Influence of Nb Content on Precipitation, Grain Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
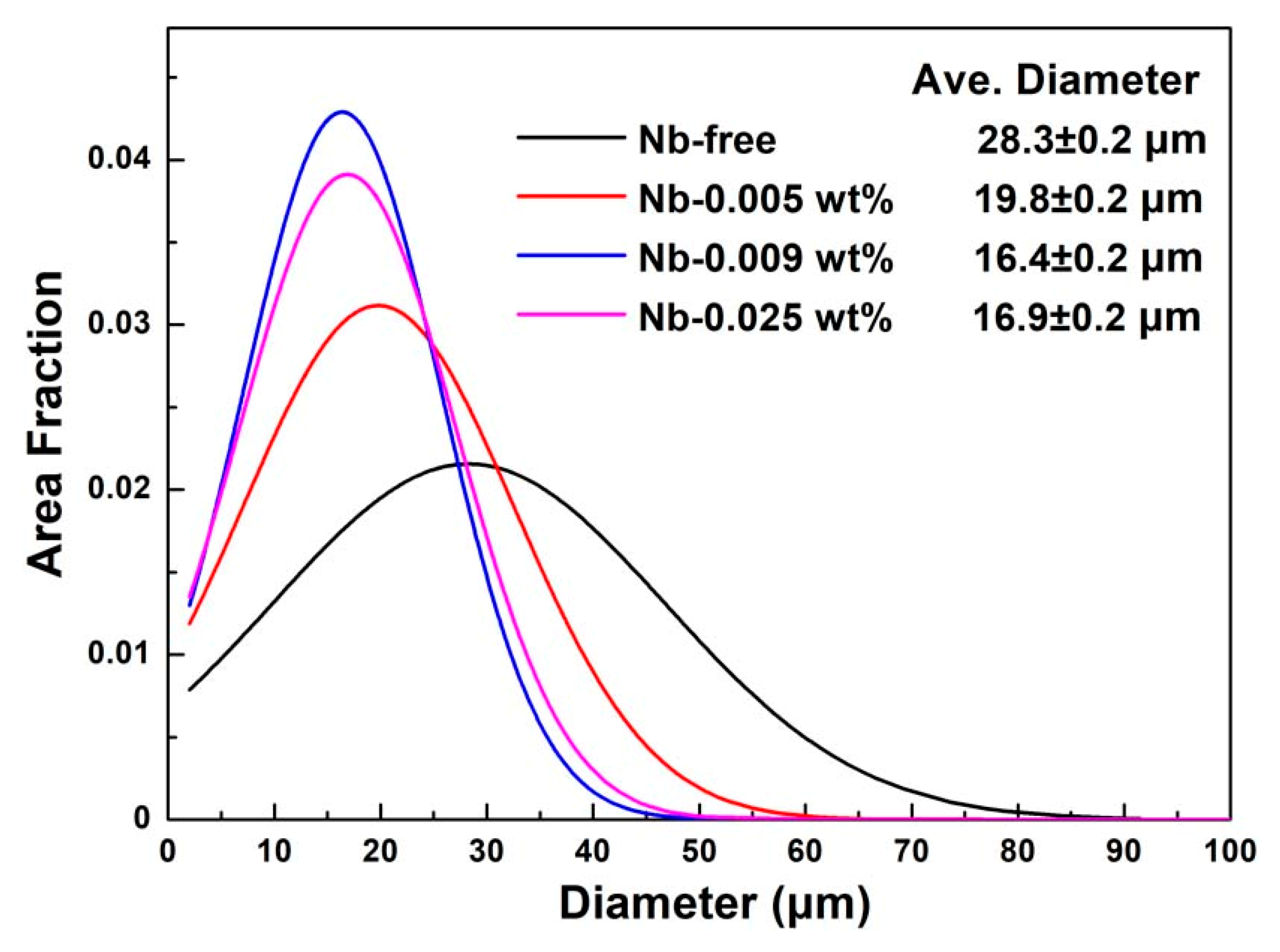
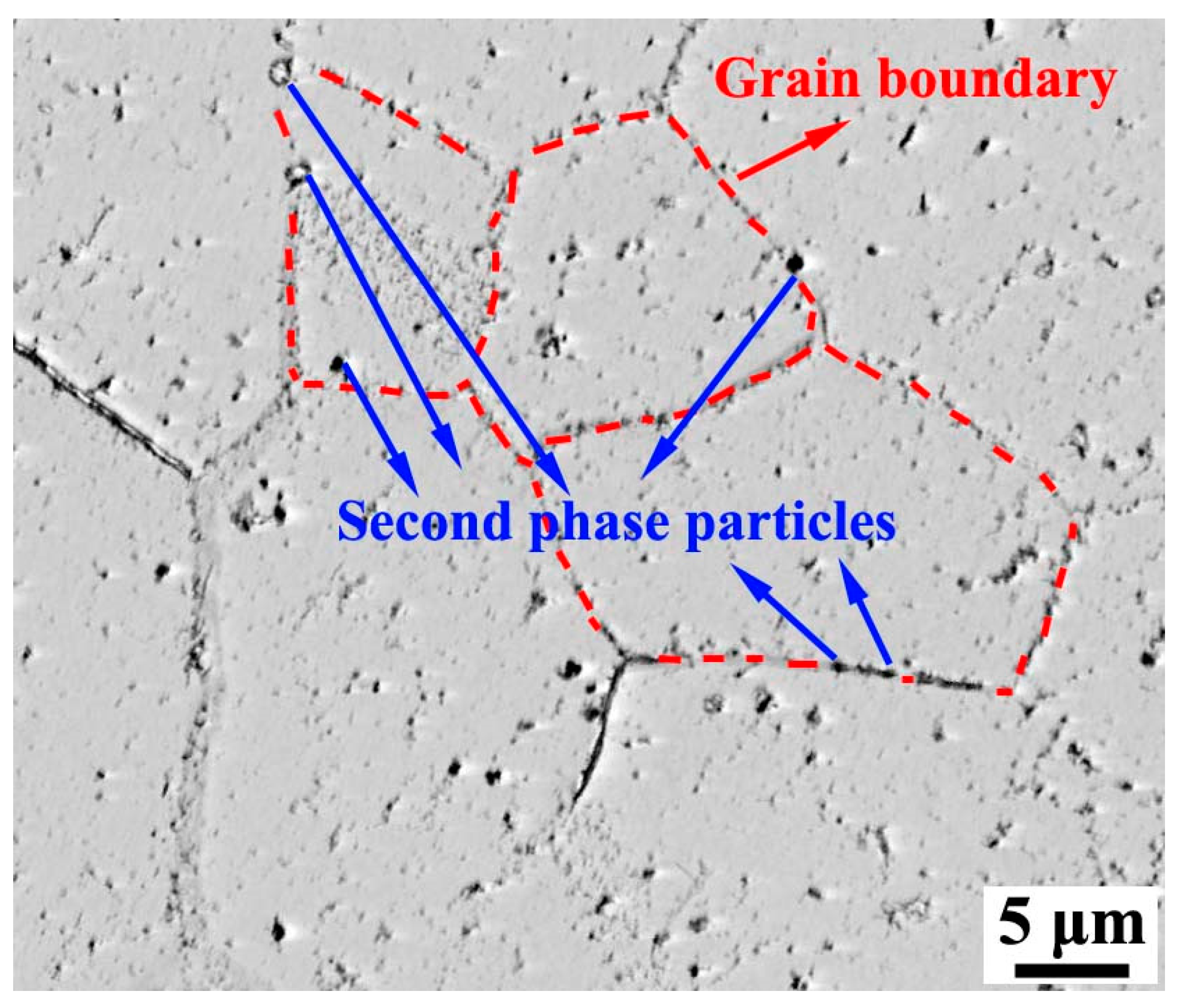
3.1. Characterization of Precipitates in Steels
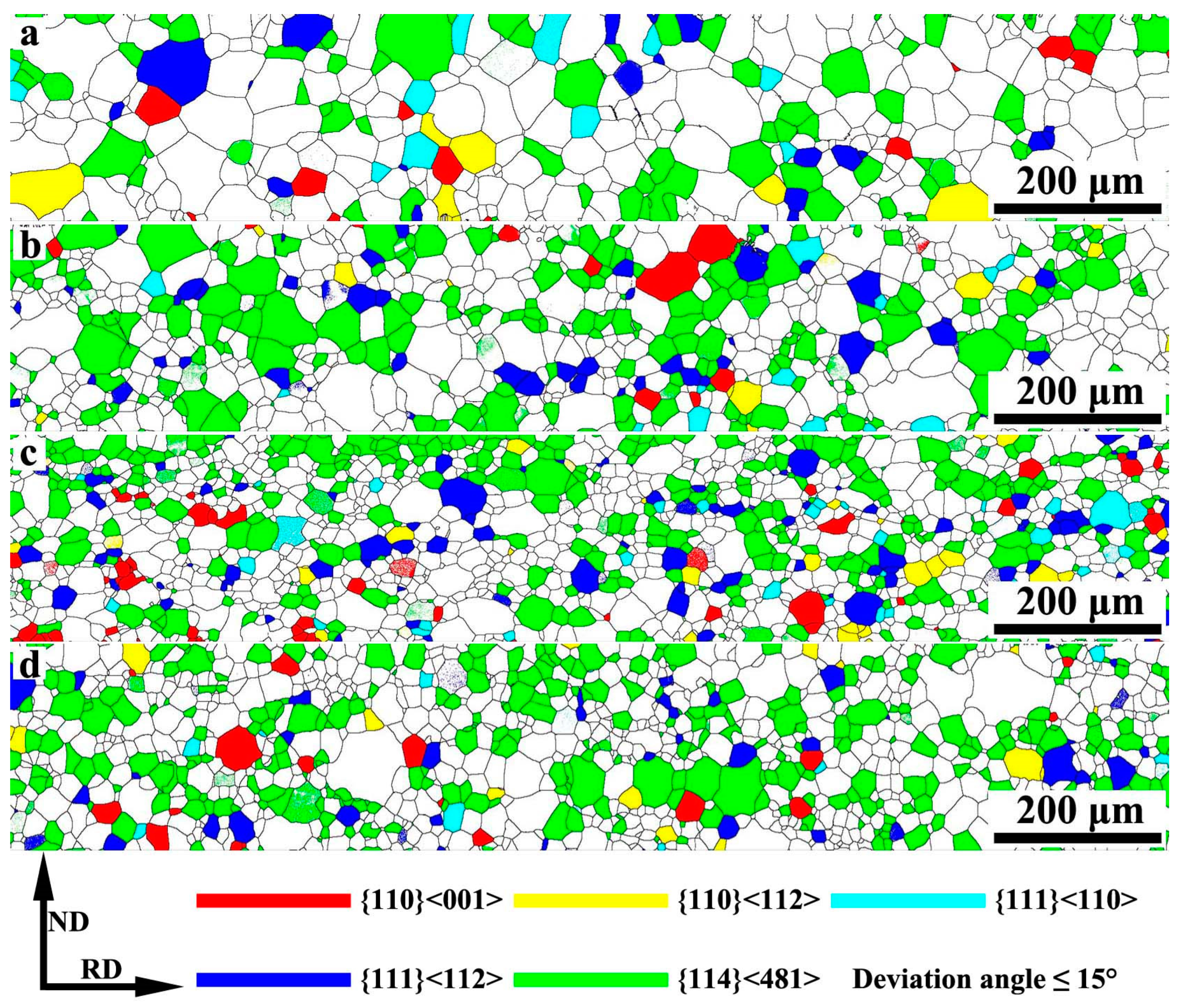
3.2. Effect of Nb on Microstructure of Primary