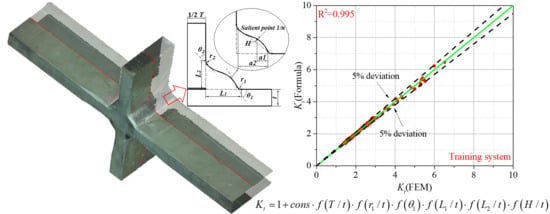
Parametric Formula for Stress Concentration Factor of Fillet Weld Joints with Spline Bead Profile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Analysis
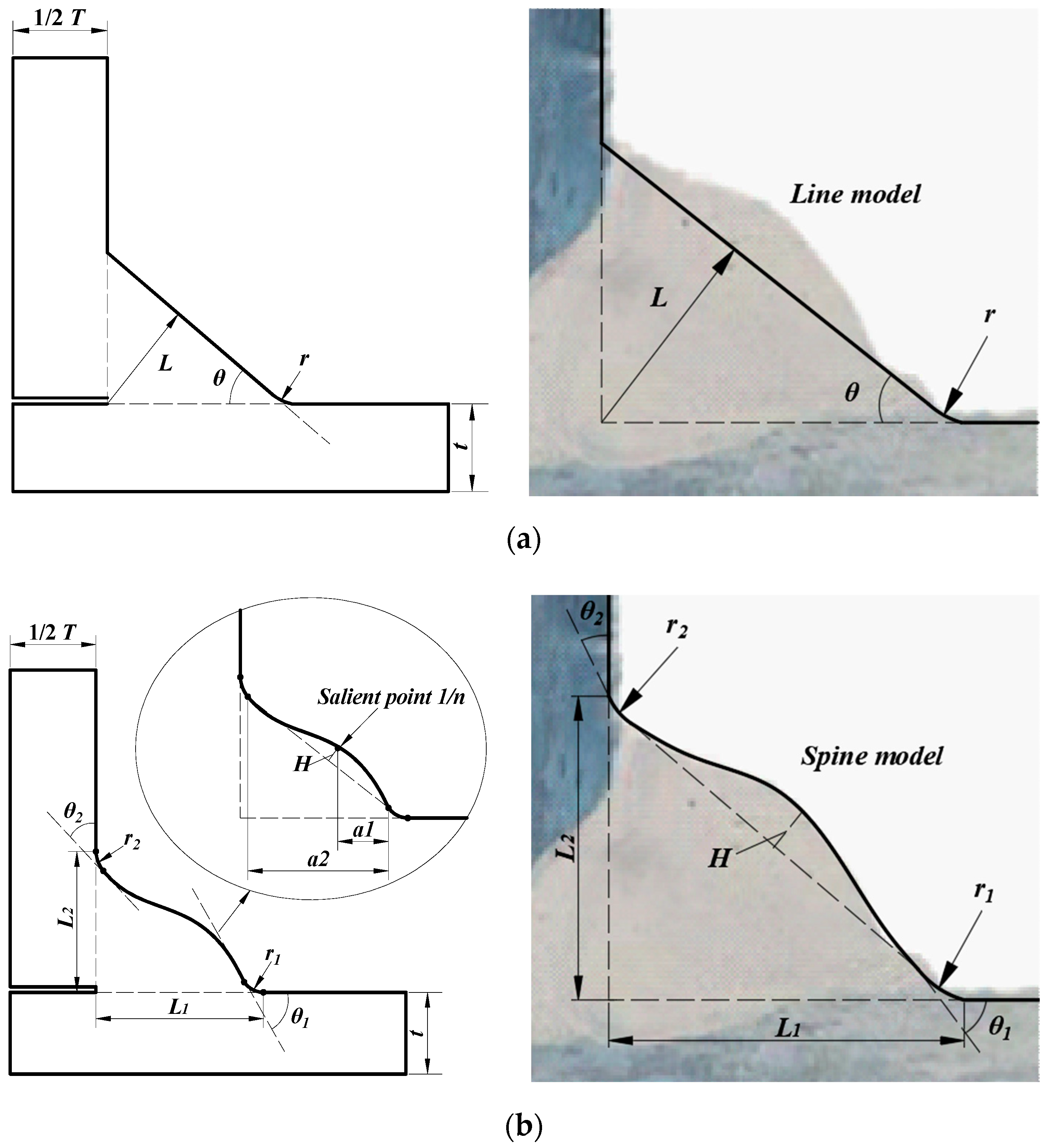
2.1. Proposed Spline Model
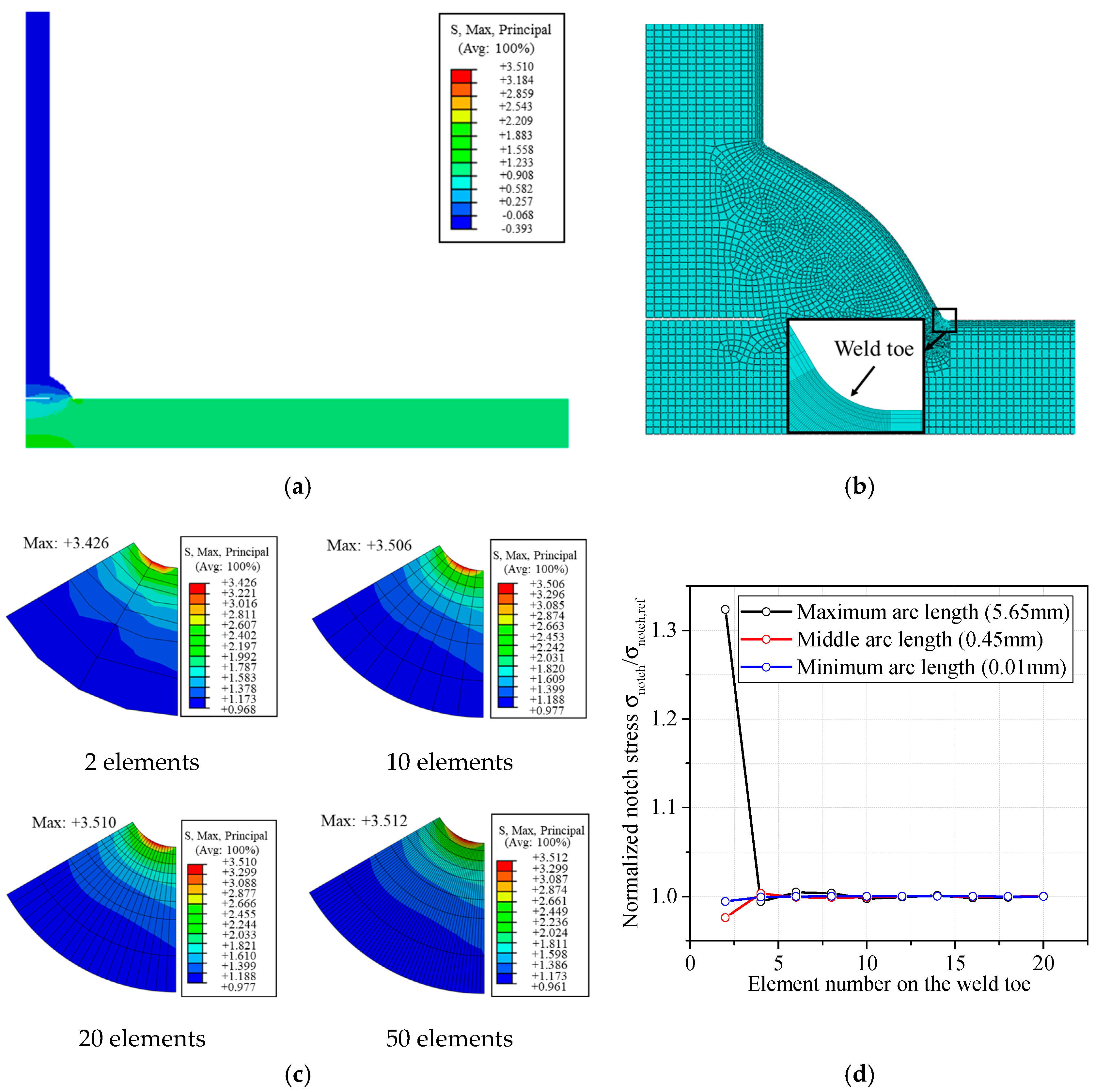
2.2. Finite Element Model for Welded Joints
2.3. Comparison between the SCF Calculated by the Spline Model and by the Line Model
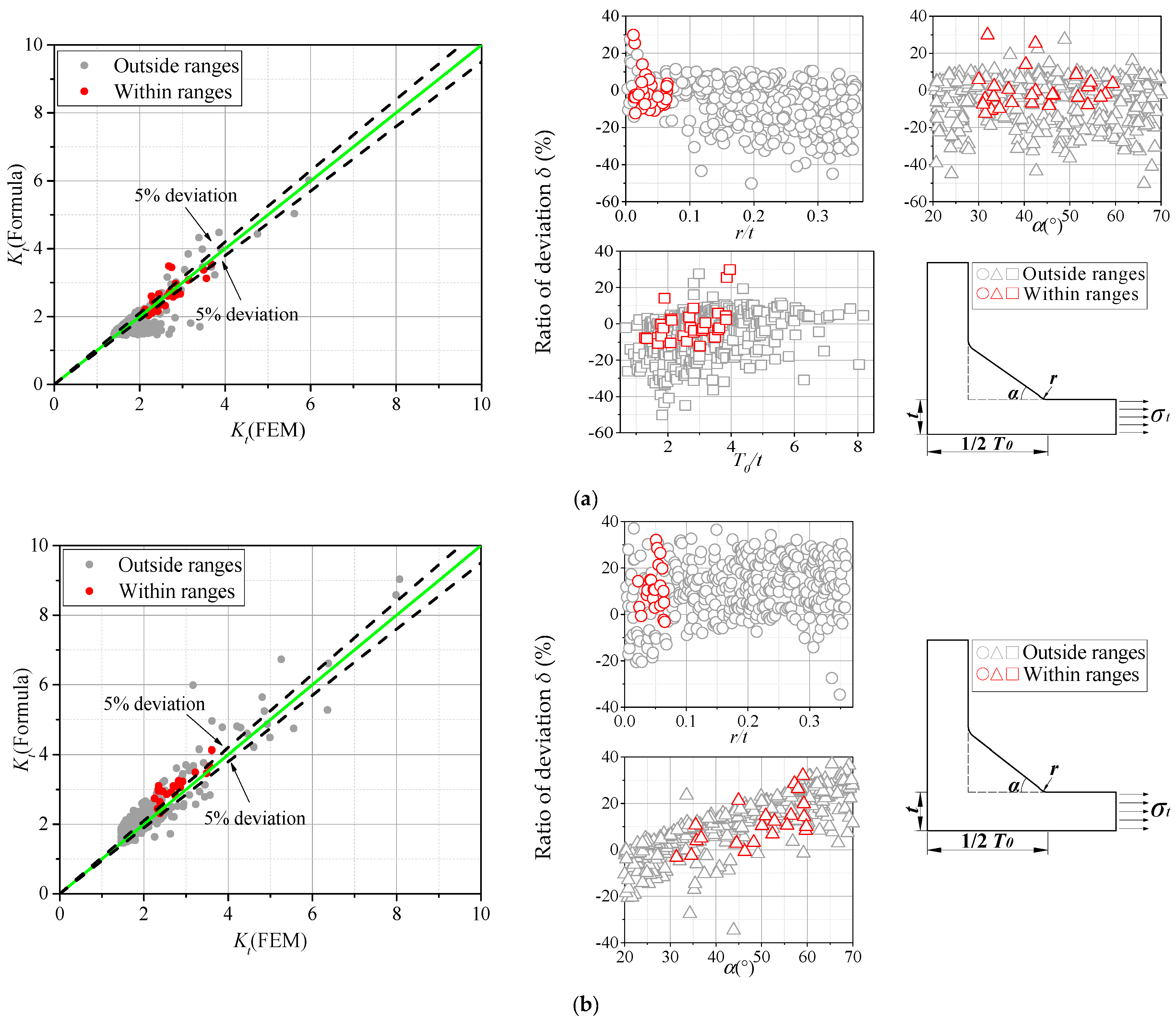
2.4. Application Ranges
- (1)
- Stiffener thickness T/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (2)
- Bottom weld toe radius r1/t: 0.003–0.36;
- (3)
- Top weld toe radius r2/t: 0.003–0.36;
- (4)
- Bottom flank angle θ1: 20°–90°
- (5)
- Top flank angle θ2: 20°–90°
- (6)
- Bottom weld leg length L1/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (7)
- Top weld leg length L2/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (8)
- Salient point position 1/n: 0.2–0.9; and
- (9)
- Hump height H/t: 0.0–0.3.
3. Proposed Parametric Formula for Fillet Weld
3.1. Overview of Existing SCF Formulae
3.2. Influence of Parameters on the SCF
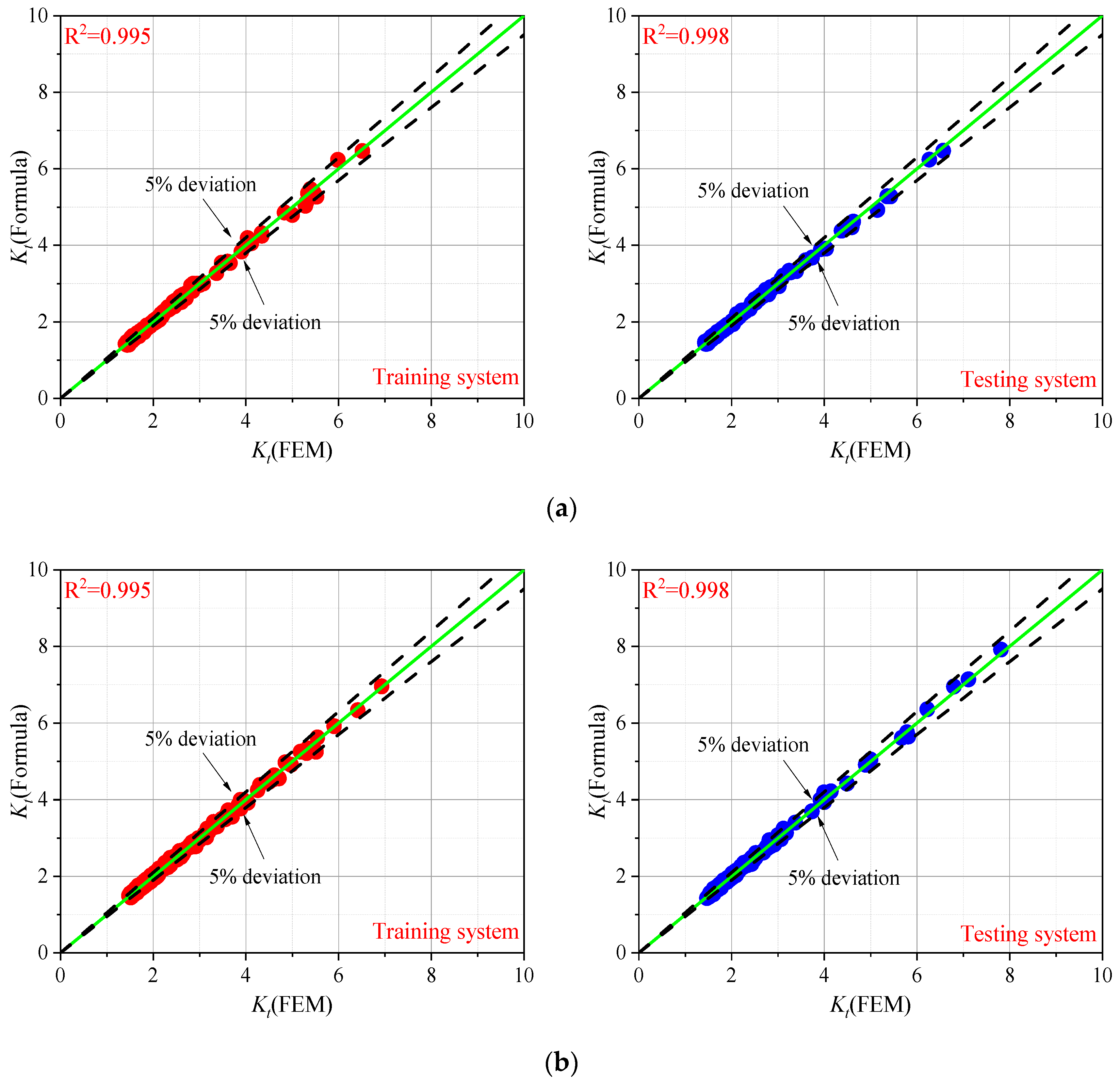
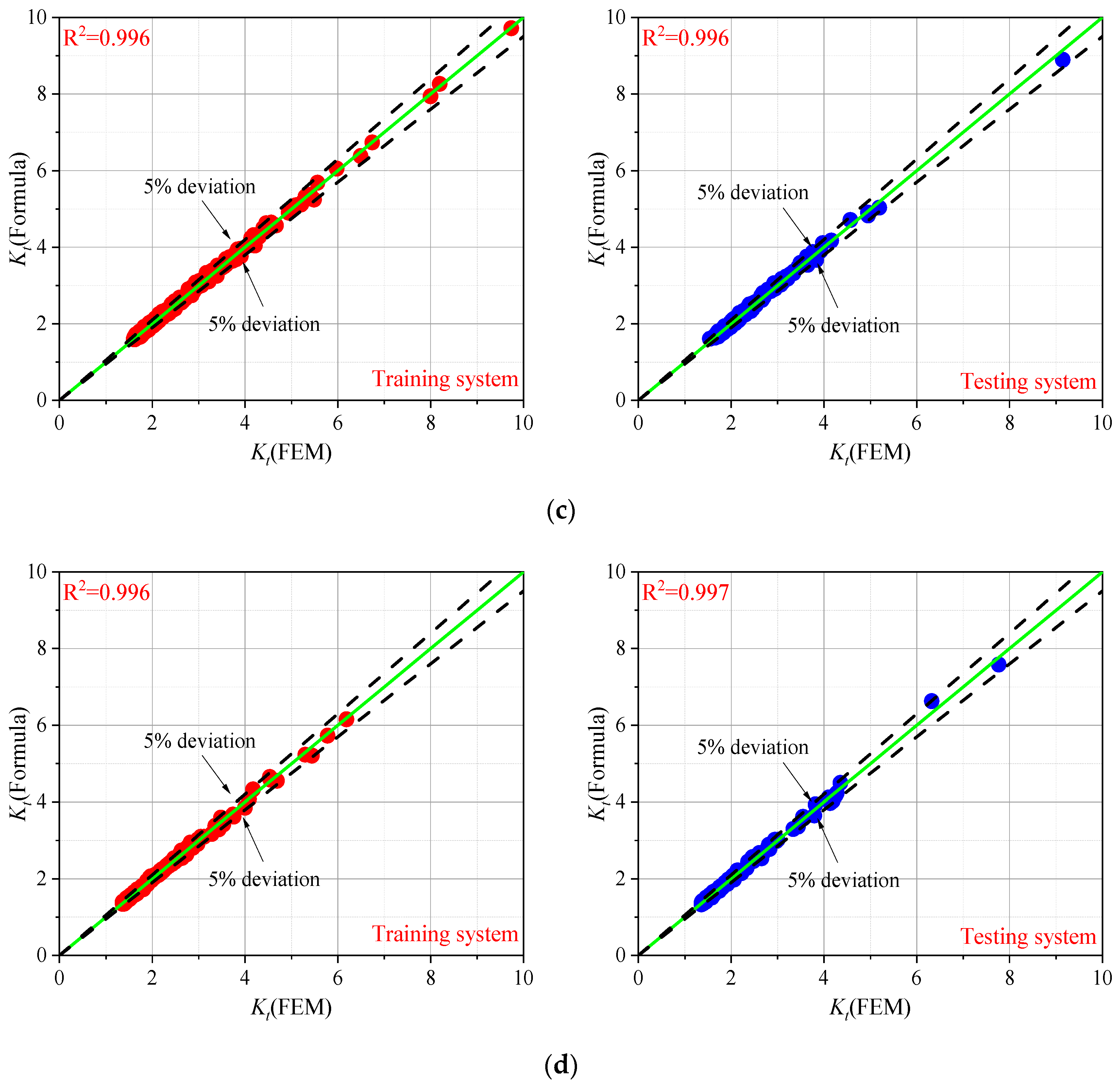
3.3. Parametric Formulae of SCF
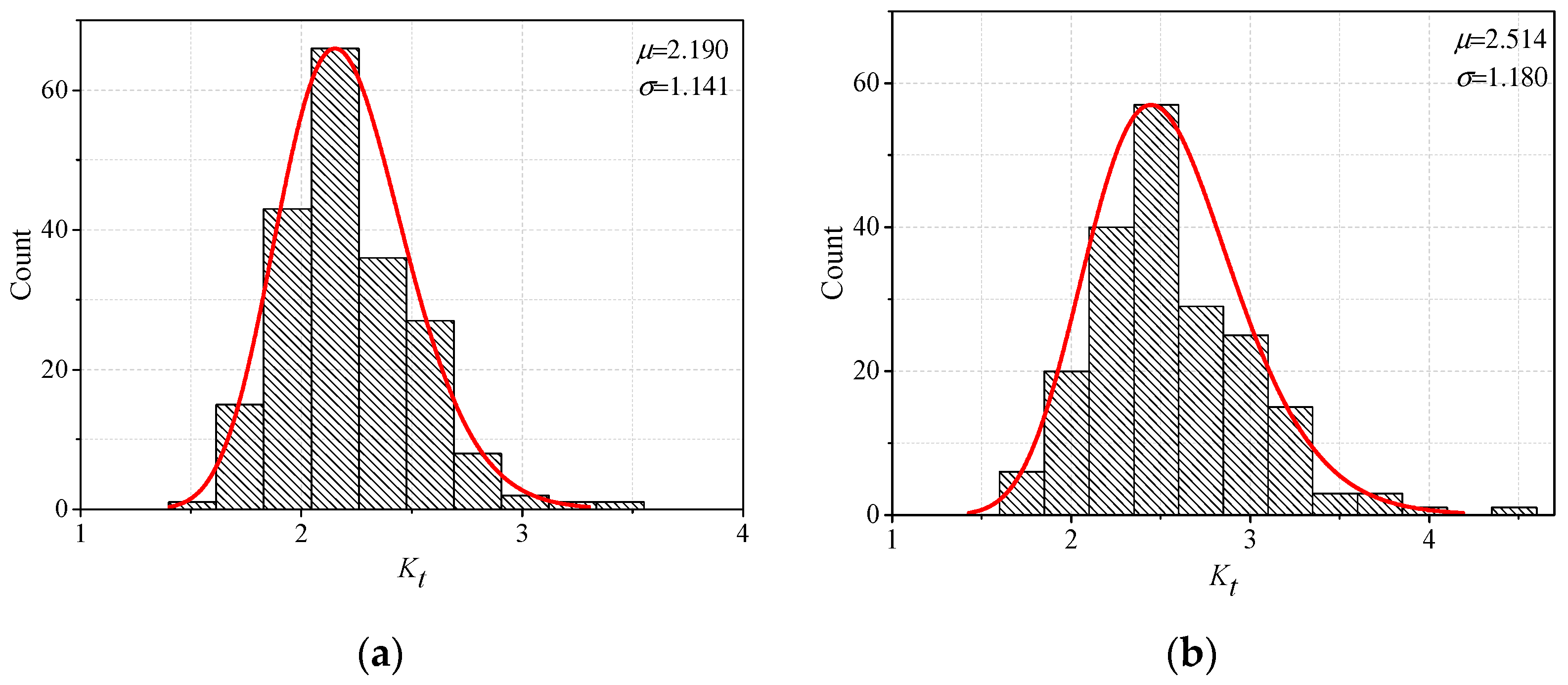
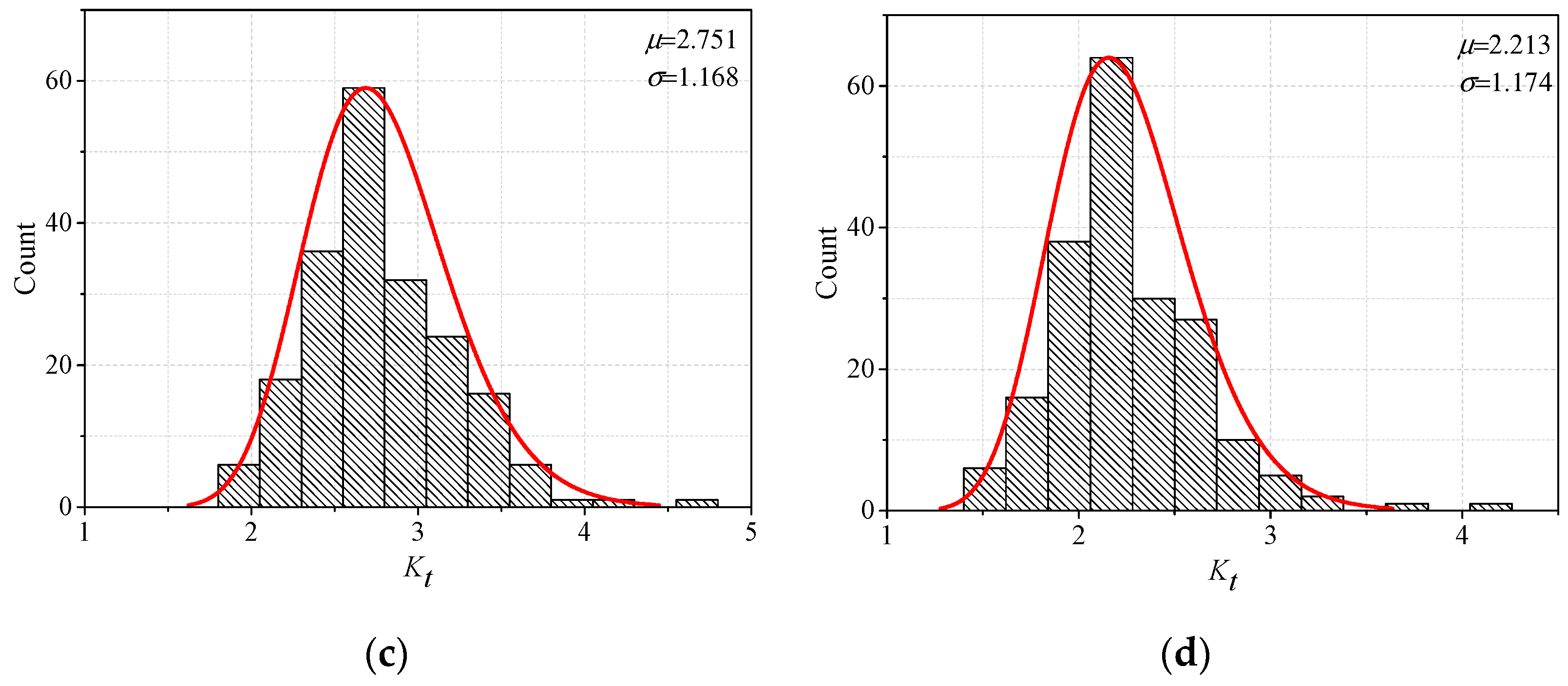
