Manufacturing Parameters, Materials, and Welds Properties of Butt Friction Stir Welded Joints–Overview
Abstract
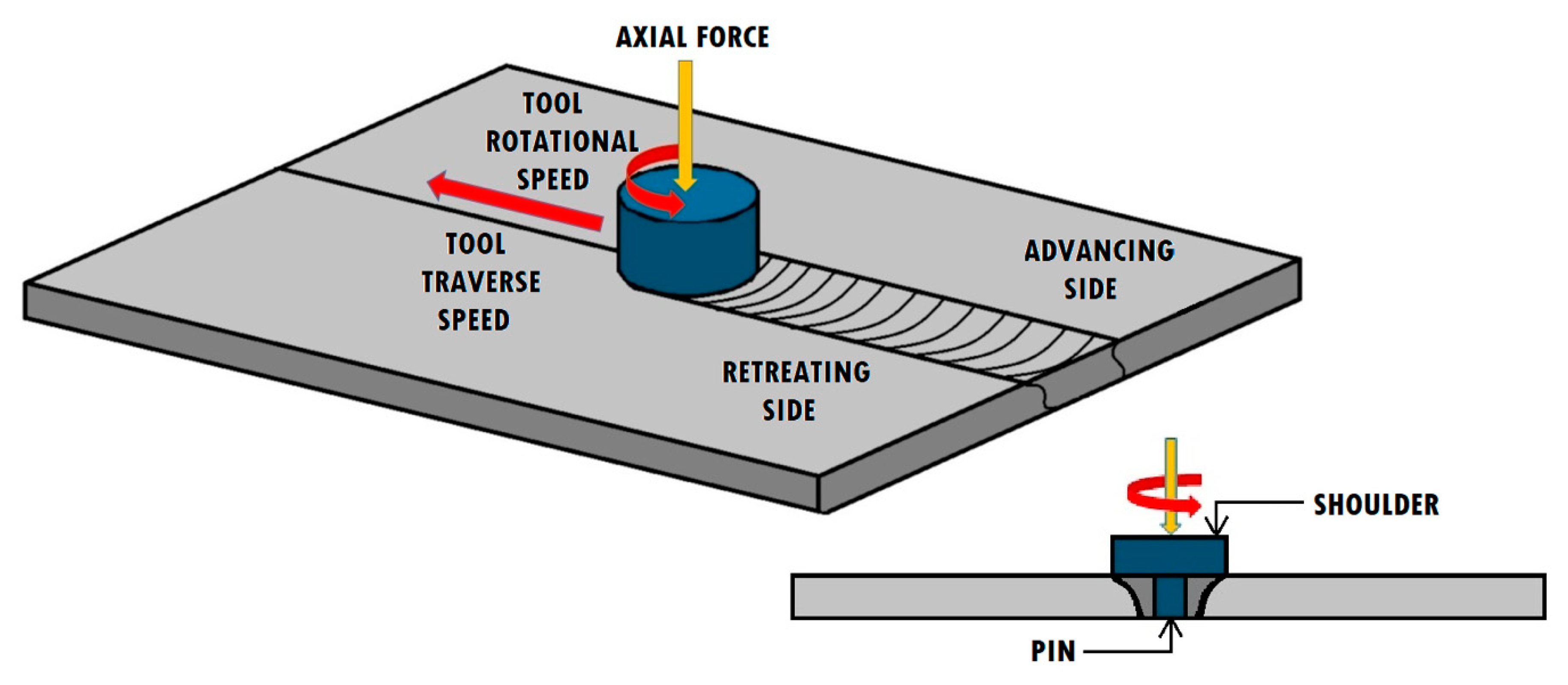
1. Introduction
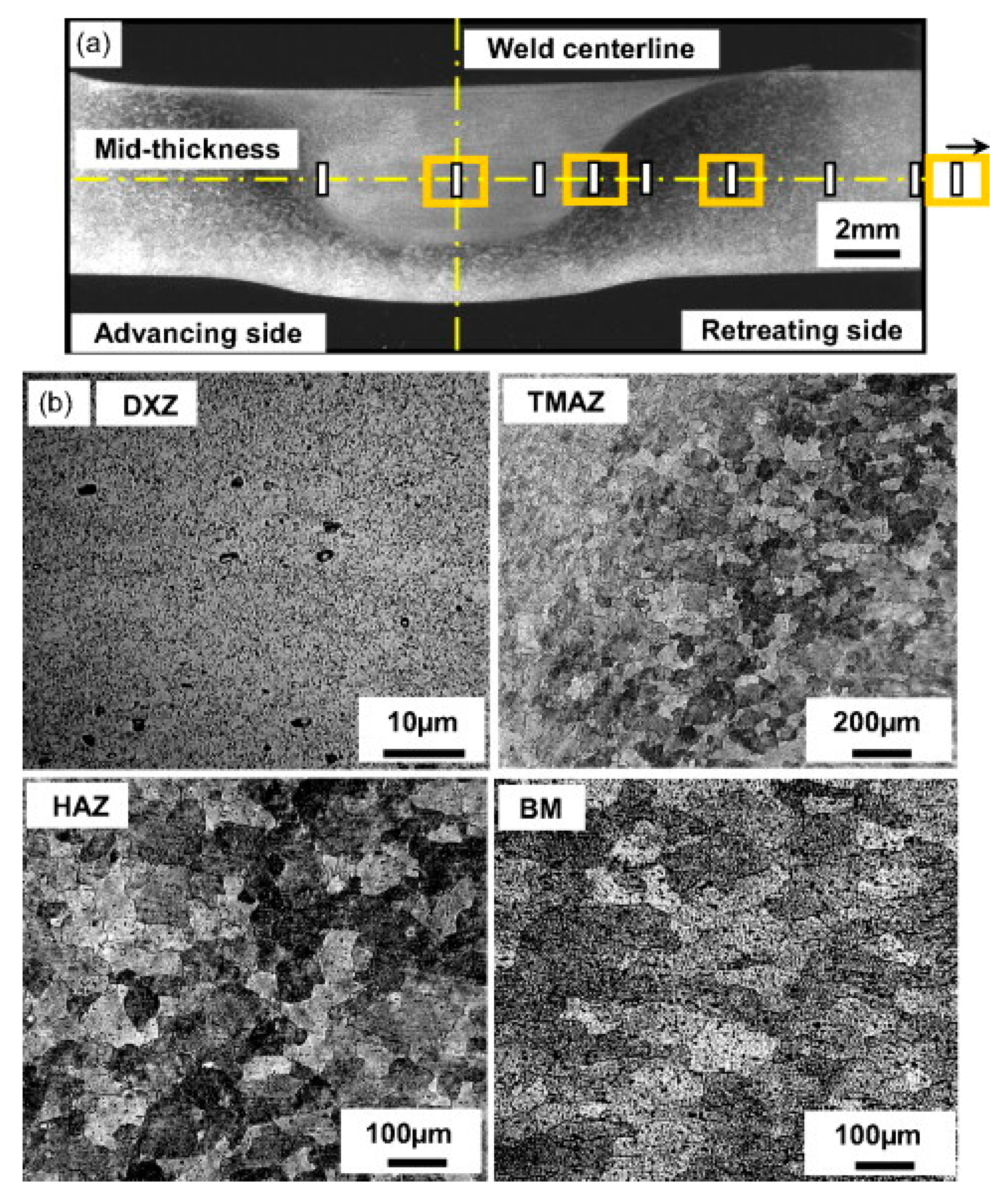
2. Methodology
3. Aluminum and Its Alloys
4. Magnesium and Its Alloys
5. Steel and Ferrous Alloys
6. Titanium and Its Alloys
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| Pure Ti | 2 | 200 | 200 | - | 2.5 | - | ~430 (420) | - | 180 (146) | - | - | [131] |
| Pure Ti | 5.6 | 50 | 110 | - | - | - | 430 (440) | - | - | 20 (25) | Defect free | [119] |
| Ti-54M fine grain | 0.1 | 100 | 275 | - | - | - | ~950 (972) | ~780 (889) | - | ~5.9 (16.5) | Defect free | [128] |
| Ti-6Al-4V fine grain | 0.1 | 125 | 325 | - | - | - | ~950 | ~760 | - | ~4.3 | Defect free | [128] |
| Ti-6Al-4V standard grain | 0.1 | 100 | 275 | - | - | - | ~930 (950) | ~720 (880) | - | ~7.7 (14) | Defect free | [128] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 2 | 101.6 | 900 | Smooth cylindrical pin | 1.6 | 2.5 | 1156.2 (1014.7) | 1067.4(941.8) | - | 21.7 (23.1) | Processing defects | [129] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 2 | 50 | 250 | Tapered pin | 2 | - | 813 (1013) | - | - | 3.2 (8.5) | - | [128] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 3 | 75 | 300 | Small shoulder and large tapered pin | - | - | 1025.0 (higher than BM) | 973.6 (higher than BM) | - | 9.7 | - | [132] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 3 | 60 | 300 | Convex shoulder and tapered pin | ~3 | - | ~1050 (~920) | ~950 (~830) | ~315 | ~33 (~21) | Cavity defects | [120] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 3 | 45 | 550 | Tapered pin | 1.75 | 0.5 | 1059 (1000) | - | - | 4 (18) | Small root flaws | [133] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 3.17 | 40 | 500 | Flat shoulder surface and tapered smooth pin | 2 | 1.5 | 1040 (1017) | - | - | 9 (20) | - | [130] |
| Ti-6Al-4V | 6 | 100 | 280 | - | - | - | 1016 (1045) | 971 (978) | 335.6 (315.4) | 9 (16) | - | [134] |
| Ti-6242 fine grain | 0.1 | 125 | 325 | - | - | - | ~950 | ~730 | - | ~4.1 | Defect free | [128] |
| Ti-6242 standard grain | 0.1 | 125 | 325 | - | - | - | ~880 (1000) | ~730 (895) | - | ~8.4 (12) | Defect free | [128] |
| TC4 | 2 | 50 | 400 | Smooth tapered pin | - | 2.5 | 953 (1036) | - | ~345 (~325) | - | - | [135] |
7. Copper and Its Alloys
8. Polymers
9. Composites
10. Dissimilar Materials
11. Conclusions and Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arunprasad, R.V.; Surendhiran, G.; Ragul, M.; Soundarrajan, T.; Moutheepan, S.; Boopathi, S. Review on Friction Stir Welding Process. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. ISSN 2018, 13, 5750–5758. [Google Scholar]
- Kossakowski, P.; Wciślik, W.; Bakalarz, M. Macrostructural Analysis of Friction Stir Welding (FSW) Joints. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 1, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, P.; Rajan, R.; Martikainen, J.; Suoranta, R. Investigation of weld defects in friction-stir welding and fusion welding of aluminum alloys. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2015, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeen, M.W.; Spena, P.R. Main issues in quality of friction stir welding joints of aluminum alloy and steel sheets. Metals 2019, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, A.; Reddy, R.P.; Ahmad Khan, I. Influence of Process and Tool Parameters on Friction Stir Welding–Over View. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Technol. 2014, 4, 54–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.S.; Urata, M.; Kokawa, H. Parameters controlling microstructure and hardness during friction-stir welding of precipitation-hardenable aluminum alloy 6063. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colligan, K.J. The Friction Stir Welding Process: An Overview; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Raweni, A.; Majstorović, V.; Sedmak, A.; Tadić, S.; Kirin, S. Optimization of AA5083 friction stir welding parameters using taguchi method. Teh. Vjesn. 2018, 25, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micari, F.; Buffa, G.; Pellegrino, S.; Fratini, L. Friction Stir Welding as an effective alternative technique for light structural alloys mixed joints. Procedia Eng. 2014, 81, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; DebRoy, T.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Recent advances in friction-stir welding-Process, weldment structure and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, D.; Mao, Z.; Tong, Y.; Ran, Y. Influence of tool rotation rates on temperature profiles and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A. Friction Stir Welding of Aerospace Alloys. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2019, 7, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Cheema, G.S.; Kang, A.S. An experimental approach to study the effect of welding parameters on similar friction stir welded joints of AZ31B-O Mg alloy. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gesella, G.; Czechowski, M. The application of friction stir welding (FSW) of aluminum alloys in shipbuilding and railway industry. J. KONES 2017, 24, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Makino, T.; Masai, K.; Ohba, H.; Ina, Y.; Ezumi, M. Application of friction stir welding to construction of railway vehicles. JSME Int. J. Ser. A Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 2004, 47, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, G.; Singh, H. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ61 magnesium alloy joint. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2018, 6, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevvel, P.; Jaiganesh, V. An detailed examination on the future prospects of friction stir welding–a green technology. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Advances in Industrial Engineering Applications (ICAIEA 2014), Chennai, India, 6–8 January 2014; pp. 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, A.; Schulze, S.; Silva, A.; Göbel, G.; Standfuss, J.; Brenner, B.; Beyer, E.; Füssel, U. Friction Stir welding of Light Metals for Industrial Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S169–S178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singarapu, U.; Adepu, K.; Arumalle, S.R. Influence of tool material and rotational speed on mechanical properties of friction stir welded AZ31B magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2015, 3, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, V.M.; Leitão, C.; Rodrigues, D.M. Friction stir welding industrialisation and research status. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, C.G.; Mahoney, M.W.; Bingel, W.H.; Spurling, R.A.; Bampton, C.C. Effects of friction stir welding on microstructure of 7075 aluminum. Scr. Mater. 1997, 36, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Murr, L.E.; Niou, C.S.; McClure, J.C.; Vega, F.R. Microstructural aspects of the friction-stir welding of 6061-T6 aluminum. Scr. Mater. 1997, 37, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kokawa, H.; Enomoto, M.; Jogan, S. Microstructural evolution of 6063 aluminum during friction-stir welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1999, 30, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jata, K.V.; Sankaran, K.K.; Ruschau, J.J. Friction-stir welding effects on microstructure and fatigue of aluminum alloy 7050-T7451. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2000, 31, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, B.; Skrotzki, B. Characterization of a friction-stir-welded aluminum alloy 6013. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2002, 33, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colligan, K.J. Failure Mechanisms of Advanced Welding Processes; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 137–163. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, W.; Balogh, L.; Ungár, T.; Choo, H.; Feng, Z. Grain structure and dislocation density measurements in a friction-stir welded aluminum alloy using X-ray peak profile analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 498, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasi, P.; Hajro, I.; Hodži, D.; Dobraš, D. Energy Efficient Welding Technology: Fsw. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Accomplishments in Electrical and Mechanical Engieering and Information Technology, 30 May–1 June 2013; pp. 429–442. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraj, P.; Kanagarajan, D.; Balasubramanian, V. Effect of post weld heat treatment on tensile properties and microstructure characteristics of friction stir welded armour grade AA7075-T651 aluminum alloy. Def. Technol. 2014, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendrababu, P.; Gopala Krishna, A.; Srinivasa Rao, C. Material Flow Behaviour in Friction Stir Welding Process-A Critical Review on Process Parameters and Modeling Methodologies. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2013, 3, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi Aval, H.; Serajzadeh, S.; Kokabi, A.H. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical properties in similar and dissimilar friction stir welding of AA5086 and AA6061. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 8071–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction Stir Welding and Processing. Mater. Sci. Eng.: R: Rep. 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.K.; Azam, S.; Quadri, P. Evaluation of Parameters of Friction Stir Welding for Aluminum Aa6351 Alloy. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 5977–5984. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.R.; Kotadiya, D.J.; Kapopara, J.M.; Dalwadi, C.G.; Patel, N.P.; Rana, H.G. Investigation of Mechanical Properties for Hybrid Joint of Aluminum to Polymer using Friction Stir Welding (FSW). Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 4242–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Liao, J.; Nakata, K. Joining of metal to plastic using friction lap welding. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Dalwadi, C.G.; Rana, H.G. A Review: Dissimilar Material Joining of Metal to Polymer using Friction Stir Welding (FSW). IJSTE-Int. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 2, 702–706. [Google Scholar]
