Alloy Design, Thermodynamics, and Electron Microscopy of Ternary Ti-Ag-Nb Alloy with Liquid Phase Separation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Alloy Design
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
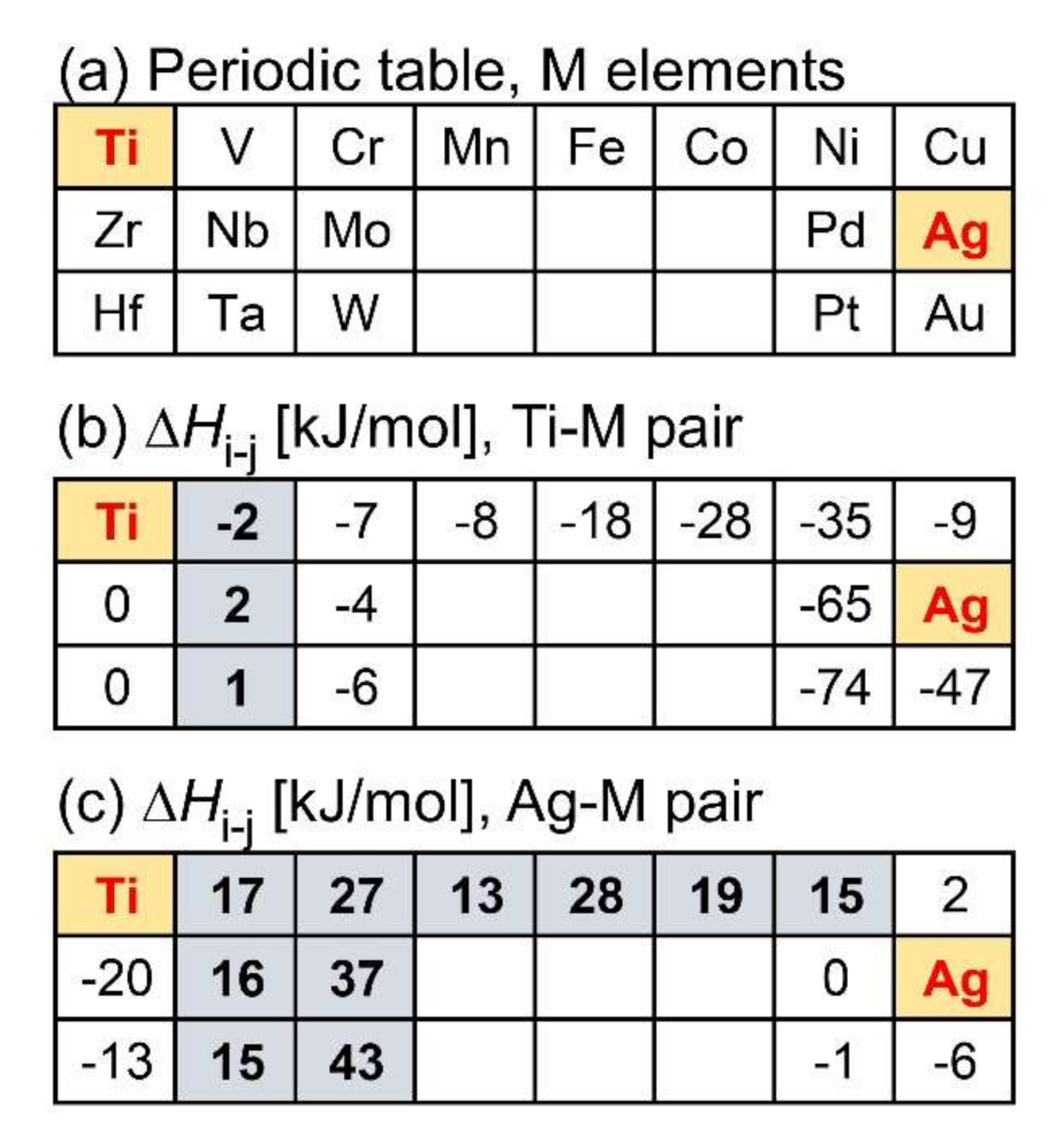
