Experimental Study of Abrasive, Mechanical and Corrosion Effects in Ring-on-Ring Sliding Contact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
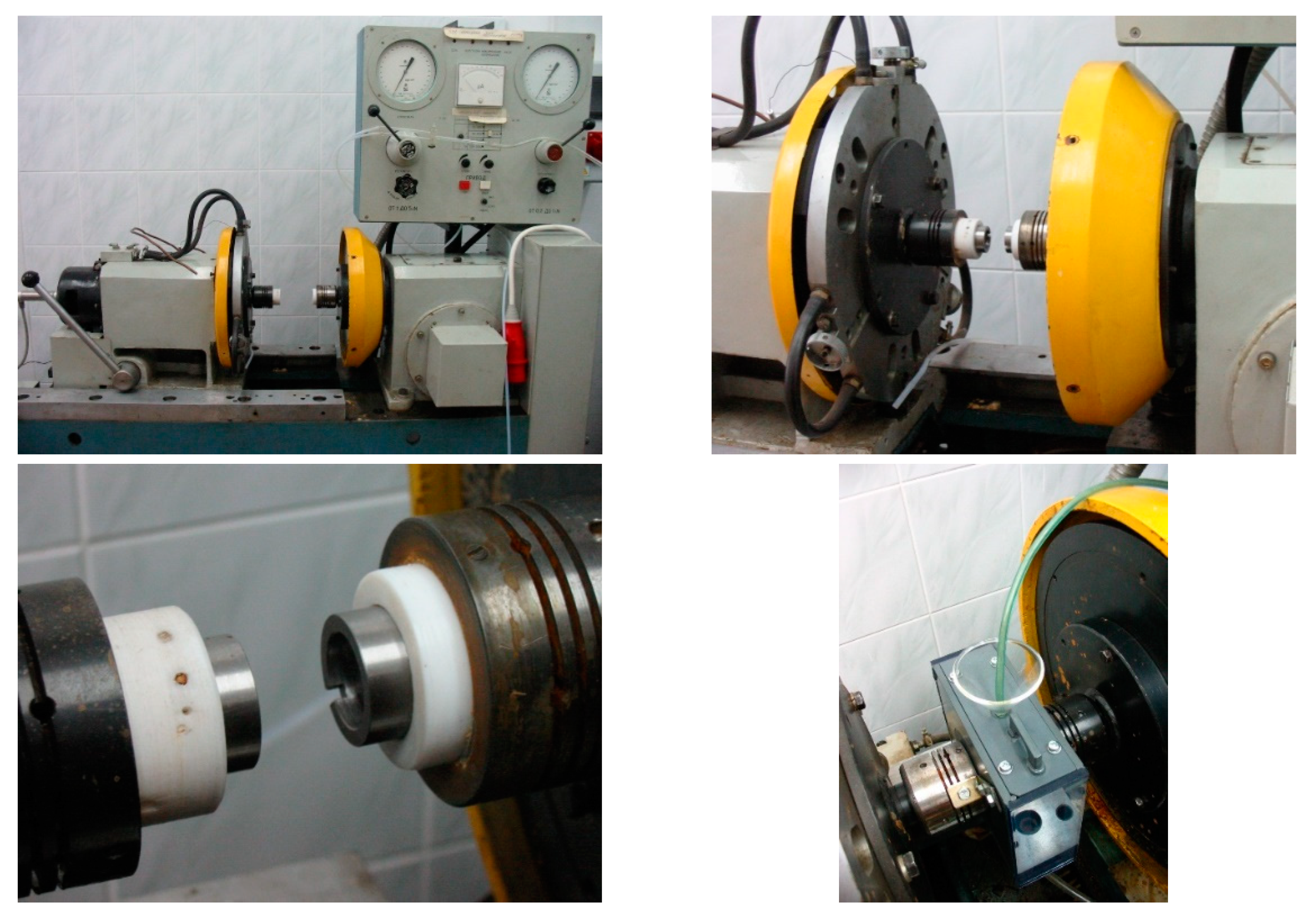
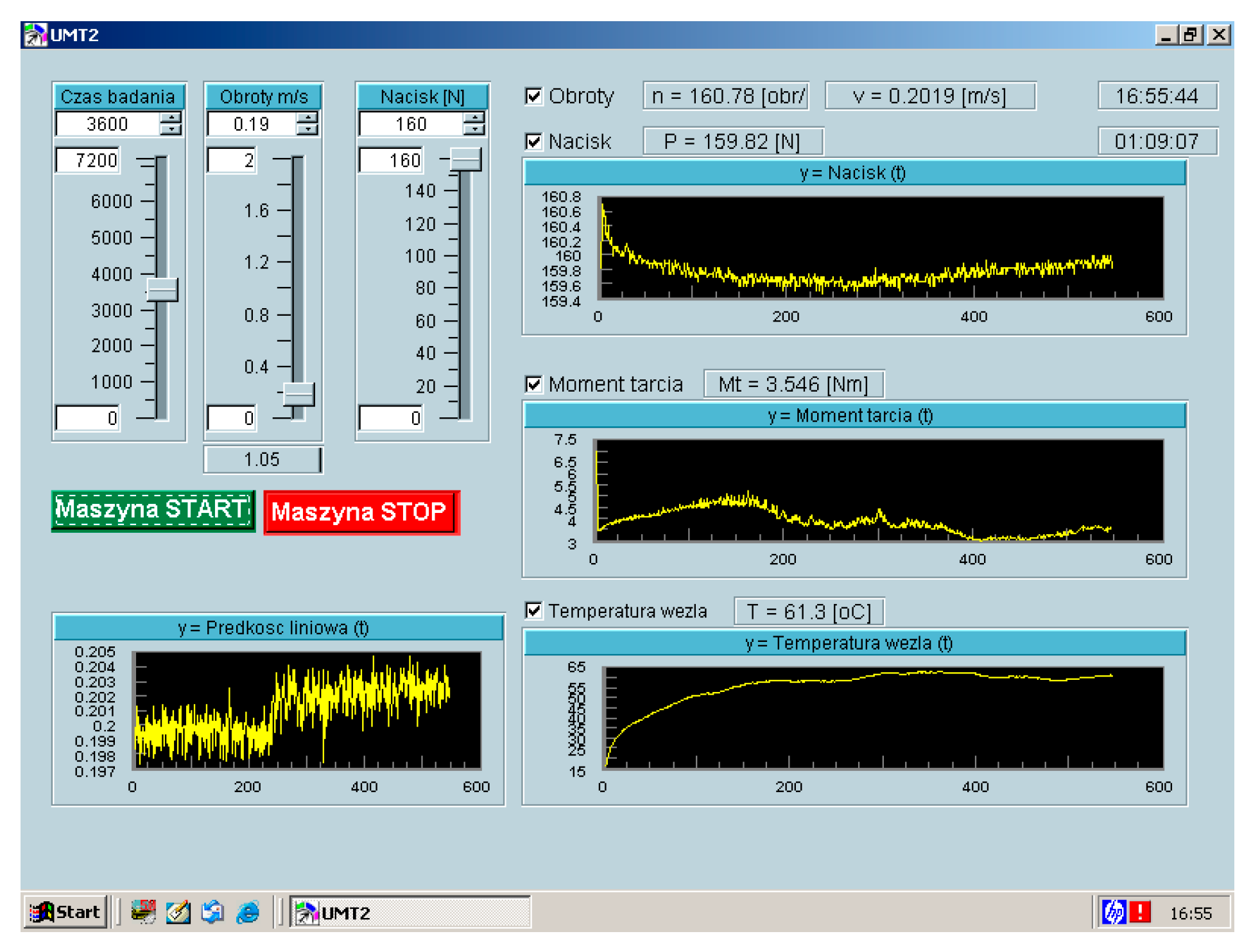
