Bearing Thickness Is Not a Predictive Factor for Damage and Penetration in Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—A Retrieval Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
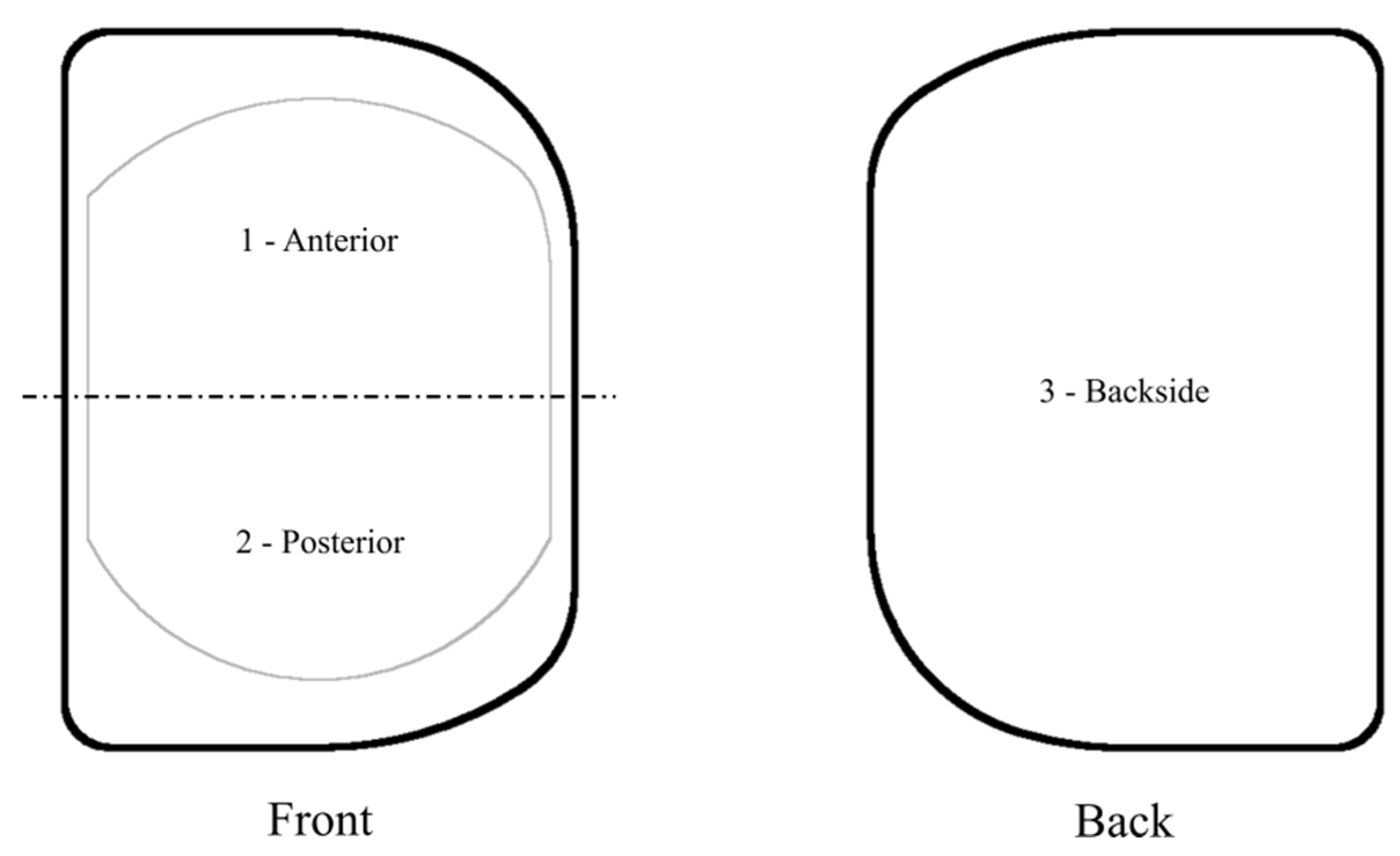
2. Materials and Methods
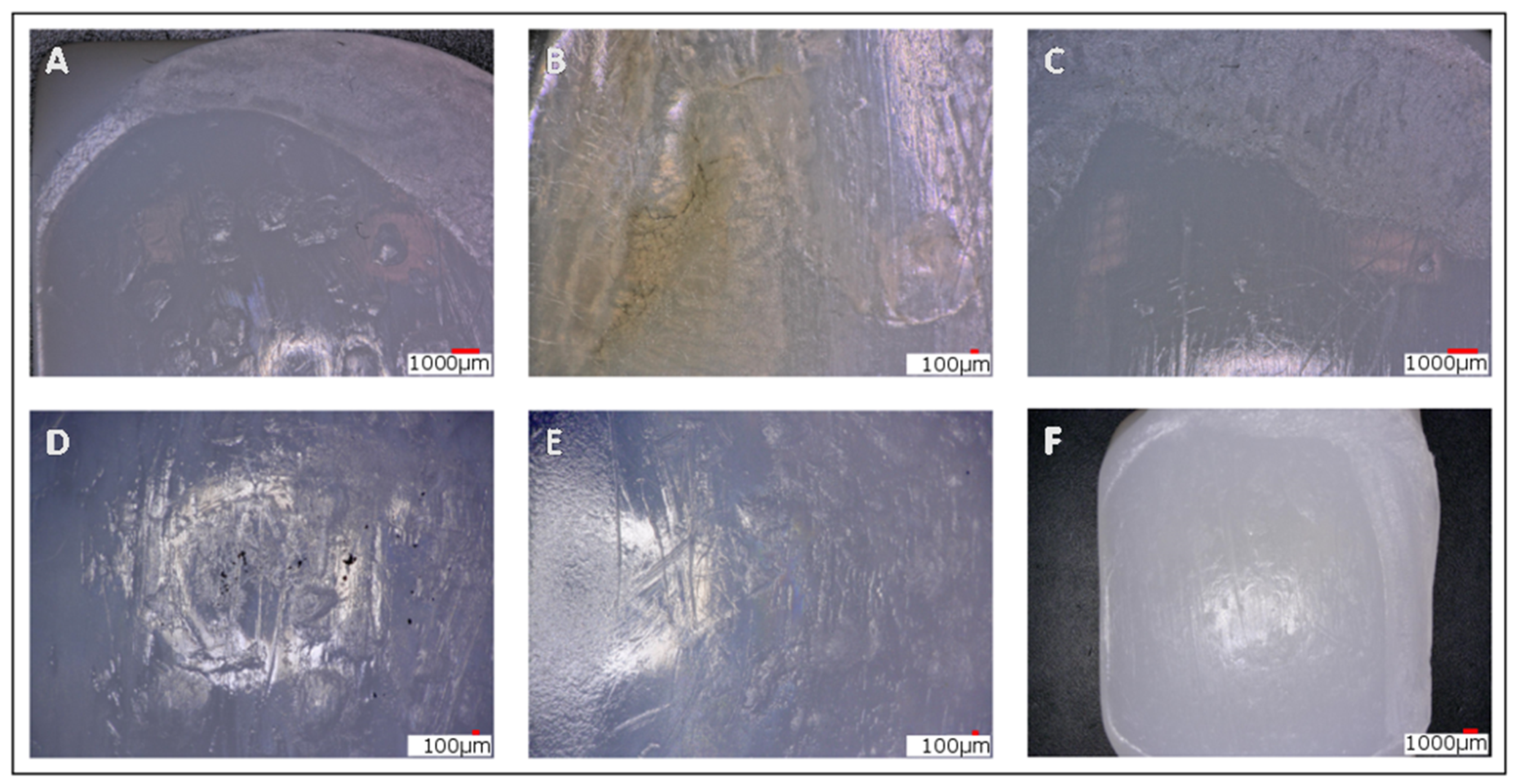
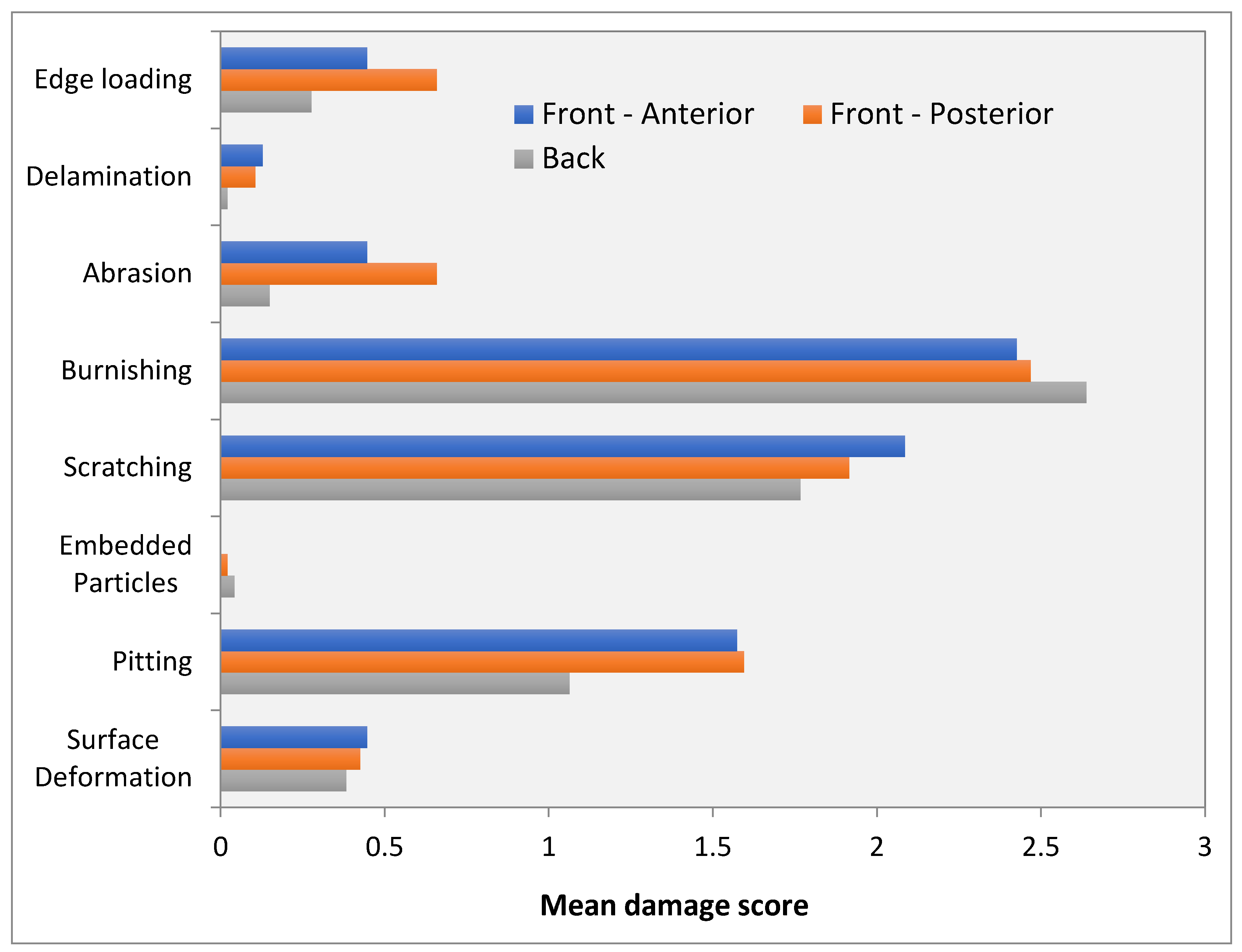
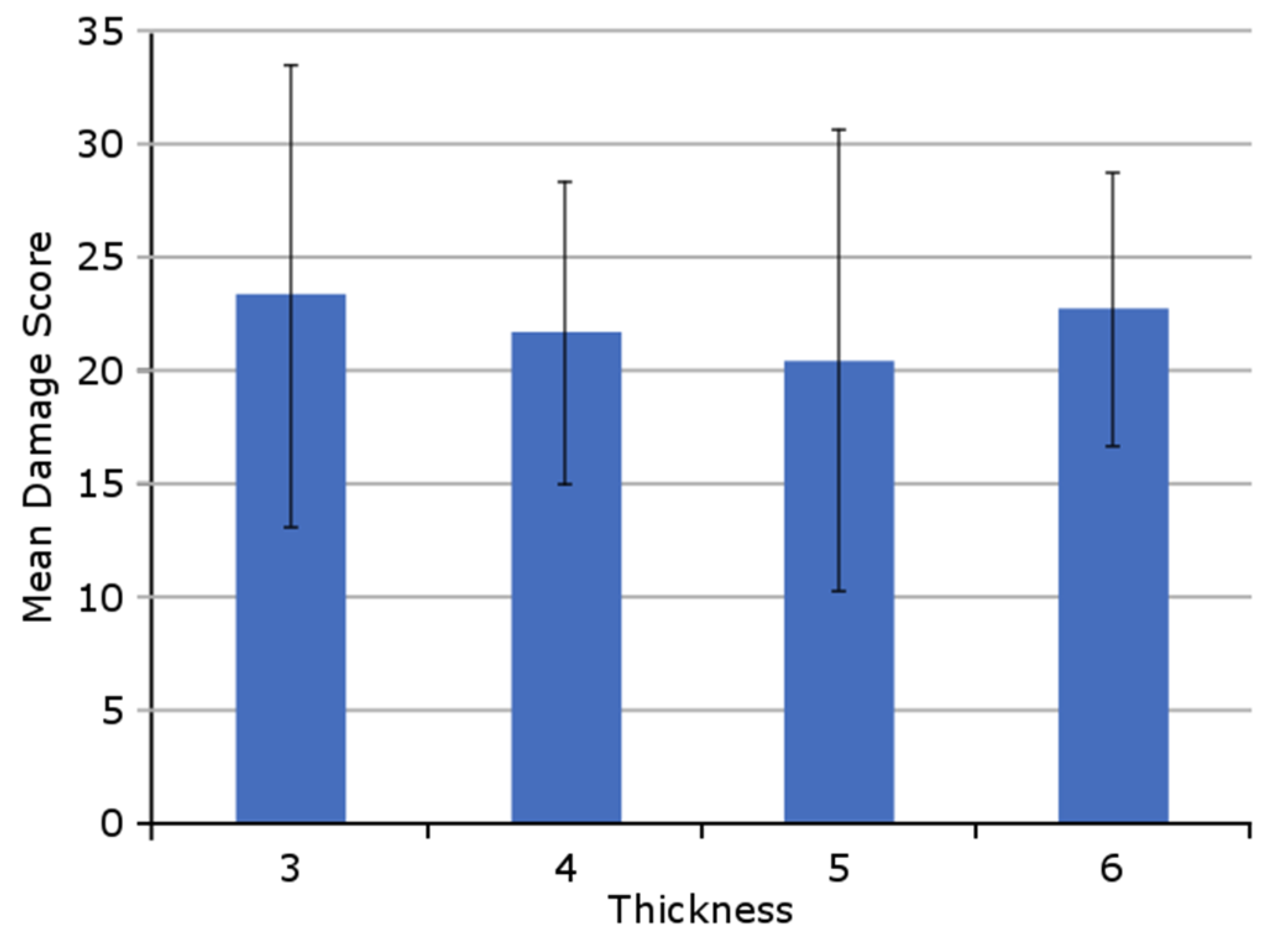
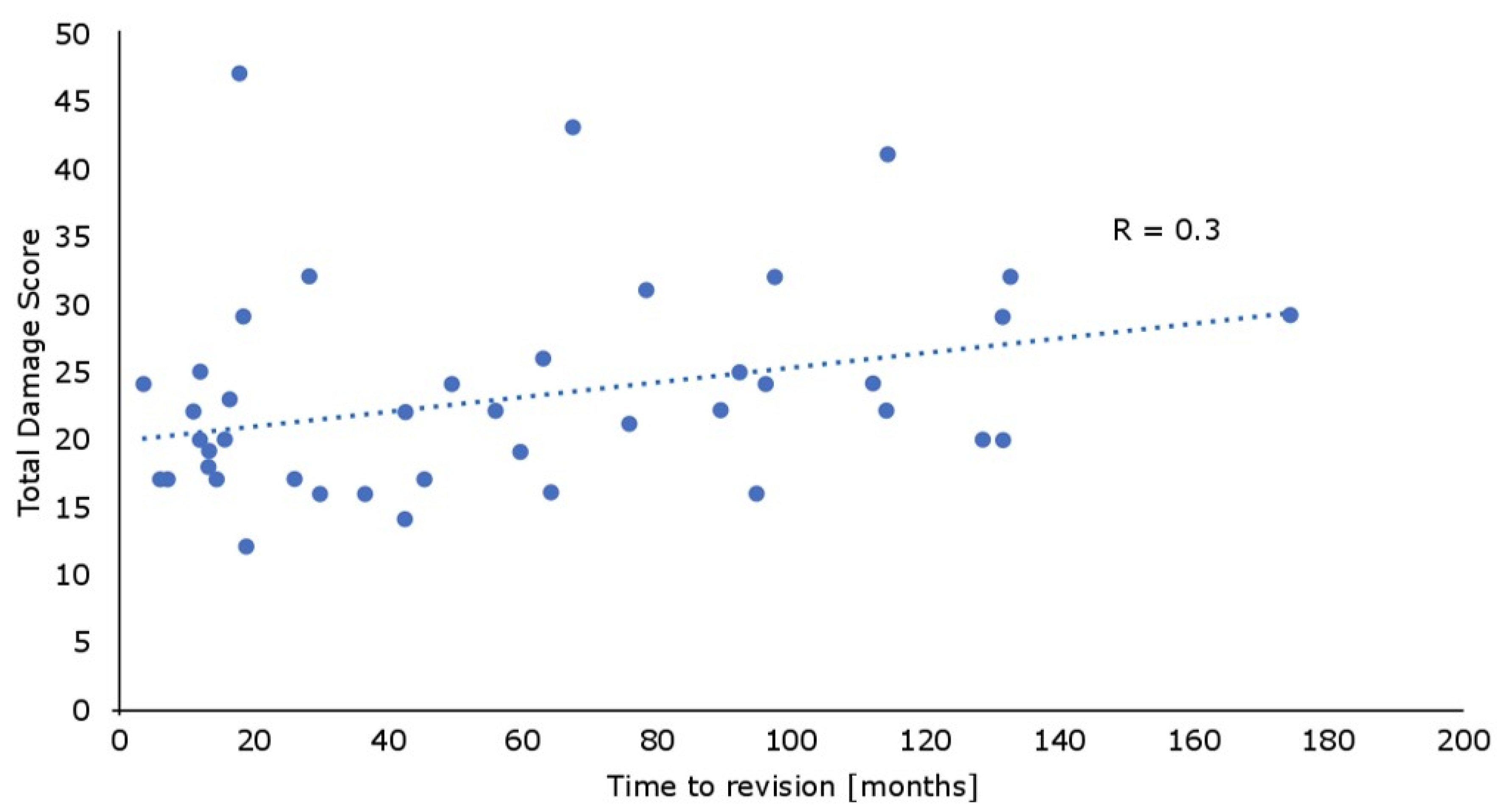
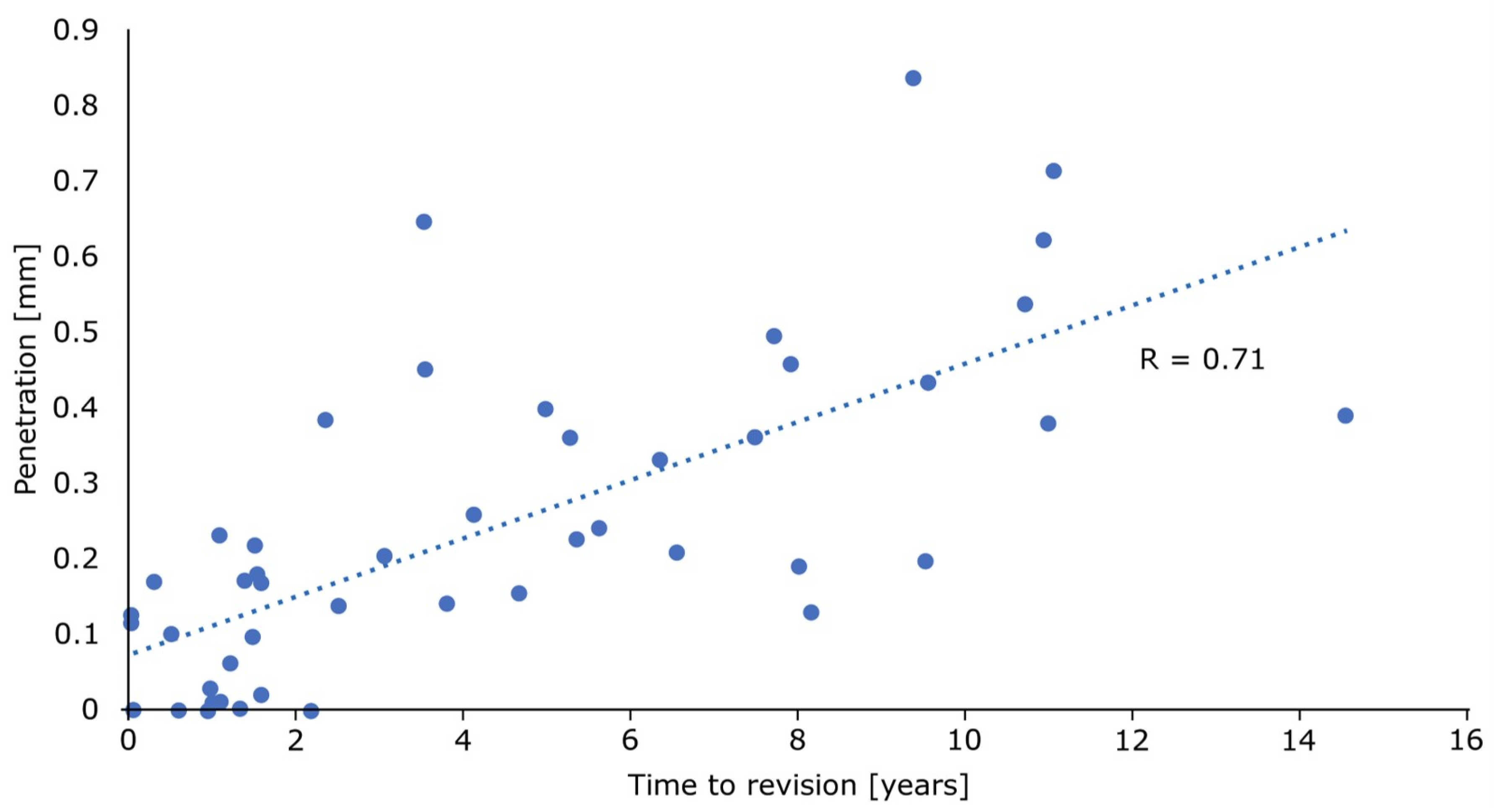
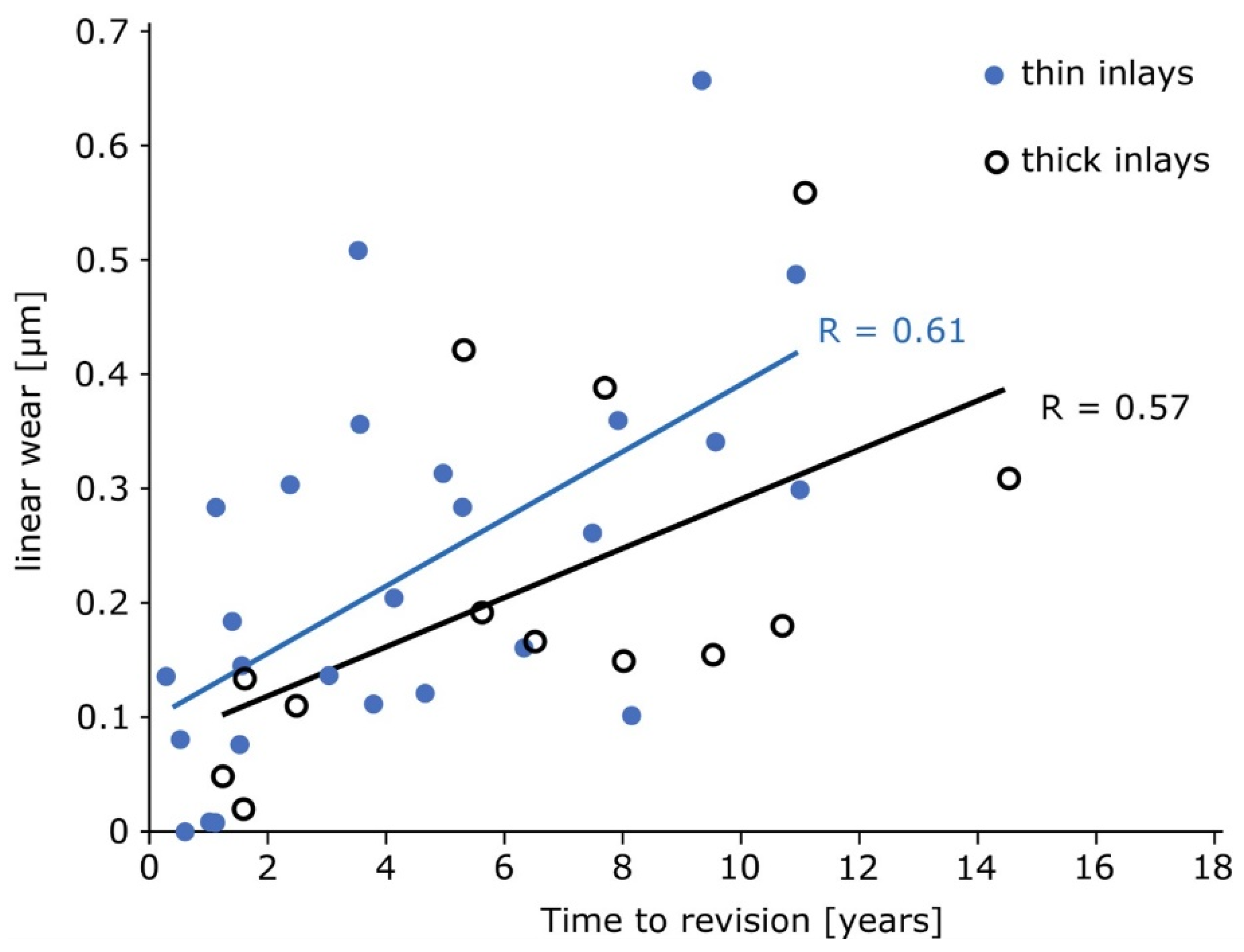
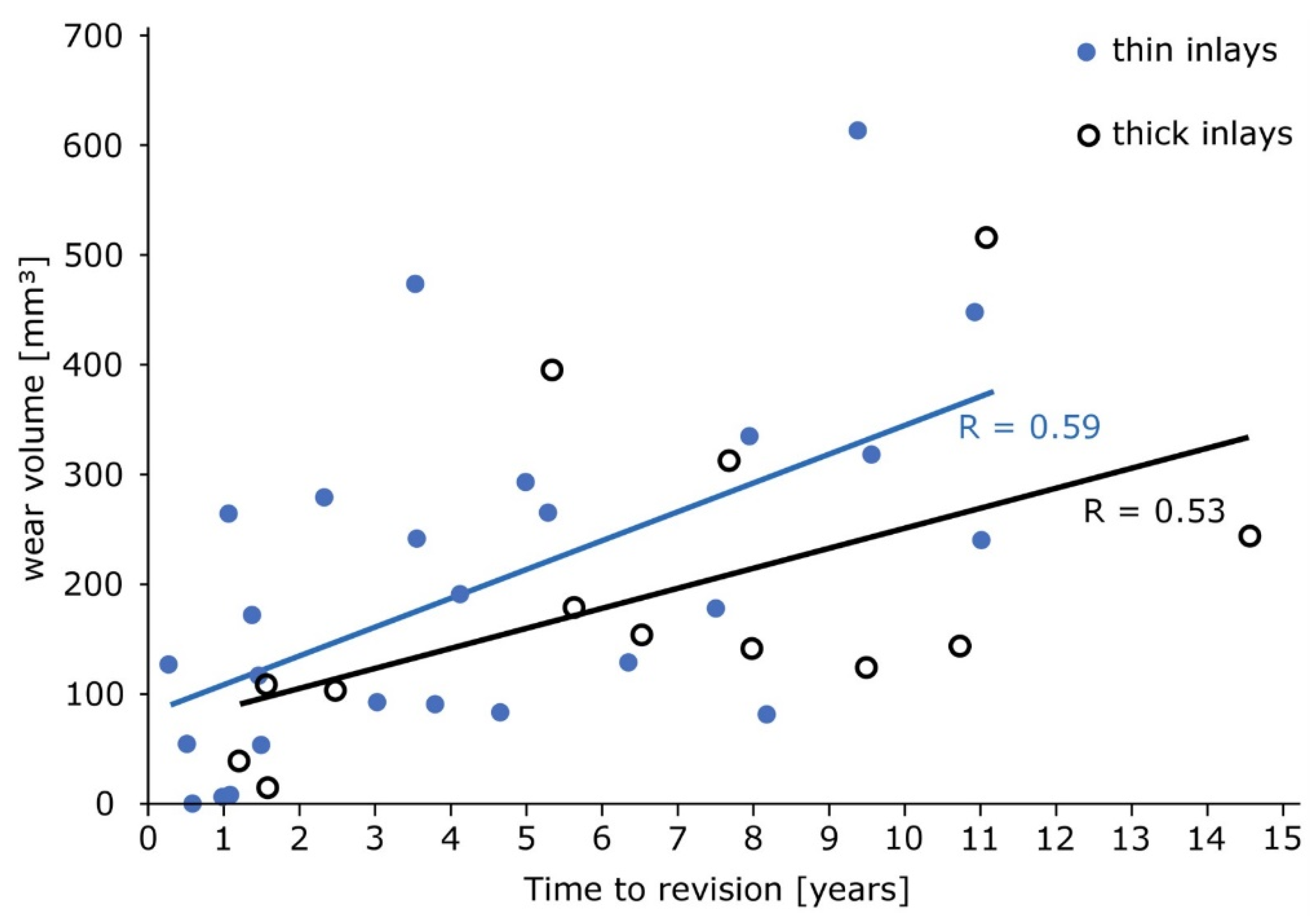
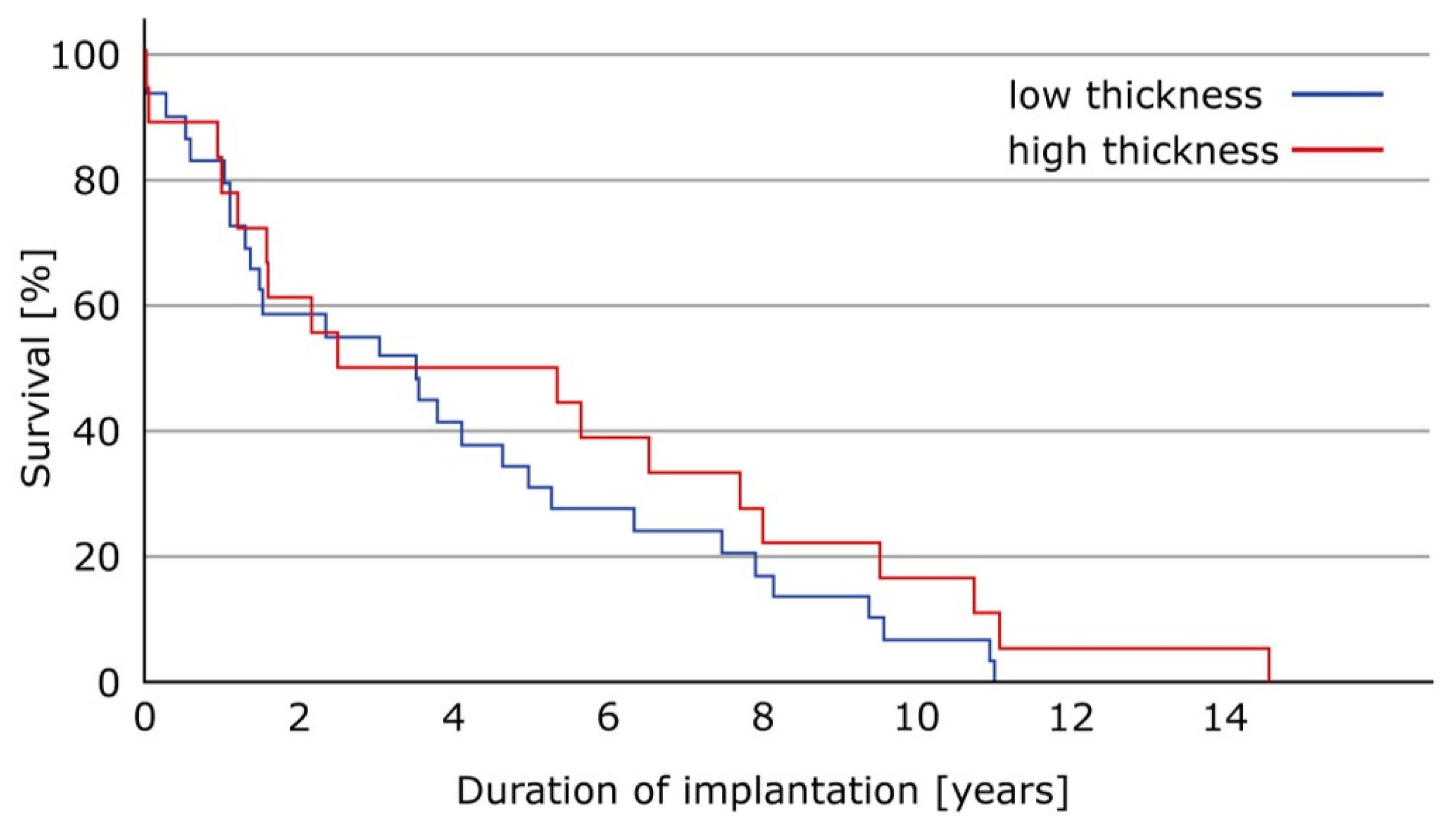
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyrhovden, G.S.; Lygre, S.H.L.; Badawy, M.; Gøthesen, Ø.; Furnes, O. Have the causes of revision for total and unicompartmental knee arthroplasties changed during the past two decades? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1874–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.S.; Van Citters, D.W.; Berry, D.J.; Abdel, M.P. The use of highly crosslinked polyethylene in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, R.; Elmallah, R.D.K.; Cherian, J.J.; Kurtz, S.M.; Mont, M.A. Polyethylene Wear in Knee Arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2015, 28, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annual Report Australian Orthopaedic Association. 