The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Properties of Niobium–Vanadium Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
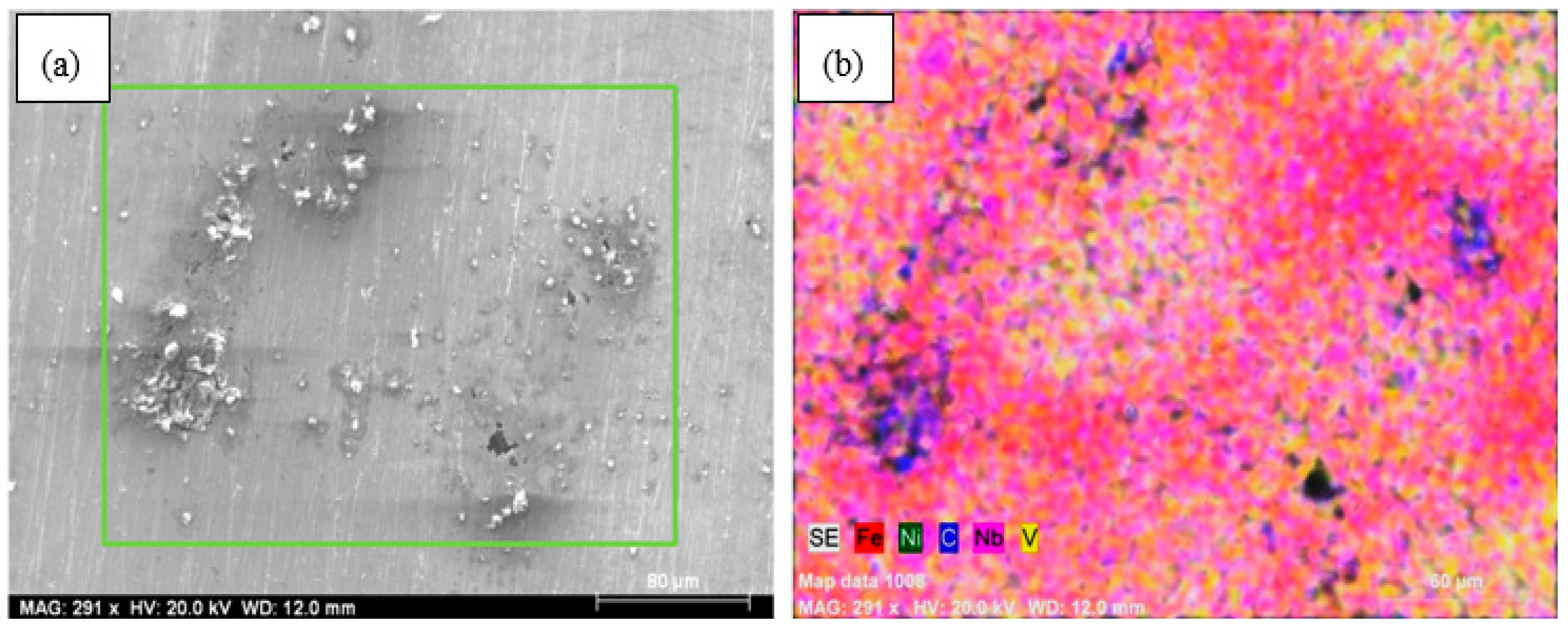
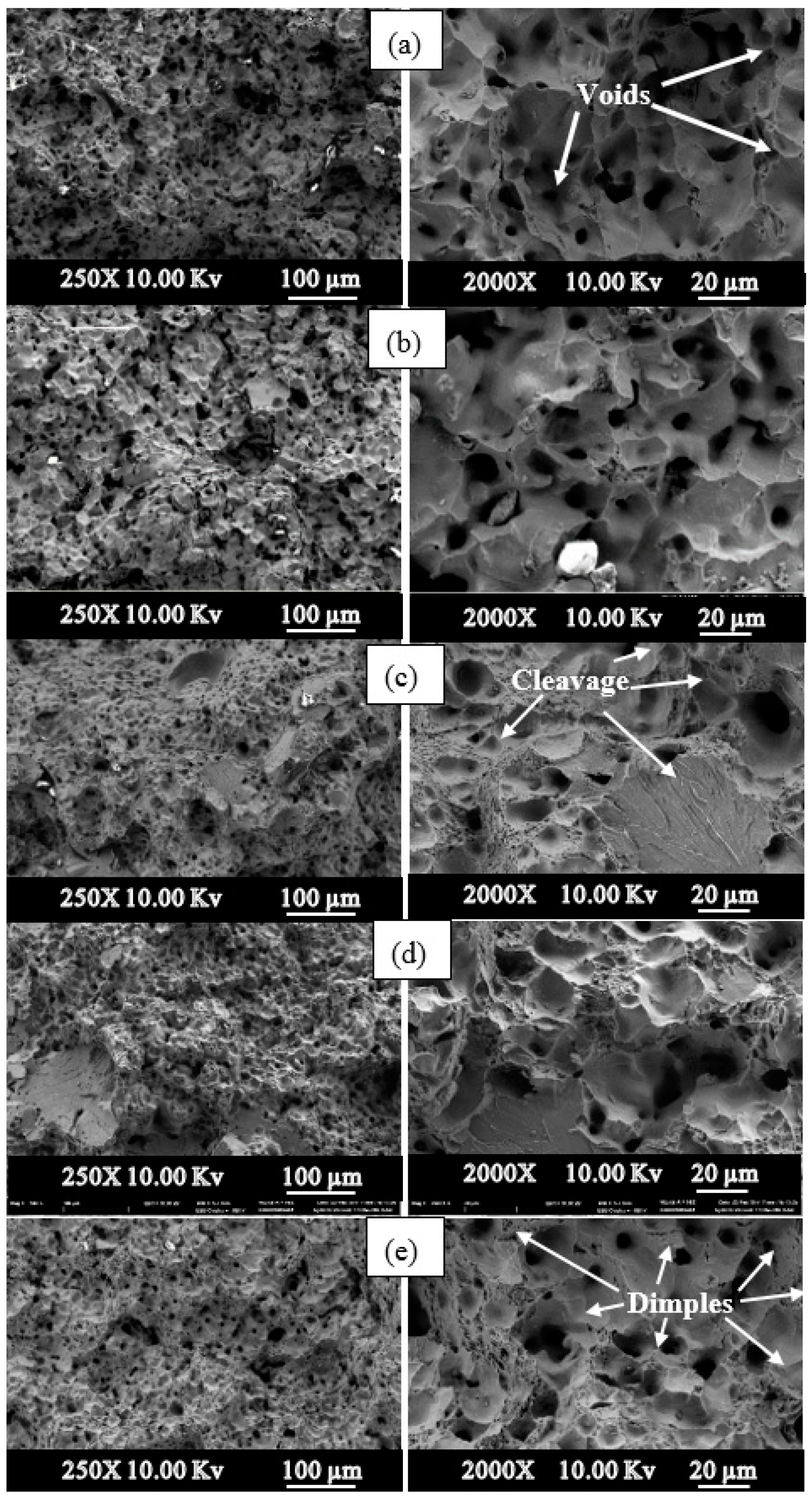
3. Results
4. Conclusions
- 1.