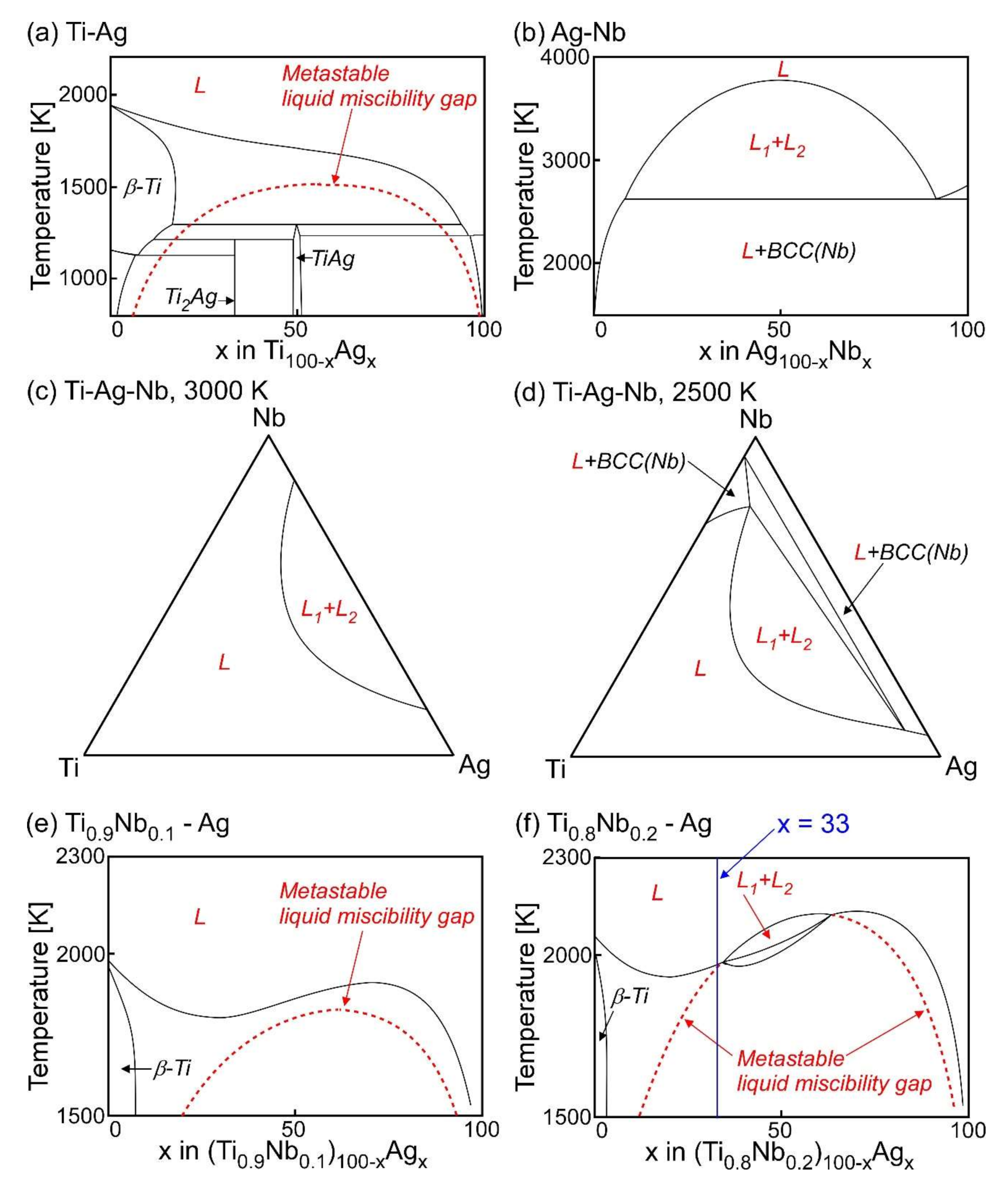
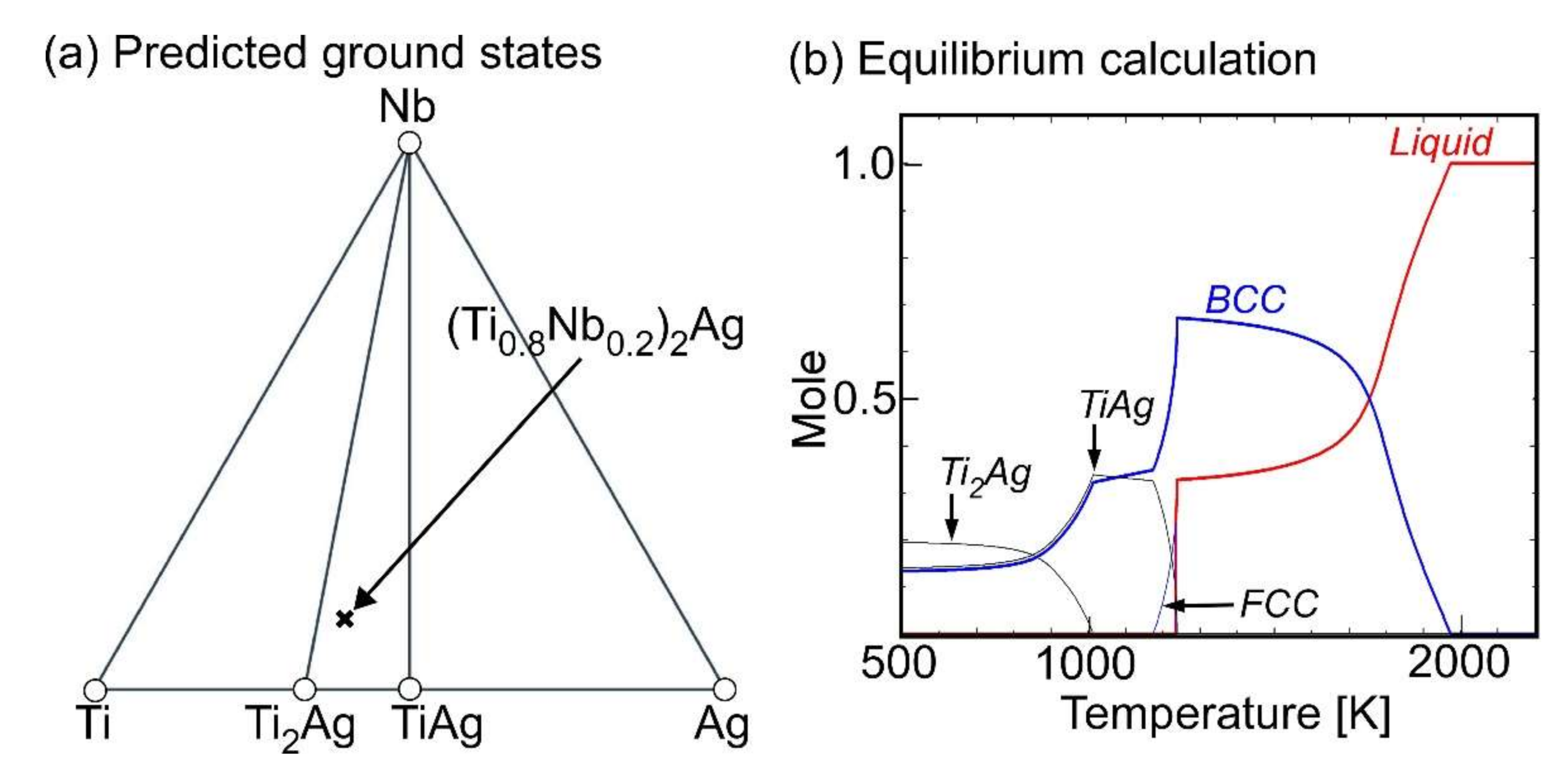
- Ternary Ti–Ag-based alloys with LPS was discussed based on the mixing enthalpy of the constituent elements, thermodynamic calculation, and predicted phase diagrams constructed by the Materials Project.
