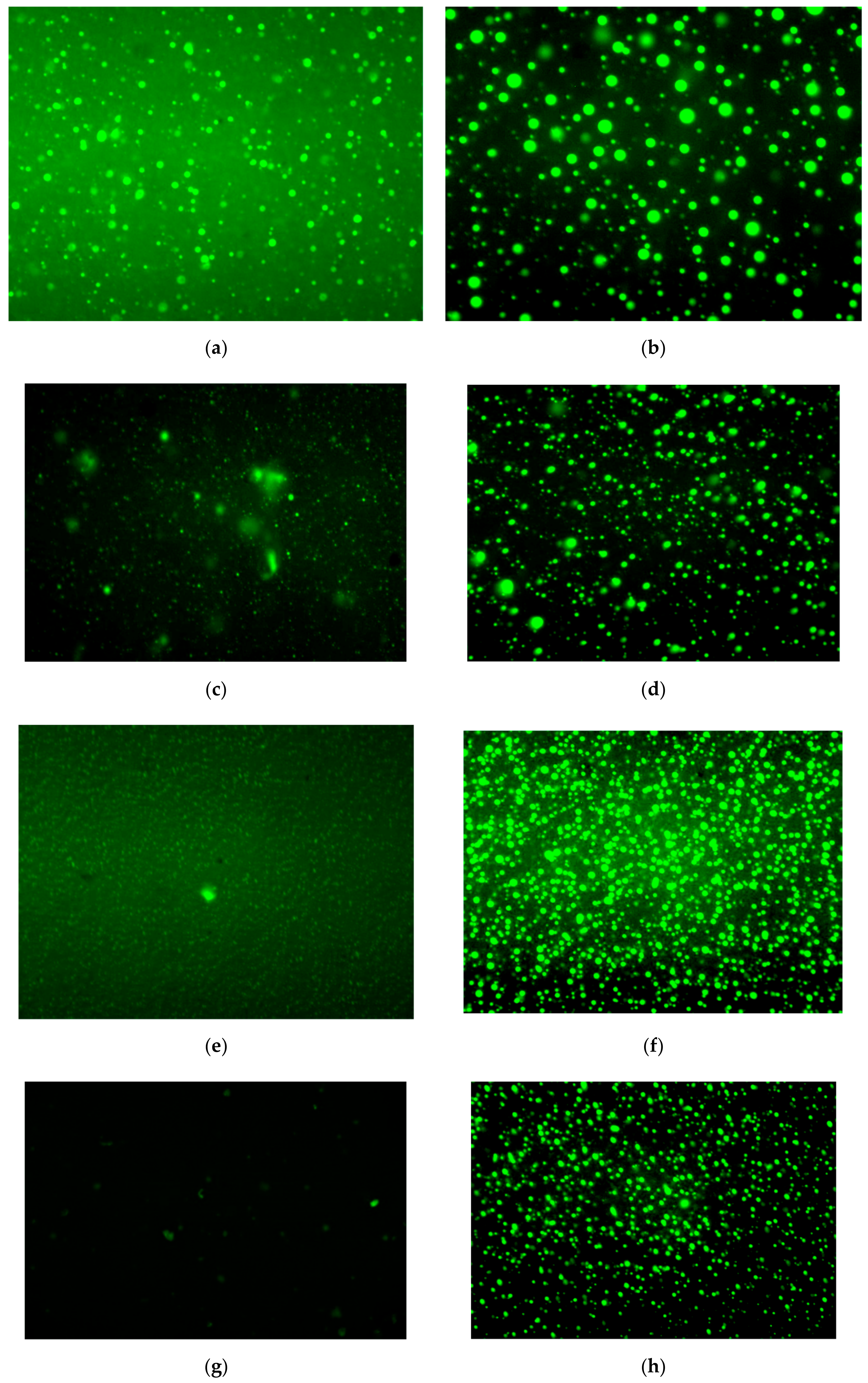
3.6. Morphology Evolution
4. Conclusions
- PF improves the rheological properties of SBR-modified asphalt. S4P3 has good deformation resistance at high temperatures and maintains good flexibility at low temperatures.