- Murr, L.E.; Li, Y.; Trillo, E.; McClure, J.C. Fundamental Issues and Industrial Applications of Friction-Stir Welding. Mater. Technol. 2000, 15, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threadgill, P.L.; Johnson, R. The Potential for Friction Stir Welding in Oil and Gas Applications. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Offshore Polar Engineering Conference, Toulon, France, 23–28 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shtrikman, M.M. Current state and development of friction stir welding Part 3. Industrial application of friction stir welding. Weld. Int. 2008, 22, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.M.; Nicholas, E.D. Friction stir welding for the transportation industries. Mater. Des. 1997, 18, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Guo, X.; McClure, J.C.; Murr, L.E.; Nunes, A. Heat input and temperature distribution in friction stir welding. J. Mater. Process. Manuf. Sci. 1998, 7, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, M.W.; Rhodes, C.G.; Flintoff, J.G.; Spurling, R.A.; Bingel, W.H. Properties of friction-stir-welded 7075 T651 aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1998, 29, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.P.; Lockwood, W.D.; Seidel, T.U. Processing-property correlation in friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 331, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrove, P.A.; Shercliff, H.R. Experimental and numerical analysis of aluminum alloy 7075-T7351 friction stir welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2003, 8, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Enomoto, M.; Jogan, S.; Hashimoto, T. Microtexture in the friction-stir weld of an aluminum alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2001, 32, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnowski, K.; Sedek, P.; Łomozik, M.; Pietras, A. Impact of selected FSW process parameters on mechanical properties of 6082-T6 aluminum alloy butt joints. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2011, 56, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, M.S.; Ravi Kumar, B.V.R.; Manzoor Hussain, M. Experimental study on the effect of welding parameters and tool pin profiles on the IS:65032 aluminum alloy FSW joints. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, S.; Awang, M.; Hussai, P.; Meyghani, B.; Zafar, A. Influences of tool pin profile on the friction stir welding of AA6061. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 12258–12261. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, C.; Srinivasan, K.; Balasubramanian, V.; Balaji, H.; Selvaraj, P. Effect of tool tilt angle on strength and microstructural characteristics of friction stir welded lap joints of AA2014-T6 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, Z.; Ozsarac, U. Effects of FSW parameters on joint properties of AlMg3 Alloy. Weld. J. 2012, 91, 16S–22S. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, M.; Steuwer, A.; Preuss, M.; Withers, P.J. Microstructure, mechanical properties and residual stresses as a function of welding speed in aluminum AA5083 friction stir welds. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4791–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Siddiquee, A.N. Effect of Shoulder Diameter to Pin Diameter (D/d) Ratio on Tensile Strength of Friction Stir Welded 6063 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Qiao, K.; Che, Q.; Xi, X.; Zhang, B.; Cai, J. High-performance aluminum foam sandwich prepared through friction stir welding. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busic, M.; Kozuh, Z.; Klobcar, D.; Samardzic, I. Friction Stir Welding (FSW) of Aluminum Foam Sandwich Panels. Metalurgija 2016, 55, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.T.; Yoon, J.H.; Min, K.J.; Lee, H.S. Effect of Friction Stir Welding Process Parameters on Mechanical Properties and Macro Structure of Al-Li Alloy. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 2, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, C.G.; Kim, S. Tensile behavior of friction-stir-welded A356-T6/Al 6061-T651 bi-alloy plate. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2004, 35, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, S.; Ceyhun, V.; Tezcan, Ö. The influence of friction stir welding parameters on the mechanical properties and low cycle fatigue in AA 6063 (AlMgSi0.5) alloy. Kov. Mater. 2008, 46, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Distribution of tensile property and microstructure in friction stir weld of 6063 aluminum. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2001, 32, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonchouytan, W.; Ratanawilai, T.; Muangjunburee, P. Effect of pre/post heat treatment on the friction stir welded SSM 356 aluminum alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 32, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, G. Friction stir welded structural materials: Beyond Al-alloys. Int. Mater. Rev. 2011, 56, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, G.; Singh, H. Review on friction stir welding of magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2018, 6, 399–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargusch, M.S.; Bowles, A.L.; Pettersen, K.; Bakke, P.; Dunlop, G.L. The effect of silicon content on the microstruture and creep behavior in die-cast magnesium AS alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2004, 35, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Recent research and developments on wrought magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2017, 5, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F.H.; Eliezer, D.; Aghion, E. The Science, Technology, and Applications of Magnesium. J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 1998, 50, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Liu, D.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q. Mechanisms of fracture and inhomogeneous deformation on transverse tensile test of friction-stir-processed AZ31 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 565, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Ni, D.R.; Xue, P.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Evolution of local texture and its effect on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of friction stir welded joint of extruded Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy. Mater. Charact. 2017, 128, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z.Y. Effects of heat input on tensile properties and fracture behavior of friction stir welded Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commin, L.; Dumont, M.; Rotinat, R.; Pierron, F.; Masse, J.E.; Barrallier, L. Influence of the microstructural changes and induced residual stresses on tensile properties of wrought magnesium alloy friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 551, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, C.G.; Yim, C.D.; Kim, S.J. Tensile behavior of friction-stir-welded AZ31-H24 Mg alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2005, 36, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Yeon, Y.M.; Jung, S.B. Joint properties of friction stir welded AZ31B-H24 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pragash, M.S.; Varghese, S. Optimizing the process parameters of FSW on AZ31B Mg alloy by Taguchi-grey method. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 15, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, L.; Tan, S.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yi, H. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of friction stir processed Mg-14Gd alloys. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Pal, S. Effect of FSW parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of AM20 welds. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2018, 33, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevvel, P.; Jaiganesh, V. Characterization of mechanical properties and microstructural analysis of friction stir welded AZ31B Mg alloy thorough optimized process parameters. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, M.; Polar, A.; Rumiche, F.; Indacochea, J.E. Metallurgical evaluation of AZ31B-H24 magnesium alloy friction stir welds. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2007, 16, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, J.A.; Davis, W.C.; Murr, L.E. Microstructure-property studies in friction-stir welded, thixomolded magnesium alloy AM60. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.C.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Effect of micro-texture on fracture location in friction stir weld of Mg alloy AZ61 during tensile test. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Geng, L.; Chen, R.S. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 471, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Suzuki, M.; Maruyama, K. Microstructural evolution of a heat-resistant magnesium alloy due to friction stir welding. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xunhong, W.; Kuaishe, W. Microstructure and properties of friction stir butt-welded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 431, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugender, S.; Kumar, A.; Reddy, A.S. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy by Friction Stir Welding. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanaban, G.; Balasubramanian, V. Selection of FSW tool pin profile, shoulder diameter and material for joining AZ31B magnesium alloy-An experimental approach. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, N.; Chen, D.L.; Cao, X.; Jahazi, M. Strain hardening behavior of a friction stir welded magnesium alloy. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Bhatt, K.D.; Mehta, V. Influence of Tool Pin Profile and Welding Parameter on Tensile Strength of Magnesium Alloy AZ91 During FSW. Procedia Technol. 2016, 23, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y. Microstructures and tensile properties of submerged friction stir processed AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2015, 3, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadigithala, N.K.; Vanitha, C. Effects of welding speeds on the microstructural and mechanical properties of AZ91D Mg alloy by friction stir welding. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 2020, 11, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri-Henni, A.; Barrallier, L. Mechanical properties, microstructure and crystallographic texture of magnesium AZ91-D alloy welded by friction stir welding (FSW). Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2014, 45, 4983–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.S.; Shen, Y.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, X.H.; Xu, K.W. Evaluation of Microstructure and Mechanical Property of FSW Welded MB3 Magnesium Alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2006, 13, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Liu, Y.; Chew, Y.; Lee, B.Y.; Ng, F.L.; Bi, G. Double-side friction stir welding of thick magnesium alloy: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2020, 25, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.P.; Tang, W.; Posada, M.; DeLoach, J. Friction stir welding of DH36 steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2003, 8, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, C.; Nelson, T. Friction stir welding of ferrous and nickel alloys. Frict. Stir Weld. Process. 2007, 111–121. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267856005_Friction_Stir_Welding_of_Ferrous_and_Nickel_Alloys (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Perrett, J.; Martin, J.; Peterson, J.; Steel, R.; Packer, S. Friction Stir Welding of Industrial Steels; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Cater, S.; Martin, J.; Galloway, A.; McPherson, N. Comparison between Friction Stir and Submerged Arc Welding Applied to Joining DH36 and E36 Shipbuilding Steel. In Friction Stir Welding and Processing VII; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.M.; Threadgill, P.L.; Nicholas, E.D. Feasibility of friction stir welding steel. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1999, 4, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienert, T.J.; Lippold, J.C. Improved weldability diagram for pulsed laser welded austenitic stainless steels. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2003, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cui, L.; Tsuji, N.; Maeda, M.; Nakata, K.; Nogi, K. Friction stir welding of carbon steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 429, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Fujii, H.; Tsuji, N.; Nogi, K. Friction stir welding of a high carbon steel. Scr. Mater. 2007, 56, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, T.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Assadi, H.; Malek Ghaini, F. Effect of friction stir welding speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Kumar, K.; Mishra, R.S. Analysis of microstructural evolution during friction stir welding of ultrahigh-strength steel. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Ueji, R.; Fujii, H.; Komine, H.; Yanagimoto, J. Phase transformation behavior of Cr-Mo steel during FSW. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Ueji, R.; Morisada, Y.; Tanigawa, H. High strength and ductility of friction-stir-welded steel joints due to mechanically stabilized metastable austenite. Scr. Mater. 2014, 70, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, M.; Nelson, T.; Sorenson, C.; Packer, S. Friction stir welding of ferrous alloys: Current status. Mater. Sci. Forum 2010, 638–642, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Ueji, R.; Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H. Enhanced tensile properties of Fe-Ni-C steel resulting from stabilization of austenite by friction stir welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 216, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Cui, L.; Nakata, K.; Nogi, K. Mechanical properties of friction stir welded carbon steel joints-Friction stir welding with and without transformation. Weld. World 2008, 52, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, M.P.; Kodli, B.K.; Dey, S.R. Mechanical Properties and Microstructural Characterization of Friction Stir Welded AISI 316 Austenitic Stainless Steel. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maltin, C.A.; Nolton, L.J.; Scott, J.L.; Toumpis, A.I.; Galloway, A.M. The potential adaptation of stationary shoulder friction stir welding technology to steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Debroy, T. Critical assessment: Friction stir welding of steels. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragu Nathan, S.; Balasubramanian, V.; Malarvizhi, S.; Rao, A.G. Effect of welding processes on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of high strength low alloy naval grade steel joints. Def. Technol. 2015, 11, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabooni, S.; Karimzadeh, F.; Enayati, M.H.; Ngan, A.H.W.; Jabbari, H. Gas Tungsten arc Welding and Friction Stir Welding of Ultrafine Grained AISI 304L Stainless Steel: Microstructural and Mechanical Behavior Characterization; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 109, ISBN 8415683111. [Google Scholar]
- Meshram, M.P.; Kodli, B.K.; Dey, S.R. Friction Stir Welding of Austenitic Stainless Steel by PCBN Tool and its Joint Analyses. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, A.K.; Balasubramanian, V.; Salahuddin, M. Microstructure, tensile and impact toughness properties of friction stir welded mild steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Jiang, Z.H.; Feng, H.; Zhang, S.C.; Li, L.; Han, P.D.; Misra, R.D.K.; Li, J.Z. Microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of friction stir welded high nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ni, D.R.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, K. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir welded joint of Fe-Cr-Mn-Mo-N austenite stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Fu, R.; Li, Y.; Jing, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, K. Gradient characteristics and strength matching in friction stir welded joints of Fe-18Cr-16Mn-2Mo-0.85N austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiese, J.; Siemers, C.; Schmidt, C. A New Class of Oxidation-Resistant, Microstructural-Stabilized and Cold-Workable Titanium Alloys for Exhaust Applications; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 733–737. ISBN 9781119293668. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, V.; Rajakumar, S.; Banerjee, N.; Amuthakkannan, R. Effect of shoulder diameter to pin diameter ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welded AA2024-T6 and AA7075-T6 aluminum alloy joints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 3637–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayavel, P.; Balasubramanian, V.; Sundaram, S. Effect of shoulder diameter to pin diameter (D/d) ratio on tensile strength and ductility of friction stir processed LM25AA-5% SiCp metal matrix composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, S.; Reynolds, A.P. Residual stress effects on fatigue crack growth in a Ti-6Al-4V friction stir weld. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2008, 31, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Lee, C.Y.; Chang, W.S.; Yeon, Y.M.; Jung, S.B. Microstructural investigation of friction stir welded pure titanium. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 3315–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H.; Park, S.H.C.; Hirano, S. Microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, S.; Sato, Y.S.; Kokawa, H. Development of grain structure during friction stir welding of pure titanium. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4519–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, K.E.; Fonda, R.W. Texture development in the stir zone of near-α titanium friction stir welds. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilchak, A.L.; Juhas, M.C.; Williams, J.C. Microstructural changes due to friction stir processing of investment-cast Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; De, A.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; DebRoy, T. Review: Friction stir welding tools. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2011, 16, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, K.; Mamidala, R.; Sanders, D.G. Friction stir welding of near α and α + β titanium alloys: Metallurgical and mechanical characterization. Metals 2017, 7, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonda, R.W.; Bingert, J.F. Texture variations in an aluminum friction stir weld. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, K.; Ramulu, M. Friction stir welding of titanium alloys: A review. Mater. Des. 2018, 141, 230–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, N.; Ramulu, M. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Mechanical Behavior in Frcition Stir Welded Different Titanium Alloys. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–20 November 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Wang, J.; Mishra, R.S.; Xu, R.; Baumann, J.A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a friction stir processed Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 573, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashinini, P.M.; Hattingh, D.G.; Lombard, H. Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Friction Stir and Laser Beam Welded 3mm Ti6Al4V Alloy. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 29 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, H.; Sun, Y.; Kato, H.; Nakata, K. Investigation of welding parameter dependent microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure Ti joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 527, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.; Ramulu, M. Identification of process parameters for friction stir welding Ti-6Al-4V. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 2010, 132, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuwer, A.; Hattingh, D.G.; James, M.N.; Singh, U.; Buslaps, T. Residual stresses, microstructure and tensile properties in Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.; Ramulu, M. Fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth in Ti-6Al-4V friction stir welds. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2015, 38, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhou, L. Microstructural zones and tensile characteristics of friction stir welded joint of TC4 titanium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1873–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Par, M.A. Twenty-year uninterrupted endeavor of friction stir processing by focusing on copper and its alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 781, 1074–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederqvist, L.; Sorensen, C.D.; Reynolds, A.P.; Öberg, T. Improved process stability during friction stir welding of 5 cm thick copper canisters through shoulder geometry and parameter studies. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederqvist, L.; Öberg, T. Reliability study of friction stir welded copper canisters containing Sweden’s nuclear waste. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartigueyen, S.; Mahadevan, K. Role of Friction Stir Processing on Copper and Copper based Particle Reinforced Composites–A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Surf. Eng. 2015, 2, 133–145. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, K. Friction stir welding of copper and copper alloys. Weld. Int. 2010, 55, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kimura, T.; Murakami, T.; Nagano, Y.; Nakata, K.; Ushio, M. Microstructures and mechanical properties of friction stir welds of 60% Cu-40% Zn copper alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 371, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, G.; Serindaǧ, H.T.; Çakan, A.; Mistikoglu, S.; Yavuz, H. The effect of weld parameters on friction stir welding of brass plates. Materwiss. Werksttech. 2008, 39, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machniewicz, T.; Nosal, P.; Korbel, A.; Hebda, M. Effect of FSW Traverse Speed on Mechanical Properties of Copper Plate Joints. Materials 2020, 13, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.B.; Jung, S.B. The joint properties of copper by friction stir welding. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Xie, G.M.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; Geng, L. Effect of heat input conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction-stir-welded pure copper. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2010, 41, 2010–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaverdizadeh, H.; Mahmoudi, A.; Heidarzadeh, A.; Nazari, E. Effect of friction stir welding (FSW) parameters on strain hardening behavior of pure copper joints. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serio, L.M.; Palumbo, D.; De Filippis, L.A.C.; Galietti, U.; Ludovico, A.D. Effect of friction stir process parameters on the mechanical and thermal behavior of 5754-H111 aluminum plates. Materials 2016, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.D.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Borrego, L.P.; Abreu, L.P. Fatigue behaviour of AA6082 friction stir welds under variable loadings. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 37, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, S.; Yapici, G.G. Fatigue Behavior of Friction Stir Welded Joints of Pure Copper with Ultra-fine Grains. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2015, 11, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, K.; Els-Botes, A. Development of high strength, high conductivity copper by friction stir processing. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Shen, J.J.; Huang, Y.X.; Kuang, L.Y.; Liu, C.; Li, C. Effect of tool rotation rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded copper. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlot, P.; Singh, A.K.; Badheka, V.J.; Arora, A. Friction Stir Welding of Copper: Numerical Modeling and Validation. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.M.; Ma, Z.Y.; Geng, L. Development of a fine-grained microstructure and the properties of a nugget zone in friction stir welded pure copper. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartigueyen, S.; Mahadevan, K. Influence of rotational speed on the formation of friction stir processed zone in pure copper at low-heat input conditions. J. Manuf. Process. 2015, 18, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartigueyen, S.; Mahadevan, K. Study of friction stir processed zone under different tool pin profiles in pure copper. IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2014, 11, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethiraj, N.; Sivabalan, T.; Meikeerthy, S.; Kumar, K.L.V.R.; Chaithanya, G.; Reddy, G.P.K. Comparative study on conventional and underwater friction stir welding of copper plates. In Proceedings of the Int. Conf. Mater. Manuf. Mach. 2019, Sibiu, Romania, 5–7 June 2019; Volume 2128, p. 30003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, T.; Mukhopadhyay, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded copper. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 8126–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.W.; Chang, H.C.; Wu, M.H. Comparison of mechanical properties of pure copper welded using friction stir welding and tungsten inert gas welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, L.S.; Kumar, A.; Prasad, S.R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded pure copper. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 592–594, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagabharam, P.; Srikanth Rao, D.; Manoj Kumar, J.; Gopikrishna, N. Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded pure Copper Plates. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, A.A.; Shirazi, A. Effects of different friction stir welding conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of copper plates. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmouz, M.; Givi, M.K.B.; Jafari, J. Evaluation of tensile deformation properties of friction stir processed pure copper: Effect of processing parameters and pass number. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.N.; Naik, L.S.; Srinivas, C. Evaluation and Impacts of Tool Profile and Rotational Speed on Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Copper 2200 Alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H. Submerged friction stir weld of polyethylene sheets. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, A.; Sinmaz, T. Effects of double passes of the tool on friction stir welding of polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 3313–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Y. The optimization of friction stir welding process parameters to achieve maximum tensile strength in polyethylene sheets. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M. Effects of welding parameters and pre-heating on the friction stir welding of UHMW-polyethylene. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafapour, A.; Azarsa, E. A study on the role of processing parameters in joining polyethylene sheets via heat assisted friction stir welding: Investigating microstructure, tensile and flexural properties. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2012, 7, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedy, S.; Besharati, M.K. Investigation of the effects of critical process parameters of friction stir welding of polyethyleneg. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2011, 225, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Sahu, S.K.; Mahto, R.P.; Pal, S.K. Strengthening and Joining by Plastic Deformation; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-0377-7. [Google Scholar]
- Inaniwa, S.; Kurabe, Y.; Miyashita, Y.; Hori, H. Application of friction stir welding for several plastic materials. In Proceedings of the 1st International Joint Symposium on Joining and Welding, Osaka, Japan, 6–8 November 2013; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Rezgui, M.-A.; Trabelsi, A.-C.; Ayadi, M.; Hamrouni, K. Optimization of Friction Stir Welding Process of High Density Polyethylene. Int. J. Prod. Qual. Eng. 2011, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Panneerselvam, K.; Lenin, K. Joining of Nylon 6 plate by friction stir welding process using threaded pin profile. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Awang, M.; Khan, S.R.; Emamian, S. Investigating friction stir welding on thick nylon 6 plates. Weld. J. 2016, 95, 210s–218s. [Google Scholar]