- (2)
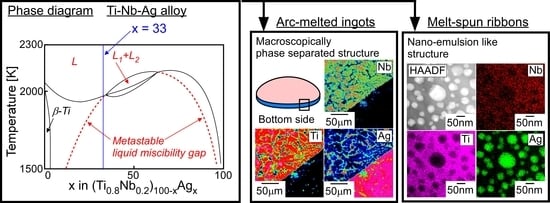
- LPS was experimentally found in the ternary Ti–Ag-Nb alloy of Ti53.4Ag33.3Nb13.3.
- (3)
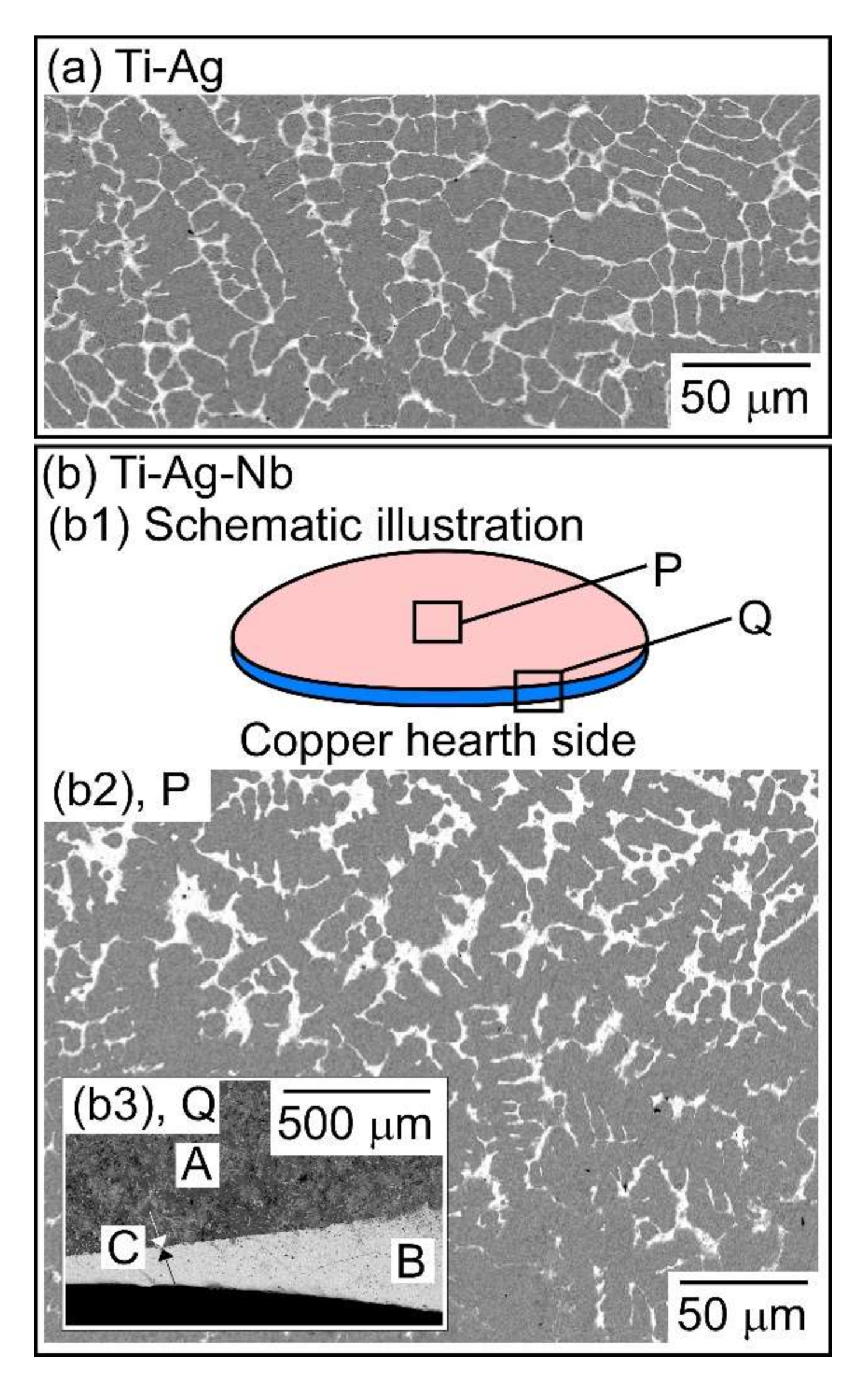
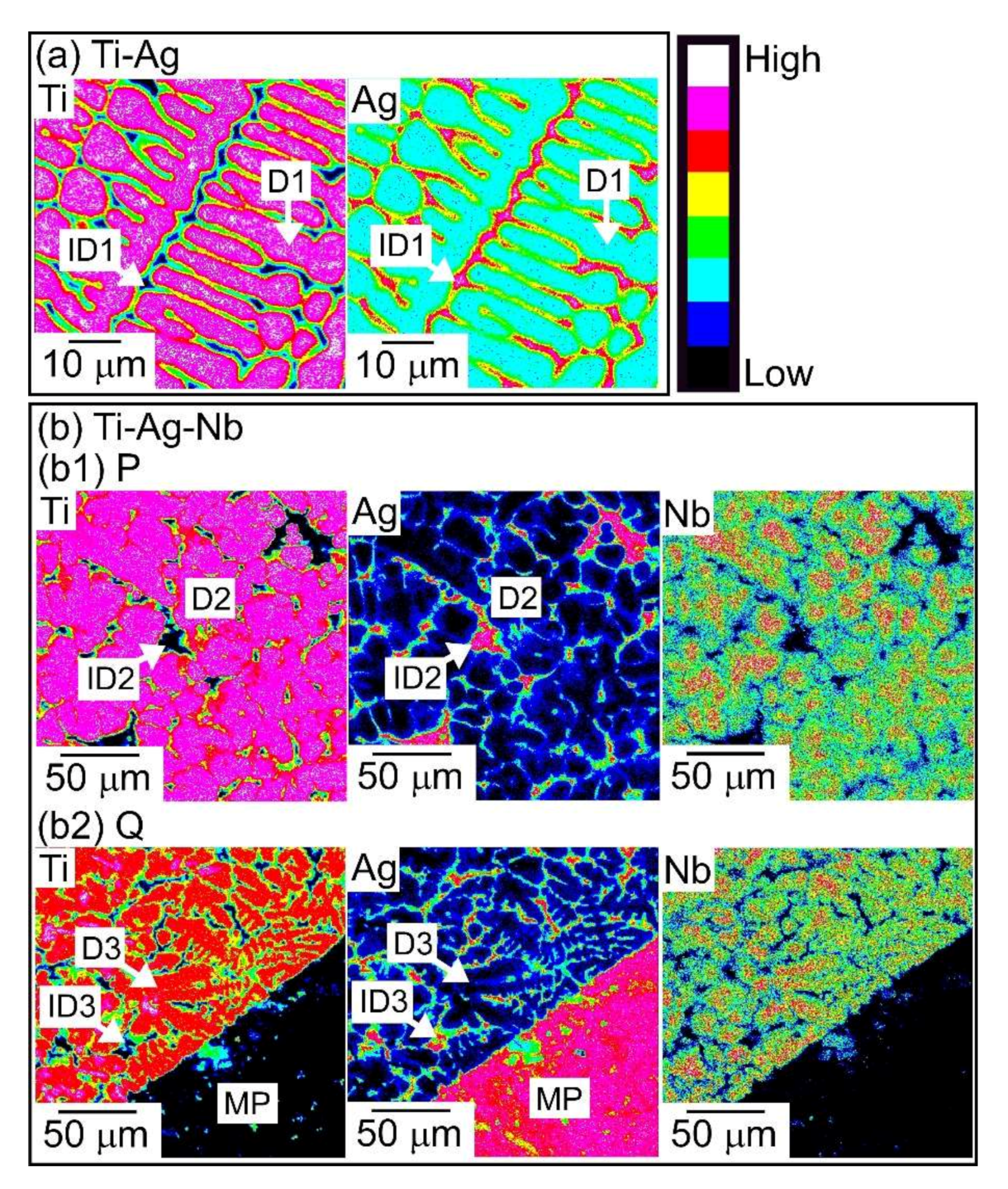
- A macroscopically phase-separated structure was observed in the arc-melted ingots, where the cooling rate of arc-melting was approximately 2000 K/s. The macroscopically phase-separated structure Ag-rich phase existed in the copper hearth contacted region in the arc-melted ingots. In the central region of the ingots, an equiaxis dendrite structure composed of a Ti-rich dendrite and Ag-rich interdendrite was observed.