- The addition of PF improves the thermal aging resistance of SBR-modified asphalt and reduces the influence of aging on its performance. S4P3 has a lower degree of aging at the same aging time.
- The FTIR and GPC results show that S4P3 has good chemical system stability and it can remain stable when the aging time is less than 5 h. Under the same aging degree, S4P3 formed fewer carbonyl and sulfoxide compounds and has a slower deterioration rate of the polymer.
- In the S4P3 asphalt binder, PF and SBR have good compatibility with asphalt and form an embedded network structure in combination with the chemical reaction, the content of LMS in the asphalt is increased and the impact of aging and temperature on its performance is reduced.
- As the aging time increases, the polymers will gradually decompose. After 3 h of aging, the size of the polymer in S4 is reduced, and the deterioration of the polymer is significant. After adding PF, the polymer can maintain a better core size for a longer period.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Xi, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. The effect of styrene-butadiene-rubber/montmorillonite modification on the characteristics and properties of asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angius, E.; Ding, H.; Hesp, S.A.M. Durability assessment of asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 165, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Isacsson, U. Modification of road bitumens with thermoplastic polymers. Polym. Test. 2000, 20, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbouche, J.; Hajj, E.Y.; Sebaaly, P.E.; Piratheepan, M. A critical review of high polymer-modified asphalt binders and mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, G.D. Rheological properties of styrene butadiene styrene polymer modified road bitumens. Fuel 2003, 82, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatović, V.O.; Rek, V.; Marković, K.J. Effect of polymer modifiers on the properties of bitumen. J. Elastomers Plast. 2014, 46, 448–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Blazejowski, K.; Pecak, P. Effect of Type of Modified Bitumen on Selected Properties of Stone Mastic Asphalt Mixtures. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure CETRA, Šibenik, Croatia, 23–25 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C. Evaluation of Thermal Oxidative Aging Effect on the Rheological Performance of Modified Asphalt Binders. Master’s Thesis, University of Nevada, Reno, NV, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sengoz, B.; Isikyakar, G. Analysis of styrene-butadiene-styrene polymer modified bitumen using fluorescent microscopy and conventional test methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahhab, H.A.; Dalhat, M.; Habib, M. Storage stability and high-temperature performance of asphalt binder modified with recycled plastic. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Y. Polymer modified asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, R.; Birgisson, B.; Tia, M.; Kim, B.; Cui, Z. Guidelines for Use of Modifiers in Superpave Mixtures: Executive Summary and Volume 1 of 3 Volumes: Evaluation of SBS Modifier; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, Y.; Mendez, M.P.; Rodriguez, Y. Polymer modified asphalt. Vis. Tecnol. 2001, 9, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, J. The research for high-performance SBR compound modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, C. The research for SBS and SBR compound modified asphalts with polyphosphoric acid and sulfur. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of the improved properties of SBR/weathered coal modified bitumen containing carbon black. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Leng, Z.; Li, F.; Zhu, H.; Bao, S. Early-age strength and long-term performance of asphalt emulsion cold recycled mixes with various cement contents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. High and low temperature properties of nano-particles/polymer modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Liang, M.