Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
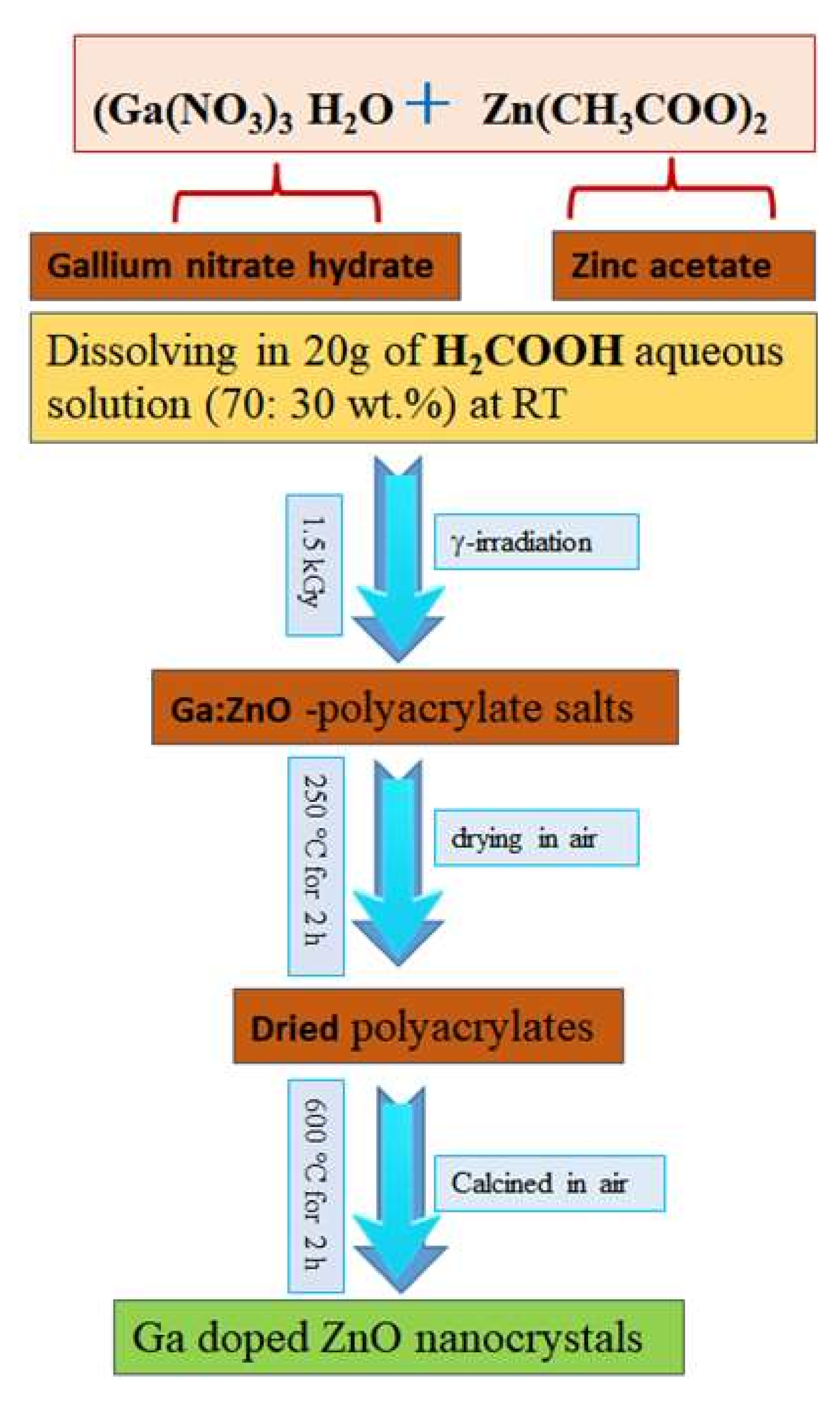
2.1. Synthesization of Ga Doped ZnO Nanocrystals
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
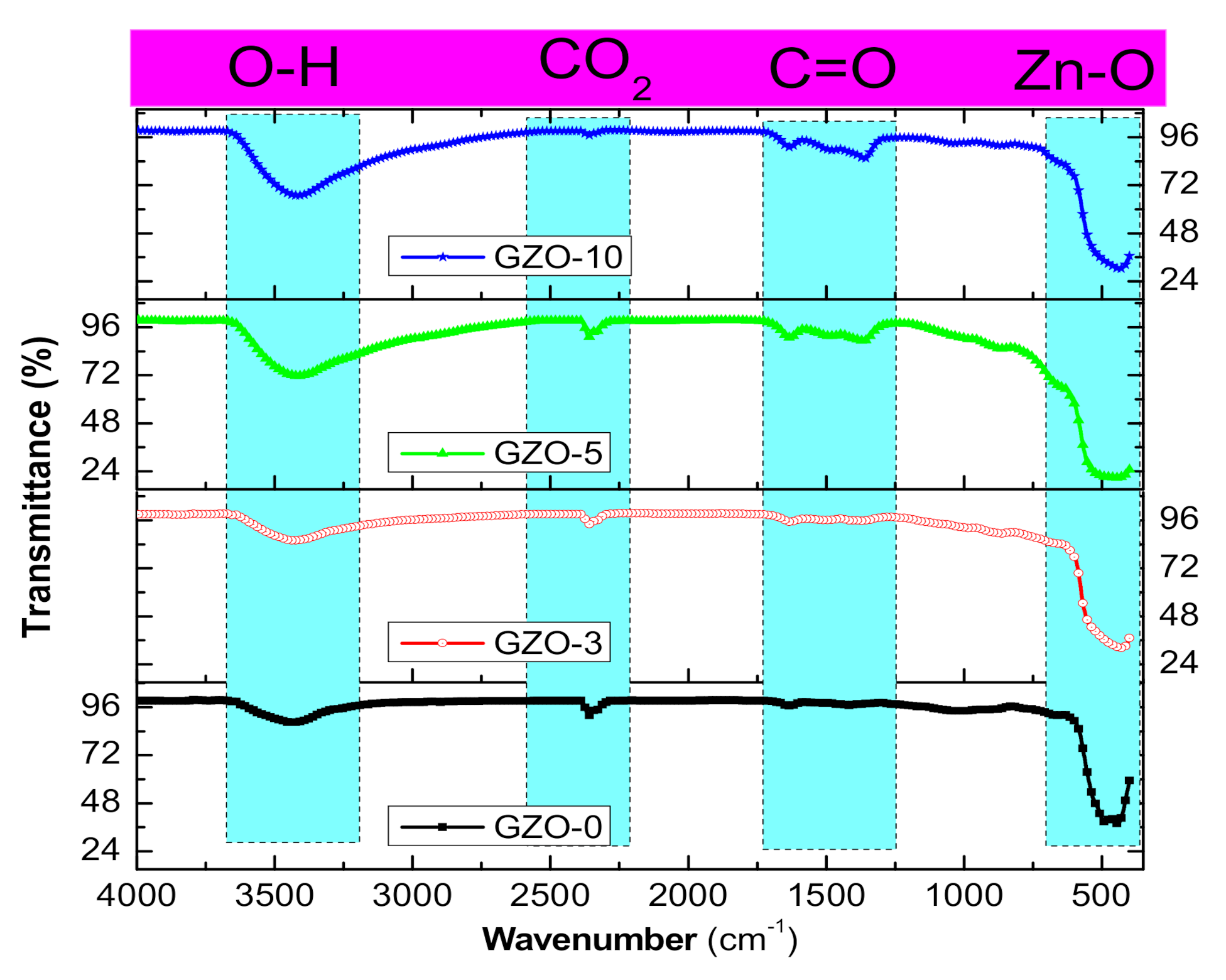
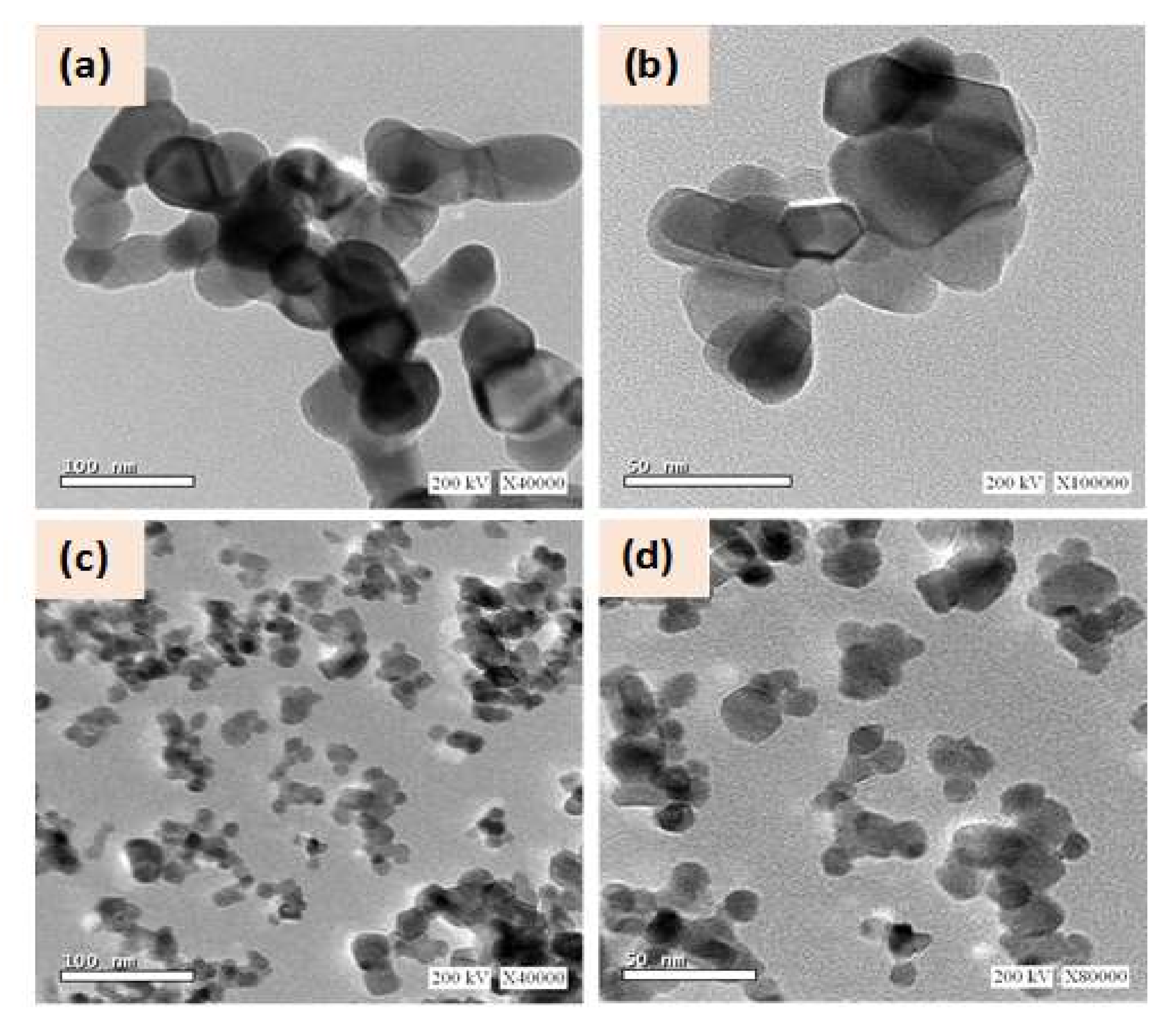
3.1. Structural and Morphological Characterizations of Ga:ZnO Nanocrystals
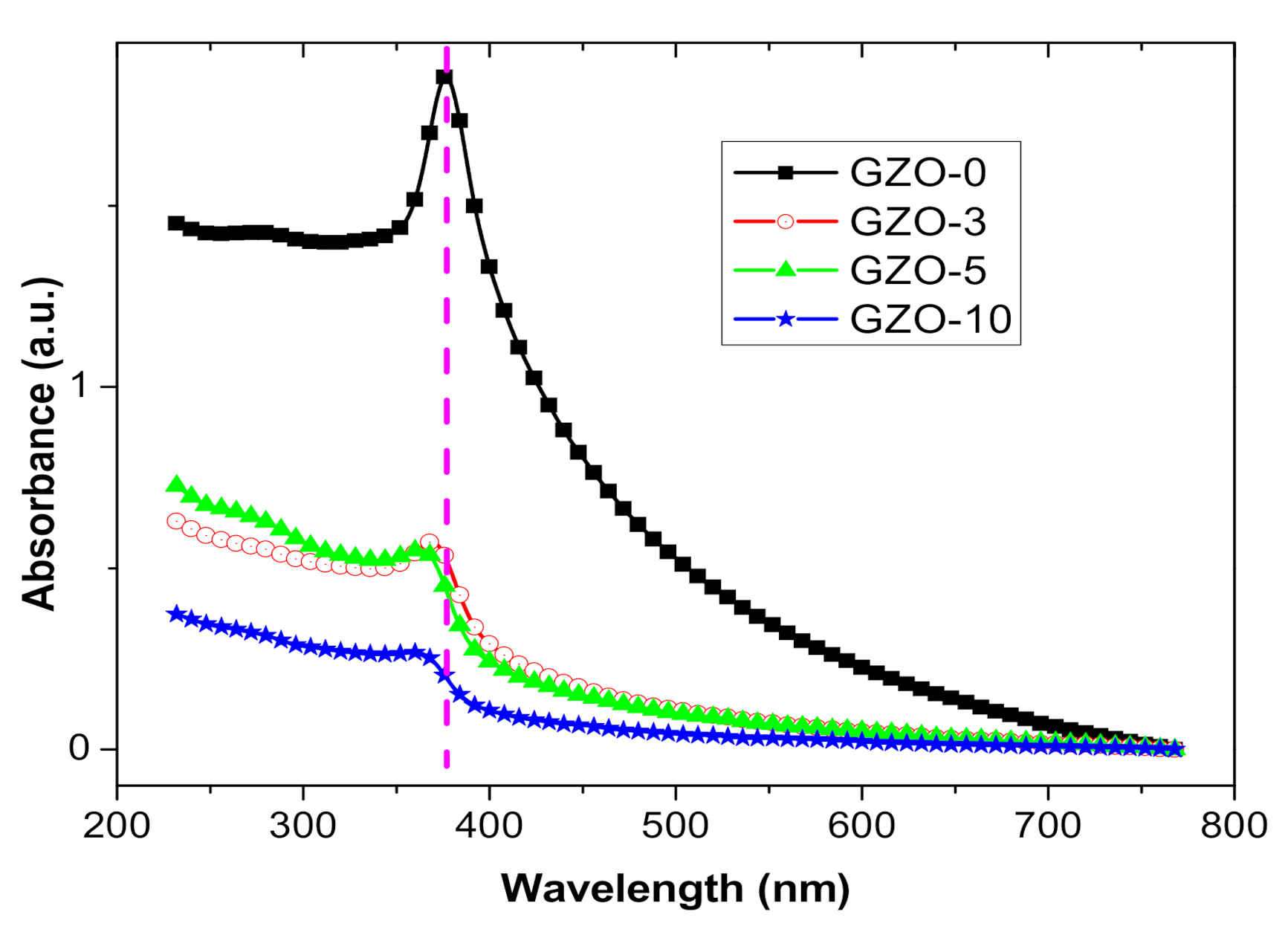
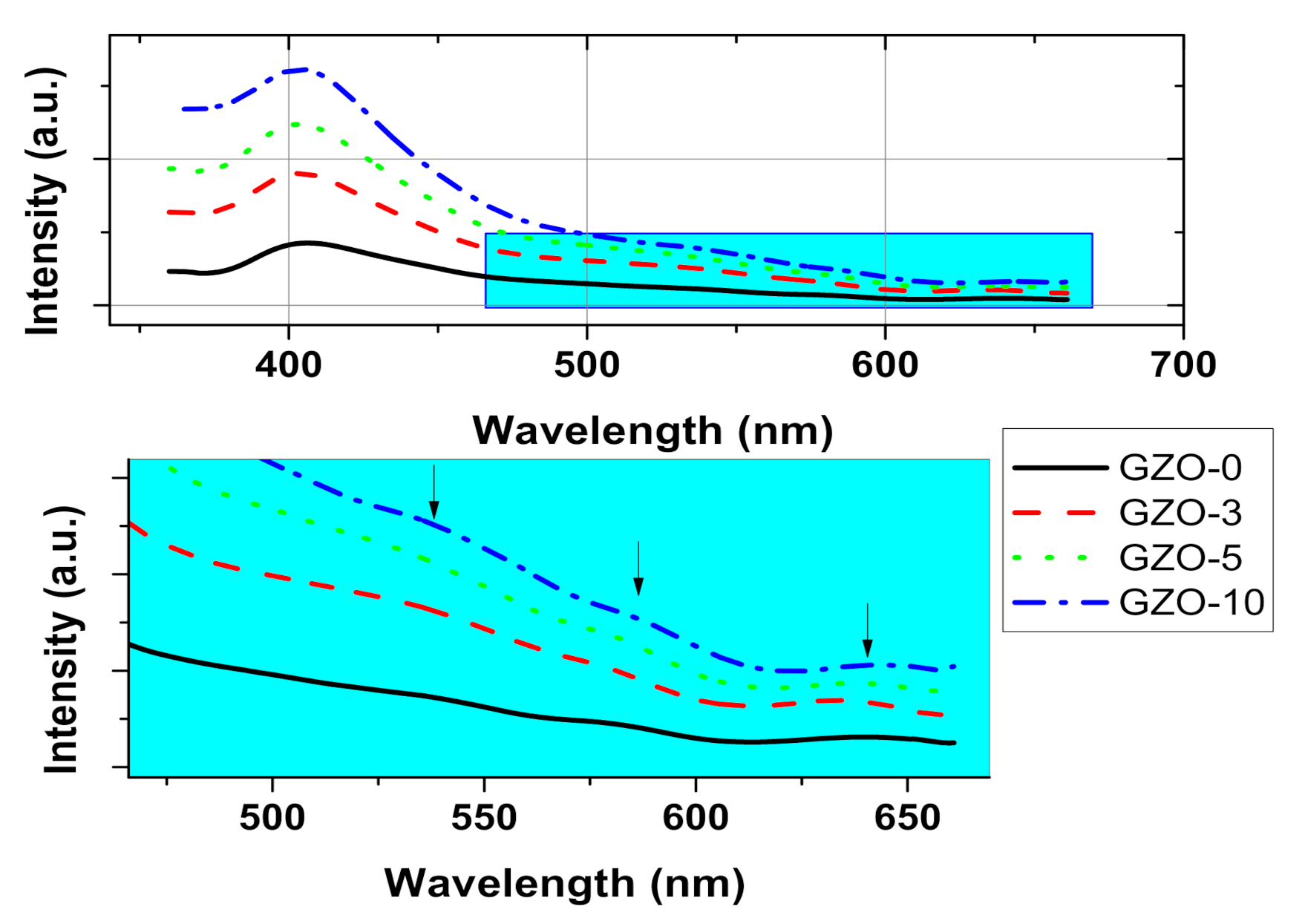
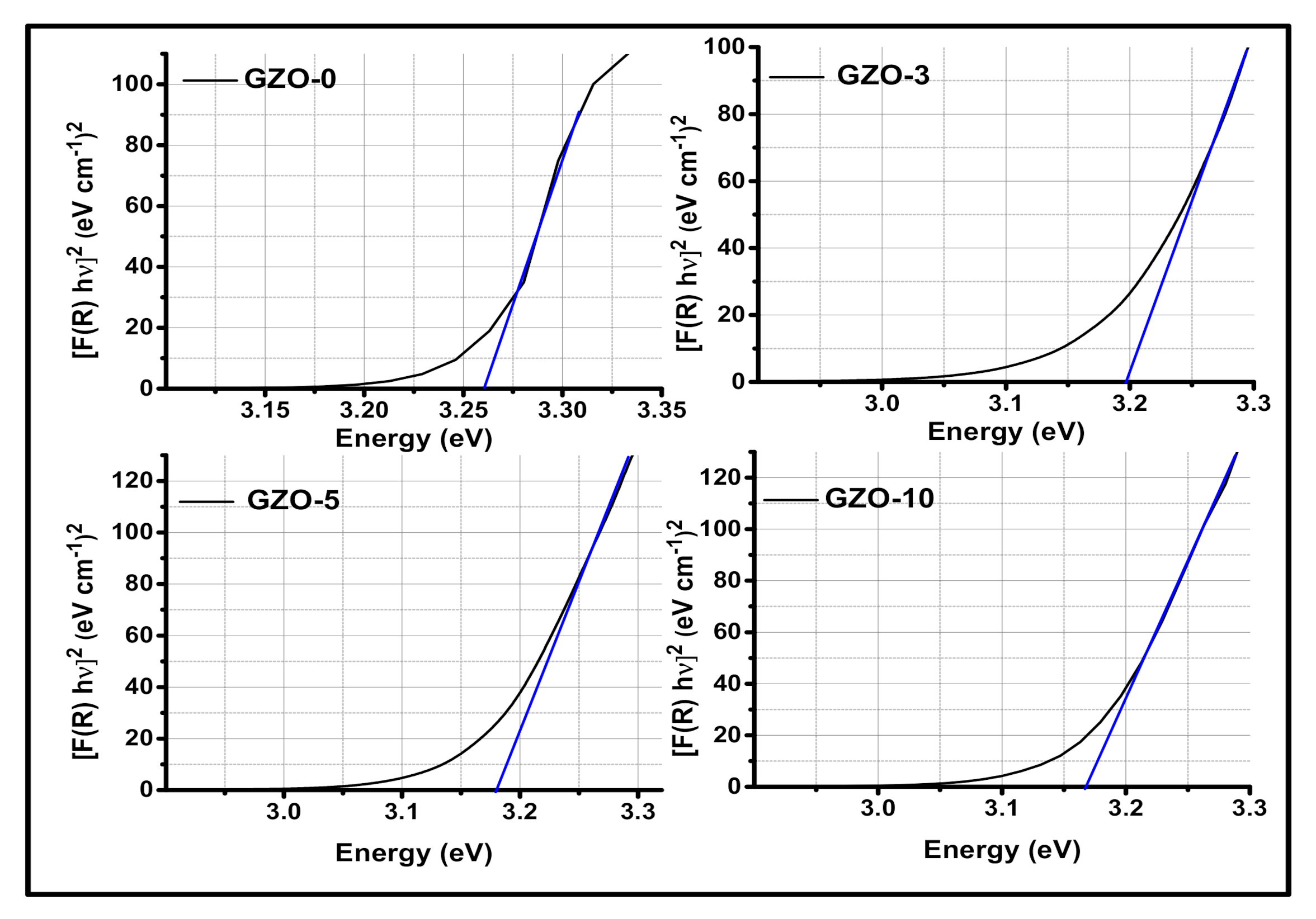
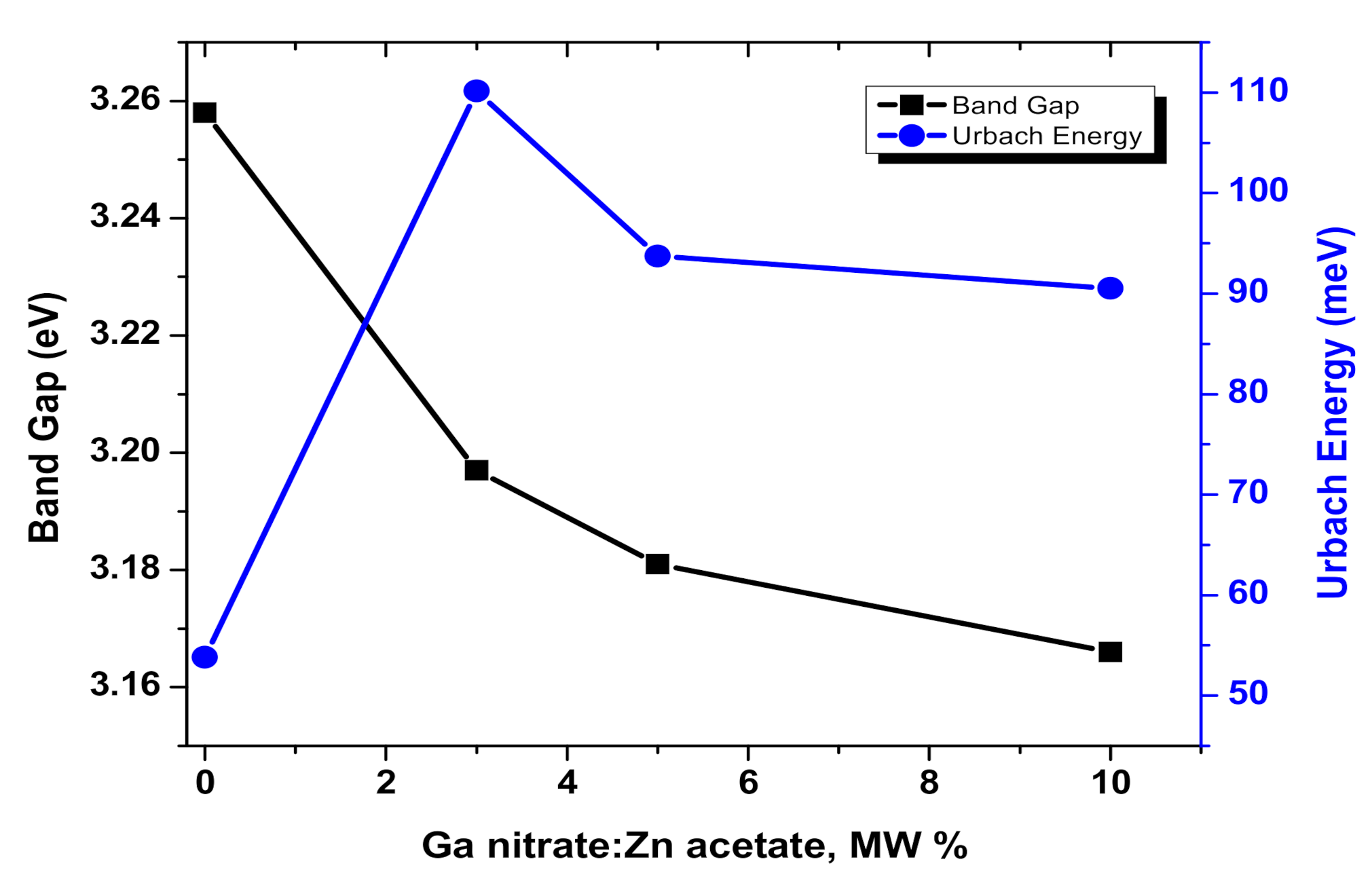
3.2. Optical Characterization
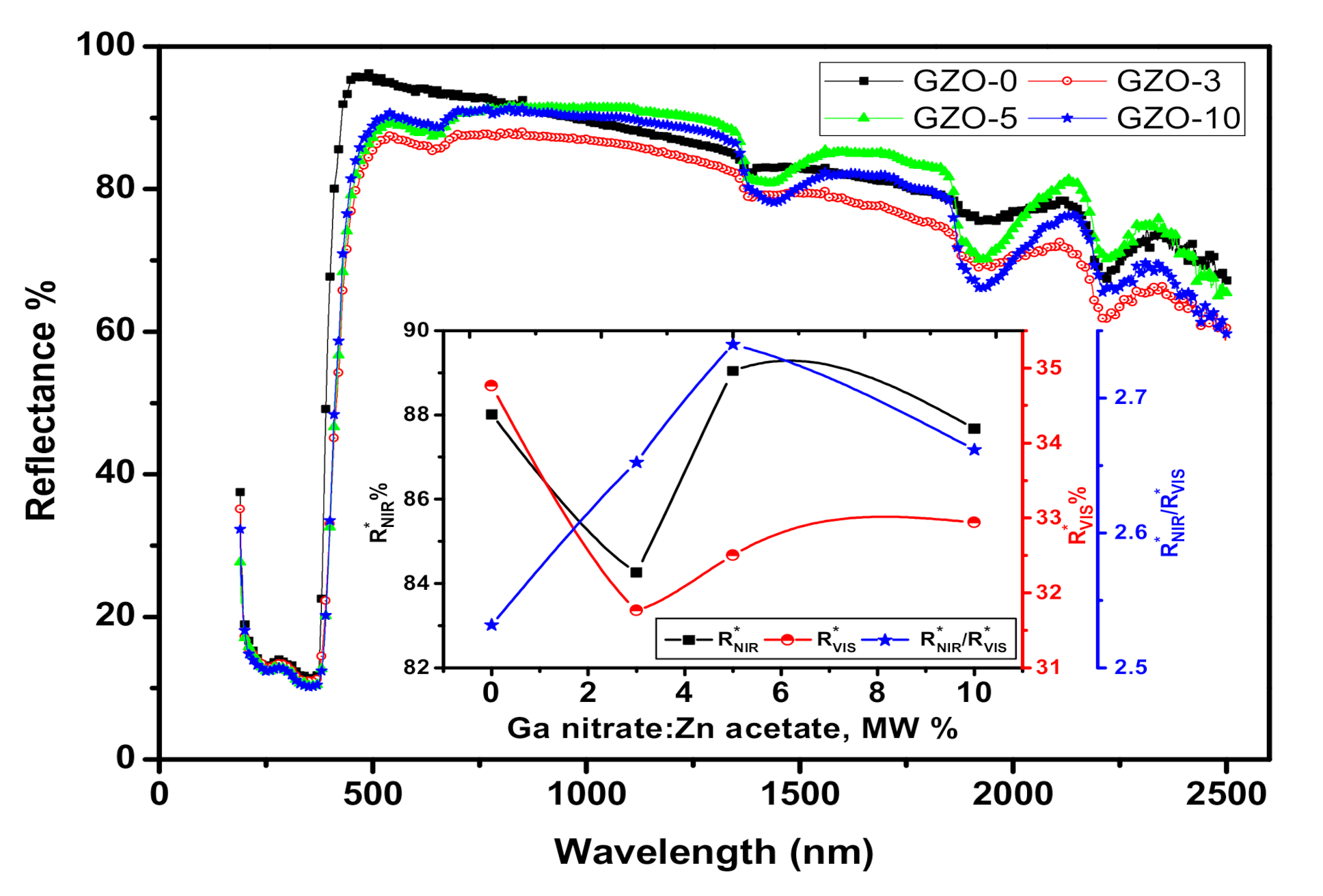
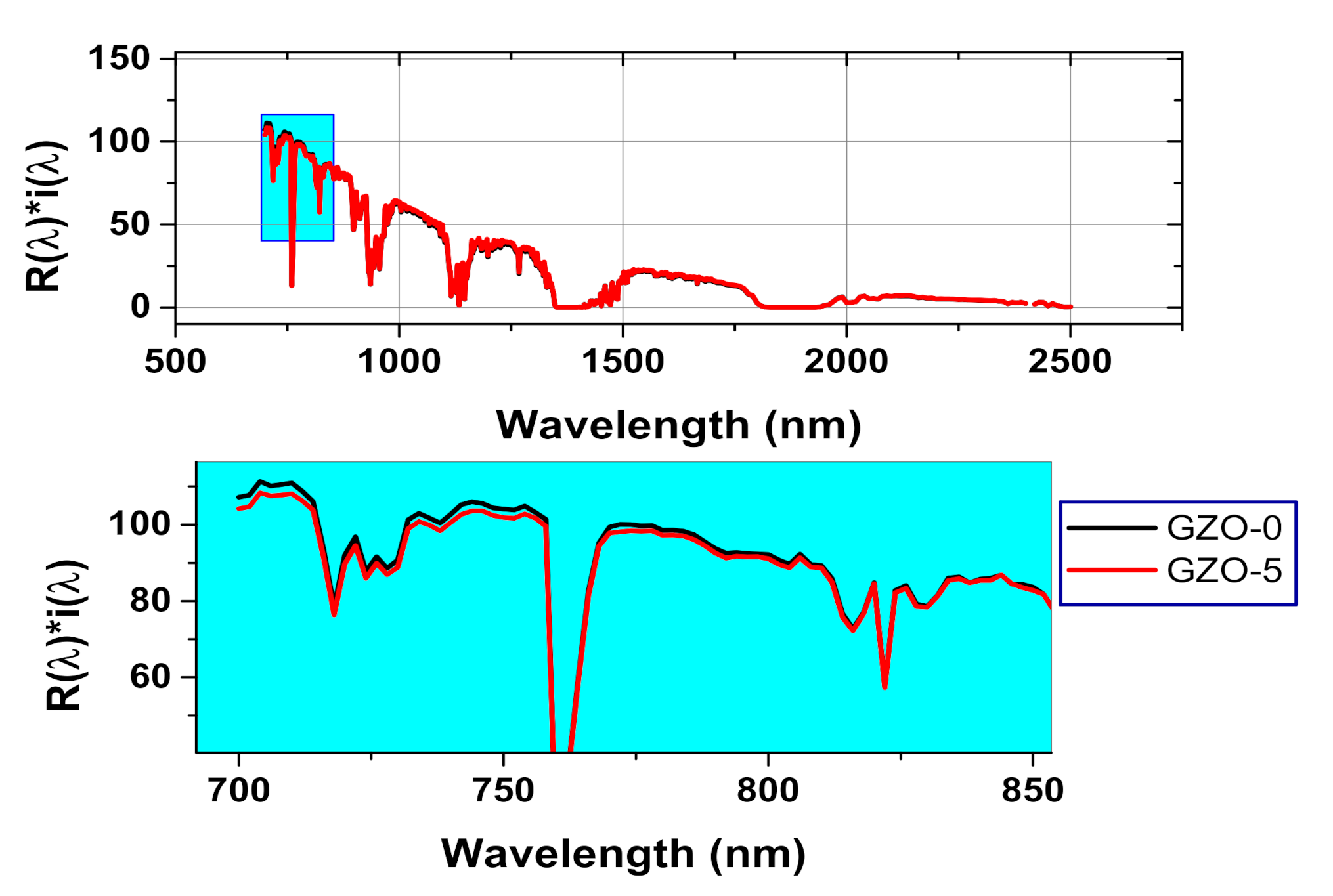
4. UV-Vis-NIR Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopic Characterization of the Synthesized Ga-Doped ZnO Nanocrystals
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgür, Ü.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Doğan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.-J.; Morkoç, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 041301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearton, S.; Norton, D.P.; Ip, K.; Heo, Y.; Steiner, T. Recent advances in processing of ZnO. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2004, 22, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-L.; Yang, C.-B.; Huang, C.-H.; Hsu, C.Y. Electrical and optical studies of Ga-doped ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 24, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Schmidt, H.; Zhou, S.; Potzger, K.; Helm, M.; Hochmuth, H.; Lorenz, M.; Setzer, A.; Esquinazi, P.D.; Meinecke, C.; et al. Room temperature ferromagnetism in ZnO films due to defects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 82508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkallas, F.; Elshokrofy, K.; Mansour, S. Structural and diffuse reflectance characterization of cobalt-doped titanium dioxide nanostructured powder prepared via facile sonochemical hydrolysis technique. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavat, A.E.; Wagner, C.C.; Tasca, J.E. Interaction of Co–ZnO pigments with ceramic frits: A combined study by XRD, FTIR and UV–visible. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.G.; Morrell, R. Nanostructured ceramics: A review of their potential. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2001, 15, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synnefa, A.; Karlessi, T.; Gaitani, N.; Santamouris, M.; Assimakopoulos, D.; Papakatsikas, C. Experimental testing of cool colored thin layer asphalt and estimation of its potential to improve the urban microclimate. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.; Berdahl, P.; Akbari, H.; Miller, W.; Joedicke, I.; Reilly, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Vondran, M. Methods of creating solar-reflective nonwhite surfaces and their application to residential roofing materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, H.; Moriyama, M. Surface heat budget on green roof and high reflection roof for mitigation of urban heat island. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemoto, K.L.; Sato, N.M.N.; John, V.M. Estimating thermal performance of cool colored paints. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.Q.; Chua, S.J. Gallium and indium co-doping of epitaxial zinc oxide thin films grown in water at 90 °C. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, C.-Y.; Yu, S.-H. Optoelectronic characteristics of UV photodetectors based on sol–gel synthesized GZO semiconductor thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 596, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-W.; Lei, C.-M.; Chen, F.-S.; Lin, C.-K. Microstructural and optical properties of Ga-doped ZnO semiconductor thin films prepared by sol–gel process. Thin Solid Films 2010, 519, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, C.-Y.; Lee, W.