Effects of Cooling Rate during Quenching and Tempering Conditions on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Steel Flange
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Materials and Methods
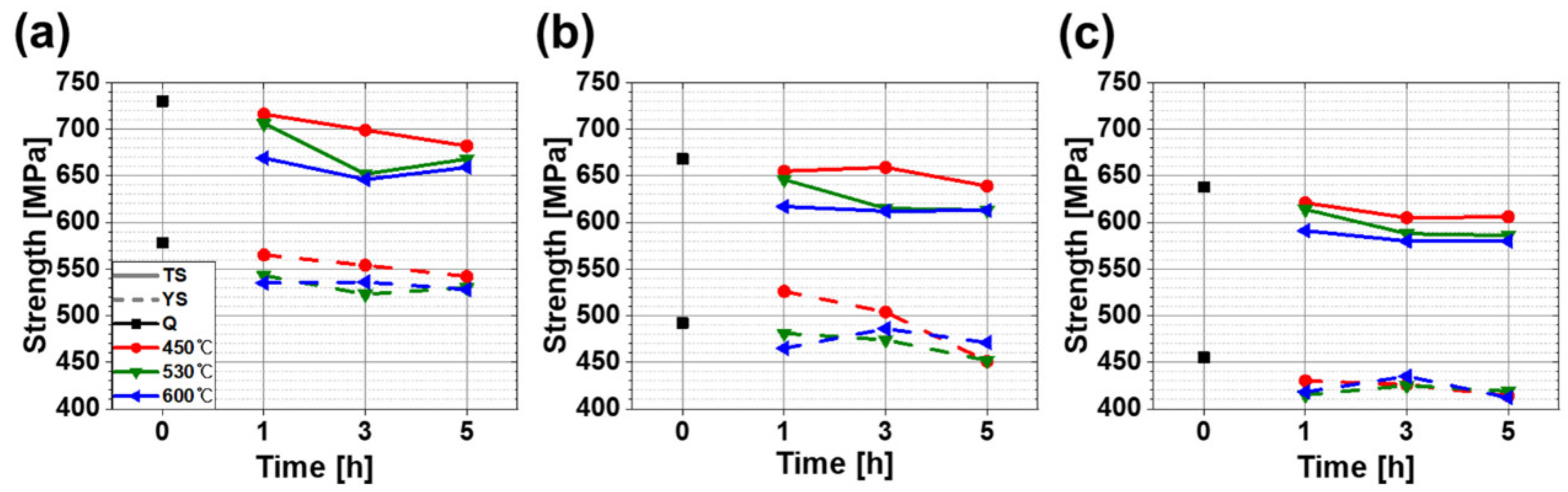
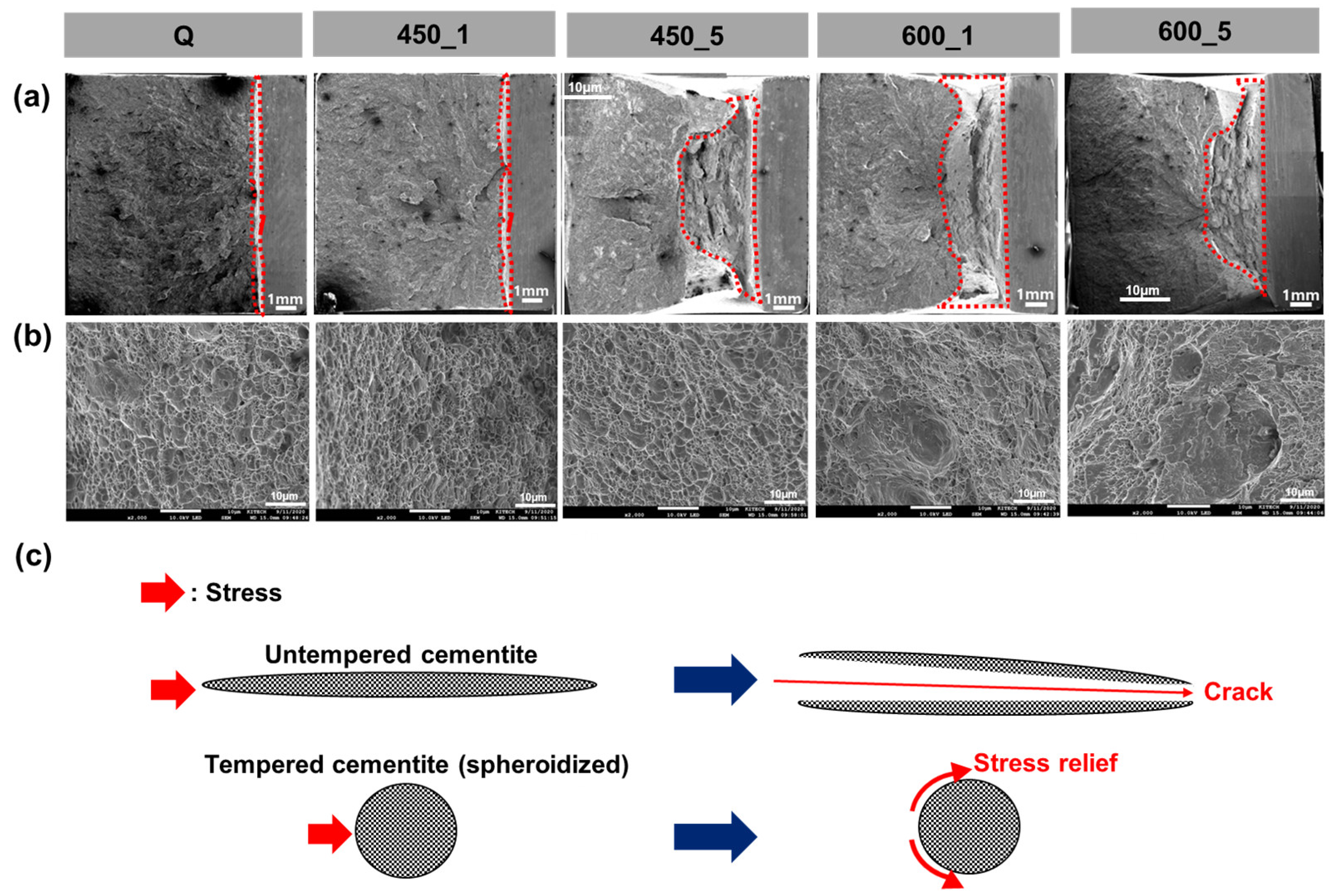
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
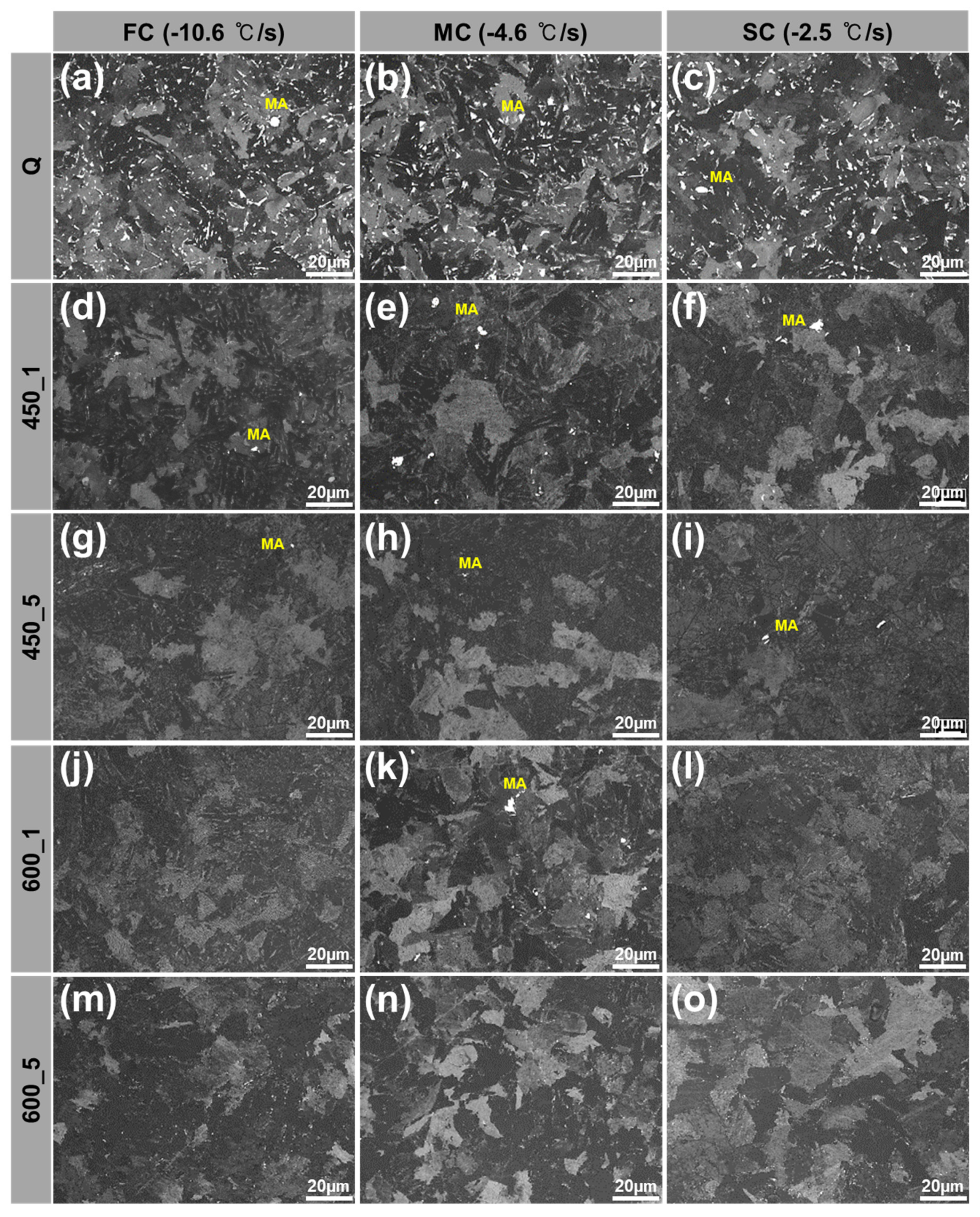
- During quenching, cooling rates varied among locations due to non-uniform cooling in flanges. Microstructure was strongly affected by cooling rates in