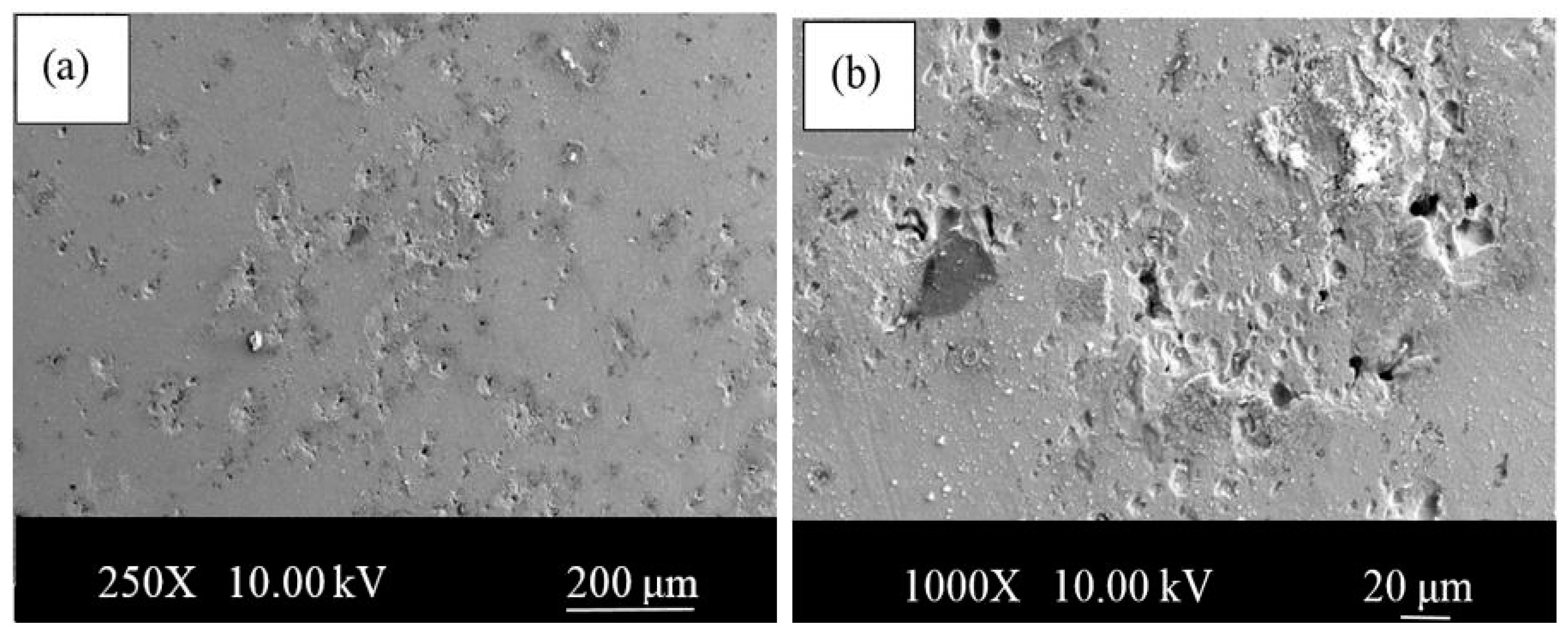
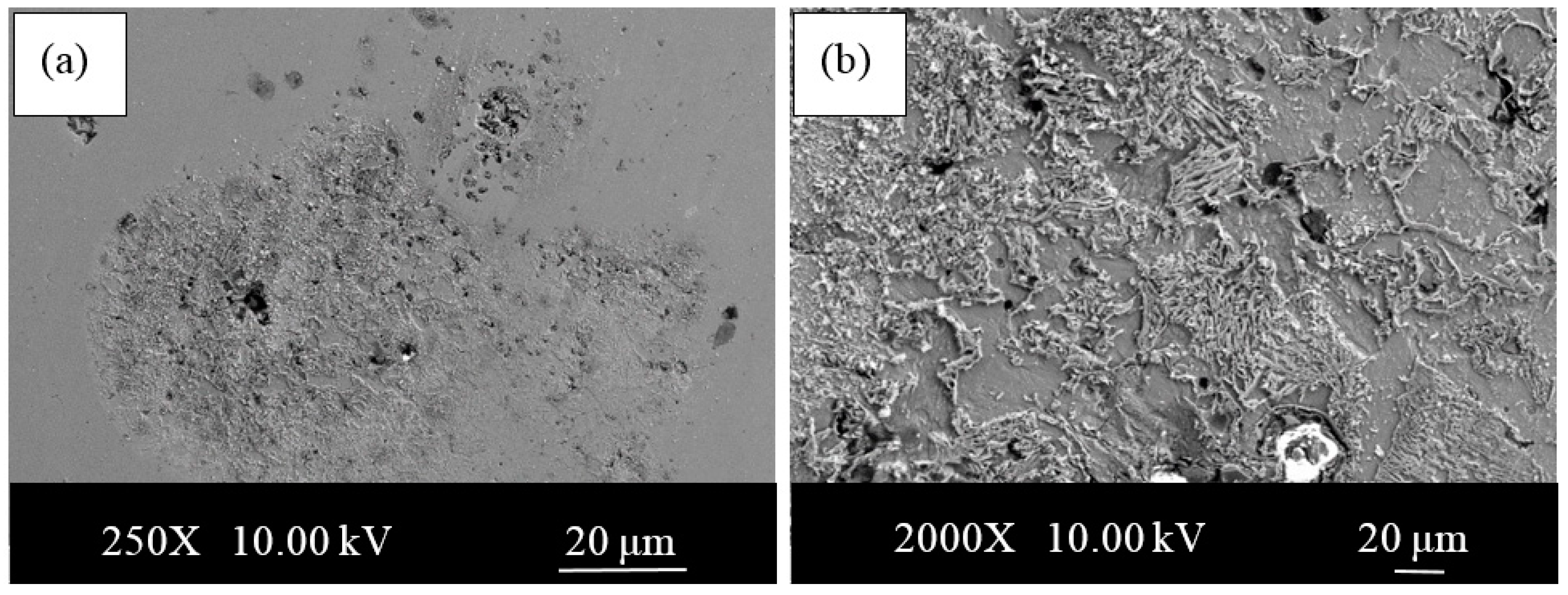
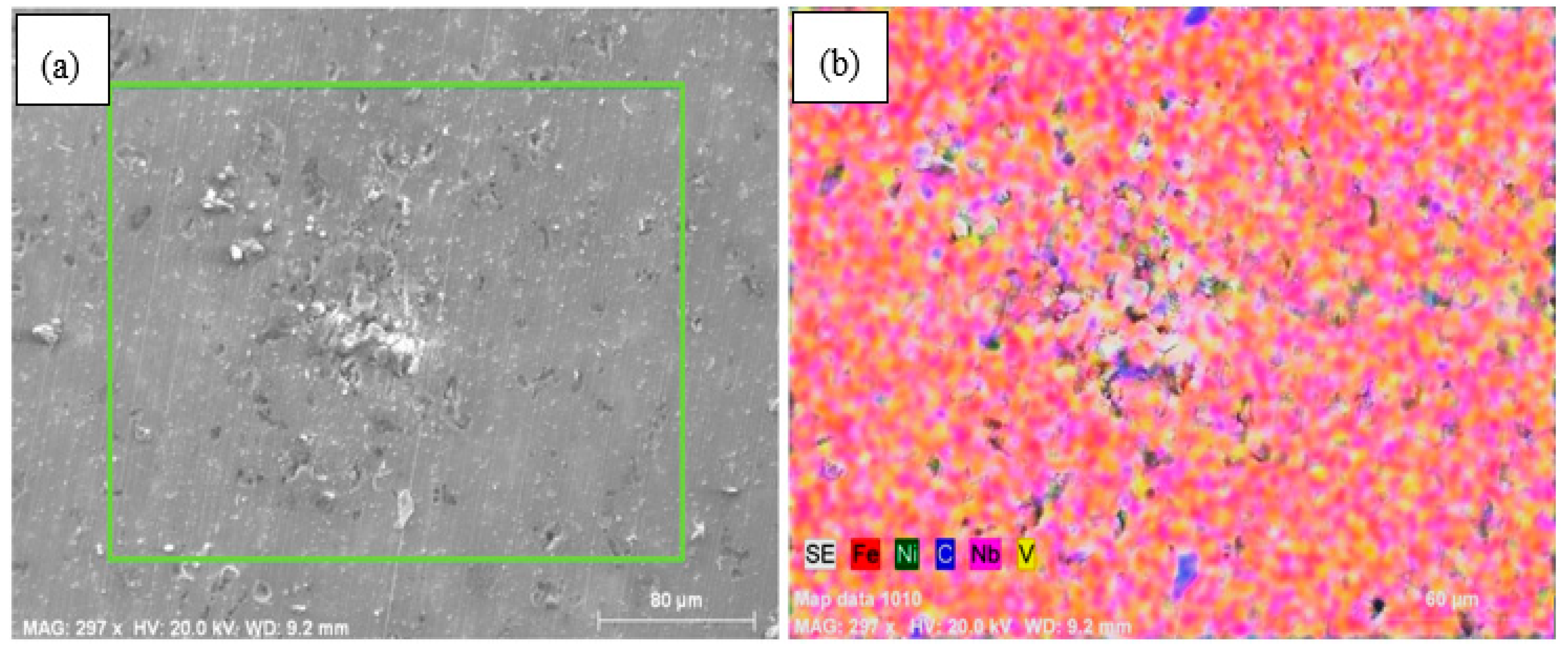
- The microstructures of the alloys with nonalloyed steel and Nb–V microalloyed steel without Ni have ferrite and pearlite. However, increasing Ni content caused the transformation to austenite and the formation of Fe3Ni2 FeNi FeNi3 intermetallic compounds.
- 2.
- Ni addition up to 13% increased the yield and tensile strength with hardness. More addition of that decreased the strength but increased the elongation.
- 3.