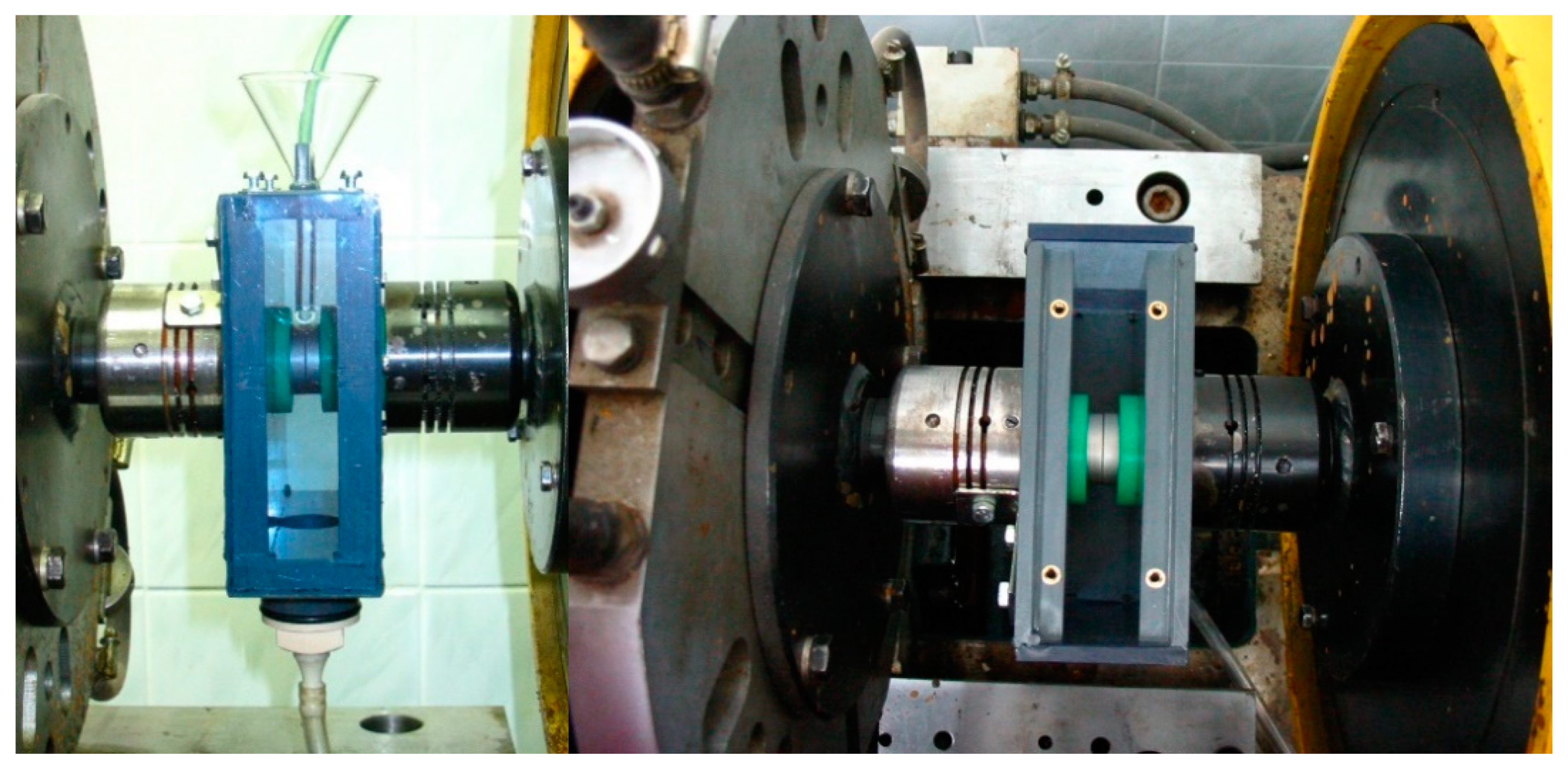
2.1. Experimental Set-Up
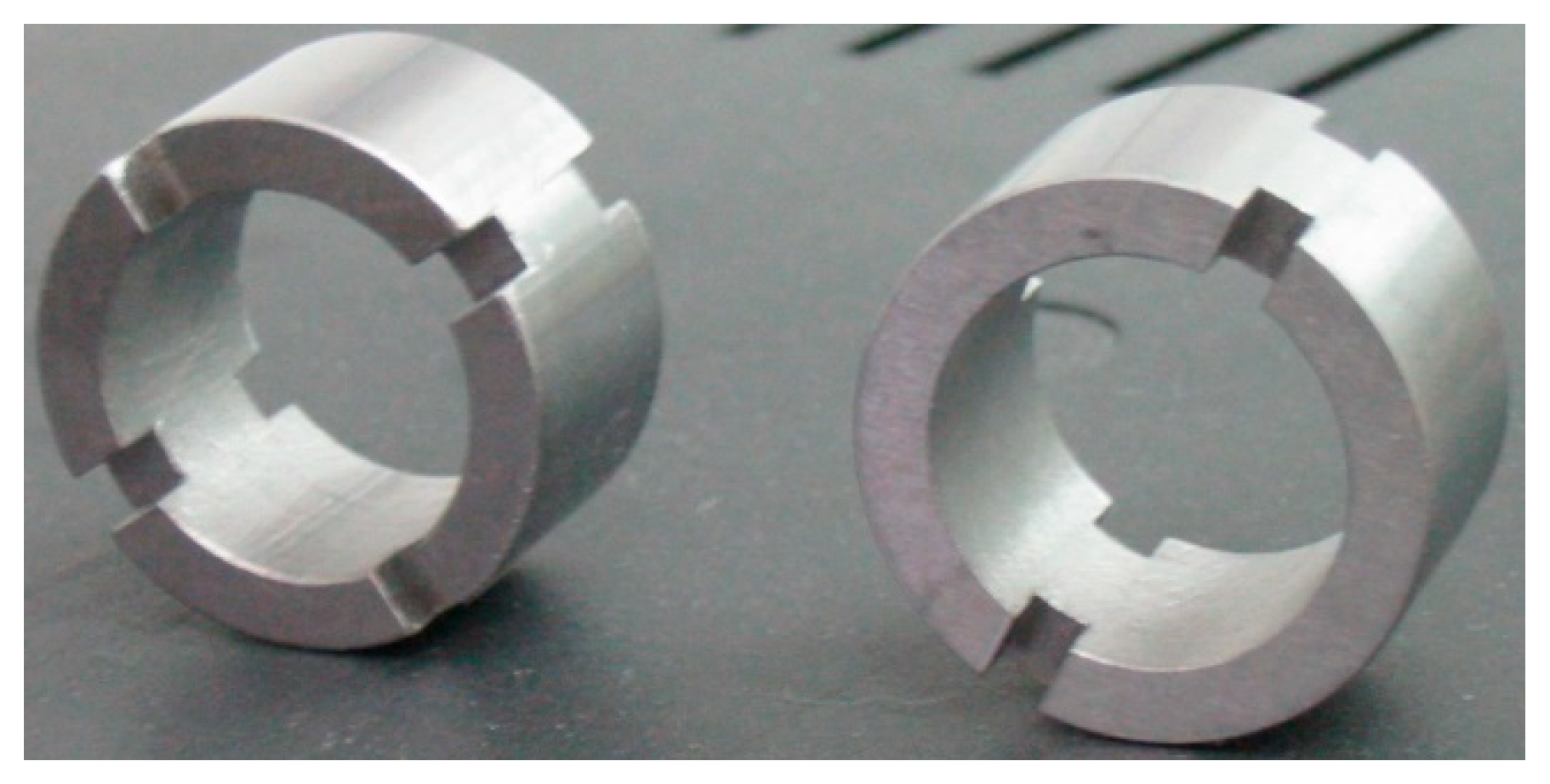
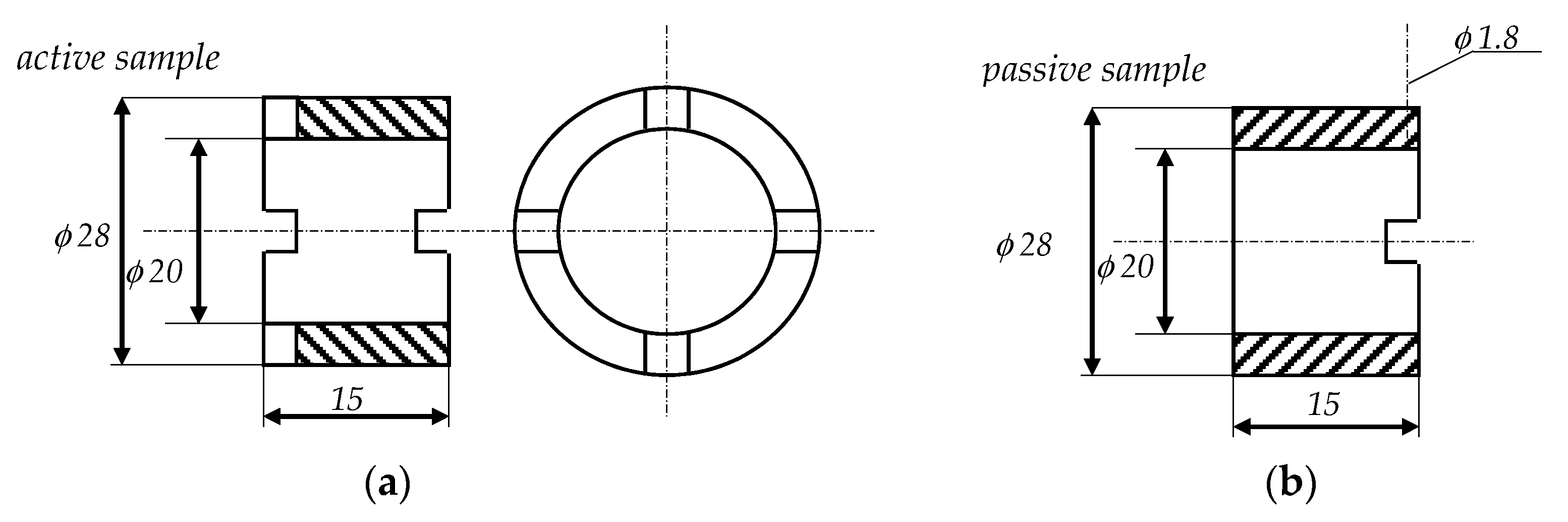
2.2. Material Properties and Specimen Dimensions
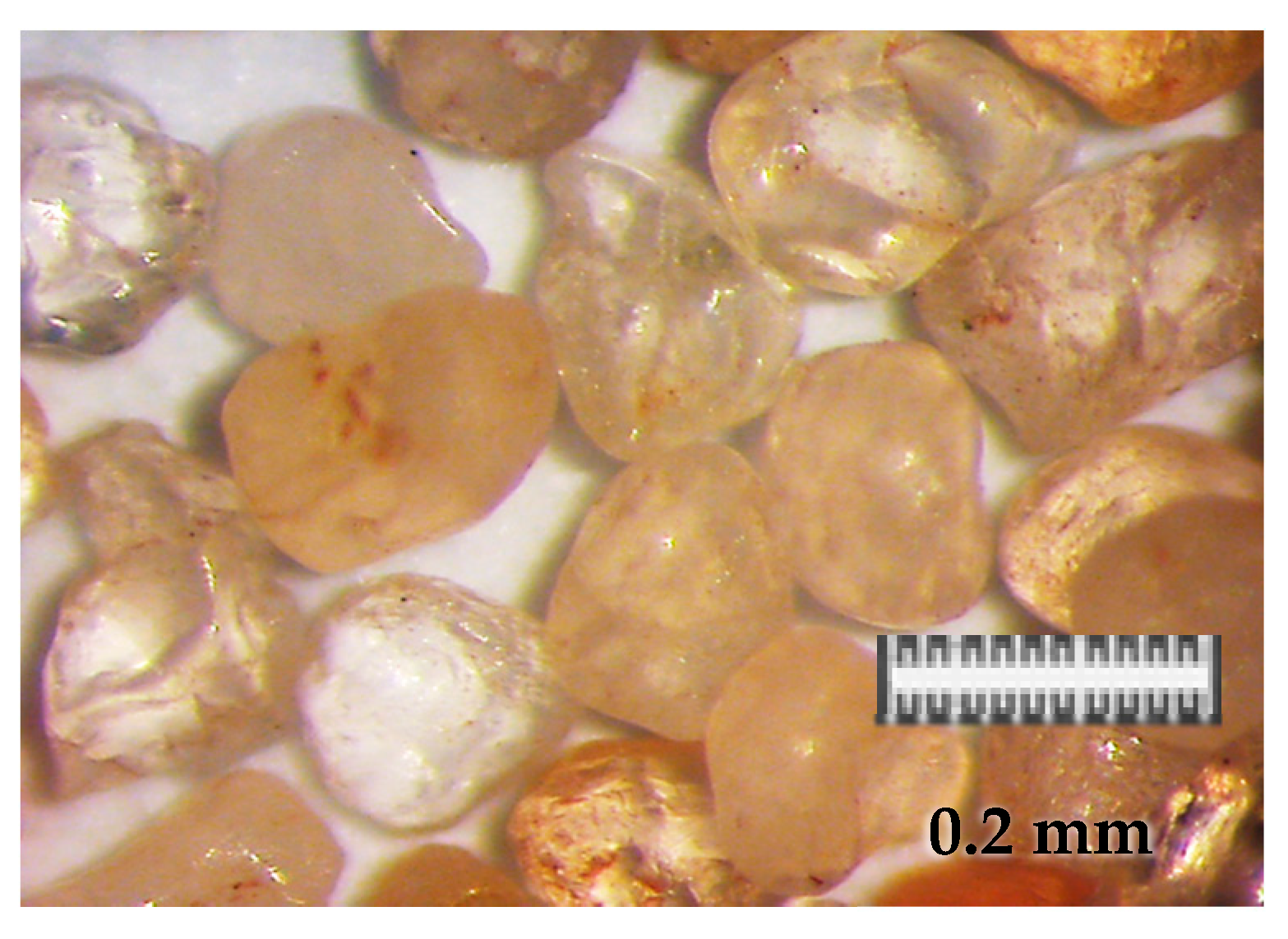
2.3. Abrasive Characterization