- (4)
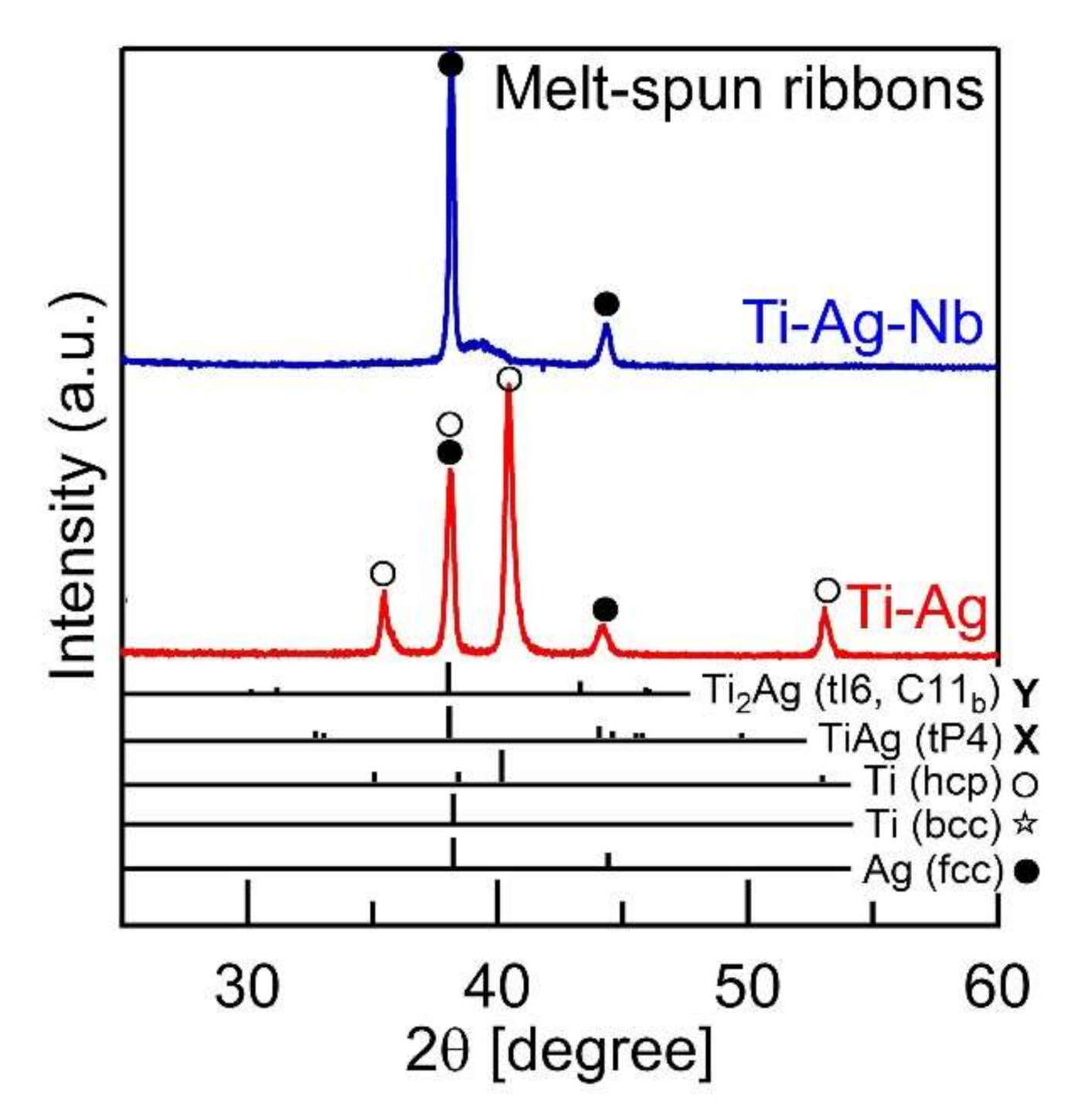
- A composite of fine Ag globules and Ti–Nb-based alloy matrix was obtained in rapidly solidified melt-spun ribbons in the Ti53.4Ag33.3Nb13.3 alloy. Super-cooling of the thermal melt leads to LPS and the suppression of the aggregation of Ag-rich liquid globules, resulting in the formation of a particular microstructure comprising 100 nm order Ag globules and Ti alloy matrix.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sastry, S.M.L.; Peng, T.C.; Beckerman, L.P. Structure and properties of rapidly solidified dispersion strengthened titanium alloys: Part II. tensile and creep properties. Metall. Trans. A 1984, 15, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, S.H. Review—Rapidly solidified titanium alloys for high-temperature applications. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 24, 2224–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, S.A.; Sears, J.W.; Loretto, M.H.; Fraser, H.L. The Effect of Liquid Phase Separation on the Microstructure of Rapidly Solidified Titanium-Rare Earth Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1988, 98, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Froes, F.H.; Rowe, R.G. Rapid solidification processing of titanium alloys. Inter. Mater. Rev. 1991, 36, 85–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, M.F.X.; Woodfield, A.P. The Roles of Rare Earth Dispersoids and Process Route on the Low Cycle Fatigue Behavior of a Rapidly Solidified Powder Metallurgy Titanium Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1993, 24, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, M.V.; Hofmeister, W.H.; Witting, J.E. Interphase Boundary Precipitation in a Ti-1.7 At. Pct Er Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Close, C.M.; Partridge, P.G. The production of titanium-magnesium alloys by vapour quenching. Mater. Lett. 1991, 11, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Close, C.M.; Lu, G.; Partridge, P.G. Microstructure of vapour-quenched Ti-Mg alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 189, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujii, Y. Microstructure of Ti-Ag immiscible alloys with metastable liquid phase separation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 738, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujii, Y. Microstructure of Ti-Nb-Ag immiscible alloys with liquid phase separation. Microscopy 2017, 66 (Suppl. S1), i22. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Ti-Y, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 3497–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, La-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 2432–2434. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Ce-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 1118–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Pr-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 3105–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Nd-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 2817–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Gd-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 1935–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Dy-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; p. 1568. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Ti-Yb, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; p. 3499. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Mg-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 2559–2560. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Calculations of Mixing Enthalpy and Mismatch Entropy for Ternary Amorphous Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2000, 41, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W. Experimental study and thermodynamic assessment of the Ag-Ti system. Calphad 2005, 29, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Ag-Ti. In Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Okuno, O.; Okabe, T. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Binary Titanium Alloys with Beta-stabilizing Elements. Dent. Mater. J. 2001, 20, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Takada, Y.; Okuno, O. Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of Dental Cast Ti-Ag and Ti-Cu Alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2002, 21, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Okabe, T.; Okuno, O. Grindability of Dental Cast Ti-Ag and Ti-Cu Alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2003, 22, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.-T.; Shim, H.-M.; Kim, K.-N. Properties of titanium-silver alloys for dental application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 74, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Okuno, O. Machinability of Experimental Ti-Ag Alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2008, 27, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.B.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, Y. Effect of Ag on the corrosion behavior of Ti-Ag alloys in artificial saliva solutions. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Takada, Y.; Okuno, O. Corrosion Resistance of Dental Ti-Ag Alloys in NaCl Solution. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.B.; Qiu, K.J.; Wang, B.L.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Surface Characterization and Cell Response of Binary Ti-Ag Alloys with CP Ti as Material Control. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Takada, Y. Mechanical properties of dental Ti-Ag alloys with 22.5, 25, 27.5, and 30 mass% Ag. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.-K.; Hwang, M.-J.; Won, D.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Song, H.-J.; Park, Y.-J. Massive Transformation in Titanium-Silver Alloys and Its Effect on Their Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior. Materials 2014, 7, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Takada, Y.; Okuno, O.; Sasaki, K.; Takahashi, N. Inhibitory effect of Ti-Ag alloy on artificial biofilm formation. Dent. Mater. J. 2014, 33, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tian, A.; You, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Bai, X.; Lei, Z.; Shi, X.; Xue, X.; Wang, H. Antibacterial abilities and biocompatibilities of Ti-Ag alloys with nanotubular coatings. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5743–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Tsoi, J.K.H.; Matinlinna, J.P. Binary titanium alloys as dental implant materials-a review. Regen. Biomater. 2017, 4, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, E.; You, J.; Ma, X.; Bai, X. Antibacterial activities and biocompatibilities of Ti-Ag alloys prepared by spark plasma sintering and acid etching. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawy, W.A.; Al-Hassani, E.S. Effect of Ag Addition on Cp-Ti Dental Implant; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2190, p. 020017. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, A.; Zhu, C.; Fu, S.; Wang, R.; Qin, G.; Chen, D.; Zhang, E. What controls the antibacterial activity of Ti-Ag alloy, Ag ion or Ti2Ag particles? Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, E.; You, J.; Ma, X.; Bai, X. Antibacterial activities and cell responses of Ti-Ag alloys with a hybrid micro- to nanostructured surface. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 34, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Wen, C.; Hodgson, P.; Li, Y. Fabrication of Ti-Nb-Ag alloy via powder metallurgy for biomedical applications. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdobnyakov, N.Y.; Myasnichenko, V.S.; San, C.-H.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Ershov, P.M.; Ivanov, V.A.; Komarov, P.V. Simulation of phase transformations in titanium nanoalloy at different cooling rates. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 238, 121895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasnichenko, V.S.; Sdobnyakov, N.Y.; Ershov, P.M.; Sokolov, D.N.; Kolosov, A.Y.; Davydenkova, E.M. Simulation of Crystalline Phase Formation in Titanium-Based Bimetallic Clusters. J. Nano Res. 2020, 61, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.; Martinez, C.; Tello, K.; Palma, S.; Delonca, A.; Martin, F.S.; Alfonso, I. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Formation of FCC and BCC Solid Solutions of Ti-Based Ternary Alloys by Mechanical Alloying. Metals 2020, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Mizuuchi, K.; Nakano, T. Solidification Microstructures of the Ingots Obtained by Arc Melting and Cold Crucible Levitation Melting in TiNbTaZr Medium-Entropy Alloy and TiNbTaZrX (X = V, Mo, W) High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2019, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Takemura, M.; Matsumuro, M.; Maruyama, T. Solidification Microstructure of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High Entropy Alloy Ingots. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Matsumura, K.; Nakazawa, K.; Furuya, S.; Ozoe, N.; Yoshino, K. Development of Fe-Co-Cr-Mn-Ni-C high entropy cast iron (HE cast iron) available for casting in air atmosphere. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, R.W. Physical Metallurgy, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, H.; Furusawa, A.; Ariyasu, T.; Okada, A. Optical Measurement of Cooling Rate During Splat Cooling Process. J. Jpn. Foundar. Soc. 1994, 66, 734–738. [Google Scholar]
- FactSage Home Page. Available online: http://www.factsage.com/ (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- SGTE—SGTE 2017 Alloy Phase Diagrams (1176) Home Page. Available online: http://www.crct.polymtl.ca/fact/documentation/SGTE2017/SGTE2017_Figs.htm (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Nagase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, T. Formation of amorphous phase with crystalline globules in Fe-Cu-Nb-B immiscible alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, T. Formation of amorphous phase with crystalline globules in Fe-Cu-Si-B and Fe-Cu-Zr-B immiscible alloys. Intermetallics 2015, 61, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Tanaka, T. Amorphous phase formation in Fe-Ag-based immiscible alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 619, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Takemura, M.; Matsumuro, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Fujii, Y. Design and microstructure analysis of globules in Al-Co-La-Pb immiscible alloys with an amorphous phase. Mater. Des. 2017, 117, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Todai, M.; Nakano, T. Development of Co-Cr-Mo-Fe-Mn-W and Co-Cr-Mo-Fe-Mn-W-Ag High-Entropy Alloys Based on Co-Cr-Mo alloys. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Todai, M.; Nakano, T. Liquid Phase Separation in Ag-Co-Cr-Fe-Mn-Ni, Co-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni and Co-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni-B High Entropy Alloys for Biomedical Application. Crystals 2020, 10, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinemann, S.G. Evaluation of Biomaterials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, H. Cytotoxicity of Implantable Metals and Alloys. Bull. Jpn. Inst. Metals. 1992, 31, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okazaki, Y. Cytocompatibility of Various Metals and Development of New Titanium Alloy for Medical Implant. Mater. Jpn. 1998, 37, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narushima, T. Titanium and its alloys as biomaterials. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Metals. 2005, 55, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, R.H.; Stewart, A.M.; Daniel, M.R. Phase relations and a15-phase diffusion layer formation in the system Ag-Nb-Ga. Metall. Mater. Trans. 1978, 9, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.R.; Simmons, J.P. Phase equilibria in the vicinity of the DO22 Al3Nb composition in the Al-Nb-W, Al-Nb-Co, Al-Nb-Pt, and Al-Nb-Ag systems. Scripta Metall. Mater. 1991, 24, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Ong, S.P.; Hautier, G.; Chen, W.; Richards, W.D.; Dacek, S.; Cholia, S.; Gunter, D.; Skinner, D.; Ceder, G.; et al. The Materials Project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater. 2013, 1, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materials Projects Home Page. Available online: https://materialsproject.org/ (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Nagase, T.; Todai, M.; Nakano, T. Development of Ti-Zr-Hf-Y-La high-entropy alloys with dual hexagonal-close-packed structure. Scr. Mater. 2020, 186, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materials Projects, TiAg, ID: Mp-1017985; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2013.