-C. Effect of dopants on the structural, optical and electrical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO semiconductor thin films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Sen, S. Sol–gel preparation, characterization and studies on electrical and thermoelectrical properties of gallium doped zinc oxide films. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, A.H.; Mansour, S.A.; Kotkata, M.F. Structural, optical, and magnetic study of dilute magnetic semiconducting Co-doped ZnO nanocrystals synthesized using polymer-pyrolysis route. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 9855–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangon, K.; Khamon, W.; Pecharapa, W. Influence of baking temperature on relevant properties of sol-gel Ga-doped ZnO thin films annealed at low temperature. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 14155–14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Chang, B.; Sun, X.; Ye, L. Growth and characterization of high transmittance GZO films prepared by sol-gel method. Thin Solid Films 2016, 615, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tsay, C.-Y.; Fan, K.-S.; Lei, C.-M. Synthesis and characterization of sol–gel derived gallium-doped zinc oxide thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 512, 216–222. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.-M.; Chen, Y.-Y. Improvement of electrical properties of sol–gel derived ZnO:Ga films by infrared heating method. J. Sol Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 51, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Shan, F.K.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, G.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Sohn, J.Y. Photoluminescence of ZnO:Ga Thin Films Fabricated by Pulsed Laser Deposition Technique. J. Electroceramics 2004, 13, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Mo, H.S.; Kim, T.S.; Jeong, T.S.; Youn, C.J.; Hongb, K.J. Rapid-thermal post-annealing effect of room-temperature grown ZnO: Ga layers by the radio-frequency co-sputtering. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2013, 14, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Gokulakrishnan, V.; Purushothaman, V.; Arthi, E.; Jeganathan, K.; Ramamurthi, K. Effect of vacuum annealing on the structural, optical, and electrical properties of spray-deposited Ga-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 2012, 209, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; Oh, Y.; Haranath, D.; Bhosale, C.; Rajpure, K.; Shinde, P.S. Structural, optoelectronic, luminescence and thermal properties of Ga-doped zinc oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 9969–9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Singh, S.; Kumar, U.; Srinivasa, R.S.; Singh, G. Transparent conducting Ga-doped ZnO thin films grown by reactive co-sputtering of Zn and GaAs. Thin Solid Films 2014, 555, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. Improved electrical and optical properties of GZO films with a thin TiO2 buffer layer deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Q.; Yong, K.; Xiao, H.-M.; Ma, W.-J.; Zhang, G.-L.; Fu, S.-Y. Preparation and electrical properties of Ga-doped ZnO nanoparticles by a polymer pyrolysis method. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1735–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimifard, R.; Golobostanfard, M.R.; Abdizadeh, H. Sol–gel derived Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: An optoelectronic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Farha, A.; Kotkata, M.F. Synthesis and study of ZnO nanoparticles by polymer pyrolysis route using two different polymerization initiators. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2017, 14, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassas, M. Non-equilibrium energy transport in nano-layer gold coating onto silica. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-W.; Seo, J.-H.; Seong, T.