2.4. Test Parametres and Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
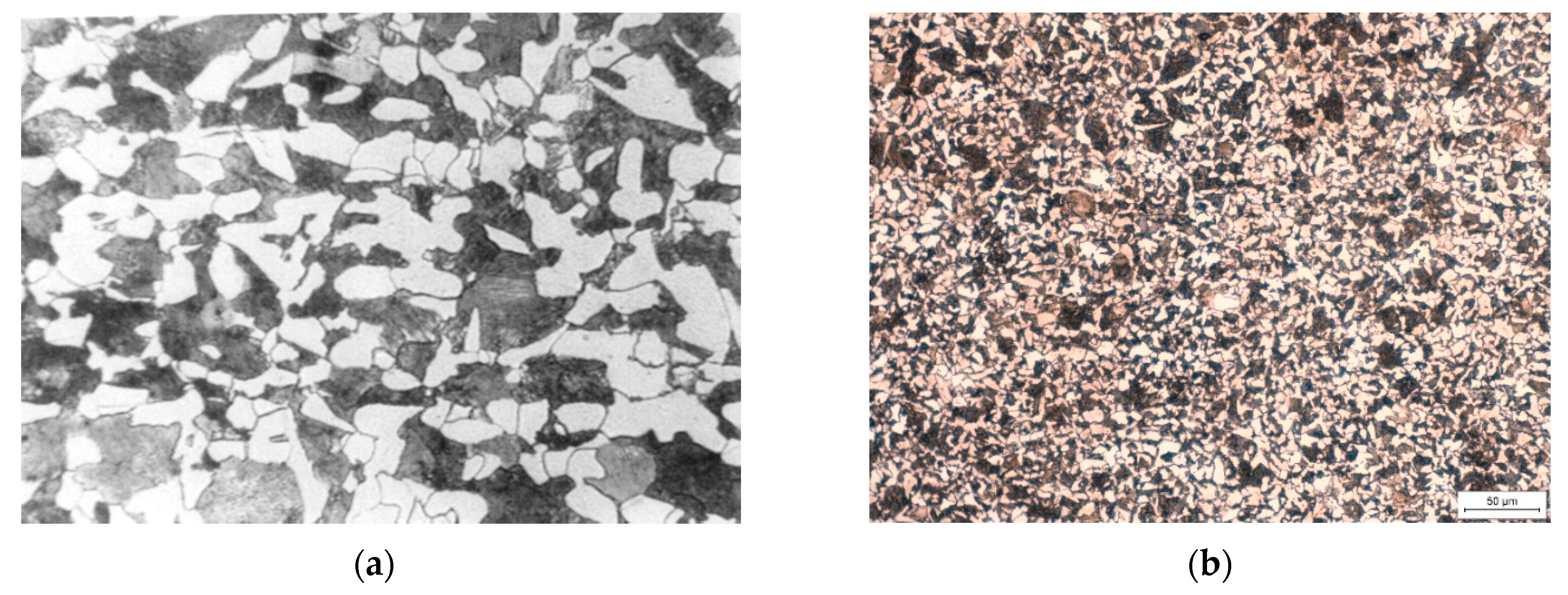
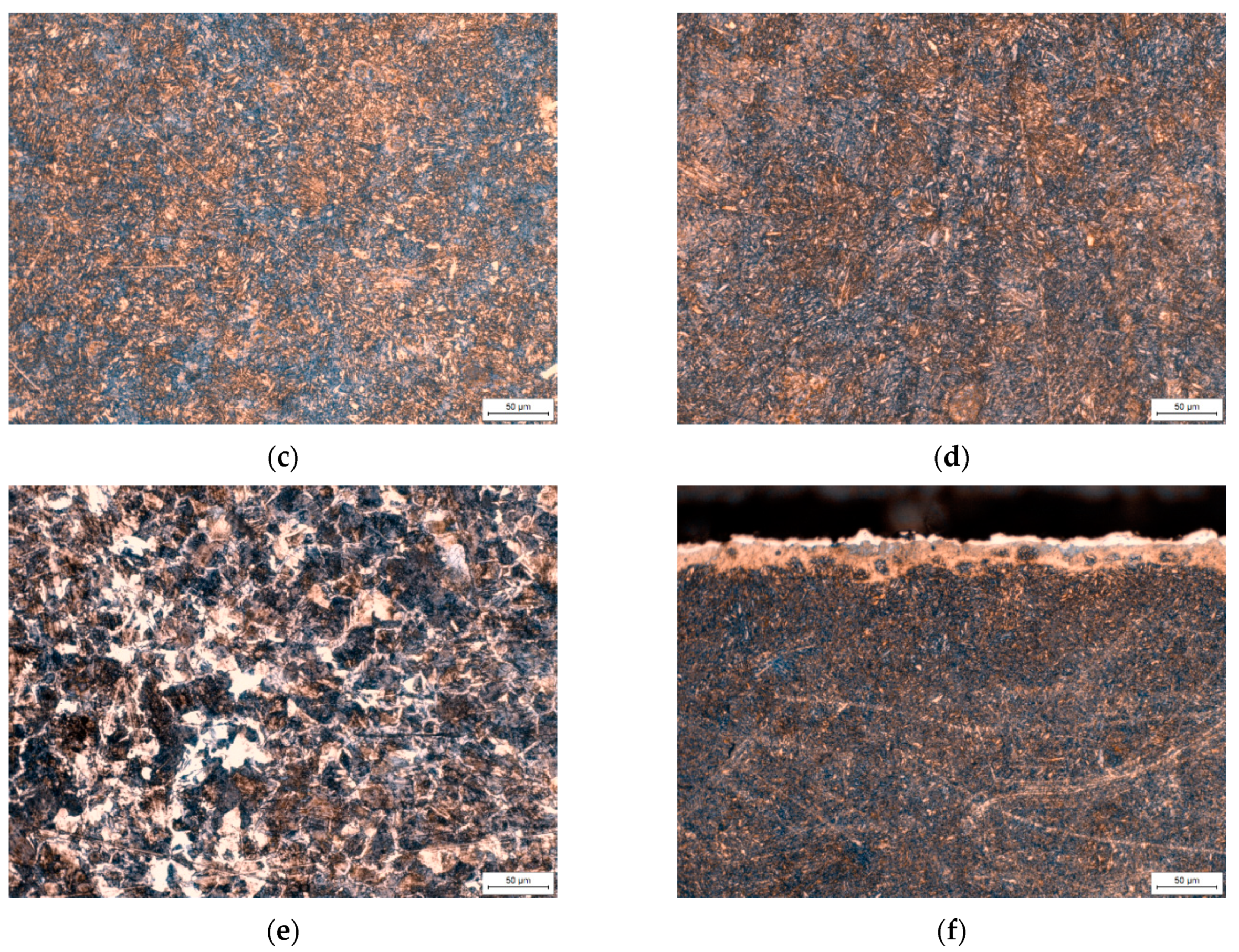
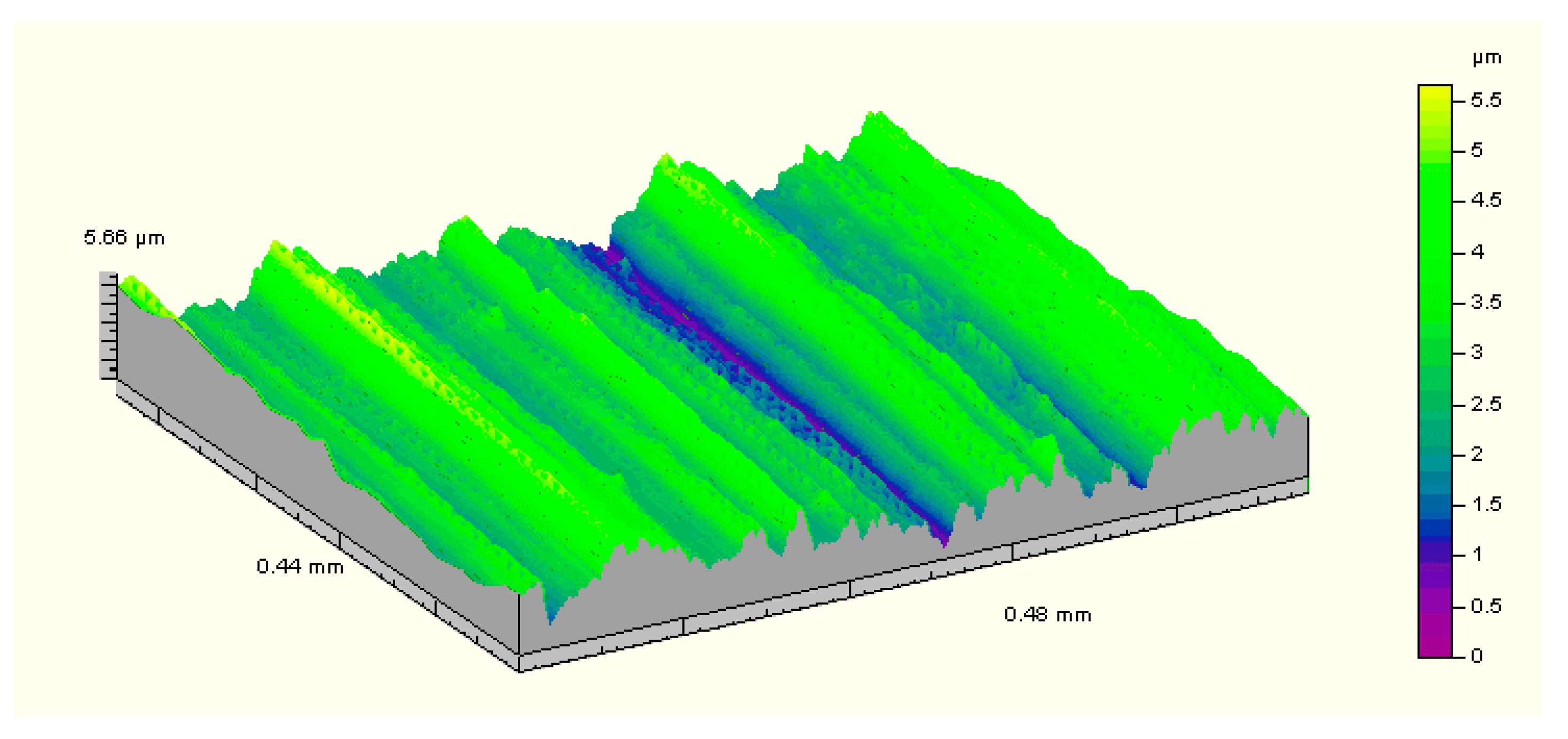
3.1. Sample Properties
- (1)