- Materials Projects, Ti2Ag, ID: Mp-979115; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2013.
- Antonova, N.V.; Firstov, S.A.; Miracle, D.B. Investigation of phase equilibria in the Ti-Al-Si-Nb system at low Nb contents. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Nb-Ti (Niobium-Titanium). J. Ph. Equilib. 2002, 23, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R. (Eds.) Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Nb-Ti, 2nd ed.; ASM: Georg County, OH, USA, 1990; pp. 1699–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Materials Projects, Ti (HCP), ID: Mp-46; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2013.
- Materials Projects, Ti (BCC), ID: Mp-73; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2013.
- Materials Projects, Ag, ID: Mp-124; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2013.
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA: A three-dimensional visualization system for electronic and structural analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Ju, C.P.; Lin, J.H.C. Structure-property relationship of cast Ti–Nb alloys. J. Oral Rehabilitation. 2002, 29, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantani, Y.; Tajima, M. Phase transformation of quenched a’’ martensite by aging in Ti–Nb alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2006, 438–440, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banumathy, S.; Mandal, R.K.; Singh, A.K. Structure of orthorhombic martensitic phase in binary Ti–Nb alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 093518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonisch, M.; Calin, M.; Waitz, T.; Panigrahi, A.; Zehetbauer, M.; Gebert, A.; Skrotzki, W.; Eckert, J. Thermal stability and phase transformations of martensitic Ti–Nb alloys. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2013, 14, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantani, Y.; Takemoto, Y. Change in Crystal Structure and Material Properties with Deformation of Quenched Martensite in Ti-Nb Alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. Mater. 2015, 79, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

