3D-Printable Carbon Nanotubes-Based Composite for Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
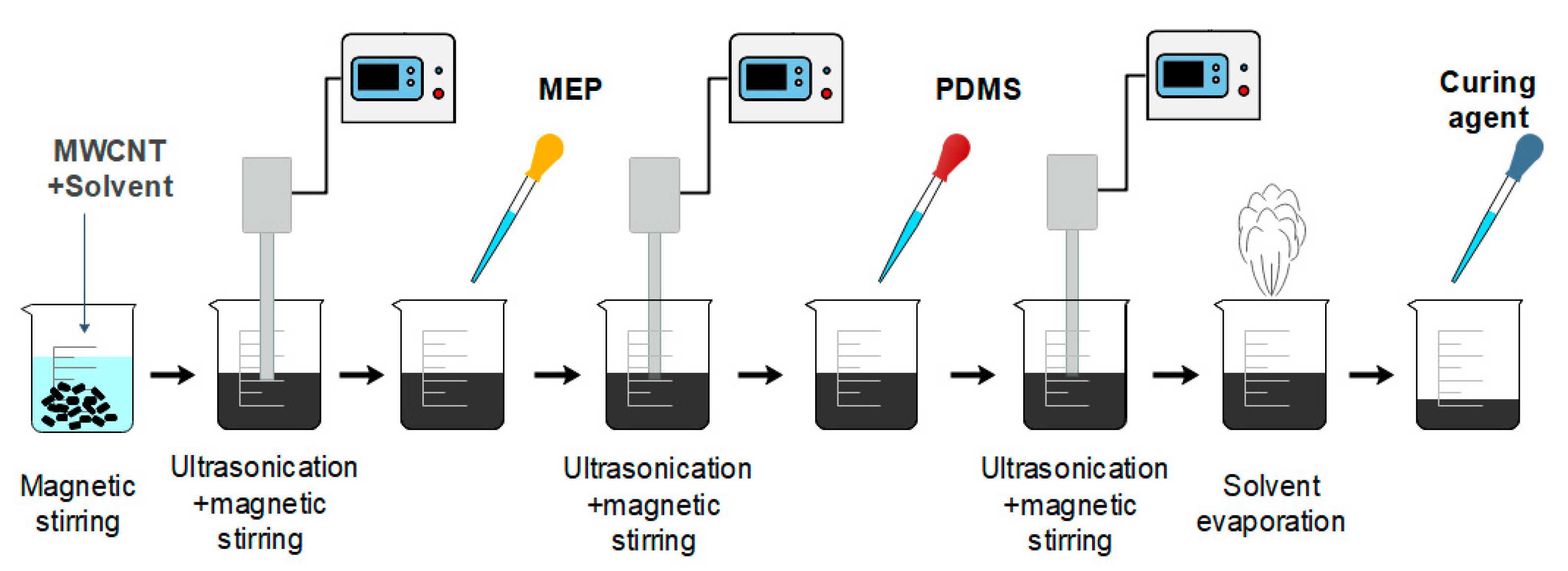
2.1. Materials Formulation
2.2. Sensor Fabrication
2.2.1. Direct Ink Writing Process
2.2.2. Sensor Fabrication
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Sensor Performance
3.3. Sensitivity
3.4. Hysteresis Error
3.5. Linearity Error
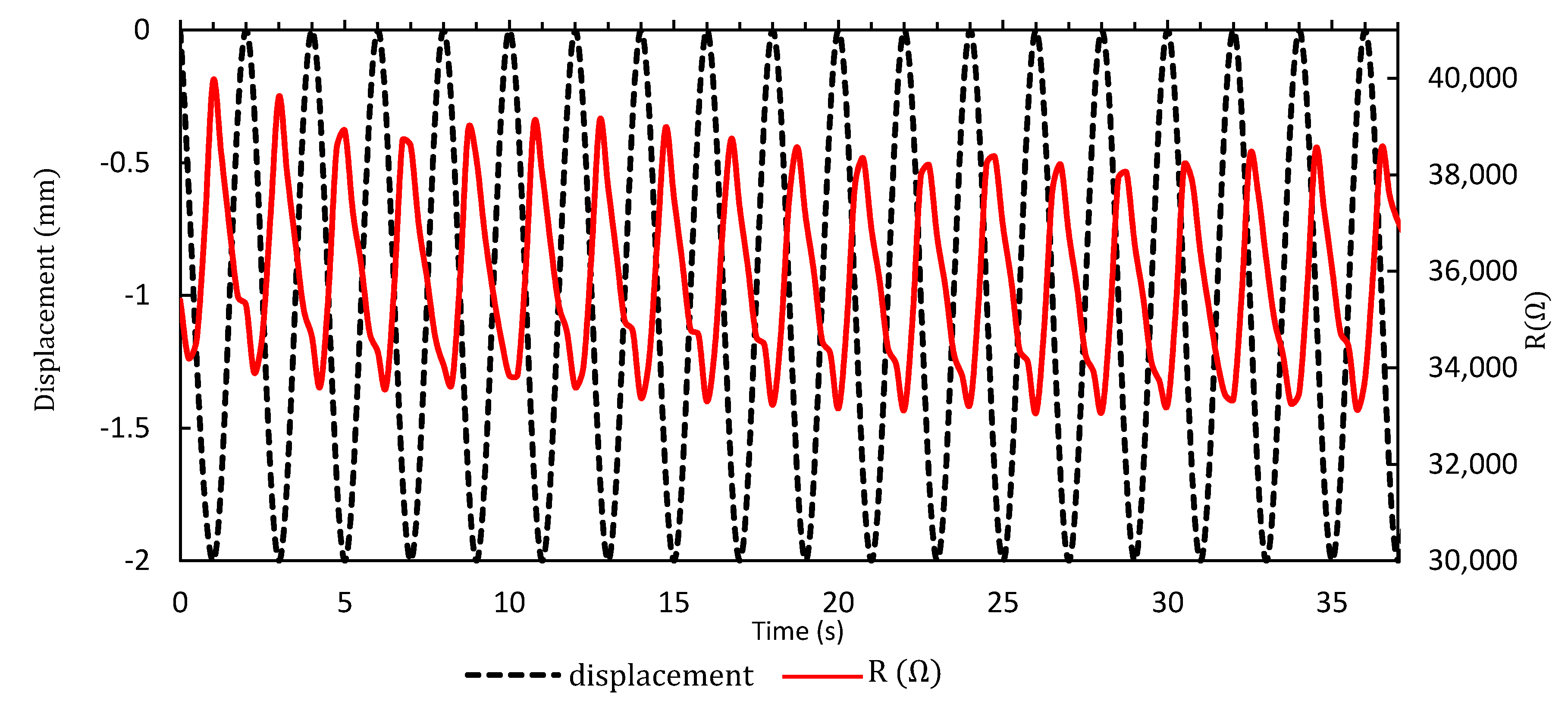
3.6. Dynamic Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, Z. Printed Electronics: Materials, Technologies and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Singapore Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 978-1-118-92095-4. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, T. T(trillion) Sensors Summit for Trillion Sensor Roadmap in Munich; European Photonics Industry Consortium: Munich, Germany, 2014; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Printing Conductive Nanomaterials for Flexible and Stretchable Electronics: A Review of Materials, Processes, and Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Wei, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Fan, P.; Xu, X.; Xie, B. Printing Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Silicone Elastomers via Direct Writing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44796–44802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Magdassi, S. Conductive Nanomaterials for Printed Electronics. Small 2014, 10, 3515–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Novel method for printing high-quality metal wires. SPIE Newsroom 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, W.J.; Secor, E.B.; Rojas, G.A.; Hersam, M.C.; Francis, L.F.; Frisbie, C.D. All-Printed, Foldable Organic Thin-Film Transistors on Glassine Paper. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7058–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, S.D.; Sabolsky, K.; Sabolsky, E.M.; Sierros, K.A. Dip pen nanolithography and transfer of ZnO patterns on plastics for large-area flexible optoelectronic applications. Thin Solid Films 2014, 552, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsoom, U.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Paull, B. Recent developments in 3D printable composite materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60355–60371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Yeo, W.-H. Advanced Nanomaterials, Printing Processes, and Applications for Flexible Hybrid Electronics. Materials 2020, 13, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, D.; Jiang, W.; Gu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z. 3D Printable Graphene Composite. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.J.; Bradley, R.J.; Purssell, C.P.; Billson, D.R.; Hutchins, D.A. A Simple, Low-Cost Conductive Composite Material for 3D Printing of Electronic Sensors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Azumi, R. Carbon nanotube based transparent conductive films: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.C.; Spina, F.; Lugoda, P.; Garcia-Garcia, L.; Roggen, D.; Münzenrieder, N. Flexible Sensors—From Materials to Applications. Technologies 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Dang, W.