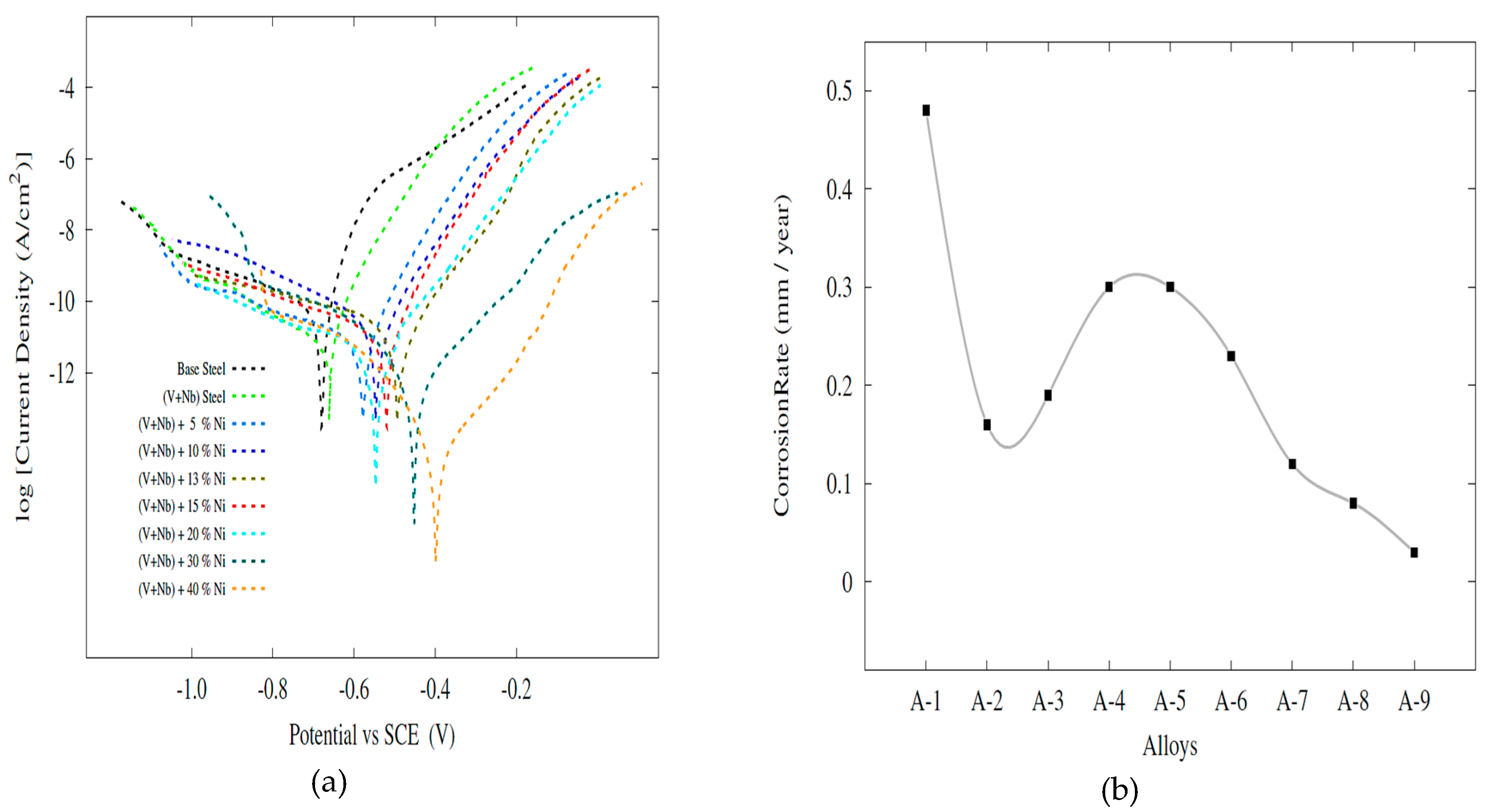
- Ni content increased the corrosion resistance almost systematically, although it was also low in the alloys with 5%, 10%, 13% and 15% Ni due to possible microstructure inhomogeneity and martensitic structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gladman, T. The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, 1st ed.; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gündüz, S.; Karabulut, H.; Erden, M.A.; Türkmen, M. Microstructural Effects on Fatigue Behaviour of a Forged Medium Carbon Microalloyed Steel. Mater. Test. 2013, 55, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.A. An Investigation on the Relation Sheep Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Microalloyed Steels Produced by Powder Metallurgy. Ph.D. Thesis, Karabük University, Karabük, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, W.; Yisan, W.; Yichao, D. Reaction synthesis of Fe–(Ti,V)C composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 197, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.A. The Effect of the Sintering Temperature and Addition of Niobium and Vanadium on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Microalloyed PM Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, V. Nickel sintered steels—Developments, status and prospects. Met. Powder Rep. 1992, 47, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, G.S. Sintered Metallic and Ceramic Materials-Sintered Low-Alloy Ferrous Materials; John Wiley & Sons LTD: West Sussex, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Türkmen, M.; Karabulut, H.; Erden, M.A.; Gündüz, S. Effect of TIN Addition on The Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of PM Steels. E-J. New World Sci. Acad. 2017, 12, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtaş, H.; Erden, M.A. The Effect of Cr and Ni Addition on Mechanical Properties of Plain Carbon Steel. Düzce Uni. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 7, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M. Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM B328-96. Standard Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Interconnected Porosity of Sintered Metal Structural Parts and Oil-Impregnated Bearings; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fischmeister, H.F. Applications of quantitative microscopy in materials engineering. J. Microsc. 