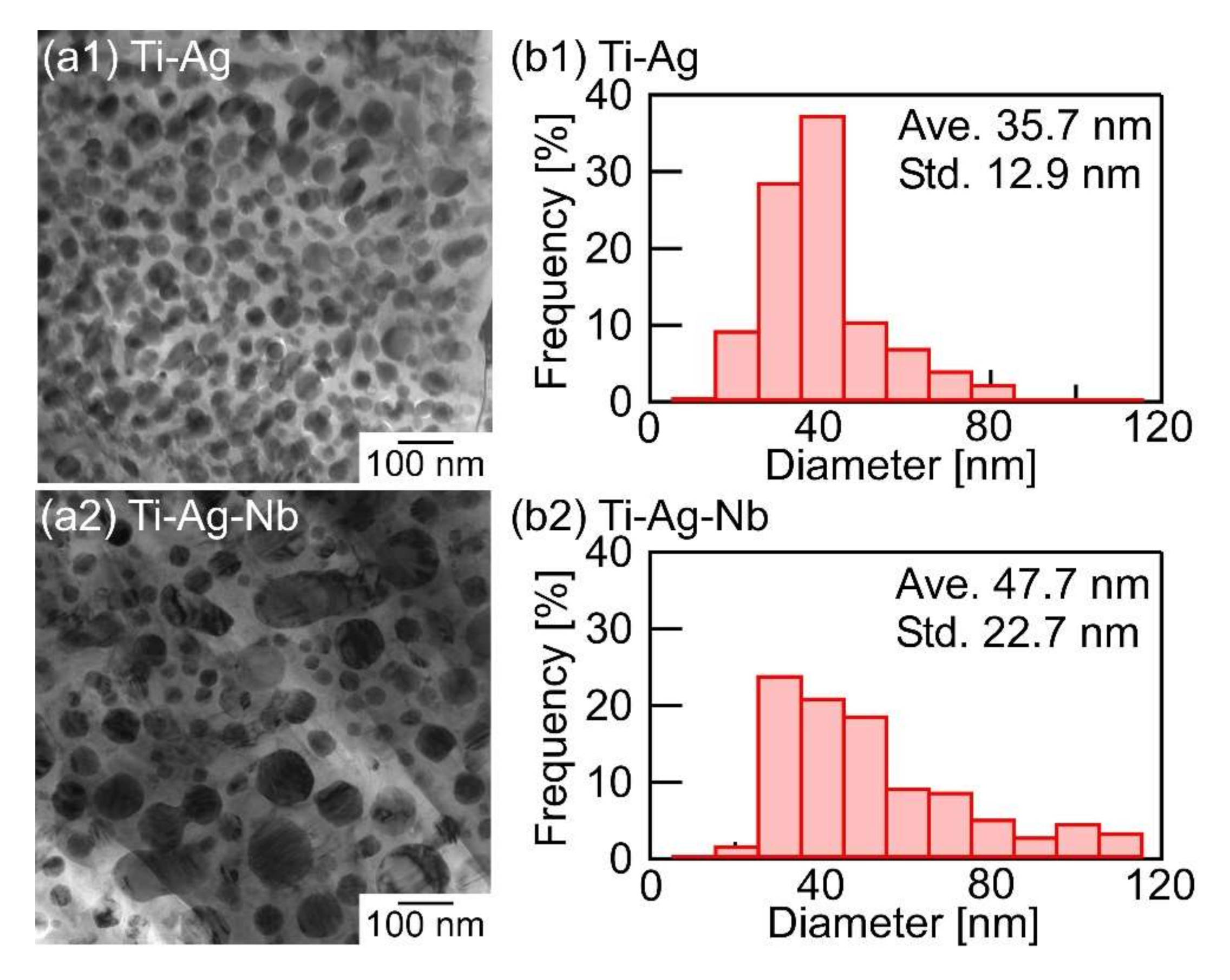
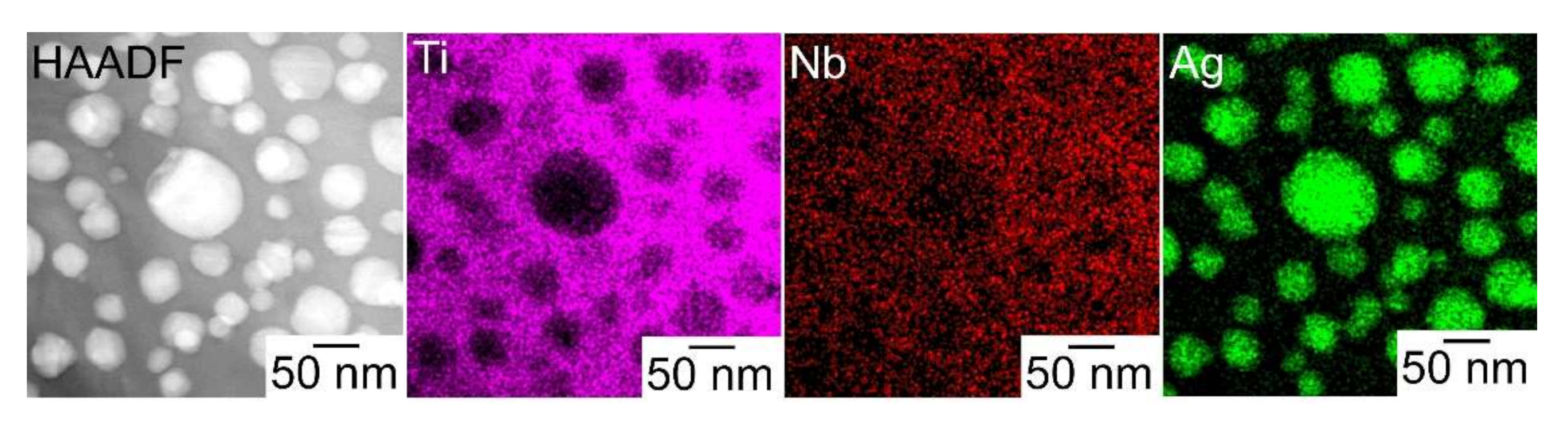

| Phases | Temperature (K) | Ti | Ag | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Ti-rich liquid | 1900 | 57.4 | 27.1 | 15.4 |
| 1800 | 61.4 | 21.6 | 16.9 | |
| 1700 | 64.5 | 17.7 | 17.8 | |
| 1400 | 71.6 | 9.4 | 19.0 | |
| (b) Ag-rich liquid | 1900 | 37.7 | 57.0 | 5.3 |
| 1800 | 30.6 | 66.3 | 3.2 | |
| 1700 | 24.4 | 73.7 | 1.9 | |
| 1400 | 11.2 | 88.4 | 0.4 |
| Regions | Regions | Ti | Ag | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Ti-Ag | D1 (dendrite) | 82.0 | 18.0 | - |
| ID1 (interdenbdrite) | 3.7 | 96.3 | - | |
| (b1) Ti-Ag-Nb, region P (central part) | D2 (dendrite) | 78.0 | 10.9 | 11.1 |
| ID2 (interdenbdrite) | 3.0 | 96.7 | 0.3 | |
| (b2) Ti-Ag-Nb, region Q (bottom part) | D3 (dendrite) | 78.7 | 10.7 | 10.6 |
| ID3 (interdenbdrite) | 3.8 | 95.9 | 0.3 | |
| MP | 0.5 | 99.4 | 0. |
| Regions | Ti | Ag | Nb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix | 75.4 | 9.6 | 15.0 |
| Globules | 6.9 | 92.4 | 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagase, T. Alloy Design, Thermodynamics, and Electron Microscopy of Ternary Ti-Ag-Nb Alloy with Liquid Phase Separation. Materials 2020, 13, 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225268
Nagase T. Alloy Design, Thermodynamics, and Electron Microscopy of Ternary Ti-Ag-Nb Alloy with Liquid Phase Separation. Materials. 2020; 13(22):5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225268
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagase, Takeshi. 2020. "Alloy Design, Thermodynamics, and Electron Microscopy of Ternary Ti-Ag-Nb Alloy with Liquid Phase Separation" Materials 13, no. 22: 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225268
APA StyleNagase, T. (2020). Alloy Design, Thermodynamics, and Electron Microscopy of Ternary Ti-Ag-Nb Alloy with Liquid Phase Separation. Materials, 13(22), 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225268