a way that area fraction of either hard or soft constituent phases was determined by cooling rate. FC-Q has the highest area fraction of hard phase such as LBF, AF and M while SC-Q showed the area volume fraction of softer phases like QPF and DP/P.
- (2)
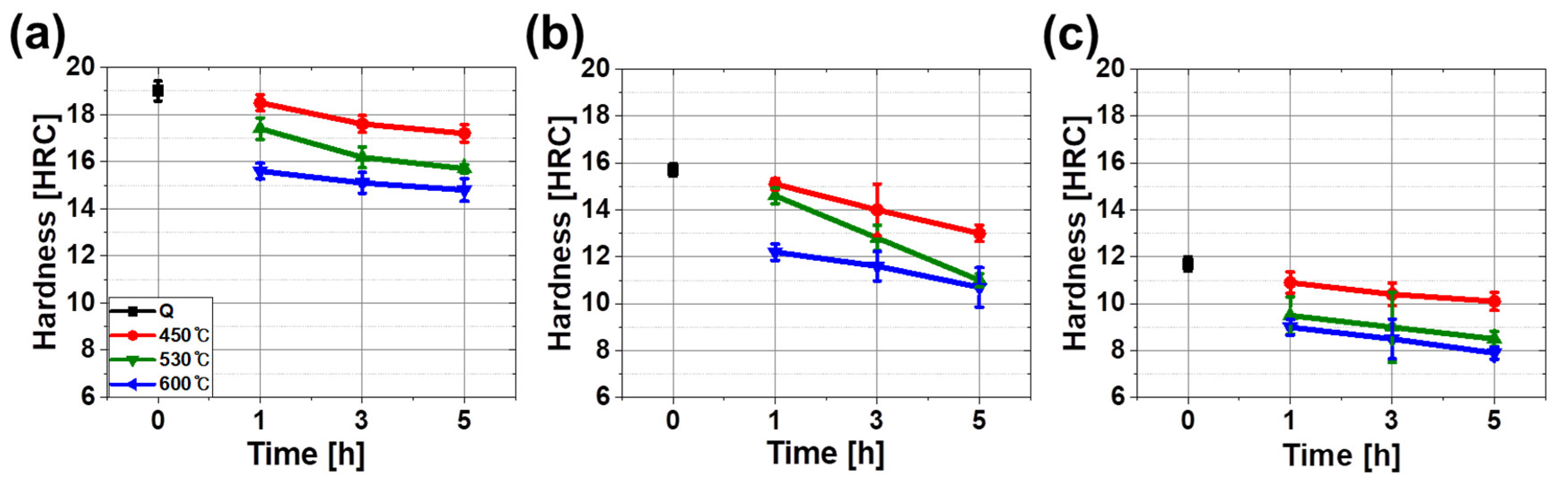
- Both strength and hardness were dependent on cooling rates; faster cooling rates induced hard phases so that hardness and strength resultantly increased. CVN impact energy at −46 °C, however, did not show clear dependence on cooling rates.