1972, 95, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T.; Woodhead, J. The accuracy of point counting in metallographic investigation. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1960, 194, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Erden, M.A.; Gündüz, S.; Türkmen, M.; Karabulut, H. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of microalloyed powder metallurgy steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkmen, M.; Erden, M.; Karabulut, H.; Gündüz, S. The Effects of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Nb-V Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2019, 135, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündüz, S.; Erden, M.A.; Karabulut, H.; Türkmen, M. Effect of the addition of niobium and aluminium on the microstructures and mechanical properties of micro-alloyed PM steels. Mater. Teh. 2016, 50, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavapootanont, G.; Wongpanya, P.; Viyanit, E.; Lothongkum, G. Corrosion Behavior of Ni Steels in Aerated 3.5-wt.% NaCl Solution at 25 °C by Potentiodynamic Method. Eng. J. 2018, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, N.; Sherif, E.-S.M.; Abdo, H.S.; El Abedin, S.Z. Effect of Nickel Content on the Corrosion Resistance of Iron-Nickel Alloys in Concentrated Hydrochloric Acid Pickling Solutions. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.M. An overview of the use of mikroalloys in HSLA steels with particular reference to vanadyum and titanium, processing, properties and applications. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on HSLA Steels, Bejing, China, 1992; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.-G.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Carbide precipitation kinetics in austenite of a Nb–Ti–V microalloyed steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5529–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, R.; Arenas, F. TiC–VC–Co: A study on its sintering and microstructure. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2001, 19, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.A.; Gündüz, S.; Karabulut, H.; Türkmen, M. Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of low carbon micro-alloyed powder metallurgy steels. Mater. Test. 2016, 58, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.-D.; Mao, X.; Lü, S.