2017. Available online: https://aoanjrr.sahmri.com/de/annual-reports-2017 (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Jennings, J.M.; Kleeman-Forsthuber, L.T.; Bolognesi, M.P. Medial unicompartmental arthroplasty of the knee. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, H.R.; Strickland, L.; Hamilton, T.W.; Murray, D.W. Long-term outcomes of over 8,000 medial Oxford Phase 3 Unicompartmental Knees—A systematic review. Acta Orthop. 2018, 89, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.J.; Gray, H.; D’Lima, D.; Murray, D.W.; Gill, H.S. The effect of bearing congruency, thickness and alignment on the stresses in unicompartmental knee replacements. Clin. Biomech. 2008, 23, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzer, J.P.; Jakubowitz, E.; Reinders, J.; Lietz, E.; Moradi, B.; Hofmann, K.; Sonntag, R. Wear analysis of unicondylar mobile bearing and fixed bearing knee systems: A knee simulator study. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, T.T.; Kelly, N.H.; Lipman, J.D.; Wright, T.M.; Westrich, G.H. Unicondylar knee retrieval analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, H.; Hamilton, T.W.; Jenkins, C.; Mellon, S.J.; Dodd, C.A.F.; Murray, D.W. The clinical outcome of minimally invasive Phase 3 Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A 15-year follow-up of 1000 UKAs. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Bae, J.-H.; Lim, H.C. Factors Affecting the postoperative limb alignment and clinical outcome after oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.L.; Bicknell, V.L.; Wright, T.M. The effect of conformity, thickness, and material on stresses in ultra-high molecular weight components for total joint replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1986, 68, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.L.; Rawlinson, J.J.; Burstein, A.H.; Ranawat, C.S.; Flynn, W.F. Stresses in polyethylene components of contemporary total knee replacements. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1995, 317, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Engh, G.A.; Dwyer, K.A.; Hanes, C.K. Polyethylene wear of metal-backed tibial components in total and unicompartmental knee prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1992, 74, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.P.; Engh, G.A.; Ammeen, D.J. Revision of failed unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.A.; Pandit, H.G.; Ramos, J.L.; Grover, M.L. Analysis of polyethylene thickness of tibial components in total knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, R.W.; Wright, T.M.; Burstein, A.H. Retrieval analysis of total knee prostheses: A method and its application to 48 total condylar prostheses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1983, 17, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.R.; Campi, S.; Kennedy, J.A.; Judge, A.; Murray, D.W.; Mellon, S.J. Long-term in vivo wear of different bearing types used for the oxford unicompartmental knee replacement. Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquiglini, A.; Henckel, J.; Hothi, H.; Rotigliano, N.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Hart, A.J. 3D patient imaging and retrieval analysis help understand the clinical importance of rotation in knee replacements. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 3351–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Pezzotti, G.; Puppulin, L.; Sudo, A. Effect of e-beam sterilization on the in vivo performance of conventional UHMWPE tibial plates for total knee arthroplasty. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychoyios, V.; Crawford, R.W.; O’Connor, J.J.; Murray, D.W. Wear of congruent meniscal bearings in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A retrieval study of 16 specimens. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1998, 80, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engh, G.A.; Zimmerman, R.L.; Parks, N.L.; Engh, C.A. Analysis of wear in retrieved mobile and fixed bearing knee inserts. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, M.; Affatato, S.; Spinelli, M.; Zavalloni, M.; Stea, S.; Toni, A. Polyethylene insert damage in unicondylar knee replacement: A comparison of in vivo function and in vitro simulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2010, 224, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Huang, C.H.; Chang, T.K.; Ho, F.Y.; Cheng, C.K.; Huang, C.H. Wear-pattern analysis in retrieved tibial inserts of mobile-bearing and fixed-bearing total knee prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, F.-Y.; Ma, H.-M.; Liau, J.-J.; Yeh, C.-R.; Huang, C.-H. Mobile-bearing knees reduce rotational asymmetric wear. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 462, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, B.J.L.; Longino, D.; Pandit, H.; Svard, U.; Gill, H.S.; Dodd, C.A.F.; Murray, D.W.; Price, A.J. Polyethylene wear in Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2010, 92, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingaraj, K.; Morris, H.; Bartlett, J. Polyethylene thickness in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Knee 2011, 18, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pijls, B.G.; Van der Linden-Van der Zwaag, H.M.J.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H. Polyethylene thickness is a risk factor for wear necessitating insert exchange. Int. Orthop. 2012, 36, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, C.B.; Bhutani, P.; Wimmer, M.A. Relationship of surface damage appearance and volumetric wear in retrieved TKR polyethylene liners: Retrieved tkr polyethylene damage patterns and volumetric wear. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2053–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquiglini, A.; Henckel, J.; Hothi, H.; Moser, L.B.; Eskelinen, A.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Hart, A.J. Retrieval analysis of contemporary antioxidant polyethylene: Multiple material and design changes may decrease implant performance. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop, A.M.; Swarts, E. Quantification of polyethylene degradation in mobile bearing knees: A retrieval analysis of the Anterior-Posterior-Glide (APG) and Rotating Platform (RP) Low Contact Stress (LCS) knee. Acta Orthop. 