Recrystallized Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel
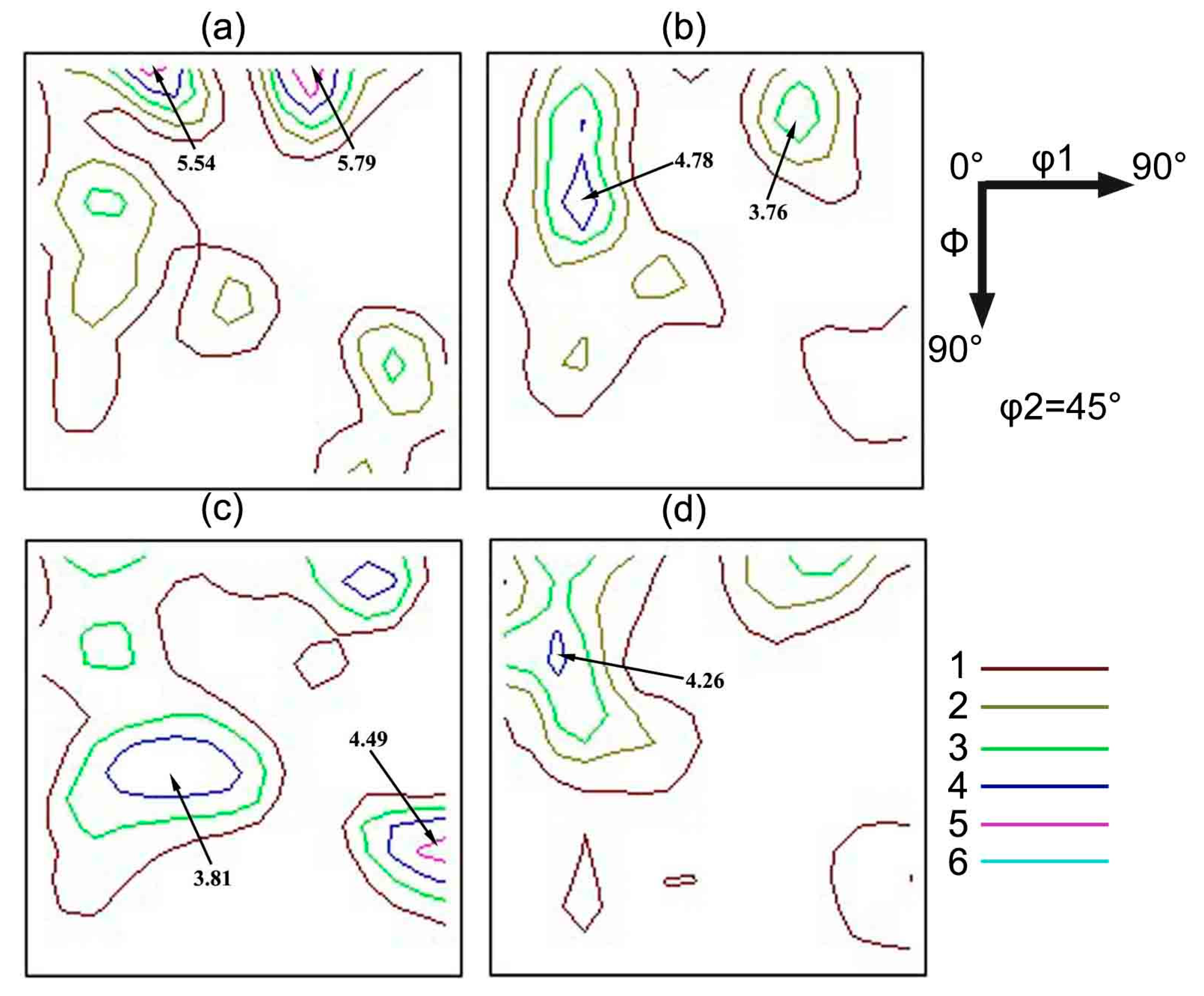
3.3. Effect of Nb on Texture of Primary Recrystallized Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel
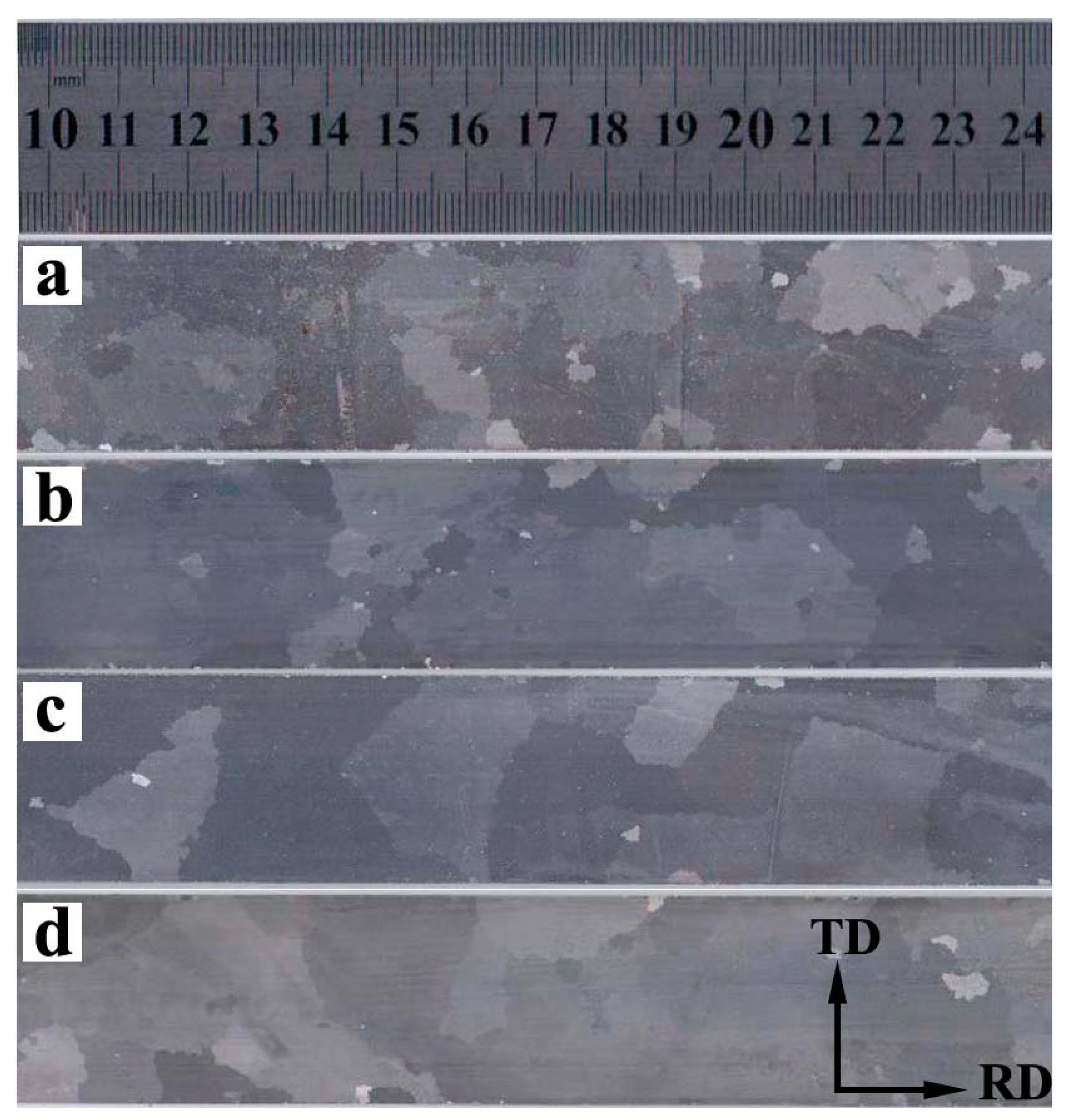
3.4. Effect of Nb on Macrostructure and Magnetic Properties of Secondary Annealed Sheet
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The precipitates can be refined by niobium addition, and the finest and the most dispersed precipitates were obtained in steel with 0.009 wt% Nb addition.
- (2)
- The finest primary recrystallized microstructure is obtained in steel with 0.009 wt% Nb due to the strongest pinning force, and the primary recrystallized microstructure changes little when the Nb content is higher than 0.009 wt%.
- (3)
- Adding niobium is beneficial to obtain large volume fraction favorable texture for grain-oriented silicon steel, and the effect of Nb addition is not obvious when the content is higher than 0.009 wt%.