-X. Effect of Annealing Temperature on Recrystalization Behavior of Cold Rolled Ti-Microaloyed Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erden, M.A. The Effect of Sintering Time on Tensile Strength of NB-V Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels. E-J. New World Sci. Acad. 2020, 15, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, A.I.; Gilmutdinov, A.K.; Yanbaev, R.M. Effect of coaxial laser cladding parameters on bead formation. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2017, 24, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, J. Effect of powders refinement on the tribological behavior of Ni-based composite coatings by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6697–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Northwood, D.O. Effect of temperature on the lower yield strength and static strain ageing in low-carbon steels. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwood, C.G. The Effect of Nickel Content on the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of a High Toughness Secondary Hardening Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aparova, A.I.; Lyapunov, A.I.; Eremin, V. Effect of nickel and manganese on the structure and properties of steel R3M3F2. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 1987, 29, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemirler, D.; Gündüz, S.; Erden, M.A. Influence of NbC Addition on the Sintering Behaviour of Medium Carbon PM Steels. Metals 2017, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, D.; Tripathi, P.; Chaubey, A. Effect of Nickel on Mechanical Properties of Alloy Steel Produced by Powder Metallurgy. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G102-89. Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information from Electrochemical Measurements, 1st ed.; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Uygur, İ.; Gerengi, H.; Erden, M.A.; Yıldız, M. The Effect of Niobium and Vanadium on Corrosıon Of Low Carbon Steel Obtained By Powder Metallurgy In 3.5%Nacl Envıronment. Tech. App. Sci. 2017, 12, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, K.; Yuan, J.; Qiao, K.; Zhang, B.; Cai, J. Mechanical and corrosion properties of low-carbon steel prepared by friction stir processing. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2019, 26, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura-Bińczyk, E.; Dobkowska, A.; Płocińska, M.; Płociński, T.; Adamczyk-Cieślak, B.; Mazurkiewicz, B.; Solarski, W.; Banaś, J.; Mizera, J. The influence of grain refinement on the corrosion rate of carbon steels in fracturing fluids used in shale gas production. Mater. Corros. 2017, 68, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerdtfeger, W. Corrosion rates of binary alloys of nickel and iron measured by polarization methods. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. Sect. C Eng. Instrum. 1966, 70, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Zou, Y.; Kong, X.; Gao, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, W. The influence of the corrosion product layer generated on the high strength low-alloy steels welded by underwater wet welding with stainless steel electrodes in seawater. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaQue, F.L.; Copson, H.R. Corrosion Resistance of Metals and Alloys, 2nd ed.; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.S. Alloys of Iron and Nickel; McGraw-Hill Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugasundaram, D.; Chandramouli, R. Tensile and impact behaviour of sinter-forged Cr, Ni and Mo alloyed powder metallurgy steels. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 3444–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
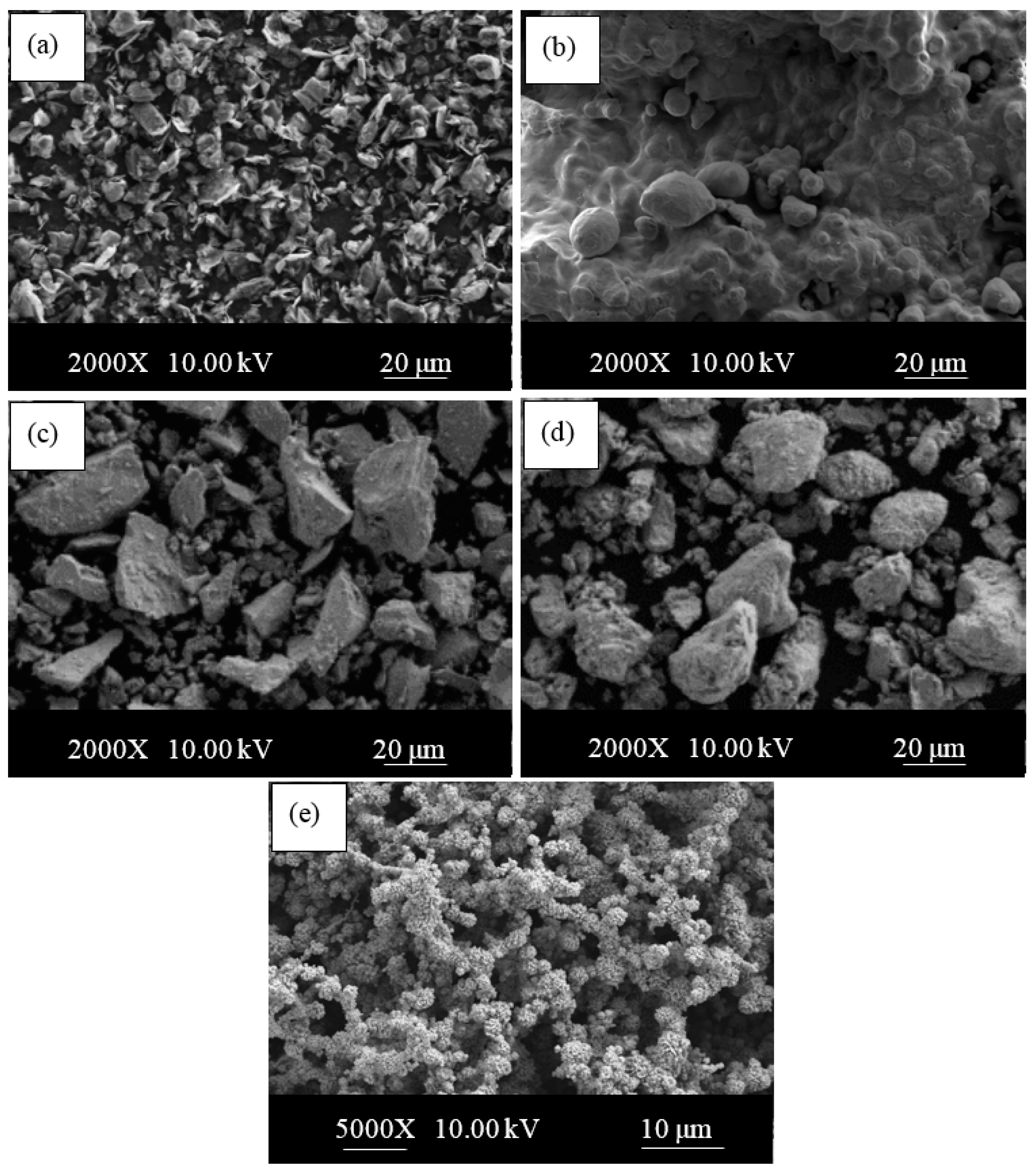
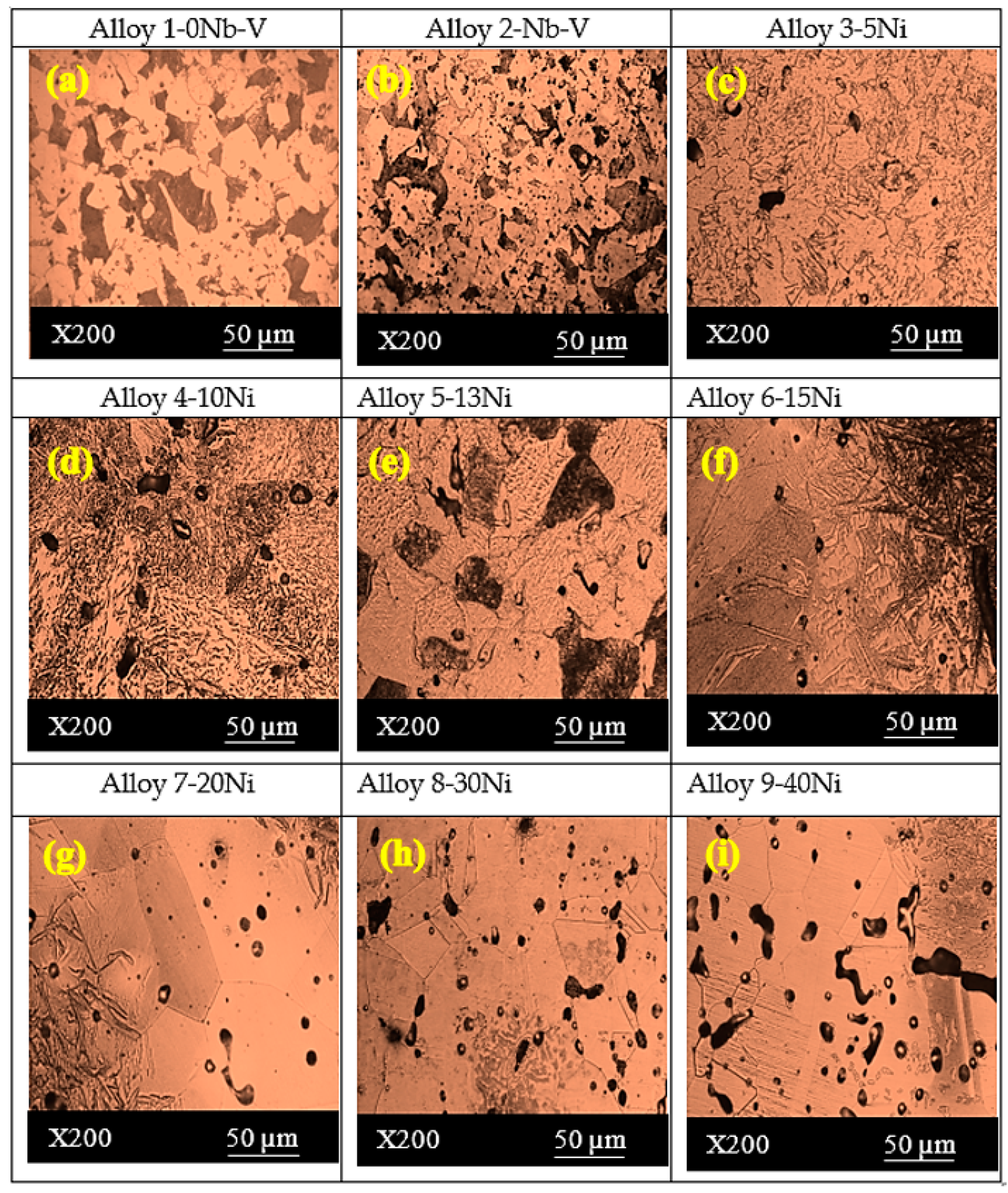


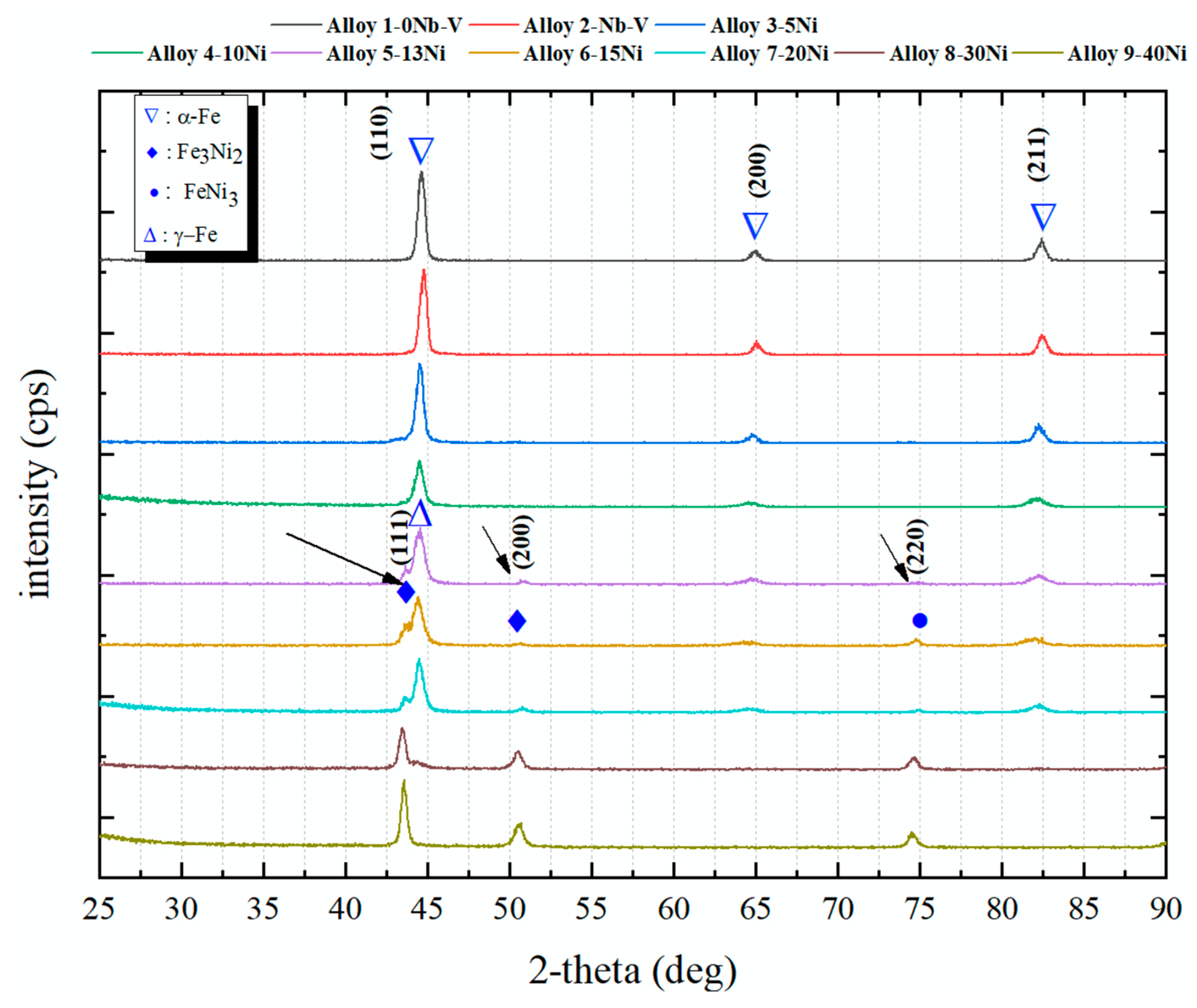
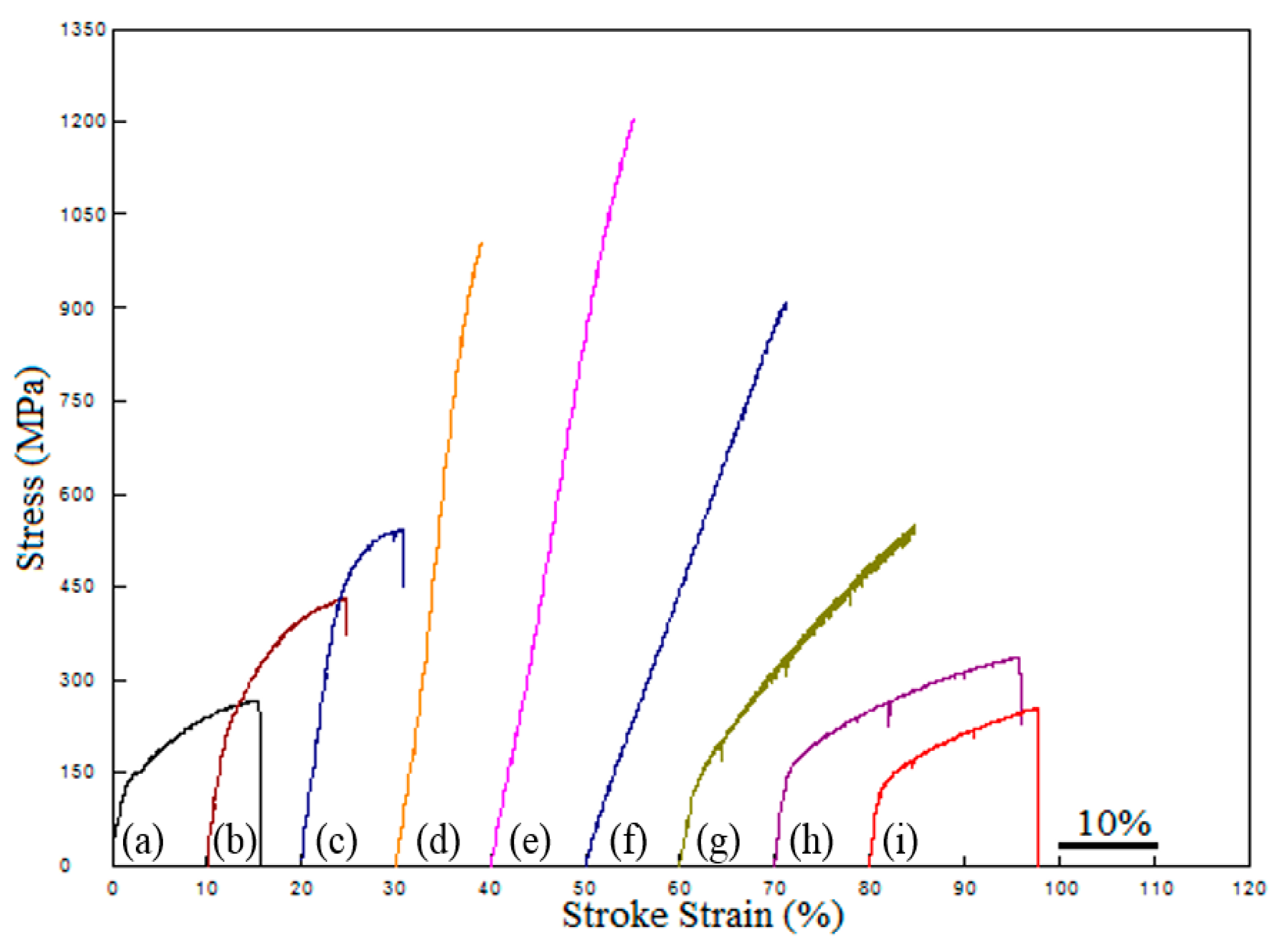
| Sample | C (wt.%) | Nb (wt.%) | V (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Densities (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 1-0Ni | 0.55 | - | - | - | Rest | 7.2837 |
| Alloy 2-NbV-0Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | - | Rest | 7.2787 |
| Alloy 3-NbV-5Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 5 | Rest | 7.4102 |
| Alloy 4-NbV-10Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 10 | Rest | 7.2347 |
| Alloy 5-NbV-13Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 13 | Rest | 7.5947 |
| Alloy 6-NbV-16Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 16 | Rest | 7.6724 |
| Alloy 7-NbV-20Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 20 | Rest | 7.5484 |
| Alloy 8-NbV-30Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 30 | Rest | 7.2903 |
| Alloy 9-NbV-40Ni | 0.55 | 0.075 | 0.075 | 40 | Rest | 7.2231 |