- Khaliel Youssif, M.S.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Khourshid, A.E.F.M. Influence of critical process parameters on the quality of friction stir welded nylon 6. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 2016, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Azdast, T.; Doniavi, A. An experimental study on mechanical properties of friction stir welded ABS sheets. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, N.; Besharati Givi, M.K. Experimental optimization of the mechanical properties of friction stir welded Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene sheets. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirizadeh, M.; Azdast, T.; Rash Ahmadi, S.; Mamaghani Shishavan, S.; Bagheri, A. Friction stir welding of thermoplastics using a newly designed tool. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, N.; Loureiro, A.; Martins, C.; Neto, P.; Pires, J.N. Morphology and strength of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene welds performed by robotic friction stir welding. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Mishra, D.; Mahto, R.P.; Sharma, V.M.; Pal, S.K.; Pal, K.; Banerjee, S.; Dash, P. Friction stir welding of polypropylene sheet. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, Z.; Czigány, T. Microscopic analysis of the morphology of seams in friction stir welded polypropylene. Express Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, Z.; Czigány, T. Effect of Welding Parameters on the Heat Affected Zone and the Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded Poly(ethylene-terephthalate-glycol). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, K.; Lenin, K. Investigation on effect of tool forces and joint defects during FSW of polypropylene plate. Procedia Eng. 2012, 38, 3927–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, K.; Lenin, K. Effects and Defects of the Polypropylene Plate for Different Parameters in Friction Stir Welding Process. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, F.; Rodrigues, D.M. Material flow and thermo-mechanical conditions during Friction Stir Welding of polymers: Literature review, experimental results and empirical analysis. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squeo, E.A.; Bruno, G.; Guglielmotti, A.; Quadrini, F. Friction Stir Welding of Polyethylene Sheets. The Annals of “Dunarea de Jos” University of Galati Fascicle V. 2009, pp. 241–246. Available online: https://wwww.researchgate.net/publication/267842113_Friction_stir_welding_of_polyethylene_sheets (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Arbegast, W.J. A flow-partitioned deformation zone model for defect formation during friction stir welding. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezgui, M.A.; Ayadi, M.; Cherouat, A.; Hamrouni, K.; Zghal, A.; Bejaoui, S. Application of Taguchi approach to optimize friction stir welding parameters of polyethylene. EPJ Web Conf. 2010, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, S.R. Effects of Friction Stir Welding on Polymer Microstructure. Master’s Thesis, Ira A. Fulton College of Engineering and Technology, Tempe, AZ, USA, February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, T.W.; Sorensen, C.D.; John, C.J. Friction Stir Welding of Polymeric Materials. U.S. Patent 681,163,2B2, 2 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Banjare, P.N.; Sahlot, P.; Arora, A. An assisted heating tool design for FSW of thermoplastics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 239, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laieghi, H.; Alipour, S.; Mostafapour, A. Heat-assisted friction stir welding of polymeric nanocomposite. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2020, 25, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, I.M.; Salim, R.K.; Azdast, T.; Hasanifard, S.; Shishavan, S.M.; Lee, R.E. Mechanical properties of friction-stir-welded polyamide sheets. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2015, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhao, W.; Yan, J. Designing high-performance composite joints close to parent materials of aluminum matrix composites. arXiv 2017, 34, 660–663. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, I.W.; Kyono, T.; Diwanji, A. On the fibre/matrix interface in boron/aluminum metal matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, S.J.; Murugan, N. Influence of tool pin profile on the metallurgical and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al-10wt.% TiB2 metal matrix composite. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3585–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Qasim, T.; Ghaithan, A. Effect of pin profile on friction stir welded aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.R.I.; Takahashi, M.; Shibayanagi, T.; Ikeuchi, K. Effect of friction stir processing tool probe on fabrication of SiC particle reinforced composite on aluminum surface. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; Cerri, E.; Marzoli, L.; Dos Santos, J. Friction stir welding of ceramic particle reinforced aluminum based metal matrix composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2004, 11, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzoli, L.M.; Strombeck, A.V.; Dos Santos, J.F.; Gambaro, C.; Volpone, L.M. Friction stir welding of an AA6061/Al2O3/20p reinforced alloy. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, R.A.; Murr, L.E.; Shindo, D.J.; Soto, K.F. Tool wear in the friction-stir welding of aluminum alloy 6061 + 20% Al2O3: A preliminary study. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, S.C.; Reynolds, A.P. Characterization of Reinforcing Particle Size Distribution in a Friction Stir Welded Al-SiC Extrusion. In Proceedings of the Lightweight Alloys for Aerospace Application; Jata, K., Lee, E., Frazier, W., Kim, N.J., Eds.; The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2001; pp. 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, M.W.; Harrigan, W.; Wert, J.A. Friction Stir Welding SiC Discontinuously Reinforced Aluminuium. In Proceedings of the 7th Int. Conf. Joints in Aluminum, Cambridge, UK, 15–17 April 1998; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, A.H.; Ma, Z.Y. Formation of Cu2FeAl7 phase in friction-stir-welded SiCp/Al-Cu-Mg composite. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.H.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Effect of microstructural evolution on mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA2009/SiCp composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschini, L.; Boromei, I.; Minak, G.; Morri, A.; Tarterini, F. Microstructure, tensile and fatigue properties of AA6061/20 vol.%Al2O3p friction stir welded joints. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.; Roy, B.S.; Saha, S.C. Torque and force perspectives on particle size and its effect on mechanical property of friction stir welded AA6092/17.5SiC p -T6 composite joints. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 38, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Medhi, T.; Roy, B.S. Friction Stir Welding of Thermoplastic Composites; Springer: Singapore, 2019; ISBN 978-981-13-6412-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushan, R.K.; Sharma, D. Optimization of FSW parameters for maximum UTS of AA6082/SiC/10 P composites. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2019, 28, 96369351986770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafrey, D.D.; Panneerselvam, K. Study on Tensile Strength, Impact Strength and Analytical Model for Heat Generation in Friction Vibration Joining of Polymeric Nanocomposite Joints Daniel. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 57, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fujii, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AC4A+30vol.%SiCp composite. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Q.Z.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Achieving friction stir welded SiCp/Al–Cu–Mg composite joint of nearly equal strength to base material at high welding speed. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 589, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozammil, S.; Karloopia, J.; Verma, R.; Jha, P.K. Mechanical response of friction stir butt weld Al-4.5%Cu/TiB2/2.5p in situ composite: Statistical modelling and optimization. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 826, 154184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendranath, S.; Chakradhar, D. Effect of FSW on microstructure and hardness of AA6061/SiC/fly ash MMCs. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 17866–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Y.; Uzun, H.; Salman, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded particulate reinforced AA2124/SiC/25p-T4 composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, U.; Saha Roy, B.; Chandra Saha, S. A Study of Tool Wear and its Effect on the Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded AA6092/17.5 Sicp Composite Material Joint. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 20371–20379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.R.; Chen, D.L.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z.Y. Residual stresses and high cycle fatigue properties of friction stir welded SiCp/AA2009 composites. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 55, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Y.; Boumerzoug, Z. Tool material effect on the friction stir butt welding of AA2124-T4 Alloy Matrix MMC. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2018, 7, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Ibáñez, J.; Cioffi, F.; Verdera, D.; González-Doncel, G. Friction stir welding of 25%SiC/2124Al composite with optimal mechanical properties and minimal tool wear. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2017, 22, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, P.; Mohan, B.; Balasubramanian, V. Effect of heat input on mechanical and metallurgical properties of friction stir welded AA6061-10% SiCp MMCs. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2417–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Wang, Q.Z.; Ma, Z.Y. Evolution of the Microstructure and Strength in the Nugget Zone of Friction Stir Welded SiCp/Al-Cu-Mg Composite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, O.S.; Ou, H.; Wei, X.; Sun, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA6092/SiC metal matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 742, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzdor, V.; Kou, S. Al-to-Mg friction stir welding: Effect of material position, travel speed, and rotation speed. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2010, 41, 2914–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.P.; Badheka, V.J. A review on dissimilar friction stir welding of copper to aluminum: Process, properties, and variants. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, M.P.; Melton, D.W.; Nelson, T.W. Formability of friction-stir-welded dissimilar-aluminum-alloy sheets. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2005, 36, 3335–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simar, A.; Jonckheere, C.; Deplus, K.; Pardoen, T.; De Meester, B. Comparing similar and dissimilar friction stir welds of 2017-6005A aluminum alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2010, 15, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipekoglu, G.; Cam, G. Effects of initial temper condition and postweld heat treatment on the properties of dissimilar friction-stir-welded joints between AA7075 and AA6061 aluminum alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2014, 45, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia, M.; Shahraki, S.; Kamarposhti, M.A. Experimental studies on optimized mechanical properties while dissimilar joining AA6061 and AA5010 in a friction stir welding process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 2337–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.S.; Park, S.H.C.; Michiuchi, M.; Kokawa, H. Constitutional liquation during dissimilar friction stir welding of Al and Mg alloys. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, S. Microstructure characteristics and performance of dissimilar welds between magnesium alloy and aluminum formed by friction stirring. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzdor, V.; Kou, S. Formation of liquid and intermetallics in Al-to-Mg friction stir welding. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2010, 41, 3238–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh, A.; Shokuhfar, A.; Cabrera, J.M.; Zhilyaev, A.P.; Omidvar, H. The effect of changing chemical composition in dissimilar Mg/Al friction stir welded butt joints using zinc interlayer. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 34, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Yarrapareddy, E.; Kovacevic, R. Microstructural evolution in the friction stir welded 6061 aluminum alloy (T6-temper condition) to copper. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2006, 172, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Effect of interfacial microstructure evolution on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of friction-stir-welded Al-Cu joints. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3091–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, H.; Li, B. Investigation on dissimilar underwater friction stir lap welding of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy to pure copper. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, P.; Reynolds, A.P. Factors affecting the properties of Friction Stir Welds between aluminum and magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.S. Effect of welding energy on interface zone of Al-Cu ultrasonic welded joint. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 18, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Kilbourne, J.; Gerlich, A.P.; North, T.H. Joint formation in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and Mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.F. Metallurgy of Welding; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 1999; ISBN 978-1-85573-428-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Qin, G.; Li, F.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. Friction stir welding process of dissimilar metals of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy to AZ31B magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 218, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, R.; Da Silva, A.A.M.; Rodrigues, S.; Blanco, A.; Dos Santos, J.F. Dissimilar Al to Mg alloy friction stir welds. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, H.; Morisada, Y.; Fujii, H. Dissimilar FSW of immiscible materials: Steel/magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 624, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.J.; Steuwer, A.; Withers, P.J.; Dickerson, T.; Shi, Q.; Shercliff, H. Dissimilar friction stir welds in AA5083-AA6082. Part I: Process parameter effects on thermal history and weld properties. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodir, S.A.; Shibayanagi, T. Friction stir welding of dissimilar AA2024 and AA7075 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2008, 148, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avinash, P.; Manikandan, M.; Arivazhagan, N.; Devendranath, R.K.; Narayanan, S. Friction stir welded butt joints of AA2024 T3 and AA7075 T6 aluminum alloys. Procedia Eng. 2014, 75, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Koshy Mathews, P.; Murugan, N.; Dinaharan, I. Effect of tool rotational speed and pin profile on microstructure and tensile strength of dissimilar friction stir welded AA5083-H111 and AA6351-T6 aluminum alloys. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarvizhi, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Influences of tool shoulder diameter to plate thickness ratio (D/T) on stir zone formation and tensile properties of friction stir welded dissimilar joints of AA6061 aluminum-AZ31B magnesium alloys. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RajKumar, V.; VenkateshKannan, M.; Sadeesh, P.; Arivazhagan, N.; Devendranath Ramkumar, K. Studies on effect of tool design and welding parameters on the friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloys AA 5052-AA 6061. Procedia Eng. 2014, 75, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadegan, M.; Abdollah-zadeh, A.; Feng, A.H.; Saeid, T.; Shen, J.; Assadi, H. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Dissimilar Friction Stir Weld between Austenitic Stainless Steel and Low Carbon Steel. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Amadeh, A.; Akbari Mousavi, S.A.A. Investigations on the effects of friction stir welding parameters on intermetallic and defect formation in joining aluminum alloy to mild steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishige, T.; Kawaguchi, A.; Tsujikawa, M.; Hino, M.; Hirata, T.; Higashi, K. Dissimilar welding of Al and Mg alloys by FSW. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudian, A.; Tahaei, A.; Shakiba, A.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Mohandesi, J.A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir weld of dissimilar AZ31-O magnesium alloy to 6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizieh, M.; Sadeghi Alavijeh, A.; Abbasi, M.; Balak, Z.; Kim, H.S. Mechanical properties and microstructural evaluation of AA1100 to AZ31 dissimilar friction stir welds. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 170, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Tanabe, H.; Kagiya, K. Dissimilar metal joining of magnesium alloy to steel by FSW. Adv. Mater. Res. 2007, 15–17, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.R.; Badheka, V.J. Microstructures and Properties of Copper to Stainless Steel Joints by Hybrid FSW. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2017, 6, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Chattopadhyaya, S. Friction stir welding of commercially pure copper and 1050 aluminum alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 25, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Ni, D.R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, B.L.; Ma, Z.Y. Effect of friction stir welding parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the dissimilar Al-Cu joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4683–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| AA2195-T8 | 7.4 | 300 | 400 | Cone shape threaded pin, threaded surface of the shoulder | - | - | 445.0 (607.9) | - | - | 12.50 (12.49) | No defects | [55] |
| AA356.0-T6 (double side welded) | 8 | 200 | 1200 | Threaded conical pin | 3.25 | - | 200 (244) | 123 (140) | - | 16.3 (13.4) | - | [56] |
| AA5083 | 3 | 100 | - | M6 threaded pin | 3.6 | 2 | 304 (457) | 154 (392) | - | - | - | [51] |
| AA5086-O | 5 | 150 | 900 | Tapered pin with 3 threads and concave shoulder surface | 3.3 | - | 250 (253) | 123 (112) | - | - | - | [31] |
| AA6013-T4 | 2.5 | 450 | 1400 | - | - | - | 300 (320) | - | - | - | - | [25] |
| AA6013-T6 | 2.5 | 400 | 1400 | - | - | - | 295 (394) | - | - | - | - | [25] |
| AA6061 | 5 | 100 | 1300 | Cylindrical smooth | - | - | 227 (308.5) | ~153 (266.6) | - | ~7.3 (16.28) | Defect free | [47] |
| AA6061 | 10 | 100 | 1600 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 214.4 (305) | - | - | - | No defects | [48] |