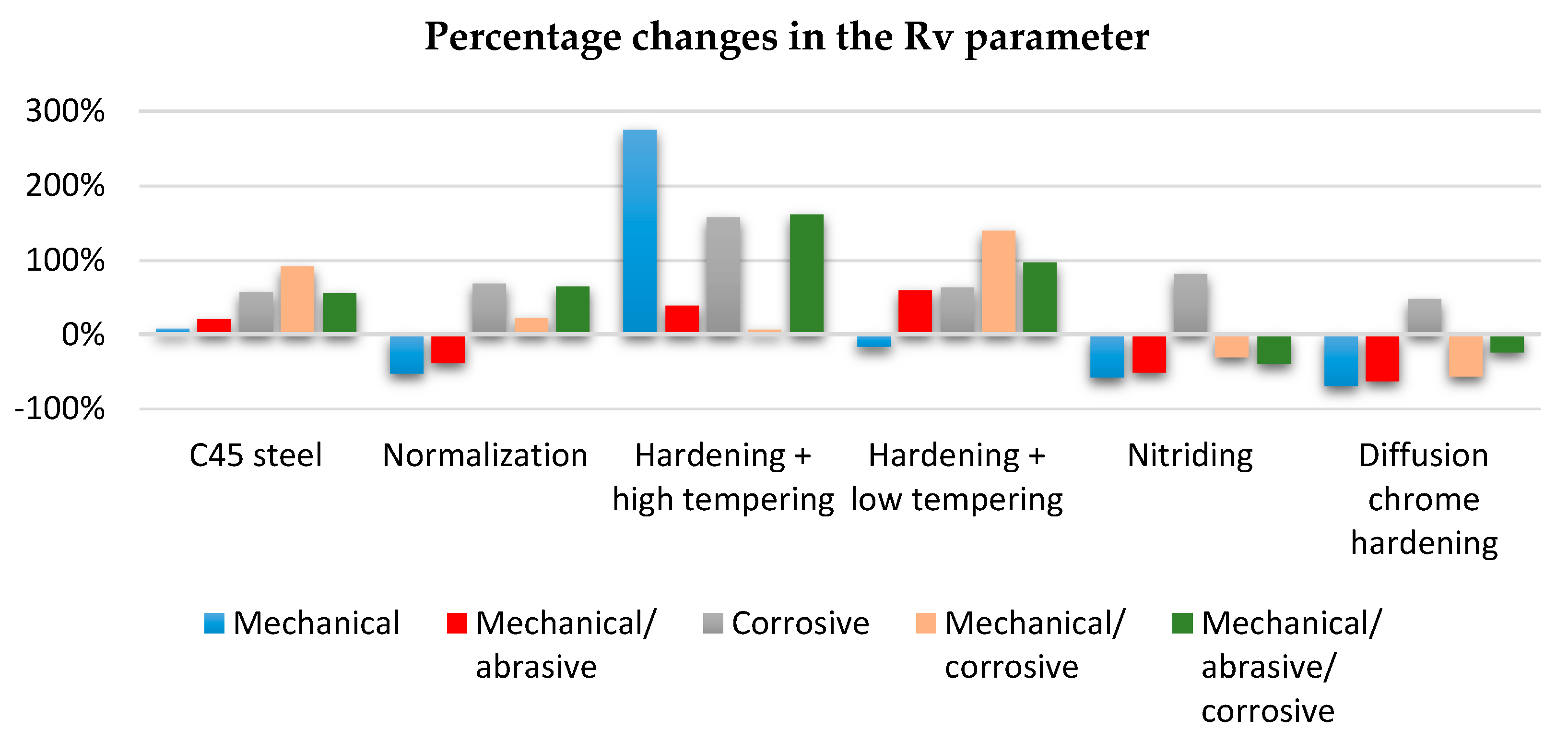
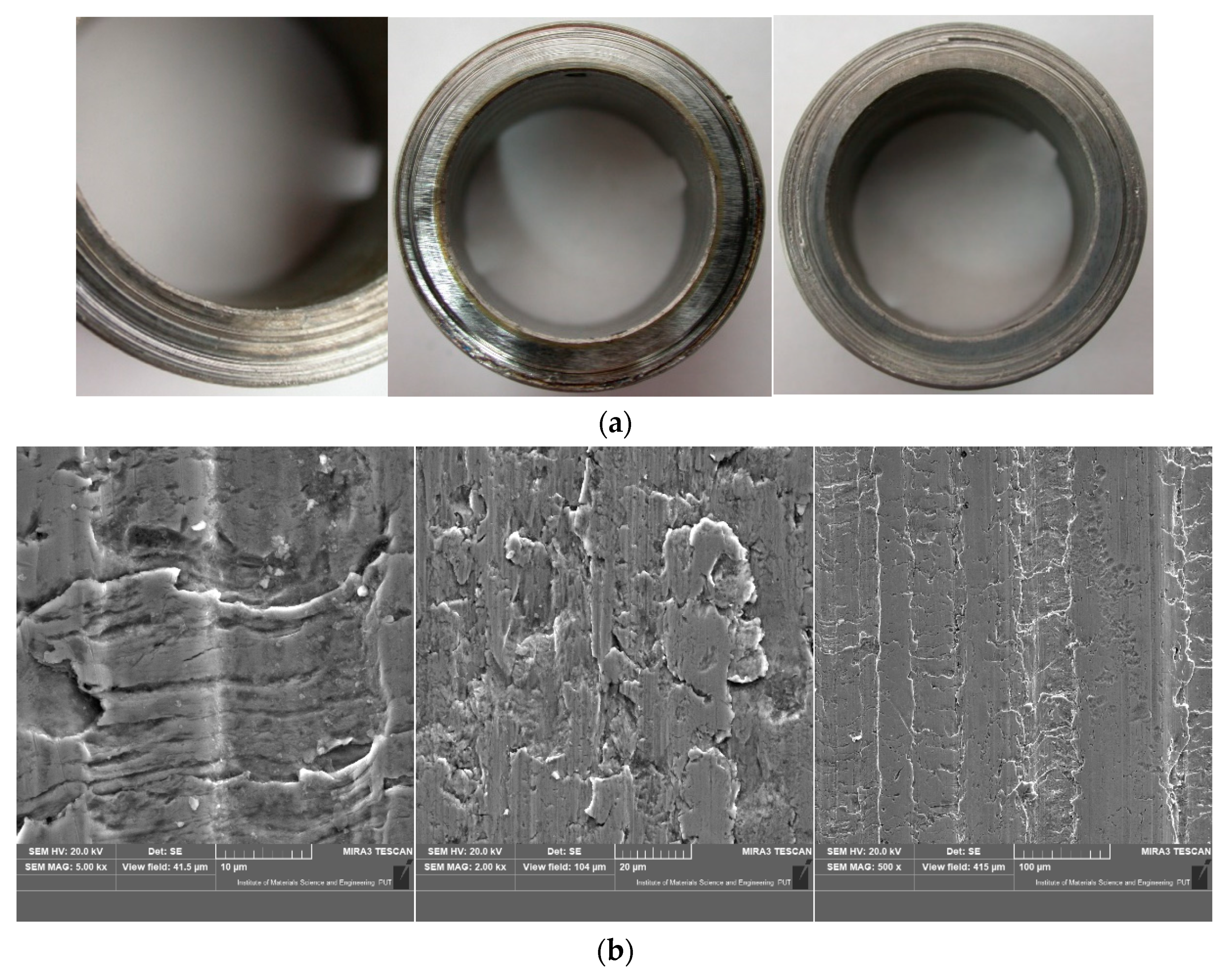
- In the process of tribological wear, the thermochemically treated surface layers (nitriding and chroming) were smoothed, which indicates a decrease in the Rv parameter.