- (4)
- After final annealing, a macrostructure consisting of entirely large grains is obtained in steel with 0.009 wt% Nb, the magnetic induction B800 and core loss P1.7/50 are 1.872 T and 1.25 W/kg, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goss, N.P. New development in electrical strip steels characterized by fine grain structure approaching the properties of a single crystal. Trans. Am. Soc. Met. 1935, 23, 511–531. [Google Scholar]
- Dorothée, D.; Stefan, Z.; Ludger, L.; Dierk, R. Overview of Microstructure and Microtexture Development in Grain-oriented Silicon Steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M. Texture control in the production of grain oriented silicon steels. ISIJ Int. 1989, 29, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Zhang, H.; Shan, N.; Sha, Y.H.; Zhang, F.; Zuo, L. Improvement of Texture and Magnetic Properties in 4.5 wt.% Si Grain-Oriented Electrical Steels. Mater. Res Lbero Am. J. 2019, 22, e20180756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Texture and microstructure evolution during different rolling methods in strip-cast grain-oriented 6.5% Si steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; He, Y.; Jiao, H.; Li, J. Influence of hot rolling reduction rate on the microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of a strip-cast Fe-6.5 wt.% Si grain-oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 494, 165755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Y.; He, C.X.; Meng, L.; Ma, G.; Chen, X.; Mao, W.M. Effect of annealing atmosphere on secondary recrystallization in thin-gauge grain-oriented silicon steel: Evolution of inhibitors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiuhua, G.; Kemin, Q.; Chunlin, Q. Magnetic properties of grain oriented ultra-thin silicon steel sheets processed by conventional rolling and cross shear rolling. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2006, 430, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, T.D.; Lavernia, E.J.; Lee, Z.H. Ordering-disordering phenomena and micro-hardness characteristics of B2 phase in Fe-(5–6.5%) Si alloys. Mat. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2005, 407, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Woo, J.S.; Chang, S.K. Influence of annealing before cold rolling on the evolution of sharp Goss texture in Fe-3%Si alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 215–216, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Fujikura, M.; Ushigami, Y. Recent progress and future trend on grain-oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2000, 215–216, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Takamiya, T.; Kan, T. Control of inhibitor precipitation for producing grain-oriented silicon steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1993, 2, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Shimazu, T.; Chikuma, K.; Tanino, M.; Matsuo, M. Improvement of magnetic properties by Cu addition in grain-oriented silicon steel. Tetsu-to-Hagane 1984, 70, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Butler, J.; Melzer, S. Effect of asymmetric hot rolling on texture, microstructure and magnetic properties in a non-grain oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 368, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, M.; Ashcroft, I.; Simonelli, M.; Hague, R. Metallurgy of high-silicon steel parts produced using Selective Laser Melting. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Ning, J. Effect of Nb on solution and precipitation of inhibitors in grain-oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Du, T. Effect of slab reheating temperature on recrystallization microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of Nb-containing grain-oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 439, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulka, K.; Vlad, C.; Doniga, A. The role of niobium as microalloying element in electrical sheet. Steel Res. Int. 2002, 73, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Lan, M.F.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Cao, G.M.; Xu, Y.B.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.D. The impact of niobium on the microstructure, texture and magnetic properties of strip-cast grain oriented silicon steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 442, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B. The effect of Nb content on precipitates, microstructure and texture of grain oriented silicon steel. High. Temp. Mat. Process. 