- (3)
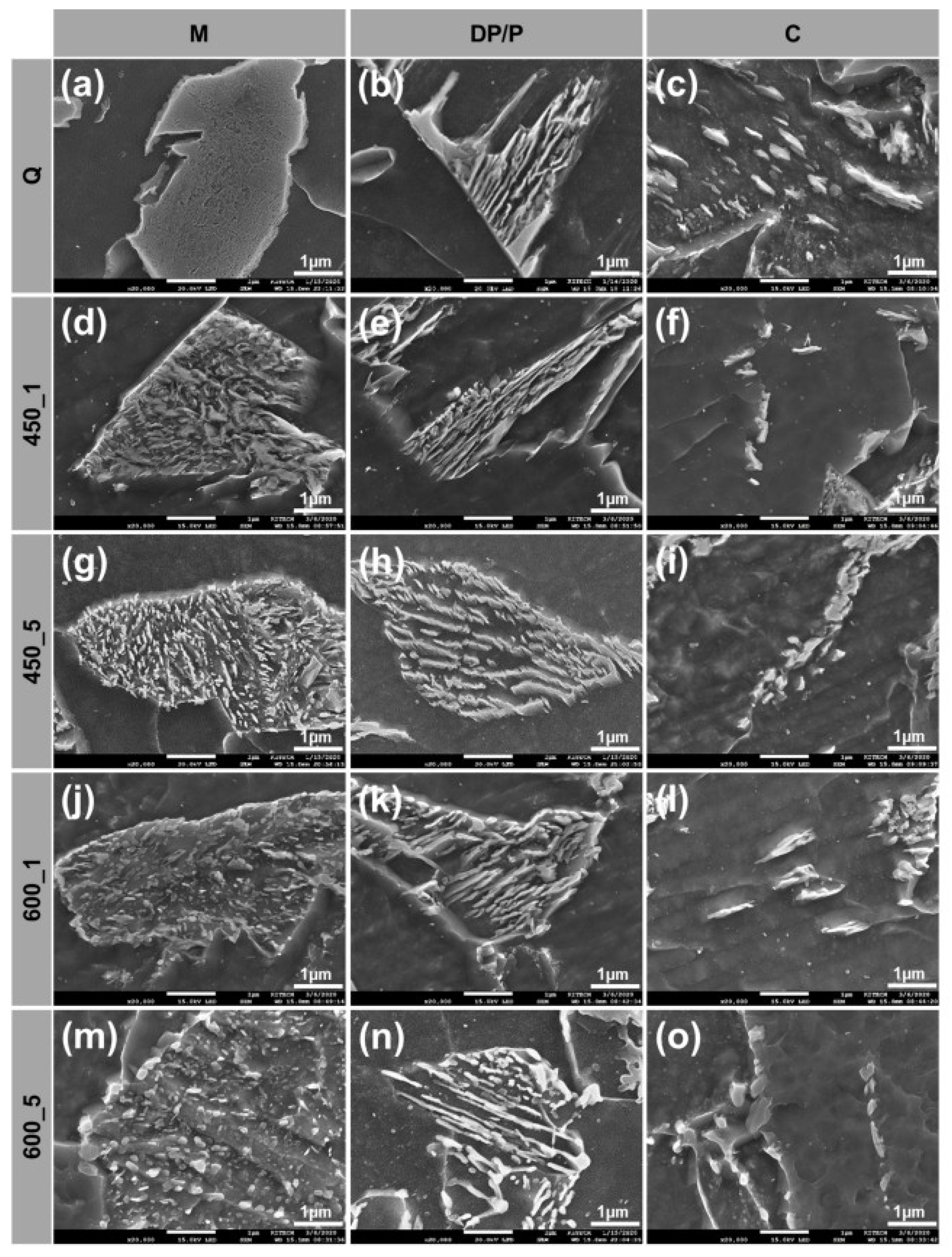
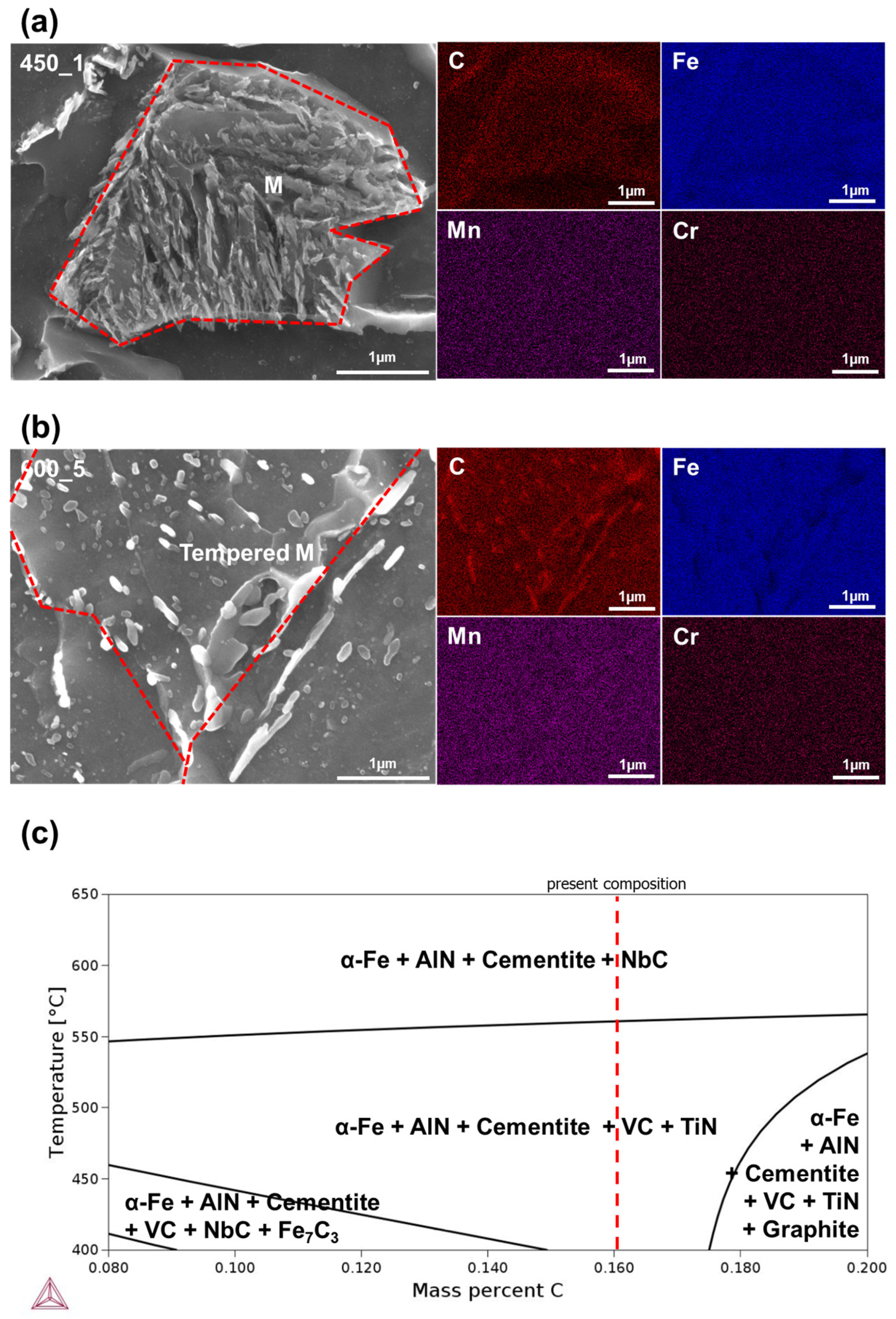
- Tempering evidently changed microstructure by decomposing of secondary phases such as M and P and spheroidizing cementite carbide. Accordingly, hardness, strength and CVN impact energy were improved.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Suh, Y.; Hwang, S.; Shin, S.Y. Effect of Rolling Conditions on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Thick Steel Plates for Offshore Platforms. Korean J. Mater. Res. 2018, 28, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.A.; Kheirandish, S. Affect of the Tempering Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Dual Phase Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radionova, L.V.; Ivanov, V.A.; Strugov, S.S. Study of Force and Kinematic Parameters of the Low-Waste, Zero-Draft Hot Forging of Welding Neck Flanges on the Basis of a Combined Expansion-Extrusion Deforming Procedure. Mater. Sci. Forum 2019, 946, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jia, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Misra, R. Investigation on Tempering of Granular Bainite in an Offshore Platform Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 626, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I. Current Status of Offshore Plant Equipment Industry. Korean Soc. Mech. Eng. 2012, 52, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, A.I.; Da Silva, R.V.; De Oliveira, P.G.B.; Martins, J.B.R.; Strangwood, M. Influence of Niobium and Molybdenum on Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance of Microalloyed Steels. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ren, J.; Tu, X.; Chen, L. Strength and Toughness of Fe-1.2Mn-0.3Cr-1.4Ni-0.4Mo-C Tempered Steel Plate in Three Cooling Processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 754, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.P.D.S.; De Faria, G.L.; Filho, V.B.D.T.; Cândido, L.C. Effect of the Chemical Homogeneity of a Quenched and Tempered C-Mn Steel Pipe on the Mechanical Properties and Phase Transformations. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Li, J. Thickness Dependence of Toughness in Ultra-Heavy Low-Alloyed Steel Plate after Quenching and Tempering. Metals 2018, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ma, X.; Shang, C.; Wang, X.; Subramanian, S. Nano-Sized Precipitation and Properties of a Low Carbon Niobium Micro-Alloyed Bainitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 641, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Effects of Rare Earth on Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Low Alloy Cr-Mo-V Steels for Hydrogenation Reactor Vessels. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Chen, H.