| AA6061-T6 | 5 | 150 | 900 | Tapered pin with 3 threads and concave shoulder surface | 3.3 | - | 285 (315) | 241 (278) | 57 | - | - | [31] |
| AA6061-T651 (double side welded) | 8 | 200 | 1200 | Threaded conical pin | 3.25 | - | 218 (299) | 142 (264) | - | 23.3 (27.2) | - | [56] |
| AA6063 | 5 | 100 | 2800 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | 3 | ~150 (220) | ~70 (170) | - | 4.5 (13) | - | [57] |
| AA6063-T5 | 4 | 600 | - | - | - | - | ~155 (~220) | ~105 (~185) | - | 10 (~19) | No defects | [58] |
| AA6063-T6 | 4.75 | 40 | 900 | Cylindrical smooth pin | 2.6 | 1.5 | 145.34 (220) | - | - | 20.85 (14.00) | - | [52] |
| AA6082-T6 | 8 | 900 | 710 | Cylindrical pin with threads and three flutes | 3.3 | 1.5 | 243.4 | - | - | - | - | [46] |
| AA6352 (double side welded) | 6 | 115 | 1350 | Tapered pin | - | 2 | 172 (250) | - | 90.2 (93.5) | - | No significant defects | [33] |
| AA7050-T7451 | 6.35 | 103 | 396 | - | - | - | 429 (555) | 304 (489) | - | 6 (16.7) | - | [24] |
| AA7075-T651 | 6.35 | 127 | - | - | - | - | 525 (622) | 365 (571) | - | 15 (14.5) | - | [42] |
| SSM 356 | 4 | 160 | 1750 | Cylindrical pin | 4 | 3 | 173.5 (168.7) | 138.8 (134.9) | 40.9 (36.4) | 3.1 (5.3) | - | [59] |
| SSM 356-T6 | 4 | 160 | 1750 | Cylindrical pin | 4 | 3 | 172.9 (295.6) | 138.3 (236.5) | 68.4 (61.2) | 4.5 (4.8) | - | [59] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| AM20 | 4 | 63 | 600 | Cylindrical pin | 4 | - | 132.17 (202) | 115.56 (160) | 61 (46) | 2.17 (7) | - | [73] |
| AZ31 | 4 | 90 | 1500 | - | 3 | - | 255 (275) | - | - | - | - | [80] |
| AZ31 | 8 | 120 | 1200 | Conical pin | 2 | 2.5 | 225.1 (249.5) | 130.5 (156.3) | - | 5.4 (14) | - | [11] |
| AZ31-O | 2 | 200 | 1000 | - | 2.6 | - | ~170 (~250) | ~90 (~150) | - | - | - | [68] |
| AZ31B | 5 | 0.5 | 1000 | Tapered cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 183 (262) | 101 (179) | - | - | No defects | [74] |
| AZ31B | 5 | 40 | 1400 | Threaded conical pin | 3 | 2.5 | 186.76 (215) | 139.1 (171) | 71 (69) | 5.00 (14.7) | - | [81] |
| AZ31B | 5 | 40 | 1120 | Taper threaded pin | 3 | 2 | 188 (215) | 148 (171) | 121 (69.3) | 7.3 (14.3) | - | [19] |
| AZ31B | 6 | 40.2 | 1600 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 3.0 | 0 | 205 (215) | 166 (171) | 75 (69.3) | 7.3 (14.7) | Defect free | [82] |
| AZ31B | 6 | 50.8 | 1200 | - | - | - | 248 | - | 67.95 HB | - | - | [71] |
| AZ31B-O | 5 | 60 | 1200 | Left handed threaded pin | 3 | - | 187.8 (206) | - | 64.77 (50) | 16.73 (20) | - | [13] |
| AZ31-H24 | 3.175 | 204 | 2000 | - | - | - | 225.6 (307.7) | 115.3 (227.6) | - | - | No defects | [75] |
| AZ31B-H24 | 4.95 | 4 | 1000 | - | - | - | 208 (315) | 115 (202) | - | - | - | [83] |
| AZ61 | 4 | 25 | 1400 | Left-handed threaded pin with three flutes | 3 | - | 220 (270) | 175 (219) | 81 (70) | 7.2 (~8.2) | - | [16] |
| AZ91 | 6 | 28 | 710 | Threaded straight cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 76.17 | - | - | - | No defects | [84] |
| AZ91 | 6 | 60 | 600 | - | 2.8 | 2.5 | 262 (106) | 132 (55) | - | 18.9 (15.2) | No defects on the top surface | [85] |
| AZ91D | 3 | 75 | 500 | Left-handed tapered cylindrical pin | 2.6 | 2.5 | 107 (107) | - | - | - | Defect free | [86] |
| AZ91D | 3 | 90 | 1200 | - | 2 | - | 200 (220) | 140 (150) | - | 2 (3.6) | - | [87] |
| MB3 | 3 | 120 | 1500 | - | - | - | 240 (245) | - | - | - | No macro defects | [88] |
| Mg-Y-Nd alloy (double side welded) | 20 | 240 | 700 | Threaded conical pin with three flutes | 2 | 3 | 277.6 (336.1) | 204.1 (245.9) | - | 7.27 (10.43) | Defect free | [89] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| HSLA-65 | 6 | 154.2 | 600 | Convex step-spiral scroll shoulder | - | - | 852 (538-690) | 662 (448) | - | 22.3 (min 18) | - | [102] |
| HSLA DMR-249A | 5 | 30 | 600 | Tapered pin with no threads | 5 | 0 | 664 (610) | - | 410 (270) | 19 (29) | Free from macro-level defects | [108] |
| IF | 1.6 | 400 | 400 | Cylindrical pin with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~310 (284) | - | - | - | - | [104] |
| S12C | 1.6 | 400 | 400 | Cylindrical pin with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~480 (317) | - | - | - | - | [104] |
| S35C | 1.6 | 200 | 400 | Cylindrical pin with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~780 (574) | - | - | - | - | [104] |
| DH36 | 6 | 450 | 600 | - | - | 0 | 832.51 (531.62) | 656.68 (376.71) | - | 5.57 | - | [106] |
| DH36 | 6.4 | 306 | 526 | Slightly tapered pin with no threads | - | 2.5 | ~940 (~580) | ~650 (~350) | - | - | No volumetric defects | [90] |
| Ultrafine grained AISI 304L | 2 | 80 | 630 | Conical pin | ~3 | 3 | ~760 (920) | ~500 (720) | 285 (330) | ~42 (47) | - | [109] |
| AISI 316 | 4 | 8 | 1100 | - | - | - | 610 (608) | - | 230 (190) | 35 (49) | - | [105] |
| AISI 316 | 4 | 8 | 1000 | - | - | - | 630 (608) | - | - | 37 (49) | Defect free | [110] |
| AISI 1018 | 5 | 50 | 1000 | Tapered pin with no threads | 2.2 | - | 457 (421) | 424 (361) | - | 20 (27) | - | [111] |
| HNAS (High nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel) | 2.4 | 100 | 400 | Tapered pin | 3.3 | 0 | ~1100 (~1060) | ~760 (~680) | 400 (370) | ~37 (~43) | No groove-like defects | [112] |
| Fe-18,4Cr- 15,8Mn-2,1Mo-0,66N-0,04C | 2 | 100 | 800 | - | 3 | - | 980 (967) | 580 (604) | - | 30 (53) | - | [113] |
| Fe-18Cr-16Mn-2Mo-0,85N | 3 | 50 | 800 | - | - | 2 | 1375 (1234) | 908 (782) | - | 25.13 (39.8) | - | [114] |
| Fe-24Ni-0,1C | 1.6 | 400 | 200 | - | 3 | 3 | 1283 (793) | 390 (336) | - | 29.0 (5.6) | - | [103] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| Pure copper | 2 | 50 | 1200 | Conical pin | 2 | 0 | 217.56 (237.81) | - | - | 2.03 (39) | Defect free | [156] |
| Pure copper | 2 | 30 | 1000 | - | - | - | 231 (273) | 1.2 (3.1) | 136 | - | Defect free | [157] |
| Pure copper | 3 | 30 | 2000 | Tapered pin | 2.9 | - | ~195 (217) | - | - | - | Defect free | [152] |
| Pure copper | 3 | 100 | 400 | Right hand threaded cylindrical pin and concave shoulder | 4 | - | 282 (282) | - | - | 16.4 | Defect free | [151] |
| Pure copper | 3 | 25 | 1100 | - | - | 2.5 | 194 (212) | 70 (68) | - | 22.8 (28.1) | - | [158] |
| Pure copper | 3 | 40 | 900 | Flat shoulder and cylindrical pin | 3 | 3 | 168 (260) | 109 (231) | 85 (110) | 13.5 (31) | Defect free | [159] |
| Pure copper | 3 | 250 | 300 | Non-threaded cylindrical pin | 2.4 | - | 328 (270) | 261 (209) | 113.6 (84.6) | 23 (22) | Defect free | [150] |
| Pure copper | 4 | 61 | 1250 | - | - | 3 | ~225 (~260) | - | ~90 (105-110) | - | Defect free | [144] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 30 | 910 | Straight cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 216.9 | - | 77.37 HB | 9.2 | No defects | [160] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 40 | 580 | Taper pin | ~3 | 0 | 220.7 (261.2) | 101.3 (232.0) | - | - | Defect free | [143] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 75 | 600 | - | - | - | 221 (234) | 127 (178) | 88 (107) | 43 (47) | - | [146] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 50 | 400 | - | - | 2.5 | 235.9 (236.7) | 207.7 (222.9) | - | 15.1 (27.7) | Defect free | [145] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 50 | 800 | Cylindrical threaded pin | ~3.3 | 2.5 | ~240 (~240) | ~140 (~225) | 63.1 (82.2) | ~45 (~28) | Defect free | [153] |
| Pure copper | 5 | 112 | 500 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 2.5 | 2.5 | 326 (331) | 134 (137) | ~105 (~78) | 31 (29) | Defect free | [161] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 50 | 350 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | 0 | 228 (279) | 209 (271) | 92 (82) | - | - | [155] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 50 | 350 | Square pin | - | 0 | 207 (279) | 203 (271) | 88 (82) | - | - | [155] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 50 | 350 | Triflute pin | - | 0 | 196 (279) | 196 (271) | 90 (82) | - | - | [155] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 50 | 350 | Hexagonal pin | - | 0 | 165 (279) | 163 (271) | 97 (82) | - | - | [155] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 50 | 500 | Concave shoulder and threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | 0 | 229 (279) | 229 (271) | 88 (82) | 49.9 (34.4) | Defect free | [154] |
| Pure copper | 6 | 315 | 630 | Square pin | 2.4 | 2 | 215 (150) | 190 (145) | - | 33 (14) | - | [162] |
| 2200 Copper Alloy | 5 | 31.25 | 900 | Taper pin with no threads | 3.3 | 1 | - | - | - | 26.98 | - | [163] |
| 2200 Copper Alloy | 5 | 31.25 | 900 | Cylindrical with no threads | 3.3 | 1 | - | - | - | 10.56 | - | [163] |
| Brass 60%-Cu, 40%-Zn | 2 | 500 | 1000 | - | 3 | 3 | ~390 (381) | ~180 (192) | ~132 (97) | ~52 (61) | Defect free | [141] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| Polyethylene (PE) | 5 | 25 | 1000 | Cylindrical pin with no threads | 3.2 | 1 | 19.30 (20.00) | - | - | - | - | [165] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 6 | 15 | 750 | Square pin with no threads | 2 | 1 | 19.74 (33) | - | - | - | Peeling defects | [180] |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | 5 | 10 | 1800 | Right-hand screw pin | ~4.2 | 0 | 23.5 (66.5) | - | Around 78% of base material | - | - | [171] |
| Nylon 6 | 10 | 10 | 1000 | Left handed threaded cylindrical pin | 4 | - | 34.8 (73.4) | - | 64 SD (shore-D hardness) (70 SD) | - | Defect free | [173] |
| Nylon 6 | 13 | 10 | 1250 | Right handed threaded cylindrical pin | - | - | 25.75 (54) | - | - | 8.7 (43) | - | [175] |
| Nylon 6 | 16 | 25 | 300 | Right-hand threaded pin | 2.4 | 0 | 27.22 (85) | - | - | - | Lack of bonding, minor weld defects at the bottom | [174] |
| Polyamide 6 (PA6) | 5 | 40 | 440 | Right-hand screw pin | ~4.2 | 0 | 30 (67.1) | - | 60% of base material | - | - | [171] |