4. Probability Analysis of Fillet Weld Based on the Parametric Formulae
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Stiffener thickness T/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (2)
- Bottom weld toe radius r1/t: 0.003–0.36;
- (3)
- Top weld toe radius r2/t: 0.003–0.36;
- (4)
- Bottom flank angle θ1: 20°–90°
- (5)
- Top flank angle θ2: 20°–90°
- (6)
- Bottom weld leg length L1/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (7)
- Top weld leg length L2/t: 0.3–2.0;
- (8)
- Salient point position 1/n: 0.2–0.9; and
- (9)
- Hump height H/t: 0.0–0.3.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
- (1)
- T-shape welded joint under tensile stress:where:
- (2)
- T-shape welded joint under bending stress:where:
- (3)
- Cruciform welded joint under tensile stress:where:
- (4)
- Cruciform welded joint under bending stress:where:
References
- Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ji, B.; Jiang, F. Effects of multiaxial fatigue on typical details of orthotropic steel bridge deck. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 135, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Kitamura, T.; Fincato, R. Ductile behaviour of carbon steel for welded structures: Experiments and numerical simulations. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 172, 106185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ge, H.; Ji, B.; Hayakawa, N. Cracking reasons and features of fatigue details in the diaphragm of curved steel box girder. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ji, B.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Optimization of stop-hole parameters for cracks at diaphragm-to-rib weld in steel bridges. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 162, 105747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Fincato, R. Cyclic plasticity model for fatigue with softening behaviour below macroscopic yielding. Mater. Des. 2019, 165, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molski, K.L.; Tarasiuk, P. Stress concentration factors for butt-welded plates subjected to tensile, bending and shearing loads. Materials 2020, 13, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavian, S.; Fatemi, A. Effects of mean stress and stress concentration on fatigue behavior of short fiber reinforced polymer composites. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2016, 39, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Ji, B.; Kong, X.; Chen, X. Grinding treatment effect on rib-to-roof weld fatigue performance of steel bridge decks. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 129, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowicz, P.J.; Szybiński, B.; Wygoda, M. Application of DIC method in the analysis of stress concentration and plastic zone development problems. Materials 2020, 13, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schijve, J. Fatigue of Structures and Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Ferreira, E.; Corbella, S.; Zanatta, L.C.; Taschieri, S.; del Fabbro, M.; Gehrke, S.A. Photo-elastic investigation of influence of dental implant shape and prosthetic materials to patterns of stress distribution. Minerva Stomatol. 2012, 61, 263–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; Dang, Z. Fiber Bragg gratings based cyclic strain measuring of weld toes of cruciform joints. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tian, H. FEM study on the stress concentration factors of K-joints with welding residual stress. Appl. Ocean Res. 2013, 43, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerit, M.; Genel, K.; Eksi, S. Numerical investigation on stress concentration of corrosion pit. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, M.; Ghafouri, M.; Raftar, H.R.R.; Björk, T. Neural network-based assessment of the stress concentration factor in a T-welded joint. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 128, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, K.; Uemura, T. Stress Concentration Factor Formulae Widely Used in Japan. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1996, 19, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, F.P.; Peleties, P.; Hellier, A.K. Predicting weld toe stress concentration factors for T and skewed T-joint plate connections. Int. J. Fatigue 2000, 22, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Tamai, Y.; Hiramoto, J.; Ogawa, K. Effect of weld toe geometry on fatigue life of lap fillet welded ultra-high strength steel joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 116, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ma, R.; Tsutsumi, S. Parametric formulae for elastic stress concentration factor at the weld toe of distorted butt-welded joints. Materials 2020, 13, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyak, Y.; Madia, M.; Zerbst, U. Extended parametric equations for weld toe stress concentration factors and through-thickness stress distributions in butt-welded plates subject to tensile and bending loading. Weld World 2016, 60, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola, D.; Williams, C.L. Estimating the fatigue stress concentration factor of machined surfaces. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, C.; Anami, K. Improving fatigue strength by additional welding with low temperature transformation welding electrodes. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2001, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Meneghetti, G.; Campagnolo, A.; Berto, F. Fatigue strength assessment of partial and full-penetration steel and aluminium butt-welded joints according to the peak stress method. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2015, 38, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molski, K.L.; Tarasiuk, P.; Glinka, G. Stress concentration at cruciform welded joints under axial and bending loading modes. Weld World 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.Y. Fatigue analysis of welded joints with the aid of real three-dimensional weld toe geometry. Int. J. Fatigue 2007, 29, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellier, A.K.; Brennan, F.P.; Carr, D.G. Weld toe SCF and stress distribution parametric equations for tension (membrane) loading. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 891, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.D.M.; Jesus, J.S.; Loureiro, A.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Borrego, L.P. Fatigue life improvement of mig welded aluminium T-joints by friction stir processing. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 61, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, C.C. Early Fatigue Crack Growth at Welds (Topics in Engineering); Computational Mechanics: Southampton, UK, 1995; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, F.V.; Ho, N.J.; Mazumdar, P.K. Predicting the fatigue stress analysis of weldments. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1981, 11, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, I. Estimation of stress concentration factor at weld toe of non-load carrying fillet welded joints. West. Jpn. Soc. Naval Archit. 1990, 80, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zoran, D. The Weld Profile Effect on Stress Concentration Factors in Weldments. In Proceedings of the 15th International Research/Expert Conference “Trends in the Development of Machinery and Associated Technology”, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–18 September 2011; pp. 977–980. [Google Scholar]
- Pachoud, A.; Manso, P.; Schleiss, A. New parametric equations to estimate notch stress concentration factors at butt welded joints modeling the weld profile with splines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 72, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


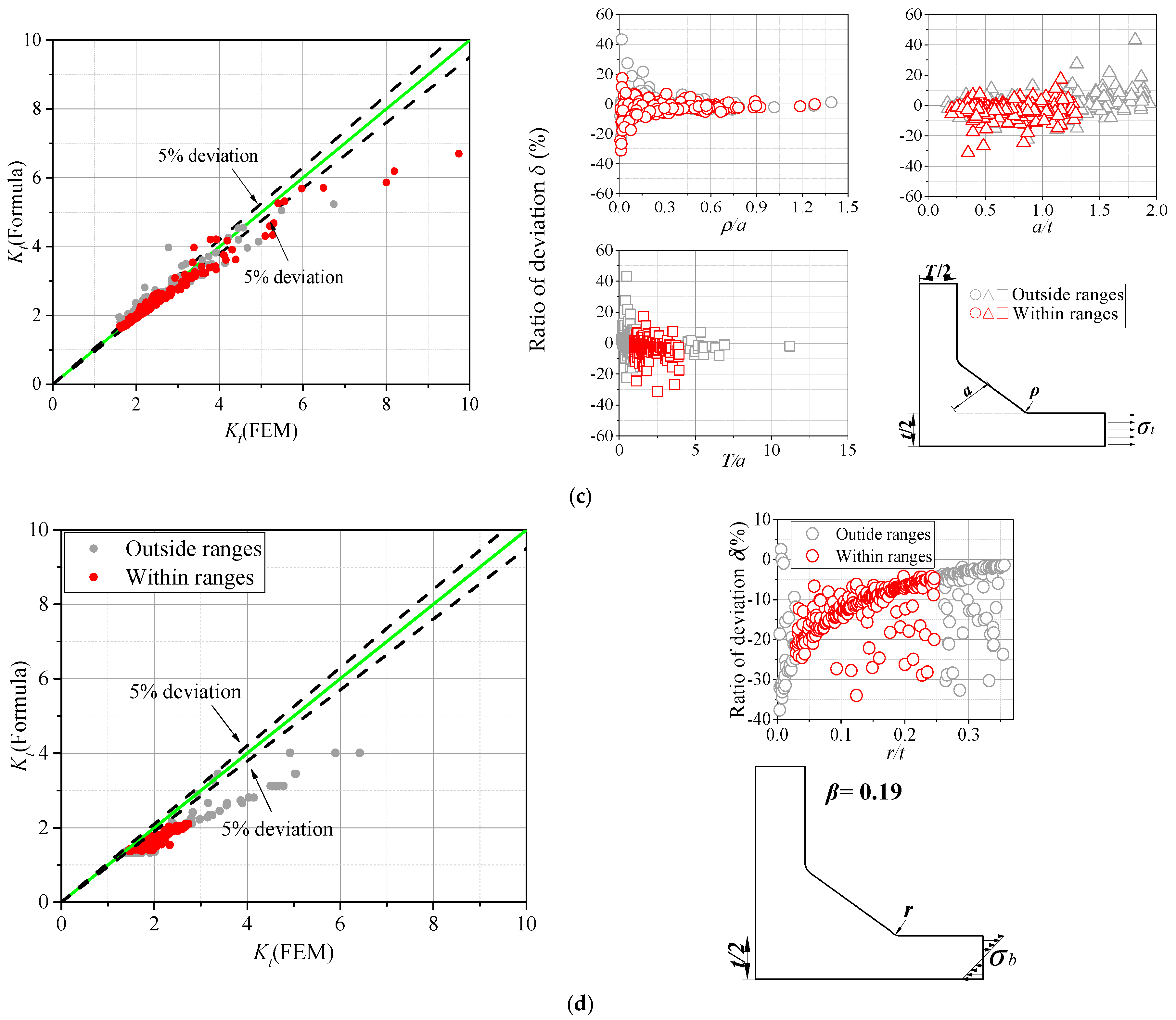


| References | Parametric Formulae | Application Ranges | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brennan et al. [17] | Equation (A1) | r/t: 0.01–0.066 α: 30°–60° T0/t: 0.3–4.0 | T-shape joint under tensile stress |
| Monahan [28] | Equation (A2) | r/t: 0.02–0.066 α: 30°–60° | T-shape joint under bending stress |