- (2)
- After the corrosive wear processes, there was an increase in roughness expressed by the Rv parameter.
- (3)
- As a result of wear tests, there was no clear tendency for the Rv parameter.
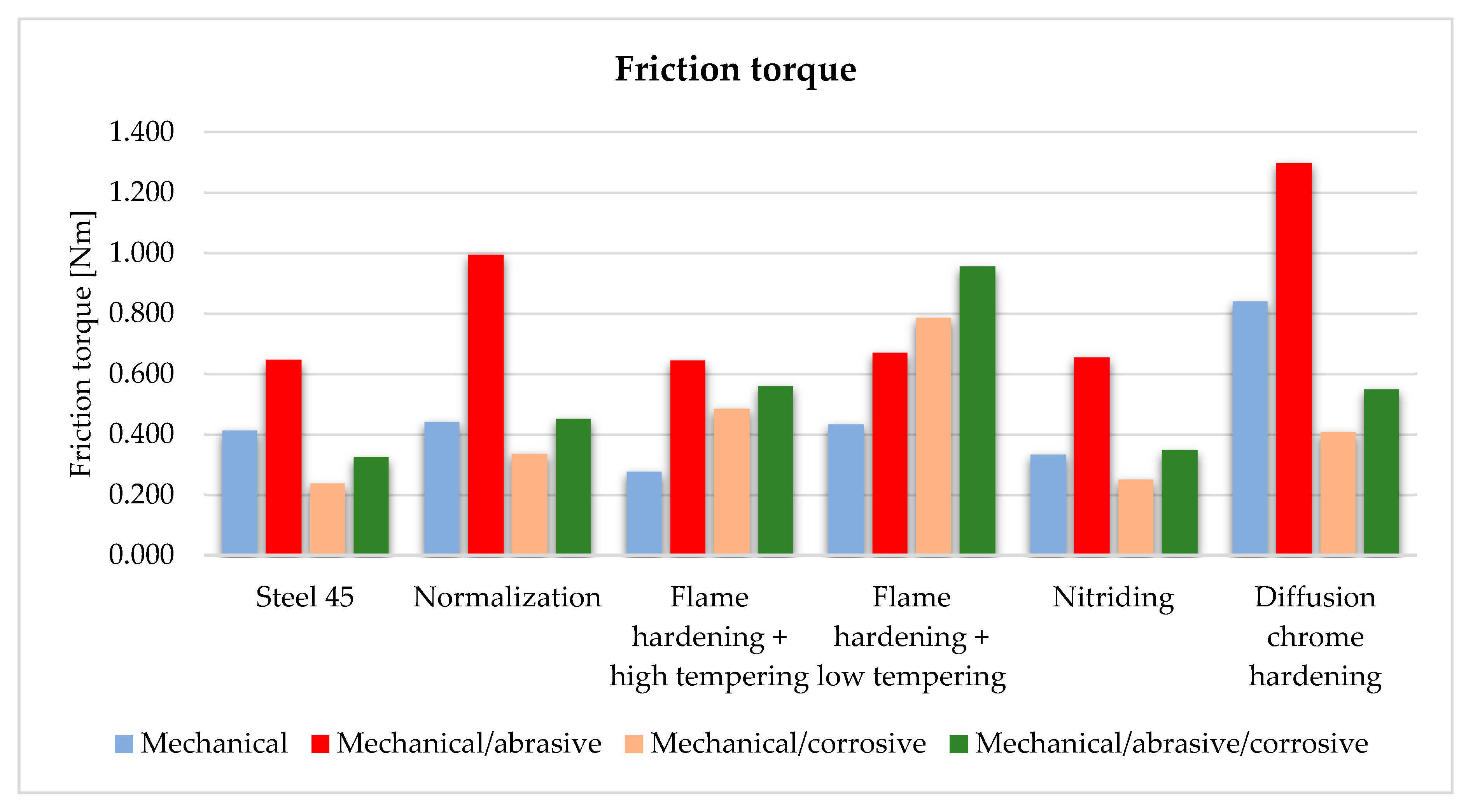
3.2. Friction Torque Calculation
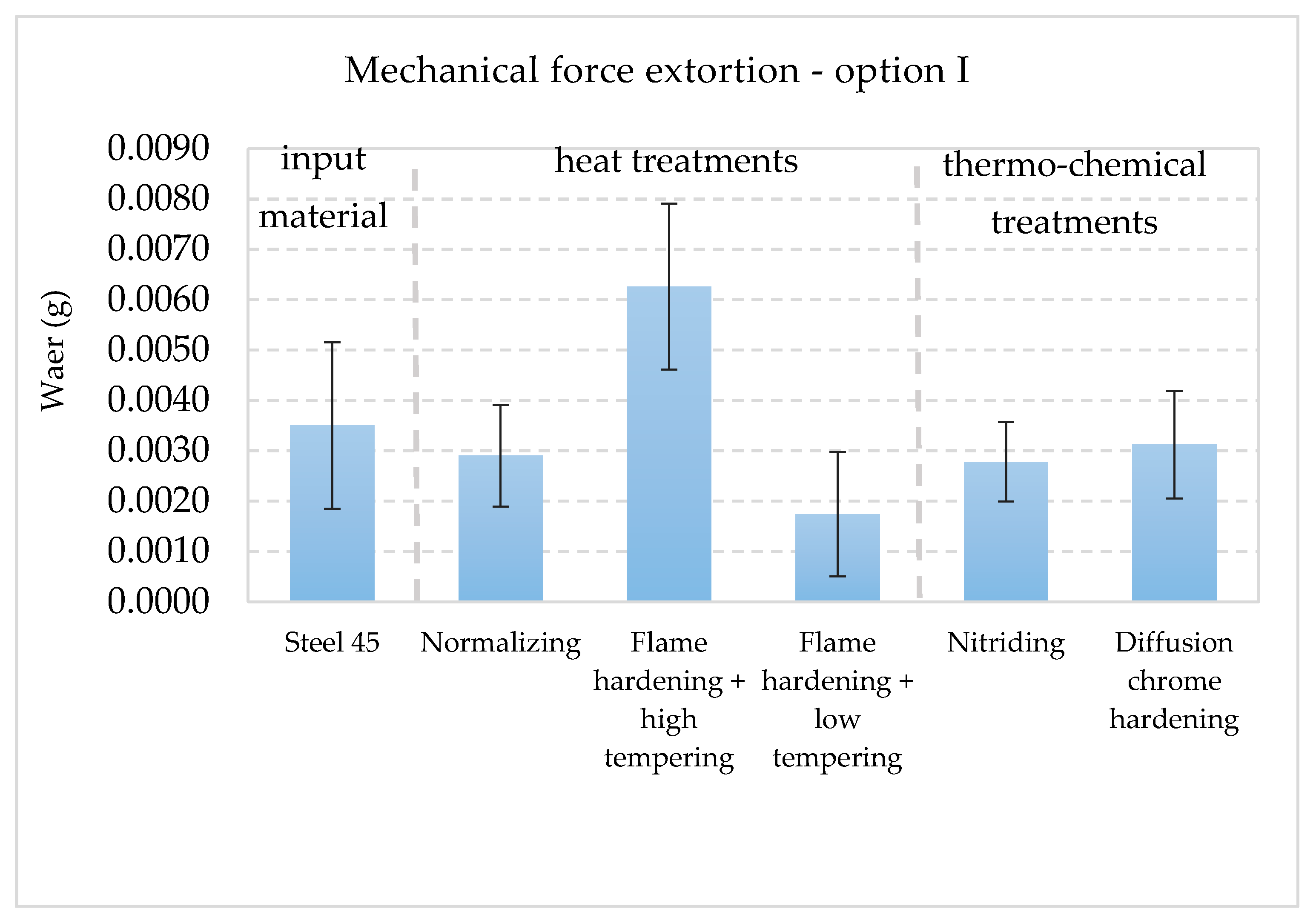
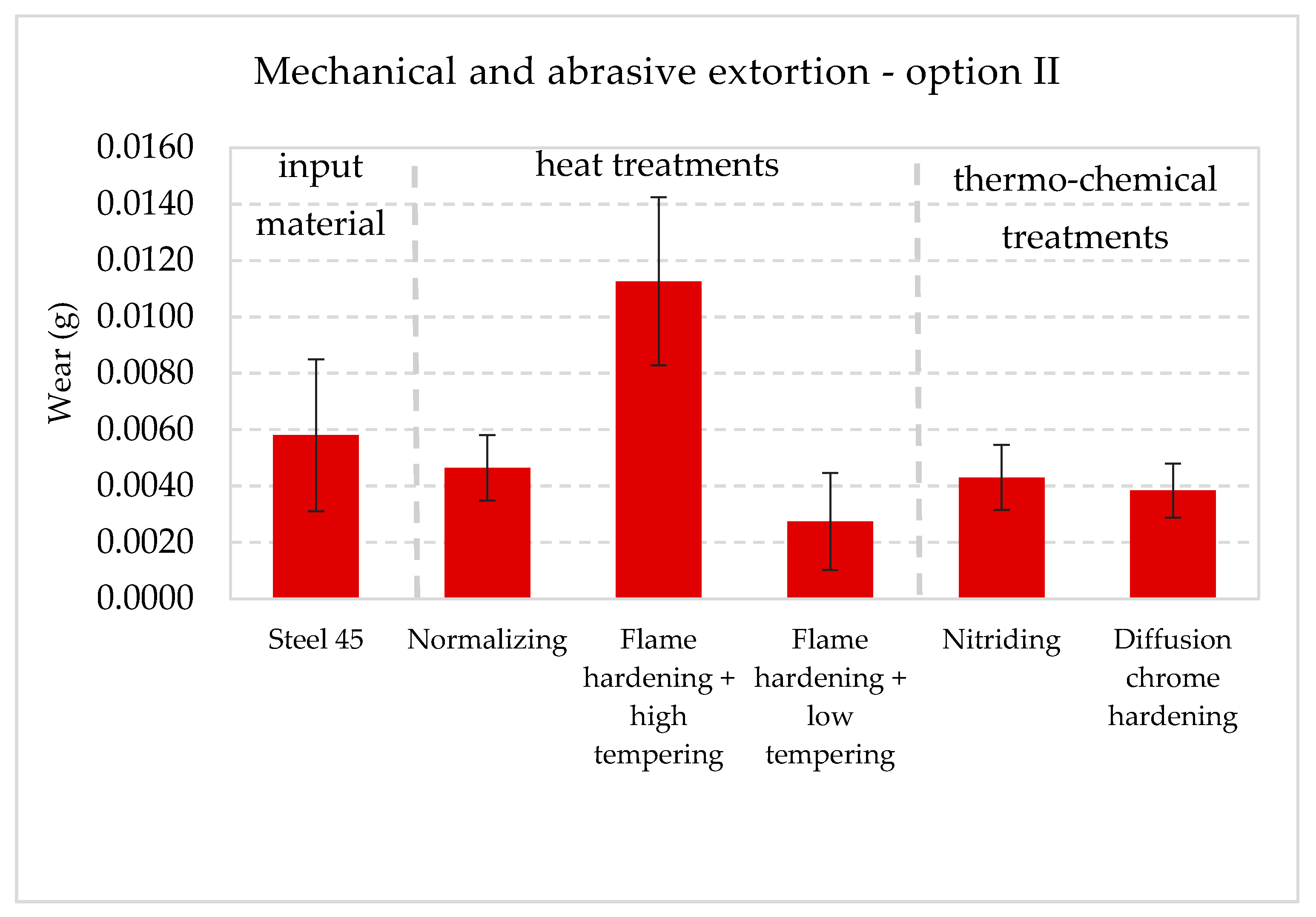
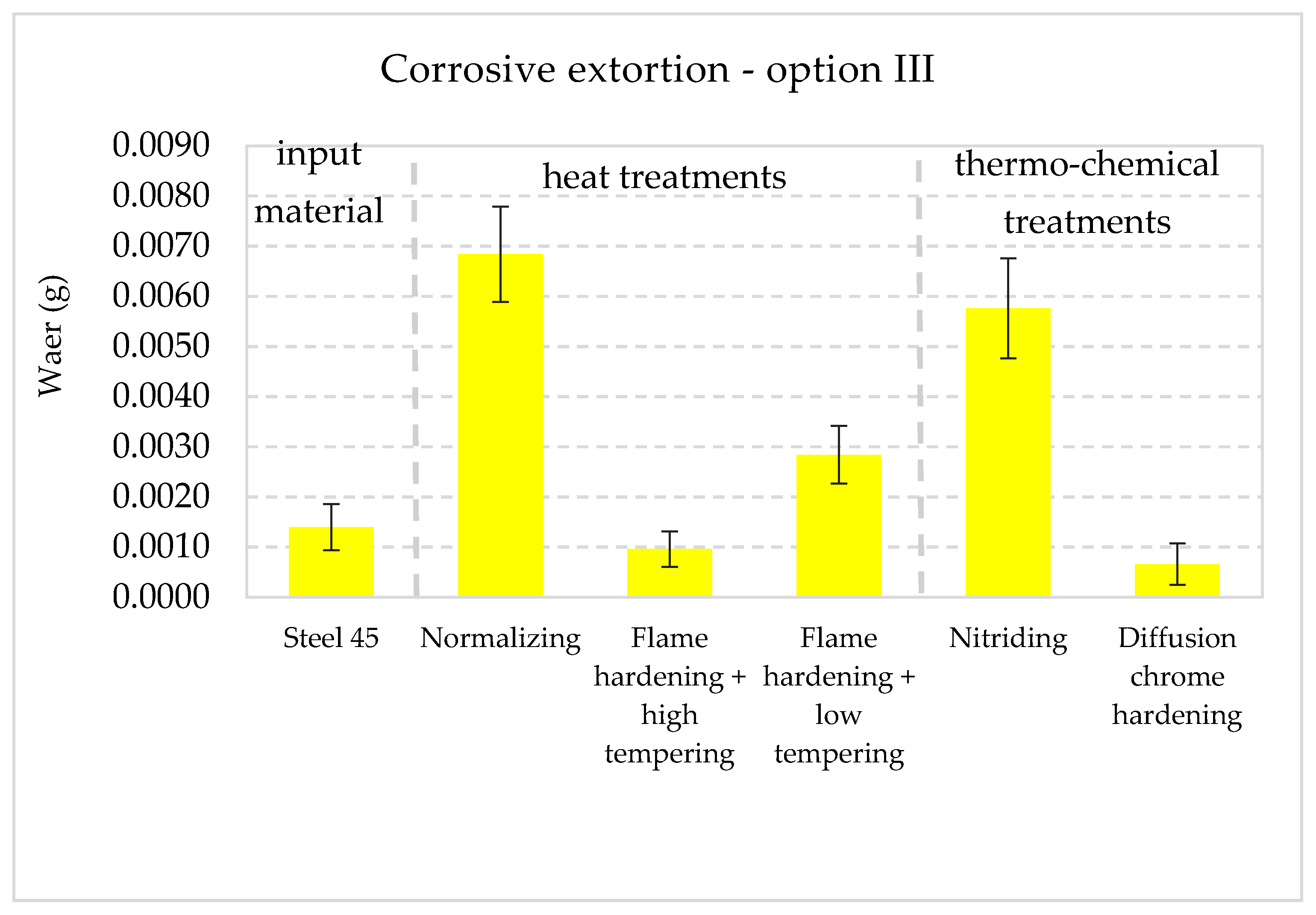
3.3. Wear Test Results
- (1)
- Radical increase in wear for option II,
- (2)
- Values of wear in increasing order were similar to option I, except for the chrome hardened layer.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selech, J. Assessment of the Surface Layer Influence on the Components of Abrasive-Corrosive Wear. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Machines and Transportation, Poznan University of Technology, Poznan, Poland, 5 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Medyński, A.; Janus, A. Effect of heat treatment parameters on abrasive wear and corrosion resistance of austenitic nodular cast iron Ni–Mn–Cu. Arch. Civil Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.W.; Friedersdorf, F.J.; Madsen, B.W.; Cramar, S.D. Methods of measuring wear—Corrosion synergism. Wear 1995, 181–183, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, R.E.J.; Ball, A. On the synergistic effects of abrasion and corrosion during wear. Wear 1983, 87, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, A.W.; Stachowiak, G.W. Predicting synergism between corrosion and abrasive wear. Wear 1988, 123, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A. Experimental studies on the influence of abrasive materials on the wear of hard-wearing steels. Tribologia 2018, 5, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoria, E.S. Application of the ring-on-ring test for abrasive wear modeling of rolling undercarriage components in track-type machines. Wear 2004, 257, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duanjie, L.; Thomas, J.; Leroux, P. Block-On-Ring Sliding Wear Evaluation; Nanovea: Irvine, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Smazalova, E.; Houdkova, S.; Svantner, M. Tribological effects of discontinuous block-on-ring test. In Proceedings of the METAL 2014, Brno, Czech Republic, 21–23 May 2014; pp. 1004–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Zambrano, O.A.; Gomez, J.A.; Coronado, J.J.; Rodriguez, S.A. The sliding wear behaviour of steels with the same hardness. Wear 2019, 418–419, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Mischler, S. Modeling tribocorrosion of passive metals—A review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2018, 22, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, F. Effect of halide concentration on tribocorrosion behaviour of 304SS in artificial seawater. Corros. Sci. 2015, 99, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, S.; Gok, M.S. Effect of sliding wear and electrochemical potential on tribocorrosion behaviour of AISI 316 stainless steel in seawater. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Bayon, R.; Pagano, F.; Igartua, A.; Arredondo, A.; Arana, J.L.; Gonzalez, J.J. Tribocorrosion behaviour of mooring high strength low alloy steels in synthetic seawater. Wear 2015, 338–339, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, P.; Reizer, R.; Wieczorowski, M.; Krolczyk, G. Material ratio curve as information on the state of surface topography—A review. Precis. Eng. 2020, 65, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annappa, S.; Basavarajappa, S. Some studies on three-body abrasive wear behaviour of hardfaced steel alloy for agricultural plough tool application. Int. J. Abras. Technol. 2016, 7, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Xing, J.; Li, W.; Tu, X.; Jian, Y. Effect of chromium-inducted (Fe, Cr)3C toughness improvement on the two-body abrasive wear behaviors of white cast irons. Wear 2020, 456–457, 203363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-Z.; Liu, C.-P.; Ren, R.-M.; Wu, S.; Yin, H.-X.; Cong, T.; Li, X. Effect of nonuniform microstructure on wear property of ER8 wheel steel. Wear 2020, 458, 203416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligier, K.; Napiórkowski, J.; Lemecha, M. Effect of Abrasive Soil Mass Grain Size on the Steel Wear Process. Tribol. Ind. 2020, 42, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, R.; Zhao, X.; Chen, C.; Pan, R. Study on the surface microstructure evolution and wear property of bainitic rail steel under dry sliding wear. Wear 2020, 448–449, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatorski, J.; Sierpecka, B. Prevention against tribocorrosion throughout thermochemical treatment. Tribologia 2003, 5, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Z.; Zhou, P.; Shi, J. Some Factors Influencing Corrosion-Erosion Performance of Materials. Wear Mater. 