-L.; Su, Y.-H.; Su, Y.-H.; Hwang, W.-S. Inclusions Properties at 1673 K and Room Temperature with Ce Addition in SS400 Steel. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.S. Change of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Mn-Mo-Ni Low Alloy Steel with Respect to Intercritical Heat Treatment Conditions. J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. 2000, 38, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Goodall, A.; Strangwood, M.; Davis, C. Characterisation of Precipitation and Carbide Coarsening in Low Carbon Low Alloy Q&T Steels during the Early Stages of Tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 738, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, C.; Kim, M.-C.; Lee, B.-S. Effects of Microstructure Variation on Tensile and Charpy Impact Properties in Heavy-Section SA508 Gr.3 Low Alloy Steels for Commercial Reactor Pressure Vessel. J. Korean Inst. Met. Mater. 2017, 55, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C.; Yu, C.; Yang, T.C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Shiue, R.-K. Microstructure and Impact Toughness of Offshore Steel. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2018, 63, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q. Influence of Cooling Process on Microstructure and Property of Low-Carbon V–N Micro-Alloyed Medium and Heavy High-Strength Steel Plate. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2018, 7, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.-J.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H. Effects of Continuous Cooling Rate on Morphology of Granular Bainite in Pipeline Steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, A.; Kaijalainen, A.; Heikkala, J.; Porter, D.; Suikkanen, P. The Effect of Tempering Temperature on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Bendability of Direct-Quenched Low-Alloy Strip Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 730, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, A.; Sahu, P.; Neogy, S.; Chakrabarti, D.; Mitra, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, S. Effect of Cooling Rate and Chemical Composition on Microstructure and Properties of Naturally Cooled Vanadium-Microalloyed Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2017, 48, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Nash, P.; Zhang, Y. Correlation of Cooling Rate, Microstructure and Hardness of S34MnV Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2019, 50, 1718–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.-W.; Chiang, M.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, D.