| Alloy | YS (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (Hv 0.5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 1-0Ni | 140 | 270 | 16 | 75 |
| Alloy 2-NbV-0Ni | 220 | 435 | 15 | 125 |
| Alloy 3-NbV-5Ni | 390 | 545 | 11 | 160 |
| Alloy 4-NbV-10Ni | 555 | 1010 | 10 | 243 |
| Alloy 5-NbV-13Ni | 630 | 1205 | 16 | 244 |
| Alloy 6-NbV-15Ni | 480 | 910 | 21 | 191 |
| Alloy 7-NbV-20Ni | 135 | 552 | 25 | 133 |
| Alloy 8-NbV-30Ni | 155 | 340 | 26 | 93 |
| Alloy 9-NbV-40Ni | 118 | 259 | 18 | 78 |
| Specimen | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (μA/cm2) | CR (mm/year) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-1 | Pure Steel | −0.68 | 37.9 | 0.48 |
| A-2 | (V + Nb) Steel | −0.66 | 12.5 | 0.16 |
| A-3 | (V + Nb) Steel + 5% Ni | −0.58 | 14.9 | 0.19 |
| A-4 | (V + Nb) Steel + 10% Ni | −0.54 | 23.8 | 0.30 |
| A-5 | (V + Nb) Steel + 13% Ni | −0.49 | 23.9 | 0.30 |
| A-6 | (V + Nb) Steel + 15% Ni | −0.52 | 18.3 | 0.23 |
| A-7 | (V + Nb) Steel + 20% Ni | −0.54 | 9.3 | 0.12 |
| A-8 | (V + Nb) Steel + 30% Ni | −0.45 | 6.12 | 0.08 |
| A-9 | (V + Nb) Steel + 40% Ni | −0.40 | 2.3 | 0.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahssi, M.A.M.; Erden, M.A.; Acarer, M.; Çuğ, H. The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Properties of Niobium–Vanadium Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels. Materials 2020, 13, 4021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184021
Ahssi MAM, Erden MA, Acarer M, Çuğ H. The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Properties of Niobium–Vanadium Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels. Materials. 2020; 13(18):4021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184021
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhssi, Mohamed Ahmed Mohamed, Mehmet Akif Erden, Mustafa Acarer, and Harun Çuğ. 2020. "The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Properties of Niobium–Vanadium Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels" Materials 13, no. 18: 4021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184021
APA StyleAhssi, M. A. M., Erden, M. A., Acarer, M., & Çuğ, H. (2020). The Effect of Nickel on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Properties of Niobium–Vanadium Microalloyed Powder Metallurgy Steels. Materials, 13(18), 4021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184021