2007, 78, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsager, K.; Madsen, F.; Odgaard, A.; Fink Jepsen, C.; Rømer, L.; Kristensen, P.W.; Kaptein, B.L.; Søballe, K.; Stilling, M. Similar polyethylene wear between cemented and cementless Oxford medial UKA: A 5-year follow-up randomized controlled trial on 79 patients using radiostereometry. Acta Orthop. 2019, 90, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ijsseldijk, E.A.; Valstar, E.R.; Stoel, B.C.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; Reiber, J.H.C.; Kaptein, B.L. The robustness and accuracy of in vivo linear wear measurements for knee prostheses based on model-based RSA. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 2724–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ijsseldijk, E.A.; Harman, M.K.; Luetzner, J.; Valstar, E.R.; Stoel, B.C.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; Kaptein, B.L. Validation of a model-based measurement of the minimum insert thickness of knee prostheses: A retrieval study. Bone Jt. Res. 2014, 3, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eckert, J.A.; Mueller, U.; Walker, T.; Schwarze, M.; Jaeger, S.; Kretzer, J.P. Bearing Thickness Is Not a Predictive Factor for Damage and Penetration in Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—A Retrieval Analysis. Materials 2020, 13, 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204589
Eckert JA, Mueller U, Walker T, Schwarze M, Jaeger S, Kretzer JP. Bearing Thickness Is Not a Predictive Factor for Damage and Penetration in Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—A Retrieval Analysis. Materials. 2020; 13(20):4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204589
Chicago/Turabian StyleEckert, Johannes Adrian, Ulrike Mueller, Tilman Walker, Martin Schwarze, Sebastian Jaeger, and Jan Philippe Kretzer. 2020. "Bearing Thickness Is Not a Predictive Factor for Damage and Penetration in Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—A Retrieval Analysis" Materials 13, no. 20: 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204589
APA StyleEckert, J. A., Mueller, U., Walker, T., Schwarze, M., Jaeger, S., & Kretzer, J. P. (2020). Bearing Thickness Is Not a Predictive Factor for Damage and Penetration in Oxford Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty—A Retrieval Analysis. Materials, 13(20), 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13204589