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, H. High-Temperature Tempered Martensite Embrittlement in Quenched-and-Tempered Offshore Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramfitt, B.L.; Speer, J.G. A Perspective on the Morphology of Bainite. Metall. Trans. A 1990, 21, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Bainite in Steels, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; Volume 21A, pp. 1–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G.; Thompson, S.W. Ferritic Microstructures in Continuously Cooled Low- and Ultralow-Carbon Steels. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Hwang, B.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.J. Effects of Molybdenum and Vanadium Addition on Tensile and Charpy Impact Properties of API X70 Linepipe Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wynne, B.P.; Palmiere, E.J. Conditions for the Occurrence of Acicular Ferrite Transformation in HSLA Steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3785–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.; Honeycombe, R. Steels: Microstructure and Properties, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson, B.; Andrén, H.O. Microstructure of Granular Bainite. J. Phys. 1988, 49, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, D.; Li, Y. The Evolutions of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V Steel with Different Initial Microstructures during Tempering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 699, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, F.H. A Crystallographic Study of Pearlite Growth in Steels. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1983, 23, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Becker, W.T. Toughness of Tempered Upper and Lower Bainitic Microstructures in a 4150 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1993, 2, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, S.; Schwinnand, V.; Tacke, K.H. Characterisation and Quantification of Complex Bainitic Microstructures in High and Ultra-High Strength Linepipe Steels. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 500–501, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Developments in Martensitic and Bainitic Steels: Role of the Shape Deformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 378, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.J.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, K. Effects of Cooling Conditions on Tensile and Charpy Impact Properties of API X80 Linepipe Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2010, 41, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Yang, J.R. Effects of Chemical Composition, Rolling and Cooling Conditions on the Amount of Martensite/Austenite (M/A) Constituent Formation in Low Carbon Bainitic Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1992, 154, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, N. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Martensite/Austenite Islands in Pipeline Steel X70. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisinger, S.; Ressel, G.; Eck, S.; Marsoner, S. Differentiation of Grain Orientation with Corrosive and Colour Etching on a Granular Bainitic Steel. Micron 2017, 99, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, N.; Midawi, A.R.; Gianetto, J.; Lazor, R.; Gerlich, A.P. Influence of Martensite-Austenite (MA) on Impact Toughness of X80 Line Pipe Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 662, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, A.M.; Faulkner, R.G.; Lyne, A.T. Cementite Particle Coarsening during Spheroidisation of Bearing Steel SAE 52100. Mater. Sci. Technol. (UK) 1995, 11, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Steels Processing, Structure, and Performance, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Leng, Y.; Fu, D.; Teng, J. Effects of Niobium and Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Cast Steels. Mater. Des. 2016, 105, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, E. Influence of Different Initial Microstructure on the Process of Spheroidization in Cold Forging. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi-Gol, A.; Sheikh-Amiri, M. Spheroidizing Kinetics and Optimization of Heat Treatment Parameters in CK60 Steel Using Taguchi Robust Design. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mateo, C.; Peet, M.; Caballero, F.G.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Tempering of Hard Mixture of Bainitic Ferrite and Austenite. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.; Kabir, A.S. Effect of Heat Treatments on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Ti-5553 Alloy. In TMS 2020 149th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 18, pp. 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Miyata, K.; Katsuki, F.; Ishimoto, T.; Nakano, T. Individual Mechanical Properties of Ferrite and Martensite in Fe-0.16 Mass% C-1.0 Mass% Si-1.5 Mass% Mn Steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Hernández, V.H.; Panda, S.; Kuntz, M.; Zhou, Y. Nanoindentation and Microstructure Analysis of Resistance Spot Welded Dual Phase Steel. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, M.; Goutianos, S.; Hansen, N.; Winther, G.; Huang, X. Effect of Hardness of Martensite and Ferrite on Void Formation in Dual Phase Steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. (UK) 2012, 28, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinakorn, T.; Uthaisangsuk, V. Effects of The Tempering Temperature on Mechanical Properties. J. Met. Mater. Miner. 