2019, 38, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.; Lindenmo, M. Precipitates in electrical steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2423–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillert, M. On the theory of normal and abnormal grain growth. Acta Mater. 1965, 13, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, F.J. A unified theory of recovery, recrystallization and grain growth, based on the stability and growth of cellular microstructures—I. The basic model. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Yao, S.J.; Sun, Y.; Gao, F.; Song, H.Y.; Liu, G.H.; Li, L.; Geng, D.Q.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.D. Evolution of microstructure, texture and inhibitor along the processing route for grain-oriented electrical steels using strip casting. Mater. Charact. 2015, 106, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Cao, G.; Yuan, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Misra, R.D.K. Inhibitor induced secondary recrystallization in thin-gauge grain oriented silicon steel with high permeability. Mater. Des. 2016, 105, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.C.; Pei, W.; Sha, Y.H.; Zuo, L. Effect of magnetic annealing on recrystallization texture and microstructure of non-oriented silicon steel. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 28, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Urabe, T.; Jonas, J.J. Modeling Texture Change during the Recrystallization of an IF Steel. ISIJ Int. 1994, 34, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Qian, H.; Yang, P.; Mao, W.; Jian, Q.; Jin, W. Analysis of Micro-texture during Secondary Recrystallization in a Hi-B Electrical Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, H.; Hutchinson, B. Orientation dependence of secondary recrystallisation in silicon–iron. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
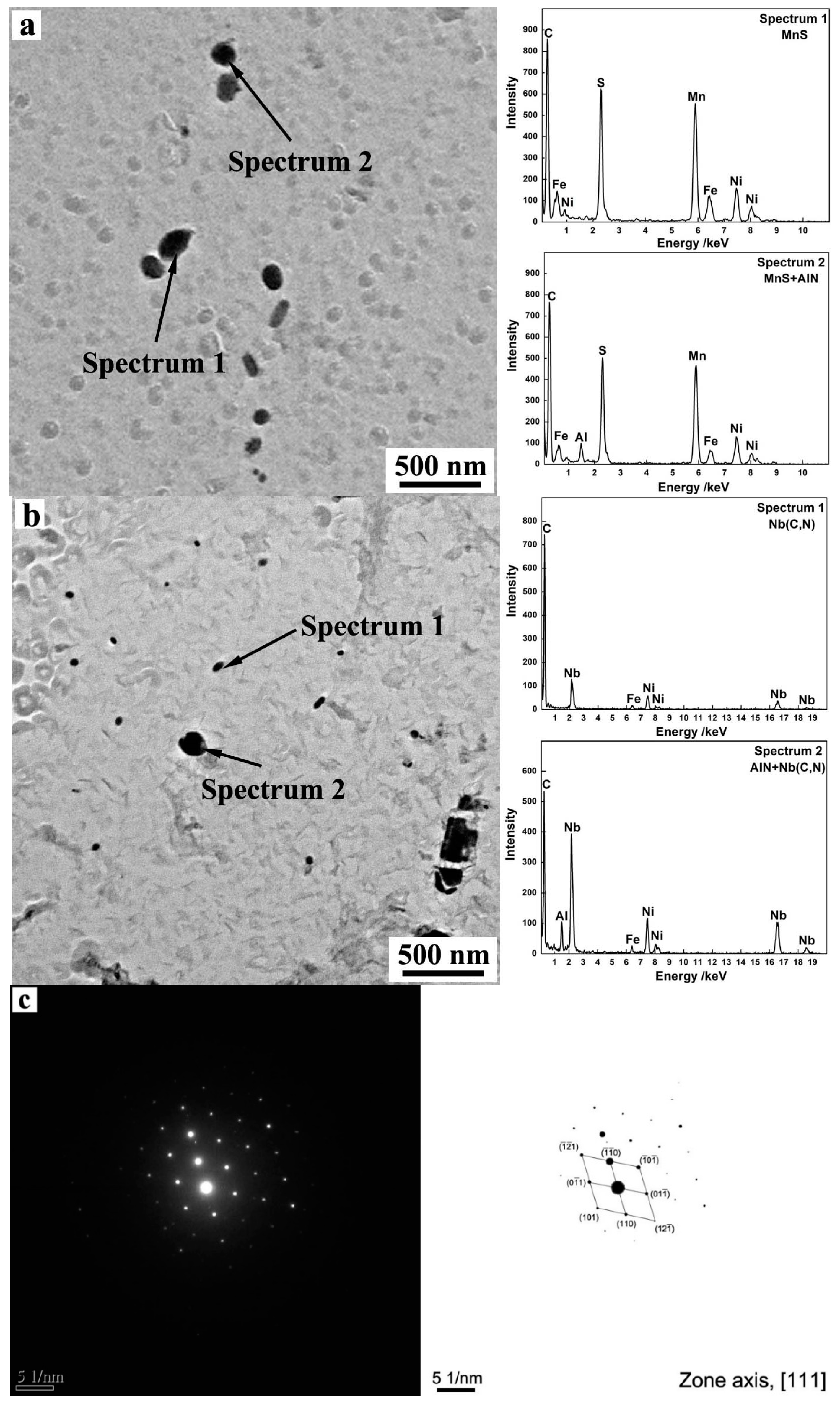
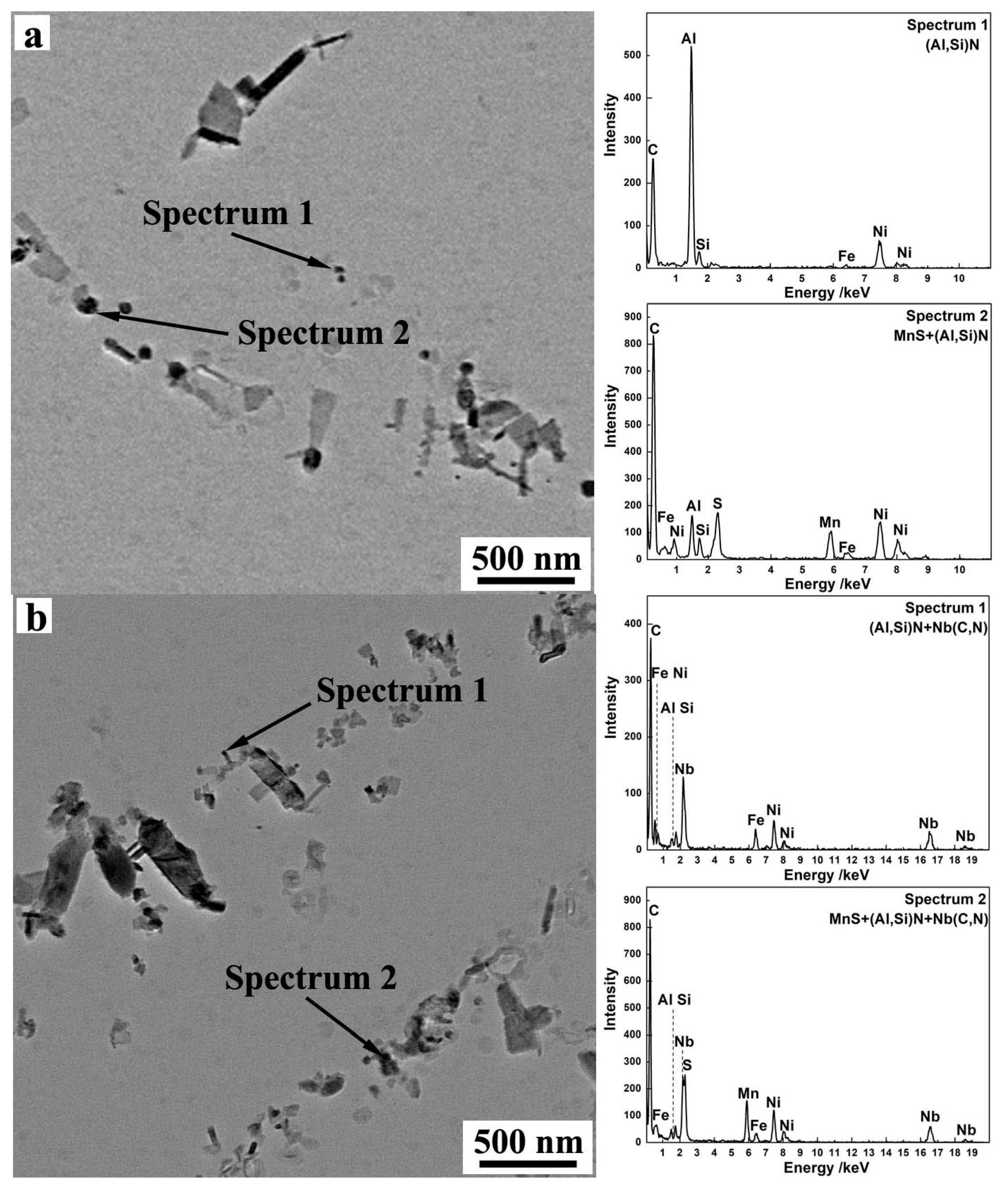