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R. Printing of high concentration nanocomposites (MWNTs/PDMS) using 3D-printed shadow masks. In Proceedings of the 2015 XVIII AISEM Annual Conference; IEEE: Trento, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rim, Y.S.; Bae, S.-H.; Chen, H.; De Marco, N.; Yang, Y. Recent Progress in Materials and Devices toward Printable and Flexible Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4415–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abshirini, M.; Charara, M.; Marashizadeh, P.; Saha, M.C.; Altan, M.C.; Liu, Y. Functional nanocomposites for 3D printing of stretchable and wearable sensors. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abshirini, M.; Charara, M.; Liu, Y.; Saha, M.; Altan, M.C. 3D Printing of Highly Stretchable Strain Sensors Based on Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1800425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emon, M.O.F.; Alkadi, F.; Philip, D.G.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, K.-C.; Choi, J.-W. Multi-material 3D printing of a soft pressure sensor. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 28, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Feng, S.; Nag, A.; Afsarimanesh, N.; Han, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Recent Progress in 3D Printed Mold-Based Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Tian, X.; Luo, Z.; Qiao, F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J. Review of Printed Electrodes for Flexible Devices. Front. Mater. 2019, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Huang, N.; Xu, F.; Tong, J.; Chen, Z.; Gui, X.; Fu, Y.; Lao, C. 3D Printing Technologies for Flexible Tactile Sensors toward Wearable Electronics and Electronic Skin. Polymers 2018, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.-Z.; Qiu, K.; Meng, F.; Park, S.H.; McAlpine, M.C. 3D Printed Stretchable Tactile Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Engeberg, E.D.; Choi, J.-W. Force and slip detection with direct-write compliant tactile sensors using multi-walled carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 195, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Lu, Y.; Engeberg, E.D.; Choi, J.-W. Combined 3D Printing Technologies and Material for Fabrication of Tactile Sensors. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.K.B.; Li, L.; Hutchings, I.M. Direct writing technology—Advances and developments. CIRP Ann. 2008, 57, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.S.; Wang, Y. 3D printing of conjugated polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2019, 57, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekiri, C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, I.H. Improved resistance stability for tactile sensor fabrication and investigation of the dispensing parameters of a nanocomposite material. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 5631–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Tinku, S.; Lorenzelli, L.; Dahiya, R.S. Flexible Tactile Sensors Using Screen-Printed P(VDF-TrFE) and MWCNT/PDMS Composites. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Hu, X.; Lim, H.; Kim, C. Remote tactile sensing system integrated with magnetic synapse. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Lee, K.-F.; Lee, M.-Y. A flexible PDMS capacitive tactile sensor with adjustable measurement range for plantar pressure measurement. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, C.; Gupta, D. Large area flexible pressure/strain sensors and arrays using nanomaterials and printing techniques. Nano Converg. 2019, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingame, R.; Chandraker, P.; Kanoun, O. Investigation on the Influence of Solvents on MWCNT- PDMS Nanocomposite Pressure Sensitive Films. Proceedings 2017, 1, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Hwang, H.R.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, J.-W.; Shin, U.S.; Lee, S.-H. Simple and cost-effective method of highly conductive and elastic carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane composite for wearable electronics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingame, R.; Rajendran, D.; Lakshmanan, A.; Kanoun, O. Effect of Organic Solvent on MWCNT-PDMS Nanocomposite Based Capacitive Pressure Sensors. In Proceedings of the 15th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Hammamet, Tunisia, 19–22 March 2018; IEEE Tunisia Section: Sfax, Tunisia, 2018; pp. 1208–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Alamusi; Hu, N.; Fukunaga, H.; Atobe, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Piezoresistive Strain Sensors Made from Carbon Nanotubes Based Polymer Nanocomposites. Sensors 2011, 11, 10691–10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, L.; Wagner, H.D.; Marom, G. The role of surfactants in dispersion of carbon nanotubes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128–130, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Chen, G.H.; Lu, L. Piezoresistive Behavior Study on Finger-Sensing Silicone Rubber/Graphite Nanosheet Nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassi, S.; Cauda, V.; Canavese, G.; Pirri, C.F. Flexible Tactile Sensing Based on Piezoresistive Composites: A Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 5296–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraden, J. Handbook of Modern Sensors; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4419-6465-6. [Google Scholar]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fekiri, C.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, I.H. 3D-Printable Carbon Nanotubes-Based Composite for Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors. Materials 2020, 13, 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235482
Fekiri C, Kim HC, Lee IH. 3D-Printable Carbon Nanotubes-Based Composite for Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors. Materials. 2020; 13(23):5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235482
Chicago/Turabian StyleFekiri, Chaima, Ho Chan Kim, and In Hwan Lee. 2020. "3D-Printable Carbon Nanotubes-Based Composite for Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors" Materials 13, no. 23: 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235482
APA StyleFekiri, C., Kim, H. C., & Lee, I. H. (2020). 3D-Printable Carbon Nanotubes-Based Composite for Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors. Materials, 13(23), 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13235482