2014, 24, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Zhu, L.; Sha, W.; Shan, Y.; Yang, K. Change of Tensile Behavior of a High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel with Tempering Temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 517, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, B.; Liang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Han, K.; Song, C. Grain Boundary Pop-in, Yield Point Phenomenon and Carbon Segregation in Aged Low Carbon Steel. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-M.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Shen, Z.-Y.; Wang, B.-L.; Zhao, S.-L.; Liang, G.-F.; Song, C.-J. Effect of Coiling and Annealing Temperatures on Yield Point Behavior of Low-Carbon Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Toplosky, V.J.; Min, N.; Xin, Y.; Walsh, R.; Lu, J. Yielding and Strain-Hardening of Reinforcement Materials. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2019, 29, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.-H.; Oh, C.-S.; Lee, K.; George, E.P.; Han, H.N. Relationship between Yield Point Phenomena and the Nanoindentation Pop-in Behavior of Steel. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, A.H.; Bilby, B.A. Dislocation Theory of Yielding and Strain Ageing of Iron. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. A 1949, 62, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamura, T.; Yin, F.; Nagai, K. Ductile-Brittle Transition Temperature of Ultrafine Ferrite/Cementite Microstructure in a Low Carbon Steel Controlled by Effective Grain Size. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Yu, D.; Xie, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Effect of Thermal Aging on Mechanical Properties of a Bainitic Forging Steel for Reactor Pressure Vessel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 720, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Lee, W.I. Study on Fracture Behavior of Mild Steel Under Cryogenic Condition. J. Korean Inst. Gas. 2015, 19, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahn, Y.-S.; Kim, H.-D.; Byun, T.-S.; Oh, Y.-J.; Kim, G.-M.; Hong, J.-H. Application of Intercritical Heat Treatment to Improve Toughness of SA508 Cl.3 Reactor Pressure Vessel Steel. Nucl. Eng. Des. 1999, 194, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Liu, Z.; Bao, H.; Weng, Y.; Liu, W. Effect of Tempering Temperature on the Toughness of 9Cr-3W-3Co Martensitic Heat Resistant Steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.L.; King, J.E. Cleavage Initiation in the Intercritically Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat Affected Zone: Part II. Failure Criteria and Statistical Effects. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. A 1996, 27, 3019–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