1987, 2, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Bialobrzeska, B.; Kostencki, P. Abrasive wear characteristics of selected low-alloy boron steels as measured in both field experiments and laboratory tests. Wear 2015, 328, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Szafran, M.; Macek, W.; Marchenko, S.; Hejwowski, T. Abrasion Resistance of S235, S355, C45, AISI 304 and Hardox 500 Steels with Usage of Garnet, Corundum and Carborundum Abrasives. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Gao, Y.; Yang, K.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, Y. Microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-Cr13-C-Nb hardfacing alloy with Ti addition. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatorski, J.; Kasprzyska, E. Tribologcal properties of chromized difussion layers in conditions of sliding friction and concentrated contact. Tribologia 2002, 6, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Mahu, G.; Munteanu, C.; Istrate, B.; Benchea, M.; Lupescu, S. Influence of Al2O3-13TiO2 powder on a C45 steel using atmospheric plasma spray process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 444, 032010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming-xue, S.; Jin-peng, Z.; Xiang-kai, M.; Xiao, L.; Xu-dong, P. Influence of Al2O3 particles on the friction and wear behaviors of nitrile rubber against 316L stainless steel. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2015, 16, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.C.; Li, S.Z.; Jiang, X.X.; Zhang, T.C. Effect of γ phase on corrosive wear of duplex stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Corrosion 1995, 51, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.X.; Li, S.Z.; Tao, D.D.; Yang, J.X. Accelerative effect of wear on corrosion of high-alloy stainless steel. Corrosion 1993, 49, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, B. Measurement of erosion—Corrosion synergism with a slurry wear test apparatus. Wear 1988, 123, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, N.B.; Hutchings, I.M. Influence of particle fracture in the high-stress and low-stress abrasive wear of steel. Wear 1999, 233–235, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diomidis, N.; Celis, J.-P.; Ponthiaux, P.; Wenger, F. Tribocorrosion of stainless steel in sulfuric acid: Identification of corrosion–wear components and effect of contact area. Wear 2010, 269, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.; Salasi, M.; Stachowiak, G. Three-Body Abrasion Corrosion Studies of High-Cr Cast Irons: Benefits and Limitations of Tribo electrochemical Methods. J. Bio. Tribo. Corros. 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahagi, Y.; Mizutani, Y. Corrosive Wear of Cast iron in Sulphuric Acid. Trans. ASME 1987, 109, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.measurement.ru/gk/mehan/03/020.htm (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Helsel, R. Visual Programming with HP VEE; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Selech, J.; Nadolny, K. Analysis of abrasive-mechanical effects of tribological processes in model conditions. Sci. Pap. Poznan Univ. Technol. Ser. Mach. Transp. 2006, 60, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatsen, K.; Subramanian, C.; Summerville, E. Three-body abrasion of surface engineered die steel at elevated temperatures. Wear 1997, 203–204, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolny, K.; Selech, J. Analysis of abrasive-mechanical effects of tribological processes in modelled conditions. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2007, 52, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Tyczewski, P. Interpretative Models of the Abrasive-Corrosive Wear Mechanism. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Machines and Transportation, Poznan University of Technology, Poznań, Poland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Adamiak, M.; Górka, J.; Kik, T. Comparison of abrasion resistance of selected constructional materials. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 37, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Pixiang, L.