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, C.; Ren, S. Improving thermo-rheological behavior and compatibility of SBR modified asphalt by addition of polyphosphoric acid (PPA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Shi, C. Aging rheological characteristics of SBR modified asphalt with multi-dimensional nanomaterials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, C. Advances in addition-cure phenolic resins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 401–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L. Performance and mechanism of epoxy resin for reinforcement of styrene–butadiene rubber. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2011, 50, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yan, H.; Huang, Z. Dynamic mechanical properties of phenolic resin/chlorinated butyl rubber composites. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2014, 53, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshandeh, B.; Shojaei, A.; Faghihi, M. Effects of rubber curing ingredients and phenolic-resin on mechanical, thermal, and morphological characteristics of rubber/phenolic-resin blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 3808–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, A.; Faghihi, M. Physico-mechanical properties and thermal stability of thermoset nanocomposites based on styrene-butadiene rubber/phenolic resin blend. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabedini, A.S.; Karrabi, M.; Ghasemi, I. Viscoelastic behavior of NBR/phenolic compounds. Iran. Polym. J. 2013, 22, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L.Y.; Feng, C.P.; Siddig, E.A.A. Effect of phenolic resin on the performance of the styrene-butadiene rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofko, B.; Porot, L.; Cannone, A.F.; Poulikakos, L.; Huber, L.; Lu, X.; Mollenhauer, K.; Grothe, H. FTIR spectral analysis of bituminous binders: Reproducibility and impact of ageing temperature. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kumar, P. Effect of polymer modification on the ageing properties of asphalt binders: Chemical and morphological investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Yao, H. Rheological and structural evolution of SBS modified asphalts under natural weathering. Fuel 2016, 184, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, F.; Hesp, S. Spectroscopic analysis of pressure aging vessel protocols for the accelerated laboratory aging of asphalt cements. In Proceedings of the First Conference of Transportation Research Group of India, Bangalore, India, 7–10 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhang, E.; Fatokoun, S.; Shan, L. Effect of the softer binder on the performance of repeated RAP binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Lv, L. The relationships between asphalt ageing in lab and field based on the neural network. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2015, 16, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Tetteh, N.; Hesp, S.A.M. Preliminary experience with improved asphalt cement specifications in the City of Kingston, Ontario, Canada. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, E.A.A.; Feng, C.P.; Ming, L.Y. Effects of ethylene vinyl acetate and nanoclay additions on high-temperature performance of asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, P.; Siddig, E.A.A.; Han, C. Investigation on thermal aging stability of crosslinked styrene butadiene rubber modified asphalt binder. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1902–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Wang, S.-J.; Bian, H.-J.; Guo, Q.-L.; Li, X.-J. Ftir and rheology analysis of aging on different ultraviolet absorber modified bitumens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.; Kanabar, A.; Moult, E.; Rubab, S.; Hesp, S. Oxidative Aging of Asphalt Cements from an Ontario Pavement Trial. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2011, 4, 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Nivitha, M.R.; Prasad, E.; Krishnan, J.M. Ageing in modified bitumen using FTIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2015, 17, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branthaver, J.F.; Petersen, J.; Robertson, R.; Duvall, J.; Kim, S.; Harnsberger, P.; Mill, T.; Ensley, E.; Barbour, F.; Scharbron, J. Binder Characterization and Evaluation. Volume 2: Chemistry; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Herrington, P.R. Thermal decomposition of asphalt sulfoxides. Fuel 1995, 74, 1232–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, J.; Dumas, P.; Mouillet, V.; Kister, J. Comparison by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of different ageing techniques: Application to road bitumens. Fuel 2001, 80, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, E.V.; Amirkhanian, S.N.; Burati, J.L., Jr. HP-GPC characterization of asphalt aging and selected properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1995, 7, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Amirkhanian, S.N.; Lee, S.-J. HP-GPC characterization of rejuvenated aged CRM binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ma, Y.; Ling, T.; Ma, T.; Huang, X. Analysis on crumb rubber modified asphalt and its aging characteristic on microscale. J. Funct. Mater. 2015, 46, 21093–21098. [Google Scholar]