| Polyamide (nylon 66) | 8 | 42 | 1570 | Smooth cylindrical pin | 4 | - | 8.51 (15.57) | - | - | - | - | [193] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 5 | 20 | 1600 | Right-hand threaded cylindrical pin | 1.7 | - | 32.62 (36.76) | - | - | - | - | [176] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) (double side welded) | 5 | 40 | 400 | Smooth cylindrical pin, flat shoulders surfaces | - | - | 15.58 (34.14) | - | - | - | - | [178] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) (double side welded) | 5 | 40 | 400 | Smooth convex pin, flat shoulders surfaces | - | - | 20.70 (34.14) | - | - | - | - | [178] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 6 | 200 | 1500 | Conical threaded pin | - | - | 30.6 (40.5) | - | - | - | Defect free | [179] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 8 | 16 | 1400 | Cylindrical with no threads | 3.3 | 1 | 41.42 (41.80) | - | - | - | - | [177] |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 8 | 25 | 900 | Conical with no threads | 3.3 | 2 | 41.95 (41.80) | - | - | - | - | [177] |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | 4 | 115 | 3000 | - | 3 | 2 | 19.4 (22.5) | - | - | - | - | [166] |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) | 5 | 15 | 1240 | Right-hand screw pin | ~4.2 | 0 | 22.3 (31.9) | - | Above 90% of base material | - | No significant defects | [171] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | |||
| Al-4.5%Cu/TiB2/2.5p | 6 | 26 | 931 | Full flat shoulder surface, cylindrical pin with no threads | ~2.9 | 2 | 190.39 (no inf about parent material) | - | 69.86 | 16.875 | - | [213] |
| Al-4.5%Cu/TiB2/2.5p | 6 | 26 | 931 | 1 mm flat shoulder and 7° concave, cylindrical pin with no threads | ~2.9 | 2 | 198.62 | - | 57.63 | 18.825 | - | [213] |
| Al-4.5%Cu/TiB2/2.5p | 6 | 26 | 931 | 2 mm flat shoulder and 7° concave, cylindrical pin with no threads | ~2.9 | 2 | 191.39 | - | 60.76 | 17.050 | - | [213] |
| AA6061/SiC (10wt%) /fly ash (7.5 wt%) | 6 | 60 | 1200 | Square profile pin | - | 2 | - | - | ~130 (102) | - | No major defects | [214] |
| AA2124/SiC/25p-T4 | 3 | 40 | 1120 | Cylindrical left-handed screwed pin | 3.3 | 2 | 366 (454) | - | 170 (185) | 1.4 (2.4) | - | [215] |
| AA6092/SiC/17.5p | 6 | 120 | 1500 | Taper cylindrical pin | 3 | 2 | 347 (415) | 290 (360) | 140 (157) | 5.46 (7.76) | No major defects | [208,216] |
| AC4A + 30vol%SiCp | 5 | 150 | 2000 | Columnar pin with right-handed threads | 2.3 | 3 | 140 (163) | - | - | 0.33 | Defect free | [211] |
| 17vol%SiCp/2009Al-T4 | 3 | 800 | 1000 | Threaded conical pin | 2.8 | - | 501 (514) | 341 (344) | - | 3.5 (4.0) | No defects | [212] |
| 17vol%SiCp/AA2009 | 3 | 50 | 1000 | Cylindrical pin | 2.8 | - | 443 (581) | 278 (508) | - | 4.7 (4.3) | No defects | [217] |
| AA2124/SiC/25p-T4 | 3 | 45 | 900 | - | 3 | 2 | 355.15 (454) | - | - | - | Flash defects on the surface | [218] |
| 25%SiC/2124Al | 8 | 15 | 400 | Tapered conical pin | 3.5 | 1.5 | 359 (372) | - | - | - | Small voids | [219] |
| AA6061-10%SiCp | 6 | 45 | 1100 | Threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 206 (278) | 126 (200) | 95 (105) | 6.5 (8.0) | No defects | [220] |
| 15vol%SiCp/2009Al | 6 | 100 | 800 | Conical pin | 2.5 | - | 441 (537) | 306 (343) | - | 5.4 (10.1) | No defects | [221] |
| AA6092/SiC/17.5p-T6 | 3.1 | 100 | 1500 | Flat edge featureless concave shoulder and M6 threaded cylindrical pin with a domed end | - | 2 | 314 (420) | 220 (370) | - | 5 (3.5) | - | [222] |
| AA6082/SiC/10p | 6 | 100 | 1800 | Cylindrical | 2.5 | 1 | 359 | - | - | - | - | [209] |
| LM25AA-5% SiCp | 12 | 40 | 1000 | Plain taper pin | 3 | - | 192 (155) | - | ~105 (68) | 7.2 (2) | - | [116] |
| PP/C30B/EA nanocomposite | 5 | 18 | - | Square pin with no threads | 1 | - | 13.533 (25.08) | - | - | - | - | [210] |
| PP/C30B/EA nanocomposite | 5 | 18 | - | Cylindrical pin with no threads | 1 | - | 16.300 (25.08) | - | - | - | - | [210] |
| PP/C30B/EA nanocomposite | 5 | 18 | - | Triangle pin with no threads | 1 | - | 13.500 (25.08) | - | - | - | - | [210] |
| Glass-filled Nylon 6 | 5 | 12 | 600 | Cylindrical pin with cylindrical shank | 3 | 2 | 36.51 (86.01) | - | - | 7.35 (13.68) | Defect free | [208] |
| Material | Plate Thickness [mm] | Process Parameters | Weld Properties | Reference | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advancing Side | Retreating Side | v [mm/min] | ω [rpm] | Tool Shape | Pin D/d Ratio | Tilt Angle [°] | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Hardness of the Stir Zone [HV] | Elongation [%] | Defects | ||
| AA2024-T3 | AA7075-T6 | 3 | 102 | 1200 | Cylindrical threaded pin | 3 | - | 423 (416 for AA2024-T3 and 593 for AA7075-T6) | 290.0 (327 for AA2024-T3 and 498 for AA7075-T6) | - | 14.9 (29.5 for AA2024-T3 and 17.7 for AA7075-T6) | - | [244] |
| AA2024-T6 | AA7075-T6 | 5 | 12 | 1200 | Flat shoulder and smooth cylindrical pin | 3 | - | 356 (416 for AA2024-T6 and 485 for AA7075-T6) | - | - | - | Defect free | [116] |
| AA5052 | AA6061 | - | 28 | 710 | Cylindrical pin with two threads | 3 | - | 180 | - | 82 | 10.6 | - | [248] |
| AA5083 | AA6082 | 3 | 300 | 840 | Conical surface of the shoulder, threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | 2 | 241 | - | - | 3.05 | - | [243] |
| AA5086-O | AA6061-T6 | 5 | 150 | 840 | Tapered pin with 3 threads and concave shoulder surface | 3.3 | - | 221 (253 for AA5086-O; 315 for AA6061-T6) | 136 (112 for AA5086-O; 278 for AA6061-T6) | - | - | - | [31] |
| AA6061-T6 | AA5086-O | 5 | 150 | 840 | Tapered pin with 3 threads and concave shoulder surface | 3.3 | - | 224 (315 for AA6061-T6; 253 for AA5086-O) | 139 (278 for AA6061-T6; 112 for AA5086-O) | - | - | - | [31] |
| AA6082 | AA5083 | 3 | 200 | 840 | Conical surface of the shoulder, threaded cylindrical pin | 3 | 2 | 227 | - | - | 2.67 | - | [243] |
| AA6351-T6 | AA5083-H111 | 6 | 60 | 950 | Flat shoulder surface, straight square pin with no threads | 3 | 0 | 273 (AA6351-T6: 310 AA5083H111: 308) | - | - | - | No defects | [246] |
| AA7075-T6 | AA2024-T3 | 6.5 (AA7075-T6); 5 (AA2024-T3) | 80 | 1400 | Square pin | - | - | 261 | - | - | - | Defect-free | [245] |
| AA7075-T6 | AA2024-T3 | 3 | 102 | 1200 | Cylindrical threaded pin | 3 | - | 381 (593 for AA7075-T6 and 416 for AA2024-T3) | 280.0 (498 for AA7075-T6 and 327 for AA2024-T3) | - | 9.0 (17.7 for AA7075-T6 and 29.5 for AA2024-T3) | - | [244] |
| St37 | 304 austenitic stainless steel | 3 | 50 | 600 | - | 2.9 | 3 | 494 (446 for St37 and 679 for 304 steel) | 290 (305 for St37 and 287 for 304 steel) | 240 (120 for St37 and 180 for 304 steel) | 28 (42 for St37 and 111 for 304 steel) | No macro defects | [249] |
| St52 mild steel | AA5186 | 3 | 56 | 355 | M3 threaded pin | 6 | 3 | 246 (520 for St52 and 275 for AA5186) | - | - | - | No defects | [250] |
| Low carbon steel | Pure Mg | 2 | 100 | 1000 | Cylindrical with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~70 (316 for low carbon steel and 170 for pure Mg) | - | - | - | - | [242] |
| Low carbon steel | AZ31 | 2 | 100 | 500 | Cylindrical with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~165 (316 for low carbo steel and 260 for AZ31) | - | - | - | - | [242] |
| Low carbon steel | AZ61 | 2 | 100 | 750 | Cylindrical with no threads | 3 | 3 | ~220 (316 for low carbon steel and 280 for AZ61) | - | - | - | - | [242] |
| AZ31 | AA6040-T61 | 2 | 225 | 1400 | Threaded tapered pin | 2.6 | 2.5 | 189 (228–238 for AZ31 and 175-205 for Al6040-T61) | - | - | - | - | [241] |
| AA6040-T61 | AZ31 | 2 | 200 | 1400 | Threaded tapered pin | 2.6 | 2.5 | 127 (175–205 for Al6040-T61 and 228–238 for AZ31) | - | - | - | - | [241] |
| AA5052-H | AZ31B | 3 | 200 | 1000 | - | 3 | 3 | 147 (244 for A5052-H and 241 for AZ31B) | 64.0 (181 for A5052-H and 200 for AZ31B) | - | 3.4 (18.0 for A5052-H and 21.6 for AZ31B) | No defects | [251] |
| AA6061 | AZ31 | 3 | 40 | 1000 | Concave shoulder and cylindrical pin | 5 | 2.5 | 178 (295 for 6061 Al and 235 for AZ31) | 170 (235 for 6061 Al and 130 for AZ31) | - | 2.4 (12.5 for 6061 Al and 18.7 for AZ31) | Defect free | [252] |
| AZ31B-0 | AA6061-T6 | 6 | 20 | 400 | Tapered smooth pin | 3.5 | - | 192 (216 for AZ31B-0 and 311 for AA6061-T6) | 153 (175 for AZ31B-0 and 280 for AA6061-T6) | - | 10 (15 for AZ31B-0 and 20 for AA6061-T6) | Defect free | [247] |
| AZ31B | AA1100 | 3 | 20 | 570 | Cylindrical threaded pin | 3.6 | - | 122 (228 for AZ31B; 175 AA1100) | 101 (145 AZ31B; 105 AA1100) | - | 9 (17 AZ31B; 11 AA1100) | - | [253] |
| SS400 mild steel | AZ31B-O | 2 | 100 | 1250 | Unthreaded cylindrical pin | 5 | - | 178.5 (455 for SS400; 257 AZ31B-O) | - | - | ~2.7 (39 for SS400 and 23.3 for AZ31B-O) | - | [254] |
| 304L stainless steel | Pure Cu | 3 | 31.5 | 1500 | Taper pin | - | 2 | 173.05 (574 for 304L; 227 for copper) | - | - | 8.22 (51 for 304L; 23 for copper) | - | [255] |
| Pure Cu | AA1050 | 6 | 63 | 1400 | - | - | - | 88.466 (91% of AA1050) | - | - | - | - | [256] |
| Pure Cu | AA1060 | 5 | 100 | 600 | Cylindrical pin | ~3.3 | - | 110 | - | - | - | Defect free | [257] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laska, A.; Szkodo, M. Manufacturing Parameters, Materials, and Welds Properties of Butt Friction Stir Welded Joints–Overview. Materials 2020, 13, 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214940
Laska A, Szkodo M. Manufacturing Parameters, Materials, and Welds Properties of Butt Friction Stir Welded Joints–Overview. Materials. 2020; 13(21):4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214940
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaska, Aleksandra, and Marek Szkodo. 2020. "Manufacturing Parameters, Materials, and Welds Properties of Butt Friction Stir Welded Joints–Overview" Materials 13, no. 21: 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214940
APA StyleLaska, A., & Szkodo, M. (2020). Manufacturing Parameters, Materials, and Welds Properties of Butt Friction Stir Welded Joints–Overview. Materials, 13(21), 4940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13214940