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Polycarpou, A. Three-body abrasive wear by (silica) sand of advanced polymeric coatings for tilting pad bearings. Wear 2017, 382–383, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, M.G.; Gant, A.; Hutchings, I.M. Rotating wheel abrasive wear testing. In Measurement Good Practice Guide No. 55; National Physical Laboratory: Teddington, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Quraishi, M.A. Investigation of Adsorption of Isoniazid Derivatives at Mild Steel/Hydro-chloric Acid Interface: Electrochemical and Weight Loss Methods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 123, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljourani, J.; Golozar, M.A.; Raeissi, K. The Inhibition of Carbon Steel Corrosion in Hydrochloric and Sulfuric Acid Media Using Some Benzimidazole Derivatives. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 121, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Yu, B.D. Effect of N+Cr alloying on the microstructures and tensile properties of Hadfield steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.L.; Tang, J.-L. Wear-corrosion behavior of cast-in composite materials reinforced by WC particles. Wear 1990, 138, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- De Mello, J.D.B.; Labiapari, W.S. Ardila, Strain Hardening: Can it Affect Abrasion Resistance. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardell, J.; Prakash, B. High-temperature friction and wear behavior of different tool steels during sliding against Al–Si coated high-strength steel. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, G.W. Particle angularity and its relationship to abrasive and erosive wear. Wear 2000, 241, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, A.; Rendnón, J.; Olsson, M. Wear behaviour of some low alloyed steels under combined impact/abrasion contact conditions. Wear 2001, 250, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of Wear | Tested Material | Abrasive | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| abrasive | bainitic steel | - | [20] |
| abrasive, corrosive, erosive | steel 45 | fused alumina | [21,22,23,24,25,26] |
| abrasive, corrosive | - | ||
| abrasive, corrosive, erosive | alloy cast iron | fused alumina | [22,26] |
| abrasive, corrosive | stainless steel | Al2O3 | [27,28,29] |
| abrasive, corrosive | abrasive strip | [30] | |
| abrasive, corrosive | 2% mixture of silica sand in water | [31] | |
| abrasive | mild steel | silica sand abrasive particles | [32] |
| Content (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu |
| 0.45–0.50 | 0.50–0.58 | 0.17–0.37 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.30 |
| Resistance to Strain | Plasticity Limit | Elongation | Impact Resistance | Hardness | Density | Thermal Conduction Coefficient | Modulus of Elasticity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rm | Re | A | KU | HV | ρ | l | E |
| MPa | MPa | % | J | HV 10 | g·cm−3 | W·m−1·K−1 | GPa |
| ≥600 | ≥355 | 16 | ≥32 | 240 | 7.821 | 48.1 | 206 |
| No. | Treatment Option | Parameters of Basic Types of Treatment | Additional Treatment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. To (°C) | Time to (h) | Cooling/Ambience | |||
| 1 | Normalizing | 840 | 1.2 | in the air | - |
| 2 | Flame hardening + high tempering | 880 580 | 7 min. 1 | in water and in the air | - |
| 3 | Flame hardening + low tempering | 880 170 | 7 min. 1.5 | in water and in the air | - |
| 4 | Nitriding | 530 | 5 | atmosphere of ionized nitrogen | normalizing before nitriding; at the temperature of 840 °C, cooling in the air |
| 5 | Diffusion chrome hardening | 1000–1050 | 4 | chrome hardening powder | heat hardening after chrome hardening; hardening at 850 °C tampering at 160 °C (in oil) for 2 h |
| No. | Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pressure force | P | 160 | N |
| 2. | Peripheral speed | v | 0.2 | m/s |
| 3. | Corrosive liquid concentration | m | 10% | H2SO4 |
| 4. | Abrasive material (sand) fraction | D | 0.2–0.3 | mm |
| 5. | Stream of abrasive material inflow | Q | 0.2 | g/cm2·s |
| 6. | Friction node temperature | T | 23 ± 2 | °C |
| Experiment | Extortion—The Factor | Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Abrasive | Corrosive | ||
| I | + | − | − | II = IM |
| II | + | + | − | III = IM + IA |
| III | − | − | + | IIII = IC |
| IV | + | − | + | IIV = IM + IC |
| V | + | + | + | IV = IM +IC + IA |
| Condition of the Surface Layer | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Confidence Half Interval | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel 45 | 218.59 | 16.36 | 28.687 | 0.075 |
| Normalizing | 253.22 | 11.92 | 20.901 | 0.047 |
| Flame hardening + high tempering | 321.05 | 14.11 | 24.733 | 0.044 |
| Flame hardening + low tempering | 704.31 | 26.47 | 46.394 | 0.038 |