| Type | Physical Properties | Standard | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| A9 | Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | ASTM D5 | 86.4 |
| S4 | 80.4 | ||
| S4P3 | 74.1 | ||
| A9 | Ductility (5 °C, 5 cm/min, cm) | ASTM D113 | 11 |
| S4 | 150 | ||
| S4P3 | 150 | ||
| A9 | Softening point (°C) | ASTM D36 | 47.8 |
| S4 | 51 | ||
| S4P3 | 55.9 | ||
| A9 | Viscosity (135 °C, Pa·s) | ASTM D4402 | 0.68 |
| S4 | 0.97 | ||
| S4P3 | 1.17 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | ≤2.0 |
| Softening point (°C) | 98–110 |
| Fluidity (mm) | 20–40 |
| Polymerization speeds (150 °C) | 49~88 |
| Free phenol (%) | 2.0–4.0 |
| Fineness% (140 mesh) | ≥96 |
| Aging Time | AI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 52 °C | 58 °C | 64 °C | 70 °C | 76 °C | Average | ||
| A9 | 1 | 2.63 | 2.60 | 2.51 | 2.61 | 2.87 | 2.64 |
| 3 | 6.52 | 6.46 | 6.61 | 6.56 | 6.97 | 6.62 | |
| 5 | 12.51 | 12.42 | 12.42 | 12.33 | 12.27 | 12.39 | |
| 7 | 19.09 | 20.17 | 19.70 | 20.21 | 21.13 | 20.06 | |
| S4 | 1 | 1.89 | 1.87 | 1.87 | 1.90 | 1.84 | 1.87 |
| 3 | 4.71 | 4.88 | 4.71 | 4.84 | 4.84 | 4.80 | |
| 5 | 10.88 | 10.71 | 10.67 | 10.34 | 10.39 | 10.60 | |
| 7 | 16.90 | 17.03 | 17.02 | 17.27 | 17.52 | 17.15 | |
| S4P3 | 1 | 1.48 | 1.44 | 1.47 | 1.41 | 1.49 | 1.46 |
| 3 | 2.70 | 2.75 | 2.71 | 2.76 | 2.68 | 2.72 | |
| 5 | 5.76 | 5.68 | 5.83 | 5.63 | 5.52 | 5.68 | |
| 7 | 11.98 | 12.01 | 12.08 | 11.81 | 12.08 | 11.99 | |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignations |
|---|---|
| 2924 | C-H stretching vibration |
| 1705 | C=O stretching vibration |
| 1604 | C=C in aromatics stretching vibration |
| 1515 | C-C stretching vibration |
| 1024 | S=O stretching vibration |
| 964 | Trans-C-H wagging vibration (butadiene block) |
| 940 | C-H deformation vibration of ring hydrogens |
| 848 | C-H deformation vibration |
| 695 | Ring deformation vibration |
| Size | Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A9 | S4 | 3P3 | S4P3 | |
| Large molecules (LMS) | 15.01% | 15.21% | 13.40% | 15.68% |
| Medium molecules (MMS) | 49.02% | 44.06% | 42.07% | 44.13% |
| Small molecules (SMS) | 35.97% | 40.73% | 44.53% | 40.19% |
| Type | Size | Virgin | Aged 1 h | Aged 3 h | Aged 5 h | Aged 7 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A9 | LMS | 15.01% | 17.67% | 17.73% | 17.80% | 17.78% |
| MMS | 49.02% | 44.53% | 43.53% | 43.39% | 43.33% | |
| SMS | 35.97% | 37.80% | 38.74% | 38.81% | 38.89% | |
| S4 | LMS | 15.09% | 16.57% | 15.68% | 16.66% | 17.96% |
| MMS | 44.06% | 45.30% | 43.06% | 43.35% | 41.93% | |
| SMS | 40.85% | 38.13% | 41.26% | 39.99% | 40.11% | |
| S4P3 | LMS | 15.68% | 18.29% | 18.35% | 19.18% | 18.24% |
| MMS | 44.13% | 40.79% | 38.52% | 37.70% | 36.00% | |
| SMS | 40.19% | 40.92% | 43.13% | 43.12% | 45.76% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Phenolic Resin on the Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Materials 2020, 13, 5836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245836
Cheng P, Li Y, Zhang Z. Effect of Phenolic Resin on the Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Materials. 2020; 13(24):5836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245836
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Peifeng, Yiming Li, and Zhanming Zhang. 2020. "Effect of Phenolic Resin on the Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber-Modified Asphalt" Materials 13, no. 24: 5836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245836
APA StyleCheng, P., Li, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Effect of Phenolic Resin on the Rheological and Morphological Characteristics of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber-Modified Asphalt. Materials, 13(24), 5836. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13245836