| Molski [24] | Equation (A3) | ρ/a: 0.0–1.3 a/t: 0.0–1.3 T/a: 1.0–4.0 | Cruciform joint under tensile stress |
| Lawrence et al. [29] | Equation (A4) | r/t: 0.03–0.25 | Cruciform joint under bending stress |
| Welding Method | Welding Position | Welding Wire | Welding Current | Welding Voltage | Welding Speed | Interpass Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMA(CO2) | Downhand | MX-Z200 | 270 A | 34 V | 26.1 cm/min | Below 80 °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tsutsumi, S. Parametric Formula for Stress Concentration Factor of Fillet Weld Joints with Spline Bead Profile. Materials 2020, 13, 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204639
Wang Y, Luo Y, Tsutsumi S. Parametric Formula for Stress Concentration Factor of Fillet Weld Joints with Spline Bead Profile. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yixun, Yuxiao Luo, and Seiichiro Tsutsumi. 2020. "Parametric Formula for Stress Concentration Factor of Fillet Weld Joints with Spline Bead Profile" Materials 13, no. 20: 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204639
APA StyleWang, Y., Luo, Y., & Tsutsumi, S. (2020). Parametric Formula for Stress Concentration Factor of Fillet Weld Joints with Spline Bead Profile. Materials, 13(20), 4639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204639