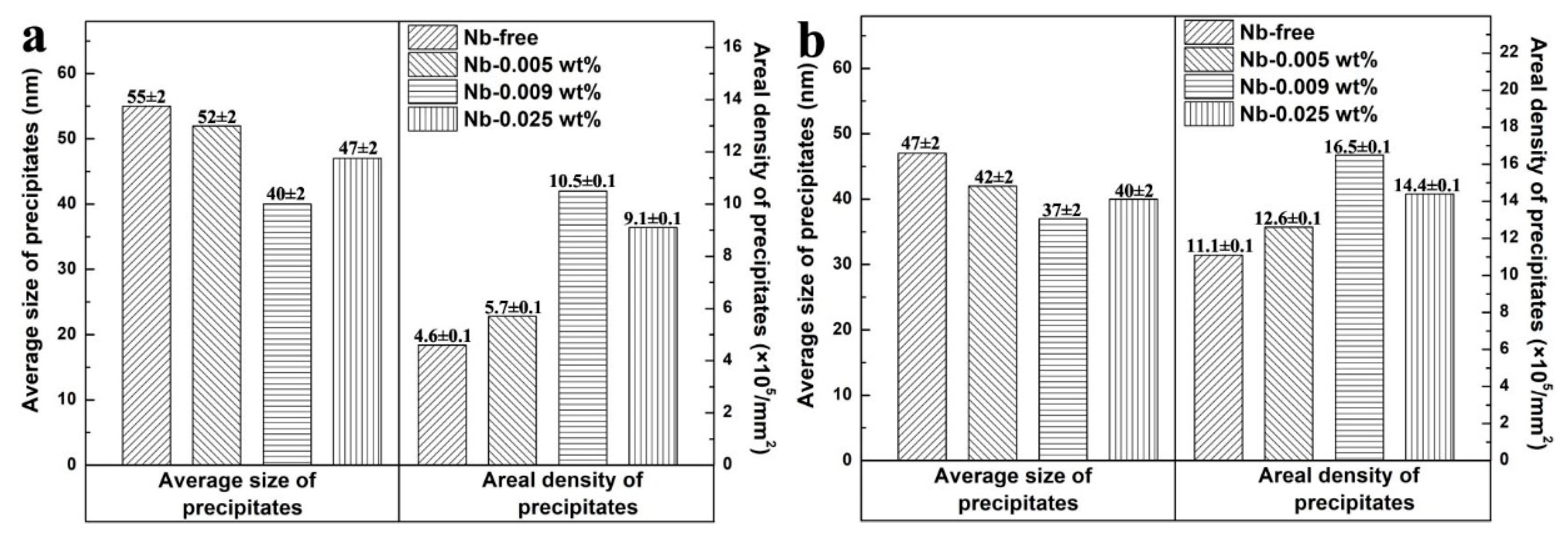
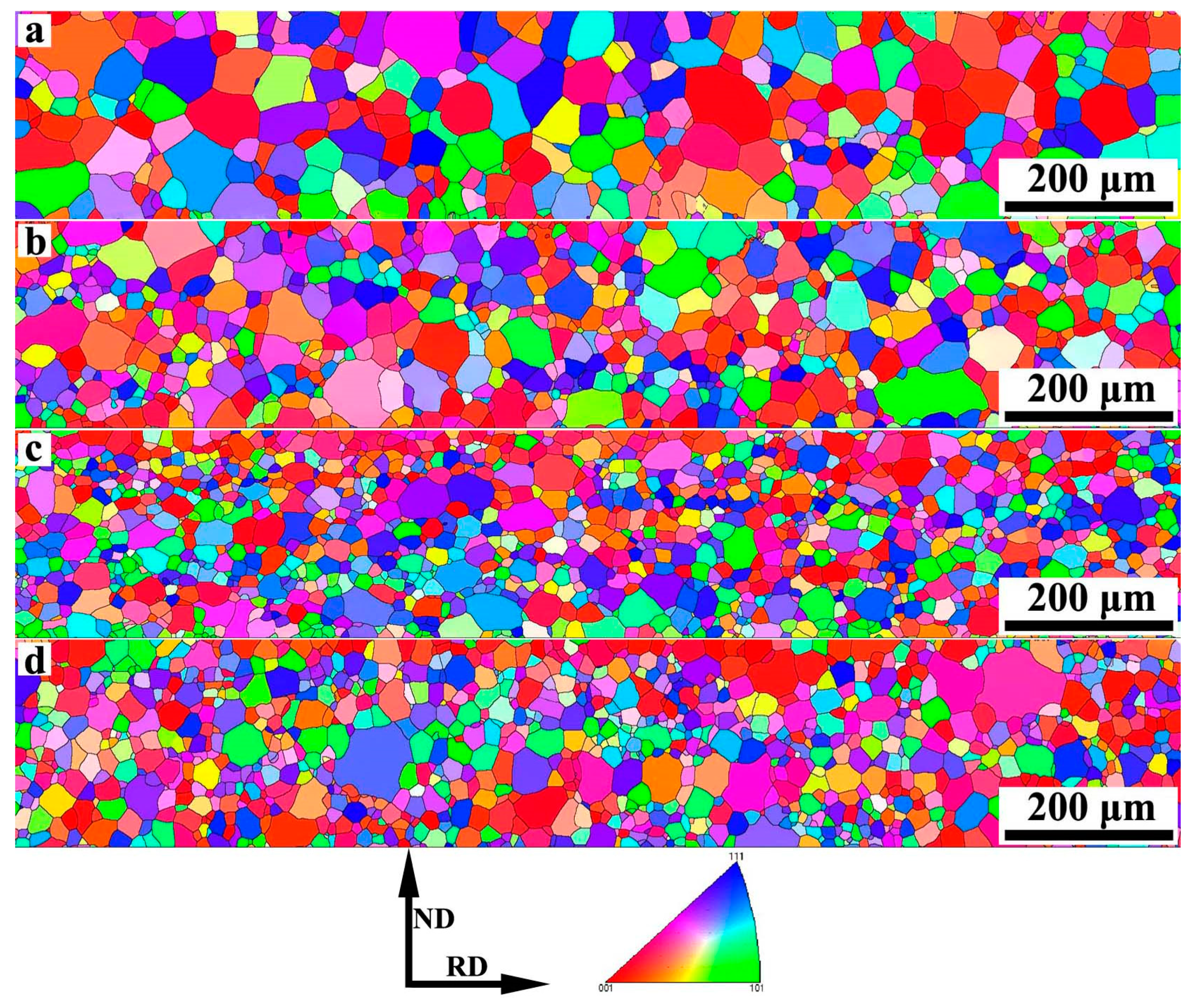

| Sample | C | Si | Mn | S | Als | Nb | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.056 | 3.14 | 0.110 | 0.0068 | 0.024 | - | 0.0076 | Balance |
| S2 | 0.056 | 3.11 | 0.092 | 0.0064 | 0.026 | 0.0050 | 0.0083 | Balance |
| S3 | 0.057 | 3.13 | 0.091 | 0.0079 | 0.025 | 0.0090 | 0.0082 | Balance |
| S4 | 0.060 | 3.23 | 0.110 | 0.0064 | 0.026 | 0.0250 | 0.0075 | Balance |
| Main Textures | Volume Fraction in Different Specimens, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | |
| {110}<001> | 1.94 | 2.39 | 3.24 | 2.46 |
| {110}<112> | 3.39 | 2.44 | 2.06 | 1.55 |
| {111}<110> | 2.85 | 2.36 | 2.21 | 1.41 |
| {111}<112> | 4.00 | 5.16 | 6.61 | 3.88 |
| {114}<481> | 16.5 | 19.8 | 23.7 | 27.7 |
| Sample | Magnetic Induction B800 (T) | Core Loss P1.7/50 (W/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1.715 ± 0.003 | 1.68 ± 0.01 |
| S2 | 1.806 ± 0.003 | 1.39 ± 0.01 |
| S3 | 1.872 ± 0.003 | 1.25 ± 0.01 |
| S4 | 1.834 ± 0.003 | 1.34 ± 0.01 |
| C-GOES [19] | 1.84 | 1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Influence of Nb Content on Precipitation, Grain Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel. Materials 2020, 13, 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235581
Wang Y, Zhu C, Li G, Liu Y, Liu Y. Influence of Nb Content on Precipitation, Grain Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel. Materials. 2020; 13(23):5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235581
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yong, Chengyi Zhu, Guangqiang Li, Yulong Liu, and Yu Liu. 2020. "Influence of Nb Content on Precipitation, Grain Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel" Materials 13, no. 23: 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235581
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhu, C., Li, G., Liu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2020). Influence of Nb Content on Precipitation, Grain Microstructure, Texture and Magnetic Properties of Grain-Oriented Silicon Steel. Materials, 13(23), 5581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235581