| Nitriding | 481.95 | 18.64 | 32.680 | 0.039 |
| Diffusion chrome hardening | 1918.75 | 75.78 | 132.834 | 0.039 |
| Condition of the Core | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Confidence Half Interval | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel 45 | 201.70 | 8.35 | 14.635 | 0.041 |
| Normalizing | 214.87 | 3.07 | 5.381 | 0.014 |
| Flame hardening + high tempering | 283.83 | 7.61 | 13.342 | 0.027 |
| Flame hardening + low tempering | 734.20 | 14.21 | 24.910 | 0.019 |
| Nitriding | 284.60 | 14.13 | 24.762 | 0.050 |
| Diffusion chrome hardening | 611.40 | 26.14 | 45.825 | 0.043 |
| Parameter | Unit | Steel 45 | Normalizing | Flame Hardening + High Tempering | Flame Hardening + Low Tempering | Nitriding | Diffusion Chrome Hardening |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | µm | 0.567 | 0.670 | 0.683 | 0.667 | 0.730 | 1.423 |
| Rtm | µm | 3.147 | 3.780 | 3.810 | 3.743 | 4.757 | 7.997 |
| Rz | µm | 3.260 | 3.907 | 3.953 | 3.863 | 4.930 | 8.510 |
| Rv | µm | 4.093 | 4.877 | 4.753 | 4.563 | 7.243 | 10.833 |
| Rq | µm | 0.703 | 0.833 | 0.843 | 0.827 | 0.977 | 1.827 |
| Rpk | µm | 0.440 | 0.570 | 0.567 | 0.583 | 1.217 | 2.227 |
| Rk | µm | 1.750 | 2.153 | 2.187 | 2.233 | 2.217 | 4.400 |
| Rvk | µm | 0.900 | 1.023 | 1.007 | 0.900 | 1.093 | 1.697 |
| Sa | µm | 0.751 | 0.542 | 0.442 | 0.777 | 0.895 | 1.022 |
| Sq | µm | 0.910 | 0.687 | 0.550 | 0.950 | 1.145 | 1.320 |
| Sp | µm | 2.245 | 2.150 | 1.883 | 2.630 | 7.170 | 7.197 |
| Sv | µm | 2.340 | 2.040 | 1.803 | 3.160 | 3.680 | 4.900 |
| St | µm | 4.585 | 4.190 | 3.687 | 5.790 | 10.850 | 12.133 |
| Sz | µm | 4.410 | 4.027 | 3.603 | 5.305 | 9.435 | 10.960 |
| Ssk | - | −0.233 | −0.193 | −0.231 | −0.237 | 0.525 | 0.432 |
| Sku | - | 2.360 | 3.450 | 2.990 | 2.655 | 5.190 | 4.630 |
| Extortion | C45E Steel | Normalizing | Flame Hardening + High Tempering | Flame Hardening + Low Tempering | Nitriding | Diffusion Chrome Hardening |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
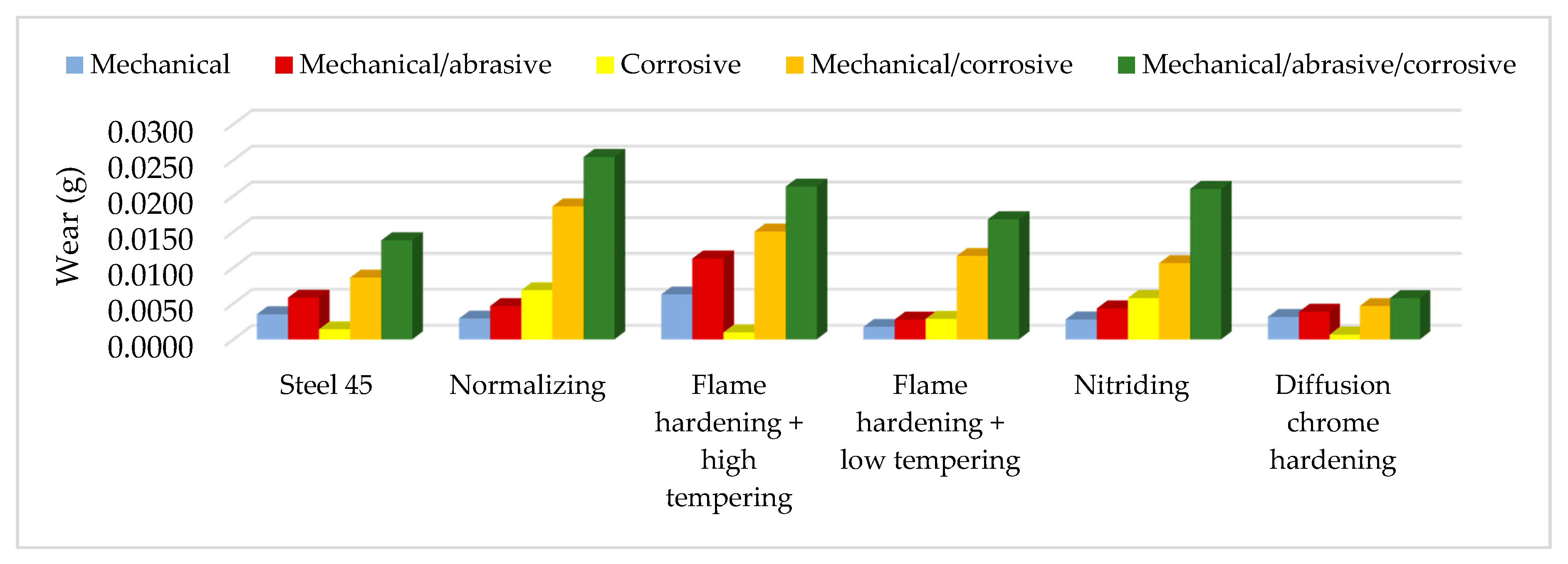
| Mechanical | 8% | −52% | 276% | −17% | −58% | −69% |
| Mechanical/abrasive | 21% | −38% | 40% | 60% | −50% | −62% |
| Corrosive | 58% | 69% | 159% | 64% | 82% | 48% |
| Mechanical/corrosive | 92% | 23% | 7% | 141% | −30% | −56% |
| Mechanical/abrasive/corrosive | 56% | 65% | 162% | 97% | −39% | −23% |
| Type of Extortion | Mechanical | Mechanical/Abrasive | Corrosive | Mechanical/Corrosive | Mechanical/Abrasive/Corrosive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Research option | I | II | III | IV | V |
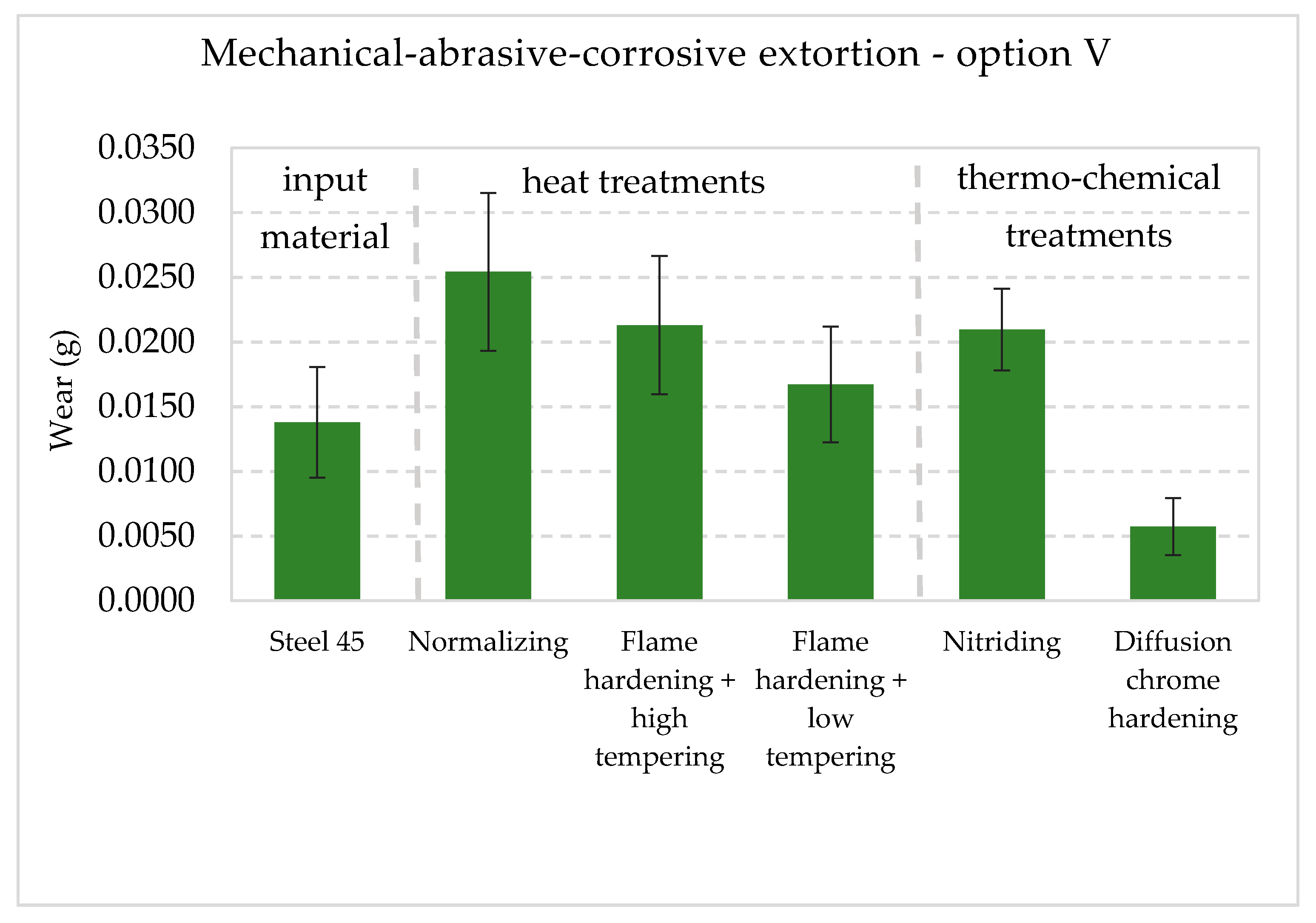
| C45 steel | 0.0035 | 0.0058 | 0.0014 | 0.0086 | 0.0138 |
| Normalization | 0.0029 | 0.0046 | 0.0068 | 0.0185 | 0.0254 |
| Hardening + high tempering | 0.0063 | 0.0113 | 0.0010 | 0.0150 | 0.0213 |
| Hardening + low tempering | 0.0017 | 0.0027 | 0.0028 | 0.0116 | 0.0167 |
| Nitriding | 0.0028 | 0.0043 | 0.0058 | 0.0106 | 0.0210 |
| Chrome hardening | 0.0031 | 0.0038 | 0.0007 | 0.0046 | 0.0057 |
| Extortion/Surface Layer | Steel 45 | Normalizing | Flame Hardening + High Tempering | Flame Hardening + Low Tempering | Nitriding | Diffusion Chrome Hardening |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | −21 | 0 | −117 | 41 | 3 | −7 |
| Mechanical/Abrasive | −26 | 0 | −146 | 53 | 7 | 17 |
| Corrosive | 79 | 0 | 85 | 59 | 15 | 90 |
| Mechanical/Corrosive | 54 | 0 | 19 | 37 | 43 | 75 |
| Mechanical/Abrasive/Corrosive | 46 | 0 | 16 | 34 | 17 | 78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selech, J.; Ulbrich, D.; Romek, D.; Kowalczyk, J.; Wlodarczyk, K.; Nadolny, K. Experimental Study of Abrasive, Mechanical and Corrosion Effects in Ring-on-Ring Sliding Contact. Materials 2020, 13, 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214950
Selech J, Ulbrich D, Romek D, Kowalczyk J, Wlodarczyk K, Nadolny K. Experimental Study of Abrasive, Mechanical and Corrosion Effects in Ring-on-Ring Sliding Contact. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214950
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelech, Jaroslaw, Dariusz Ulbrich, Dawid Romek, Jakub Kowalczyk, Konrad Wlodarczyk, and Karol Nadolny. 2020. "Experimental Study of Abrasive, Mechanical and Corrosion Effects in Ring-on-Ring Sliding Contact" Materials 13, no. 21: 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214950
APA StyleSelech, J., Ulbrich, D., Romek, D., Kowalczyk, J., Wlodarczyk, K., & Nadolny, K. (2020). Experimental Study of Abrasive, Mechanical and Corrosion Effects in Ring-on-Ring Sliding Contact. Materials, 13(21), 4950. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214950