-Y.; Yu, T.H.; You, Y.H.; Lee, K.B.; Kwon, H.; Ahn, J.-P. Ga Ordering and Electrical Conductivity in Nanotwin and Superlattice-Structured Ga-Doped ZnO. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Dalela, B.; Rathore, R.; Vats, V.; Choudhary, B.; Alvi, P.A.; Kumar, S.; Dalela, S. Influence of Co doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanocrystals. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 578, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Basak, D.; Fujihara, S. Effect of substrate-induced strain on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of polycrystalline ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ashok, V.D.; De, S.K. Carrier concentration dependent optical and electrical properties of Ga doped ZnO hexagonal nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 16067–16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, S.A.; Elsad, R.A.; Izzularab, M.A. Dielectric investigation of high density polyethylene loaded by ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel route. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qindeel, R. Effect of gamma radiation on morphological & optical properties of ZnO nanopowder. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, A.H.; Al Naim, A.F.; Mazher, J.; Nasr, O.; Alouane, M.H. Structural and Optical Characteristics of Highly UV-Blue Luminescent ZnNiO Nanoparticles Prepared by Sol–Gel Method. Materials 2020, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, J.A.; Sánchez-Royo, J.F.; Segura, A.; Tobias, G.; Canadell, E. Chemical effects on the optical band-gap of heavily doped ZnO: M III (M= Al, Ga, In): An investigation by means of photoelectron spectroscopy, optical measurements under pressure, and band structure calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 195105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiQiang, J.; Yichun, Q.; Baiqi, W.; Shudan, L.; Baojiang, J.; Libin, Y.; Wei, F.; Honggang, F.; Jiazhong, S. Review of photoluminescence performance of nano-sized semiconductor materials and its relationships with photocatalytic activity. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 1773–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.D.; Li, X.M.; Yu, W.D. Synthesis and optical properties of ZnO nanocluster porous films deposited by modified SILAR method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 229, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serenko, O.A.; Roldughin, V.I.; Askadskii, А.; Serkova, E.S.; Strashnov, P.V.; Shifrina, Z.B. The effect of size and concentration of nanoparticles on the glass transition temperature of polymer nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50113–50120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Naik, G.V.; Gavrilenko, A.V.; Dondapati, K.; Gavrilenko, V.I.; Prokes, S.M.; Glembocki, O.J.; Shalaev, V.M.; Boltasseva, A. Optical Properties of Gallium-Doped Zinc Oxide—A Low-Loss Plasmonic Material: First-Principles Theory and Experiment. Phys. Rev. X 2013, 3, 041037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Li, X. Defect evolution in ZnO and its effect on radiation tolerance. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 11882–11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbalagan, A.K.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, A.; Haw, S.-C.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Tai, N.-H.; Tseng, F.G.; Hwang, K.C.; Lee, C.-H. Gamma Ray Irradiation Enhances the Linkage of Cotton Fabrics Coated with ZnO Nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 15129–15135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugmore, C.W. Zwingli. By, GR Potter. Pp. xx + 432 including 3 maps. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1976. £18.50. J. Ecclesiastical Hist. 1978, 29, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, R.; Berdahl, P.; Akbari, H. Solar spectral optical properties of pigments—Part II: Survey of common colorants. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 89, 351–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Prakash, A.; Laha, S.; Natarajan, S.; Reddy, M.L. Green colored nano-pigments derived from Y2BaCuO5: NIR reflective coatings. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 107, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, V.; Kennedy, J.V.; Futter, J.; Manning, J. A Review of Near Infrared Reflectance Properties of Metal Oxide Nanostructures; GNS Science: Lower Hutt, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alkallas, F.H.; Elshokrofy, K.M.; Mansour, S. Structural and Diffuse Reflectance Study of Cr-Doped ZnO Nanorod-Pigments Prepared via Facile Thermal Decomposition Technique. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 29, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevanandam, P.; Mulukutla, R.S.; Phillips, M.; Chaudhuri, S.; Erickson, L.E.; Klabunde, K.J. Near Infrared Reflectance Properties of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1912–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneshi, M.; Maruyama, S.; Komiya, A. The Effects of Using Some Common White Pigments on Thermal and Aesthetic Performances of Pigmented Coatings. J. Therm. Sci. Technol. 2009, 4, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W. Modern Optical Engineering: The Design of Optical Systems; Tata McGraw-Hill Education: New York City, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kortüm, G. Reflectance Spectroscopy Principles, Methods, Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A.E.; Mora, E.S.; Pal, U. Use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for optical characterization of un-supported nanostructures. Revista Mexicana de Física 2007, 53, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, B.; Dey, M.; Choudhury, A. Defect generation, d-d transition, and band gap reduction in Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2013, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Tanaka, S.; Hirao, K. Effects of substrate temperature on nanostructure and band structure of sputtered Co3O4 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, L.; Abbate, M.; Vogel, J.; Fuggle, J.; Fernández, A.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Sacchi, M.; Sanz, J.M. The electronic structure of mesoscopic NiO particles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1993, 208, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, K. A physical explanation to the controversial Urbach tailing universality. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2011, 126, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | D, nm | a, Å | c, Å | V, Å | c/a | ε |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZO-0 | 31.5 | 3.254 | 5.214 | 47.820 | 1.602 | 0.156 |
| GZO-3 | 17.4 | 3.257 | 5.212 | 47.896 | 1.600 | 0.132 |
| GZO-5 | 13.7 | 3.267 | 5.226 | 48.302 | 1.599 | 0.389 |
| CZO-10 | 10.9 | 3.261 | 5.240 | 48.248 | 1.603 | 0.654 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farha, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Mansour, S.A. Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 5152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225152
Farha AH, Ibrahim MM, Mansour SA. Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications. Materials. 2020; 13(22):5152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225152
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarha, Ashraf H., Mervat M. Ibrahim, and Shehab A. Mansour. 2020. "Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications" Materials 13, no. 22: 5152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225152
APA StyleFarha, A. H., Ibrahim, M. M., & Mansour, S. A. (2020). Ga-Doped ZnO Nanostructured Powder for Cool-Nanopigment in Environment Applications. Materials, 13(22), 5152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225152