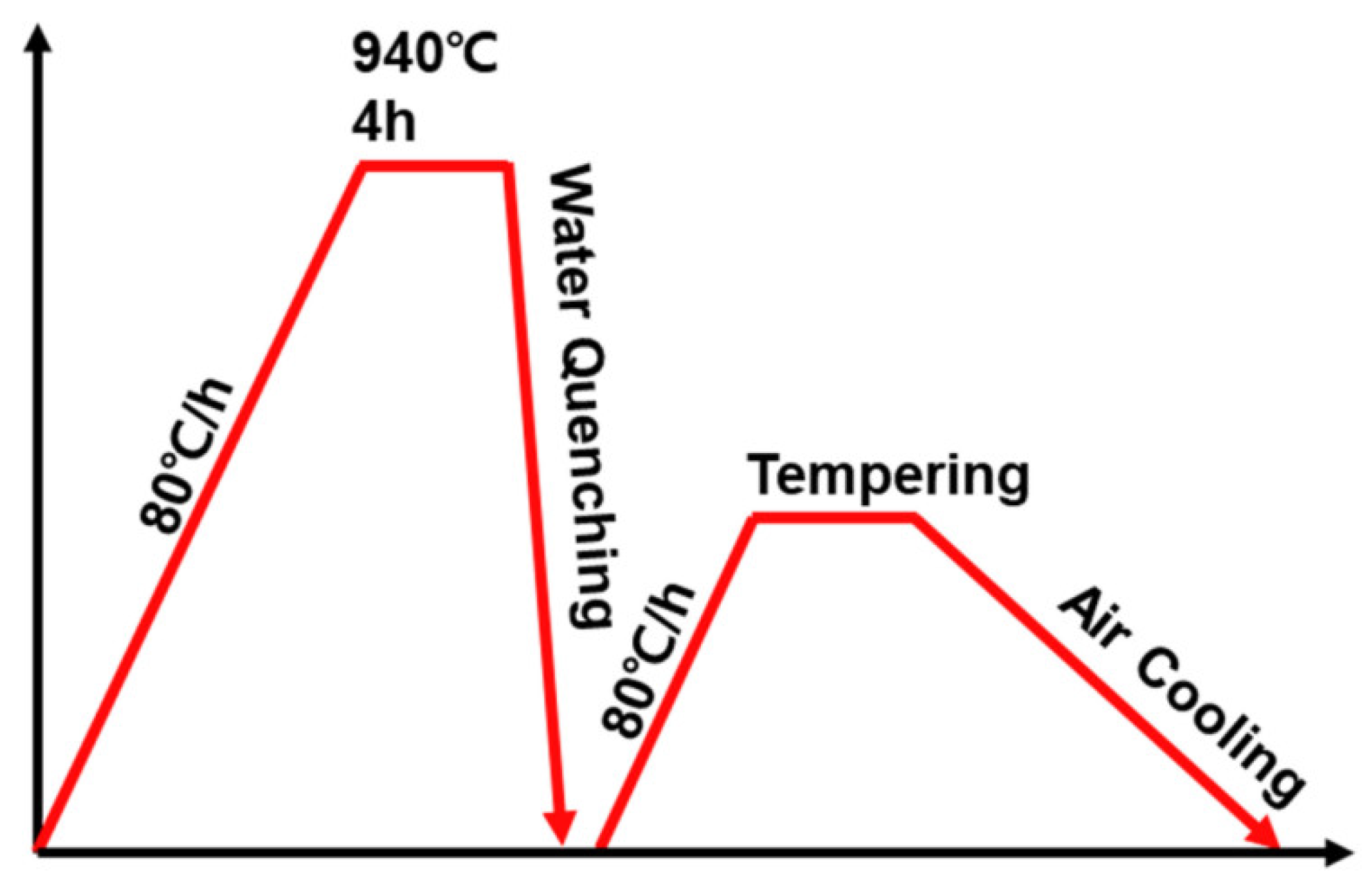
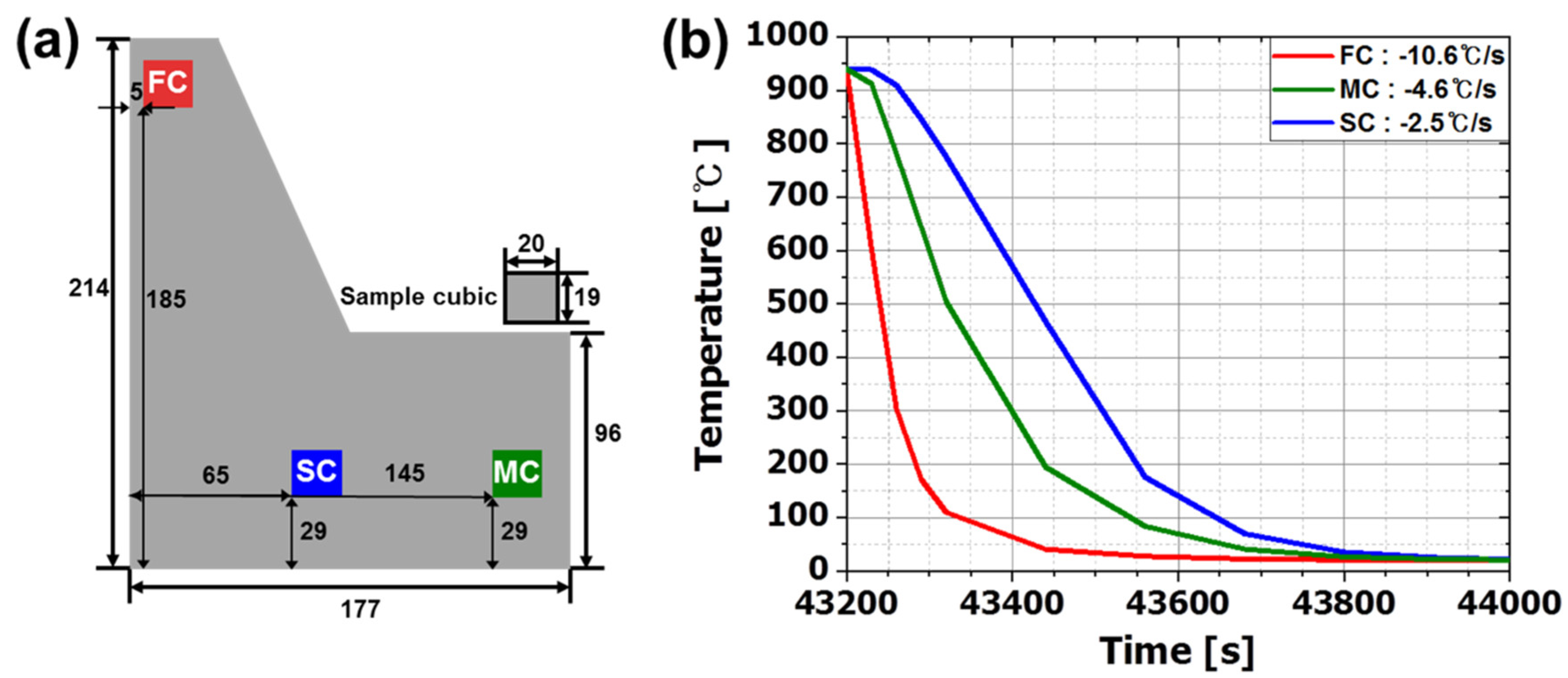
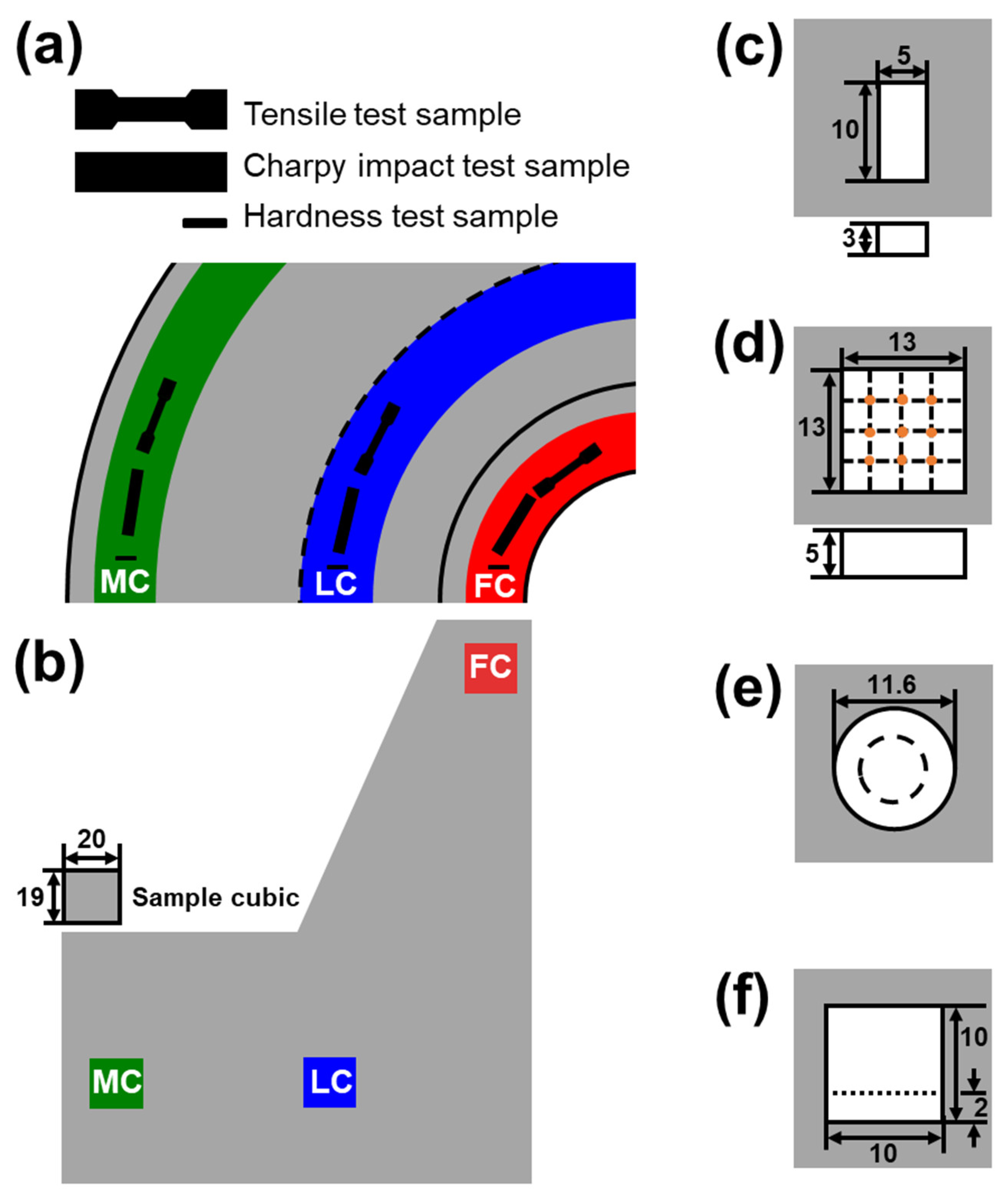
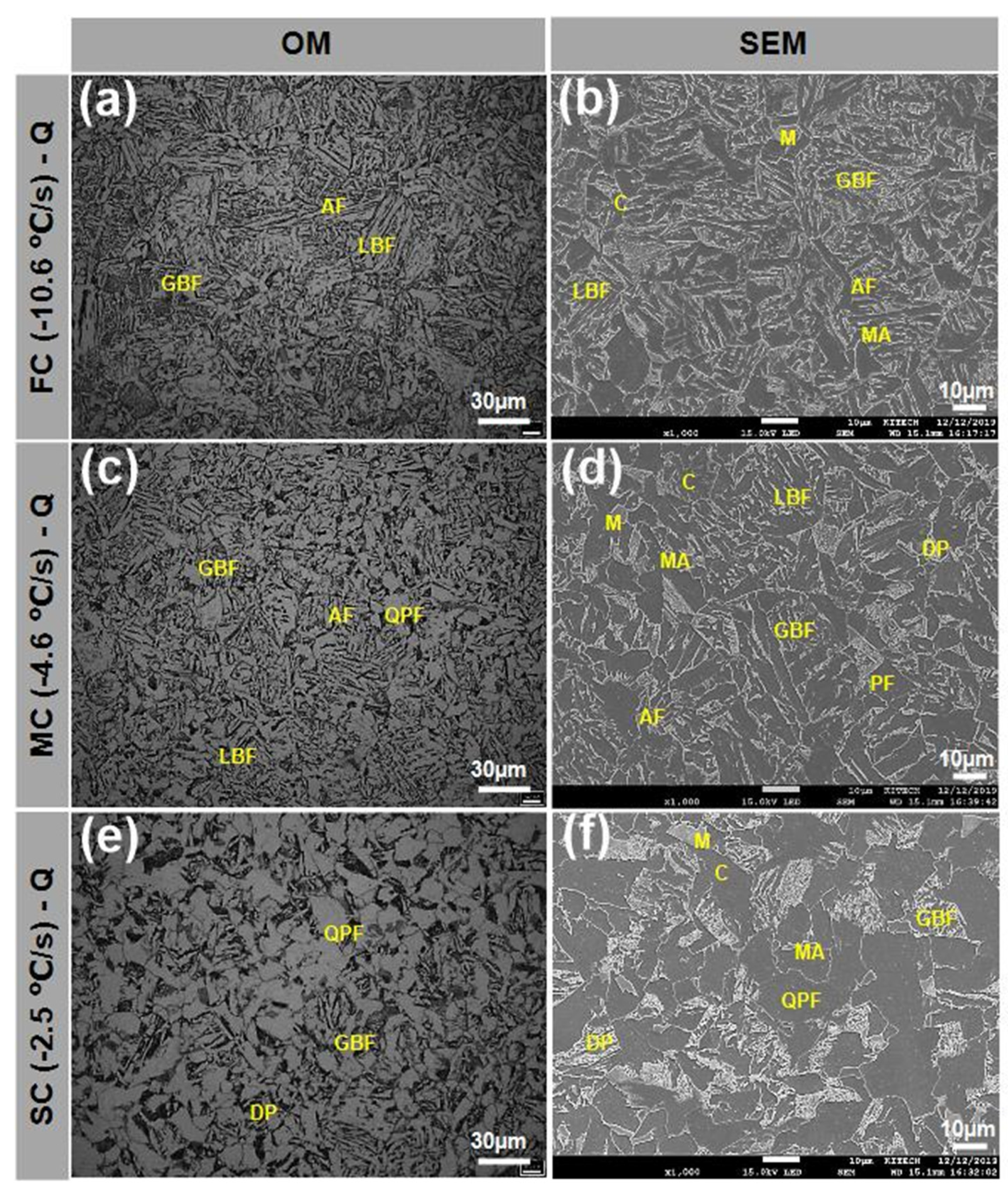


| Element | Fe | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | As |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | Bal. | 0.1605 | 0.246 | 1.266 | 0.0147 | 0.0045 | 0.191 | 0.014 | 0.004 |
| B | Ca | Cu | Mo | N | Nb | Sn | Ti | V | Al |
| 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.027 | 0.082 | 0.0037 | 0.0019 | 0.002 | 0.0016 | 0.054 | 0.026 |
| Specimen Name | Tempering Temperature (°C) | Tempering Time (h) |
|---|---|---|
| Q | × | × |
| 450_1 | 450 | 1 |
| 450_3 | 450 | 3 |
| 450_5 | 450 | 5 |
| 530_1 | 530 | 1 |
| 530_3 | 530 | 3 |
| 530_5 | 530 | 5 |
| 600_1 | 600 | 1 |
| 600_3 | 600 | 3 |
| 600_5 | 600 | 5 |
| Name | Matrix | Secondary Phase | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBF | AF | GBF | QPF | M | DP/P | MA | |
| FC-Q | 13 ± 1.0 | 16 ± 4.0 | 47 ± 4.1 | - | 17 ± 2.0 | 5 ± 1.5 | 2 ± 0.2 |
| MC-Q | 8 ± 3.0 | 12 ± 4.4 | 51 ± 4.7 | 6 ± 3.4 | 11 ± 3.1 | 10 ± 0.7 | 2 ± 0.1 |
| SC-Q | - | - | 37 ± 7.9 | 39 ± 5.9 | 7 ± 1.3 | 15 ± 1.4 | 2 ± 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, H.; Kang, M.; Park, G.-W.; Kim, B.-J.; Choi, C.Y.; Park, H.S.; Shin, S.; Lee, W.; Ahn, Y.-S.; Jeon, J.B. Effects of Cooling Rate during Quenching and Tempering Conditions on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Steel Flange. Materials 2020, 13, 4186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184186
Jo H, Kang M, Park G-W, Kim B-J, Choi CY, Park HS, Shin S, Lee W, Ahn Y-S, Jeon JB. Effects of Cooling Rate during Quenching and Tempering Conditions on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Steel Flange. Materials. 2020; 13(18):4186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184186
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Haeju, Moonseok Kang, Geon-Woo Park, Byung-Jun Kim, Chang Yong Choi, Hee Sang Park, Sunmi Shin, Wookjin Lee, Yong-Sik Ahn, and Jong Bae Jeon. 2020. "Effects of Cooling Rate during Quenching and Tempering Conditions on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Steel Flange" Materials 13, no. 18: 4186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184186
APA StyleJo, H., Kang, M., Park, G.-W., Kim, B.-J., Choi, C. Y., Park, H. S., Shin, S., Lee, W., Ahn, Y.-S., & Jeon, J. B. (2020). Effects of Cooling Rate during Quenching and Tempering Conditions on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Steel Flange. Materials, 13(18), 4186. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184186







